#medieval history
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

⊹ ࣪ ﹏𓊝﹏𓂁﹏⊹ ࣪ ˖
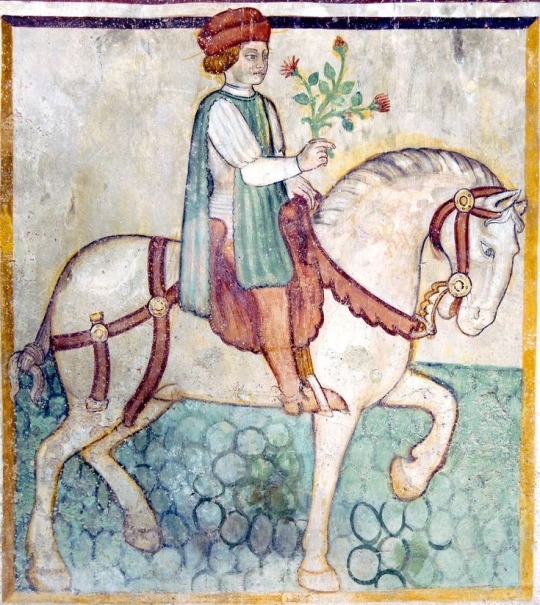
nobleman on horseback, flowers in hand - source
#artwork#traditional art#medieval#medieval art#art#medieval horses#equestrian#equidae#equine#equines#horse#horse posting#horseblr#horses#horse art#painting#tapestry#history#medieval history#medieval painting
22 notes
·
View notes
Text
Maelgwn Gwynedd

