#i found an article from 2016
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
the paywall does suck here are some more sources;
#i guess this isnt a NEW discover#*discovery#i found an article from 2016#but there was a new documentary that came out
31K notes
·
View notes
Text

"Great news from @.PREMA_Team : Mick Schumacher will enter #FIAF3 for 2017 campaign." - december 24, 2016 📷 @.Formula_em_ / twitter
#mick schumacher#f1#formula 1#flashback fic ref#flashback fic ref 2016#race unknown#2016 race unknown#tag not tagged#f4#f4 2016#adac f4#adac f4 2016#childhood photos#not a race#2016 not a race#post-season#post-season 2016#(note to self: i tried to match up the race from the trophy but got nothin. it's def adac f4 not italian f4 bc of#the suit and it's def 2016 bc prema. that trophy doesn't match any race incl the italian ones and the only race i couldn't#find a single pic from was red bull ring that year. found an article that labeled the pic as from instagram.)
4 notes
·
View notes
Text

#my posts#what do i even tag this as#i found this article awhile back while doing research for an assignment and was reminded today of this insane sentence#this was allegedly written in 2016 so part of me doubts it's written by ai#but i checked the website and they were advertising nfts so you can judge their credibility on your own with that#some could chalk it up to translation errors but i assure you this also makes zero sense in malay#bc the website its from is a malaysian website and the person they're talking about is a famous malaysian artist#coming from a malay. i can assure you this makes zero sense and sounds just as insane in malay
0 notes
Text
WOW.
Scientists found an amazingly well-preserved village from 3,000 years ago


