#coenzyme
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
0 notes
Text
Take care of your skin with these top 7 Timeless Skincare Products that will refresh and hydrate, leaving it wrinkle-free, smooth, and moisturized. Gen C Beauty offers Timeless Skincare Products such as Timeless 10% Vitamin C + E Ferulic Acid Serum, Timeless Skin Care Hyaluronic Acid Spray with Matrixyl 3000 and Rose Extract, Timeless Skin Care Hydrating Eye Cream, Timeless Matrixyl Synthe'6 Serum, Vitamin B5 Hydration Unisex Serum, Timeless 20% Vitamin C + E Ferulic Acid Serum, Timeless Coenzyme Q10 Serum, and Timeless Matrixyl 3000 Serum at affordable price. Visit now!
#timeless-skincare-products#Timeless-10%-Vitamin-C#timeless-hydrating-eye-cream#Best-timeless-skincare-product#Timeless-Coenzyme-Q10-Serum
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Vitamin B3, niacin (from tobacco)
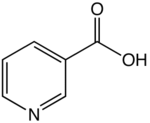
Nicotinic acid (Na) is one of the three structural isomers of pyridinecarboxylic acid. Nicotinic acid and nicotinamide are collectively called niacin. Niacin corresponds to vitamin B3 in the vitamin B group.
history
In 1867, it was discovered as a carboxylic acid obtained by oxidizing the alkaloid nicotine, and was given the common name nicotinic acid. In 1911, Umetaro Suzuki and C. Funk isolated it from living organisms as a pellagra-preventive factor. In 1937 C.A.Elvehjem revealed that nicotinic acid is a vitamin. Around the end of the 20th century, annual global production of nicotinic acid reached more than 10,000 tons[2]. However, most of it was produced for feed, and nicotinic acid for human food additives and pharmaceuticals was less than 10% of the total production.
Manufacturing method/Biosynthesis
It is obtained by oxidizing pyridine derivatives such as β-picoline with a side chain at the 3-position with strong oxidizing agents such as nitric acid and potassium permanganate. It is also synthesized by a method of constructing a pyridine ring. Salts of nicotinic acid and copper are sparingly soluble in water.
In animals and fungi, it is synthesized in vivo from tryptophan via kynurenine and 3-hydroxyanthranilic acid, while in plants and bacteria it is biosynthesized from aspartic acid and the C3 unit, a glycerol-related metabolite.
physiological activity
Main article: Niacin
In vivo, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate containing nicotinic acid in a partial structure are hydrogen acceptors of oxidoreductases and are important as coenzymes.
ニコチン酸(ニコチンさん、英: nicotinic acid、Na)とは、ピリジンカルボン酸(英語版)の3つの構造異性体の中の1つである。ニコチン酸とニコチン酸アミドを総称してナイアシンと呼ばれる。ナイアシンは、ビタミンB群の中のビタミンB3に当たる。
歴史
1867年にアルカロイドのニコチンを酸化して得られるカルボン酸として発見され、ニコチン酸という慣用名が与えられた。1911年に鈴木梅太郎およびC.Funkらが生体より抗ペラグラ因子(こうペラグラいんし、pellagra‐preventive factor)として単離した。ニコチン酸がビタミンであることは、1937年にC.A.Elvehjemによって明らかにされた。 20世紀末頃で世界中の1年間のニコチン酸の生産量を合算すると、1万トン以上に達していた[2]。ただし、その大部分は飼料用として生産されていた物であって、ヒトに用いる食品添加物や医薬品用のニコチン酸は、全生産量の1割にも満たない量であった。
製法・生合成
3位に側鎖を持つβ-ピコリンなどピリジン誘導体を、硝酸や過マンガン酸カリウムなど強い酸化剤で酸化すると得られる。また、ピリジン環を構築する方法でも合成される。ニコチン酸と銅との塩は、水に溶けにくい。
動物・菌類では生体内で、トリプトファンからキヌレニン、3‐ヒドロキシアントラニル酸を経由して、一方、植物や細菌ではアスパラギン酸とグリセロール近縁代謝物質であるC3ユニットから生合成される。
生理活性
詳細は「ナイアシン」を参照
生体内では、ニコチン酸を部分構造に含むニコチンアミドアデニンジヌクレオチドやニコチンアミドアデニンジヌクレオチドリン酸が、酸化還元酵素の水素受容体であり、補酵素として重要である。
Wikipediaより
Smoke (tobacco) is an indispensable material for human beings.
