#judean desert
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

M A S A D A
151 notes
·
View notes
Text
I love the idea of people leaving things in caves for safekeeping and then just never returning or never being able to return.
83 notes
·
View notes
Text



The incredible pastel colors of the Dead Sea.
Spring 2022.
Shot with a Fujifilm X-T20 with Samyang 12mm F/2.0 lens.
#yzshot#travel#israel#the Dead Sea#dead sea#judean desert#pastel#pastel colors#original photographers#photographers on tumblr#fujifilm#fuji xt20#fujixseries#samyang
14 notes
·
View notes
Text
1,900-12 months-Outdated Papyrus Reveals Prison Case from Roman Empire
Written in Greek, this papyrus is a memorandum for a judicial listening to earlier than a Roman official within the province of Judea or Arabia within the reign of the Roman emperor Hadrian, after his go to to the area in 129/130 CE and earlier than the outbreak of the Bar Kokhba Revolt in 132. The papyrus comprises an off-the-cuff report of the listening to, which issues the prosecution of a lot…

View On WordPress
#Arabia#Bar Kokhba Revolt#Greek#Hadrian#Iudaea#Judea#Judean Desert#Papyrus#Papyrus Cotton#Roman Empire#Trial
0 notes
Text

Yehuda Desert
photographed by Eyal Asaf
1 note
·
View note
Text

Lenten drawings from last week.





0 notes
Text
😃👍💝
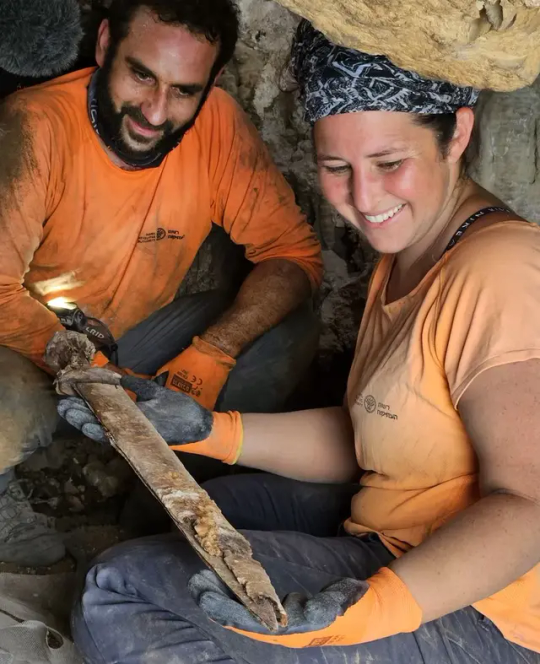



Four 1,900-Year-Old Roman Swords Found in a Judean Desert Cave
Apparently stolen by Jewish rebels, the incredibly well-preserved weapons are ‘an extremely rare find, the likes of which have never been found in Israel’
Archaeologists have discovered four 1,900-year-old Roman swords in a cave in the Judean Desert, which experts believe were captured by the Judean rebels during the Bar Kochba revolt and placed in a narrow crevice in the rock.
“We’re talking about an extremely rare find, the likes of which have never been found in Israel,” Dr. Eitan Klein, one of the directors of the Israel Antiquities Authority’s Judean Desert Survey, said in a video accompanying the announcement of the discovery. “Four swords amazingly preserved, including the fine condition of the metal, the handles, and the scabbards.”
The preliminary article on the swords is published in the volume “New Studies in the Archaeology of the Judean Desert: Collected Papers,” which explores new archaeological finds discovered in the Judean Desert Survey Project. A conference launching the book is taking place Wednesday in Jerusalem.
The four swords were discovered shoved into a small fissure in a cave near Ein Gedi National Park, near the Dead Sea. The cave is already well-known to archaeologists, as it contains a stalactite with a fragmentary ink inscription written in ancient Hebrew script characteristic of the First Temple period.
Recently, Dr. Asaf Gayer of Ariel University, geologist Boaz Langford of Hebrew University, and Israel Antiquities Authority photographer Shai Halevi returned to the cave to photograph the stalactite with multispectral photography, which can decipher additional parts of the inscription not visible to the naked eye. While inside the cave, Gayer spotted an extremely well-preserved Roman pilum — a shafted weapon — in a deep, narrow crack in the rock. He also found pieces of carved wood in an adjacent niche that turned out to be parts of the swords’ scabbards.




