#general lafayette
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
'The War of the Districts, or the Flight of Marat…'
Part 1 (of 5)
Some years ago I photographed a fantastic, satirical poem from a compendium of French Revolutionary verse in the BnF (réserve). It’s been gathering virtual dust ever since. But no more! It’s a witty take on a key moment from early in the Revolution, when the Paris authorities pitted themselves against the radical Cordeliers district (under Danton’s leadership). With help from @anotherhumaninthisworld (merci encore!), we managed to produce a rough translation, which I revised, added some footnotes (to clarify the more obscure references) and added this brief intro to put it in context. While the translation is a literal one, I’ve tried to preserve some of the rhyming spirit of the original where possible. So boil the kettle, get a brew on and settle down to an epic account of Maranton vs Neckerette…
In the early hours of 22 January 1790, General Lafayette, commander of the National Guard, authorized a large military force to arrest the radical journalist Jean-Paul Marat, following a request from Sylvain Bailly, the Mayor of Paris, to provide the Chatelet with sufficient armed force [“main-forte’] to enable its bailiff to enforce the warrant.[1] Bailly’s request was in response to the outrage caused by the publication, four days earlier, of Marat’s 78-page Denunciation of the finance minister, Jacques Necker.[2] Marat had moved into the district the Cordeliers district in December to seek its declared protection against arbitrary prosecution.
His best-selling pamphlet denounced Necker – probably the most popular man in France after the King in July 1789 – of covertly supporting the Ancien Régime and working to undermine the Revolution. His accusations included plotting to dissolve the National Assembly and remove the royal family to Metz on 5 October, colluding in grain hoarding and speculation, and generally compromising the King’s honour. The charges were intended to reveal a cumulative (and damning) pattern of behaviour since Necker’s reappointment in July 1788, and again in July 1789. Bearing his Rousseau-derived epigraph, Vitam impendere vero (‘To devote one’s life to the truth’) – now used as a kind of personal branding, Marat adopted the role of “avocat” to ‘try’ Necker before the court of public opinion.[3] Its general tone came in the context of a wider distrust of international capitalism, with which Necker was closely associated, and which appearted to violate many traditional values.[4] For those interested in the nitty gritty, here’s a footnote explaining why Marat had completely lost faith in Necker.[5]
It caused such a sensation that the first print-run sold out in 24 hours. Most of the radical press hailed Marat’s audacity in challenging Necker’s ‘virtuous’ reputation, while providing invaluable publicity for his pamphlet. The legal pursuit of Marat was largely prompted by the rigid adherence of the Chatelet to Ancien Régime values against the offence of libel (attacking a person in print).[6] I suspect that Marat was hoping a high-profile campaign against Necker would help to establish his name in the public eye by provoking a strong response. However, this was one of the rare occasions when Necker delegated his defence to ‘hired’ pens, providing Marat with valuable extra publicity.
If libel was the main reason for going after Marat, the impetus for pursuit was further motivated by wider political concerns over the extreme volatility that had gripped Paris since mid-December. After pre-emptive popular action in July and October against perceived counter-revolutionary plotting, a new wave of similar rumours was seen by many as a signal that the thermometer was about to explode again. The arrest of the marquis de Favras on Christmas Eve, for allegedly conspiring to raise a force to whisk the King away to safety, assassinate revolutionary leaders, and put his master, Monsieur (the King’s middle brother) on the throne as regent, only served to intensify popular fears. This, combined with the continuing failure to prosecute any royal officers, including the baron de Besenval, commander of the King’s troops around Paris during 12-14 July – who would be acquitted on 29 January for ‘counter-revolutionary’ actions – led to large crowds milling daily outside the Palais de Justice, as the legal action against both men dragged on through January.[7] On the 7th January, a bread riot in Versailles led to the declaration of martial law; on the 10th, a large march on the Hotel de Ville had been stopped in its tracks by Lafayette; on the 11th, there was an unruly 10,000-strong demonstration, screaming death-threats against defendants and judges, in the worst disturbances to public order since the October Days march on Versailles (and the most severe for another year); and on the 13th, tensions were further exacerbated by a threatened mutiny amongst disgruntled National Guards, which was efficiently snuffed out by Lafayette.[8] As a result, Marat’s Denunciation, and earlier attacks on Boucher d’Argis, the trial’s presiding judge, were seen as encouraging a dangerous distrust towards the authorities. Hence the pressing need to set an example of him.
So much for the background. Do we know anything about the poem’s authorship? it appeared around the same time (July/August) as Louis de Champcenetz & Antoine Rivarol’s sarcastic Petit dictionnaire des grands hommes de la Révolution, par un citoyen actif, ci-devant Rien(July/Aug 1790), which featured a brief entry on how Marat had eluded the attention of 5000 National Guardsmen and hid in southern France, disguised as a deserter. These figures would become the subject of wildly varying estimates, depending on who was reporting the ‘Affair’ – all, technically, primary sources! The higher the number of soldiers, the greater the degree of ridicule.[9] Contemporary accounts ranged from 400 to 12,000, although the latter exaggerated figure, included the extensive reserves positioned outside the district.[10] Since the poem also suggests around 5000 men, this similarity of numbers, alongside other literary and satirical clues, such as both men’s involvement in the Actes des apôtres, and the Petit dictionnaire’s targeting of Mme de Stael, suggest a possible common authorship.[11] While the poem took delight in mocking the ineptitude of the Paris Commune, the lattertook aim at the pretensions of the new class of revolutionary. While it is impossible to estimate the public reception of this poem, its cheap cover price of 15 sols suggests it was aimed at a wide audience. It was also republished under at least two different titles, sometimes alongside other counter-revolutionary pamphlets.[12]
Both act as important markers of Marat’s growing celebrity, just six months after the storming of the Bastille. A celebrity that reached far beyond the confines of his district (now section) and readership (which peaked at around 3000).[13] Marat was no longer being spoken of as just a malignant slanderer [“calomniateur”] but as the embodiment of a certain revolutionary stereotype. While he lacked the dedicated ‘fan base’ of a true celebrity, such as a Rousseau, a Voltaire or (even) a Necker, he did not lack for public curiosity, which was satisfied in his absence by a mediatized presence in pamphlets, poems, and the new lexicology.[14] For example, Marat would earn nine, separate entries in Pierre-Nicolas Chantreau’s Dictionnaire national et anecdotique (Aug 1790), the first in a series of dictionaries to capitalize on the Revolution’s fluid redefinition of language.
There seems little doubt that Marat’s Denunciation was intended to provoke the authorities into a strong reaction, and create “quelque sensation”, of which this mock-heroic poem forms one small part.[15] It would prove a pivotal moment in his revolutionary career, transforming him from the failed savant of 1789 to a vigorous symbol of press freedom and independence in 1790. Who knows what might have happened, if, as one royalist later remarked, the authorities had simply ignored this scribbling “dwarf”, whose only weapon was his pen.[16]
I'll post the 3 parts of the poem under #la fuite de Marat. enjoy!
[1] The Chatelet represented legal authority within Paris.
[2] Dénonciation faite au tribunal public par M. Marat, l’Ami du Peuple, contre M. Necker, premier ministre des finances (18 Jan 1790).
[3] The slogan was borrowed from Rousseau’s Lettre à d’Alembert, itself a misquote from Juvenal’s Satires (Vitam inpendere vero = ‘To sacrifice one’s life for the truth’).
[4] See Steven Kaplan’s excellent analysis of the mechanisms of famine plots and popular beliefs in the collusion between state and grain merchants. In part, this reflected a lack of transparency and poor PR in the state’s dealings with the public. During 1789-1790, when anxieties over grain supply were the main cause of rumours and popular tension, Necker made little effort to explain government policies. The Famine Plot Persuasion in Eighteenth-Century France (1982).
