#housing and urban development
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
#tiktok#donald trump#rachel maddow#fuck trump#trump administration#hud#ai video#ai#elon musk#elongated muskrat#fuck elon#elon mask#fuck musk#president musk#president trump#trump and musk#crooked donald#housing and urban development#government#us government#ai generated#trump#us politics
99 notes
·
View notes
Text

Billboard at Walthamstow motorway, north London
* * * *
LETTERS FROM AN AMERICAN
March 13, 2025
Heather Cox Richardson
Mar 14, 2025
Stocks fell again today.
The S&P 500, which tracks the stock performance of 500 of the biggest companies that are listed on U.S. stock exchanges and is the world’s most widely followed stock market benchmark, dropped 77.78 points, or 1.39%, ending the day more than 10% off its record high of less than a month ago and entering into “correction” territory. A market correction is a period of rapid change that drops the value of stocks by at least 10%.
Other major indexes have also fallen into correction as President Donald Trump’s tariffs and tariff threats, along with dramatic cuts to federal funding and federal employment, are hobbling the national economy. The Dow Jones Industrial Average fell 537 points, or 1.3%, and the Nasdaq Composite fell 2%.
In the wake of the dropping markets, Trump announced on his social media platform today that if the European Union did not drop its 50% tariff on whiskey, imposed as retaliation for Trump’s tariffs on aluminum and steel, he would impose a 200% tariff on all “WINES, CHAMPAGNES, & ALCOHOLIC PRODUCTS COMING OUT OF FRANCE AND OTHER E.U. REPRESENTED COUNTRIES.” He added: “This will be great for the Wine and Champagne businesses in the U.S.”
In fact, journalist Dave Infante, who covers drinking in America at Fingers, noted that while it seems counterintuitive, such a tariff would “crush the US wine industry. Booze gets to market on distributors' trucks,” he posted. “These fleets need volume to run efficiently. Subtract EU wine from the equation & it no longer pencils out. Any gains from less competition would likely be paid back out in margin loss.”
Kai Ryssdal of the radio show Marketplace posted: “I'm honestly running out of words I can use on the air to describe what's happening in and to this economy.”
There is a grim fascination in the 1929 stock market crash, when Americans watched with horror as the bottom fell out of the economy. In our memories, reinforced by jerky black-and-white newsreels, that crisis shows businessmen aghast as fortunes disappeared in heavy trading that left the ticker tape that recorded prices running hours behind only to toll men’s destruction when it finally reached the end of the day’s sales.
But the stock market crisis of 1929 came from structural imbalances in the nation that created a weak economy in which about 5% of the country received about one third of the nation’s income. What really jumps out today is that, in contrast to 1929, the national economy is strong—or was just a month ago. In fact, before Trump took office, it was the strongest of any economically developed country in the world.
The blame for the falling market in the United States today can be laid squarely at the feet of the new presidential administration, with the tariff war it has instigated and the sweeping cuts it has made to United States government employment. President Donald Trump and his staff insist that the pain he is inflicting on Americans will pay off in long-term economic development, but they have deliberately thrust a stick into the wheels of a strong economy.
It is an astonishing thing to watch a single man hamstring the United States economy. It is also astonishing to watch Republican senators try to convince the American people that a falling stock market and contracting economy is a good thing. “Our economy has been on a sugar high for a long time. It’s been distorted by excess government spending,” Montana Senator Tim Sheehy told Fox News Channel host Larry Kudlow today. “What we're seeing here from this administration and what you're gonna see from this Congress is re-disciplining to ensure that our economy is based on private investment and free-market growth, not public sector spending.”
In fact, until a brief spike in spending during the coronavirus crisis, government expenditure in the United States as a percentage of gross domestic product has held relatively steady around 20% since the 1950s.
Today, Trump met with Secretary-General Mark Rutte of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) who was eager to get Trump to reiterate U.S. support for NATO. Trump told Rutte that the United States needs control of Denmark’s autonomous territory of Greenland “for international security, not just security—international—we have a lot of our favorite players cruising around the coast, and we have to be careful.” Asked about whether the U.S. would annex Greenland, he answered: “I think that will happen.”
