#essential amino energy
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
#mino Acids#Essential Amino Acids#Protein Supplements#Muscle Recovery#Nutritional Supplements#Gut Health Supplements#Energy Boosting Supplements#Immune Support#Vegan Amino Acids#Natural Health Products#Dietary Supplements#H&M Herbs and Vitamins
1 note
·
View note
Text

Spirulina powder is a nutrient-dense superfood that is high in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. Rich in protein, it boosts vitality and aids in muscle growth and repair. Spirulina also helps with heart health, cleansing, and immune system boosting by reducing cholesterol levels. Its high antioxidant content also reduces irritation illnesses, prevents oxidative stress, and enhances general health. Drinks, beverages, and foods all benefit from the inclusion of spirulina powder, which gives you an easy way to increase your daily nutrient intake. Please visit our website or amazon page to explore our organic supplements products.
#natural#organic#all natural#spirulina#spirulina powder#algae supplement#antioxidants#detox supplement#energy boost#green powder#immuneboost#nutrient-rich#organic spirulina#pure&organic#superfood#veganproduct#plant-based nutrition#healthy life style#weight management#essential amino acids#spirulina benefits#natural supplement#raw spirulina#digestive health#sustainable food#brain health#metabolism support#green super food
1 note
·
View note
Text
The pack includes: 1 x 480g pot of Beyond Tangy Tangerine 2.0 and1 x bottle 90 soft-gels of Ultimate EFA Plus.
The Healthy Start Basic Pack 2.0 provides all 90 essential nutrients for human health. Beyond Tangy Tangerine® 2.0 Citrus Peach Fusion contains a base of Majestic Earth® Plant Derived Minerals® blended with vitamins, amino acids, 115 fruits and vegetables, PrePro™ prebiotic and probiotic blend, and other beneficial nutrients for optimal health. Ultimate™ EFA Plus™ is a proprietary blend of essential fatty acids from Borage, Flax and Fish Oils. Used as part of a healthy diet, essential fatty acids may support the body in many ways, especially cardiovascular health.
Youngevity has developed a convenient nutrition plan that will give your body all the nutrients it needs to quickly get fit, gain energy, lose weight and get healthy.
#The Healthy Start Basic Pack 2.0#90 essential nutrients#Beyond Tangy Tangerine® 2.0 Citrus Peach Fusion#Majestic Earth® Plant Derived Minerals®#Vitamins#Amino acids#Fruits and vegetables#PrePro™ prebiotic and probiotic blend#Ultimate™ EFA Plus™#Essential fatty acids#Borage#Flax#and Fish Oils#Cardiovascular health#Youngevity#Nutrition plan#Get fit#Gain energy#Lose weight#Get healthy
0 notes
Text
Essential Amino Acids: The Building Blocks for Optimal Health and Wellness