[5] As a rule, the King, and his ministers, did not consider the workings of government to be anyone’s business, and was not accountable to the public. However, in 1781, Necker undermined this precedent by publishing his Compte-rendu – a transparent snapshot of the royal finances – yet on his return in 1788, he failed to promote equivalent transparency over grain provision. In consequence, local administrators suffered from a lack of reliable information. Given the underlying food insecurity that followed the poor harvest of 1788, any rumours only unsettled the public. The most dramatic example of this came in the summer of 1789, when rumours of large-scale movements of brigands & beggars created the violent, rural panic known as ‘The Great Fear’. It was Necker’s continuing silence on these matters that lost Marat’s trust.
[6] Necker had a history of published interventions defending himself before the tribunal of public opinion, confessing that a thirst for gloire (renown) had motivated his continual courting of PO, then dismissing it as a fickle creature after it turned against him in 1790. eg Sur l’Administration de M. Necker (1791). For the best demonstration of continuity with Ancien Régime values after 1789, see Charles Walton, Policing Public Opinion in the French Revolution (2009).
[7] The erosion of Necker’s popularity began on 30 July after he asked the Commune to grant amnesty to all political prisoners, including Besenval.
[8] While the evidence was slight, Favras’ sentence to be hanged on 18 February made him a convenient scapegoat, allowing Besenval and Monsieur to escape further action. See Barry M. Shapiro, Revolutionary Justice in Paris, 1789-1790 (1993).
[9] The most likely figure appears 300-500. See Eugène Babut, ‘Une journée au district des Cordeliers etc’, in Revue historique (1903), p.287 (fn); Olivier Coquard, Marat (1996), pp.251-55; and Jacques de Cock & Charlotte Goetz, eds., Oeuvres Politiques de Marat (1995), i:130*-197*.
[10] For example, figures cited, included 400 in the Révolutions de Paris (16-23 Jan); 600 (with canon) in Mercure de France (30 Jan), repeated in a letter by Thomas Lindet (22 Jan); 2000 in a fake Ami du peuple (28 March); 3000 in Grande motion etc. (March); 4000 in Révolutions de France; 6000 (with canon) in Montjoie’s Histoire de la conjuration etc. (1796), pp.157-58; 10,000 in Parisian clair-voyant; 12,000 in Marat’s Appel à la Nation (Feb), repeated in AdP (23 July), reduced to 4000 in AdP (9 Feb 1791), but restored to 12,000 inPubliciste de la République française (24 April 1793).
[11] “Five to six large battalions/Followed by two squadrons” = approximately 5000 men (4800 + 300). A royalist journal edited and published by Jean-Gabriel Peltier, who also appears the most likely publisher of this poem.
[12] For example, Crimes envers le Roi, et envers la nation. Ou Confession patriotique (n.d., n.p,) & Le Triumvirat, ou messieurs Necker, Bailly et Lafayette, poème comique en trois chants (n.d., n.p.). Note the unusual use of ‘triumvirate’ at a time when this generally applied to the trio of Antoine Barnave, Alexandre Lameth and Adrien Duport.
[13] By the time the poem appeared, the Cordeliers district had been renamed section Théåtre-français, following the administrative redivision of Paris from 60 districts to 48 sections on 21 May 1790.
[14] For the growth of mediatized celebrity, see Antoine Lilti, Figures publiques (2014).
[15] As Marat explained in a footnote (‘Profession de foi’) at the end of his Denunciation, “Comme ma plume a fait quelque sensation, les ennemis publics qui sont les miens ont répandu dans le monde qu’elle était vendue…”
[16] Felix Galart de Montjoie, Histoire de la conjuration de Louis-Philippe-Joseph d’Orléans (1796), pp.157-58.
#la fuite de Marat#french revolution#poetry#counter-revolutionary#Jean-Paul Marat#Antoine de Rivarol#Louis de Champcenetz#1790#libel#Jacques Necker#General Lafayette#marat
25 notes
·
View notes
Text

“Welcome, thrice welcome, to our shores; and withersoever throughout the limits of the continent your course shall take you, the ear that hears you shall bless you, the eye that sees you shall bear witness to you, and every tongue exclaim, with heartfelt joy, welcome, welcome Lafayette." —NY Evening Post, Sept. 15, 1824
OTD(Sept. 15) in 1824 General Lafayette was forced to spend time in Haverstraw Bay due to the grounding of the steamboat “James Kent” on the Oyster Bank. This unfortunate turn of events marked the beginning of the North (Hudson) River segment of Lafayette’s Tour and had a significant impact on the rest of Lafayette’s day on September 15, 1824. Indeed, originally scheduled to be welcomed at the United States Military Academy at West Point around 10 AM, Lafayette would only arrive there early in the afternoon because of the delay accumulated near Haverstraw.
We are pleased to announce the upcoming unveiling of a new Lafayette Trail marker to be installed in Haverstraw on Sunday, September 15, 2024, at 10 am.
The marker commemorates the bicentennial of the Marquis de Lafayette’s stop in the Haverstraw Bay on September 15, 1824 — exactly 200 years ago to the day (and nearly to the hour!)
Join The Lafayette Trail, Inc., the Village of Haverstraw, the Haverstraw Brick Museum, the Historical Society of Rockland County, and the William G. Pomeroy Foundation as we (quite literally) mark the historical kickoff of this important segment of the tour!
The event is FREE AND OPEN TO THE PUBLIC. It will take place at Emeline Park (30 Liberty St, Haverstraw, NY 10927). Street parking will be available along the park. The ceremony is expected to last approximately 45 minutes and will include remarks from all stakeholders involved in the preparation of the monument, the marker unveiling, and photo opportunities.
#rockland history#local history#rocklandhistory#rockland county#nyshistory#nys history#hudson river valley#Haverstraw#general Lafayette#marquis de lafayette
5 notes
·
View notes
Text




General Lafayette, a French officer in the American Revolutionary War, spoke at what would become Lafayette Square, Buffalo, during his visit to the United States on June 4, 1825.
#Soldiers and Sailors Monument (Civil War Monument) by Caspar Bubert#USA#General Lafayette#speech#Lafayette Square#Buffalo#4 June 1825#travel#anniversary#US history#Shea's Performing Arts Center#Shea's Buffalo#architecture#Rapp Brothers#646 Main Street#American Revolutionary War#American War of Independence#original photography#summer 2018#cityscape#sculpture#tourist attraction#landmark#vacation
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Starter for @general-lafayette
A much needed Eloise and Lafayette first meet! //Not that we had done that already once before

It was a quiet evening around the Continental Camp. Eloise strolled amongst the men in breeches and a shirt. Her blue eyes flashed, taking in her surroundings and she laid a hand on her weapon. A long sword that had been a gift from her father two birthdays ago and she had cherished it ever since. It was one of her prize possessions. The other was a stuffed fox currently in her tent. The fox had been a gift from her father long ago when she had been a child. Her blonde hair had been pulled up into a bun. If there was one thing she was vain about it was her hair. She loved her hair and had cut it short once before.
The wind ruffled past. She raised her head and sniffed the air. It smelled like rain and she loved the rain. She nodded to a few men as they passed her. They bowed and she returned the bow. She had learned long ago not to wear dresses in the camp. It had been a painful lesson but Martha had been able to repair the damage done to the skirts of her favorite dress. Eloise had learned then not to wear the fancier ones. Otherwise she would have already gone through them all. In some ways Eloise was the picture of a noble woman well raised by her parents. In others she was different.
Eloise came up to a commotion and she raised her eyebrows. Some of the men had surrounded an unfortunate person. She had forgotten that a young French man would be arriving in the camp. "What is going on?" Her clear and somewhat sharp voice rang through the air. She walked forward. "I highly doubt that you all are bored and must have something better…..o-oh-" Eloise trailed off as she stared up at a very young nobleman. She bowed low.
24 notes
·
View notes
Text

When I think of Gilbert du Motier, Marquis de Lafayette, this is who I always think of: Philippe Forquet, Viscount de Dorne, who played General Lafayette for 13 episodes in the short-lived series The Young Rebels (which coincidentally also starred Louis Gossett Jr. in a very early role).
