#low cost country sourcing
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Currently, companies are looking for ways to enhance their operations and reduce overall costs without compromising quality. Low cost country sourcing from GainEdge has emerged as the most extraordinary strategy for organizations to grab cost efficiency in their supply chains. Through this blog, you can explore the concept of low cost country sourcing, its challenges, benefits, and major considerations for successful implementation.
0 notes
Text
Things Biden and the Democrats did, this week #24
June 21-28 2024
The US Surgeon General declared for the first time ever, firearm violence a public health crisis. The nation's top doctor recommended the banning of assault weapons and large-capacity magazines, the introduce universal background checks for purchasing guns, regulate the industry, pass laws that would restrict their use in public spaces and penalize people who fail to safely store their weapons. President Trump dismissed Surgeon General Dr. Vivek Murthy in 2017 in part for his criticism of guns before his time in government, he was renominated for his post by President Biden in 2021. While the Surgeon General's reconstructions aren't binding a similar report on the risks of smoking in 1964 was the start of a national shift toward regulation of tobacco.
Vice-President Harris announced the first grants to be awarded through a ground breaking program to remove barriers to building more housing. Under President Biden more housing units are under construction than at any time in the last 50 years. Vice President Harris was announcing 85 million dollars in grants giving to communities in 21 states through the Pathways to Removing Obstacles to Housing (PRO) program. The administration plans another 100 million in PRO grants at the end of the summer and has requested 100 million more for next year. The Treasury also announced it'll moved 100 million of left over Covid funds toward housing. All of this is part of plans to build 2 million affordable housing units and invest $258 billion in housing overall.
President Biden pardoned all former US service members convicted under the US Military's ban on gay sex. The pardon is believed to cover 2,000 veterans convicted of "consensual sodomy". Consensual sodomy was banned and a felony offense under the Uniform Code of Justice from 1951 till 2013. The Pardon will wipe clean those felony records and allow veterans to apply to change their discharge status.
The Department of Transportation announced $1.8 Billion in new infrastructure building across all 50 states, 4 territories and Washington DC. The program focuses on smaller, often community-oriented projects that span jurisdictions. This award saw a number of projects focused on climate and energy, like $25 million to help repair damage caused by permafrost melting amid higher temperatures in Alaska, or $23 million to help electrify the Downeast bus fleet in Maine.
The Department of Energy announced $2.7 billion to support domestic sources of nuclear fuel. The Biden administration hopes to build up America's domestic nuclear fuel to allow for greater stability and lower costs. Currently Russia is the world's top exporter of enriched uranium, supplying 24% of US nuclear fuel.
The Department of Interior awarded $127 million to 6 states to help clean up legacy pollution from orphaned oil and gas wells. The funding will help cap 600 wells in Alaska, Arizona, Indiana, New York and Ohio. So far thanks to administration efforts over 7,000 orphaned wells across the country have been capped, reduced approximately 11,530 metric tons of carbon dioxide equivalent emissions
HUD announced $469 million to help remove dangerous lead from older homes. This program will focus on helping homeowners particularly low income ones remove lead paint and replace lead pipes in homes built before 1978. This represents one of the largest investments by the federal government to help private homeowners deal with a health and safety hazard.
Bonus: President Biden's efforts to forgive more student debt through his administration's SAVE plan hit a snag this week when federal courts in Kansas and Missouri blocked elements the Administration also suffered a set back at the Supreme Court as its efforts to regular smog causing pollution was rejected by the conservative majority in a 5-4 ruling that saw Amy Coney Barrett join the 3 liberals against the conservatives. This week's legal setbacks underline the importance of courts and the ability to nominate judges and Justices over the next 4 years.
#Thanks Biden#Joe Biden#politics#us politics#american politics#election 2024#gun control#gun violence#LGBT rights#gay rights#Pride#housing#climate change
4K notes
·
View notes
Text
🙄🙄🙄🙄 are we seriously still doing the "wow things are bad here in the U.S., what are we, a bunch of Asians?" thing? It is actually extremely possible to discuss homegrown usamerican fascism without virtue signaling about Official Foreign Boogeymen
and as far as I've been able to discern, the second photo is celebrating teachers who volunteered to teach in impoverished rural areas, which idk how you can twist into being some evil plot, & has literally nothing to do with ANYTHING happening in Florida. Oh, but yeah, because it's North Korea, nobody has agency to participate in improving their country of their own free will, they're all poor little creatures living under constant threat of murder for having a smidge of dust on a portrait.
Jesus christ, I beg my fellow yankees to grow some critical analysis skills and stop believing anything that comes out of Yeonmi "Besties-With-Joe-Rogan-&-Matt-Walsh" Park's liar mouth. *Obligatory of course the DPRK has problems & isn't perfect so people will keep reading* but no country lacks problems!!! so stop treating North Koreans who support their government like they're a special kind of too stupid to know better, or a special kind of evil who gleefully feed babies to rats or whatever. It's chauvinism, it's racism, and I for one am done letting it slide when I see it. North Koreans are not props for westerners to whip out whenever white american christians commit acts of evil, and those affected by the loss of reproductive rights are not props to whip out for orientalist warmongering. We can see the fascism happening in the U.S. with our very own eyes, with ample evidence-- the Special Kind of Authoritarian Evil call is coming from inside the house.
See, this post wanted to make a point about the genuine horror show happening in Florida & other states, but by using a lazy dunk you've also distracted your point. Great job, you're reeeeeeally helping protect abortion access and trans kids with this 😒😒😒
Do better.
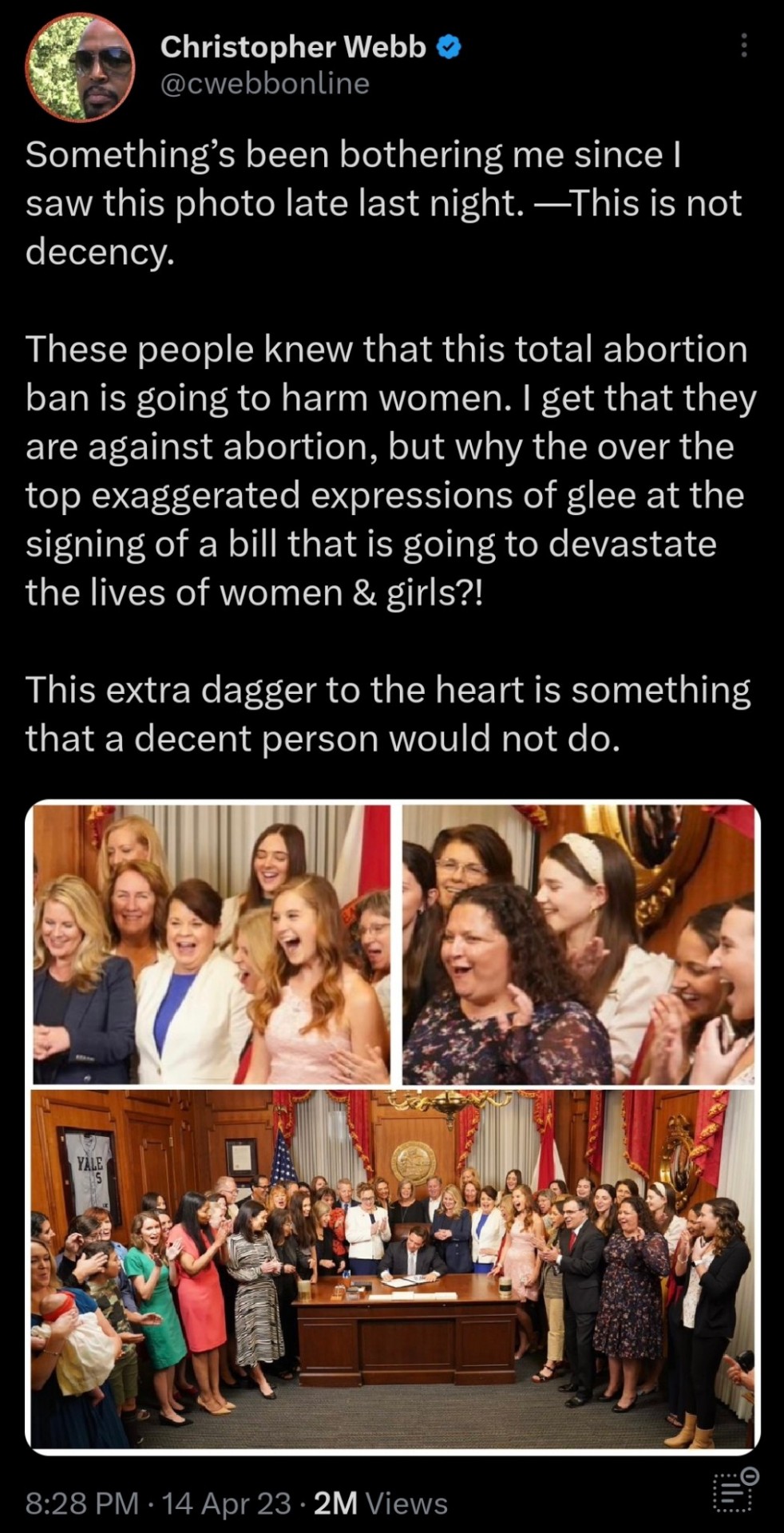
This staged photo looks familiar. What other authoritarian am I thinking of?