What are Essential Amino Acids?
Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins, which are essential for the structure, function, and regulation of the body's tissues and organs. Protein-rich foods like meat & eggs are excellent sources of amino acids. Certain amino acids are also taken as supplements by some people looking for a natural way to improve athletic performance, muscle growth and recovery.There are over 20 different amino acids, and 8 of them cannot be produced by the body and must be obtained through the diet. These are called the "Essential Amino Acids," which include isoleucine, leucine, lysine, methionine, phenylalanine, threonine, tryptophan, and valine—all of which are essential to human health, athletic performance, and general well-being. These essential amino acids play important roles in various processes in the body, including protein synthesis, immune function, and hormone regulation.
In this blog, we will explore and focus on the benefits of essential amino acids and how they can support optimal health and performance. From improved muscle building and recovery to better mental clarity and energy, essential amino acids offer a wide range of benefits that cannot be ignored. So if you want to feel your best and perform at your peak, read on to learn more about the power of essential amino acids!
1. Protein Synthesis
Essential amino acids play a crucial role in the synthesis of proteins, which are needed for the growth, repair, and maintenance of tissues and organs. When you consume protein, your body breaks it down into individual amino acids, which are then used to build and repair tissues in the body. This process is especially important for athletes, as exercise can cause microtears in muscle tissue. Getting enough protein and essential amino acids can help repair these tears and promote muscle growth and recovery. They also help make enzymes, hormones, and other substances that your body needs to function well.
2. Energy Production
Essential amino acids are used by the body to produce energy. When the body needs energy, it breaks down stored fats and sugars and uses them as fuel. Amino acids can also be used as an energy source, especially during prolonged exercise or when the body is in a fasting state primarily through a process called gluconeogenisis. However, it is important to note that ATP*, glycogen*, and fats are the primary sources of energy for the body, and a diet that includes a variety of micronutrients is important for overall health and energy production.
*ATP is a substance present in all living cells that provides energy for many metabolic processes.
*Glycogen is a form of glucose, a source of energy that your body stores primarily in your liver and muscles.
3. Immune System Function
Essential amino acids are necessary for the proper functioning of the immune system and are involved in the production of antibodies, immune cells, and other immune system components. For example, the amino acid lysine has been shown to support immune system function by inhibiting the replication of viruses and helping to reduce inflammation. Supplements with lysine are becoming widely recognized as a natural aid to improving the body's immune system. Additionally, other essential amino acids such as tryptophan and arginine have been shown to have immune-boosting effects.
4. Brain Function
Essential amino acids can help with brain function in several ways. They are crucial for the synthesis of neurotransmitters, which are chemicals that transmit signals in the brain and play a vital role in mood, cognition, and behavior. According to Lieberman, U.S. Army Research Institute of Environmental Medicine, the central nervous system requires a number of amino acids found in protein foods. Amino acids such as tryptophan, tyrosine, and arginine are used by the brain for the synthesis of various neurotransmitters and neuromodulators.
Essential amino acids also play a role in the development and maintenance of brain cells, including neurons and glial cells. They are involved in the production of proteins that are essential for brain function, such as myelin, which is a protective layer around nerve fibers that helps with the transmission of nerve impulses. Additionally, essential amino acids have been shown to have a positive effect on mood and cognitive function, possibly due to their role in the production of neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine. Overall, maintaining an adequate intake of essential amino acids is important for optimal brain function and overall health.
5. Heart Health
Essential amino acids play a crucial role in maintaining the proper function of the cardiovascular system by helping to regulate blood pressure and heart rate, as well as aiding in the production of proteins that are necessary for healthy heart function. Some specific essential amino acids that may be particularly beneficial for heart health include arginine, which helps to dilate blood vessels and improve blood flow, and taurine, which helps to regulate heart contractions and maintain electrolyte balance in the body. Additionally, consuming a diet rich in essential amino acids may help to lower the risk of developing certain cardiovascular diseases, such as hypertension and coronary artery disease.
6. Muscle Growth and Repair
Essential amino acids are essential for the growth and repair of muscles. They are involved in the production of collagen, which is a protein that helps to hold muscles together while also helping to reduce muscle breakdown during exercise or injury. In addition, essential amino acids stimulate the production of hormones, such as insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) and leucine in particular, increases MTOR signaling leading to higher MPS - muscle protein synthesis. Both are very crucial for muscle growth. Therefore, adequate intake of essential amino acids is important for optimizing muscle growth and repair.
7. Hormone Production
Some essential amino acids, such as tryptophan, tyrosine, and lysine, are precursors for the synthesis of various hormones, including serotonin, dopamine, norepinephrine, thyroid hormones, and growth hormone. These hormones play important roles in various bodily functions, including mood, energy, metabolism, and growth. Therefore, sufficient intake of essential amino acids is important for maintaining proper hormone balance and function.
8. Bone Health
Essential amino acids play a crucial role in bone health. They help to form and maintain bone tissue by providing the building blocks for bon collagen and other bone proteins. These amino acids also help to regulate bone metabolism and promote bone formation. Essential amino acids, such as lysine and methionine synthesize collagen, a major component of bone tissue, while arginine and histidine have been shown to have a positive effect on bone growth and repair. Essential amino acids also help to prevent bone loss and osteoporosis by improving bone density and strength. It is important to consume a high protein diet that includes all essential amino acids to support optimal bone health.
9. Skin Health
Certain key and essential amino acids can help with skin health by supporting the synthesis of proteins that are important for maintaining the structure and function of the skin. Lysine synthesizes collagen, a protein that helps to maintain the structural integrity of the skin; methionine synthesizes keratin, a protein that helps to protect and strengthen the skin; histidine synthesizes histamine, a chemical that helps to regulate inflammation in the skin; and arginine synthesizes nitric oxide, a molecule that helps to maintain blood flow to the skin and improve its elasticity while playing an important role in the maintenance and regulation of the skin and the integrity of its environment.
10. Weight Management
Essential amino acids can potentially help with weight management in a few ways: A) Essential amino acids play a vital role in the synthesis of protein in the body. When you consume enough protein, your body is better able to build and repair tissues, including muscles. This can help increase metabolism and promote weight loss. B) Essential amino acids can also help increase feelings of fullness and satisfaction after a meal, which can lead to reduced food intake and weight loss. C) Additionally, essential amino acids are involved in the production of various hormones, including ghrelin and leptin, which regulate appetite and energy expenditure.
Consuming enough essential amino acids can help regulate these hormones and potentially promote weight loss. It's important to note that while essential amino acids may have some weight management benefits, they should not be relied upon as a sole means of weight loss. A high protein, nutrient dense diet and regular physical activity are crucial for weight management.
11. Sleep
There is some evidence to suggest that essential amino acids may help improve sleep quality. According to Medical News Today, tryptophan is an essential amino acid that is important for the production of serotonin in the body. It is also key to brain function and has a role in healthy sleep. People cannot make tryptophan in their bodies, so must obtain it from their diet. Additionally, GABA (a neurotransmitter that is synthesized from the amino acid glutamine) has been shown to have a calming effect on the brain and may help to promote sleep.
12. Mood and Mental Health
Essential amino acids can potentially have a positive effect on mood and mental health. Some essential amino acids, such as tryptophan and tyrosine, have been shown to have a positive effect on mood and mental health. Tryptophan is converted to serotonin in the body, which is a neurotransmitter that plays a role in mood regulation. Tyrosine is converted to dopamine, another neurotransmitter that is involved in motivation and pleasure. Low levels of certain essential amino acids have been linked to conditions such as depression and anxiety. Supplementing these amino acids may help improve mood and mental health in some individuals.
SURPO Takeaways
Essential amino acids play a vital role in maintaining overall health and wellness. They help to build and repair tissues, produce hormones and enzymes, and support a strong immune system. They are also necessary for muscle growth and maintenance, and can even help with weight loss efforts. While essential amino acids can be obtained through a high protein diet, they can also be supplemented through EAA drinks and protein powders. Amino Hydrate+ by SURPO has an EAA formula which results in significantly higher absorption rates than any protein powder or other EAA drink. Overall, incorporating essential amino acids into your diet can provide numerous benefits for both physical and mental health.
Amino Hydrate +
Amino Hydrate+ helps replenish lost minerals & electrolytes while supplementing all the key amino acids your body needs to perform at its best. This combination will help you stay hydrated, prevent muscle breakdown, aid in athletic recovery, boost energy levels, & support muscle growth & overall health.
Higher Athletic Performance
When you engage in strenuous or prolonged physical activity, your body depletes its energy reserves & starts to break down muscle protein to convert its essential amino acids into energy. This process also leads to a decrease in muscle protein production, resulting in muscle weakness & reduced exercise performance. Amino Hydrate + replenishes lost electrolytes needed for energy & endurance while supplementing all the key amino acids needed to prevent muscle breakdown.
Optimum Hydration
The negative effects of dehydration can be avoided through proper hydration. Hydration involves not only drinking water but also replenishing the body with essential electrolytes. Amino Hydrate + offers better hydration over water alone. It enhances muscle water absorption & retention and replaces the vital electrolytes that are lost due to sweating. Our amino acid powder fully hydrates your body, keeping you fueled to tackle even the most intense workout while reaching your greater Survival Potential!
Workout Recovery and Muscle Growth
Essential Amino Acids activate a certain pathway in the body that stimulates muscle protein synthesis while decreasing muscle soreness & exercise fatigue. Our unique Amino Hydrate+ formula has been thoughtfully designed to replenish lost electrolytes while supplementing all the key amino acids in your body. This combination will help you to prevent muscle breakdown, support muscle growth, and is perfect any time during the day your muscles need extra recovery.
SURPO exists to help people fundamentally obtain higher levels of survival across all aspects of life and that experience begins with physical health. We strive to empower individuals to live a healthier, more active lifestyle through the promotion of proper nutrition. Our supplement is specifically designed to help you reach your health and fitness goals. Good hydration and high-quality supplements make all the difference in the world and have the power to transform your life.
#Amino Hydrate+Sale#Amino Hydrate+ formula#Surpo Nutrition#Amino Hydrate+#Sale Amino Hydrate+#Amino Hydrate+ Sale#Amino Acids multivitamins#Amino Acids Vitamins#Higher Athletic Endurance#Amino Acids supplements#Optimum Hydration#Caffeine Free Energy#high-quality supplements#Increased MPS#Essential Amino Acids#Essential Electrolytes#workout#running#nutrition#meal prep#marathon#healthy eating#bodybuilding
0 notes
Text
💪Ryder Steele’s Muscle Gain Instruction Manual. 💪
A surface-level yet comprehensive beginner’s guide to working out/body building/gaining muscle written by a tboy with a degree in human physiology, with tboys in mind. Speed training, toning, and cardio/lung health training will not be explored.
(Part 1) Diet. Talking about food, their molecules and how the body responds.
An aspect of bodybuilding/exercizing that is just as important as the weights and workouts themselves. Generally, the more a human does, the more nutrition they need in every sense.
Protein is needed to survive as a human, 0.8 grams per kilogram of weight MINIMUM. (source) To gain muscle you need to consume more protein than that. 1 gram per pound of body is a good goal.
There are additional ingredients, Amino Acids, you can ingest to give your body more of what it needs to build muscle. The most common is creatine, and it can be found naturally in foods or bought alone. 14mg per pound is a good dose, (source) but you could do as low as you like.
Carbohydrates, fats, vitamins, minerals, and water are other things essential to keep you running, but aren’t the building block of muscle.
For vitamins, minerals, and water be sure to get the daily recommended dose. It’s worth considering a little more than recommend water, potassium, magnesium, and sodium in your diet for adequate muscle usage before and during working out. Also, a bit more calcium in general for muscle movement and the strength your bones must gain to support stronger muscles and weight loads.
For carbohydrates and fats, it’s important to have adequate levels of these. The body uses carbohydrates for energy first and mainly, then uses fats, then proteins. How much? Well it depends on how much you care about the image of your body, and what your goals are.
The Bulk is for people who want to gain muscle and mass a bit quicker. There is clean bulking and dirty bulking. Dirty bulking is eating a lot without much regard to amounts. Clean bulking is to gain muscle mass while keeping your body fat percentage at relatively the same level.
The Cut is for people who want to reduce their body fat percentage. Eating at a slight/moderate deficit to force the body to consume fat cells as energy. High protein is still consumed.
Before working out, you should consume something 30-40 minutes before starting. Preworkout, a caffeinated substance, or complex carbohydrates to give you the energy needed to begin and not crash.
After working out, you should consume a good portion of your daily proteins 30 minutes to four hours later.
(Part 2)Working out. Utilizing and ripping the telomeres of your muscles and forming neural pathways.
To build muscle, you need to utilize the muscles. To get bigger muscles, your body needs to move with more resistance than what it normally does. Weight acts as the resistance.
Warming up is an important first step to working out, as you need to prime your body’s systems and cells. Heart rate is the primary thing to warm up, because using muscles required your heart pump harder and faster. 5-10 minutes of warmup minimum of cardio is best. The intensity of this cardio is your choice. Dancing, fast walking, jogging/running, jump rope, cycling, etc. are good. Stretching is also a good precursor to the warmup as the warmup uses your muscles also. It’s a process, but its important to warm up properly to avoid tightness, cramps, or even things snapping.
The weightlifting a complicated and highly discussed thing. There are hundreds of motions across gym machines, tools, and muscles for you to chose from. Which ones you do depend on what is available, and the muscles you want to work. Write stuff down if you must. Here is an exercise dictionary.
Muscle names are good to know to decide which motions to do. Look at this diagram to learn, and build your own encyclopedia and routine.
Frequency of working out is important. If your body does not use muscles, they deteriorate. You can work certain muscles more frequently than others. Just keep adequate rest. You may see things like push/pull day, arm day. This is the type of motions and muscles focused. Dedicating a workout session/day to one muscle group helps keep track of avoiding overuse. See Rest for more. Once a week at minimum you should work a muscle group to keep it from deteriorating. Here’s an example: Sunday rest. Monday arms&core. Tuesday whole back. Wednesday rest. Thursday whole arms. Friday rest. Saturday whole legs.
Duration of working the muscle during a session/day impacts its growth. A rep is one time going through a motion. Sets is how many times you do a group of reps. 3x15 pushups is I’m doing 15 pushups. Rest. 15 more. Rest. 15 more. Three sets of fifteen. To build endourance, lower weight at higher reps. To build mass and strength, higher weight at lower reps.
Finally, the weight heaviness. You should slightly push your muscles to start, then base your weight patterns off of what is a good amount of strain for you. The more you challenge/strain yourself, the more it will hurt and build muscle mass. Also, the faster you increase the weight your muscles fight against, the higher the risk of injury. However, if you stick to a weight that is not challenging, your muscles will not grow. There must always be some element of challenge your muscles must always be chasing to keep up with. Thats what growing is. For example: I’ve been bicep curling single dumbbells of 10 pounds for months. 12 pounds is a comfortable challenge, and I can do 15 also but not the whole set. So, I may warm up with 1 set of 10lbs. Two sets of 12lbs, then finish with one set of 15 at lower reps. The number of reps per set could be 15,12,10,6. Decreasing reps while increasing weight to prep the body, but not injure too much.
(Part 3) Rest. Your body building new muscle, and preparing to work again.
In between sets of exercise, you need to rest your muscles for enough time for them to become reloaded with their energy, ATP. ~1 minute for heavily lifting. Ensure you’re breathing well also to give your blood oxygen. Deeper, healthy breaths during rest is good.
After training it’s recommended to give a muscle group ~48 hours of rest to rebuild the fibers. Rest means not training it, but of course if you need to use them, use them. Additionally, you can still be active and rest, doing a thing called active rest. Doing nothing at all, which has its benefits, is called passive rest.
Sleep is your body’s way of storing information and taking out the cerebral trash. During sleep your body produces growth hormone, your brain works to retain all of the information you and your body learned during the day, and generally refreshes itself. Napping can be beneficial also if it doesn't interfere with getting the minimum 8-10 hours depending on your age group.
Thank you for reading! If you have any questions, would like help creating workout plans, or would like a bit of praise or encouragement feel free to reach out. Also if there are any errors. Now go have fun!
#androphilia#autoandrophilia#forcemasc#forced masculinization#weightlifting#body building#finally here!
290 notes
·
View notes
Text
Supplements & Vitamins
Here's a list of some of the most commonly used supplements and their benefits. Please remember that while supplements can be beneficial for certain people, everyones nutritional needs are different. It's always a good idea to consult with a specialist before adding any new supplements to your routine, as individual needs may vary.
Multivitamin: Provides a range of essential vitamins and minerals to support overall health and fill potential nutrient gaps in your diet.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Promote heart health, brain function, and reduce inflammation. Typically derived from fish oil or algae.
Vitamin D: Supports bone health, immune function, and may have a positive impact on mood. It's commonly obtained through sun exposure, but supplements can be useful, especially in winter or for those with limited sun exposure.
Probiotics: Help promote a healthy gut microbiome, aiding digestion, nutrient absorption, and immune function.
Magnesium: Important for muscle and nerve function, bone health, and energy production. It may also help with relaxation and sleep.
B vitamins: Help convert food into energy, support brain function, and maintain healthy hair, skin, and nails.
Vitamin C: Boosts immune function, acts as an antioxidant, supports collagen production, and aids in iron absorption.
Zinc: Essential for immune function, wound healing, and cell division. It also supports normal growth and development during pregnancy, childhood, and adolescence.
Iron: Required for red blood cell production and oxygen transport. Iron deficiency can lead to anemia and fatigue, but it's essential to get iron levels checked before supplementing.
Calcium: Crucial for bone health and muscle function. It's often combined with vitamin D for better absorption.
Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10): Plays a vital role in energy production within cells and acts as an antioxidant. It may benefit heart health and cellular energy metabolism.
Curcumin (Turmeric extract): Possesses anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, potentially supporting joint health and cognitive function.
Ashwagandha: An adaptogenic herb that may help reduce stress, promote relaxation, and support cognitive function.
Green Tea Extract: Contains antioxidants and may support cardiovascular health, weight management, and cognitive function.
Glucosamine: Commonly used for joint health and may help alleviate symptoms of osteoarthritis.
Chondroitin: Often taken alongside glucosamine, it may help reduce joint pain and improve joint mobility.
Probiotics for Gut Health: Certain strains of probiotics can help restore and maintain a healthy balance of gut bacteria, supporting digestion and immune function.
Melatonin: A hormone that regulates sleep-wake cycles, melatonin supplements can help with insomnia or jet lag.
Vitamin E: An antioxidant that supports immune function and may help protect against cellular damage.
Ginseng: An adaptogenic herb that may help increase energy, reduce stress, and support cognitive function.
Prebiotics: These are non-digestible fibers that promote the growth of beneficial gut bacteria, supporting gut health and digestion.
Magnesium: In addition to its previous benefits, magnesium may help reduce muscle cramps, improve mood, and promote relaxation.
Probiotics for Vaginal Health: Certain strains of probiotics can help maintain a healthy balance of vaginal flora, reducing the risk of infections.
Cranberry Extract: Often used for urinary tract health, cranberry extract may help prevent urinary tract infections.
Resveratrol: Found in grapes and berries, resveratrol has antioxidant properties and may support heart health and longevity.
L-theanine: An amino acid commonly found in green tea, L-theanine may promote relaxation, improve focus, and reduce anxiety.
#vitamins#supplements#health tips#healthy diet#health is wealth#healthy living#health and wellness#healthy lifestyle#health#clean girl#glow up tips#level up journey#wellness
3K notes
·
View notes
Text