1 note
·
View note
Text

Side doodle while figuring out how to draw Washington part N
#jennicatzies art-chive#hamilton#hamilton musical#hamilton the musical#hamilton fanart#george washington#marquis de lafayette#alexander hamilton#general gwash and his feral children.#I know alexander's act 1 coloring is brown/washed orange but shhhh
189 notes
·
View notes
Note
I love your depiction of Hamilton and Lafayette, it’s so funny! Lafayette is so sweet and happy and Hamilton just has beef w/ the entire world. I can’t wait to see more of their brotherly relations in ur AMAZING art style
God, they're so narrative foil coded

Seriously though, there's some fantastic contrast between them. They're just similar enough (both roughly the same age, both insecure and glory hungry, + their "shared father" or whatever Lafayette said) - and yet they manage to be exact opposites at the same time.
I could say more but I think this bit from Mike Duncan's biography about Lafayette basically gets at what I'm trying to say:
"Like Lafayette, Hamilton grew up without a father. He also lost his mother to a fatal illness at almost the same age Lafayette lost his. But where the tragedies of Lafayette’s childhood made him the heir of a fabulous fortune, the tragedies of Hamilton’s illegitimate childhood left him systematically cut out of his family’s inheritance. So where the dark clouds of Lafayette’s life were lined with silver, the dark clouds of Hamilton’s life were simply dark. Lafayette emerged from childhood buoyant and effusive, Hamilton cynical and reticent. But even though Hamilton started life a penniless bastard on the periphery of European civilization, and Lafayette started life an insanely wealthy heir in the heart of a great kingdom, they fell into an easy friendship. French was not the only language the two young men shared. The also shared a code of personal honor and a desire to prove themselves to the world." -Mike Duncan, Hero of Two Worlds, The Marquis de Lafayette in the Age of Revolution
Now, I am not qualified to speak on the real figures, but I do like to write. So, there is a narrative opportunity here that drives me insane.
Like, cast Hamilton as brilliant, but overly cynical with a habit of assuming the worst in people, and give him a negative character arc where he comes close to recognizing the potential good of humanity but ultimately falls into his more authoritarian tendencies. Then contrast him with Lafayette who's more naive. He's not quite sheltered but unfamiliar with the sort of selfishness and greed he'd have encountered if he grew up in a more vulnerable financial position. In coming to America he, like Hamilton, is forced to reckon with contempt, greed, and the failings of democratic government. But, unlike Hamilton, still manages to come out of it with a generally positive opinion of humanity.
I'm just saying, if I were writing history to contain ✨themes ✨ they are a perfect opportunity.
#this is the most I've ever ranted outside of my tags#it feels weird to have thoughts publicly lol#even if this is still generally nonspecific#is Lafayette's optimism just a symptom of his comparative naivete or do Hamiltons existing prejudices blind him to positivity#ok im done for now#amrev#alexander hamilton#marquis de lafayette#also I am glad people like my art style#because I#well Im pretty sure yall are talking about the way I color but I have spent ages trying to figure out how the hell human faces work#and I still dont get it#I spend most of my day on construction drawings which is a completely non-transferable skill#anyway literally the only thing to be done about it is to keep practicing so
200 notes
·
View notes
Text
General Andrew Jackson Statue 🏇🏹

#POTUS#General Andrew Jackson#Horse#Cannon#Tree#Bronze#Sculpture#Equestrian#Statue#War Memorial#Cloudy Sky#Lafayette Park#Lafayette Square#Pennsylvania Avenue#Washington D.C.
78 notes
·
View notes
Note
Idk if you’ve already answered this but how much English did Lafayette know before he came to the colonies? Did he practice English when he came to the colonies outside of being surrounded by English speakers? Did he speak French while he was in the colonies?
Dear Anon,
thank you for the question!
La Fayette spoke very little English before he came to America. At this point in time and in his circles of society French was the universal and cosmopolitan language and therefor the need never arose for him to learn English, unlike for many of us today. He certainly met British officers in France, and he also spent a few weeks with his uncle-by-marriage in London – said uncle was the French ambassador to Great Britan. It is reasonable to assume that La Fayette caught on to some expressions and phrases but nothing that could be called a substantial understanding of the English language.
He was however determined to learn English as soon as he decided to embark for America – as he told Washington, he came to learn and not to teach and understanding English was vital for getting along with the locals, the troops he hoped to command and his fellow officers – it was also a sign of respect since many French officers who came to America never bothered to learn English.
It took approximately six weeks (depending on weather, the type of ship, etc.) to cross the Atlantic Ocean at that time and La Fayette (after his seasickness abated) used the time to learn English. Therefore, when he finally arrived in America, his English was still very much a work in progress, but he could hold simple conversations. He and his party arrived in America on June 13th 1777, and this is an example of his English skills on August 13th:

Idzerda Stanley J. et al., editors, Lafayette in the Age of the American Revolution: Selected Letters and Papers, 1776–1790, Volume 1, December 7, 1776–March 30, 1778, Cornell University Press, 1977, p. 103.
This is the earliest known letter that La Fayette wrote in English, and it is believed that he had help in writing it. For comparison, here is an excerpt from his first letter known to George Washington from October 14th:
Give me leave, dear general, to Speack to you about my own ⟨business⟩ with all the confidence of a son, of a friend, as you favoured me with those two so precious titles—my respect, my affection for you, answer to my own heart that I deserve them on that side as well as possible—Since our last great conversation I would not tell any thing to your excellency, for my taking a division of the army—you were in too important occupations to be disturbed—for the Congress he was in a great hurry, and in such a time I take my only right of fighting; I forget the others—now that the honorable Congress is settled quiete, and making promotions, that some changements are ready to happen in the divisions, and that I endeavoured myself the 11 september to be acquainted with a part of the army and Known by them, advise me, dear general, for what I am to do—it is not in my character to examine if they have had, if they can have never some obligations to me, I am not usued to tell what I am, I wo’nt Make no more any petition to Congress because I can now refuse, but not ask from them, therefore, dear general, I’l conduct myself by your advices. consider, if you please, that europe and particularly france is looking upon me—That I want to do some thing by myself, and justify that love of glory which I left be known to the world in making those sacrifices which have appeard so surprising, some say so foolish[.] do not you think that this want is right? in the begining I refused a division because I was diffident of my being able to conduct it without Knowing the character of the men who would be under me. now that I am better acquainted no difficulty comes from me—therefore I am ready to do all what your excellency will think proper—you Know I hope with what pleasure and satisfaction I live in your family: be certain that I schall be very happy if you judge that I can Stay in america without any particular employement when Strangers come to take divisions of the army, and when myself by the only right of my birth should get in my country without any difficulty a body of troops as numerous as is here a division
“To George Washington from Major General Lafayette, 14 October 1777,” Founders Online, National Archives, https://founders.archives.gov/documents/Washington/03-11-02-0515. [Original source: The Papers of George Washington, Revolutionary War Series, vol. 11, 19 August 1777 – 25 October 1777, ed. Philander D. Chase and Edward G. Lengel. Charlottesville: University Press of Virginia, 2001, pp. 505–508.] (01/02/2025)
You can read the letter just fine and understand what he wanted to say but there are still mistakes and especially when compared to his letter to Hancock.
I could imagen that La Fayette used his convalescence after the Battle of Brandywine to further study English, but I have no hard proof to that. With Washington’s aide-de-camps, particularly John Laurens and Alexander Hamilton, he was surrounded by people who knew both French and English and were willing to help him and translate for him if need be. But by all accounts, being surrounded by English speaking people and very eager to learn (and having a talent for languages in general) La Fayette fairly quickly got the hang of it.