Text below, in case article access dries up:
LONDON — A half-eaten bowl of porridge complete with wooden spoon, communal rubbish bins, and a decorative necklace made with amber and glass beads are just a handful of the extraordinarily well-preserved remnants of a late Bronze Age hamlet unearthed in eastern England that’s been dubbed “Britain’s Pompeii” and a “time capsule” into village life almost 3,000 years ago.
The findings from the site, excavated in 2015 to 2016, are now the subject of two reports, complete with previously unseen photos, published this week by University of Cambridge archaeologists, who said they cast light onto the “cosy domesticity” of ancient settlement life.
“It might be the best prehistoric settlement that we’ve found in Britain,” Mark Knight, the excavation director and a co-author of the reports, said in an interviewThursday. “We took the roofs off and inside was pretty much the contents,” he said. “It’s so comprehensive and so coherent.”
The reason for the rare preservation: disaster.
The settlement, thought to have originally consisted of several large roundhouses made of wood and constructed on stilts above a slow-moving river, was engulfed by a fire less than a year after being built.
During the blaze, the buildings and much of their contents collapsed into a muddy river below that “cushioned the scorched remains where they fell,” the university said of the findings. This combination of charring from the fire and waterlogging led to “exceptional preservation,” the researchers found.
“Because of the nature of the settlement, that it was burned down and its abandonment unplanned, everything was captured,” Knight added.
“As we excavated it, there was that feeling that we were picking over someone else’s tragedy,” he said of the eerie site in the swampy fenland of East Anglia. “I don’t think we could smell the fire but the amount of ash around us — it felt close.”
Researchers said they eventually unearthed four large wooden roundhouses and an entranceway structure, but the original settlement was probably “twice as big.”
The site at Must Farm dates to about 850 B.C., eight centuries before Romans came to Britain. Archaeologists have been shocked at “just how clear the picture is” of late Bronze Age life based on the level of detail uncovered, Knight said.
The findings also showed that the communities lived “a way of life that was more sophisticated than we could have imagined,” Duncan Wilson, head of Historic England, the public body responsible for preserving England’s historic environment, said in a statement.
The findings unearthed include a stack of spears, possibly for hunting or defense; a decorative necklace “with beads from as far away as Denmark and Iran”; clothes of fine flax linen; and a female adult skull rendered smooth, “perhaps a memento of a lost loved one,” the research found.
The inhabitants’ diet was also rich and varied, including boar, pike and bream, along with wheat and barley.
A pottery bowl with the finger marks of its maker in the clay was also unearthed, researchers said, still containing its final meal — “a wheat-grain porridge mixed with animal fats” — with a wooden spatula resting inside the bowl.
“It appears the occupants saved their meat juices to use as toppings for porridge,” project archaeologist Chris Wakefield said in the university’s news release. “Chemical analyses of the bowls and jars showed traces of honey along with ruminant meats such as deer, suggesting these ingredients were combined to create a form of prehistoric honey-glazed venison,” he added.
Skulls of dogs — probably kept as pets and to help with hunting — were also uncovered, and the dogs’ fossilized feces showed they fed on scraps from their owners’ meals, the research found.
The buildings, some connected by walkways, may have had up to 60 people living there all together, Knight said, along with animals.
Although no intact sets of human remains were found at the site, indicating that the inhabitants probably fled the fire safely, several sheep bones were found burned indoors. “Skeletal remains showed the lambs were three to six months old, suggesting the settlement was destroyed sometime in late summer or early autumn,” according to the university’s news release.
Ceramic and wooden vessels including tiny cups, bowls and large storage jars were also found. Some pots were even designed to nest, stacked inside one another, Knight said — evidence of an interest in aesthetics as well as practicality.
A lot of similar items were found replicated in each home, Knight added, painting the picture of completely independent homesteads for each family unit rather than distinct buildings for shared tasks — much like we live today.
Household inventories often included metal tools, loom weights, sickles for crop harvesting, axes and even handheld razors for cutting hair.
The roundhouses — one of which had almost 50 square meters (nearly 540 square feet) of floor space — had hearths and insulated straw and clay roofs. Some featured activity zones for cooking, sleeping and working akin to modern-day rooms.
The Must Farm settlement has produced the largest collection of everyday Bronze Age artifacts ever discovered in the United Kingdom, according to Historic England, which partly funded the 1.1 million pound ($1.4 million) excavation project.
The public body labeled the site a “time capsule,” including almost 200 wooden artifacts, over 150 fiber and textile items, 128 pottery vessels and more than 90 pieces of metalwork. Some items will go on display at the nearby Peterborough Museum next month.
Archaeologists never found a “smoking gun” cause for the fire, Knight said. Instead, they suspect it was either an attack from “outside forces,” which may explain why the inhabitants never returned to collect their possessions from the debris, or an accidental blaze that spread rapidly across the tightly nestled homes.
“Probably all that was left was the people and what they were wearing; everything else was left behind,” Knight said of the fire.
But the preservation has left a window for people to look back through in the future. “You could almost see and smell their world,” he said.
“The only thing that was missing was the inhabitants,” Knight added. “And yet … I think they were there — you certainly got glimpses.”
4K notes
·
View notes
Text
an alton article about senpai's b-day! :D
#robert wadlow#robert wadlow trash#this is technically belated but i found it last night so it's sort of on time! ;)#it's neat that alton wrote an article about his special day! :D#they didn't write one last year (st. louis post dispatch did tho!) or in 2020/17#before that there were 2 articles from other sites in 2016 one german website in 2013 a wired article in 2012... and that's it! :o#b-day articles are a recent tradition that didn't really get going until i came along (that sure is a coincidence... ;) )#i'm glad it's a thing since they're always so fun to read! :D#this one features a story from one of his classmates! ...technically ;)#it's told by her daughter#the arm smacking part sounded really familiar so i looked up the classmate's name and found it in a 2018 advantagenews story!#it's worded differently but the smack is there! :)
1 note
·
View note
Text
Double dose of articles about how crime is actually plummeting
From the UK:
"Seventy-eight per cent of people in England and Wales think that crime has gone up in the last few years, according to the latest survey. But the data on actual crime shows the exact opposite.
As of 2024, violence, burglary and car crime have been declining for 30 years and by close to 90%, according to the Crime Survey for England and Wales (CSEW) – our best indicator of true crime levels. Unlike police data, the CSEW is not subject to variations in reporting and recording.
The drop in violence includes domestic violence and other violence against women. Anti-social behaviour has similarly declined. While increased fraud and computer misuse now make up half of crime, this mainly reflects how far the rates of other crimes have fallen.
All high-income countries have experienced similar trends, and there is scientific consensus that the decline in crime is a real phenomenon.
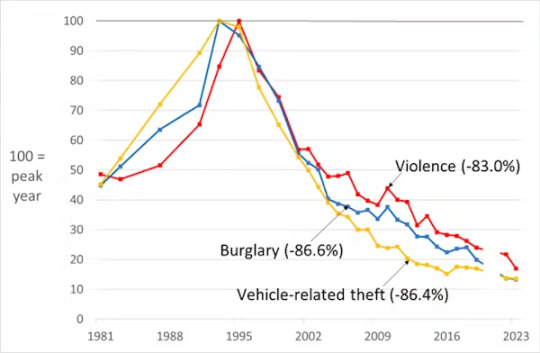
The perception gap
So why is there such a gulf between public perception and the reality of crime trends? A regular YouGov poll asks respondents for their top three concerns from a broad set of issues. Concern about crime went from a low in 2016 (when people were more concerned with Brexit), quadrupled by 2019 and plummeted during the pandemic when people had other worries. But in the last year, the public’s concern about crime has risen again.
There are many possible explanations for this, of which the first is poor information. A study published in 1998 found that “people who watch a lot of television or who read a lot of newspapers will be exposed to a steady diet of crime stories” that does not reflect official statistics.
The old news media adage “if it bleeds, it leads” reflects how violent news stories, including crime increases and serious crimes, capture public attention. Knife crime grabs headlines in the UK, but our shock at individual incidents is testament to their rarity and our relative success in controlling violence – many gun crimes do not make the news in the US.
Most recent terrorist attacks in the UK have featured knives (plus a thwarted Liverpool bomber), but there is little discussion of how this indicates that measures to restrict guns and bomb-making resources are effective."
-via The Conversation, May 13, 2024
And the United States:
"[The United States experienced a spike in crime rates in 2020, during the pandemic.] But in 2023, crime in America looked very different.
"At some point in 2022 — at the end of 2022 or through 2023 — there was just a tipping point where violence started to fall and it just continued to fall," said Jeff Asher, a crime analyst and co-founder of AH Datalytics.
In cities big and small, from both coasts, violence has dropped.
"The national picture shows that murder is falling. We have data from over 200 cities showing a 12.2% decline ... in 2023 relative to 2022," Asher said, citing his own analysis of public data. He found instances of rape, robbery and aggravated assault were all down too.
Yet when you ask people about crime in the country, the perception is it's getting a lot worse.
A Gallup poll released in November found 77% of Americans believed there was more crime in the country than the year before. And 63% felt there was either a "very" or "extremely" serious crime problem — the highest in the poll's history going back to 2000.
So what's going on?
What the cities are seeing
What you see depends a lot on what you're looking at, according to Asher.
"There's never been a news story that said, 'There were no robberies yesterday, nobody really shoplifted at Walgreens,'" he said.
"Especially with murder, there's no doubt that it is falling at [a] really fast pace right now. And the only way that I find to discuss it with people is to talk about what the data says." ...
For cities like San Francisco, Baltimore and Minneapolis, there may be different factors at play [in crime declining]. And in some instances, it comes as the number of police officers declines too.
Baltimore police are chronically short of their recruitment goal, and as of last September had more than 750 vacant positions, according to a state audit report...
In Minneapolis, police staffing has plummeted. According to the Star Tribune, there are about 560 active officers — down from nearly 900 in 2019. Mannix said the 2020 police killing of George Floyd resulted in an unprecedented exodus from the department...
In Minneapolis, the city is putting more financial resources into nontraditional policing initiatives. The Department of Neighborhood Safety, which addresses violence through a public health lens, received $22 million in the 2024 budget."
-via NPR, February 12, 2024
#crime#violate crime#united kingdom#england#wales#united states#us politics#baltimore#san francisco#police#defund the police#good news#hope
1K notes
·
View notes
Note
wondering about whether you could rec some "romance is a social construct" texts? ofc it is, but i like having books and articles to reference/learn specifics from/see how these ideas have developed.
Sure! Here's a quick reading list. Bear in mind that I am not a professional historian and my reading on this subject is a little diffuse. I'm not tackling the behavioral ecology stuff right now because a) I don't have a more direct book rec off the top of my head than Evolution's Rainbow, which is not technically focused on social monogamy, and also b) I approach that whole field with my eyes wide open for people letting their own perspectives and cultural views get in the way of their observations of animals, and I do not have the energy to go deal with it right now.
If you're going to read two books, read these two:
Stephanie Coontz, Marriage, A History: how love conquered marriage. 2006. All of Coontz' work, having to do with the social construction of the family, is relevant reading to this question (and I'd also recommend The Nostalgia Trap, because the historical context of how we conceptualize families is a major part of the construction of romantic love), but this one is most focused on the social construction of romantic love specifically and what it has replaced. Coontz is, I will disclose cheerfully, a major formative influence on my thinking.
Moira Wegel, Labor of Love: The Invention of Dating. 2016. Exactly what it says on the tin; focuses more closely on the modern invention of dating and romance.
Other useful readings to help inform your understanding of different ways that various people have conceptualized sex, sexuality, society and long-term connection include:
George Chauncey, Why Marriage? 2015. Chauncey is best known for Gay New York, which also offers a useful history of the way that relationship models and social constructs for understanding homosexuality changed among men having sex with men c. 1900 to 1950. This book, published just before Obergefell v. Hodges, is a discussion of why contemporary queer rights organizations focused on same-sex marriage as an activism plank in the wake of AIDS organizing. I find it really useful to read queer history when I'm thinking about how we understand and construct the concept of romantic relationships, because queers complicate the mainstream, heteronormative concepts of what marriage and romantic relationships actually are. More importantly, queer activist organizing around marriage has played a major role in shaping our collective understanding of romance and marriage in the past twenty years.
Elizabeth Abbott, A History of Celibacy, 2000. In order to understand how various cultures construct understandings of marriage and spousal relationships, it can be illustrative to consider what the people who are explicitly not participating in the institution are doing and why not. I found this an interesting pass over historical and social institutions that forbid (or forbade) marriage with a discussion about general trends driving these institutions, individuals, and movements towards celibacy.
Eleanor Janega, The Once and Future Sex, 2023. This is a very pointed historical look at gender roles, concepts of beauty, and concepts of sex, attraction, and marriage among medieval Europeans with an extended meditation on what ideas have and have not changed between that time and today. I include this work because I think a deep dive into medieval notions of courtly romance is useful, partly because it is an important origin of our modern notion of romantic love and partly because it is so usefully and starkly different from that modern notion! Sometimes the best way to understand the cultural construction of ideas in your own society is to go look at someone else's and see where things are the same versus different.
It's a mish-mash of recommendations, and I'm reaching more for books that have stuck with me over the years than a clean scholarly approach to the subject. I hope other folks will chime in for you with their own recommendations!
461 notes
·
View notes
Text
"Much ink has already been spilled on Harris’s prosecutorial background. What is significant about the topic of sex work is how recently the vice president–elect’s actions contradicted her alleged views. During her tenure as AG, she led a campaign to shut down Backpage, a classified advertising website frequently used by sex workers, calling it “the world’s top online brothel” in 2016 and claiming that the site made “millions of dollars from trafficking.” While Backpage did make millions off of sex work ads, its “adult services” listings offered a safer and more transparent platform for sex workers and their clients to conduct consensual transactions than had historically been available. Harris’s grandiose mischaracterization led to a Senate investigation, and the shuttering of the site by the FBI in 2018.
“Backpage being gone has devastated our community,” said Andrews. The platform allowed sex workers to work more safely: They were able to vet clients and promote their services online. “It’s very heartbreaking to see the fallout,” said dominatrix Yevgeniya Ivanyutenko. “A lot of people lost their ability to safely make a living. A lot of people were forced to go on the street or do other things that they wouldn’t have otherwise considered.” M.F. Akynos, the founder and executive director of the Black Sex Worker Collective, thinks Harris should “apologize to the community. She needs to admit that she really fucked up with Backpage, and really ruined a lot of people’s lives.”
After Harris became a senator, she cosponsored the now-infamous Stop Enabling Sex Traffickers Act (SESTA), which—along with the House’s Allow States and Victims to Fight Online Sex Trafficking Act (FOSTA)—was signed into law by President Trump in 2018. FOSTA-SESTA created a loophole in Section 230 of the Communications Decency Act, the so-called “safe harbor” provision that allows websites to be free from liability for user-generated content (e.g., Amazon reviews, Craigslist ads). The Electronic Frontier Foundation argues that Section 230 is the backbone of the Internet, calling it “the most important law protecting internet free speech.” Now, website publishers are liable if third parties post sex-work ads on their platforms.
That spelled the end of any number of platforms—mostly famously Craigslist’s “personal encounters” section—that sex workers used to vet prospective clients, leaving an already vulnerable workforce even more exposed. (The Woodhull Freedom Foundation has filed a lawsuit challenging FOSTA on First Amendment grounds; in January 2020, it won an appeal in D.C.’s district court).
“I sent a bunch of stats [to Harris and Senator Diane Feinstein] about decriminalization and how much SESTA-FOSTA would hurt American sex workers and open them up to violence,” said Cara (a pseudonym), who was working as a sex worker in the San Francisco and a member of SWOP when the bill passed. Both senators ignored her.
The bill both demonstrably harmed sex workers and failed to drop sex trafficking. “Within one month of FOSTA’s enactment, 13 sex workers were reported missing, and two were dead from suicide,” wrote Lura Chamberlain in her Fordham Law Review article “FOSTA: A Hostile Law with a Human Cost.” “Sex workers operating independently faced a tremendous and immediate uptick in unwanted solicitation from individuals offering or demanding to traffic them. Numerous others were raped, assaulted, and rendered homeless or unable to feed their children.” A 2020 survey of the effects of FOSTA-SESTA found that “99% of online respondents reported that this law does not make them feel safer” and 80.61 percent “say they are now facing difficulties advertising their services.” "
-What Sex Workers Want Kamala Harris to Know by Hallie Liberman
#personal#sw#sex work is work#kamala harris#one of the MANY many reasons i hate harris#she directly put so many sex workers at risk. i lost multiple community members because of her#whorephobia#fosta/sesta
436 notes
·
View notes
Text
America’s richest Medicare fraudsters are untouchable