Hey everyone!
I’m excited to share this comprehensive list of essential minerals and their roles in our bodies. As many of you know, understanding the function of each mineral can be incredibly empowering for maintaining our health and well-being. From supporting bone strength to aiding in energy production and immune function, each mineral plays a unique and crucial role.
This list not only highlights the importance of these minerals but also serves as a handy reference for anyone interested in optimizing their diet and health. Whether you’re a health enthusiast, someone looking to boost their nutrition, or just curious about how your body functions, this information is invaluable.
Feel free to save this post for easy access and share it with friends who might find it helpful. Let’s make informed choices about our health together!
Here’s a rundown of some key minerals and their roles:
Boron - Supports bone health and hormone regulation.
Phosphorus - Vital for bone and teeth formation, energy production.
Manganese - Involved in metabolism, bone formation, and antioxidant function.
Iron - Essential for oxygen transport and energy production.
Calcium - Critical for bone and teeth health, muscle function, and nerve signaling.
Selenium - Acts as an antioxidant, supports immune function and thyroid health.
Sulfur - Important for amino acid synthesis and detoxification.
Sodium - Regulates fluid balance, nerve function, and muscle contraction.
Magnesium - Supports muscle and nerve function, blood glucose control, and bone health.
Potassium - Helps maintain fluid balance, nerve function, and muscle contractions.
Zinc - Crucial for immune function, protein synthesis, and wound healing.
Copper - Involved in iron metabolism, connective tissue formation, and antioxidant defense.
Iodine - Essential for thyroid hormone production and metabolism regulation.
Fluoride - Strengthens tooth enamel and supports bone health.
Chromium - Enhances insulin action and glucose metabolism.
Cobalt - Part of vitamin B12, essential for red blood cell formation.
Molybdenum - Helps with enzyme function and detoxification.
Nickel - Involved in the metabolism of fats, carbohydrates, and proteins.
Silicon - Supports bone health and connective tissue integrity.
Vanadium - Plays a role in bone health and insulin regulation.
Strontium - Supports bone health and may aid in bone density.
Lithium - May influence mood regulation and neurological health.
Calcium - Important for cardiovascular health and muscle function.
Magnesium - Helps in enzyme reactions and DNA synthesis.
Iron - Supports cognitive function and immune health.
Potassium - Essential for heart function and muscle contractions.
Zinc - Important for DNA synthesis and cell division.
Selenium - Enhances antioxidant defenses and thyroid function.
Manganese - Assists in wound healing and bone development.
Phosphorus - Aids in energy production and bone health.
Copper - Crucial for brain development and cardiovascular health.
Sodium - Regulates blood pressure and volume.
Iodine - Essential for thyroid hormone production and metabolic regulation.
Fluoride - Helps prevent dental cavities and strengthens bones.
Chromium - Supports metabolism of carbohydrates and fats.
Molybdenum - Important for enzyme activity and metabolic processes.
Nickel - Assists in the metabolism of fatty acids and hormones.
Silicon - Enhances skin health and bone strength.
Vanadium - Potentially involved in glucose metabolism and bone health.
Strontium - May contribute to bone density and overall skeletal health.
Cobalt - Key component of vitamin B12, important for nerve function.
Lithium - May have effects on mood and mental health.
Calcium - Supports cardiovascular function and muscle contraction.
Magnesium - Contributes to heart health and muscle relaxation.
Iron - Essential for energy production and oxygen transport.
Potassium - Important for maintaining electrolyte balance and cellular function.
Zinc - Aids in immune function and skin health.
Selenium - Helps protect cells from damage and supports thyroid function.
Manganese - Facilitates enzyme reactions and antioxidant defense.
Phosphorus - Integral to energy storage and bone mineralization.
Hope you find this list as enlightening as I do! Feel free to save and share.
35 notes
·
View notes
Text
Tutoring Sessions with Johnny Joestar: Macromolecules