(The lad himself. He looks how I look when confronted with any question at all. An expression of surprise mixed with apprehension. Note the tiny sword and orb.)
Entering the final stretch of 2024 with Arthuriana's favourite 'sodomitical grape' as Gildas called him. Seriously, Gildas has beef with him, almost as much as he has with dubious historical personage, King Arthur.
Not much is known about Maelgwn's reign considering how big of a guy he's become in the Arthurian mythos but what we do know of him is cool!!!
His great-granddad was Cunedda, who was the first king of Gwynedd, and from whom all others were descended. Cunedda had conquered Gwynedd after the fall of Roman Britain. His title, Wledig, is obscure and I won't go into it too much, but Cambrian Chronicles has done a video about it which I will link to at the end! It means 'of a country' but it's more likely it was an expression of some Roman title.
And his great-great-grandad was Edern - yes, the basis of THAT Edern in Welsh mythology - who was a romano-briton. Maelgwn's dad, Cadwallon Lawhir* (long-hand), was *maybe* king but there are also questions about that. Mainly from Gildas. He suggests that his brother, Owain Danwyn (White Tooth), was King and Cadwallon was his right-hand man - which perhaps would fit with him being the guy who drove the last of the Irish from Ynys Môn - and suggests that Maelgwn murdered his uncle to gain the throne. Peter Bartrum also suggests this but does caveat that the term used, 'avunculus' is normally only applied to a maternal uncle.
(Fun fact: Owain Danwyn was the father of St. Seriol who gave his name to Ynys Seriol otherwise referred to as Puffin Island in English. Maelgwn would later be buried here after he died of, well, we'll get to that.)
Regardless of who was and wasn't king, Maelgwn was the first to reap the rewards of his great-granddad's conquest.
He is normally regarded as the House of Aberffraw's founder from which all other kings of that line were descended. (Yes, including Law Lad, Hywel Dda) This would make them one of the oldest royal lineages until the English chopped off the last king of Gwynedd and Wales, Llywelyn Ein Llew Olaf's head. Gwynedd is the territory that they ruled over. Basically near enough to the whole of North Wales. At its biggest, would've stretched from Anglesey to Ceredigion. Maelgwn - like Owain Gwynedd - was referred to as 'Maelgwn Gwynedd' because Maelgwn ap Cadwallon was a v common name at the time and it would be fuckin confusing.)
Now, sorting fact from fiction with Maelgwn is... um, difficult, shall we say. Gildas himself said that Maelgwn killed his uncle as previously mentioned, killed his nephew so he could marry his wife, and killed his wife to ensure that she wouldn't object to her husband sharing her bed with another woman. I'm not going into that because I want to keep it short but IT'S WILD.* What we do know suggests that Maelgwn was a deeply religious man, and I'm not being funny, but Gildas smeared like five kings - including Maelgwn's nephew, Cynlas, otherwise known as Cuneglas.
Anyways, while the seat of Aberffraw was traditionally the village of Aberffraw - as the name suggests - Maelgwn's llys (court) was held in Deganwy and where Llywelyn Fawr would later build another llys many years later. 'It is supposed,' Timothy Venning writes, 'that his fort was 'Dinerth on the Clwyd coast, due to which the owner might have been nicknamed 'Artos.' But there is no clear evidence that he was called that but there is plenty of Arthurian sites in Gwynedd! Also, there's a Dinerth in Llandrillo-yn-Rhos near me, and like I like to think maybe there was a fort there somewhere.
He's also known to have given money to many churches and saints which puts Gildas assertions that he was a bad dude in doubt but, I mean, you can make up your mind. In Historia Brittonum, Nennius, remarks, 'the great king Mailcun reigned among the Britons, i.e., in Gwynedd,' and further adds that Cunedda, Maelgwn's ancestor arrived in Gwynedd 146 years ago and slaughtered the Irish living there. He also appears only once in the Welsh Triads in the 'The Tribal Thrones of the Island of Britain' each ruled by King Arthur. Maelgwn was Arthur's Chief of Elders in Mynwy (St. David's, itself a major religious site both for Celts and Christians.)
Honestly, Maelgwn's intertwining with saints is fascinating. It's known, as I've said previously, that he gave to various churches in Gwynedd, while the Book of Llandaff (written in 1125) says he was a benefactor of the Diocese of Llandaff when that first started. Also, his nephew, St. Seriol's, bestie was St Cybi, otherwise known as the lad who gave his name to the Welsh name for Holyhead, 'Caergybi,' which means Cybi's Fort. Maelgwn was, by all accounts, the one who gave the fort to him!
Now, Historium Brittonum is of further interest to us because it, in Kari Maund's words, 'reflects the 9th-century context in which it was written when the rulers of Gwynedd advanced claims of primacy all over Wales.' It would've been, within the rulers of Gwynedd's interests to present Maelgwn and his pedigree as 'pan-Welsh figures,' and many pedigrees further reflect that. (See, when I said sorting fact from fiction was difficult I meant it!)
HB says: 'These are the names of the sons of Cunedda who numbered nine. Tybion was the first-born who died in the land of Manaw of Gododdin and thus did not come with his father and aforesaid brothers. Merrion his son divided the possessions amongst Tybion's brothers: Oswael the second-born, the third Rhufen, the fourth Dunod, the fifth Ceredig, the sixth Afloeg, the seventh Einion Yrth, the eighth Dogfael, the ninth Edern.' The names of these sons became attached to territories within Gwynedd I.e. Dunoding, Rhufeniog, Ceredigion, and, therefore, the divisions (or Cantrefi) of Gwynedd with them. This is propaganda by other monarchs who wanted to show that the Gwyddelian line were the rightful rulers of Ceredigion but it also shows what a Big Fuckin Deal Cunedda and therefore Maelgwn are both as a historical figure and as a propaganda piece. Timothy Venning also suggests that the 'parcelling out' of Gwynedd to members of Cunedda's family was presented by Nennius as 'justification for its reunification by his patron King Merfyn.' Some even say that Owain Gwynedd (him again!) used the legend to 'provide an earlier precedent for its [Gwynedd's] current division' between his sons.' I'm telling u this cuz a) it's of interest because it shows just how embedded this family are in Welsh mythology and culture. Like u cannot go five fuckin mins without seeing them, and b) Maelgwn comes from a fighting pedigree. (And also because I think this is fun.)
Now, Maelgwn's death is pretty confusing. Reports say he died from the 'Yellow Plague or Justinian's Plague' which had made its way over from Byzantium. My school and grandad both said to me when I was little that Maelgwn died from yellow fever passing through a keyhole and infecting him that way which I think is very scary. I would cry if I was confronted with that. Thank you, Ysgol Nant-y-Coed and Grandad Barry, you gave me nightmares about a yellow fog coming to claim me late at night. That's why I now have to block the keyhole of my room door up with blutac. He was buried off Ynys Seriol so yeah. The throne would eventually pass to Maelgwn's son, Rhun, otherwise known as that 'hot lecher of women' himself.
As for Maelgwn, he's bound up in Arthuriana as are his family. Many kings of his line claimed descent from Arthur further down the line and it's not a stretch to think that maybe that's why he's such a big part of Arthuriana. Also, he's such a cool character in his own right that it would be a disservice not to include him. Edern, Maelgwn's great-grandad, is sometimes said to be Guinevere's lover in Welsh mythology, and that would make him and his line have the genes of the wife defender of Britain and the literal Lad Everybody Gets Their Knickers In A Twist Over, Arthur. It's not a stretch to think that later chronicles went fuckin Mad with this info. I would!
*The video about the term 'Wledig' is here.
* If you want to learn more about these events can I suggest this web page which explains it far better than I ever could:
https://www.ancientwalesstudies.org/id166.html
Tagging people I think might get a kick out of this: @dullyn @gwalch-mei @gawrkin @crwbannwen @believerindaydreams @queer-ragnelle @cesarescabinet
Okay, hwyl fawr! I'll be back next year to chew your ears off about the Mabinogion in the context of ladies or something.
#arthuriana#arthurian legend#arthurian history#arthurian legends#arthurian personages#arthurian literature#arthurian mythology#arthurian myth#welsh mythology#welsh myth#welsh folklore#the house of aberffraw#medieval history#welsh history#hanes gymraeg#maelgwn gwynedd#king arthur#once again i find a way to include Guinevere in this#it ran away with me im so sorry
21 notes
·
View notes
Text

