#coastal marine ecosystems
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Excerpt from this story from Inside Climate News:
The Constitutional Court of Ecuador ruled that coastal marine ecosystems have legal rights that must be protected, potentially requiring stricter limits on human activities like industrial fishing.
Those ecosystems, the court said, have a right to maintain their natural “life cycles, structure, functions and evolutionary processes” and the Ecuadorian government must adopt sufficient protective measures to ensure those “vital processes” persist.
Marine coastal ecosystems have “intrinsic value,” the court added, and Ecuador made a commitment in its constitution to “build a new form of citizen coexistence, in diversity and harmony with nature.”
Ecuador, in 2008, became the first country in the world to recognize in a national constitution that nature, similar to humans and corporations, has legal rights. More than a dozen other countries have through legislation or court rulings recognized that ecosystems or individual species have rights, including to live, persist and regenerate.
Until now, all of Ecuador’s Constitutional Court rulings regarding nature’s rights have involved ecosystems on land, mangroves and wild animals. Lawyers familiar with rights of nature jurisprudence say the coastal marine ecosystem case, released late last year, is a landmark decision that extends heightened protections to the country’s vast aquatic ecosystems.
Ecuador, which includes the Galapagos Islands, is home to hundreds of fish species, whales, sea turtles, dolphins, sharks, manta rays and corals.
111 notes
·
View notes
Text

This majestic osprey is king of the beach in the Torrey Pines State Reserve in La Jolla, California! Resident birds include brown and white pelicans, plovers, American avocets, western sandpipers, willets, whimbrels, sanderlings, great egrets, and longbilled curlews.
youtube
#california#travel#beach#la jolla#north county san diego#southern california#san diego#youtube#socal#ocean#Osprey#Ospreys#Wildlife#Birdlife#Coastal Birds#Ecology#nature#Ecosystem#Nature Study#Marine Biology#Marine Life#Tidepools#Tide Pool#Youtube
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Vanishing Waters: Unveiling the Alarming Rate of Degradation in Our World's Water-Related Ecosystems

Our planet's water-related ecosystems are the lifeblood of biodiversity and play a crucial role in sustaining life on Earth. These diverse habitats, ranging from serene lakes and flowing rivers to vibrant coral reefs and teeming wetlands, provide essential services that are essential for human survival and the well-being of countless species. However, a looming crisis threatens the very existence of these vital ecosystems. The world's water-related ecosystems are being degraded at an alarming rate, putting our environment, wildlife, and even our own future at risk. In this article, we will delve into the causes, consequences, and potential solutions to combat this pressing issue and ensure the survival of these precious ecosystems.
The Magnitude of the Crisis
The degradation of water-related ecosystems is a global challenge that requires immediate attention. Around the world, these habitats are facing a range of threats, including pollution, habitat destruction, overfishing, climate change, and invasive species. These factors, often interconnected, are wreaking havoc on the delicate balance within these ecosystems.
Pollution: A Slow Poison
One of the leading culprits behind the deterioration of water-related ecosystems is pollution. Industrial waste, agricultural runoff, and untreated sewage find their way into our waters, contaminating them with harmful chemicals and plastics. These pollutants not only harm aquatic life but also have far-reaching consequences for humans who rely on these water sources for drinking and agriculture.
Habitat Destruction: Losing Our Natural Havens
The relentless expansion of human activities, including deforestation and urbanization, is rapidly encroaching upon the habitats of various aquatic species. Wetlands are drained, mangroves are cleared, and rivers are diverted, disrupting the natural flow and interconnectedness of these ecosystems. As a result, countless species lose their homes and face the threat of extinction.
Overfishing: Depleting the Ocean's Bounty
Overfishing is pushing marine ecosystems to the brink of collapse. Unregulated and unsustainable fishing practices, coupled with the demand for seafood, are causing a decline in fish populations, disrupting food chains, and jeopardizing the livelihoods of coastal communities that depend on fishing for survival.