The researchers reported the find to the Israel Antiquities Authority and returned to the site with the Judean Desert Archaeological Survey Team, which is conducting a multi-year comprehensive survey of more than 800 caves in the Judean Desert to find and preserve archaeological remains before they are looted.
It was then that they discovered the four swords, three of which were found with the blades still inside their scabbards. Researchers also found ornate handles made of wood and metal with leather strips nearby. The arid climate in the Judean Desert helps preserve fragile artifacts that might otherwise be lost to the ravages of time, including materials such as leather and wood, which are rarely found in wetter parts of the country.
Three of the swords are Roman spatha swords, with blades 60 to 65 centimeters (23.5 to 25.5 inches) long. The fourth weapon, a ring-pommel sword, is shorter, with a 45-centimeter (18-inch) blade. The swords likely belonged to Roman soldiers and were stolen by Judean rebels who hid them in a cave either for later use or to avoid being caught with them.
“The blades have been preserved so well, they look like they could be picked up and used right now, even 2,000 years after they were forged,” said Langford. “You just realize that you are touching history, because here you are touching a find whose story you know.”
The Bar Kochba revolt, from 132 to 135 CE, also called the Second Jewish Revolt, was a Jewish rebellion against Roman rule in Judea led by rebel leader Simon Bar Kochba. Archaeologists believe the swords were likely hidden in the crevices inside the cave sometime during the revolt, as it was dangerous for Jews to be found with Roman weapons.



“This is a very rare and unique find on an international level that will shed light on the last moments of the war between the Jewish rebels and the Roman army at the time of the Bar Kochba revolt,” said Klein.
‘A unique time capsule’
The cave survey is being undertaken by the IAA in cooperation with the Archaeology Department of the Civil Administration in Judea and Samaria, and has been funded in part by the Ministry of Jerusalem Affairs and Heritage. Each body allocated about a third of the project budget.
Earlier this year, archaeologists carrying out the Judean Desert cave surveys discovered a rare half-shekel coin minted by the Bar Kochba underground economy.
The cave survey started in 2017 and helped archaeologists discover at least 20 new caves they had not previously known. In 2021, archaeologists announced that one of the caves contained previously undiscovered fragments of the Dead Sea Scrolls, some 60 years after the last pieces of the Dead Sea Scrolls were discovered.