Republicans men are restructuring the lives of women as 'less than'. When you have no control over your body and must obey the State, you are not free.
#liberals are not cool they are spineless worms with no sense for solidarity & mindlessly repeat state department lines with no evidence#op could have more specifically addressed the fascist policies in-depth instead of superficially fixating on photo staging. so useless.#or delve into the phenomenon of pick me white feminism as an aid to fascism that the women in the 1st phot are engaging in#you dont have to become the dprk's strongest warrior or whatever but for the low low cost of zero dollars yankees can simply not continue#to demonize & dehumanize north koreans & spread claims that are not substantiated#and maybe take some time to learn about the dprk from sources that arent seeking its destruction. listen to them without infantilizing#learn some history learn some media analysis learn that radio free asia is not a viable source to form your entire viewpoint of a country#also comparing kim jong un to desantis is so disrespectful even if half of the kim fam supervillian claims are true desantis is still worse#yeah i said it! and if you want to know why i think so follow my above advice and get to learning
695 notes
·
View notes
Text
"The story of 'John Doe 1' of the Democratic Republic of the Congo is tucked in a lawsuit filed five years ago against several U.S. tech companies, including Tesla, the world’s largest electric vehicle producer. In a country where the earth hides its treasures beneath its surface, those who chip away at its bounty pay an unfair price. As a pre-teen, his family could no longer afford to pay his $6 monthly school fee, leaving him with one option: a life working underground in a tunnel, digging for cobalt rocks. But soon after he began working for roughly two U.S. dollars per day, the child was buried alive under the rubble of a collapsed mine tunnel. His body was never recovered.
The nation, fractured by war, disease, and famine, has seen more than 6 million people die since the mid-1990s, making the conflict the deadliest since World War II. But, in recent years, the death and destruction have been aided by the growing number of electric vehicles humming down American streets. In 2022, the U.S., the world’s third-largest importer of cobalt, spent nearly $525 million on the mineral, much of which came from the Congo.
As America’s dependence on the Congo has grown, Black-led labor and environmental organizers here in the U.S. have worked to build a transnational solidarity movement. Activists also say that the inequities faced in the Congo relate to those that Black Americans experience. And thanks in part to social media, the desire to better understand what’s happening in the Congo has grown in the past 10 years. In some ways, the Black Lives Matter movement first took root in the Congo after the uprising in Ferguson in 2014, advocates say. And since the murder of George Floyd and the outrage over the Gaza war, there has been an uptick in Congolese and Black American groups working on solidarity campaigns.
Throughout it all, the inequities faced by Congolese people and Black Americans show how the supply chain highlights similar patterns of exploitation and disenfranchisement. ... While the American South has picked up about two-thirds of the electric vehicle production jobs, Black workers there are more likely to work in non-unionized warehouses, receiving less pay and protections. The White House has also failed to share data that definitively proves whether Black workers are receiving these jobs, rather than them just being placed near Black communities. 'Automakers are moving their EV manufacturing and operations to the South in hopes of exploiting low labor costs and making higher profits,' explained Yterenickia Bell, an at-large council member in Clarkston, Georgia, last year. While Georgia has been targeted for investment by the Biden administration, workers are 'refusing to stand idly by and let them repeat a cycle that harms Black communities and working families.'
... Of the 255,000 Congolese mining for cobalt, 40,000 are children. They are not only exposed to physical threats but environmental ones. Cobalt mining pollutes critical water sources, plus the air and land. It is linked to respiratory illnesses, food insecurity, and violence. Still, in March, a U.S. court ruled on the case, finding that American companies could not be held liable for child labor in the Congo, even as they helped intensify the prevalence. ... Recently, the push for mining in the Congo has reached new heights because of a rift in China-U.S. relations regarding EV production. Earlier this month, the Biden administration issued a 100% tariff on Chinese-produced EVs to deter their purchase in the U.S. Currently, China owns about 80% of the legal mines in the Congo, but tens of thousands of Congolese work in 'artisanal' mines outside these facilities, where there are no rules or regulations, and where the U.S. gets much of its cobalt imports. 'Cobalt mining is the slave farm perfected,' wrote Siddharth Kara last year in the award-winning investigative book Cobalt Red: How The Blood of the Congo Powers Our Lives. 'It is a system of absolute exploitation for absolute profit.' While it is the world’s richest country in terms of wealth from natural resources, Congo is among the poorest in terms of life outcomes. Of the 201 countries recognized by the World Bank Group, it has the 191st lowest life expectancy."
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
The Real Cost of the Fashion Industry