If you'd like an essay-formatted version of this post to read or share, here's a link to it on pluralistic.net, my surveillance-free, ad-free, tracker-free blog:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/11/13/last-gasp/#i-cant-breathe

"When you're famous, they let you do it": eight words that encapsulate the terrifying rot at the heart of our lived experience, a world where impunity for the powerful trumps the pain of their victims.
"Populism," is shorthand for many things: rage, despair, distrust of institutions and a desire to destroy them. True populism seeks to channel those totally legitimate feelings into transformative change for a caring and fair society for all. So-called "right populism" exploits those feelings, using them to drive a wedge between different groups of victims, turning them against each other, so that elites can go on screwing the squabbling factions.
The far-right parties that are marching to victory through a series global elections are different in many ways, but they all share one trait: they appeal to mistrust of institutions, claiming that the government has been captured by elites who serve them at the expense of the governed. This has the benefit of being actually true, and while the fact that far-right parties are owned by these government-capturing elites might erode their credibility, the fact that so many "progressive" parties have stepped in to defend the institutional status quo leaves an open field for reactionary wreckers:
https://www.politico.com/blogs/2016-dem-primary-live-updates-and-results/2016/02/hillary-clinton-donald-trump-slogan-219908
Why would voters turn out to support a "Department of Government Efficiency," run by a bully whose career has been defined by abusing the people he is in charge of? Maybe they're turkeys voting for Christmas, but they also have personal, traumatic experience with government departments that protected the abusive corporations that preyed on them.
Today on Propublica, Peter Elkind tells the incredible story of Lincare, the nation's leading supplier of home oxygen, a repeat-offender fraudster and predator that has made billions in public money without any real consequences:
https://www.propublica.org/article/lincare-medicare-lawsuit-settlements-oxygen-equipment
Lincare has been repeatedly found guilty of defrauding Medicare; in this century alone, they have been put on probation four times, with a "death penalty" provision that would permanently disqualify them from ever doing business with the federal government. In every case, Lincare committed fresh acts of fraud, but never faced that death penalty.
Why not? Lincare is far too big to fail. In America's bizarre, worst-in-class, world-beatingly expensive privatized health care system, even public health provision (like Medicare) is outsourced to the private sector. Lincare has monopolized oxygen, a famously very important molecule for human survival, and if it were disqualified from serving Medicare, large numbers of Americans would literally asphyxiate.
Lincare clearly knows this. Too big to fail is too big to jail, and too big to jail is too big to care. They are the poster children for impunity, repeat offenders, multiply convicted, and still offending, even today. Lincare has been convicted of fraud under the administrations of GW Bush, Obama, Trump and Biden, and they're still in business.
What a business it is! Elkind takes us to the asbestos-poisoned town of Libby, Montana, where more than 2,000 of the 2.857 population suffer from respiratory diseases from the open-pit mine that operated there from 1963-1990. The elderly, dying population of this town rely on Medicare and Medicare Advantage oxygen concentrators to draw breath, and that means they rely on Lincare.
That means they are prey to Lincare's signature scam: charging Medicare (and 20% co-paying patients) to rent an oxygen concentrator every month, until they have paid for it several times over. This is illegal: under federal rules, patients are deemed to have bought their oxygen concentrators after 36 months and contractors are no longer allowed to charge them. Lincare doesn't give a fuck: the bills keep coming, and Lincare patients who survive long enough have paid the company $16,000 for a $799 gadget.
When Brandon Haugen, a local Lincare customer service rep, noticed this and queried the company's home office in Clearwater, Florida (home to Scientology and the Flexidisc), he was given the brushoff. After multiple attempts to get company leadership to acknowledge that this was illegal, he quit his job, along with his colleague and childhood friend Ben Montgomery. Between them, Haugen and Montgomery had 14 children who depended on their Lincare paychecks. Despite this, they both quit and turned whistleblower, with no job lined up. Eventually, Lincare paid $29m to settle the claim, with $5.7m to the whistleblowers and their lawyers. For Lincare, this was part of the cost of doing business and the fraud rolls on.
Lincare doesn't just defraud Medicare, they also have a high-pressure commissioned sales force that has repeatedly been caught defrauding Lincare customers – overwhelming sick, poor, elderly people. Patients are pressured to accept auto-billing, then Lincare piles medically dubious gadgets onto their monthly bills, as well as useless, overpriced "patient monitoring" services. Customers with apnea machines are mis-sold ventilators by salesmen who falsely claim these are medically necessary.
Salespeople illegally auto-shipped parts and consumables for Lincare machines to patients, then billed them for it. To satisfy the legal requirement that they telephone patients before placing these orders, sales agents would call patients, put them on hold, then part the call until the patient hung up.
Salespeople are motivated by equal parts greed and terror. Make quota and you can get up to $8,000 per month in bonuses. Miss that punishing quota and you're out on your ass (which is why one salesperson ordered a medically unnecessary ventilator).
Lincare also habitually ignores requests to pick up medically unnecessary equipment, because so long as the equipment is on the patient's premises, they can continue to bill for it. As one Ohio manager wrote to their staff: "As we have already discussed, absolutely no pick-ups/inactivation’s are to be do[ne] until I give you the green light. Even if they are deceased." Execs send out company-wide emails celebrating regional managers who have abandoned pick-ups, like a Feb 2022 "Achievement Rankings" email that touted the fact that most regional centers had at least 150 overdue pickups.
Lincare represents a deep, structural rot in American society. They are too big to punish, and too powerful to regulate. A 2006 law meant to curb oxygen payments was gutted by industry lobbyists. Today, Congress is weighing legislation, the SOAR (Supplemental Oxygen Access Reform) Act, which will allow Lincare to bill the public for hundreds of millions more every year, raising rates and eliminating competitive billing. The bill is supported by patient advocates who are rightly interested in getting oxygen to patients who have been locked out of the system, but the cost of that inclusion is that Lincare will be even more firmly insulated from its corruption.
The Trump Administration will doubtless crack down on some of America's worst companies, and the furious voters who elected the only candidate who campaigned on the idea that America was rotten will cheer him on. But Trump has made it clear that he will select the targets of his administration based on whether they are loyal to him or stand in his way, without regard to whether they harm his supporters:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/11/12/the-enemy-of-your-enemy/#is-your-enemy
Companies like Lincare, repeatedly caught paying illegal kickbacks, know how to play this game.