At that same meeting, Trump talked about his order to release water from two California dams in January allegedly to deliver water to Los Angeles after the devastating wildfires in that region, although water managers in Los Angeles said they had plenty of water for firefighting. A February 3 memo from the Army Corps of Engineers, obtained by Scott Dance and Joshua Partlow of the Washington Post under the Freedom of Information Act, makes it clear that officials knew that the 2.5 billion gallons they released in response to Trump’s order “could not be delivered to Southern California.”
In fact, as Ian James explained in the Los Angeles Times, water releases are usually carefully considered, and local water managers and lawmakers thought the sudden plan was potentially “ruinous,” worrying that an abrupt surge of water could damage the lands and people downstream while wasting water that would be needed during the hot growing season.
That’s not how Trump portrayed the sudden release of water. After talking to reporters about the upcoming congressional budget fight, he suddenly pivoted to Los Angeles, and from there to water. "I broke into Los Angeles, can you believe it, I had to break in,” he said. “I invaded Los Angeles and we opened up the water, and the water is now flowing down. They have so much water they don't know what to do. They were sending it out to the Pacific for environmental reasons. Ok, can you believe it? And in the meantime they lost 25,000 houses. They lost, and nobody’s ever seen anything like it. But, uh, we have the water—uh, love to show you a picture, you’ve seen the picture—the water’s flowing through the half-pipes, you know, we have the big half-pipes that go down. Used to, twenty-five years ago they used to have plenty of water but they turned it off for, again, for environmental reasons. Well, I turned it on for environmental reasons and also fire reasons but, ah, and I’ve been asking them to do that during my first term, I said do it, I didn’t think anything like could happen like this, but they didn’t have enough water. Now the farmers are going to have water for their land and the water’s in there, but I actually had to break in. We broke in to do it because, ah, we had people who were afraid to give water. In particular they were trying to protect a certain little fish. And I said, how do you protect a fish if you don’t have water? They didn’t have any water so they’re protecting a fish. And that didn’t work out too well by the way….”
Today, U.S. District Judge William Alsup ruled that federal agencies must immediately offer thousands of probationary workers purged from the government in the early weeks of Trump’s administration their jobs back. Mass firings from the Defense, Treasury, Energy, Interior, Agriculture and Veterans Affairs departments did not follow the law, Alsup said.
The government declined to make witnesses available to the court although Alsup had ordered the acting head of the Office of Personnel Management to appear today. Alsup told lawyers from the Justice Department that he believed they were hiding how the firings had taken place and who was responsible. “You will not bring the people in here to be cross-examined. You’re afraid to do so because you know cross examination would reveal the truth…. I tend to doubt that you’re telling me the truth.… I’m tired of seeing you stonewall on trying to get at the truth.”
Tonight, U.S. District Judge James Bredar ordered the administration to reinstate thousands of probationary workers in the departments of Agriculture, Commerce, Education, Energy, Health and Human Services, Homeland Security, Housing and Urban Development, Interior, Labor, Transportation, Treasury, and Veterans Affairs, as well as the U.S. Agency for International Development, the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau, the Environmental Protection Agency, the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation, the General Service Administration, and the Small Business Administration.
Bredar said it was “likely” that “the Government has engaged in an illegal scheme spanning broad swaths of the federal workforce.” The government claimed it did not have to give advance notice of the firings because it had dismissed the probationary workers for “performance” or other individual reasons. "On the record before the Court, this isn’t true,” Bredar said. “There were no individualized assessments of employees. They were all just fired. Collectively.”
LETTERS FROM AN AMERICAN
HEATHER COX RICHARDSON
#Heather Cox Richardson#Letters From An American#Federal Judges#Federal Courts#Illegal Government Actions#EPA#Treasury#Financial Protection Bureau#Housing and Urban Development#the Economy#economic news#the Stock Market#Market correction#market crash#tariffs#lies and the lying liars
17 notes
·
View notes
Text
15 notes
·
View notes
Text

Did they happen to think about accessibility and their future?