Atacama Desert, in Alto Hospicio, Iquique, Chile. (source)
The textile industry is destroying the world. The industry is wasting massive amounts of energy and materials, and polluting the air, the ground and the water supplies. It overwhelmingly exploits it's labour and extracts wealth from colonized countries, especially in Asia. I assume we all broadly understand this, but I think it's useful to have it all laid out in front of you to see the big picture, the core issues causing this destruction and find ways how to effectively move forward.
The concerning trend behind this ever-increasing devastation are shortening of trend cycles, lowering clothing prices and massive amount of wasted products. Still in year 2000 it was common for fashion brands to have two collections per year, while now e.g. Zara produces 24 collections and H&M produces 12-16 collections per year. Clothing prices have fallen (at leas in EU) 30% from 1996 to 2018 when adjusted to inflation, which has contributed to the 40% increase in clothing consumption per person between 1996 and 2012 (in EU). (source) As the revenue made by the clothing industry keep rising - from 2017 to 2021 they doubled (source) - falling prices can only be achieved with increasing worker exploitation and decreasing quality. I think the 36% degrees times clothing are used in average during the last 15 years (source) is a clear indication on the continuing drop in quality of clothing. Clothing production doubled between 2000 and 2015, while 30% of the clothes produced per year are never sold and are often burned instead (source), presumably to prevent the returns from falling due to oversupply.
These all factors are driving people to overconsume. While people in EU keep buying more clothes, they haven't used up to 50% of the clothes in their wardrobe for over a year (source). This overconsumption is only made much worse by the new type of hyper fast fashion companies like SHEIN and Temu, which are using addictive psychological tactics developed by social media companies (source 1, source 2). They are cranking up all those concerning trends I mentioned above.
Under the cut I will go through the statistics of the most significant effects of the industry on environment and people. I will warn you it will be bleak. This is not just a fast fashion problem, basically the whole industry is engaging in destructive practices leading to this damage. Clothing is one of those things that would be actually relatively easy to make without massive environmental and human cost, so while that makes the current state of the industry even more heinous, it also means there's hope and it's possible to fix things. In the end, I will be giving some suggestions for actions we could be doing right now to unfuck this mess.
Carbon emissions
The textile industry is responsible for roughly 10% of the global CO2 emissions, more than aviation and shipping industry combined. This is due to the massive supply chains and energy intensive production methods of fabrics. Most of it can be contributed to the fashion sector since around 60% of all the textile production is clothing. Polyester, a synthetic fiber made from oil which accounts for more than half of the fibers used in the textile industry, produces double the amount of carbon emissions than cotton, accounting for very large proportions of all the emissions by the industry. (source 1, source 2)
Worker exploitation
Majority of the textiles are produced in Asia. Some of the worst working conditions are in Bangladesh, one of the most important garment producers, and Pakistan. Here's an excerpt from EU Parliament's briefing document from 2014 after the catastrophic Rana Plaza disaster:
The customers of garment producers are most often global brands looking for low prices and tight production timeframes. They also make changes to product design, product volume, and production timeframes, and place last-minute orders without accepting increased costs or adjustments to delivery dates. The stresses of such policies usually fall on factory workers.
The wage exploitation is bleak. According to the 2015 documentary The True Cost less than 2% of all garment factory workers earned a living wage (source). Hourly wages are so low and the daily quotas so high, garment workers are often forced through conditions or threats and demand to work extra hours, which regularly leads to 10-12 hour work days (source) and at worst 16 hour workdays (source), often without days off. Sometimes factories won't compensate for extra hours, breaching regulations (source).
Long working hours, repetitive work, lack of breaks and high pressure leads to increased risks of injuries and accidents. Small and even major injuries are extremely common in the industry. A study in three factories in India found that 70% of the workers suffered from musculosceletal symptoms (source). Another qualitative study of female garment workers and factory doctors in Dhaka found that long hours led to eye strain, headaches, fatigue and weight loss in addition to muscular and back pains. According to the doctors interviewed, weight loss was common because the workers work such long hours without breaks, they didn't have enough time to eat properly. (source) Another study in 8 factories in India found that minor injuries were extremely common and caused by unergonomic work stations, poor organization in the work place and lack of safety gear, guidelines and training (source). Safety precautions too are often overlooked to cut corners, which periodically leads to factory accidents, like in 2023 lack of fire exists and fire extinguishers, and goods stacked beyond capacity led to a factory fire in Pakistan which injured dozens of workers (source) or like in 2022 dangerous factory site led to one dead worker and 9 injured workers (source).
Rana Plaza collapse in 2013 is the worst industrial accident in recent history. The factory building did not have proper permits and the factory owner blatantly ignored signs of danger (other businesses abandoned the building a day before the collapse), which led to deaths of 1 134 workers and injuries to 2 500 workers. The factory had or were at the time working for orders of at least Prada, Versace, Primark, Walmart, Zara, H&M, C&A, Mango, Benetton, the Children's Place, El Corte Inglés, Joe Fresh, Carrefour, Auchan, KiK, Loblaw, Bonmarche and Matalan. None of the brands were held legally accountable for the unsafe working conditions which they profited off of. Only 9 of the brands attended a meeting to agree on compensation for the victim's families. Walmart, Carrefour, Auchan, Mango and KiK refused to sight the agreement, it was only signed by Primark, Loblaw, Bonmarche and El Corte Ingles. The compension these companies provided was laughable though. Primemark demanded DNA evidence that they are relatives of one of the victims from these struggling families who had lost their often sole breadwinner for a meager sum of 200 USD (which doesn't even count for two months of living wage in Bangladesh (source)). This obviously proved to be extremely difficult for most families even though US government agreed to donate DNA kits. This is often said to be a turning point in working conditions in the industry, at least in Bangladesh, but while there's more oversight now, as we have seen, there's clearly still massive issues. (source 1, source 2)
One last major concern of working conditions in the industry I will mention is the Xinjiang raw cotton production, which is likely produced mainly with forced labour from Uighur concentration camps, aka slave labour of a suspected genocide. 90% of China's raw cotton production comes from Xinjiang (source). China is the second largest cotton producer in the world, after India, accounting 20% of the yearly global cotton production (source).
Pollution
Synthetic dyes, which synthetic fibers require, are the main cause of water pollution caused by the textile industry, which is estimated to account for 20% of global clean water pollution (source). This water pollution by the textile industry is suspected of causing a lot of health issues like digestive issues in the short term, and allergies, dermatitis, skin inflammation, tumors and human mutations in the long term. Toxins also effect fish and aquatic bacteria. Azo dyes, one of the major pollutants, can cause detrimental effects to aquatic ecosystems by decreasing photosynthetic activity of algae. Synthetic dyes and heavy metals also cause large amounts of soil pollution. Large amounts of heavy metals in soil, which occurs around factories that don't take proper environmental procautions, can cause anaemia, kidney failure, and cortical edoem in humans. That also causes changes in soil texture, decrease in soil microbial diversity and plant health, and changes in genetic structure of organisms growing in the soil. Textile factory waste water has been used for irrigation in Turkey, where other sources of water have been lacking, causing significant damage to the soil. (source)
Rayon produced through viscose process causes significant carbon disulphide and hydrogen sulphide pollution to the environment. CS2 causes cardiovascular, psychiatric, neuropsychological, endocrinal and reproductive disorders. Abortion rates among workers and their partners exposed to CS2 are reported to be significantly higher than in control groups. Many times higher amounts of sick days are reported for workers in spinning rooms of viscose fiber factories. China and India are largest producers of CS2 pollution, accounting respectively 65.74% and 11,11% of the global pollution, since they are also the major viscose producers. Emission of CS2 has increased significantly in India from 26.8 Gg in 2001 to 78.32 Gg in 2020. (source)
Waste
The textile industry is estimated to produce around 92 million tons of textile waste per year. As said before around 30% of the production is never sold and with shortening lifespans used the amount of used clothing that goes to waster is only increasing. This waste is large burned or thrown into landfills in poor countries. (source) H&M was accused in 2017 by investigative journalists of burning up to 12 tonnes of clothes per year themselves, including usable clothing, which they denied claiming they donated clothing they couldn't sell to charity instead (source). Most of the clothing donated to charity though is burned or dumbed to landfills (source).
Most of the waste clothing from rich countries like European countries, US, Australia and Canada are shipped to Chile (source) or African countries, mostly Ghana, but also Burkina Faso and Côte d'Ivoire (source). There's major second-hand fashion industries in these places, but most of the charity clothing is dumbed to landfills, because they are in such bad condition or the quality is too poor. Burning and filling landfills with synthetic fabrics with synthetic dyes causes major air, water and soil pollution. The second-hand clothing industry also suppresses any local clothing production as donated clothing is inherently more competitive than anything else, making these places economically reliant on dumbed clothing, which is destroying their environment and health, and prevents them from creating a more sustainable economy that would befit them more locally. This is not an accident, but required part of the clothing industry. Overproduction let's these companies tap on every new trend quickly, while not letting clothing the prices in rich countries drop so low it would hurt their profits. Production is cheaper than missing a trend.
Micro- and nanoplastics
There is massive amounts of micro- and nanoplastics in all of our environment. It's in our food, drinking water, even sea salt (source). Washing synthetic textiles accounts for roughly 35% of all microplastics released to the environment. It's estimated that it has caused 14 million tonnes of microplastics to accumulate into the bottom of the ocean. (source)
Microplastics build up into the intestines of animals (including humans), and have shown to probably cause cause DNA damage and altered organism behavior in aquatic fauna. Microplastics also contain a lot of the usual pollutants from textile industry like synthetic dyes and heavy metals, which absorb in higher quantities to tissues of animals through microplastics in the intestines. Studies have shown that the adverse effect are higher the longer the microplastics stay in the organism. The effects cause major risks to aquatic biodiversity. (source) The health effects of microplastics to humans are not well known, but studies have shown that they could have adverse effects on digestive, respiratory, endocrine, reproductive and immune systems. (source)
Microplastics degrade in the environment even further to nanoplastics. Nanoplastic being even smaller are found to enter blood circulation, get inside cells and cross the blood-brain barrier. In fishes they have been found to cause neurological damage. Nanoplastics are also in the air, and humans frequently breath them in. Study in office buildings found higher concentration of nanoplastics in indoor air than outdoor air. Inside the nanoplastics are likely caused mostly by synthetic household textiles, and outdoors mostly by car tires. (source) An association between nanoplastics and mitochondrial damage in human respiratory cells was found in a recent study. (source)
Micro and nano plastics are also extremely hard to remove from the environment, making it even more important that we reduce the amount of microplastics we produce as fast as possible.
What can we do?
This is a question that deserves it's own essays and articles written about it, but I will leave you with some action points. Reading about these very bleak realities can easily lead to overwhelming apathy, but we need to channel these horrors into actions. Whatever you do, do not fall into apathy. We don't have the luxury for that, we need to act. These are industry wide problems, that simply cannot be fixed by consumerism. Do not trust any clothing companies, even those who market themselves as ethical and responsible, always assume they are lying. Most of them are, even the so called "good ones". We need legislation. We cannot allow the industry to regulate itself, they will always take the easy way out and lie to their graves. I will for sure write more in dept about what we can do, but for now here's some actions to take, both political and individual ones.
Political actions
Let's start with political actions, since they will be the much more important ones. While we are trying to dismantle capitalism and neocolonialism (the roots of these issues), here's some things that we could do right now. These will be policies that we should be doing everywhere in the world, but especially rich countries, where most of the clothing consumption is taking place. Vote, speak to others, write to your representative, write opinion pieces to your local papers, engage with democracy.
Higher requirements of transparency. Right now product transparency in clothing is laughably low. In EU only the material make up and the origin country of the final product are required to be disclosed. Everything else is up to the company. Mandatory transparency is the only way we can force any positive changes in the production. The minimum of transparency should be: origin countries of the fibers and textiles in the product itself; mandatory reports of the lifecycle emissions; mandatory reports of whole chain of production. Right now the clothing companies make their chain of production intentionally complex, so they have plausible deniability when inevitably they are caught violating environmental or worker protection laws (source). They intentionally don't want to be able to track down their production chain. Forcing them to do so anyway would make it very expensive for them to keep up this unnecessarily complex production chain. These laws are most effective when put in place in large economies like EU or US.
Restrictions on the use of synthetic fibers. Honestly I think they should be banned entirely, since the amount of microplastics in our environment is already extremely distressing and the other environmental effects of synthetic fibers are also massive, but I know there are functions for which they are not easily replaced (though I think they can be replaces in those too, but that's a subject of another post), so we should start with restrictions. I'm not sure how they should be specifically made, I'm not a law expert, but they shouldn't be used in everyday textiles, where there are very easy and obvious other options.
Banning viscose. There are much better options for viscose method that don't cause massive health issues and environmental destruction where ever it's made, like Lyocell. There is absolutely no reason why viscose should be allowed to be sold anywhere.
Governmental support for local production by local businesses. Most of the issues could be much more easily solved and monitored if most clothing were not produced by massive global conglomerations, but rather by local businesses that produce locally. All clothing are made by hand, so centralizing production doesn't even give it advantage in effectiveness (only more profits for the few). Producing locally would make it much more easier to enforce regulations and it would reduce production chains, making production more effective, leaving more profits into the hands of the workers and reducing emissions from transportation. When the production is done by local businesses, the profits would stay in the producing country and they could be taxed and utilized to help the local communities. This would be helpful to do in both exploited and exploiter countries. When done in rich countries who exploit poorer ones, it would reduce the demand for exploitation. In poor countries this is not as easily done, since poor means they don't have money to give around, but maybe this could be a good cause to put some reparations from colonizers and global corporations, which they should pay.
Preventing strategic accounting between subsidiaries and parent companies. Corporate law is obviously not my area of expertise, but I know that allowing corporations to move around the accounting of profits and losses between subsidiaries and parent companies in roughly 1980s, was a major factor in creating this modern global capitalist system, where corporations can very easily manipulate their accounting to utilize tax heavens and avoid taxes where they actually operate, which is how they are upholding this terrible system and extracting the profits from the production countries. How specifically this would be done I can't tell because again I know shit about corporate law, so experts of that field should plan the specifics. Overall this would help deal with a lot of other problems than just the fashion industry. Again for it to be effective a large economic area like EU or US should do this.
Holding companies accountable for their whole chain of production. These companies should be dragged to court and made to answer for the crimes they are profiting of off. We should put fear back into them. This is possible. Victims of child slavery are already doing this for chocolate companies. If it's already not how law works everywhere, the laws should be changed so that the companies are responsible even if they didn't know, because it's their responsibility to find out and make sure they know. They should have been held accountable for the Rana Plaza disaster. Maybe they still could be. Sue the mother fuckers. They should be afraid of us.
Individual actions
I will stress that the previous section is much more important and that there's no need to feel guilty for individual actions. This is not the fault of the average consumer. Still we do need to change our relationship to fashion and consumption. While it's not our fault, one of the ways this system is perpetuated, is by the consumerist propaganda by fashion industry. And it is easier to change our own habits than to change the industry, even if our own habits have little impact. So these are quite easy things we all could do as we are trying to do bigger change to gain some sense of control and keep us from falling to apathy.
Consume less. Better consumption will not save us, since consumption itself is the problem. We consume too much clothing. Don't make impulse purchases. Consider carefully weather you actually need something or if you really really want it. Even only buying second-hand still fuels the industry, so while it's better than buying new, it's still better to not buy.
Take proper care of your clothing. Learn how to properly wash your clothing. There's a lot of internet resources for that. Never wash your wool textiles in washing machine, even if the textile's official instructions allow it. Instead air them regularly, rinse them in cool water if they still smell after airing and wash stains with water or small amount of (wool) detergent. Never use fabric softener! It damages the fabrics, prevents them from properly getting clean and is environmentally damaging. Instead use laundry vinegar for making textiles softer or removing bad smells. (You can easily make laundry vinegar yourself too from white vinegar and water (and essential oils, if you want to add a scent to it) which is much cheaper.) Learn how to take care of your leather products. Most leather can be kept in very good condition for a very long time by occasional waxing with beeswax.
Use the services of dressmakers and shoemakers. Take your broken clothing or clothing which doesn't fit anymore to your local dressmaker and ask them if they can do something about it. Take your broken and worn leather products to your local shoemaker too. Usually it doesn't cost much to get something fixed or refitted and these expert usually have ways to fix things you couldn't even think of. So even if the situation with your clothing or accessory seems desperate, still show it to the dressmaker or shoemaker.
If it's extremely cheap, don't buy it. Remember that every clothing is handmade. Only a small fraction of the cost of the clothing will be paying the wages of the person who made it with their hands. If a shirt costs 5 euros (c. 5,39 USD), it's sewer was only payed mere cents for sewing it. I'm not a quick sewer and it takes me roughly 1-2 hours to cut, prepare and sew a simple shirt, so I'm guessing it would take around half an hour to do all that for a factory worker on a crunch, at the very least 15 minutes. So the hourly pay would still be ridiculously low. However, as I said before, the fact that the workers in clothing factories get criminally low pay is not the fault of the consumer, so if you need a clothing item, and you don't have money to buy anything else than something very cheep, don't feel guilty. And anyway expensive clothing in no way necessarily means reasonable pay or ethical working conditions, cheep clothing just guarantee them.
Learn to recognize higher quality. In addition to exploitation, low price also means low quality, but again high price doesn't guarantee high quality. High quality allows you to buy less, so even if it's not as cheep as low quality, if you can afford it, when you need it, it will be cheaper in long run, and allows you to consume less. Check the materials. Natural fibers are your friends. Do not buy plastic, if it's possible to avoid. Avoid household textiles from synthetic fibers. Avoid textiles with small amounts of spandex to give it stretch, it will shorten the lifespan of the clothing significantly as the spandex quickly wears down and the clothing looses it's shape. Also avoid clothing with rubber bands. They also loose their elasticity very quickly. In some types of clothing (sport wear, underwear) these are basically impossible to avoid, but in many other cases it's entirely possible.
Buy from artisans and local producers, if you can. As said better consumption won't fix this, but supporting artisans and your local producers could help keep them afloat, which in small ways helps create an alternative to the exploitative global corporations. With artisans especially you know the money goes to the one who did the labour and buying locally means less middlemen to take their cut. More generally buy rather from businesses that are located to the same country where the production is, even if it's not local to you. A local business doesn't necessarily produce locally.
Develop your own taste. If you care about fashion and style, it's easy to fall victim to the fashion industry's marketing and trend cycles. That's why I think it's important to develop your personal sense of style and preferences. Pay attention at what type of clothes are comfortable to you. Go through your wardrobe and track for a while which clothing you use most and which least. Understanding your own preferences helps you avoid impulse buying.
Consider learning basics of sewing. Not everyone has the time or interest for this, but if you in anyway might have a bit of both, I suggest learning some very simple and basic mending and reattaching a button.
Further reading on this blog: How to see through the greenwashing propaganda of the fashion industry - Case study 1: Shein
Bibliography
Academic sources
An overview of the contribution of the textiles sector to climate change, 2022, L. F. Walter et al., Frontiers in Environmental Science
How common are aches and pains among garment factory workers? A work-related musculoskeletal disorder assessment study in three factories of south 24 Parganas district, West Bengal, 2021, Arkaprovo Pal et al., J Family Med Prim Care
Sewing shirts with injured fingers and tears: exploring the experience of female garment workers health problems in Bangladesh, 2019, Akhter, S., Rutherford, S. & Chu, C., BMC Int Health Hum Rights
Occupation Related Accidents in Selected Garment Industries in Bangalore City, 2006, Calvin, Sam & Joseph, Bobby, Indian Journal of Community Medicine
A Review on Textile and Clothing Industry Impacts on The Environment, 2022, Nur Farzanah Binti Norarmi et al., International Journal of Academic Research in Business and Social Sciences
Carbon disulphide and hydrogen sulphide emissions from viscose fibre manufacturing industry: A case study in India, 2022, Deepanjan Majumdar et al., Atmospheric Environment: X
Microplastics Pollution: A Brief Review of Its Source and Abundance in Different Aquatic Ecosystems, 2023, Asifa Ashrafy et al., Journal of Hazardous Materials Advances
Health Effects of Microplastic Exposures: Current Issues and Perspectives in South Korea, 2023, Yongjin Lee et al., Yonsei Medical Journal
Nanoplastics and Human Health: Hazard Identification and Biointerface, 2022, Hanpeng Lai, Xing Liu, and Man Qu, Nanomaterials
Other sources
The impact of textile production and waste on the environment (infographics), 2020, EU
Chile’s desert dumping ground for fast fashion leftovers, 2021, AlJazeera
Fashion - Worldwide, 2022 (updated 2024), Statista
Fashion Industry Waste Statistics & Facts 2023, James Evans, Sustainable Ninja (magazine)
Everything You Need to Know About Waste in the Fashion Industry, 2024, Solene Rauturier, Good on You (magazine)
Textiles and the environment, 2022, Nikolina Šajn, European Parliamentary Research Service
Help! I'm addicted to secondhand shopping apps, 2023, Alice Crossley, Cosmopolitan
Addictive, absurdly cheap and controversial: the rise of China’s Temu app, 2023, Helen Davidson, Guardian
Workers' conditions in the textile and clothing sector: just an Asian affair? - Issues at stake after the Rana Plaza tragedy, 2014, Enrico D'Ambrogio, European Parliamentary Research Service
State of The Industry: Lowest Wages to Living Wages, The Lowest Wage Challenge (Industry affiliated campaign)
Fast Fashion Getting Faster: A Look at the Unethical Labor Practices Sustaining a Growing Industry, 2021, Emma Ross, International Law and Policy Brief (George Washington University Law School)
Dozens injured in Pakistan garment factory collapse and fire, 2023, Hannah Abdulla, Just Style (news media)
India: Multiple factory accidents raise concerns over health & safety in the garment industry, campaigners call for freedom of association in factories to ‘stave off’ accidents, 2022, Jasmin Malik Chua, Business & Human Rights Resource Center
Minimum Wage Level for Garment Workers in the World, 2020, Sheng Lu, FASH455 Global Apparel & Textile Trade and Sourcing (University of Delaware)
Rana Plaza collapse, Wikipedia
Buyers’ compensation for Rana Plaza victims far from reality, 2013, Ibrahim Hossain Ovi, Dhaka Tribune (news media)
World cotton production statistics, updated 2024, The World Counts
Dead white man’s clothes, 2021, Linton Besser, ABC News
#fashion#fashion industry#sustainability#sustainable fashion#sustainable clothing#environment#climate change#i will be continuing the series of how to see through fashion industry propaganda at some point#i just felt compelled to write this because i feel like people so often miss the forest for the trees in this conversation
497 notes
·
View notes
Text
I KNOW A GUY
scout: need a car pushed? need a free house sitter who won’t steal your shit? need a good playlist in thirty minutes for a very specific situation? need a group of guys in front of your place in an hour? need something delivered quickly under the radar? need someone jumped in a back alley? need a body buried? he’s your guy.
soldier: do you need a body buried? need someone’s nose broken? need some extra limbs of unknown origin? need a free bodyguard at the club so you can have a good time alone? need a free accidental hitman? need someone who will make you feel good about yourself by making you feel bad about yourself? need your gutters cleaned on your house? need someone who will come literally fight the monsters under your kids bed? he’s your guy.
pyro: need a body buried— well, cremated? got a financial emergency in which you can’t afford? need a sugar parent you don’t have to sleep with? at your nephews party and spider-man didn’t show up and now you need someone in a costume at this house pronto? need a gift for your nephew because you forgot to buy one? pyro’s your person for the low low price of kindling.
demo: need a drink that will make you experience ego death? need a ride for your bitch of an aunt so she never asks you to do anything ever again? need connections to a guy who sells peculiar cuts of meat from peculiar animals? need someone to get cussed out, for no reason? need a structure demolished in ten minutes? need someone who’s got vintage vinyls for sale? he’s your guy.
heavy: need your car pushed? need a meal made for fifteen? need someone handled? need an emergency ride to the hospital in the dead of winter? hell, need anything done in the dead of winter? need something out of a tree? need a tree cut down? need a plant sitter while you’re out of town? he’s your guy.
engineer: need your car’s computer replaced at a fraction of the cost? want someone’s tesla booted permanently? need a custom built prosthetic? need security cameras installed? need your wifi restarted? need someone who can cut a key in two minutes? need someone who can pick a lock in less than five? he’s your guy.
medic: you need some boobs? need some boobs removed? need to add or delete a penis? did you run out of testosterone or estrogen? need a binder? need a packer? hell, need a supplier for your side job of drug dealing? need a new kidney? need an abortion? need a hysterectomy under the table? need some unethically sourced body parts of unknown origin? all for the low price of free and don’t tell anyone? medic is your guy for all things medical. he does not care, he will just keep whatever he takes.
sniper: you need a body double to go with you to the store? need a guy who can do intermediate addition and subtraction without a calculator? need someone stalked? need a guy who has nothing but free time to get in an online queue and wait all day to buy your concert tickets? need a ride to and from said concert? he’s your guy.
spy: do you happen to need an armchair therapist? need access to a book in one library across the country? need a rumor spread like the plague? need someone handled? need a body buried? need a thirty minute etiquette class before you go on a date? need a new cook after you killed the last one at the restaurant? he’s your guy.
#team fortress 2#team fortress two#tf2 medic#tf2 scout#tf2 sniper#tf2 spy#tf2 demo#tf2 demoman#tf2 engineer#tf2 heavy#tf2 pyro#tf2#tf2 soldier#today we learn: every merc is capable of burying a body.#and medic is one of the girls idc idc idc#free gender changes for everyone
118 notes
·
View notes
Text
Why young people need to vote
By request, here's the text from the screenshot I shared previously. Still a good thing to show to every young person you know!
Why things won't truly change until young people vote like old people:
The government is, to put in bluntly, anti-youth — the needs and desires of young people are given the lowest priority. Social security is considered an untouchable “third rail” for politicians, yet those same politicians pay little price for ignoring climate change or paying nothing but lip service to confronting it. The US does little to address soaring education and housing costs, which disproportionately affect young people, despite being willing to spend nearly a trillion dollars annually on its military. In a particularly egregious affront, the country runs huge budget deficits — thereby offloading part of the cost of running the government onto future generations — while subsidizing fossil fuels, which means that young people are being forced to pay for their own destruction.
The reason behind all of this is simple: Old people vote at much higher rates than young people, so elected officials are incentivized to fight for them. Politicians do more to address energy prices than the future of the planet because slightly higher gas prices cause them to be punished at the polls, and young people aren’t there to back them up with their own votes.
The good news, of course, is that this can change. The beauty of democracy is that we get to choose who’s in the government, and young people exist in large enough numbers to be the driving force behind that decision. Millennials and Generation Z combine for (depending on the specific definition of the millennial generation you use) about 45% of eligible voters, but low voting rates mean that we don’t get much of a seat at the table in determining public policy. Younger generations can make up 45% of the electorate by voting at the same rates as older generations, but that’s not all — if young people can get each other to vote at higher rates than old people, we can make up a majority of the electorate and thus gain a controlling stake in the government, forcing it to finally work for us.
Tired of being screwed over by your own government? Angry at being forced to pay for your own destruction? Register to vote, and get all of your friends to do so as well. Let’s beat the boomers at their own game.
Note that (if you live in a state other than North Dakota) you have to register to vote before actually voting, and most states have registration deadlines that fall before election day — some as soon as October 6 or 7. Check your state’s deadline here, and make sure to register in time!
(source: outvote-the-boomers.blogspot.com)
128 notes
·
View notes
Note
Am I stupid or something because I agree with all of your post but I don't know what's wrong with small businesses. Am I a capitalist because I'm disabled and can only make money selling stickers or am I missing a bigger picture
Because this is tumblr and people in the notes will immediately read three lines of this and accuse me of pissing on the poor, I will begin with a disclaimer that I am neither comparing you to a Elon Musk nor calling you evil.
So, you sell stickers. I would assume that in this context you are selling your own stickers with your own designs, rather than working as a cashier selling someone else's stickers, since you're disabled and you mentioned you can't work a job. You are therefore selling a product you own (whether you produce the stickers entirely yourself or use a 3rd party company) for a profit at a (presumably) online store instead of selling your labour power for a wage. This, by definition would make you petit bourgeois.
When communists talk about class positions, it is not a question of an individual's morality, motivation or amount of income.
Being a small business owner (or petit bourgeois), means that your class interests and the class interests of the workers (the proletariat) come into conflict. As a clear example, let's say in this scenario that you are selling a sticker design on a 3rd party website that specialises in this service, and they source the actual physical stickers from factories around the world. Here, you are essentially selling your intellectual property to the company in exchange for some of the profits from its further sale. Perhaps many of those factories are in the global south, in countires with very low wages and few worker protections (due to intervention from imperial core bourgeoisie powers). One day, the political struggle for worker rights and higher wages is won in some of these countries, driving up the cost of production for the stickers. Perhaps there is also a victory for a union of delivery service workers at home in the imperial core, driving up wages and protections for them as well, further cutting into profits.
The function of the 3rd party sticker company is to strive for ever-increasing profits the capitalists who own it and its investors. The cut in profit will have to be made up elsewhere. This will be done by investing in political groups that are willing to repress worker movements within these countries, shifting production to countries that have yet to achieve these worker victories, cutting corners on their imperial core workers, increasing their price of service by taking a larger cut of your profits, or a mixture of some or all of these.
In that scenario, the proletarian class interests (higher wages, more protections and regulations) are in direct conflicts with the interests of the bourgeois 3rd party sticker company (higher profits, meaning lower wages and less protections and regulations) and by extension, yours, as your class interests also revolve around profit. When workers gain more power, it cuts into your profits. As a petit bourgeois, you are incetivised to support and pursue bourgeois and petty bourgeois politics such as IP laws.
As an individual, you can be whatever kind of person with whatever politics and views you have. As a petit bourgeois small business owner, you have a certain class position that comes with a certain set of class interests. You can always choose to forego your own class interests and instead support the class interests of the proletariat by being a communist even while continuing to be petit bourgeois or even as full on bourgeois. Very notable example being Engles who, although he was a factory owner, he was also one of the two founders of marxism, with the other one being Marx.
The point I was trying to make in the post that probably got you to send this anon, is that there isn't anything inherently communist or "leftist" about supporting small businesses. It is both an incredibly common liberal policy and talking point to support small business, and it does not serve the interests of a proletarian political movement to protect the petit bourgeoisie or ally with them, except in certain instances and involving certain sections of the petit bourgeois, rather than a blanket statement of saying that the small business owner is a nobler form of capitalist.
284 notes
·
View notes
Text
Countries That Generate 100% Renewable Energy Electricity