Image: p.Gordon (modified) https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Smoke_bomb_with_burning_fuse.jpg
CC BY 2.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0/deed.en
#pluralistic#oxygen#monopoly#medicare#medicare fraud#impunity#propublica#lincare#DHHS#HHS#health and human services#department of health and human services#kickbacks#Greg McCarthy#Jenna Pedersen#selective enforcement#too big to fail#too big to jail#Crispin Teufel#Jeff Barnhard#asbestos#Christi Grimm
285 notes
·
View notes
Note
my life has only known joy since i learned of elysia chlorotica
E X Q U I S I T E
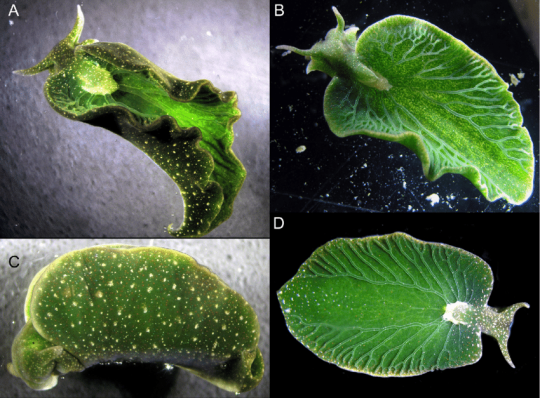
Eastern Emerald Elysia (Elysia chlorotica), family Plakobranchidae, found along the East Coast of the United States
This creature engages in kleptoplasty, taking the chloroplasts from the algae that it eats, and using the chloroplasts for the waste products they create though photosynthesis. Its kind of a... solar powered sea slug!
These sea slugs are not nudibranch, but are in a different order of gastropods.
image via: Views of Elysia chlorotica from Martha’s Vineyard. Figure 15 of Krug et al., 2016, Zootaxa 4148:1
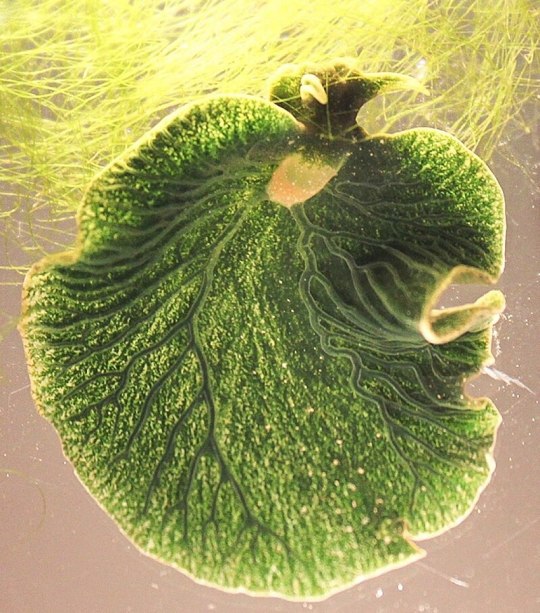

image via: Karen N. Pelletreau et al. http://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0097477
772 notes
·
View notes
Text
I see some confusion (both real and manufactured lol) about the authenticity of the claims reported by F1-Insider on the Red Bull seat.
There are two main claims in that article
That everyone, including "the Verstappen family" were told by Horner and Helmut that Sergio WILL be replaced by the next race in Zandvoort:

2. That the drastic change of course was the result of Liberty Media (the rights holder to all of F1) pressuring Red Bull not to drop Sergio during the break because it would cost Liberty too much money if the only Mexican driver, who is regarded a hero, is dropped before the Mexican GP- tanking the event:

There has been a lot of handwringing about how F1-Insider is not a reliable news source, this is only partially correct because they are not really AMuS (<- regarded as THE gold standard in f1 journalism and reporting) F1-insider mostly report on other people's interviews and sources, it is however a reliable Verstappen camp source. Ralf Bach, the owner of F1-Insider AND MORE IMPORTANTLY THE AUTHOR OF THIS ARTICLE is a career long f1 journalist (30 yr long veteran and is inducted in the paddock hall of fame) has been a Verstappen camp insider since 2016 (think of him as Erik van Haren-lite), if he says something about the Verstappens it is either from Jos or Raymond. He's also by extension close to Helmut (Helmut gave him all those exclusive interviews about how close Red Bull came to bringing Seb back into Red Bull after Ferrari refused to extend him). Most of F1-Insider's interviews are from Red Bull, specifically Helmut and camp Verstappen.
Ralf Bach and Jos are even closer than that because they're friends. In 2021, Jos complained to Bach about Lewis and Toto without knowing he was saying those comments on the record because he thought he was just chatting with Bach as a friend. When Bach wrote about those comments in F1-Insider, Jos tweeted that he doesn't know who F1-Insider is because he didn't know Bach had founded his own company and the website was still quite new. Bach then asked Jos to delete that tweet because it dented F1-insider's credibilty and Jos DID delete that tweet because didn't want to make his friend look like a liar and he HAD said those things to Bach lol. + Bach was only second to EVH when it came to reporting Jos' side of the story when they were trying to overthrow Horner after news of the allegations against him broke.
For Ralf Bach to say, and I quote ,"The Verstappen family were surprised [...] Horner and Helmut gave them a clear statement: Perez is gone" literally means only 1 of 2 things: This is coming directly from camp Verstappen, either from Raymond or most probably Jos given that's his friend and the way Ralf specifically made sure to say 'the Verstappen family' (girl who else? Sophie? Victoria?).
Whether both claims are true can be up for debate but what is a point of fact is that Ralf Bach is reporting what camp Verstappen is telling him they know. And they're telling him that they were verbatim told by both Horner and Helmut that Sergio will be booted on Sunday after the race. The heli ride with Daniel, Max, Jos and Raymond + the fact that camp Verstappen have no reason to lie about this point to at least most of this being true.
#long post#We have to dispel the disingenuous handwringing about how these are all malicious rumours :)#Sorry like Ralf Bach reporting on what the Verstappens are saying and feeling means its coming FROM the Verstappens.#I thought that was common knowledge lol??????#anyway#f1#daniel ricciardo#max verstappen#silly season 2024
289 notes
·
View notes
Text
For anyone who’s already seen Boy and the Heron i found this really interesting article where Ghibli Boss/Producer Suzuki was interviewed recently by indie wire and explains the background of the characters from the new Ghibli film, I’ve copied the full article below or you can click the link to go to the interview but once again it contains so many spoilers
‘The Boy and the Heron’ Is So Personal, Hayao Miyazaki Needed a Year to Grieve Before Pivoting in a New Direction
Miyazaki came out of retirement for his first film in a decade, about his friendships at Ghibli with the late co-founder/director Takahata and co-founder/producer Suzuki.
When Hayao Miyazaki pitched “The Boy and the Heron” (GKids, now in select L.A. and NYC theaters) to Studio Ghibli co-founder/producer Toshio Suzuki in 2016, he asked permission to make the story about himself. This took Suzuki — his friend of nearly 40 years at the time — by surprise; the legendary anime director isn’t known for getting so personal. And yet this aligned perfectly with the notion that Ghibli films are devoted to reliving memories.
“I agree that it is Miyazaki’s most personal film because he actually told me,” Suzuki told IndieWire over Zoom through an interpreter. Not only is “The Boy and the Heron” inspired by Miyazaki’s childhood (he endured the firebombing of Japan during World War II and his father was director of the family’s aircraft manufacturing factory), but also his career at Ghibli with his two closest friends: the late studio co-founder/director Isao Takahata (“Grave of the Fireflies”) and Suzuki.
“Miyazaki is Mahito [the 12-year-old protagonist voiced by Luca Padovan in the English-language version], Takahata is the great uncle [voiced by Mark Hamill], and the gray heron [voiced by Robert Pattinson] is me,” Suzuki added. “So I asked him why. He said [Takahata] discovered his talent and added him to the staff. I think Takahata san was the one who helped him develop his ability. On the other hand, the relationship between the boy and the [heron] is a relationship where they don’t give in to each other, push and pull.”
Collectively, it’s a lot to unpack: Miyazaki came out of retirement for the second time after “The Wind Rises” (2013) to make his 12th feature — the semi-autobiographical, hand-drawn fantasy for his grandchildren. It’s about destruction, loss, and rebuilding a better future through imagination, inspired by the novel he adored as a child (“How Do You Live?”).
Mahito loses his mother in the firebombing of Japan and relocates to the countryside, where his father (voiced by Christian Bale), who runs an air munitions factory, marries his sister-in-law, Natsuko (voiced by Gemma Chan). Traumatized, angry, and confused, the boy encounters a talking heron (part bird, part man), who tells him that his mother is still alive and guides him to an alternate world in a magical tower shared by the living and the dead. There he encounters his great uncle, the architect of the tower, and reunites with both his mother (voiced by Karen Fukuhara) and Natsuko.
At first, Suzuki resisted green-lighting “The Boy and the Heron” because of Miyazaki’s age (he’s 82) and the great expense (it is arguably Japan’s most expensive film but has made the equivalent of nearly $80 million at the country’s box office). Yet Miyazaki wore down his resistance with his enthusiasm and impressive storyboarding. The film took seven years to complete, and Suzuki needed to hire some of Japan’s most talented animators outside of Ghibli to handle the task (including supervising animator Takeshi Honda of “Neon Genesis Evangelion” fame). With diminished stamina and failing eyesight, Miyazaki was unable to oversee the production in the same manner as when he was at the height of his creative powers and relied on Honda to draw, redraw, and review under close advisement.
But with the death of Takahata in 20018, a grief-stricken Miyazaki was forced to scale back the role of the great uncle in the story, who had previously been more central to the boy’s life. “After Takahata passed away, he wasn’t able to continue with that story, so he changed the narrative and it became the relationship between the boy and the Heron,” Suzuki continued. “And in his mind, initially, the Heron was something that symbolizes the eeriness of the mansion and that tower, even ominous, that he goes to during war time. But he changed it to this sort of budding friendship between the boy and the Heron.”
Miyazaki first toyed with the idea of exploring the theme of friendship in “The Wind Rises” (inspired by real-life fighter design engineer Jiro Horikoshi during World War II) before abandoning it. “So this time around, when the Heron became the centerpiece of the story, and he came with the storyboards, I was careful for him to not portray me in a bad way,” Suzuki said. “Having said that, I’ve known Miyazaki for 45 years. I remember everything about him. There are things that only I know. There are things that only the two of us know. And he remembers all these small details, which I was very impressed with.”
For example, when Mahito and the Heron sit and chat at the house of Kiriko (voiced by Florence Pugh), a younger, seafaring version of one of the old maids, it is a recreation of the way Miyazaki and Suzuki would meet. “The place that we do our meetings, where we have our conversation is at his studio, his atelier,” he added. “And he has this like large table, but we don’t sit facing each other, we sit next to each other, and we never look at each other when we talk. And what we discussed was very similar.”
During production, Suzuki became impatient to see the new storyboards with the great uncle. It seemed Miyazaki was intentionally stalling while grieving about Takahata. “My question was: ‘So when is the great uncle going to appear?'” said Suzuki. “He built this great character, but he never appears in the storyboards that he would bring me. But it took him actually about a year after the passing of Takahata that he was able to draw that character into the storyboards in the second half of the story.
“And the most surprising thing for me was when I saw the storyboard where Mahito was asked by his great uncle to carry on with this work, this legacy, and he says no — he declines the offer. Miyazaki was someone who followed the path of Takahata for so many years, and I thought it was a huge thing for him [to follow a different path].”
Meanwhile, Suzuki confirmed that Miyazaki has not retired. The film has given the director renewed confidence to keep working on other stories. However, Miyazaki can’t focus on new ideas while “The Boy and the Heron” remains in theaters. “He needs to empty his mind again,” Suzuki said, “and then when he’s emptied his mind with a blank canvas, he usually comes up with new ideas. So we have to wait a little more.”
927 notes
·
View notes
Text
"Why won't Venezuelans just address the blockade?"
If you're wondering why, read below.
Let me start by saying that I wrote this after I finished work, with less than three hours of sleep and a single meal in my body, so if you find any grammar mistakes, my apologies.