a/n: the fall semester just started and this is my first time taking biology so I'm writing fanfiction to help me study LMAOOO
⋆ ˚。⋆୨୧˚⋆ ˚。⋆୨୧˚⋆ ˚。⋆୨୧˚⋆ ˚。⋆୨୧˚⋆ ˚。⋆୨୧˚⋆ ˚。⋆୨୧˚⋆ ˚。⋆୨୧˚⋆ ˚。⋆୨୧˚⋆ ˚。⋆୨୧˚⋆
It was a late afternoon, and the sun streamed through the library windows, casting a warm glow across the tables. The campus was quieting down as students finished their classes for the day, but you were still hard at work, sitting in a cozy corner with your biology textbook open in front of you.
Next to you sat Johnny Joestar, your lab partner and a cute guy you’d gotten to know over the semester. He had offered to help you study for the upcoming biology exam, and you were grateful for his help—especially since you were struggling to wrap your head around macromolecules.
Johnny leaned back in his chair, casually flipping through his notes. “Alright,” he began, glancing at you with a small smile. “Let’s start with the basics. Do you know what a macromolecule is?”
You nodded slowly. “I think so. It’s a large molecule made up of smaller units, right?”
“Exactly,” Johnny replied, leaning forward, his blue eyes focused on you. “Macromolecules are big, complex molecules that are essential for life. There are four main types: proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, and lipids. Each of these has a unique structure and function, but they’re all made up of smaller building blocks.”
“Got it,” you said, feeling a bit more confident. “And polymers?”
“Right. A polymer is a type of macromolecule. It’s basically a long chain made up of repeating units called monomers,” Johnny explained, tapping his fingers on the table as if to emphasize each point. “Think of it like a necklace, where each bead is a monomer, and the whole necklace is the polymer.”
You nodded, picturing the beads in your mind. “Okay, that makes sense. So, how are these polymers formed and broken down?”
Johnny grinned, clearly pleased with your progress. “Good question. Polymers are formed through a process called dehydration synthesis, or condensation. That’s when two monomers join together, and in the process, they release a molecule of water. On the other hand, breaking down polymers is called hydrolysis. That’s when water is added, breaking the bonds between monomers.”
You scribbled down notes, grateful that Johnny was making these concepts easier to understand. “Dehydration synthesis to build, hydrolysis to break down,” you repeated.
“Exactly,” Johnny said, giving you an approving nod. “Now, let’s go over the structures and functions of the four main types of macromolecules.”
He pulled out his own notes and started with proteins. “Proteins are made up of amino acids, which are their monomers. The sequence of these amino acids determines the protein’s shape and function. Proteins do a lot—they’re involved in everything from catalyzing chemical reactions to providing structural support to cells.”
He paused to let you catch up, then moved on. “Nucleic acids, like DNA and RNA, are made up of nucleotides. These nucleotides have three parts: a sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base. Nucleic acids store and transmit genetic information.”
“Carbohydrates,” he continued, “are made up of sugar monomers called monosaccharides. They’re the main source of energy for living organisms. Simple sugars like glucose give us quick energy, while complex carbs like starch provide a slower, more sustained release.”
Finally, Johnny turned to lipids. “Lipids are a bit different—they’re not true polymers because they’re not made up of repeating monomers. But they’re still considered macromolecules. Lipids include fats, oils, and phospholipids. They store energy, make up cell membranes, and play a role in signaling within the body.”
You finished writing and looked up at Johnny, who was watching you with a small smile. “That was really helpful,” you said, feeling a sense of accomplishment. “I think I understand this stuff a lot better now.”
Johnny chuckled softly. “I’m glad I could help. You’re doing great—just keep going over your notes, and you’ll nail that exam.”
You smiled back, feeling a warm glow that had nothing to do with the setting sun. “Thanks, Johnny. I couldn’t have done this without you.”
He shrugged, but there was a hint of shyness in his expression. “No problem. I guess being lab partners has its perks.”
You both shared a quiet laugh, the atmosphere between you light and comfortable. As you packed up your things, you couldn’t help but feel a little closer to Johnny—not just as a lab partner, but as a friend who was genuinely invested in helping you succeed.
“Maybe we can study together again sometime?” you suggested, hoping you didn’t sound too eager.
Johnny’s smile widened, and he gave you a small nod. “Yeah, I’d like that.”
With that, you both headed out of the library, the evening air cool against your skin as you walked together across the campus, discussing plans for the next study session.
⋆ ˚。⋆୨୧˚⋆ ˚。⋆୨୧˚⋆ ˚。⋆୨୧˚⋆ ˚。 Thanks for Reading! ˚⋆ ˚。⋆୨୧˚⋆ ˚。⋆୨୧˚⋆ ˚。⋆୨୧˚⋆
#sbr#sbr imagine#sbr x reader#jojo sbr#jjba sbr#jjba x reader#jjba imagine#jjba part 7#johnny joestar x reader#johnny joestar imagine#Johnny joestar
35 notes
·
View notes
Text
Xerneas and Yveltal are Fungi: Let Me Explain...
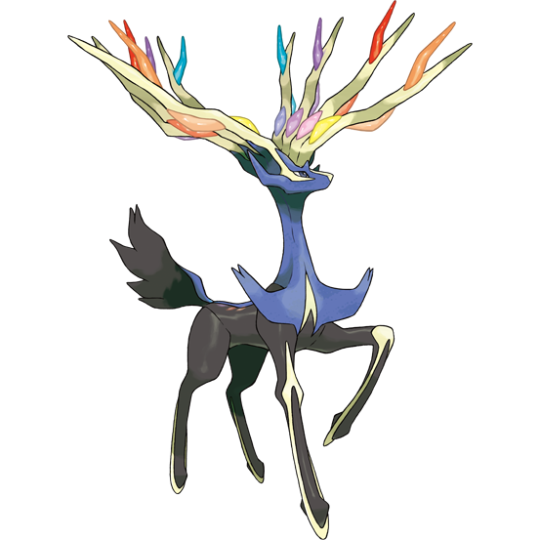
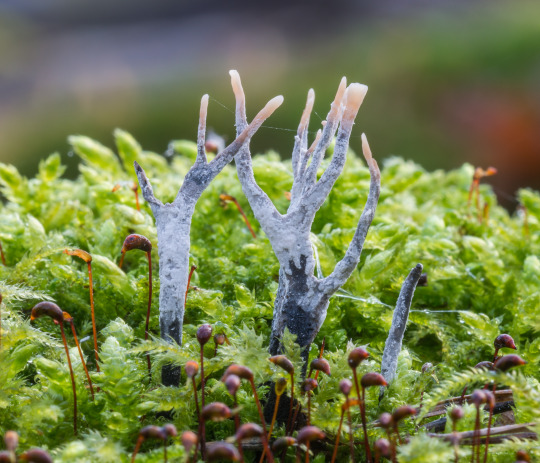