While in America, he also spoke French. He spoke French with some of the Frenchmen there (other officers, soldiers, his own staff) and famously translated for General Washington and General Rochambeau during the Conference at Hartford in September of 1780. He also still wrote some letters in French – there are for example a number of letters to Alexander Hamilton and Thomas Jefferson written in French even though the majority of La Fayette’s correspondence with these and other people was in English.
I hope that answered your question and I hope you have/had a lovely day!
#ask me anything#anon#first ask of 2025 lets gooo!#marquis de lafayette#la fayette#lafayette#french history#american history#american revolution#history#letter#1777#1780#george washington#john hancock#alexander hamilton#john laurens#thomas jefferson#general rochembeau
51 notes
·
View notes
Text
Why did the headcanon generator decide to get so fucking personal today!? hello!?
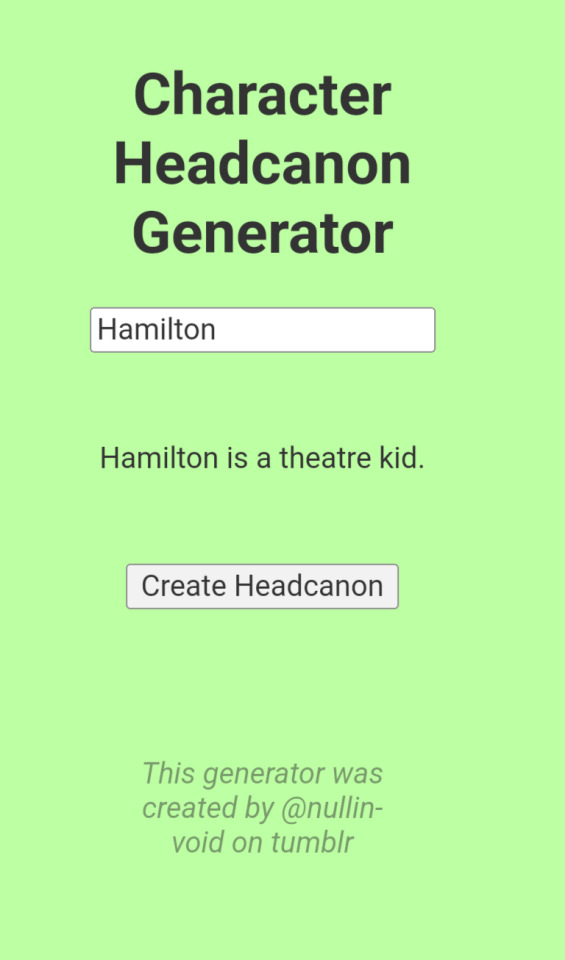