Pictured: Hydropower is the most widely used source of renewable energy-generated electricity. This dam is located near Polson, Montana.
Is 100% Renewable Resource-Generated Electricity Possible?
"With concerns growing regarding burning fossil fuels and their connection to global warming, a great debate is occurring regarding the feasibility of producing electricity entirely from non-carbon emitting green renewable energy sources such as geothermal, hydroelectric, wind, and solar. Skeptics and naysayers claim that achieving such a goal is impractical, would destroy the economy, and is in the realm of pie-in-the-sky thinking.
But is it actually impractical and unattainable? The answer is clearly "no" since there are already several countries that generate 100% of the electricity they use from renewable sources of energy. There are also many other countries that obtain over 90% of the electricity they use from renewable energy sources. Despite the negative rhetoric by some, there’s nothing impractical about using renewable energy to generate electricity on a grand scale.
The Countries Leading the Way to a 100% Renewable Energy Electricity Future
The following is a list of countries that are leading the world into the new frontier of economies that run their electrical grids either entirely or nearly entirely on renewable energy per a 2018 report by the International Renewable Energy Association (IREA) and the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA) statistics. This list and the percentages are subject to change over time, but it provides a good snapshot of just how practical renewable energy currently is for electricity generation.
Iceland obtains 100% of the electricity it needs from renewable energy sources. Iceland is somewhat unique since volcanic activity on the island provides a significant geothermal energy source that is utilized to provide approximately one-quarter of the country’s electricity. The remaining three quarters are provided by hydro-power.
Paraguay obtains 100% of the electricity it uses from renewable sources. Huge hydropower dams provide all of Paraguay's electricity needs, as well as supply neighboring Argentina and Brazil with electricity.
Costa Rica is another country leading the way towards 100% renewable-produced electricity. During 2018, Costa Rica met all of its electricity needs using renewable energy sources such as hydro-power, geothermal, biomass, wind, and solar for 300 days in a row.
Ethiopia, Kenya, Namibia, Norway, Tajikistan, and Uruguay are countries currently generating greater than 90% of the electricity they use from renewable energy sources. Some of these countries are working towards running their electric networks entirely from renewable energy.
Some things stand out from the list of countries leading the way in electricity generated from renewable energy.
They are relatively small countries.
They have abundant renewable natural resources, particularly abundant water resources available to generate hydro-power.
The list includes both wealthy developed and poor developing countries.
The fact that both developed wealthy countries and poor developing countries are leaders in renewable energy-produced electricity indicates that the cost of constructing renewable energy resources is not a limiting factor. In fact, developing countries can justify the capital cost of building renewable energy sources of electricity due to the fact that the operating costs are relatively low and predictable (not subject to commodity price swings), and renewable energy allows a country to be self-sufficient in meeting its electricity needs.
Large Developed Countries Can Also Produce 100% Of Their Electricity From Renewable Energy
Critics and naysayers might say that while these achievements by small countries are impressive, implementing renewable energy on a large scale is impractical for larger developed countries. But is it really impractical?
Cost and technological barriers are not what they once were for renewable energy. In fact, costs for renewable energy continue to decline year after year, and renewable energy technologies continue to develop and become more efficient. Many countries have not even come close to tapping their renewable energy potential or even tried some of the technologies available, such as electricity generated by wave or tidal power. Additionally, the argument that renewable energy is only useful when it is being generated is becoming irrelevant since large utility-scale batteries are now available that have the capability to store electricity generated by renewable energy and allow it to be used when needed.
Clearly, the answer is yes. Large developed countries can produce 100% of the electricity they need from renewable sources. It is only a matter of the will and investment at this point to make the changeover from fossil fuel-generated electricity to renewable energy electricity generation. The technical barriers are not as great as naysayers claim, as proven by smaller countries that have already reached the 100% threshold. Moving towards 100% renewable energy sources of electricity will become easier over time as wind, solar, and other renewables become more efficient and large utility-scale battery storage technologies become capable of storing larger quantities of energy for use when needed.