Following the discovery of the swords, archaeologists carried out an extensive excavation of the cave, discovering artifacts from the Chalcolithic period (around 6,000 years ago) and the Roman period (around 2,000 years ago). At the entrance to the cave, researchers found a Bar Kochba bronze coin from the time of the revolt that could help pinpoint the dates when the weapons were hidden.
“This is a dramatic and exciting discovery, touching on a specific moment in time,” said Eli Escusido, director of the Israel Antiquities Authority.
Noting that not all are aware that the dry climatic conditions in the Judean Desert enable the preservation of artifacts that do not survive in other parts of the country, Escusido called the area a “unique time capsule” where it is possible to find “fragments of scrolls, coins from the Jewish Revolt, leather sandals — and now even swords in their scabbards, sharp as if they had only just been hidden away today.”
By Melanie Lidman.
361 notes
·
View notes
Text
"During an archaeological dig in a desert area north of Jerusalem 40 years ago, a seed was discovered which was determined to be in pristine condition but had obviously seen many a year.
Now, despite falling from its parent 1,000 years ago, it has grown into a mature tree, and botanists examining it believe it may be an extinct species that was used for medicinal purposes for thousands of years—even receiving a nod in the Bible.
Neither Israeli botanists, nor Dr. Sarah Sallon, a physician who founded the Louis L. Borick Natural Medicine Research Center at Hadassah University Medical Center in Jerusalem, could determine what species it was from simply from the seed covering. So they did what nature intended—they planted it.
Using a well-documented technique that saw 2,000-year-old date palm fruit pits germinate, Dr. Sallon soaked the seed in hormones, liquid fertilizer, and water, and then planted it in a pot of sterile seed; then waited.
Despite its genetic code being exposed to environmental stressors for over 1,000 years, the seed sprouted after 5 weeks. The shoot was protected by a caplike feature called an operculum. As the shoot grew, the operculum was shed—leaving something for the team to radiocarbon date. It narrowed down the age of the almost 10-centuries-old seed to between the years 993 an 1202.
Fast forward 14 years and the plant has become a 10-foot-tall tree. Dr. Sallon shared images of the tree, its bark, and its leaves with botanists around the world. One expert suggested it belonged to the genus Commiphora, found across the Arabian Peninsula and parts of Africa. A genetic analysis subsequently revealed this was the case, but a perfect match was lacking.
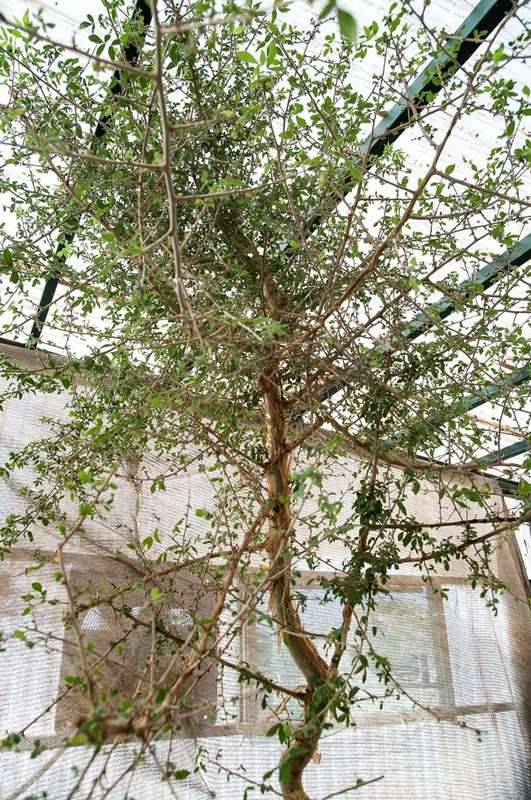

Pictured: The tree, now 14 years old.
Dr. Sallon and her team thought it was an extinct species known from history as Judean Balsam, but the best way to confirm that suspicion would be to have some aromatic traces similar to the resins of the myrrh tree to which it is related. However, no such fragrant compounds were detected.
Instead, the chemical analysis of the leaves identified a group of phytochemicals known as guggulterols which have been observed in a related species called Commiphora wightii that’s known to possess certain cancer-fighting properties in its resin.
A medicinal balm, the origin of which is not known, is mentioned in multiple historical texts including the Bible as ‘tsori,’ and rather than the fragrant Judean Balsam, it’s this tsori that Dr. Sallon and her team believe they have found.
They must wait until the tree, now 14 years old, produces flower or fruit to know for sure if it’s an extinct species, and if so, how to perhaps keep it alive.
Dr. Louise Colville, senior research leader in seed and stress biology at Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, in London who wasn’t involved in the research, told CNN that it was a major accomplishment to grow a seed that old and possibly lead to a resurrection of this Biblical botanical.
“What’s surprising in this story is it was just a single seed and to be able to have one chance for that to germinate is extremely lucky,” she said.
“Working in a seed bank, seeing the potential for that extreme longevity gives us hope that banking and storing seeds that some at least will survive for very long periods of time.”"
-via Good News Network, October 8, 2024
--
Note: This is such a good demonstration of why seed banks are so important!! They give us such real and massive hope for deextinction and the revival of endangered species.
#botany#plant biology#endangered species#extinct species#deextinction#ancient medicine#jerusalem#biblical#medicinal plants#seeds#seed bank#good news#hope#paleobotany
9K notes
·
View notes
Text
I'm experiencing a lot of Jewish tree feelings about this Judean date palm, waiting as seeds in the homeland for our entire 2,000 year diaspora, preserved and protected by the desert until our people could come back and let them blossom again, alongside us.
423 notes
·
View notes
Text
An Israeli company may have brought back a thousand years extinct myrrh tree. They grew an ancient seed and they are still trying to figure out what tree it is.
Pretty neat. So that’s the date palm and a myrrh tree.
65 notes
·
View notes
Text
Is this a male or a female tree or monoecious? Is it going to flower? If it has a gender, will it be able to reproduce? So many questions. Quite amazing, though.
12 notes
·
View notes
Text
Heritage News of the Week
Discoveries!
The discovery of an unusual "vampire" burial in Croatia shows the endurance of such beliefs in eastern medieval Europe, according to researchers.