#disability#wheelchair#sphincter-envy#humor#stroke#the future#future#your future#our future#dark humor#millennial#prospective millennial home owners#sphincter envy#disability podcast#wrwi#rollingredneck#million dollar home#home loans#million dollar home loan#prospective home owners#housing#affordable housing#public housing#private housing#HUD#housing and urban development#meme monday#meme#werollwithit#we roll with it podcast
0 notes
Text
TVs At HUD Played An AI-Generated Video of Donald Trump Kissing Elon Musk’s Feet
🤭
0 notes
Text
Mass firings set for HUD office that funds homelessness programs : NPR
#housing and urban development#housing#homeless#human rights#civil rights#social justice#us politics
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
And the final one, completing all appropriations bills clearing the committee by mid July. This one is for Transportation, Housing and Urban Development, AKA THUD, as in the sound these massive spending bills make when you drop them on the floor.
#government shutdown?#congress#house#house appropriations committee#appropriations#house of representatives#spending bills#vote#budget negotiations#fy2025#budget bill#transportation#housing#urban development#housing and urban development#THUD#to the House floor#committee vote#budget#11 weeks left#last one out the door
1 note
·
View note
Text
Conflict of interest much...

#crossroads rhode island ngo#conflict of interest#john j McConnell jr#Rhode island#usaid#usaid fraud#usaid funding freeze#fema fraud#democratic hypocrisy#using your office for personal gain#housing and urban development#hud
148 notes
·
View notes
Text
hey so i’ve seen zero posts about this yet today, which i mean the news broke only today but i feel everyone should have this amazing and disgusting imagine burned into their retinas as i haved
someone (undiscovered as of this posting) took over the tv screens on the first day of return to office at the Department of Housing and Urban Development showing a Generative AI video of donald trump giving elon musk (with two left feet) a toejob
warning: if you’re eating or have just ate, viewer discretion is advised
angle 1 [links to bluesky]
angle 2 [links to imgur]
no this is not a joke and no you will not be taken to a rickroll. this is 100% real [source: The Rolling Stones, accessed feb 24, 2025]
atop the video of, quote, “Trump making sweet, sloppy oral love to Musk’s bare feet”, are the words “LONG LIVE THE REAL KING”
it was reportedly only up for 5 minutes before they started unplugging tvs, as staff allegedly did not know how to turn off the monitors.
amazed that it happened, unfortunate that image will be in my brain for the rest of the day
#us politics#current events#donald trump#donald trump tw#elon musk#elon musk tw#department of government efficiency#department of housing and urban development#is this important? no. is it hilarious? absolutely#i had to check several sources before i believed it bc it’s giving internet trolling the libs#but nope! it’s real! it happened! goddamn#us government#us govt
25 notes
·
View notes
Text
No community anywhere would willingly choose to have a nearly 30 per cent office vacancy rate in its downtown core. But faced with that problem, one Canadian city came up with a plan that is now being held up as a model for the rest of the country amid an ongoing national housing crisis. Calgary has been busily working to convert underused office towers to residential housing, thanks to the city's one-of-a-kind incentive program for developers. In just two years, the program has resulted in the approval of 13 office-to-residential conversion projects, with four more still under review.
Continue Reading
Tagging @politicsofcanada @abpoli
228 notes
·
View notes
Text
in the face of animal crossing pocket camp closing, can i just say. i don’t understand why new horizons was like that. after acpc the next animal crossing game should have been amazing and yet,
acnh feels very stale very quickly imo. it has the bones of an animal crossing game (unlocking shops, filling the museum, etc) but the villagers are sooo samey, and it feels like there’s fewer interactions and games between them than there was in acnl. (and i know this isn't a new criticism but it feels unfinished. harv's island co-op in the final update feels like a weak alternative to letting lief, kicks, katrina, etc. have physical stores on your island.) but i do love having the ability to build and customize your own furniture, to an extent. the new furniture designs are great and i especially love that villagers have more versatile clothes options. sheep can wear shirts!! everyone can wear hats!!