Rei Morishita
#Vitamin B3#Niacin#tobacco#nicotinic acid#coenzymes#Wikipedia#Rei Morishita#Smoke (tobacco) is an indispensable material for human beings.#smoke
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
What is CoQ10 and What Are Its Health Benefits?
Benefits of CoQ10, featuring the heart, brain, mitochondria, and food sources rich in CoQ10 Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) is a naturally occurring compound found in every cell of the body. It plays a crucial role in producing energy within the mitochondria, the powerhouse of our cells, and acts as a powerful antioxidant. CoQ10 is essential for maintaining overall health, particularly for heart function,…
#antioxidants#brain health#Coenzyme Q10#CoQ10#energy production#exercise performance#fertility#health benefits#heart health#immune support#migraine relief#mitochondria#nutrition#supplements#wellness
0 notes
Text
Mitochondrial Dysfunction in the Pathogenesis of Parkinson’s Disease
Introduction
Parkinson's disease (PD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder primarily affecting motor function due to the selective degeneration of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta. The pathogenesis of PD is multifactorial, with emerging evidence pointing to mitochondrial dysfunction as a pivotal event in the onset and progression of the disease. This article provides a comprehensive technical analysis of the role of mitochondrial dysfunction in PD, focusing on key molecular mechanisms, genetic factors, and potential therapeutic strategies.
Mitochondria and Their Cellular Roles
Mitochondria are essential organelles that generate the majority of the cell's ATP via oxidative phosphorylation in the electron transport chain (ETC). In addition to their role in energy production, mitochondria are involved in maintaining cellular homeostasis by regulating calcium signaling, apoptosis, and reactive oxygen species (ROS) production. The proper functioning of mitochondria is crucial for neurons, particularly dopaminergic neurons, which have a high metabolic demand.
Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Parkinson's Disease Pathogenesis
Mitochondrial dysfunction in PD primarily manifests through alterations in mitochondrial bioenergetics, increased oxidative stress, defective mitophagy, and calcium dysregulation. These abnormalities converge on exacerbating neuronal injury, particularly in dopaminergic neurons.
1. Impaired Mitochondrial Complex I Activity
One of the hallmark features of mitochondrial dysfunction in PD is the impairment of mitochondrial complex I, the first enzyme complex in the ETC. Complex I is responsible for transferring electrons from NADH to ubiquinone, a critical step in ATP synthesis. Studies consistently show that PD patients exhibit significant reductions in complex I activity in the substantia nigra, which leads to defective ATP production. This mitochondrial dysfunction results in energy deficits, rendering dopaminergic neurons more susceptible to stressors.
Inhibition of complex I activity is not limited to genetic mutations; environmental toxins such as rotenone and paraquat, which inhibit complex I, have been implicated in Parkinsonian syndromes. Furthermore, complex I dysfunction increases the production of ROS, exacerbating oxidative stress in neurons and contributing to mitochondrial damage.
2. Oxidative Stress and ROS Generation
Mitochondria are both the primary source and target of ROS. The process of oxidative phosphorylation inevitably generates ROS as byproducts, particularly superoxide anion, hydrogen peroxide, and hydroxyl radicals. Under normal conditions, ROS are detoxified by endogenous antioxidant systems. However, in PD, mitochondrial dysfunction leads to an imbalance between ROS production and the cell’s antioxidant defenses.
The substantia nigra, which is particularly vulnerable in PD, is exposed to elevated ROS levels due to the high metabolic rate of dopaminergic neurons and the catabolism of dopamine, which generates additional ROS via the action of monoamine oxidase (MAO). Accumulation of ROS results in lipid peroxidation, protein misfolding, and mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) mutations, all of which contribute to neuronal death and the progression of Parkinson’s pathology.
3. Mitophagy and Dysfunctional Quality Control Mechanisms
Mitophagy, a selective autophagic process that removes damaged or dysfunctional mitochondria, is crucial for maintaining mitochondrial quality and function. In PD, mitophagy is impaired, leading to the accumulation of damaged mitochondria within neurons. The PINK1-parkin pathway plays a pivotal role in the initiation of mitophagy. PINK1, a mitochondrial kinase, accumulates on depolarized mitochondria and recruits the E3 ubiquitin ligase parkin, which ubiquitinates outer mitochondrial membrane proteins to tag them for autophagic degradation.