Source: Bulbapedia, Wikipedia, Bulbapedia, Enchanted Nature
Xerneas and Yveltal are my favorite legendary designs. There's something weirdly alien about these bio-luminescent approximations of fauna, like they're trying to look like animals and failing. I've always thought they looked a little bit...fungal.
Xerneas and Yveltal are like batteries. They're life energy brokers; Xerneas distributes life, while Yveltal drains it. Supporting and draining life is one of the main characteristics of fungi. In fact, it's like their whole thing.
Some fungi have a mutualistic relationship with their hosts, where they actually benefit their health. And in general, fungi are essential to supporting the ecosystem. Then there's fungi that are simply parasitic.
Fungi can also go dormant, as well as their spores. Staying still is their thing, just chilling in dark places. Xerneas and Yveltal's dormant forms are especially weird, showing just how anomalous these creatures are.
Now allow me to lichen fauna to fungi.
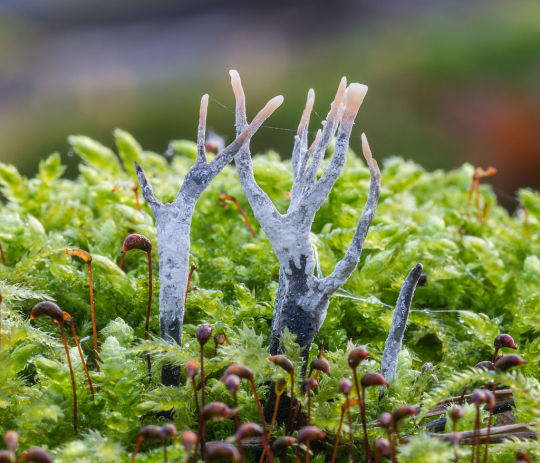


Sources: Bulbapedia, New Forest Pics, Wikipedia, Mushroom Diary Blog
This is xylaria hypoxylon, also known as Stag's Horn fungus. (Not to be confused with Yellow Staghorn.) It reminds me a lot of the dormant form of Xerneas, or the "deactivated" form it takes in the PC.
Stag's Horn is also bio-luminscent, which means the tips of the fungus faintly glow - much like the tips of Xerneas's antlers.
Speaking of the first legendary Fairy Pokemon, mushrooms are often associated with fairies. Fairy Rings are circles of mushrooms that are connected by mycelium underneath. (I'll get into mycelium in just a second.) There are too many myths about Fairy Rings to get into here, so for now I'll just point out the Fairy Ring around Valerie's Gym in Laverre City.


Sources: Bulbapedia, Sussex Wildlife Trust, Enchanted Nature, UK Wildlife
I'm not sure whether Bulbapedia or Dr. King on Pokemon Amino first likened Yveltal to Devil's Fingers, but the similarities are uncanny. Like Yveltal emerges from its cocoon, Devil's Fingers emerge from what is called their "egg stage". I tried to find the least unsettling picture of this that I could. Enjoy...?
I mean, what kind of bird turns into a cocoon, anyway? Honestly though, fungus isn't supposed to hatch from an egg either, so this is all mixed up.
Okay, so Xerneas and Yveltal are based on different aspects of Yggdrasil. But if you were going to design Pokemon based on Yggdrasil, the World Tree that connects the universe, wouldn't you base it on fungi rather than an actual tree? Mycelium can actually partner with the roots of plants and other fungus to create a widespread beneficial mycorrhizal network, a truly interconnected ecosystem of organisms.

Source: BBC News - How Trees Secretly Talk to Each Other
And that's why Xerneas and Yveltal are fungi. Or it could be part of their inspiration, at least. They're not necessarily inspired by these specific fungi, but I think the concept may be part of their design. Either way, Gen VI is especially fun to research!
Reviewed by @fluffybunnybadass.
Check out my posts about Pokemon Legends: Z-A:
Poll: What Does the Λ in Legends Z-A Symbolize?
Pokemon Legends Z-A: What Is the Λ?
Is Z-A Just Zygarde-A? (%1000 Zygarde and the Fragments of the Tree of Life)
Aaah, it's an A! Is the A in Z-A the Tree of Life?
How much longer am I going to have to wait for a freakin' Unova remake?!
#Pokemon Y#Pokemon X#cw: fungus#Yveltal#Xerneas#Pokemon Legends: Z-A#Pokemon Legends Z A#Pokemon games#Pokemon#Kalos#gaming#Pokemon XY#Generation 6#Generation VI#Generation VI Pokemon#Video games#Z-A#Devil's Fingers#Octopus Stinkhorn#fungi#wild fungi#fungus#Stag's Horn#Candlesnuff#mycelial network#mycelium
55 notes
·
View notes
Text
Human Cell Tournament Round 2
Propaganda!


Phosphocreatine, also known as creatine phosphate, is a phosphorylated form of creatine that serves as a rapidly mobilizable reserve of high-energy phosphates in skeletal muscle, myocardium and the brain to recycle adenosine triphosphate, the energy currency of the cell.
Lysine (Lys) is an α-amino acid that plays several roles in humans, most importantly proteinogenesis, but also in the crosslinking of collagen polypeptides, uptake of essential mineral nutrients, and in the production of carnitine, which is key in fatty acid metabolism. Due to its importance in several biological processes, a lack of lysine can lead to several disease states including defective connective tissues, impaired fatty acid metabolism, anemia, and systemic protein-energy deficiency.
#Phosphocreatine#Lysine#poll#polls#tumblr poll#tumblr polls#vote#tournament poll#wikipedia#cells of the human body#science tournament#biochemistry
15 notes
·
View notes
Text
fucking i just remembered that post about like. how taurine is an essential amino for cats to eat bc their bodies can't make it on their own and how it's found in a lot of energy drinks and there was some joke about feeding your cat boy monster energy drinks to make sure they get the proper nutrients in the post somewhere. anyway that's trolls to me.
#specifically sollux#to a lesser extent karkat#textsnores#it's just found in meat they are carnivorous#thinking also about trolls not just enslaving but Eating other alien races in their galactic conquest.
36 notes
·
View notes
Photo
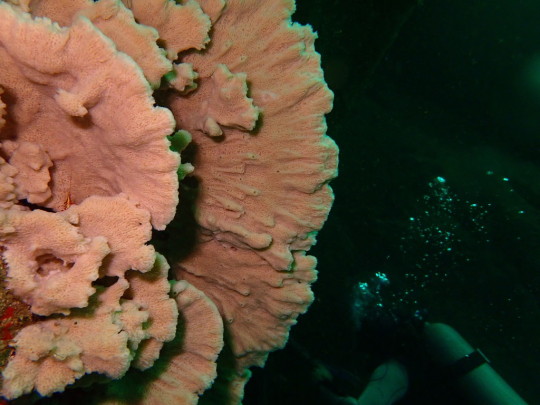

FUTURE OCEAN CONDITIONS INDUCE NECROSIS IN REEF SPONGES
Oceans are rapidly warming and acidifying in the context of climate change, threatening sensitive marine biota including coral reef sponges, oceans more acids and hot can can impact host health and associated microbiome. Now, australian scientists have found when areef sponge is exposed to a 3 °C increase in seawater temperature, as is expected in the future, the sponge loses an important microbe, which could explain why sponge tissue dies.
Marine sponges are highly diverse, filter-feeding benthic animals, which play essential roles in the ocean, such as providing shelter and home to other animals, they collect bacteria, and process carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus. Thse microbe partners play key roles that contribute to host health and survival of the sponge, including energy provision to the host, waste removal, amino acid and secondary metabolite production and chemical defence.