This is the comment that kickstarted this post. I believe I've mentioned this before, but when you're living in a country that weaponizes propaganda and hijacks every single media outlet, you have to master the fine arts of fact checking and cross-referencing. Which is exactly what we're going to do right now, addressing the claim that 40,000 Venezuelans have been killed by the US sanctions, and why We Won't Engage with You In This Particular Argument.
*Note: click the underlined text for links and sources.
In the paper Economic Sanctions as Collective Punishment: The Case of Venezuela by Mark Weisbrot and Jeffrey Sachs (who will be referred to as WS in this post), WS mention that between the years of 2017-2019, the economic sanctions caused a 31% increase in the general mortality rate in Venezuela, a number that they calculate may be of about 40,000 deaths. While they cite ENCOVI and a UN report from 2019 as the sources of this statistic, they clarify the following in the footnotes:

The ENCOVI 2018 survey has not been made public, the mortality statistic cited here is from the UN Report (2019).
As of this date, WS has not made public the data source for this estimate, and the UN report used as a source (Venezuela: Overview of Priority Humanitarian Needs, March 2019) is not publicly available.
So let's take a look at some sources that ARE publicly available.
The World Bank Group World Development Indicators registers at least a 30% increase in the infant mortality rate in Venezuela from the dates of 2013 to 2016. Similar numbers are reported in this paper, seeing a 40% increase in the infant mortality rate in Venezuela between the dates on 2008-2016. Here's an excerpt from the paper Impact of the 2017 Sanctions on Venezuela:

While different than other overall mortality rates, increases in infant mortality rates are generally interpretable as a preventable consequence of inadequate pre- and post-natal care for otherwise healthy but vulnerable infants. Thus, infant mortality is often recognized as a good proxy measure of the quality on overall public health provision.
What this tells us is that THERE HAS BEEN an increase in general mortality rate - one that started long before the 2017 sanctions.
However, this doesn't mean that in the periods of 2017-2019 there wasn't a high death toll. Let's look at another publicly available source.


The National Hospital Survey (2019) found that between November 2018 and February 2019, 1557 people died owing to the lack of supplies in hospitals [...]. 40 patients died as a result of the power outages in March 2019.
We see the first mention of a number in the 2019 Report of the United Nations High Commissioner for Human Rights.
Something interesting this report mentions is that 40 deaths were caused by the blackout in March 2019. A blackout that lasted 7 days and affected our 23 states.
The energy crisis which caused this nationwide blackout started in 2010. The Wikipedia article is a good summary, if a bit simple, of the events that led to and took place during and after the energy crisis (which affects us Venezuelans living in the country to this day)
Back to the UN Report. Something else this report indicates is the following:

In 2018, the Government registered 5,287 such killings, while the non-governmental organization Observatorio Venezolano de la Violencia reported at least 7,523 killings under this category. Between 1 January and 19 May 2019, the Government reported 1,569 killings for resistance to authority. The Observatorio Venezolano de la Violencia reported at least 2,124 such killings between January and May 2019. Information analysed by OHCHR suggests many of these killings may constitute extrajudicial executions.

[...] Six young men executed by the Special Action Forces (SEBIN) in reprisal for their role in anti-government protests in 2019.
This means that between the dates of 2018-2019, there have been approximately 9,647 deaths in the context of security operations - which includes Venezuelans that took part of the protests in 2019. Very similar to what we have been reporting since after the elections in July 28.
2017 to 2019 was one of the most difficult periods in Venezuelan history, marked by the sanctions imposed by Trump which affected oil export, access to diesel, and food and medicine imports. Some people argue that the economic recession in Venezuela was caused by the sanctions - failing to notice the negative trends in the years prior to these.
Bahar, Bustos, Morales and Santos (who will be referred to as BBMS in this post) conclude in their paper, Impact of the 2017 Sanctions on Venezuela, that while the sanctions had a negative effect in the oil production, "it is quite impossible to attribute the fall [...] to one single event (i.e., the sanctions), when many other confounding events were happening at the same time."
Oil production: Oil prices dropped during 2015, and oil production decreased as a result of lack of maintenance and investment.
Energy crisis: By 2009, when the energy crisis was first declared, the electrical grid had already been suffering from the lack of maintenance and investment since 1998. The Chávez administration distributed million dollar contracts [...] that enriched high officials of his government and the works were never built. [1] [2] [3]
Economic decline and hyper-inflation: Actions taken by the Chávez administration such as expropriation and price control, as well as the PDVSA purge in 2002 led the country to depend almost entirely on its already declining oil industry, causing shortages and price rises in common goods, food, medical supplies and so on. By 2015, 60% of the Venezuelan population was living in poverty. [1] [2] [3] [4]
From only these three points, we can establish a negative trend starting way before the first US Sanctions. Thus, we can conclude that by the time the devastating 2017-2019 sanctions took place, Venezuela was already deep in a state of generalized crisis.
WS conclude in their paper:

[...] One of the most important impacts of the sanctions is to lock Venezuela into a downward economic spiral. [...] An economic recovery could have already begun in the absence of economic sanctions.
While Bahar, Bustos, Morales and Santos declare:

[...] Our analysis finds insufficient evidence to conclude that they [sanctions] were responsible for the worsening of the socio-economic crisis. [...] The weight of evidence seems to indicate that, rather than being a result of US-imposed sanctions, much of the suffering and devastation in Venezuela has been, in line with most accounts, inflicted by those in power.
In conclusion - both papers seem to agree that the crisis in Venezuela started before 2017, but where WS claim that it worsened due to US sanctions, BBMS place a higher blame on the deterioration caused by the Venezuelan government.
Now, you may keep whichever analysis you prefer, but one thing we know for sure: the 40,000 Venezuelans that WS claimed died due to the sanctions cannot be found in any public report, while the death toll of protests and extrajudicial killings has been extensively reported.
Why is this relevant?
Contrary to what some people on this site would say, Venezuelans generally agree on the negative impacts of US-imposed sanctions (note: this poll accounts only for Venezuelans in Florida, as polls aren't often published inside Venezuela). However, the general consensus is that US-sanctions only added up to a crisis that had been building up since Chávez rose to power, and rather than the cause, it was yet another symptom.
Yes, the US is the Big Bad, but placing the blame solely on the sanctions only takes the responsibility away from the government and diverts the attention from the poor governance, rampaging corruption, violent repression and denialism that we've grown used to in the last 25 years.
So if you ask "why don't you address the blockade?", my response is: why don't you address the 9,647 extrajudicial killings, the 40 deaths caused by the energy crisis, the energy crisis itself, the economic decline, the lack of maintenance in the infrastructure, the violent repression, the forceful abductions and the censoring?
What we want you to understand is that when you center the US as the cause of the crisis, you are actively participating in our state-funded propaganda and knowingly turning a blind eye on the suffering of all Venezuelans. You are no better than imperialists - you ARE participating in imperialism.
Remember:

Last, but not least - be careful with your sources. This Venezuelanalysis article was written by Andreína Chávez, former editor-in-chief of TeleSUR, a government-funded news channel known for spreading Maduro propaganda. One of their most recent claims: dead Venezuelans are shown as having voted in the ballots shown in resultadosconvenezuela.com. Needless to say, this is false. This news portal is what some people would call, BIASED.
For more information, please read the amazing analysis written by @systhemes HERE.
A more direct response by @achillesmonochrome HERE.
For other sources, check HERE.
*Fellow Venezuelans, feel free to include anything I might have missed.
#if you're wondering wahhh why won't venezuelans simply accept that the US caused all their suffering#30 million venezuelans are imperialist gusanos wahhh#THIS IS WHY#i'm tired of y'all repeating the same talking points we hear every single day from the regime#if we wanted to consume propaganda we would just watch Con El Mazo Dando#there are many evils out there#the US is merely one of them#venezuela#venezuela libre#free venezuela#all eyes on venezuela#fuck maduro#us centrism#tankie punks fuck off#venezuelan crisis
159 notes
·
View notes
Note
Is there any specific literature you could recommend for those who want to learn more about the pre-Christian culture in Finland? (In Finnish or in English!)
Hi!
I can link both. I have some personal faves but they are only accessible through our university's accounts...
The first page is a website with multiple good texts about this subject. It is the site of Jaakko Häkkinen, which if you google him you can see that he is a credible source. There are also texts about subjects like language and history.
This article (in Finnish) discusses the claim that Finland had ancient kingdoms. I also listened to this podcast episode from Yle Areena about it (in Finnish).
Yana Borodulina's master's thesis Suomalaisten uskomustarinoiden yliluonnolliset olennot ja niiden nimityksien alkuperä (2016) (in Finnish) is a very good text if you want to read about what ancient Finns believed in (without Kalevala pseudo-Finnish stories!)
An article about the Finnish "bear cult": THE BEAR AND THE YEAR: ON THE ORIGIN OF THE FINNISH LATE IRON AGE FOLK CALENDAR AND ITS CONNECTION TO THE BEAR CULT by Marianna P. Ridderstad (in English) was very fun to read! I will include it only because I love that they mention the Finnish 13th month which has been lost to time. This one is short though.
An article in English with the absolute basics of the ancient Finnish religion, made by Anssi Alhonen from the politically independent organization Taivaannaula.
Now while I cannot give you recommendations on physical books and only have PDFs (we are very digital at our university I guess) I can tell you what to avoid when looking for these books in stores or in the library. A credible book about pre-Christian culture in Finland would NOT promote:
Finnish runic writing. If there were runes found in Finland, they were imported from Scandinavia.
Finnish pre-Latin alphabet. Nothing like this has been found to this day.
"Finnish people descended from the Mongols"/"Finns are mongoloid". Modern genetic technology says otherwise. Put the book down immediately if it says this (or don't, who am I to tell you)
Describing the pre-Christian culture as "vulgar" or similar words. (This point may be ignored if you have good media literacy)
Using the Kalevala as a credible source for Finnish culture.
Additional: beware of texts written by a specific type of people. I would avoid people who do not cite sources. (I have stumbled across so many Neopagan witches who just write stuff like "ancient Finnish spells" which cannot be found in any archive. We have real spells too! No need to make up history)
Hope this helps!
#finnish#langblr#langblog#suomen kieli#finland#finnish language#culture#I have some pet peeves as you can see
94 notes
·
View notes
Text
First, let’s address the fact that hackers recently accessed the personal data of about 14,000 23andMe customers. Because of how 23andMe works—it has a “DNA Relatives” feature that lets users find people they are probably related to—this breach created 6.9 million “other users” who had data stolen in the breach, according to reporting by TechCrunch. This data included people’s names, birth year, relationships, percentage of DNA shared with other 23andMe users, and ancestry reports.
[...]
Getting your DNA or your loved ones’ DNA sequenced means you are potentially putting people who are related to those people at risk in ways that are easily predictable, but also in ways we cannot yet predict because these databases are still relatively new. I am writing this article right now because of the hack, but my stance on this issue has been the same for years, for reasons outside of the hack. In 2016, I moderated a panel at SXSW called “Is Your Biological Data Safe?,” which was broadly about the privacy implications of companies and other entities creating gigantic databases of people’s genetic code. This panel’s experts included a 23andMe executive as well as an FBI field agent. Everyone on the panel and everyone in the industry agrees that genetic information is potentially very sensitive, and the use of DNA to solve crimes is obviously well established. At the time, many of the possible dangers of providing your genome to a DNA sequencing company were hypothetical. Since then, many of the hypothetical issues we discussed have become a reality in one way or another. For example, on that panel, we discussed the work of an artist who was turning lost strands of hair, wads of chewing gum, and other found DNA into visual genetic “portraits” of people. Last year, the Edmonton Police Service, using a company called Parabon, used a similar process to create 3D images of crime suspects using DNA from the case. The police had no idea if the portrait they generated actually looked like the suspect they wanted, and the practice is incredibly concerning. To its credit, 23andMe itself has steadfastly resisted law enforcement requests for information, but other large databases of genetic information have been used to solve crimes. Both 23andMe and Ancestry are regularly the recipients of law enforcement requests for data, meaning police do see these companies as potentially valuable data mines.
755 notes
·
View notes
Text
Made in the USA: Wage Theft, Fraud and Hidden Sweatshops
Unrolled twitter thread by derek guy (@dieworkwear)
4 Oct 24 • Read on X
ALT enabled on all images. Video has closed captions but is not transcribed.
Not trying to create a pile-on here. But let's talk about why something might still be made in unethical conditions even though it bears a "made in USA" tag. 🧵
The first thing to understand is that not all workers are covered by US labor laws. You might assume that workers get paid a minimum wage (after all, it says "minimum"). In fact, many garment workers in the US toil under what's known as the piecework system.
Piecework means you get paid not by the amount of time you work but the number of operations you complete. This system should be familiar to many of you. As a writer, I get paid per word. The pay is the same whether it takes me 100 or 10 hours to write a 1,000 word article.
My situation is fine bc I get paid enough to eat. But for a garment worker, the pay structure can be peanuts: three cents to sew a zipper or sleeve, five cents for a collar, and seven cents to prepare the top part of a skirt. These are real numbers for LA-based garment workers.
Piecework is how companies skirt minimum wage laws. Among labor organizers, the term "wage theft" refers to the difference between what a worker should have earned under min wage laws and what they actually earned through the piece rate system.
This system is incredibly common. A 2016 UCLA Labor Center study showed the median piece-rate worker in Los Angeles scrapes together $5.15 per hour—less than half the state’s mandated minimum wage. Labor conditions are also very bad: poor ventilation, dusty air, rats and mice.

A Federal Department of Labor investigation the same year found that 85 percent of Los Angeles garment factories were breaking labor laws. In 2016, these violations amounted to $1.3 million in back wages owed to 865 workers in a sample of 77 factories. This is wage theft.
In 2021, labor organizers won a fight to get piecework banned in California. But two years later, it's still incredibly common. I interviewed an LA-based garment worker who toils 12 hrs a day for $50. She sleeps in the corner of a kitchen. From my article in The Nation:

Currently, there's a new fight get piecework banned nationwide through the FABRC Act. I would link, but Twitter throttles threads that have outbound links, so I would prefer if you Google how you can support this legislation. Or follow @GarmentWorkerLA for more info.
The other reason why a "made in USA" tag may not mean much has to do with how the label is applied.
When you see this label inside your garment, what do you assume? Think about this before moving on to the next tweet.