Mutations in the PINK1 and parkin genes, which are associated with autosomal recessive forms of PD, disrupt this process and contribute to the accumulation of dysfunctional mitochondria. This failure to remove damaged mitochondria exacerbates oxidative stress and promotes the activation of apoptotic signaling pathways. As mitochondrial dysfunction progresses, neuronal survival becomes increasingly compromised, accelerating disease progression.
4. Calcium Homeostasis and Mitochondrial Regulation
Mitochondria play a critical role in buffering cytosolic calcium levels. Neurons, due to their high metabolic activity, are particularly dependent on mitochondrial calcium buffering to prevent cytotoxic calcium overload. However, in PD, mitochondrial dysfunction leads to impaired calcium handling, resulting in an increase in cytosolic calcium concentrations.
Elevated calcium levels activate a variety of calcium-dependent enzymes, such as calpains and phospholipases, that further damage cellular structures. Additionally, excessive calcium in mitochondria can activate the mitochondrial permeability transition pore (mPTP), leading to mitochondrial depolarization, the release of pro-apoptotic factors such as cytochrome c, and eventual cell death.
Genetic Factors in Mitochondrial Dysfunction in PD
Genetic mutations that directly affect mitochondrial function have been identified in familial forms of PD. These mutations often impair mitochondrial dynamics, quality control, and bioenergetics, contributing to the pathogenesis of the disease.
PINK1 and Parkin Mutations: Mutations in the PINK1 gene and the parkin gene, both involved in the regulation of mitophagy, lead to impaired mitochondrial quality control. PINK1, a serine/threonine kinase, normally accumulates on damaged mitochondria and recruits parkin to initiate mitophagy. Loss of PINK1 or parkin function results in the accumulation of dysfunctional mitochondria, contributing to neuronal degeneration.
LRRK2 Mutations: The LRRK2 gene encodes a large protein kinase involved in multiple cellular processes, including mitochondrial dynamics and autophagy. Mutations in LRRK2 are the most common genetic cause of PD, particularly in late-onset forms. LRRK2 is implicated in the regulation of mitochondrial fission and fusion, processes that control mitochondrial morphology and function. Dysregulation of these processes leads to the fragmentation of mitochondria, impaired mitochondrial function, and increased susceptibility to oxidative stress.
Alpha-Synuclein and Mitochondrial Interaction: Alpha-synuclein, the protein most notably associated with Lewy body formation in PD, has also been shown to interact with mitochondrial membranes. Aggregation of alpha-synuclein disrupts mitochondrial dynamics, leading to decreased mitochondrial respiration and increased ROS production. This interaction exacerbates mitochondrial dysfunction and accelerates neurodegeneration.
Environmental Toxins and Mitochondrial Dysfunction
Environmental exposures, particularly to pesticides like rotenone and paraquat, have been shown to inhibit mitochondrial complex I, leading to oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction. These toxins induce PD-like symptoms in animal models, supporting the hypothesis that environmental factors contribute to the pathogenesis of the disease.
Therapeutic Approaches Targeting Mitochondrial Dysfunction
Given the central role of mitochondrial dysfunction in PD, therapeutic strategies aimed at restoring mitochondrial function are being actively explored. These include:
Antioxidant Therapies: Antioxidants such as coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) have been proposed to alleviate oxidative stress by scavenging ROS. CoQ10 functions as an electron carrier in the ETC and may help restore mitochondrial bioenergetics in PD. Clinical trials, however, have shown mixed results, necessitating further research.
Gene Therapy: Gene therapy approaches aimed at correcting genetic defects that impair mitochondrial function are under investigation. For example, restoring PINK1 or parkin function in neurons may enhance mitophagy and mitigate mitochondrial damage.
Mitochondrial Replacement Therapy: Mitochondrial replacement or mitochondrial transplantation holds promise as a therapeutic strategy for restoring mitochondrial function in PD. Early-stage studies are exploring the feasibility of mitochondrial transplantation into dopaminergic neurons to restore cellular function.
Exercise and Lifestyle Interventions: Regular physical exercise has been shown to stimulate mitochondrial biogenesis and improve mitochondrial function. Exercise-induced upregulation of mitochondrial regulators such as PGC-1α may provide neuroprotective benefits in PD by enhancing mitochondrial turnover and reducing oxidative damage.