I just learned this fact and I can't help but share it with you!!!
In 13th-century European castles, separate fortresses were rarely built. Instead, one of the towers was significantly larger than the others and served as sleeping quarters for the lord or the king and his family.
Medieval life was full of changes and conflicts. Periods of peace were often interrupted by wars and sieges. To protect the ruler and his family, spiral staircases were built in the towers, winding clockwise. This design made it harder for attackers, as defenders could strike while using the wall as a shield, whereas attackers, especially right-handed ones, faced difficulties.

Additionally, the steps were uneven in height and length, making it easier for defenders, familiar with the layout, to move quickly. Attackers, in heavy armor and unfamiliar with the stairs, risked losing balance. This design significantly complicated sieges, particularly when climbing upward, giving defenders an advantage.
Thus, clockwise spiral staircases were not only convenient but also a crucial part of defensive strategy.
Another fact here
#fan fact#history facts#history#castle#medieval history#Historical Castles#architecture history#thinking aloud#text post
11K notes
·
View notes
Text

Fun fact but according to historians, tamagotchi were a popular commodity for noble ladies in the 14th century
#my source is that i made it the fuck up#medieval art#medieval history#medievalcore#illuminated manuscript#medieval#renaissance#fantasy art#history meme
7K notes
·
View notes
Text