Pictured: Researchers lay out a plan for nearly 140 countries that could be powered 100 percent by renewable energy by 2050. spectrum.ieee.org
The City of Los Angeles Leads the Way in the U.S. With Inexpensive Solar
Various forms of renewable energy have experienced significant cost reductions to a point at which they are competitive and, in some cases, cheaper than traditional electrical energy sources such as coal, oil, and natural gas. This cost reduction trend will accelerate the change over to renewable sources of electricity. For example, the City of Los Angeles signed a deal in July 2019 for a large solar electricity array that will provide 7% of the city's electricity by 2025 at only two cents per kilowatt-hour (kWh). This is far cheaper than fossil fuel-derived electricity.
In addition to being cost-competitive, the practicality and reliability of renewable energy are poised to make major advances as large utility-scale battery technologies are rolled out that can be used to capture renewable energy when it is created, so the electricity can be used at a later time when needed. The Los Angeles solar array project includes utility-scale battery backup at a cost of 1.3 cents per kWh, so the electricity generated by the sun will be available even when the sun is not shining.
Los Angeles has a goal of achieving 100% renewable electricity generation by 2050. This solar contract is a big step toward achieving their goal."
-via TurboFuture, February 21, 2023
#renewables#renewablefuture#renewable energy#clean energy#green energy#solar power#solar panels#fossil fuels#climate crisis#climate change#global warming#hydropower#geothermal#wind power#wind turbines#iceland#paraguay#costa rica#ethiopia#kenya#namibia#norway#tajikistan#uruguay#united states#los angeles#battery#hope posting#hopepunk#sustainability
323 notes
·
View notes
Text
Is BL Being Overly Influenced by Modern Western Romance Tropes?
Short answer: No. anyways, in the following essay I will explain that James Cameron is a weeb...
(okay fine~~ lets actually do this)
TLDR: discussing what media globalization is, how fandom can distill it down to only American/European cinema, showcasing how a lot of current BL is influenced by countries within it's own proximity and NOT "the west" but each other, also James Cameron is still a weeb
I had seen a post that basically proposited that BL was being influenced by modern western romance tropes and had used things like omegaverse and mafia settings as an example. I found this, in a word, fucking annoying (oh, two words I guess) because it's micro-xenophobic to me.
It positions western - and really what we mean by this is American/European countries, we're not talking about South American countries are we? - cinema as the central breadbasket of all cinema in and of itself. Inherently, all following cinema must be in some way, shape, or form, influenced by American/European standards, and as such America/European countries are directly responsible for cinema everywhere else, and these places - namely non-white countries - do not influence each other, nor have their own histories in regards to storytelling or cinema and do not, in turn, also influence American/European film making either.
Now like, do I think all of that~~ is intentionally malicious thinking on behalf of folks in fandom? No, so chill out.
I do, however, think a lot of it is birthed from simple ignorance and growing up in an environment where ~The West~ is propagated to be central, individual, and exceptional as opposed to the monolith of "Asia" - by which we mean China, Korea, Japan don't we? How often in discussions of Asian countries is Iran, India, or Saudi Arabia brought up even tho they are all Asian countries? - or the monolith that is South America - in which some folks might believe regions like the Caribbean and/or Central America belong to, but nope there both North America.
Anyway, what we're talking about here is the concept of "media globalization":
"The production, distribution, and consumption of media products on a global scale, facilitating the exchange and diffusion of ideas cross-culturally." (source)
"The media industry is, in many ways, perfect for globalization, or the spread of global trade without regard for traditional political borders. [...] the low marginal costs of media mean that reaching a wider market creates much larger profit margins for media companies. [...] Media is largely a cultural product, and the transfer of such a product is likely to have an influence on the recipient’s culture." (source)
Typically when I see fandom discussing what falls under MG the topic is usually focused on how "the west" is influencing Thai/Korean/Chinese/Japanese media.
Enter, Pit Babe.
Surely Pit Babe was influenced by Supernatural right? Omegaverse is huge in the west - love it, hate it, meh it - it originated in the west - specifically via Supernatural after all.
Nah.
Omegaverse has been popular in Japan and China for almost a decade, if not longer. The earliest omegaverse manga I can think of is Pendulum: Juujin Omegaverse by Hana Hasumi which was released in 2015, almost a decade ago.