Climate Change: The Silent Menace
Perhaps the most insidious threat to water-related ecosystems is climate change. Rising global temperatures lead to the melting of polar ice caps, causing sea levels to rise and intensifying storms and floods. These changes have devastating effects on coastal areas, submerging critical habitats, and causing the loss of biodiversity.
Consequences of Ecosystem Degradation
The degradation of water-related ecosystems has severe consequences for both the environment and human societies. As these ecosystems collapse, they disrupt the services they provide, such as water purification, flood control, and carbon sequestration, impacting human health and economies worldwide.
Biodiversity Loss: A Precarious Chain Reaction
Water-related ecosystems are home to a vast array of species, many of which are uniquely adapted to these environments. As these habitats deteriorate, many species face extinction, triggering a chain reaction that affects the entire ecosystem. The loss of one species can have cascading effects on others, disrupting the delicate web of life.
Threats to Food Security
Fisheries, both marine and freshwater, play a significant role in providing sustenance to billions of people around the globe. The depletion of fish populations due to overfishing and habitat destruction threatens the food security and livelihoods of millions, particularly in developing countries that heavily rely on fish as a primary protein source.
The Impact on Human Health
The quality of our water is directly linked to our health. Polluted water can cause waterborne diseases, affecting millions of people each year. Additionally, the loss of water-related ecosystems reduces the availability of clean water for drinking and sanitation, exacerbating the global water crisis.
Rising Economic Costs
The degradation of water-related ecosystems comes with a hefty price tag. Loss of fisheries, increased frequency of floods, and the decline of coastal protection services result in billions of dollars in economic losses each year. The expenses related to ecosystem restoration and mitigation efforts add further strain on already burdened economies.
Restoring the Balance: A Call to Action
Despite the grim picture painted by the state of our water-related ecosystems, there is hope. By acknowledging the urgency of the situation and taking collective action, we can begin the process of restoring the balance and ensuring the survival of these vital habitats.
Strengthening Environmental Regulations
Governments and policymakers must implement and enforce stringent environmental regulations to control pollution, protect habitats, and promote sustainable fishing practices. Strengthening international cooperation on environmental issues is also essential, as water-related ecosystems transcend national boundaries.
Sustainable Water Management
Water is a finite resource, and sustainable water management is key to ensuring the survival of water-related ecosystems. Implementing efficient irrigation systems, reducing water wastage, and prioritizing the conservation of natural water bodies are vital steps in this direction.
Embracing Renewable Energy
Transitioning to renewable energy sources can significantly mitigate climate change and its impact on water-related ecosystems. Embracing solar, wind, and hydroelectric power can reduce greenhouse gas emissions and limit the rise in global temperatures.
Community Involvement and Education
Engaging local communities in conservation efforts is crucial for the success of any environmental initiative. Raising awareness about the importance of water-related ecosystems and involving communities in restoration projects fosters a sense of ownership and responsibility.
Supporting Conservation Organizations
Supporting organizations like Green Thestral Inc. that are dedicated to environmental conservation can make a significant difference. Contributing to their efforts through donations or volunteer work helps fund critical projects aimed at protecting and restoring water-related ecosystems.
Conclusion
The state of the world's water-related ecosystems demands urgent attention and action from all corners of society. As individuals, communities, and nations, we hold the power to turn the tide and secure the future of these invaluable habitats. By addressing the root causes of degradation, promoting sustainable practices, and supporting conservation initiatives, we can pave the way for a healthier planet and a brighter future for all living beings. Together, let us safeguard the irreplaceable beauty and biodiversity of our water-related ecosystems for generations to come.
What's In It For Me? (WIIFM)
Are you concerned about the future of our planet and the well-being of its inhabitants? The degradation of the world's water-related ecosystems impacts us all. By understanding the urgency of this issue, we can take action to protect these vital habitats, safeguard our environment, and ensure a sustainable future for generations to come. Discover how you can make a difference in preserving the beauty and biodiversity of our precious water ecosystems.