but also, acpc has WAY more furniture and clothing options than acnh. and i love the way the villagers work there: they have a set personality and a set style. and you can help them give gifts to other villagers or give them fashion tips, and your relationship improves more (im pretty sure ?) if you pick the option that’s The Right Style. it makes it feel like you're actually getting to know them, and it gives a little bit more variation because a cranky jock FEELS markedly different than a cranky cool guy
#animal crossing#mine#this has been in my drafts for like a year but it feels like a good time to pull it out#my ideal animal crossing game is. probably unrealistic i know.#i want the urban development opportunities from acnl because i LOVED being able to build up main street#combined with the landscaping versatility from acnh#acpc villager system. and also more town activities and games. LIKE HIDE AND SEEK THAT WAS MY FAVE#i also want to work at brewsters again and figure out everyone’s coffy orders :) acnh brewsters feels pointless if u dont have amiibos :(#in acnh people are always walking into my house uninvited but never invite me over to theirs!!!!#and frankly. kappn’s tours lose their appeal if you’re just going to an endless parade of randomized blank slates#i rly only use it to get the extra DIY recipes and it just feels like a waste of miles
23 notes
·
View notes
Text
Urban Renewal vs. Public Housing: Lessons from Baltimore and Pruitt-Igoe
Urban renewal and public housing have played a central role in shaping American cities, often with conflicting results. While urban renewal aims to modernize and revitalize decaying cityscapes, it frequently displaces long-standing communities, exacerbating socioeconomic inequalities. Conversely, public housing has been used to provide affordable homes for low-income populations, yet poor planning and neglect have led to segregation, poverty concentration, and failure.
This article explores these urban planning challenges through two significant case studies: Baltimore’s Inner Harbor renewal project and the Pruitt-Igoe public housing complex in St. Louis. These examples reveal the successes and failures of 20th-century urban planning, offering critical lessons for the future of equitable city development.
The Case for Urban Renewal: Baltimore’s Inner Harbor
In the mid-to-late 20th century, Baltimore launched one of the most ambitious urban renewal projects in the U.S., aimed at revitalizing its deteriorating downtown and waterfront areas. The redevelopment of Charles Center and the Inner Harbor sought to attract businesses, tourists, and high-income residents back into the urban core.
✅ Economic Growth & Tourism Boost:
The Inner Harbor was transformed into a vibrant commercial and cultural hub, with attractions like the National Aquarium and Maryland Science Center.
New retail, office spaces, and residential developments increased property values and business investments.
✅ Mixed-Use Development & Walkability:
The project embraced modern urban design principles, making the Inner Harbor a 24-hour activity zone instead of a purely business district.
The redevelopment created public spaces, waterfront promenades, and green areas, making the area more livable and attractive.
However, despite these successes, Baltimore’s renewal came with a price—one paid disproportionately by lower-income residents.
📉 Displacement & Gentrification:
The rising cost of living forced many working-class and minority residents out of the area.
Long-standing communities were pushed to the city's margins, leading to increased inequality and social tensions.
📉 Who Really Benefited?
Many of the jobs created by urban renewal did not go to local residents but rather to suburban commuters and outside investors.
The benefits were concentrated in wealthier, predominantly White areas, deepening racial and economic disparities.
Lesson: Urban renewal can drive economic growth, but without equitable policies, it risks displacing the very communities it aims to uplift. Sustainable urban planning should incorporate affordable housing, job creation, and community input to ensure benefits reach all residents.
The Failure of Public Housing: St. Louis’ Pruitt-Igoe Disaster
While Baltimore’s renewal focused on economic revitalization, St. Louis’ Pruitt-Igoe public housing complex is a cautionary tale of poorly executed housing policies. Built in the 1950s, Pruitt-Igoe was meant to be a modern, affordable housing solution for low-income residents. However, within two decades, it became one of the most infamous failures of public housing in America.
📉 Economic & Social Isolation:
As St. Louis lost manufacturing jobs and white flight accelerated suburbanization, Pruitt-Igoe’s predominantly Black residents faced growing unemployment and poverty.
Many residents struggled to afford rent, leading to funding shortages for maintenance and services.