(what if you added furries into omegaverse? WHAT IF?? - Japan)
There's countless popular omegaverse manga too, and the dynamics only moderately resemble the ones we're familiar with in the west. Juujin is part omegaverse and part furry/beastmen - the alphas are all beastmen the omegas are humans - while something like Ookami-kun Is Not Scary only slightly resembles omegaverse dynamics as a hybrid series - beastmen are really popular in Japan in part b/c of historical mythology (you see the combination of romantic Beastmen and Japanese culture & folklore in Mamoru Hosoda's work The Boy and the Beast and Wolf Children).
Megumi & Tsugumi (2018) is so popular they're an official English edition published by VIZ's imprint SuBlime and that's a straight up omegaverse story.

(look at the omega symbol on the cover loud and proud baby)
So if Pit Babe was influenced by anything, it certainly wasn't "the west" it was Japan, Korea and China. Because those countries have a thriving omegaverse sub-genre going and have had such for 10 plus years now. Supernatural is popular in Japan, yes, and that may be where Japan and Japanese fans originally found omegaverse as a fictional sub-genre.
HOWEVER
Japanese fans took the sub-genre, bent it, played with it, and evolved it into their own thing. As such, other countries in their proximity, like Thailand, China, and Korea who read BL and GL manga, found it and were like "hey, we wanna play too!"

(is that an omegaverse yuri novel I spy?? yes, yes it is)
When I watched the Red Peafowl trailer, it had more in common with Kinnporsche, History: Trapped, along with films and shows like: Jet Li's The Enforcer, and Fist of Legend, Donnie Yen's Flash Point, Raging Fire, and Kung Fu Jungle, Han Dong-wook's The Worst of Evil, Kim Jin-Min's My Name, Lee Chung-hyeon's The Ballerina, Baik's Believer & Believer 2, Yoshie Kaoruhara's KeixYaku, popular Don Lee films The Gangster, the Cop and the Devil and Unstoppable alongside BL manga like Honto Yajuu and Bi No Isu (probably one of the most well known yazuka manga to date).
youtube
youtube
youtube
Like, we're seeing a rise in mafia based BLs and people think that's because of "western influence" and not the absolute insane success of kinnporsche??? Especially in countries like China, Korea, Taiwan, Philippines and other Asian countries???
Mafia films and gang shows aren't even that popular here in America/Europe; don't get me wrong, they still get made and exist, but the last full length film was The Irishman which did not make it's budget back, and while Power is still on-going it's not a smash hit either. The heyday of Breaking Bad, The Sopranos, The Wire, Goodfellas, and Scarface are long gone. And if you've watched any those shows or films they have very little in common with Kei x Yaku, Kinnporsche, or Red Peafowl in tone, or style.

(who knew martin just wanted to make his al pacino/robert de niro fanfic come to life all these years?)
Another example, The Sign, which is clearly taking inspiration from Chinese costume dramas: Ashes of Love, Fairy and Devil, White Snake (and it's many adaptions), Guardian, & Ying Yang Master Dream of Eternity. Alongside Hong Kong and Korean cop and romance shows like Tale of the Nine-Tailed, Hotel Del Luna, Director Who Buys Me Dinner, First Love, Again, and previously mentioned cop dramas.
youtube
youtube
youtube
Like, I know y'all don't think Twins is influenced by, what, American sports classic Angels in the Outfield?? Gridiron Gang?? Rocky?? Nah that shit is inspired by the popularity of sports manga like Haikyuu!!, Slam Dunk, Prince of Tennis (which even has a Chinese drama adaption), and the like. And also probably History 2, & Not Me but I'm like 87% sure Twins is just Haikyuu fanfic.
So like, does this mean that there's NO history in which American and European cinema influenced these countries? What, no, obviously that's not true, American/European totally have had media influence on countries like Korea, Japan, etc.
Astro Boy by Osamu Tezuka considered "the father of manga" was inspired by Walt Disney's work on Bambi. Another more recent and prominent example is director Yeon Sang-ho and his film Train to Busan.
"And it was Snyder’s movie [Dawn of the Dead, 2004], not the 1978 original, that filmmaker Yeon Sang-ho recalled as his first encounter with the undead. “That was when I started my interest in zombies,” Yeon said, in an email interview through a translator from South Korea. Even today, he added, “it’s the most memorable and intense zombie movie I’ve ever seen.”" (source)
HOWEVER, the global influence doesn't stop there. It's not a one-way street. Yeon Sang-Ho was inspired by Zack Synder's Dawn of the Dead, a remake of George Romero's own work, but Yeon Sang-Ho's work has inspired countless Korean film makers to make their own zombie media; following Train to Busan there's been: Kingdom (2019 - current), All of Us Are Dead (2022), Zombie Detective (2020), Zombieverse (2023), Alive (2020), Rampant (2018).
And hey, wouldn't you know it now we're starting to see more zombie media coming out of places like Japan (Zom 100 the manga, movie, and anime) and High School of the Dead.
Do you know what Domundi's series Zombivor (2023, pilot trailer only) reminds me of? It's NOT The Walking Dead (which is the only relevant zombie media America has created in the last decade) it's Korea's All of Us Are Dead (2022). Comparing the trailers, the settings, the tone, it's clear where Zombivor is pulling inspiration from: Korean zombie cinema. NOT American zombie cinema.
youtube
youtube
youtube
In fact a lot of Domundi's shows - Cutie Pie, Middleman's Love, Naughty Babe, Bed Friend - are all very clearly inspired by Korean filmmaking, specifically that of romantic kdramas from the 2016 - 2020 era. Not always in story, but rather in technique.
This is media globalization. It's not simply ~The West~ influencing non-American/European countries but countries who are often more close in terms of: proximity, culture, and trade are going to have more influence on each other.
It is far more likely that Aoftion (Naughty Babe, Cutie Pie, Zombivor) was influenced by watching Train to Busan, All of Us Are Dead, and other Korean zombie shows and films than a single episode of Walking Dead.
My point isn't that this goes one way only, but rather it is very literally a global thing. This includes American and European film makers being influenced by non-American and European cinema.
Martin Scorsese, Steven Spielberg, Darren Aronofsky, Christopher Nolan, the Wachowski sisters, George Lucas and James Cameron have all been influenced by Japanese film making, especially the works of Akira Kurosawa, Satoshi Kon, and Mamoru Oshii.