Ancient British coins found in Dutch field likely to be spoils of Roman conquest
A hoard of British coins bearing the inscription of King Cunobelin and found in a Dutch field have been identified as very likely to be the spoils of war of a Roman soldier from the conquest of Britain.
A Roman sanctuary with inscriptions discovered in Cova de les Dones, one of the largest rock art sites in the Iberian Peninsula
Researchers have discovered a remarkable Roman sanctuary in the Cova de les Dones, located in Millares, Valencia, Spain.
Bronze Age footprints preserved during Vesuvius eruption are found in Italy
The footprints found near the Casarzano stream in Salerno, roughly 20 miles away from Pompeii, contained rock fragments from the eruption of Mount Vesuvius. Experts believe the people who left behind these prints were trying to escape the eruption.
1,200-year-old remains of dismembered pregnant woman in Ecuador hint at 'enigmatic' sacrifice to thwart El Niño
The unusual burial of a woman and fetus in prehistoric Ecuador may reflect the community's fear of her power.
A telltale toilet reveals “lost” site shown in Bayeux Tapestry
A house in England is most likely the site of a lost residence of Harold II, the last Anglo-Saxon King of England.
DNA and radiocarbon analysis provide new insights into prehistoric mammoth bone complex
Dr. Alba Rey-Iglesia and her colleagues conducted a biomolecular analysis of the mammoth bone remains at Kostenki 11-Ia, providing fascinating insights into the enigmatic mammoth bone complexes built during the Ice Age.
The oldest evidence for lead pollution comes from ancient Greece
Researchers studying sediment cores recovered from mainland Greece and the Aegean Sea have found the oldest known evidence of lead pollution in the environment dating to around 5,200 years ago.
The longest Greek papyrus from the Judean desert sheds light on a pivotal Roman court case
New research by a group of Austrian and Israeli scholars has finally deciphered a 1,900-year-old scroll describing a tense court case during the Roman occupation of Israel.
A huge chunk of prized Egyptian blue pigment Is uncovered in Nero’s palace
Recent excavations at Domus Aurea, the former imperial residence of Roman emperor Nero, have yielded remnants of a rare blue pigment that hint at the palace’s former glory.
Archaeologists uncover traces of the Abbey of St. Savino
In a new research project to uncover the Abbey’s origins, archaeologists have identified earlier phases of the site’s expansion and construction.
1.5 million-year-old hand axes and seven Paleolithic sites discovered in Iraq’s western desert
Archaeologists from the Free University of Brussels uncovered hand axes dating back 1.5 million years and discovered seven Paleolithic sites in an area of 10 by 20 km in Iraq’s Western Desert.
1,600-year-old Roman padlock with spring mechanism discovered in Germany — and it's tiny
A miniature gold lock dated to the third to fourth centuries was found by a metal detectorist in Germany.