#history#medieval history#ish?#oh i am Deeply in my feelings about this#people have always been people#(will always be people)#“i was his closest neighbor”#(they had not wanted him to go without flowers)#excuse me i just need to cry for real. thanks.
4K notes
·
View notes
Text
all RIGHT:
Why You're Writing Medieval (and Medieval-Coded) Women Wrong: A RANT
(Or, For the Love of God, People, Stop Pretending Victorian Style Gender Roles Applied to All of History)
This is a problem I see alllll over the place - I'll be reading a medieval-coded book and the women will be told they aren't allowed to fight or learn or work, that they are only supposed to get married, keep house and have babies, &c &c.
If I point this out ppl will be like "yes but there was misogyny back then! women were treated terribly!" and OK. Stop right there.
By & large, what we as a culture think of as misogyny & patriarchy is the expression prevalent in Victorian times - not medieval. (And NO, this is not me blaming Victorians for their theme park version of "medieval history". This is me blaming 21st century people for being ignorant & refusing to do their homework).
Yes, there was misogyny in medieval times, but 1) in many ways it was actually markedly less severe than Victorian misogyny, tyvm - and 2) it was of a quite different type. (Disclaimer: I am speaking specifically of Frankish, Western European medieval women rather than those in other parts of the world. This applies to a lesser extent in Byzantium and I am still learning about women in the medieval Islamic world.)
So, here are the 2 vital things to remember about women when writing medieval or medieval-coded societies
FIRST. Where in Victorian times the primary axes of prejudice were gender and race - so that a male labourer had more rights than a female of the higher classes, and a middle class white man would be treated with more respect than an African or Indian dignitary - In medieval times, the primary axis of prejudice was, overwhelmingly, class. Thus, Frankish crusader knights arguably felt more solidarity with their Muslim opponents of knightly status, than they did their own peasants. Faith and age were also medieval axes of prejudice - children and young people were exploited ruthlessly, sent into war or marriage at 15 (boys) or 12 (girls). Gender was less important.
What this meant was that a medieval woman could expect - indeed demand - to be treated more or less the same way the men of her class were. Where no ancient legal obstacle existed, such as Salic law, a king's daughter could and did expect to rule, even after marriage.
Women of the knightly class could & did arm & fight - something that required a MASSIVE outlay of money, which was obviously at their discretion & disposal. See: Sichelgaita, Isabel de Conches, the unnamed women fighting in armour as knights during the Third Crusade, as recorded by Muslim chroniclers.
Tolkien's Eowyn is a great example of this medieval attitude to class trumping race: complaining that she's being told not to fight, she stresses her class: "I am of the house of Eorl & not a serving woman". She claims her rights, not as a woman, but as a member of the warrior class and the ruling family. Similarly in Renaissance Venice a doge protested the practice which saw 80% of noble women locked into convents for life: if these had been men they would have been "born to command & govern the world". Their class ought to have exempted them from discrimination on the basis of sex.
So, tip #1 for writing medieval women: remember that their class always outweighed their gender. They might be subordinate to the men within their own class, but not to those below.
SECOND. Whereas Victorians saw women's highest calling as marriage & children - the "angel in the house" ennobling & improving their men on a spiritual but rarely practical level - Medievals by contrast prized virginity/celibacy above marriage, seeing it as a way for women to transcend their sex. Often as nuns, saints, mystics; sometimes as warriors, queens, & ladies; always as businesswomen & merchants, women could & did forge their own paths in life
When Elizabeth I claimed to have "the heart & stomach of a king" & adopted the persona of the virgin queen, this was the norm she appealed to. Women could do things; they just had to prove they were Not Like Other Girls. By Elizabeth's time things were already changing: it was the Reformation that switched the ideal to marriage, & the Enlightenment that divorced femininity from reason, aggression & public life.
For more on this topic, read Katherine Hager's article "Endowed With Manly Courage: Medieval Perceptions of Women in Combat" on women who transcended gender to occupy a liminal space as warrior/virgin/saint.
So, tip #2: remember that for medieval women, wife and mother wasn't the ideal, virgin saint was the ideal. By proving yourself "not like other girls" you could gain significant autonomy & freedom.
Finally a bonus tip: if writing about medieval women, be sure to read writing on women's issues from the time so as to understand the terms in which these women spoke about & defended their ambitions. Start with Christine de Pisan.
I learned all this doing the reading for WATCHERS OF OUTREMER, my series of historical fantasy novels set in the medieval crusader states, which were dominated by strong medieval women! Book 5, THE HOUSE OF MOURNING (forthcoming 2023) will focus, to a greater extent than any other novel I've ever yet read or written, on the experience of women during the crusades - as warriors, captives, and political leaders. I can't wait to share it with you all!
#watchers of outremer#medieval history#the lady of kingdoms#the house of mourning#writing#writing fantasy#female characters#medieval women#eowyn#the lord of the rings#lotr#history#historical fiction#fantasy#writing tip#writing advice
30K notes
·
View notes
Text


Medieval heart-shaped music book, circa 1460-1477.
National library of France.
#beauty#oddities#antiques#middle ages#medieval history#curiosities#medieval art#european culture#french culture
903 notes
·
View notes
Text


Carolingian sword uncovered in Dendermonde, Belgium, dated 750-850 AD
from the Royal Military Museum, Brussels
1K notes
·
View notes
Text

I started reading Roland Betancourt's Byzantine Intersectionality because it has a chapter on transwomen, but it turns out that the book is heavily focused on transmasculinity and race in the Byzantine world.
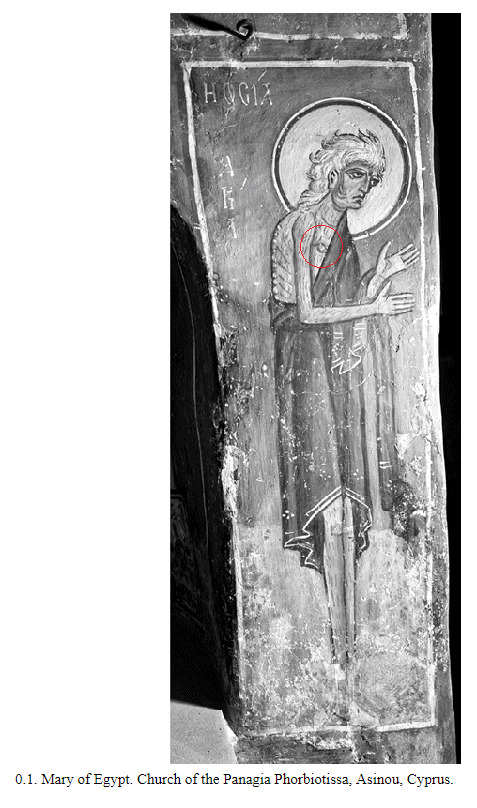