John Wick's entire gun-fu sub-genre is heavily influenced by classic Hong Kong action films, specifically John Woo films. Legend of Korra, The Boondocks, Voltron, Young Justice, My Adventures with Superman are all obviously inspired by Japanese anime but animated by a Korean animation studio (Studio Mir). Beyond that, the rise in adult animated dramas like Castlevania, Critical Role Vox Machina, and Invincible to name a few are very clearly taking inspiration from anime in terms of style. The weebs that were watching Adult Swim's Inuyasha, Bleach, and Dragon Ball Z have grown up and are now working in Hollywood.
Okay so like, what's the point of all this? What's the issue? Since American/European cinema does influence et all cinema does any of this really matter?
YES.
I take contention with this line of thinking because it centers "the west" and our supposed individual importance way to much. Declaring definitively that "BL is being influenced by western tropes" and then including tropes, narratives, and film making styles that aren't inherently western and actually have major roots in the cinema of various Asian countries, removes the existence of individual history these countries have which are rich, varied, and nuanced. It removes the "global" part of globalization by declaring "the globe" is really just America and Europe.
It distills these countries down to static places that only exist when American/European audiences discover them.
BL doesn't exist in a vacuum you can trace the development of Korean BL to the development of Korean het dramas almost to a T. You can also trace their development to the queer history of each country and how Thailand interacts culturally with China, Japan, Korea, etc and vice versa. It also ignores the history of these countries influencing American cinema as well. Don't mistake "the globe" for only your sphere of experience.
Anyway James Cameron is a damn weeb y'all have a good night.
Check out other posts in the series:
Film Making? In My BL? - The Sign ep01 Edition | Aspect Ratio in Love for Love's Sake | Cinematography in My BL - Our Skyy2 vs kinnporsche, 2gether vs semantic error, 1000 Stars vs The Sign | How The Sign Uses CGI | Is BL Being Overly Influenced by Modern Western Romance Tropes?
[like these posts? drop me a couple pennies on ko-fi]
#kinnporsche#pit babe the series#the sign the series#twins the series#red peafowl the series#domundi#gmmtv#chaos pikachu speaks#fucking a this was an entire essay#i should drop a ko-fi link cause good god damn#chaos pikachu metas#Youtube#pikachu's bl film series
307 notes
·
View notes
Text
GainEdge is the all-in-one destination for finding the Low-cost country sourcing services. LCC gives a better option for reducing costs by sourcing cheaper materials from low-cost countries. Our low-cost country sourcing gives you a better option for gaining a global approach to excellence. With the advancement in technology, there has been increased globalization, increased consumption, and increased political stability and consumer demands. This also leads to the integration of low-cost countries across the global markets.
0 notes
Text
Things Biden and the Democrats did, this week #7
Feb 23-March 1 2024
The White House announced $1.7 Billion in new commitments from local governments, health care systems, charities, business and non-profits as part of the White House Challenge to End Hunger and Build Healthy Communities. The Challenge was launched with 8 billion dollars in 2022 with the goal of ending hunger in America by 2030. The Challenge also seeks to drastically reduce diet-related diseases (like type 2 diabetes). As part of the new commitments 16 city pledged to make plans to end hunger by 2030, the largest insurance company in North Carolina made nutrition coaching and a healthy food delivery program a standard benefit for members, and since the challenge launched the USDA's Summer EBT program has allowed 37 states to feed children over the summer, its expected 21 million low income kids will use the program this summer.
The US House passed a bill on Nuclear energy representing the first update in US nuclear energy policy in decades, it expands the Nuclear Regulatory Commission and reduces reducing licensing fees. Nuclear power represents America's single largest source of clean energy, with almost half of carbon-free electricity coming from it. This bill will boost the industry and make it easier to build new plants
Vice President Harris announced key changes to the Child Care & Development Block Grant (CCDBG) program. The CCDBG supports the families of a million American children every month to help afford child care. The new changes include capping the co-pay families pay to no more than 7% of their income. Studies show that high income families pay 6-8% of their income in childcare while low income families pay 31%. The cap will reduce or eliminate fees for 100,000 families saving them an average of over $200 a month. The changes also strength payments to childcare providers insuring prompt payment.
The House passed a bill making changes to the Small Business Administration’s 8(a) program. The 8(a) is an intensive 9 year program that offers wide ranging training and support to small business owners who are socially and economically disadvantaged, predominantly native owned businesses. Under the current structure once a business reaches over 6.8 million in assets they're kicked off the program, even though the SBA counts anything under $10 million as a small business, many companies try to limit growth to stay on the program. The House also passed a bill to create an Office of Native American Affairs at the SBA, in order to support Native-owned small businesses.
The White House and HUD announced steps to boost the housing supply and lower costs plans include making permanent the Federal Financing Bank Risk Sharing program, the program has created 12,000 affordable housing units since 2021 with $2 billion and plans 38,000 additional units over ten years. As well as support for HUD's HOME program which has spent $4.35 billion since 2021 to build affordable rental homes and make home ownership a reality for Americans. For the first time an administration is making funds available specifically for investments in manufactured housing, $225 million. 20 million Americans live in manufactured housing, the largest form of unsubsidized affordable housing in the country, particularly the rural poor and people in tribal communities.
The Department of Energy announced $336 million in investments in rural and remote communities to lower energy costs and improve reliability. The projects represent communities in 20 states and across 30 Native tribes. 21% of Navajo Nation homes and 35% of Hopi Indian Tribe homes remain unelectrified, one of the projects hopes to bring that number to 0. Another project supports replacing a hydroelectric dam in Alaska replacing all the Chignik Bay Tribal Council's diesel power with clear hydro power. The DoE also announced $18 million for Transformative Energy projects lead by tribal or local governments and $25 million for Tribal clean energy projects, this comes on top of $75 million in Tribal clean energy projects in 2023
Transportation Secretary Pete Buttigieg put forward new rules to ensure airline passengers who use wheelchairs can travel safely and with dignity. Under the planned rules mishandling a wheelchair would be a violation of the ACAA, airlines would be required to immediately notify the passenger of their rights. Airlines would be required to repair or replace the wheelchair at the preferred vendor of the passenger's choice as well as provide a loaner wheelchair that fits the passenger's needs/requirements
The EPA launched a $3 Billion dollar program to help ports become zero-emission. This investment in green tech and zero-emission will help important transportation hubs fight climate change and replace some of the largest concentrations of diesel powered heavy equipment in America.
the EPA announced $1 Billion dollars to help clean up toxic Superfund sites. This is the last of $3.5 billion the Biden administration has invested in cleaning up toxic waste sites known as Superfund sites. This investment will help finish clean up at 85 sites across the country as well as start clean up at 25 new sites. Many Superfund sites are contained and then left not cleaned for years even decades. Thanks to the Biden-Harris team's investment the EPA has been able to do more clean up of Superfund sites in the last 2 years than the 5 years before it. More than 25% of America's black and hispanic population live with-in 5 miles of a Superfund site.
Bonus: Sweden cleared the final major barrier to become NATO's 32nd member. The Swedish Foreign Minster is expected to fly to Washington to deposit the articles of accession at the US State Department. NATO membership for Sweden and its neighbor Finland (joined last year) has been a major foreign policy goal of President Biden in the face of Russian aggressive against Ukraine. Former President Trump has repeatedly attacked NATO and declared he wants to leave the 75 year old Alliance, even going so far as to tell Russia to "do whatever the hell they want" with European NATO allies
#Thanks Biden#Joe Biden#Politics#US politics#Democrats#Climate change#end hunger#hunger#proverty#disability#native Americans#tribal rights#clean energy#child care#housing#housing crisis
772 notes
·
View notes
Text
Human remains as props — the Billy Boils of old horror movies
In this week's Halloween themed 9-1-1 episode, Buck rented a mummy replica from a Hollywood prop shop which turned out to be a real human body. This set off a series of misfortunate events for the firefighter, that might or might not be the result of a curse. Once again, the writers have surpassed themselves in terms of over-the-top silliness that has become the trademark of our beloved weewoo show. There's no way someone can accidentally get their hands on a real corpse... right?
Oh, you'll be surprised. You too may have seen a real cadaver or two on the silver screen.
The Economics of prop dead bodies
Using real human remains as movie props was such a common practice back in the days that prop masters working on the 1979 Vietnam war epic Apocalypse Now were totally unfazed when body broker (later revealed to be a grave robber) brought several dead bodies to the set. The plan to use those bodies as props for maximum authenticity was only scrapped after a producer ruled against it.

Source: The Independent
Interestingly, films that ended up actually featuring real bodies were the low-budget, fake looking ones. In the age before 3D printing, creating a set of realistic human skeleton was a very labor intensive process. That combining with the cost of the material used, the price of a plastic replica was in fact more expensive than a real skeleton.
A special effect make-up artist who worked on the 1982 Spielberg classic Poltergeist explained the film's decision to use actual human remains on a podcast:

Source: Snopes
Eerily, two young actresses who worked on the Poltergeist trilogy passed away unexpectedly shortly afterwards, leading to the urban legend of a curse on set.
The story of Elmer J. McCurdy
In late 1976, the production crew of the TV show The Six Million Dollar Man was filming scenes at the Pike, a then amusement zone in Long Beach, California. While shooting a scene at a thrill ride, a member of the prop department spotted a wax mannequin covered in fluorescent paint dangling from a noose. Worrying it would get in the way of the camera, they gave the dummy's arm a tug in an attempt to remove it, but instead of the whole thing coming off, only the arm broke off, exposing a human bone and muscle tissues.
A penny from 1924 and ticket stubs to the "Museum of Crime" were found in the body's mouth. Investigators contacted the museum owner's son, who identified the body as Elmer McCurdy, an outlaw killed in 1911 in the middle of a shootout with police following a botched train robbery in Oklahoma.
Unlike the fictional McCurdy in 8x05, the real McCurdy was a simple petty criminal looking for some extra cash to support his alcohol habit. Utilizing the skills he learned from the army, his robbery method of choice was explosives, but he was very terrible at it.

Source: KCRW
His body was subsequently taken to a funeral home, where he laid unclaimed for the rest of his stay. The undertaker embalmed the body, shaved his face, dressed him in a suit, but refused bury him until someone come forward to claim it and pay for the service. As time went by, the owner of the funeral home decided to dress the body as a gunslinging cowboy and allow visitors to see "the Bandit Who Wouldn't Give Up" for the price of a nickel, in order to fund his burial.
5 years later, two men claiming to be McCurdy's long lost brothers came forward to take custody of the body for a proper burial. End of the story, right? Well, of course they were travelling carnival owners lying to acquire the body for their shows. In 1922, the body was sold to yet another travelling exhibit called "Museum of Crime", which featured wax figures of other famous outlaws in history.
For the next 3 decades, McCurdy's body travelled all around the country as an attraction. He even had a brief film career. He was once used to promote the 1933 film Narcotic!, then he had a small cameo in the 1967 B-movie She Freak. In 1968, the Museum of Crime owner's son decided to sell his father's exhibits to the Hollywood Wax Museum. There, McCurdy's body started getting mixed up with other wax figure, and his origin story long forgotten.
Following over half a century of voyage, McCurdy eventually became fully mummified. The wax museum believed that the body was too gruesome and unlifelike to be showcased anymore, so he was finally sold to The Pike, an amusement zone in Long Beach, where he began his new life as a thrill ride decoration dummy.
After the shocking revelation by TV crew in 1976, McCurdy was transported back to Oklahoma, where he took his last breath 66 years ago, and finally laid to rest after a graveside service attended by 300 people. (Under 2 feet of concrete, to prevent grave robbing)

Source: Atlas Obscura
#Yes the meta posts are back#They're so fun to write#I love doing research on surprisingly interesting topics#911 spoilers#911 abc#911 meta#evan buckley#bucktommy
71 notes
·
View notes
Text
the last man in the world