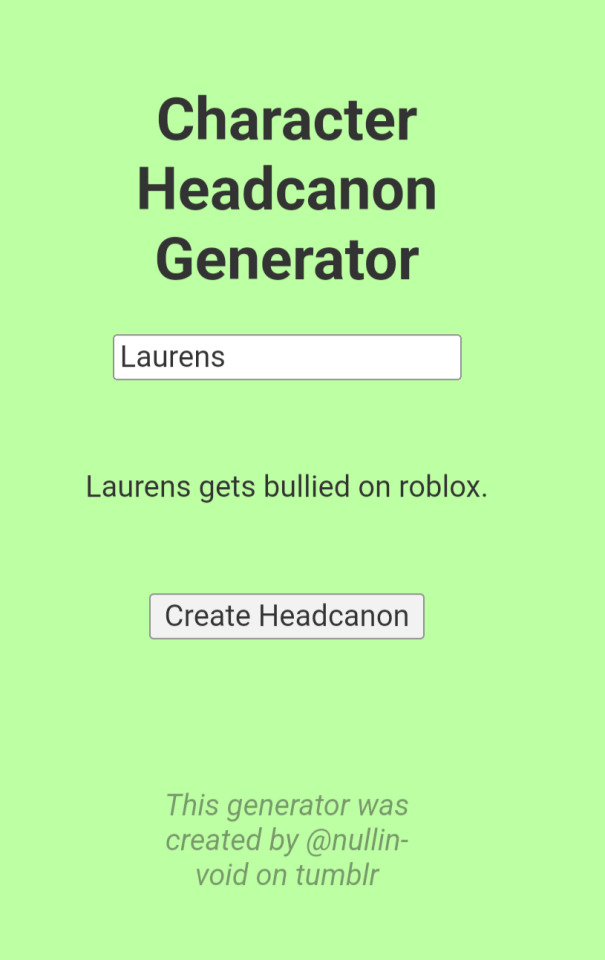
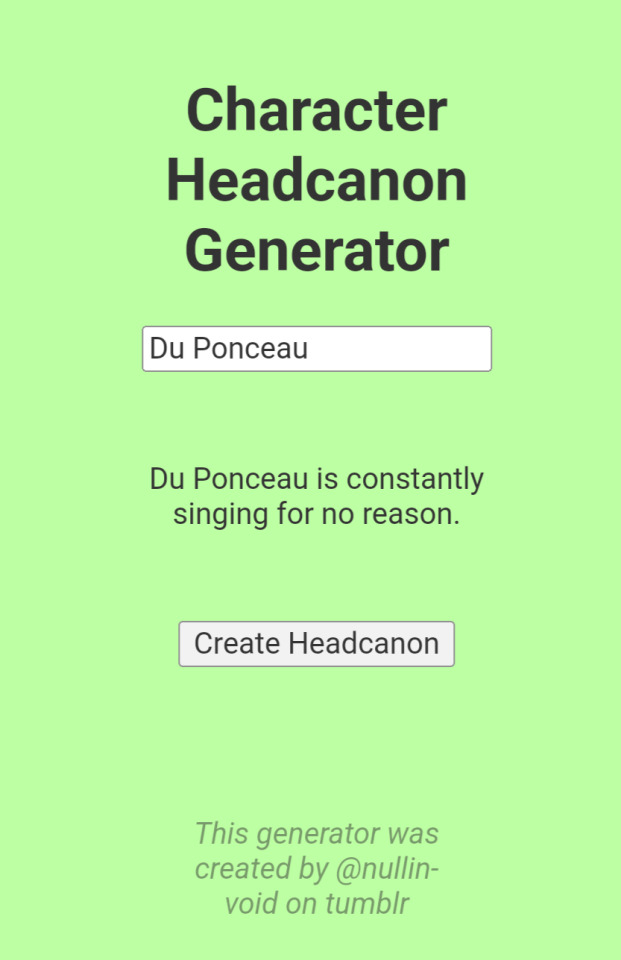
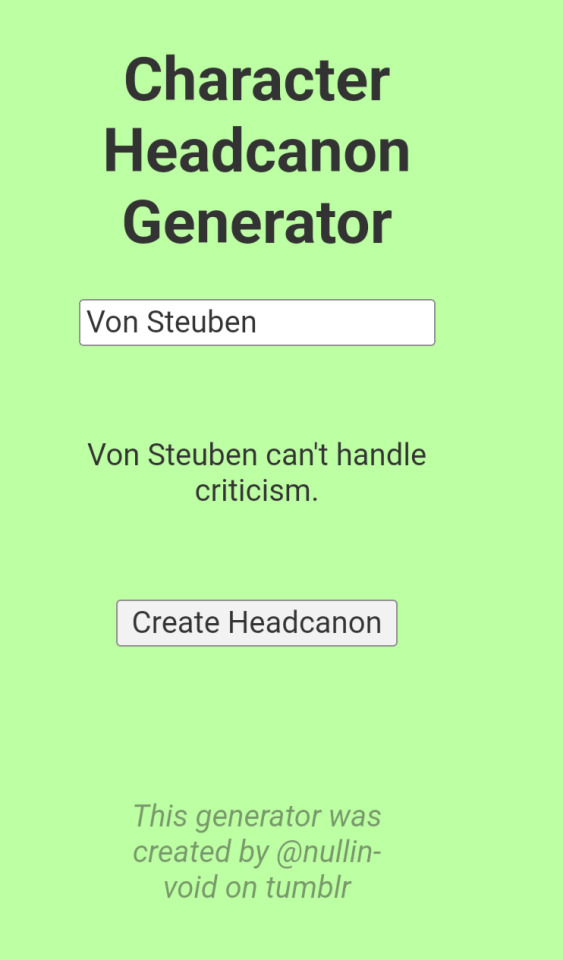
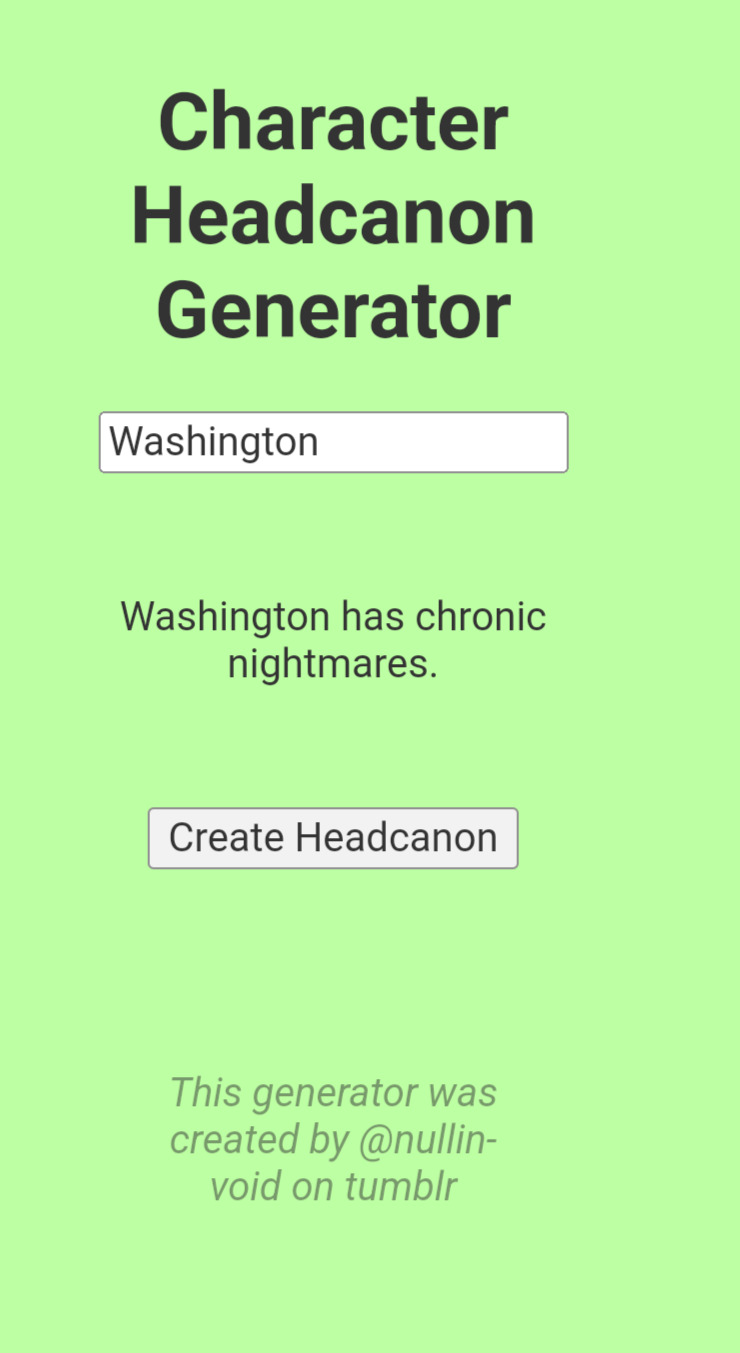

AND WE HAVE TWO (ABSOLUTELY CANON) ONES FOR LAFAYETTE...
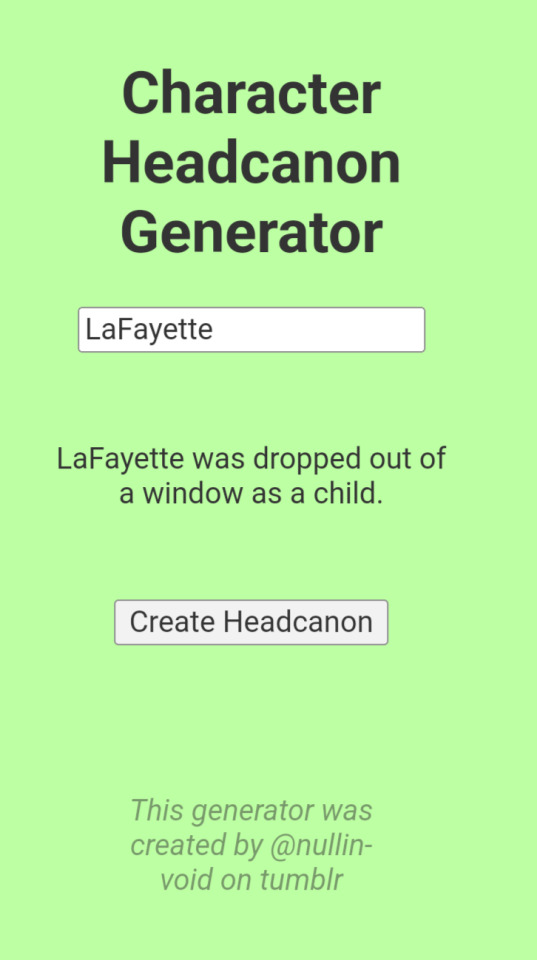
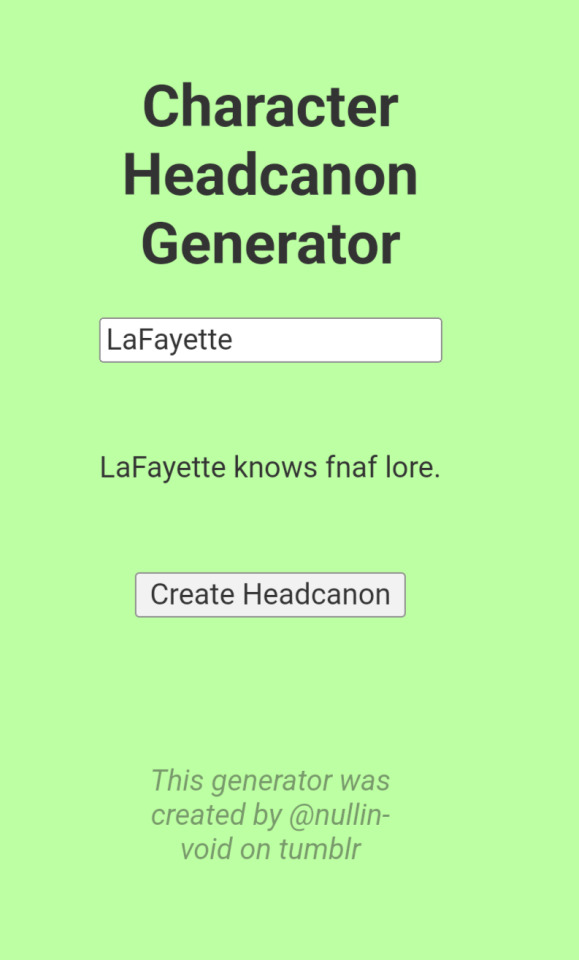
#this was the first time for all of them#amrev#alexander hamilton#john laurens#baron von steuben#von steuben#pierre duponceau#pierre etiénne du ponceau#george washington#richard kidder meade#lafayette#marquis de lafayette#Hamilton#wtf#american revolution#lams headcanon#headcanons#headcanon generator
69 notes
·
View notes
Text
Anon [Louis de Champcenetz?], The War of the Districts, or the Flight of Marat, Heroi-comical poem in three cantos (Paris: n.p., July? 1790)
Part 4 (of 5)
Last Canto:
“When the sun that lights our way,
Near SAINT-MANDÉ
Had flooded all of PARIS,
With its quicksilver light:
Five to six large battalions
Followed by two squadrons,
Silently advanced
Into OBSERVANCE.