Specifically I wanted to show you this discussion on artistic representation of top surgery and the likelihood that this actually represents top surgery.
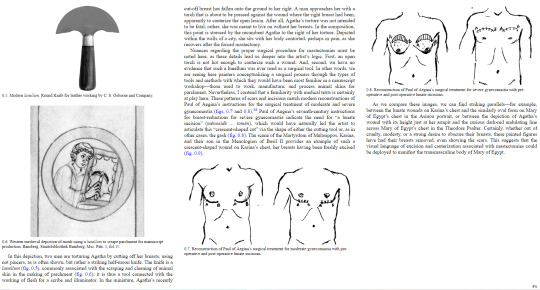
Anyway this is really fucking cool
5K notes
·
View notes
Text
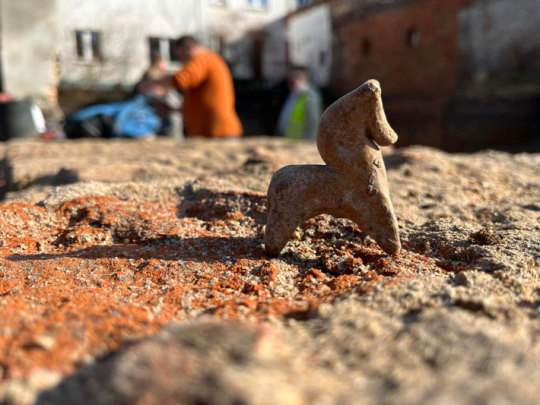

Medieval Toy Unearthed in Poland
A 800-year-old horse figurine was found during an excavation conducted as part of the construction of a new fire station in Toruń, a medieval town on the Vistula River in north-central Poland. The small clay horse was glazed and has a hole in its underside. Researchers think a stick may have fit into the hole so that playing children could pretend to make the horse gallop or use it as a puppet.

#Medieval Toy Unearthed in Poland#A 800-year-old horse figurine#Toruń#ancient artifacts#archeology#archeolgst#history#history news#ancient history#ancient culture#ancient civilizations#medieval history
1K notes
·
View notes
Text






Currently obsessed with these naturalistic illuminations from a manuscript of De Proprietatibus Rerum (1447, Bibliothèque d'Amiens, ms. 399). I just know that whoever commisioned this must have hired the nearest artist with an insane obsession for birds before proper birdwatching was even a thing. They hired the nearest De arte venandi cum avibus fanboy.



Like, the fact that despite the stylized drawings you can clearly tell that these are a corvus corax, a corvus cornix?! Hello?!?!
I love you, unknown french artist from the 15th century.
#Edit: a couple people made me rightfully notice that what I thought could be a carrion crow#in absence of better candidates#could actually be a jackdaw#and that either way it doesn't even match the text it is meant to represent as it was a total misinterpretation of it#just to let everyone know!#thank you irl french andreas maler#illuminated manuscripts#medieval manuscripts#ornithology#ravens#middle ages#corvids#medieval history#medieval art#history of art
5K notes
·
View notes
Text
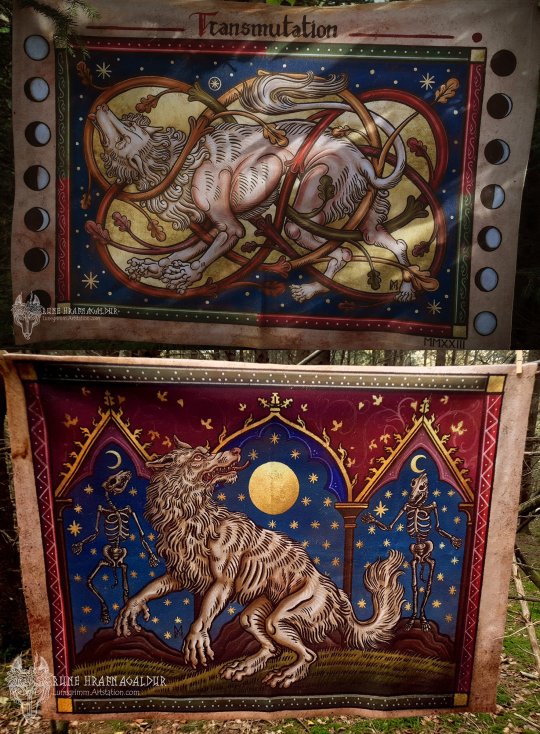