Military personnel and veterans uncover Iron Age treasures
Archaeologists from the Defence Infrastructure Organisation, working in collaboration with veterans and military personnel from Operation Nightingale, have uncovered a collection of Iron Age objects declared as national treasure by the Senior Coroner for North Wales.
One of the oldest tin-bronze artifacts in the Eurasian Steppe discovered in a unique Bronze Age cemetery in Uygur Autonomous Region
Chinese archaeologists have recently uncovered a large and uniquely structured cemetery dating back to 2800-2600 BC.
Here’s how ancient Amazonians became master maize farmers
Water engineers in ancient South America turned seasonally flooded Amazonian savannas into hotbeds of year-round maize farming.
Lidar survey maps Zapotec city in Mexico
Pedro Guillermo Ramón Celis of McGill University and his colleagues spotted the remains of more than 1,000 structures built by the Zapotec in southern Mexico between 500 and 600 years ago during an aerial survey employing lidar equipment.
Archaeologists find 4,500-year-old warrior burials in Saxony-Anhalt
Archaeologists have identified at least ten graves at a depth of approximately two metres, three of which were once covered by a burial mound.
Pyramidal structure discovered in Chupacigarro
Archaeologists excavating the Chupacigarro archaeological site have discovered a previously unknown pyramidal structure.
Denmark’s first Roman helmet found in weapons sacrifice
Two iron plates found in the massive Iron Age weapons sacrifice found near Hedensted, Denmark, have been revealed to be parts of a Roman helmet from the 4th century. It is the oldest iron helmet ever found in Denmark, and the only Roman helmet ever found within the country’s borders.
Roman pottery and human remains found in Exeter
Roman pottery and human remains have been unearthed during the installation of an underground substation in Exeter city centre.
Museums
The museum, named the Haveli, features five galleries showcasing different kinds of embroidery Askari has collected from some of the remotest corners of Pakistan, ranging from ceremonial cloths traditionally sent from a groom to a bride before a wedding, to dowry purses and vibrant animal adornments worn by camels.
Mona Lisa will be moved to its own exhibition space at Louvre
French president Emmanuel Macron announced Tuesday that the Mona Lisa, Leonardo Da Vinci’s masterpiece and one of the most iconic artworks in the world, would soon be moved to a new exhibition space.
Louvre’s decision to move Mona Lisa is a misguided act of snobbery
Crowds give life to the Paris museum and the painting is a silent, compelling mystery at the heart of the hubbub
This is a silly take. The room where the Mona Lisa is housed sees at least 20,000 people per day. It does not have the capacity to handle that many people. Have you seen what that room looks like on an average day?



It's like the top of Everest in there. Trying to visit has been described as "exhausting" and "a physical ordeal". It's not snobbery to update a 17th century building for the 21st century.
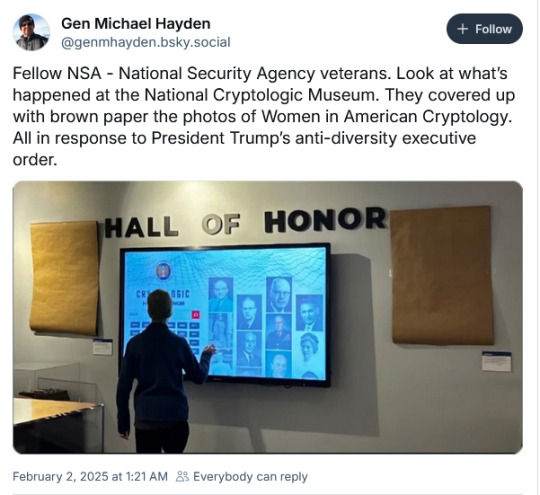
Smithsonian Institution will close its diversity offices
Just days after the National Gallery of Art in Washington D.C. said it would cancel its diversity, equity and inclusion programs, the Smithsonian Institution, a consortium that includes 21 national museums, announced its diversity office will also close. According to the New York Times, the Smithsonian will also freeze hiring for all federal positions and employees will have to return to in-person work full-time.