BAILLY knowing the moment
When the troops would be assembling,
Is chatting with his wife,
Who fancies herself a fine lady,
While pouring out the tea,
With a fair degree of glee.
‘MARAT’, she says, ‘will be captured,
How my heart is enraptured!
He sought out of his own vanity
To tarnish your immortality;
But the die is cast.’
‘Oh! my loyal spouse!’
He says to her so tenderly
Promptly back to Mr Mayor;
‘Your speech is quite delightful,
I want to have a child with you.
I find you quite an eyeful,
How I long for you anew.'
‘Moderate your friendship’,
His chaste half says to he;
‘I'm not some flirting girouette,
Just wait until la FAYETTE
Has the rascal under lock and key;’
BAILLY says, ‘I want it desperately.’
NECKER who shines with virtue,
Between his daughter & his wife,
Tasted at that moment
The best day of his life.
‘We will let the joker rot
In the corner of some cell.
He attacks my writings,
He covers me with spleen;
Me! whose noble role
Shines so brightlyeverywhere:
Me! Minister Supreme,
Getting vexed by MARAT.’
STAËL (1) the proud ambassadress,
Felt a noble wrath,
Which made her jaundice blush,
‘My father, console yourself;
I wish to make a satire [1]
Against all the insolent wretches
Which your great talents censor
And dare to slander you.
My dear NARBONNE LARA (2)
Shall help me with this work.
GUIBERT (3) could have done it,
His pen is quite light,
But he no longer knows how to please me;
And in my daring pamphlets
I shall crush CHAMPCENETZ (4),[2]
This caustic character
Whose teasing I detest.’
Her mother, reacting to her zeal,
Addresses both, ‘My children,
For that is what you are;
And when I look at you;
My heart is like my eyes;
I confuse you with each other.
Reflect well upon our glory;
And use the écritoire; [3]
Because it is by this weapon,
That this great Minister is here.
The patriotic horde
Of the MERCIERS & GUDINS, (5)
Avenge us every morning,
From the famished horde
Who crawl under DESMOULINS (a):
Their pension is not enough;
But to defeat the MARATS,
We have the proud escort
Of the SUARDS & GARATS (6).
And if we need more ducats
For this miserly cohort;
Pay them, it’s no big deal,
Since we are not short.
But let’s consider something else,
Without any mystery.
MARAT is almost in the clink;
So let’s restore ourselves with a dose
Of this frothy cocoa drink.”
However in the meantime.
The Cordeliers District,
Had armed its warriors.
With very many carts,
And those carriages one hails,
The passages are blocked,
And the guns are loaded.
But lest anyone break through
The passage du Commerce,
Two cannons are placed there
With two or three platoons.
By the door, no carriage arch,
To MARAT’S humble dwelling,
Are placed thirty grenadiers,
With fifty riflemen.
Supported fromthe riverside,
The SAINT SEVERIN District
Has prepared its terrain. [4]
When arriving from behind,
The SAINT MARCEL District,
Came to unfurl its banner
In the Place SAINT MICHEL.
NAUDET the great Captain,
Fearing a flanking move
Protected Luxembourg.
D’ANTON, this other TURENNE, [5]
Followed by some warriors,
Visited all the neighbourhoods;
Putting himself out of breath;
Encouraging the soldiery
To defend MARAT well.
Such glory & such fame
Are not acquired without pain!
Father GOD, Cordelier,
Would show no mercy.
But hidden in his attic
Monsieur FABRE D’EGLANTINE
Seeing the civil war
Quivered from head to toe;
More than if he saw the faces
Of the Bailiffs & recorders
Coming to sing his morning prayers.[6]
WASHINGTON’S monkey,
Surrounded by a battalion
And all these subalterns,
Went off prancing,
And nearly grazed in passing
The lampposts & the ropes,
Where he let a treacherous mob
String up poor FOULON. [7]
He sees that canons have been placed
On every avenue;
And that the end of every street
Armed like a bastion,
Contains a large battalion:
This troubles his genius,
And his soul is less bold
BARNAVE is quite astonished;
He was determined
To act like he’d done at Versailles;
But to risk battle and die!
D'AIGUILLON, gasping for air
From his fishwife attire
Flees at the double,
Escorted by the rabble. [8]
Brave like RODOMONT,[9]
Suddenly without any warning,
Henri SALM & Jacques AUMONT (7)
Go off to explore;
Everywhere are large platoons:
So Henri says to Jacques;
‘My dear friend, let’s decamp;
Let's not start the attack;
Don’t you see those big canons?’
‘Well said, let’s retreat’;
Jacques immediately replies;
‘Soldiers! Half turn to the right.
The obedient troops
In such pressing danger,
Turn round to find LA FAYETTE;
Whose stunned expression,
Dismayed the proud AUMONT,
And his brave companion.
Bold like NICOMEDES (b)
VILLETTE (8), finding himself there, [10]
Suggests a remedy for the ill.
‘This is really no big deal;
Trickery is as useful in war,
As in love, thank God!
We must outflank the enemy,
And attack it from behind.
On more than one occasion
FREDERIC (c) did the same.
But the assembled Troops
Keep watch and fall silent:
When at this moment,
The mistress of MARAT,
A sturdy chambermaid
And formerconventgatekeeper(9) [11]
Whose eye sparkles bright,
Addresses this prayer,
To the most unfortunate Lover,
Who is causing all her grief.
‘Do you want to be murdered?
Or even in a prison cell,
Without your JAVOTTE, starving [12]
On a shabby straw mat,
Do you want to be confined?
Take my headscarf, my petticoat,
And my cotton kerchief;
I will wear your breeches,
And followed by your JAVOTTE,
Whom they will mistake for a boy,
We will go far from the city
And find another home.
Do you wish to see Paris burn
For a few worthless lines?’
MARAT did not wish to know
But the clever maid
Crying and sobbing,
Knew how to soften up her beau.
‘I'm not worth that much blood,’
Says MARAT, in sensitive mood;
‘Let’s leave the city calm;
And swop our clothes at once;
We can do anything with love.”
This noble disguise
Was done in a trice.
Descending from their attic, [13]
They pass through the Soldiers
Without any hesitation,
And make their way outside.
Arm in arm, the couple
Lengthened their stride;[14]
When on a street corner
They find brother GRUE (10),
A subaltern, but strongwilled [15]
Who recognizes them at once…
He did not cry out in wonder,
But whispers in their ear:
‘You’re doing well,
Go now, have no fear,
Once you're in the clear
I’ll do what needs to be done.’
MARAT responds at once,
‘It’s to spare the blood
Of a District I revere,
That I’m wearing a white petticoat,
Farewell, my reverend frère.
The subaltern Cordelier,
Fearing some grapeshot
Might start the fight;
Cried out across the neighbourhood
In a loud, booming voice:
‘MARAT has chosen his story,
He fled a long time ago.’
They did not want to believe it;
D’ANTON, wanting all the glory
Sends a detachment,
To thoroughly search
His whole apartment,
And assure their escape.
He knew everything in a flash. [16]
Once peace was resolved.
Brother GRUE was dispatched
Towards the great General,
Who welcomed his Ambassador
In a most friendly manner,
And gave him a warm hug.
Immediately, from both sides
The retreat was rung;
And the delighted Bourgeois,
All cried out, PEACE IS DONE.
But dark CRUELTY,
Indignant & furious
At such a treaty,
Quickly takes flight;
And in her fearsome rage
Hastens to the Châtelet
To ponder some misdeed.
STUPIDITY, now more tranquil
Lingered within the Hotel de Ville.
Thus ended, without a melée,
But not without a dumb display,
The adventure of Marat. [17]
Notes to the Last Canto:
(1) Baroness DE STAËL is not unworthy of her father & her mother, she has as much intelligence as beauty; everyone knows that.