The time has finally come! The werewolf themed tapestry designs are available for pre-order once more! Joined by a pair of witches making for 4 new designs!
#WerewolfWednesday
#art#artists on tumblr#digitalart#medievalart#lunegrimmart#werewolf wednesday#medieval#werewolf#werewolves#wolf art#werewolf transformation#werewolf by night#werewolfwednesday#halloween#creature#lycanthrope#fantasy#fantasy art#medieval art#medieval manuscripts#medieval history#spooktober#spookyseason#halloween art#halloween vibes#furry#anthro#skeleton#manuscript#woodcut
420 notes
·
View notes
Text
"As far as we know, Ende was a Spanish illustrator who lived in the late 10th century and is regarded as the first female European artist to be recorded. She spent a portion of her life at San Salvador de Tábara Monastery in Tábara, Kingdom of León in Medieval Spain. According to the research of John Williams, one of the most eminent experts in Spanish medieval art, Ende may not have been a nun but rather belonged to a group of noble women from León who, during those years, rejected both convent life and instead managed their wealth and in a sense decided to go their way.
The Tabara scriptorium, which generated some of the Spanish Middle Ages’ most significant codices, was a cultural lighthouse at the time. Ende felt tremendously at ease working and living at Tábara Monastery, according to her illuminated manuscripts. Above all, it brought Ende closer to the dominant cultural movement of the day, recognizing the need to preserve sacred passages and everlasting images, working for her faith and herself."

#ende#history#women in history#women's history#10th century#female painters#female artists#spain#spanish history#middle ages#medieval history#medieval#medieval women
430 notes
·
View notes
Text
Time Travel Question 61: Middle Ages and Much Earlier
These Questions are the result of suggestions from the previous iteration.
This category may include suggestions made too late to fall into the correct grouping.
Please add new suggestions below if you have them for future consideration.
#Time Travel#Mastodons#Megafauna#Triceratops#Dinosaurs#Pre-History#Dimetrodons#Saber-toothed Cats#Smilodon#Chinggis Khan#Genghis Khan#Mongols#Temüjin#Mongolian History#13th Century#Medieval History#Middle Ages#Athens#Ancient World#Canaanites#Ancient Religions#History of Religion#West Asia#Denisovans#Homins#Paleolithic#Prehistory#The Ghana Empire#Ghana#Ghanata
320 notes
·
View notes
Text
Medieval Europeans regarded embroidery as an art, much as we today consider painting. It was considered a female task, and even chambermaids were expected to be competent in it. Yet it was a coveted line of work, as one early Irish law tract stated that "the woman who embroiders earns more profit even than queens." Embroiderers could find employment with professional clothing makers or in tapestry workshops.
By the thirteenth century, given that embroidery was held in high esteem and could bring in money, the field contained plenty of men as well. In England, over time women come up less frequently on the lists of embroiderers than men and more often in conjunction with a husband, even when their work was exceptional. In May 1317 "Rose, the wife of John de Bureford, citizen and merchant of London," sold "an embroidered cope for the choir" to the French queen Isabella (ca. 1295-1358), who gave it as a gift "to the Lord High Pontiff." Rose was clearly a very skilled artist, since she was commissioned by the queen, but was not skilled enough to be named as an artist in her own right. We don't know how many other working embroiderers were subsumed into their husbands' workshops with even their first names lost to us. Once a field became truly profitable, men nudged women out of it. It was all well and good to let ladies have fun with a needle and thread. But if there was cash to be made, men suddenly showed up front and center and excluded women from the role.
-Eleanor Janega, The Once and Future Sex: Going Medieval on Women’s Roles in Society
#eleanor janega#womens history#art history#embroidery#the more things change the more they stay the same#medieval history#men menning
1K notes
·
View notes