It is a truth universally acknowledged that a sole proprietorship coffee shop in possession of an ideal location and a reliable source of ethically harvested beans must be in want of adequate staff.
Elizabeth would have taken one measly part-time barista who could create a competent Rosetta in a latte.
Or someone who was not related to her, because when her sisters came to “help out,” she ended up short cash in the till (Lydia and shockingly Mary), running low on clotted cream (Kit), or with the entire kitchen scrubbed clean but with all the shelves rearranged in a way that was completely unintuitive unless you were also deeply influenced by feng shui (Jane, who needed to stop worrying so much about cultural appropriation but also needed to stop moving the espresso cups to the north side of the room.)
It was getting dire and that was not only Elizabeth’s opinion. Charlotte, her closest friend from uni and also her accountant, had started to have an expression halfway between concerned and skeptical when Elizabeth talked about the coffee-shop and had absolutely vetoed the vintage La Marzocco espresso maker.
“You’d need what they call an angel investor in the States to pull that off, Lizzie, and nothing about Bluestockings would attract an angel,” Charlotte said.
“You still think I should have accepted the offer from Collins,” Elizabeth replied.
“I’m not idealistic,” Charlotte shrugged. “Not a romantic like you. He made a solid offer and he had the cash—”
“He looked like a toad in a Fair Isle jumper and he kept calling me Bettina,” Elizabeth said.
“This is London, the costs are only getting higher, between the bloody Tories and the foreign nationals buying up entire streets— You may regret saying no."
“I’d rather that than the alternative,” Elizabeth said. “The look on his face was priceless.”
“Oh, there was a price,” Charlotte said. “You just don’t know how much it’ll cost you.”
“How much?” the tall, dark-haired man in what was very clearly Savile Row asked, after Elizabeth, most definitely not looking her best since not one sister had shown up to help, not even Jane, had pushed across a sloppily poured London fog latte and then had forgotten to ring him up.
“Four quid,” she said, rounding up. He was wearing monogrammed platinum cufflinks and had the attitude of someone with a vast estate he referred to as “the country house.” Plus, he’d ignored her the whole time she’d scrambled around to make the drink, even when she nearly knocked three tins (Jane, why, why?!) from the shelf where the Earl Grey was kept and she’d yelped most unbecomingly.
“I meant how much do you need for the back-taxes and the rent. It needs a renovation, but we’d need to get an architect in for that, Annika de Bourgh at Rosings is the best,” he said. “My friend Charlie was here last week, raved about it, said the very pretty barista with the bluest eyes told him you were her sister, the coffee-shop about to go under, even though she’d reorganized the cutlery five times to invite financial well-being, and he’s likely to do something very ill-considered unless I stop him, so how much do you need? The place is tolerable, I suppose—”
“Tolerable?” Elizabeth repeated. Sputtered, not unlike the milk frother which needed a repair.
“I’ve seen worse. I’ve seen better. It has some potential, the location is unimpeachable, the foot traffic alone should make the rent, as long as people want to walk in,” he said. “How much?”
“You’ve some nerve,” Elizabeth said.
“Yes. As well as the acumen and portfolio to back it up,” he answered coolly.
“I’d never take money from someone whose name I don’t know, who hasn’t worked with me a single day,” Elizabeth said.
“Darcy. Will Darcy. I hope you’ve a spare apron,” he said.
“I don’t,” she said.
“Then I’ll wear one of your tee-shirts,” he said, taking off his suit jacket and folding it over one forearm.
“It won’t fit,” she said.
“I’ll be careful then, not to spill,” he replied.
The tee-shirt fit, if by fit one meant that it made it clear how exquisitely well-built Will Darcy was, broad and well-muscled through the shoulders and chest, narrow waisted, the pale blue cotton concealing hardly anything, the swoopy swirly scrawl of Bluestockings seemingly designed specifically to make one consider whether he possessed a six or eight pack. And he didn’t spill a drop.
“Convinced?” he asked, after three hours, the best mid-afternoon rush she’d ever had neatly managed, the counters pristine. He’d rolled his sleeves up after the first hour and Elizabeth had resolutely determined not to give a name to the feeling the sight evoked in her.
(The name would probably include an obscenity, something she could confide to neither Jane nor Charlotte.)
“Give me a week,” she said.
“To decide?”
“Work here for a week. One afternoon doesn’t count. You might be lucky,” she said.
“I don’t believe in luck,” he said.
“Of course not,” she said.
Charlotte had been right. Elizabeth had had no idea what it would cost her.

Written but posted late (on a day when I feel like a lot of us can use a cheerful distraction!) for Janeuary 2025 @janeuary-month, Day 15, prompt: London.
#Janeuary 2025#pride and prejudice#modern reboot#coffee shop AU#London#elizabeth bennet#fitzwilliam darcy#charlotte lucas#jane bennet#humor#lots of Netflix rom-com vibes#slow burn
45 notes
·
View notes
Note
In relation to your Starop Library au post:
-Starscream suddenly starts going to the library more often, asking for assistance finding books all the way at the other end of the library despite already knowing where they are whenever Optimus is on staff.
-Star starts sitting near Optimus' desk, occasionally staring at him and taking care of his appearance even more than usual. (He'll deny it to the end of the Earth though)
-In some places (*cough cough* Amarica *cough cough*) the average salary of a librarian can be pretty low compared to living costs so if Starscream finds out Optimus has trouble with living costs he mysteriously gets a raise.
-Whenever Op has trouble finding someplace in the city due to being from the country, Starscream would immediately assist him. Trying to find a good coffee shop or bookstore? Need a ride home since it's dark outside? He'll jump at the opportunity to be near Optimus longer, although he'll probably act annoyed about it.
-If Optimus is in collage on scholarship (or highschool based on how old they are) and needs an expensive textbook(s), brand new copies of them are mysteriously donated the the library by an anonymous source, or Star would let him borrow his if he had it.
Sorry if these are out of character, I just like sharing my StarOp brainrot
-💌 anon
see you get it!! you see the vision!!
as for the out of character worry, remember that, in some iterations, starscream was actually a very different person before the main war happens, like in skybound. since this is an au where nothing goes horribly horribly wrong and nobody dies, i think we can play with that possibility here. anyway!
- he would. he absolutely would. he'll ask for the same book several times even when he should know where it is by now. he thinks he's so sly, but optimus caught onto what starscream was doing a while ago. he just plays along because he thinks it's cute.
- i could definitely see starscream switching his usual study sessions from his dorm to the library so he can be near optimus. it's no coincidence that he also wears nicer outfits and fixes up his hair on his study days. maybe he'll throw on some jewelry if he's feeling especially fancy.
- i imagine in this au, optimus is working at the library to help with paying tuition while the rest of his money goes to food and rent. starscream comes from a family rich enough to afford the full ride, so he's a little shocked. cue a "mysterious donor" paying rent for optimus and his roommates. i wonder who that could be!
- starscream knows a good opportunity when he sees one. if optimus is looking for a nice place to treat himself with his christmas bonus, starscream has a recommendation. new movie out that optimus wants to see? starscream knows the best theater and can pay for the best seats. optimus needs a ride back to his apartment because his pickup truck is in the shop? starscream drives him in his rolls royce. he acts annoyed, but really he's just emotionally constipated.
- college textbooks are ridiculously expensive, so if optimus is having trouble affording the pricey physics textbooks he needs... oh, wow! someone donated a bunch of physics textbooks to the library! how kind! definitely without any ulterior motives of any sort!
also, what would their names be in this au? i imagine optimus' would be orson ryan pax, but he always goes by ryan or orion because he sees orson as an old man's name. what about starscream? something fancy and british probably
#mmmmmm i love this premise#i also love knock out being starscream's wingman#he knows that his best friend is dow BAD#and he just wants to help starscream bag himself a beefy country bf#transformers#starscream#optimus prime#starop#starprime#starpax#starscream x optimus prime#starscream x orion pax#maccadam#answering things
47 notes
·
View notes
Text
WaPo: How car bans and heat pump rules drive voters to the far right
Shannon Osaka at WaPo:
More than a decade ago, the Netherlands embarked on a straightforward plan to cut carbon emissions. Its legislature raised taxes on natural gas, using the money earned to help Dutch households install solar panels. By most measures, the program worked: By 2022, 20 percent of homes in the Netherlands had solar panels, up from about 2 percent in 2013. Natural gas prices, meanwhile, rose by almost 50 percent. But something else happened, according to a new study. The Dutch families who were most vulnerable to the increase in gas prices — renters who paid their own utility bills — drifted to the right. Families facing increased home energy costs became 5 to 6 percent more likely to vote for one of the Netherlands’ far-right parties. A similar backlash is happening all over Europe, as far-right parties position themselves in opposition to green policies. In Germany, a law that would have required homeowners to install heat pumps galvanized the far-right Alternative for Germany party, or AfD, giving it a boost. Farmers have rolled tractors into Paris to protest E.U. agricultural rules, and drivers in Italy and Britain have protested attempts to ban gas-guzzling cars from city centers.
That resurgence of the right could slow down the green transition in Europe, which has been less polarized on global warming, and serves as a warning to the United States, where policies around electric vehicles and gas stoves have already sparked a backlash. The shift also shows how, as climate policies increasingly touch citizens’ lives, even countries whose voters are staunchly supportive of clean energy may hit roadblocks. “This has really expanded the coalition of the far right,” said Erik Voeten, a professor of geopolitics at Georgetown University and the author of the new study on the Netherlands.
Other studies have found similar results. In one study in Milan, researchers at Bocconi University studied the voting patterns of drivers whose cars were banned from the city center for being too polluting. These drivers, who on average lost the equivalent of $4,000 because of the ban, were significantly more likely to vote for the right-wing Lega party in subsequent elections. In Sweden, researchers found that low-income families facing high electricity prices were also more likely to turn toward the far right. Far-right parties in Europe have started to position themselves against climate action, expanding their platforms from anti-immigration and anti-globalization. A decade ago, the Dutch right-wing Party for Freedom emphasized that it wasn’t against renewable energy — just increasing energy prices. But by 2021, the party’s manifesto had moved to more extreme language. “Energy is a basic need, but climate madness has turned it into a very expensive luxury item,” the manifesto said. “The far right has increasingly started to campaign on opposition to environmental policies and climate change,” Voeten said.
The pushback also reflects, in part, how much Europe has decarbonized. More than 60 percent of the continent’s electricity already comes from renewable sources or nuclear power; so meeting the European Union’s climate goals means tacklingother sectors — transportation, buildings, agriculture.
[...] Some of these voting patterns have also played out in the United States. According to a study by the Princeton political scientist Alexander Gazmararian, historically-Democratic coal communities that lost jobs in the shift to natural gas increased their support for Republican candidates by 5 percent. The shift was larger in areas located farther from new gas power plants — that is, areas where voters couldn’t see that it was natural gas, not environmental regulations, that undercut coal.
Gazmararian says that while climate denial and fossil fuel misinformation have definitely played a role, many voters are motivated simply by their own financial pressures. “They’re in an economic circumstance where they don’t have many options,” he said. The solution, experts say, is todesign policies that avoid putting too much financial burden on individual consumers. In Germany, where the law to install heat pumps would have cost homeowners $7,500 to $8,500 more than installing gas boilers, policymakers quickly retreated. But by that point, far-right party membership had already surged.
The Washington Post explains what may be at least partially causing the rise of far-right extremist parties in Europe, Conservatives in Canada, and the Republicans in some parts of the US: rising energy costs that low-income people are bearing the brunt of.
In the US, right-wing hysteria about gas stove bans and electric vehicles are also playing a role.
101 notes
·
View notes