(2) Comte Louis DE NARBONNE had left Mademoiselle CONTAT for Madame de STAËL, but, like ANTHONY, he kept returning to CLEOPATRA & the Actress prevailed over the Ambassadress.[18]
(3) Comte DE GUIBERT had been dumped by Madame de STAËL; such a loss consoled him for all his disgrace. [19]
(4) The Marquis de CHAMPCENETZ is the Ambassadress’s nemesis because of this famous epigram which has been falsely attributed to him, & which he has the candour to disavow: [20]
ARMANDE holds in her mind everything she’s read,
ARMANDE has acquired a scorn for charms;
She fears the mocker whom she constantly inspires,
She avoids the lover who does not seek her.
Since she lacks the art of concealing her face,
And she is eager to display her intellect;
One must challenge her to cease being wise,
And to understand what she says. [21]
(5) Bribed writers.
(6) Ditto. [22]
(7) The Prince of SALM & the DUC D'AUMONT sign their names democratically, just as they are written in the poem, which is quite ridiculous.[23] The poor devils are taking revenge for the contempt they have always inspired in honest people & have mingled effortlessly with the rabble.
(8) All Paris knows about VILLETTE, a retroactive citizen. VOLTAIRE died inconsolable for having praised him. [24]
(9) Indeed, MARAT's mistress was a novice in a convent from where she was taken by our hero. [25]
(10) Brother GRUE, the heavyweight of the adventure, is a jolly good fellow who does not lack common sense, & to whom the Cordeliers district owes a statue; but the multitude is ungrateful.[26]
(a) Antagonist of Mr. Necker
(b) The King of Bithynia
(c) The late King of Prussia.
[1] ‘Satyre’ usually refers to the part human, part goat creature, known for revelry and bad behaviour. Possibly a pun, referring to both ‘satire’ and Mme de Stael’s ‘ugliness’, whose masculine looks were frequently commented on by contemporaries.
[2] Champcenetz often inserted himself in the third person into his own compositions.
[3] “Monsieur de Saint-Ecritoire” was Necker’s nickname for his beloved daughter, Herold (1958), p.66. Ecritoire was a portable, hinged desk set.
[4] Actually, it was the militant Saint-Antoine district that Danton threatened to summons into action as backup. Saint-Severin provided a contingent of National Guards for Lafayette’s expedition. See Babut, pp.284-85.
[5] Henri de la Tour d’Auvergne, vicomte de Turenne was a Marshal General of France from the 17th century, renowned for retaking Paris from the Prince de Condé during the civil wars of the Fronde.
[6] Fabre d’Eglantine had been a target for earlier lampoons by Rivarol & Champcenetz in their Le Petit Almanach de nos grands hommes pour l’année 1788 (1788) and Petit Dictionnaire des grands hommes de la Révolution (Aug 1790). Fabre d’Eglantine, who lived four doors away from Marat on 12 rue de l’Ancienne-Comedie, was Danton’s right-hand man and vice-president of the Cordeliers district assembly at this time. While Paré was president (Danton having served from October to December), the district was still effectively under Danton’s control, and Danton was re-elected president on 31 March.
[7] Joseph Foullon de Doué, who replaced Jacques Necker as Controller-General of finances, was deeply unpopular with the Parisians. He was lynched “à la lanterne” on 22 July 1789, and his head stuck on a pike with his mouth stuffed with straw, following a widespread rumour that he had said, “let them eat hay!”.
[8] Armand de Vignerot du Plessis, duc d’Aiguillon had been the wealthiest man in France after the king before sacrificing his title to all his feudal properties on 4 August 1789 and losing over 100,000 livres in rents. Despite having planned to launch the initiative during the debate on renunciation of noble privileges, the considerably less wealthy vicomte de Noailles beat him to the punch in a bid for popularity! Nevertheless, d’Aiguillon’s gesture had a massive impact, and his gesture became the signal for similar sacrifices, escalating events much further along than anticipated. As a result, disgusted royalists, especially from the Actes des apôtres and Gautier’s Journal general de la Cour et de la Ville, depicted him dressed as a poissarde (fisherwoman) leading a battalion of tough dames from Les Halles during the October Days march. Barnave was depicted in similar fashion. In fact, transvestism was frequently deployed in royalist lampoons, as we shall see in the later description of Marat’s escape.
[9] Rodomonte was a major character, renowned for his bravery and arrogance, in Ludovico Ariosto’s 16th-century romantic, epic poems, Orlando innamorato & Orlando furioso.
[10] While the marquis de Villette was the commandant of the Cordeliers district battalion, he opposed Danton’s wish to defend Marat, and had suggested arresting him themselves. Because of the Cordeliers’ own arreté from 19 January insisting on district autonomy, he explained to Lafyette’s commander, Gonsault de Plainville, that he must remain neutral but later thanked him for ridding the district of a “mauvais sujet”. The other battalion commander present was Carle from the Henri IV district. See Babut, p.285
[11] See later note for likely explanation of the convent reference. At this time Marat had a young assistant, Victoire Nayait, who liaised with local printers. This might also explain the erroneous reference to chambermaid.
[12] Javotte is a fictional archetype who often appears as a maidservant, or, sometimes, a prostitute.
[13] Marat had been staying nearby with Boucher de Saint Saveur as a precautionary measure since 14 January. His rooms were in the hotel Fautrière, 39 rue de l’Ancienne-Comédie, which also housed the permanent barracks (30 men) for the Cordeliers district militia. See Mémoire de Madame Boucher Saint-Sauveur contre Marat (late 1790).
[14] According to Marat’s own account of his escape in the Ami du Peuple #170 (23 July 1790), which was also published some six months later, he donned a disguise and left in the arms of a young lady (“marchant à pas comptés”). This detail that might suggest that the poem was published after this account.
[15] The word ‘Coupechou’, a variant of ‘Coupe-choux’, literally means ‘Cabbage cutter’. It was often used in conjunction with ‘frère’ to mean a novice monk (usually put in charge of the vegetables), and, by extension, a person of no importance, Dictionnaire de la langue française (1873), in Dictionnaires d’autrefois (online). In the slang of Père Duchene, ‘grue’ means a fool, or someone easily tricked, Michel Biard, Parlez-vous sans-culotte? (2009), pp.179-80.
[16] When the National Guard were finally allowed to enter Marat’s rooms, they confiscated all his papers, both presses and his type, effectively ending the newspaper and bankrupting him. Many of the papers, including valuable information on Marat’s subscribers, remain in the Archives Nationales (Pierrefitte). The most important of these were rescued by friends, most notably his detailed evidence against Necker, which he published from London in a follow-up to his original pamphlet, as Nouvelle dénoncation contre Necker (April?). Danton’s relationship with Marat would later be lampooned in a scurrilous libelle that described them having homosexual relations, Bordel patriotique etc. (1791).
[17] It is worth nothing here that as a result of Marat’s escapades, his resulting notoriety led to a considerable increase in his revolutionary profile with other journalists and politicians now paying much closer attention to his writing, especially when he began publishing fiercely hostile pamphlets from London. It also led to his inclusion in David’s sketch for his unfinished paining, Serment du Jeu de Paume (1790/91), where Marat can be seen top-right in the public gallery, wearing a broad-rimmed hat, writing with his back to the viewer. The other inclusion, not there at the time, was the deputy Bertrand Barère, editor of the Point du Jour.
[18] In fact, she appears to have had her first two children by the comte de Narbonne-Lara, born in 1790 (Auguste) and 1792 (Albert), see Herold, p.95.
[19] Guibert was a handsome salon gallant and habitué of the salons run by Madame Necker, Mme de Stael’s mother.
[20] Quite why Madame de Stael merits four uncomplimentary notes remains unclear. If Rivarol and/or the marquis de Champcenetz are the anonymous authors, it is worth noting that they also prefaced their anonymous Petit Dictionnaire des grands hommes de la Révolution (Aug 1790) with a biting (and salacious) dedication to “her excellency Madame la Baronne de Stael”, which mocked, amongst other things, the weight of her “prodige” [genius]. Champcenetz also had a fondness for using the six/seven syllable lines found in this poem.