Conclusion
Mitochondrial dysfunction is a central event in the pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease, contributing to the degeneration of dopaminergic neurons through mechanisms such as impaired mitochondrial complex I activity, oxidative stress, defective mitophagy, and disrupted calcium homeostasis. Genetic mutations in key mitochondrial regulators such as PINK1, parkin, and LRRK2 exacerbate these defects, while environmental toxins further contribute to mitochondrial damage. Targeting mitochondrial dysfunction through antioxidant therapies, gene therapy, and lifestyle interventions holds promise for mitigating the progression of Parkinson's disease. Understanding the intricate molecular mechanisms linking mitochondrial dysfunction to neurodegeneration in PD will be crucial for developing effective therapeutic strategies.

#Mitochondrial dysfunction#Parkinson’s disease (PD)#Dopaminergic neurons#Substantia nigra#Complex I activity#Oxidative stress#Reactive oxygen species (ROS)#Mitophagy#PINK1#Parkin#Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA)#Calcium homeostasis#Mitochondrial permeability transition pore(mPTP)#LRRK2#Alpha-synuclein#Mitochondrial dynamics#Genetic mutations in PD#Environmental toxins#Rotenone#Paraquat#Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10)#Antioxidant therapy#Gene therapy#Mitochondrial replacement therapy#Exercise and mitochondrial biogenesis#Neurodegeneration#Parkinsonian syndromes#Mitochondrial quality control#Mitochondrial fission and fusion#Neuroprotective therapies
0 notes
Text

TSRNOSS, p 748.
#acetyl groups#acetylcholine#acetyl coenzyme A#N-acetyl galactosamine#glucagon#radiation#dividing cells#radiation absorber
0 notes
Text
Boost Your Wellness with Coenzyme Q10 – Quantum Meta Health

Enhance your vitality with Coenzyme Q10, a powerful antioxidant known for supporting cellular energy. At Quantum Meta Health, we prioritize your health with premium wellness products. Coenzyme Q10 aids heart health, promotes skin vitality, and improves overall well-being. Experience natural rejuvenation today!
0 notes
Text
youtube
#CoQ10 levels#breast cancer#Pakistani women#oxidative stress#antioxidants#cancer biomarkers#cellular metabolism#Coenzyme Q10 deficiency#cancer progression#energy production#female patients#oncology research#cancer prevention#oxidative damage#personalized medicine#nutritional interventions#enzyme analysis#breast cancer subtypes#cancer diagnostics#prognostic markers.#Youtube
0 notes
Text
Key Benefits Coenzyme Q10 Nanoparticles - Flawless Beauty

0 notes
Text
Coenzym Q10+Vitamin E Tropfen
Die bei Dasvitamin.ch erhältlichen Coenzym Q10 + Vitamin E-Tropfen bieten eine leistungsstarke Kombination essentieller Nährstoffe zur Unterstützung der allgemeinen Gesundheit und Vitalität. Dieses Produkt nutzt die antioxidativen Eigenschaften von Vitamin E zusammen mit Coenzym Q10, das für seine Rolle bei der Energieproduktion und Zellgesundheit bekannt ist. Diese Tropfen sind ideal für alle, die ihre Wellness-Routine verbessern möchten und lassen sich leicht in den Alltag integrieren. Bestellen Sie jetzt, um die Vorteile dieses Premium-Ergänzungsmittels zu erleben. Please visit: https://www.canva.com/design/DAGP9757uM0/FC7pIUgZ5pD4ZEt8u0AFww/edit
0 notes
Text
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
0 notes
Text
3 Things Polyphenols Supplements Help With
Boosting Antioxidant Levels
Polyphenols are naturally occurring compounds found in plants that have powerful antioxidant properties. When taken as supplements, polyphenols can significantly boost the body's ability to fight off oxidative stress, which is linked to various chronic diseases. Antioxidants help neutralize free radicals, unstable molecules that can cause cellular damage. This protection is vital for maintaining long-term health and preventing conditions like heart disease, diabetes and certain cancers.
Supporting Heart Health
One of the key benefits of polyphenols vitamins is their ability to support heart health. These compounds help improve blood circulation and reduce blood pressure, which can lower the risk of cardiovascular diseases. Polyphenols also play a role in reducing inflammation, a critical factor in heart disease. By maintaining the elasticity of the arteries and inhibiting the oxidation of LDL cholesterol (often referred to as "bad" cholesterol), polyphenols help keep the cardiovascular system functioning smoothly.