📉 Poor Urban Design & Maintenance Neglect:
The "towers in the park" design created isolated, unsafe spaces that became hotspots for crime.
Elevator breakdowns, vandalism, and lack of maintenance made the complex nearly uninhabitable.
📉 Demolition: The End of an Era
By the late 1960s, Pruitt-Igoe had become a symbol of public housing failure.
In 1972, just two decades after its construction, the federal government demolished the entire complex—a moment often regarded as the death of high-rise public housing projects in the U.S.
Lesson: Public housing cannot succeed without long-term economic investment, proper maintenance, and integration into the broader urban fabric. Instead of isolating low-income populations in concentrated developments, policies should prioritize mixed-income housing, economic support, and community services.
Urban Planning Lessons for the Future
The contrasting stories of Baltimore and Pruitt-Igoe illustrate the complex challenges of urban development. Both cases emphasize the need for urban planning approaches that balance economic development with social equity.
✅ Urban Renewal Should Include Community-Driven Growth
Economic development should not come at the cost of displacing vulnerable communities.
Cities must include affordable housing policies, local hiring initiatives, and resident engagement in renewal projects.
✅ Public Housing Must Be Integrated, Not Isolated
Instead of large, isolated housing blocks, urban planners should invest in mixed-income, mixed-use developments that connect residents to jobs and services.
Public housing policies should prioritize maintenance and long-term sustainability rather than quick-fix solutions.
✅ Equitable Urban Planning Requires Thoughtful Policy
Planners and policymakers must address historical inequities in housing and economic access.
Transit, education, and workforce development programs should accompany any large-scale urban redevelopment effort.
Conclusion: Rethinking Urban Development for the 21st Century
Urban renewal and public housing remain central to urban development debates today. Baltimore’s Inner Harbor shows the power of economic revitalization—but also its risks of gentrification and exclusion. Pruitt-Igoe, on the other hand, serves as a lesson in the failure of isolated, underfunded public housing projects.
For cities to create sustainable, inclusive growth, planners must move beyond outdated models and embrace community-centered, equitable policies that ensure all residents benefit from urban progress.
#smart growth#pruittlgoe#public housing#community development#housing inequality#gentrification#baltimore#city development#economic development#gis#portfolio#strong towns#urban planning#sundusbhatti
12 notes
·
View notes
Text
Finally this week, we have the bill commonly referred to as THUD, Transportation, Housing and Urban Development.
#government shutdown?#congress#THUD#transportation#housing#urban development#housing and urban development#appropriations#budget bill#budget negotiations#FY2025#house appropriations committee#spending bill#government funding#house of representatives#three months left#press release#subcommittee
1 note
·
View note
Text
Housing is a queer issue
what's the number one reason someone has to stay somewhere unsafe? Can't afford to live somewhere else.
Queer folks are more likely to experience homelessness, trans folks even more so. And that's likely to set off a cascade of consequences with issues getting a job, accessing health care, and so on.
Wherever you live, show up for Planning & Zoning meetings or write a letter when they're considering higher density housing and especially if they're considering zone changes like Transit Oriented Development (TOD). Those aren't just for big cities!
Show up and say "Yes, I want Those People to live HERE".
Yes, In My Back Yard.
Say yes to infill especially where existing in-town lots with access to services are rezoned to higher density units. The new apartments should go where the sewer line already is, not where it requires running a whole new spur and where everyone is isolated and requires a car to get everywhere.
Say yes to that public housing in the downtown core where people can WALK to all the services they need.
Everyone should have access to safe affordable housing. You won't know who exactly you're helping, but you're helping tear down a barrier for everyone.
26 notes
·
View notes
Text

06.2023 Hamburg
23 notes
·
View notes
Note
I'm a big fan of building commie blocks to ameliorate the US housing crisis -- and putting them in the public parks that were stolen from other communities to give colonisers some trees to look at -- but what policies should be enacted to get suburbanites into beautiful and efficient bedspace apartments with kitchens and washrooms shared by a floor?