- A healthy reef sponge (left) versus a necrotic one (right) in the lab conditions. Credit: Holly Bennett
The symbiosis between the reef sponge and its microbes is weak to warm oceans, and may not be stronge to the high temperatures that are predicted to become averages by the end of the century.
Photo by David Gúmera
Reference (Open Access): Botté et al.2023 Future ocean conditions induce necrosis, microbial dysbiosis and nutrient cycling imbalance in the reef sponge Stylissa flabelliformis. ISME COMMUN.
#reef sponge#Stylissa flabelliformis#climate change#science#biology#sciblr#scienceblr#bioblr#biologyblr#marine biology#marine science#ocean acidification
126 notes
·
View notes
Text
9 Essential Amino Acids: Function, Health Benefits, and Food Sources

As health enthusiasts, we understand the importance of having a balanced diet that includes all the essential nutrients our body needs to function properly. Among these essential nutrients are Amino Acids, which play a vital role in maintaining our overall health and well-being.
Amino acids are the fundamental components of proteins and are essential for many critical functions in the body. These compounds are responsible for the formation of important structures such as proteins, hormones, and neurotransmitters. To obtain enough amino acids, it is important to consume protein-rich foods like meat, fish, and seafood. Additionally, some individuals take amino acid supplements as a natural way to boost their mood and/or enhance their athletic performance.
Our bodies require a diverse range of amino acids to maintain optimal health and function. Although there are approximately 500 different amino acids found in nature, only 20 of these are used to create the proteins found within the human body. Though each of these amino acids plays a crucial role in our well-being, 9 of them are deemed particularly essential for our survival.
These 9 essential amino acids include leucine, valine, isoleucine, lysine, threonine, phenylalanine, tryptophan, methionine, and histidine. In this blog, we will be discussing the definition, health benefits, and food sources of these essential amino acids to help you understand the significance of including them in your diet.
1. Leucine
Leucine is one of the three branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs)** along with isoleucine and valine. It plays a vital role in protein synthesis, making it important for muscle growth and repair. It can help preserve muscle mass during periods of caloric restriction or increased physical activity. Leucine is also involved in the regulation of blood sugar levels and the stimulation of wound healing. Additionally, studies have suggested that leucine may have the potential to improve bone health, and may play a role in preventing obesity.
A wide variety of healthy, tasty foods contain leucine, including eggs, beef, tuna, and salmon. These good food sources of leucine are all easy to incorporate into your diet. Leucine is also available in supplement form and is often used by athletes, bodybuilders, and other fitness enthusiasts to enhance muscle growth and recovery via a BCAA or EAA drink.
**BCAAs are a group of three amino acids that have a distinct branching structure at the molecular level. These amino acids are metabolized by the body and used as a source of energy for muscle tissue. BCAAs, which are found in high concentrations of muscle protein, have been recently recognized as vital to muscle health.
2. Valine
Like leucine, valine is classified as a branched-chain amino acid (BCAA). This essential amino acid is commonly used by athletes and bodybuilders as it helps prevent muscle breakdown, enhances athletic performance, and helps supply the muscles with extra glucose for energy production during intense exercise or workouts.
Valine promotes the growth and repair of muscle tissue, which can lead to an increase in muscle mass and strength. It also helps regulate blood sugar levels, preventing energy crashes during intense exercise. Additionally, valine helps to stimulate the formation of hormones, which can aid in the body's overall health and well-being.
Valine can be found in a variety of food sources, including red meat like lamb and beef & dairy products too, especially cottage cheese and yogurt. Eggs, turkey, and chicken; fish, including wild-caught salmon and trout are some other good sources. To ensure that you're getting enough valine, be sure to incorporate these foods into your diet regularly.
Additionally, supplements like Amino Hydrate + which contains Valine, among the other essential amino acids, are commonly taken by weightlifters and performance athletes as part of their workout routines.
3. Isoleucine
Isoleucine, as one of the BCAAs, is also critical to the physiological functions of your whole body. It helps with growth, immunity, protein metabolism, and fatty acid metabolism. Isoleucine has a role in the detoxification of nitrogenous waste like ammonia, which is then excreted from the body by the kidneys. It is also necessary for the synthesis of hemoglobin and the production of red blood cells, making it a crucial amino acid in the process of recovering from blood loss or anemia.
Isoleucine is also commonly taken by some bodybuilders and athletes, as it helps decrease post-workout muscle damage and soreness. According to a systemic review published in 2017 in the Journal of Nutrients, some studies have shown that BCAA supplementation can be successful at reducing exercise-induced muscle damage. Moreover, according to Annie Price, a Certified Holistic Health Coach, the isoleucine amino acid is also believed to mediate glucose uptake into a cell and break it down into energy. This specific isoleucine function is why it may help enhance athletic performance.
Animal-based isoleucine food sources include yogurt, tuna, lean chicken breast, lean pork chops, beef, cod, and haddock.
4. Lysine
Lysine is an essential amino acid that helps build muscle tissue, prevent cold sores, maintain a healthy immune system, produce enzymes, antibodies, and healthy hormones, and even reduce feelings of anxiety and levels of the stress hormone cortisol in some people.Additionally, lysine also plays a crucial part in the synthesis of collagen, a protein necessary for bones and connective tissues, including skin, hair, tendons, and cartilage, keeping your skin, hair, and bones healthy.
Other benefits include preventing osteoporosis and bone loss, regulating blood pressure, mitigating artery plaque buildup, assisting athletes in recovering from strenuous workouts, and building and developing muscle among bodybuilders.
Foods that will help people meet their daily lysine requirements include chicken, cottage cheese, parmesan, brewer’s yeast, red meat, fish such as tuna, cod, or sardines, eggs, seafood such as mussels, prawns, and oysters to name a few.
Moreover, supplements are also a common source of amino acids because they're convenient to use and easy to find at health food stores or online. Supplements usually come in powder form, like Surpo Amino Hydrate +, just add 1 scoop to 12-16 oz of water and you will get the dose of lysine your body needs for maximum performance and overall health. This product can be taken at any time of the day or on an empty stomach.
5. Threonine
Threonine is an essential amino acid that plays a vital role in the formation of structural proteins such as collagen and elastin, which are important for maintaining the strength and elasticity of skin, hair, and nails. Threonine is important for the proper functioning of the nervous system and has been shown to promote a healthy immune system. Additionally, threonine helps to maintain the proper balance of proteins in the body and aids in the absorption of nutrients.
It is important to consume adequate amounts of threonine through diet, as a deficiency can lead to poor immune function, skin and hair issues, and problems with the liver and nervous system. Some food sources of threonine include chicken, fish, dairy products, and eggs.
6. Phenylalanine
The human body requires phenylalanine, an essential amino acid, in order to function properly. It is a building block of proteins and is important for the formation of important neurotransmitters, such as dopamine and norepinephrine, which are responsible for regulating mood and behavior. Phenylalanine can help improve memory and concentration. It also plays a role in the production of melanin, a pigment that gives color to the skin, hair, and eyes.
Phenylalanine has been found to improve mood and cognitive function, making it beneficial for those with depression or anxiety. It may also help reduce pain and inflammation in conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Additionally, phenylalanine has been found to improve wound healing and skin health, making it beneficial for those with skin conditions such as eczema and psoriasis.
Food sources high in phenylalanine include meat, poultry, fish, eggs, and dairy products. It's also important to note that phenylalanine can be found in a different form called aspartame, which is commonly used in artificial sweeteners. People with phenylketonuria (PKU) are advised to avoid foods containing aspartame, as their bodies cannot break down the phenylalanine in the sweetener, leading to a buildup of the amino acid in the body.
7. Tryptophan
Tryptophan is an essential amino acid that is a precursor to the neurotransmitter serotonin, which is involved in regulating mood, sleep, and appetite. Tryptophan is responsible for healthier and better-quality sleep, relief from depression and anxiety, increased emotional well-being and strengthened pain tolerance. Tryptophan supplementation improves muscle development, and it has previously been shown that it has a significant impact on muscle mass via its metabolite serotonin.
Tryptophan is found in meats such as turkey and chicken. It is also found in eggs, bananas, cheese, fish, chocolate, dried dates, and milk. Tryptophan is often found in high-protein foods such as these, but it can also be taken as a dietary supplement. The amount of l-tryptophan in these foods is small compared to supplements.
However, it is important to note that supplementing with tryptophan alone may not be as effective as getting it from food sources or as part of a balanced diet, and high doses of tryptophan supplements can be harmful. It's always best to consult a healthcare professional if you are considering taking this supplement.
8. Methionine
Methionine is an essential amino acid that plays a crucial role in many bodily functions, including protein synthesis, detoxification, and the production of other essential nutrients like glutathione and creatine. Methionine is involved in the detoxification of heavy metals, pesticides, and other harmful substances. It also helps to prevent the buildup of fat in the liver. It is also essential for the production of new proteins, which are important for the growth and repair of tissues.
Additionally, methionine is necessary for the production of collagen, which is a protein that provides structure to skin, hair, and nails, and is involved in the production of neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine, which play a role in mood regulation.
Some of the best sources of methionine, with high concentrations, are found in red meat, chicken, and turkey. It is also found in eggs, dairy products like milk, cheese, and yogurt, some nuts, and seeds, like sesame seeds and sunflower seeds. It's important to note that a balanced diet that includes a variety of protein sources will provide enough methionine for most people. However, those who follow a vegetarian or vegan diet may need to pay extra attention to their methionine intake.
9. Histidine
Histidine is a nutritionally essential amino acid that plays a vital role in a variety of pathophysiological and physiological processes. It plays a crucial role in the maintenance of myelin sheaths that protect your nerve cells while metabolizing the key wake-promoting neurotransmitter called histamine. Histamine supports and reinforces your immune system and inflammatory response, and is vital for gastric secretion, sexual functions, and the production of blood cells. Additionally, histidine also plays a key role in the formation of collagen, which is necessary for maintaining healthy skin and hair.
Histidine is an amino acid that was traditionally considered non-essential, meaning that it could be produced by the body from other amino acids. However, recent research has shown that histidine may play a crucial role in certain physiological processes, such as immune function, blood vessel health, and neurotransmitter production. As a result, histidine is now considered to be conditionally essential, meaning that under certain conditions (such as during growth or development) the body may not be able to produce enough histidine on its own and it may need to be obtained from the diet.
Histidine can be made by the body by converting other amino acids, such as lysine and methionine, into histidine. However, this process can be limited by the availability of these other amino acids, as well as other nutrients such as vitamin B6 and zinc. By consuming adequate amounts of the original 8 essential amino acids, as well as other key nutrients, the body can produce enough histidine to meet its needs.
It's important to note that while histidine is considered conditionally essential, it is not considered as essential as the other 8 amino acids that are required in larger amounts and cannot be synthesized by the body. Therefore, it's important to include a variety of protein sources in the diet to obtain all essential amino acids.
Foods rich in histidine are generally protein-rich foods such as meat, poultry, fish, and dairy products such as milk, cheese, and yogurt. It is also present in some spices and herbs, like basil, thyme, and oregano.
SURPO Takeaways
Essential amino acids are an important component of a healthy diet. They are essential because our bodies cannot produce them on their own and must obtain them through our diet. These essential amino acids play a vital role in maintaining optimal health and well-being. From helping to build and repair muscles to supporting the immune system, these amino acids are necessary for many bodily functions.
Food sources such as eggs, fish, poultry, beef, and dairy products are excellent sources of essential amino acids. However, vegetarians and vegans can also obtain these essential amino acids through plant-based sources such as legumes, nuts, and seeds.
It's essential to note that a balanced diet is crucial for obtaining all the essential amino acids. Therefore, it's essential to consume a variety of foods that are rich in these nutrients. If you're concerned about your dietary intake, it's always best to speak with a registered dietitian or healthcare professional.
Amino Hydrate +
Amino Hydrate+ intra workout & hydration powder replenishes lost minerals and electrolytes needed for endurance and physical and mental energy. Formulated with 8 Essential Amino Acids (EAAs), this Pre Workout Powder & Post Workout Recovery Drink assists in muscle recovery and growth, fueling your fitness journey! Amino Hydrate’s EAAs have an unparalleled 99% absorption rate and are already broken down in the correct ratios for optimal utilization, making it ideal to consume while training.
This hydration drink is an amino acids supplement for men and women that allows you to train harder and longer in the gym or on the field—an ideal hydration electrolyte and amino-heavy pre-workout with no stimulants and for an after-workout recovery drink! Our hydration supplements for men and women fully hydrate your body, keeping you fueled to tackle even the most intense workout.
Unlike ordinary hydration electrolytes and amino acid nutritional supplements, this workout powder will help you reach your body and fitness goals. Our EAA Supplement (which contains the bcaas) increases metabolic rate and muscle protein synthesis and provides 99% NNU (amino acid absorption) to support athletic recovery and overall performance!
#Amino Hydrate+Sale#Amino Hydrate+ formula#Surpo Nutrition#Amino Hydrate+#Sale Amino Hydrate+#Amino Hydrate+ Sale#Amino Acids multivitamins#Amino Acids Vitamins#Higher Athletic Endurance#Amino Acids supplements#Optimum Hydration#Caffeine Free Energy#high-quality supplements#Increased MPS#Essential Amino Acids#Essential Electrolytes#bodybuilding#gymmotivation#workout#runspo#running#nutrition#meal prep#marathon#healthy eating#runblr
0 notes
Text
Moringa Magic Supplements - health
Moringa Magic Supplements: A Natural Boost for Optimal Health
I recently used the Moringa Magic Supplements, and I must say, they have had a transformative effect on my health and wellness. This natural, plant-based supplement has proven to be a valuable addition to my daily routine. Here’s my detailed review of the product, highlighting my experience and its many benefits.