[21] These lines first appeared in a pamphlet erroneously attributed to Rivarol, Réponse à la réponse de M. de Champcenetz; Au sujet de l'Ouvrage de Madame la B. de S***. sur Rousseau (1789), p.7. It is most likely by Champcenetz, who also wrote the original Réponse aux Lettres sur le caractère et les ouvrages de J.J. Rousseau. Bagatelle que vingt libraires ont refusé de faire imprimer (1789). He had also used the alter ego ‘Armande’ to describe Mme de Stael in the anonymous Petit traité de l’amour des femmes pour les sots (1788). The reference to the mother-worshiping Armande comes from Molière’s play, Les Femmes Savantes. The satire is piquant since Mme de Stael was presented by her adoring family as a child prodigy under the tutelage of her doting mother, described by William Beckford as a “précieuse-ridicule”. Moreover, and it is hard to see how the author knew this unless a salon regular, or informed by one, Mme de Stael had privately acted in Les Femmes Savantes. See Helen Borowitz, ‘The unconfessed Précieuse etc.’, in 19th Century French Studies (1982), p.39.
[22] These names suggest someone with intimate knowledge of Necker’s propaganda ‘factory’. Marat had also accused Mercier, Suard and Gudin of being on Necker’s payroll (check). Paul-Philippe Gudin de la Brenellerie, Beaumarchais’s friend and publisher, would later publish a Supplément au Contrat Social (1792, Maradan), which came with an appendix on the need to breed to keep breeding to secure a steady increase in the population! Garat’s Journal de Paris was openly subsidized by Necker. Amongst the more patriotic writers, Cerutti, later editor of La Feuille Villageoise, was also the only one writer to openly defend him in his Lettre sur Necker (1790).
[23] Probably a reference to Charles Albert Henry (b.1761), ninth son of Philip Joseph, Prince of Salm-Kyrburg.
[24] Charles (the former marquis) de Villette was a noted homosexual frequently attacked in scurrilous pamphlets during this time, including, Vie privée et public du ci-derrière marquis de Villette, citoyen rétroactif (1791) and Les Enfants de Sodome à l’Assemblée Nationale etc. (1790, ‘Chez le Marquis de Villette’). ‘Rétroactif’ here appears to be both a pun on being an ‘active’ citizen (referring to the law passed in Oct 1789, discriminating between active and passive citizens for the purpose of voting and standing for office, and a possible synonym for homosexuality (viz its synonym, ‘posterior’).
[25] This reference to an imaginary, ex-novice lover probably alludes to a recent article in Marat’s paper, describing how his services were regularly sought by readers seeking redress. In this particular issue (Ami du peuple #88, from 5 Jan 1790), he gave the singular example (“aussi piquante par sa singularité qu’elle est intéressante par sa nature”) of a nun called “sister Catherine” (Anne Barbier) who had escaped from Pantémon Abbey after suffering countless abuses due to her patriotic views. She had come to see Marat in the company of her landlady (Mme Lavoire), she had sought his help in securing her liberty and reclaiming her possessions.
[26] While I can find no trace of a ‘brother Grue’ in any of the surviving accounts, the most likely candidate would appear to be the powerfully built butcher, Louis Legendre, co-founder of the Cordeliers Club in April 1790 with Danton. In this context, ‘Lourdis’ probably derives from the figurative use of ‘lourd’ to suggest heavyweight, possibly by association with the other meaning of ‘grue’ as ‘crane’ (both bird and a lifting mechanism for heavy loads). Legendre hid Marat several times in his cellar on the rue de Beaune; see speech to the Jacobins on 24 Jan 1794, in Aulard, op.cit.
Alternatively, a letter from 9 May 1790 describes the arrest of Louis Gruet, a fusilier in the Cordeliers battalion. See Alexandre Tuetey, Répertoire général des sources manuscrites de l’histoire de Paris pendant la Révolution française, Tome 2 (1890), p.420 (3982).
Finally, ‘Grue’ might be a nickname for François Heron (viz ‘crane’), who later acquired notoriety as the main police agent for the Committee of General Security. While I can find no record of his playing any role in these events, he also hid Marat in his home, on 275 rue St Honoré, during 1790, and probably knew him from their time working for the king’s youngest brother, the comte d’Artois.
#la fuite de Marat#Jean-Paul Marat#French Revolution#Georges Danton#General Lafayette#libel#counter-revolutionary#poetry#1790#Jacques Necker#marat
2 notes
·
View notes
Text


Didn't you think her so cute when she slept like the dead?
#ARGH IM SO NOT NORMAL ABOUT THEM#also i tried some new techniques to get texture in the locs with traditional art#what do we think? did it work? does it look ok?#texture like. in general. with anything is not my strong point in art but its something im trying to get better at!#my artwork#jrwi#jrwi fanart#jrwi lizzie#jrwi ava#jrwi waning crescent#jrwi frigatebird#ava ferin#lizzie lafayette#jrwi riptide#jrwi riptide fanart#just roll with it
59 notes
·
View notes
Text
Let the good times roll! ⚜️

Source.
#meeramakesgifs#meeraedits#american revolution#mardis gras#history#18th century#18th century history#historical reenactment#colonial williamsburg#marquis de lafayette#mark schneider#my edit#by userquaintrelle#my gifs#reenactment#usersource#markschneiderlover#general-lafayette#keepxsolxinxsolxinvictus#nordleuchten#mine
35 notes
·
View notes
Text
All i can say is that Turn: Washington's Spies is one of the BEST historical dramas I've ever watched. I loved every single episode of it. The characters, the ambientations, the writing, the soundtrack. Perfect. Just Perfect.
(well, expect for Anna and Abe's drama: i've found it unbearable, even when they already had such amazing patners like Mary Woodhull and Selah Strong)
#turn: washington's spies#s1#s2#s3#s4#the culper ring#abraham woodhull#mary woodhull#richard woodhull#benjamin tallmadge#caleb brewster#general george washington#anna strong#selah strong#robert townsend#alexander hamilton#marquis de lafayette#major hewlett#captain simcoe#masterpiece#i've cried a lot during s3#s3 was my favorite season#why do i always miss out and take back later such jewels like this one#american revolution#it made me love the American revolution once again#Abraham x Mary#Selah x Anna
93 notes
·
View notes
Text
Hey guys! Reminder that I do commissions and would really appreciate if you checked me out, reblogged, or recommended me to anyone! 🩷
Here's some examples of my art:










My prices and terms:
I can take cashapp or payment through kofi, 50/50 method or full
halfbody
line art $10
colored art $15
shaded art $25
2nd character + %50 base price
fullbody + $10
background + $5
TAT is usually a week or less, at *most* two weeks.
I do ✅
- Anthros/furrys
- Ship art (not sexual content)
- Ocs, fanart, or real people (will not do romantic themes involving real people)
- Light gore
- Mobility aids
I do not do ❎
- nsfw/sexual content
- mechs
- vehicles
- pieces that are just animals
https://ko-fi.com/starsinoursystem
examples of my art:
#art commissions#commissions#commission#my commissions#my art#my oc art#my ocs#some characters are not my ocs#digital#digital artist#digital drawing#digital art#digital illustration#not ai generated#not ai art#jrwi riptide#jrwi#just roll with it#gillion tidestrider#chip jrwi#lizzie lafayette#dead plate game#dead plate#dead plate rody#dead plate vincent#dead plate manon#vincent charbonneau#rody lamoree#manon vacher
2 notes
·
View notes
Text




Here is another update for my art as I wanna post what I have drew and finished yesterday I tried my best but then I really put my love on this one because y’know general Washington is the main hero helping his people freedoms from Brit’s haha
3 notes
·
View notes