The Federal Trade Commission has pretty strict rules on who gets to apply that label. For clothes, the item has to be cut and sewn in the US using materials that were made in the US. The FTC tries to match its rules with the common understanding of what "made in US" means.
If you're a giant company like Levi's or LL Bean, you may have lawyers who are advising you on these rules. This is why you see labels like "imported," which means the item was made abroad. Or "made in the US from imported materials" when they can't meet the MiUSA standard.
But it's incredibly common for companies to violate FTC rules. In 2022, the FTC fined the pro-Trump brand Lions Not Sheep $211k for labeling their t-shirts "made in USA" when the shirts were actually imported from China and other countries.
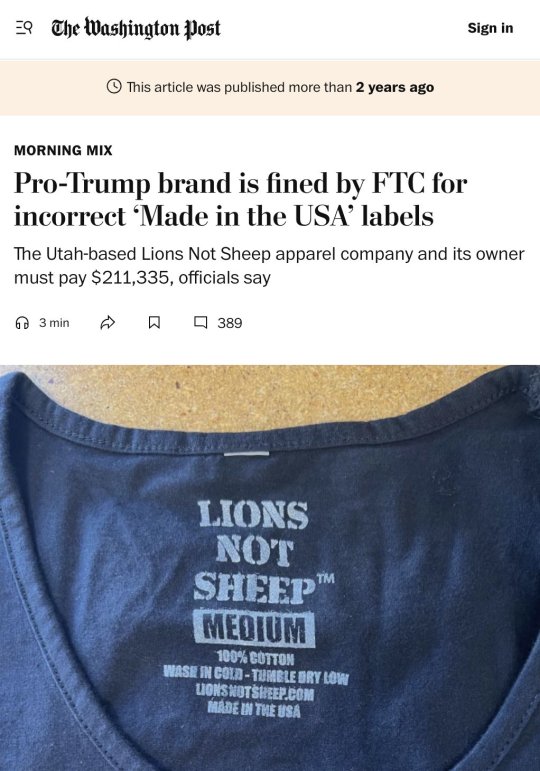
The company was basically importing blanks from China, ripping out the "made in China" label, screen printing the shirt in the US, and then applying a new screen-printed "made in US" label. CEO Sean Whalen claimed he was being persecuted for his pro-Trump views.
But the whole thing started bc Whalen made a video about how his customers are price sensitive, so he imports blanks from China. That's what kicked off the FTC investigation. So while this mislabeling is common, it's hard to get caught unless you make a video about your crimes.
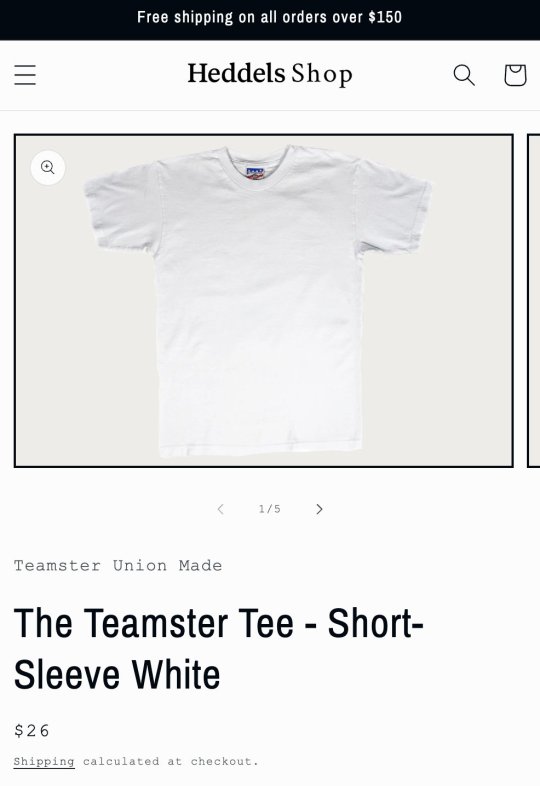
The truth is that making a t-shirt in the USA according to FTC standards will result in a relatively expensive garment. Heddels and Velva Sheen both produce shirts in the US from US grown cotton. The first is $26; second is $90 for a two-pack.

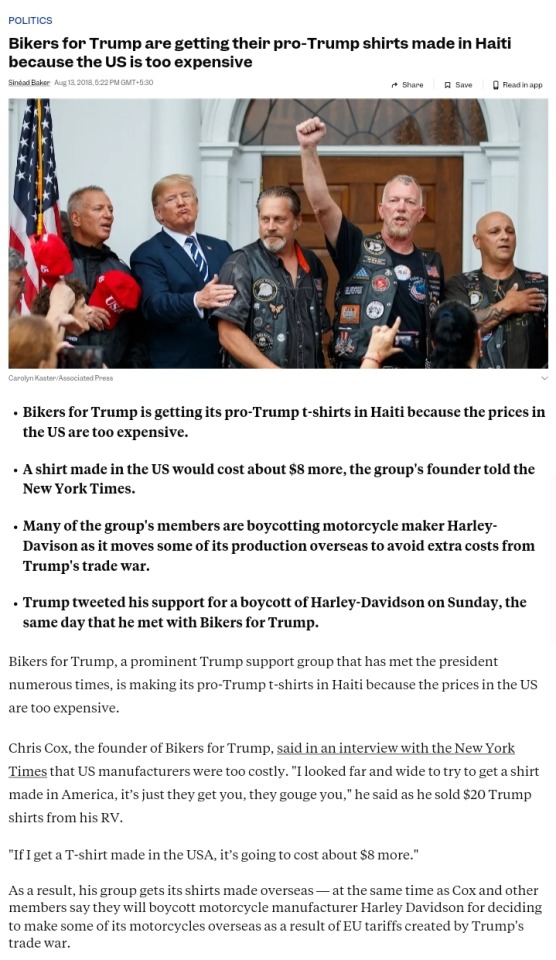
Once you add things such as screenprinting—or if you want a more unique cut and not just basic blanks—the costs go up. This is why Bikers for Trump sourced their merch from Haiti. They knew their customers would not pay an extra $8 for true made-in-USA production.
Today, there are countless companies that make merch for other organizations. They source their t-shirts from a variety of places—some made in the US, most not—and then screenprint a design and fulfill orders. This way, the other org doesn't have to do any work but marketing.
When you see a screenprinted t-shirt for $20, ask yourself: Where was the material grown? Where were the yarns spun? Where was the cutting, sewing, and finishing performed? Where was the screenprinted done? What were the wages and labor conditions along these steps?
I'm not a nationalist, so I don't prioritize American jobs over foreign ones. But I do care about fair wages and labor protections. Just because something was made abroad doesn't mean it was made in a sweatshop. Just because it was made in the US doesn't mean fair wages.

Paying more for a garment is also no guarantee of ethical manufacturing. But when the price of a garment is so low, you leave little on the table for workers. Just because you see a $20 t-shirt that says "made in USA" doesn't mean it was made fairly.
Please don't harass the person who posted that original tweet. My intention is not to cause harm or stress for anyone. Only to help shed light on what goes into garment manufacturing, fair labor, and labeling. Hopefully, you will consider these issues when shopping.
For the inevitable question: "How do I make sure my clothes were made ethically?" This is very difficult to answer in a thread. My simplest answer is that we should elect pro-worker politicians, fight for pro-labor laws, and empower unions so workers can advocate for themselves.

--------------------End----------------------
TL; DR: Doesn't matter if it's the US, if it's not union it's probably a sweatshop. And not all merch is priced high because of fair labour conditions (looking at Taylor Swift and Beyoncé). Look for supply chain transparency.
#sweatshops#fashion#american sweatshop#chappell roan merch#sweatshirt#chappell roan#merchandise#made in usa#garment industry#fast fashion#worker rights#labour rights#labour unions#capitalism#worker exploitation#us politics#us law#knee of huss
133 notes
·
View notes