A Natural Source of Energy
From the first week of using Moringa Magic Supplements, I noticed a significant improvement in my energy levels. I no longer felt fatigued by midday, and I was able to stay productive throughout the day. Unlike caffeine or sugary energy drinks, this supplement provided a steady, natural boost without any crashes, making it an excellent choice for those with busy lifestyles.

Packed with Nutrients and Antioxidants
Moringa Magic lives up to its name by delivering an impressive array of nutrients and antioxidants. It is rich in vitamins, minerals, and amino acids that support overall health. As someone who sometimes struggles to meet daily nutritional needs through diet alone, this supplement has been a lifesaver. Knowing I’m giving my body such a potent dose of goodness every day is incredibly reassuring.

Improved Digestion and Gut Health
One unexpected yet welcome benefit of Moringa Magic was the improvement in my digestion. I’ve had occasional digestive issues in the past, but since incorporating this supplement into my routine, my gut health has felt more balanced and regular. The plant-based ingredients seem to work harmoniously to support a healthy digestive system, which has enhanced my overall wellbeing.

Boosted Immunity and Resilience
Another noticeable effect of Moringa Magic was its positive impact on my immune system. I’ve felt more resilient and less prone to seasonal illnesses since I started using this supplement. With its powerful blend of antioxidants and essential nutrients, it’s clear that this product plays a vital role in strengthening the body’s natural defences.

Support for Skin and Hair Health
I also observed improvements in the health of my skin and hair. The natural nutrients in Moringa Magic seem to nourish from within, leaving my skin looking more radiant and my hair feeling stronger and shinier. This unexpected bonus has only added to my overall satisfaction with the product.

Convenient and Easy to Use
Moringa Magic Supplements are incredibly easy to incorporate into daily life. The capsules are small and easy to swallow, and the packaging is compact and convenient. With clear instructions provided, using this product has been a hassle-free experience, which is perfect for someone like me who values simplicity.

High-Quality and Reliable
It’s clear that Moringa Magic has been formulated with great care and quality in mind. Knowing that the product is made with pure, natural ingredients and adheres to high manufacturing standards gives me confidence in its safety and effectiveness.

Conclusion: A Truly Magical Supplement
Having used the Moringa Magic Supplements for over a month, I can confidently say they are a fantastic addition to anyone’s health routine. From increased energy and improved immunity to better digestion and glowing skin, the benefits have been undeniable.
If you’re looking for a natural, nutrient-rich supplement to enhance your health, I highly recommend Moringa Magic. It’s an investment in your well being that truly delivers on its promises. Give it a try—you’ll feel the difference!