Enhancing Brain Function
Polyphenols have shown promising results in enhancing brain function and protecting against neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's and Parkinson's. These compounds interact with the pathways involved in brain aging and can help improve memory, learning and cognitive function. By increasing blood flow to the brain and modulating neurotransmitter activity, polyphenols can help maintain cognitive abilities as we age.
Including polyphenols vitamins in your diet through supplements can be a proactive way to enhance your overall health and protect against various age-related diseases. Their broad range of benefits makes them a valuable addition to a health-conscious lifestyle.
Read a similar article about DHA omega vitamins here at this page.
#prenatal vitamins#sleep aid with valerian#mint tea for sleep#coenzyme Q10 supplement#gut health drink elixir#supplement for osteoporosis
0 notes
Text
Revitalize Your Heart: The Benefits of Simply Herbal CoQ10
Meta Description: Discover how Simply Herbal CoQ10 Tablets can support heart health and energy metabolism, promoting overall well-being.
Introduction: Simply Herbal CoQ10 Natural Coenzyme Q10 Tablets are a powerful dietary supplement designed to promote heart health and enhance energy metabolism. Coenzyme Q10, often referred to as CoQ10, is a vital nutrient found in every cell of the body, playing a crucial role in the production of energy. This article explores the heart health benefits of CoQ10 and how Simply Herbal’s formulation can support your cardiovascular wellness.
1. What is Coenzyme Q10? CoQ10 is a naturally occurring antioxidant that helps convert food into energy, particularly in the heart, which requires a significant amount of energy to function effectively. As we age, the levels of CoQ10 in our bodies may decrease, making supplementation important for maintaining optimal heart health.
2. Heart Health Benefits of CoQ10:

Supports Cardiovascular Function: CoQ10 has been shown to improve endothelial function, which is vital for maintaining healthy blood vessels and proper circulation. This can lead to improved overall heart function and reduced strain on the heart.
Reduces Oxidative Stress: As a powerful antioxidant, CoQ10 helps neutralize free radicals that can cause oxidative damage to heart cells. By reducing oxidative stress, CoQ10 supports overall heart health and longevity.
Improves Energy Metabolism: CoQ10 plays a key role in the production of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the energy currency of cells. By enhancing energy metabolism, CoQ10 helps ensure that the heart has the energy it needs to function efficiently.
May Support Healthy Blood Pressure: Some studies suggest that CoQ10 supplementation can help maintain healthy blood pressure levels, contributing to overall cardiovascular health.
3. Why Choose Simply Herbal CoQ10? Simply Herbal CoQ10 Tablets are formulated with Bioperine to enhance absorption, ensuring that your body receives the maximum benefits from each tablet. With 200mg of natural CoQ10 per serving, these tablets provide a potent dose for those looking to support their heart health.
4. How to Use Simply Herbal CoQ10:
Recommended Dosage: For optimal results, take one tablet daily with a meal. Consistency is key to experiencing the full benefits of CoQ10 supplementation.
Consultation: It’s advisable to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement, especially if you have existing heart conditions or are taking medications.
Conclusion: Simply Herbal CoQ10 Natural Coenzyme Q10 Tablets offer a convenient and effective way to support heart health and energy metabolism. With its powerful antioxidant properties and role in energy production, CoQ10 is essential for maintaining a healthy cardiovascular system. Incorporate Simply Herbal CoQ10 into your daily routine to promote heart health and enhance overall well-being.
#Heart Health#Coenzyme Q10#CoQ10 Benefits#Dietary Supplement#Antioxidants#Energy Metabolism#Cardiovascular Health#Natural Supplements#Simply Herbal#CoQ10 Tablets
0 notes
Text
Introducing Timeless Skincare Products | GenC Beauty
Timeless Skin Care offers a range of products that blend science with nature to deliver effective skincare solutions. From their vitamin C serums to their hyaluronic acid, each product is crafted to promote healthy, radiant skin that defies the passage of time. Order now from gencbeauty.com

#timeless-vitamin-c-e-ferulic-acid-serum#timeless-skin-care#timeless-skin-care-serum#timeless-vitamin-c-serum#timeless-skincare-canada#timeless-skin-care-vitamin-b5-serum#timeless-coenzyme-q10-serum
0 notes