‘African art is not a fleeting trend’: Moroccan museum to celebrate rich creativity of continent’s artists
Reopening after renovation, the Museum of African Contemporary Art Al Maaden will provide a permanent home for the extensive Lazraq family collection
WW2 bomber group museum appeals for repair funds
Urgent repairs are needed to conserve and repair a military museum that was created to commemorate the US servicemen who were based there during World War Two.
Museum dash sees speedy Londoner set new record
A man has sped his way across London using a kick scooter to set a Guinness World Records title for the most museums visited in 24 hours.
Crabs 'poo from their chests', museum says
An unusual museum in a Kent seaside town which aims to engage the public in the natural world has plans for expansion. Crab Museum in Margate claims to be Europe's first and only exhibition space dedicated to the world of the decapod highlighting the "weirdness" of crabs.

National museum shuts for maintenance work
Wales' leading museum has been temporarily closed due to maintenance work and safety concerns. A sign outside the National Museum in Cathays Park, Cardiff, on Sunday, said it will be closed to the public until further notice.
California Historical Society shutters, transfers collection to Stanford University
Financial stability became a challenge over the last decade as attendance declined and donations dwindled, with the problems only further exacerbated by the Covid-19 pandemic. As such, CHS’s board voted to dissolve the organization last summer.
Museums scramble to grasp impact of Trump’s DEI mandate
Widespread uncertainty pervades as institutions either roll back initiatives or try to determine whether their programs are in compliance.
17 employees helped save the Getty Villa from the fires. They're telling other museums how it was done
On Tuesday, Jan. 7, at about 7 a.m., the Getty’s Emergency Planning Specialist Les Borsay arrived at the Getty Villa in Malibu. “This was not normally a day I would have necessarily been out there." Then came the message from the Getty in Brentwood: a small brush fire up started up at the Highlands, sparked by embers of the Palisades Fire. For the next 28 hours, Borsay and 16 other staffers organized themselves to supplement fire department efforts and along the way contributed to helping keep the Getty Villa and its priceless art collections from going up in flames.
House next to Auschwitz opens to public amid alarming international survey results on Holocaust
Through the efforts of the American non-profit Counter Extremism Project, in coordination with the Auschwitz-Birkenau State Museum, the Polish foreign ministry and UNESCO, the villa will become the home of the ‘Auschwitz Research Centre on Hate, Extremism and Radicalisation’.
It boggles my mind that people were actually living in this house until last year, when they were convinced to sell it. You know how you go some places and you're like, "wow, the vibes here are bad"? The vibes in that house must be rancid.
Anyway, Dan Snow got to do a tour of the house, and on the one hand, it's just a house, but on the other, it's absolutely the most cursed house ever.
Heritage at risk
Dutch police have arrested three men in connection with the robbery of ancient Romanian artefacts from a museum in the north-east of the Netherlands, after an intensive four-day hunt.
Anger in Romania over theft of national treasures in heist at Dutch museum
News of the heist had set off an “uproar” across Romania, she said, as mourning over the potential loss of the objects gave way to fury among the art world, politicians and media.
US Air Force will still teach about black pilots
The US Air Force will continue to teach about its first black pilots, known as the Tuskegee Airmen, in its basic training, following a review about what to prohibit under President Donald Trump's ban on diversity, equity and inclusion (DEI) programmes in the federal government.
From Bluesky:
Australia tried to influence other countries and Unesco to keep Great Barrier Reef off in-danger list
While this story is specifically about the Great Barrier Reef, this bit:
In 2021 the Great Barrier Reef became the first site globally to be recommended for the danger list primarily because of the impacts of climate change. But after extensive lobbying from the Morrison government, the recommendation from Unesco and its advisers, the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN), was ignored by the world heritage committee. That decision raised concerns among world heritage experts that the committee was becoming increasingly politicised and too often was ignoring scientific and technical advice.
should be a cause for concern regarding all UNESCO and potential UNESCO sites.
Odds and ends
The team building the replica of a famous Anglo-Saxon burial ship have told of their aspirations to eventually sail it down the River Thames and across the English Channel.
Butrint: The ancient site helping Albania reclaim its identity
Once known as "the North Korea of Europe", Albania is turning to its millennia-old sites and rich cultural heritage to recast its image.
Since when is neoclassical architecture “populist”?
Donald Trump’s move to revive “traditional” architecture in federal buildings betrays his ignorance of its elitist roots.
Long-lost anti-fascist mural from 1930s restored and back on show in Mexico
A long-neglected 1930s mural in Mexico that warns about the rise of fascism has been revealed and restored �� just as some historians say the world faces that threat once more.
'The truth is she did the right thing': The mystery of why Jane Austen's letters were destroyed – by her own sister
Austen is one of the greatest writers in the English language – but relatively little is known about her. And that's in part because of an act that infuriates many to this day.
Ancient forest uncovered by melting ice in the Rocky Mountains
A nearly 6,000-year-old forest is once again seeing daylight after millennia hidden under ice in the Rocky Mountains.
‘An unusual find’: 66m-year-old animal vomit discovered in Denmark
Experts say vomit, probably from a fish, is made up of sea lilies and is an important contribution to reconstructing past ecosystems