#Moringa Magic#Supplements - health#healthcare#skincare#leadhealthylife#moringa#supercharge#veggiecapsules#health and wellness#skinglow
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Essential Guide to a Balanced Vegetarian Diet
Eating healthy is something we all strive for, but it can often feel like navigating a maze. One moment, we’re told to eat more vegetables, and the next, we’re bombarded with the latest superfood trend. For vegetarians, ensuring you get all the nutrients you need, especially protein, can be a bit of a challenge. But worry not! In this article, we’ll explore the secrets to maintaining a balanced diet, highlight some protein rich foods for vegetarians, and help you craft an effective diet plan.

Understanding a Balanced Diet
A balanced diet is like a well-orchestrated symphony. Each food group plays its part to create a harmonious melody that fuels your body. But what exactly does a balanced diet entail?
The Basics
A diet that is balanced comprises different foods in appropriate amounts. This means consuming the right amounts of carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, and minerals. Imagine your body as a car; it requires a variety of nutrients to operate at its best, just as a car needs the correct fuel to run well.
Importance of Balance
Without a balanced diet, you might feel sluggish, experience mood swings, or even become more susceptible to illnesses. It’s essential to get a good mix of nutrients to maintain energy levels, support bodily functions, and promote overall well-being.
Protein-Rich Foods for Vegetarians
When people think of protein, they often picture a big, juicy steak. However, protein-rich foods for vegetarians are plentiful and just as effective in providing the necessary nutrients.
Legumes and Pulses
Chickpeas, lentils, and beans are excellent sources of protein. Not only are they versatile, but they also pack a punch with fibre, which aids in digestion.
Nuts and Seeds
Almonds, chia seeds, and flaxseeds are excellent for a protein boost. They’re great for snacking and can easily be added to salads, smoothies, or yoghurts.
Dairy and Alternatives
Greek yoghurt, cottage cheese, and even plant-based options like soy milk or tofu are rich in protein. They’re perfect for breakfast or as part of a light meal.
Whole Grains
Quinoa and brown rice not only provide protein but also supply essential amino acids that your body needs.

Crafting a Perfect Diet Plan
Creating a diet plan that works for you is crucial. It’s not about strict limitations but about feeling great, having more energy, and improving your health.
Setting Realistic Goals
Start with small, manageable changes. Instead of overhauling your entire diet, try incorporating more vegetables into your meals or swapping out white rice for quinoa.
Meal Planning
Plan your meals ahead of time. This helps you avoid last-minute unhealthy choices and ensures you have the necessary ingredients for nutritious meals.
Balanced Meals
Make sure you get a good balance of fats, carbohydrates, and proteins in each meal. A balanced meal keeps you full longer and provides sustained energy throughout the day.
Tips for Maintaining Your Diet
Maintaining a balanced diet can sometimes feel like walking a tightrope, but with a few tips, you can stay on track without feeling deprived.
Stay Hydrated
Drinking plenty of water is essential. Our bodies can occasionally mistake thirst for hunger, which causes us to overindulge in snacks.
Mindful Eating
Observe your diet and the effects it has on your body. This practice can help you make better food choices and enjoy your meals more.
Allow Flexibility
It’s okay to indulge occasionally. The key is moderation. Enjoy your favourite treats without guilt, but balance them with healthier options.
Conclusion
Adopting a balanced diet and including protein-rich foods for vegetarians doesn’t have to be a daunting task. By understanding the essentials, crafting a thoughtful diet plan, and following practical tips, you can embark on a journey to better health and wellness. Remember, it’s about progress, not perfection. So, start small, stay committed, and enjoy the positive changes in your life.
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
Can I build muscle and lose fat at the same time?

Yes, it is possible to build muscle and lose fat simultaneously, though it can be challenging and typically requires a well-structured approach. This process is often referred to as “recomping” (short for recomposition). Here are some key strategies to achieve this:
1. Nutrition
Caloric Balance: Aim for a slight caloric deficit to lose fat while providing enough nutrients to support muscle growth. This typically means consuming slightly fewer calories than your body needs to maintain its current weight.
Protein Intake: Ensure a high protein intake (1.6 to 2.2 grams per kilogram of body weight) to support muscle repair and growth.
Macronutrient Balance: Balance your diet with a good mix of carbohydrates and fats to provide energy and support overall health.
2. Strength Training
Progressive Overload: Continuously challenge your muscles by increasing the weight, reps, or intensity of your workouts over time.
Compound Movements: Focus on compound exercises (squats, deadlifts, bench presses) that work multiple muscle groups simultaneously.
Consistency: Maintain a regular workout schedule, typically 3–5 times per week, to consistently stimulate muscle growth.
3. Cardio
Moderation: Incorporate moderate cardio to support fat loss without compromising muscle gains. High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) can be particularly effective.
Timing: Consider doing cardio on non-lifting days or after strength training sessions to prioritize muscle preservation.
4. Recovery
Sleep: Ensure adequate sleep (7–9 hours per night) to allow your body to recover and grow.
Rest Days: Incorporate rest days to prevent overtraining and reduce the risk of injury.
5. Consistency and Patience
Long-Term Commitment: Body recomposition is a gradual process that requires consistent effort over time. Patience and persistence are crucial.
Monitor Progress: Track your progress with measurements, photos, and performance in the gym rather than just focusing on the scale.
6. Individual Factors
Starting Point: Beginners or individuals returning after a long break often see more dramatic changes in body composition.
Genetics: Genetic factors can influence how easily you gain muscle or lose fat.
7. Nutrient Timing
Pre-Workout Nutrition: Consume a meal or snack rich in protein and carbohydrates about 1–2 hours before your workout to fuel performance.
Post-Workout Nutrition: Have a post-workout meal or shake with protein and carbs within 30–60 minutes after your workout to aid recovery and muscle growth.
8. Hydration
Stay Hydrated: Adequate hydration is essential for overall health, performance, and recovery. Aim to drink plenty of water throughout the day, particularly before, during, and after workouts.
9. Supplementation
Protein Supplements: Whey or plant-based protein powders can help you meet your daily protein requirements.
Creatine: Creatine monohydrate is a well-researched supplement that can enhance strength, power, and muscle mass.
Branched-Chain Amino Acids (BCAAs): These can help reduce muscle soreness and promote muscle protein synthesis, particularly when training in a fasted state.
10. Mind-Muscle Connection
Focus on Form: Pay attention to proper form and technique to maximize muscle engagement and prevent injury.
Contraction: Emphasize the contraction of the target muscles during each exercise to improve muscle activation.
11. Variation in Training
Periodization: Incorporate different phases in your training program, such as strength, hypertrophy, and endurance phases, to continually challenge your muscles and prevent plateaus.
Exercise Variety: Regularly change your exercises, rep ranges, and workout routines to keep your muscles guessing and promote continuous adaptation.
12. Tracking and Adjustment
Regular Assessments: Keep track of your body composition, strength levels, and overall progress. Adjust your diet and training plan based on these assessments to ensure continued progress.
Listen to Your Body: Be mindful of signs of overtraining or injury. Adjust your training intensity and volume as needed to prevent burnout and maintain long-term progress.
13. Metabolic Rate and Muscle Mass
Muscle Increases Metabolism: Building muscle increases your resting metabolic rate (RMR), helping you burn more calories even at rest, which aids in fat loss.
14. Hormonal Balance
Manage Stress: High-stress levels can lead to elevated cortisol, which can negatively impact muscle growth and fat loss. Incorporate stress management techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises.
Hormonal Health: Ensure adequate intake of essential fats and micronutrients to support hormonal health, which is crucial for muscle growth and fat loss.
15. Support System
Accountability: Having a workout partner, or coach, or joining a fitness community can provide motivation, accountability, and support.
Education: Continuously educate yourself about nutrition, training, and recovery to make informed decisions and optimize your body recomposition efforts.
By paying attention to these important factors, you can further enhance your ability to build muscle and lose fat simultaneously. Remember, consistency, patience, and a holistic approach are key to achieving long-term success in body recomposition.
#weightloss#health#weight loss#fatloss#lose weight#healthy#diet to lose weight#fat loss#losing weight#fatlosstips#how to lose weigth fast#weigthloss#lose stomach weight#weight loss tips#weight loss motivation#weight loss success stori#weightwatchers#i wanna lose weight#i need to lose so much weight#gaining weight on purpose#i need to lose this weight#diet#weight loss journey#how to lose weight#muscles#bodybuilder#muscular#flexing
15 notes
·
View notes