As a good social democrat, I'm contractually obligated to prefer Red Vienna to your proper commie block. Short of a complete class revolution that completely upends the social hierarchy, a significant part of ensuring that social housing pulls off being "a living tapestry of a mixed community" is building it to middle-class standards (including aesthetic standards) so that people with the money to find alternatives don't all leave. Art Deco is a hell of a lot chic-er than the boring minimalist crap that luxury developers are getting away with these days.

Also, don't build them in parks: green space is not only important for environmental sustainability but also the health and mental health of working-class and poor communities who can't afford houses in the suburbs, and we should be encouraging in-fill development instead. (Build them on golf courses instead, because they are classist, invasive, artificial monocultures that do nothing for the environment.)
In terms of how to make suburbia more in synch with dense, sustainable social housing, there are a number of necessary changes:

Commuter rail: suburbs predate the car by a fair few decades, and originally sprung up along the routes of commuter rail lines. Well, it turns out that transit-oriented development and dense transit corridors go hand-in-hand: if you can build higher-density units near transit lines, people will use mass transit to commute, and if there are well-planned areas of higher density around major urban areas, the increased number of commuters can support more regular transit services.
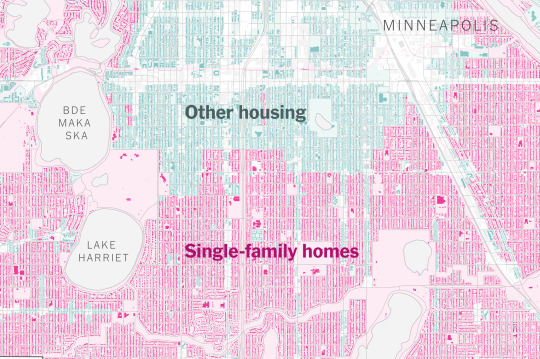
Planning/zoning/ligitation revolution: as I mentioned in my student housing post, one of the major reasons why it's so hard to build affordable housing projects is that local NIMBY groups use every legal tool in the book to bury them. So there needs to be pretty comprehensive reforms of zoning regulations (banning single-family zoning, reducing set-backs and eliminating mandatory parking, getting rid of "unrelated persons" limitations, getting rid of building heights limits, etc.), standardization of the permitting and development approval process, streamlining of the public comment/hearing process and environmental review process for model projects, and extreme limits on litigation for model projects.

Financing reform: as I sort of imply in my Red Vienna section above, a big part of making social housing/public housing successful and avoiding replicating or increasing class and racial segregation is adhering to middle-class minimum standards. This has important knock-on implications:
you need to eliminate requirements for absolute lowest possible land costs (which restrict social housing to economically and socially isolated areas).
you need to raise allowable construction costs, so that you can achieve those aesthetic standards and avoid corner-cutting like smaller rooms and lower ceilings, single-thickness walls/floors/ceilings, no doors on cabinets or closets, cheap cladding and wiring and pipes and other building materials, low-quality insulation and HVAC, etc. Not only do middle-class folks notice this stuff and go elsewhere, but it's all penny-wise and pound-foolish, because cheap construction runs down faster which increases maintenance costs, and sometimes it just straight-up kills people.
you need to adequately finance maintenance, services, and amenities. This is crucial to keeping tenants with deeper pockets, but it's also another one of those things where penny-pinching is counter-productive in the long-run. The more you save on maintenance costs, the faster the buildings run down and the more expensive repairs you have to make. The more you save on services like superintendants and doormen, the more your tenants end up having to spend on handymen and the more you have to spend on police and repair costs. And so forth.
And there is a real potential here for all kinds of positive feedback loops: spending money on achieving higher standards of construction and operation means that you can hang onto and attract higher-income tenants, which means you can have sliding scale rents that cross-subsidize tenants and pay for higher construction and operating costs, and the poor and working class tenants who couldn't have paid for those higher costs and amenities on their own enjoy a "positive externality" for once.
#public policy#public housing#social housing#social democracy#urban development#urbanism#urban planning#urban studies#housing#nimbyism#nimby#red vienna#commie blocks
114 notes
·
View notes