Blergh
#heritage news of the week#things down south are very not great bob#history#museums#archaeology#paleontology#gifs
24 notes
·
View notes
Text

A rare coin from the Bar Kokhba Revolt, engraved with the name “Eleazar the Priest” in ancient Hebrew and “Year One of the Redemption of Israel” was discovered in the Judean Desert.
Going to show that Israel is the eternal homeland of the Jews and no amount of historical revisionism will change that.
📸 @antiquities_il
143 notes
·
View notes
Photo

The Bar-Kochba Revolt
The Bar Kochba Revolt (132–136 CE) was the third and final war between the Jewish people and the Roman Empire. It followed a long period of tension and violence, marked by the first Jewish uprising of 66-70 CE, which ended with the destruction of the Second Temple, and the Kitos War (115-117 CE). In many ways, the Bar Kochba Revolt differed markedly from its predecessors. For the first time, the Jews presented a united front against Roman forces and fought underneath a single charismatic leader, the eponymous Simon Bar Kochba (also given as Shimon Bar-Cochba, Bar Kokhba, Ben-Cozba, Cosiba or Coziba). It was marked as well by strong religious passions, with many apparently believing that Bar Kochba was the promised messiah who would lead the Jewish people to final victory against their enemies.
In its initial stages, the revolt was surprisingly successful and may have resulted in the destruction of an entire Roman legion. It is possible that the rebels regained control of the city of Jerusalem, and they must have held large portions of ancient Judea. The Romans, however, regrouped and adopted a scorched-earth strategy that ultimately extirpated the rebels and laid waste to the country. The war shattered Judean society and led to far-reaching demographic and political changes, with the majority of the Jewish population of the province killed, enslaved, or exiled, and their national hopes definitively crushed. The Jewish people would not regain their political independence until the Zionist era and the establishment of the State of Israel in 1948 CE.
The Problem of Sources
Unlike the revolt of 66 CE, the historical sources on the Bar Kochba Revolt are scanty at best. The war had no chronicler such as Josephus Flavius, at least none whose work has survived. The primary non-Jewish sources are an epitome of Cassius Dio's Roman History and a handful of lines by the ecclesiastical historian Eusebius, the bishop of Caesarea. The war is also briefly mentioned by the Church father Jerome. While by no means comprehensive, these sources do provide several important details.
The Jewish sources are not per se historical and, while also scanty, are found throughout the rabbinical literature of the period and after, in particular, in the Jerusalem and Babylonian Talmuds. While they are often clearly legendary and unreliable in nature, they do paint a general picture of the Jewish experience of the war and its aftermath.
In addition, several important archaeological finds have shed light on certain aspects of the revolt. Coins minted while Judea was temporarily freed from Roman rule indicate the existence of an independent Jewish state for a brief period. In the 1960s CE, a cave in the Judean desert was found that likely once housed refugees from the revolt. Called the “Cave of Letters,” it contained a cache of documents that included several letters from Bar Kochba himself, which shed unprecedented light on his personality and style of rule.
Continue reading...
53 notes
·
View notes
Photo
THIS looks like home

Yehuda Desert
photographed by Eyal Asaf source
5 notes
·
View notes