Call to Action (CTA)
Join the movement to save our water-related ecosystems! Take action today by supporting Green Thestral Inc., an organization dedicated to environmental conservation. Donate to fund critical projects, volunteer to restore habitats, and spread awareness about the urgent need to protect these fragile ecosystems. Together, we can make a positive impact and secure the future of our planet's water habitats. Act now and be a part of the solution!
Blog Excerpt
The world's water-related ecosystems are under siege, facing a grave threat from human activities and climate change. These habitats, from serene lakes and rivers to vibrant coral reefs and wetlands, are essential for biodiversity and provide crucial services that sustain life on Earth. However, pollution, habitat destruction, overfishing, and rising temperatures are pushing these ecosystems to the brink of collapse. In our latest blog article, we delve into the alarming rate of degradation in these habitats, the consequences of their decline, and the actions we can take to protect and restore them. Join us in the fight to safeguard the future of our water-related ecosystems.
Meta Description (320 characters)
Discover the alarming rate of degradation in the world's water-related ecosystems and its impact on our environment. Learn how you can take action and be a part of the solution to protect these vital habitats. Join Green Thestral Inc. in the fight for environmental conservation.
#Degradation of water ecosystems#Alarming rate of habitat loss#Water pollution consequences#Impact of overfishing on ecosystems#Climate change and water habitats#Threats to marine biodiversity#Importance of wetland conservation#Coral reef degradation causes#Solutions for protecting rivers#Restoring freshwater habitats#Role of mangroves in coastal protection#Human impact on aquatic ecosystems#Water conservation and sustainability#Protecting endangered marine species#Ecosystem restoration initiatives#The link between human health and water quality#Economic effects of ecosystem collapse#Sustainable fishing practices#Conservation NGOs for water ecosystems#Community involvement in environmental protection#Global water crisis and its solutions#Rising sea levels and coastal ecosystems#Biodiversity loss in freshwater environments#Importance of clean drinking water#Erosion and riverbank degradation#Wetland restoration projects#Climate resilience of coral reefs#Protecting estuaries and deltas#Urbanization and water ecosystem destruction#The role of education in environmental awareness
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
youtube
Puffins: The Amazing Underwater Divers!
Did you know puffins can dive over 200 feet deep? Discover this and more about these fascinating sea birds!
Check out my other videos here: Animal Kingdom Animal Facts Animal Education
#Helpful Tips#Wild Wow Facts#Puffins#Underwater Diving#Wildlife Documentaries#Nature Films#Bird Watching#Marine Life#Animal Behavior#Puffin Facts#Puffin Habitat#Sea Birds#Ocean Exploration#Wildlife Conservation#Avian Species#Puffin Nesting#Bird Migration#Nature Education#Ocean Life#Coastal Ecosystems#Diving Birds#Puffin Feeding#Nature Lovers#Bird Enthusiasts#Environmental Awareness#Fun Facts About Puffins#Puffin Videos.#Youtube
0 notes
Text
youtube
Glacier Calving: The Powerful Force Behind Massive Waves and Climate Change Insights
Glaciers, those monumental rivers of ice flowing from high mountain peaks and polar regions, are not only stunningly beautiful but also hold incredible, often unpredictable power. Among the most captivating and intense events involving glaciers is glacier calving—a natural process where enormous ice chunks break away from a glacier’s edge and crash into surrounding water. This dramatic phenomenon not only creates an unforgettable visual display but also generates massive waves. In this article, we’ll explore glacier calving, what causes it, the powerful waves it creates, and the broader implications for ecosystems, human activity, and climate science.
What is Glacier Calving?
Definition: What is Glacier Calving?
Glacier calving is the process where large pieces of ice detach from a glacier's edge and fall into the adjacent water. These ice chunks vary in size, from small pieces to massive blocks as large as multi-story buildings. Calving is a powerful and visually spectacular event that can produce waves felt miles away.
Where Does Glacier Calving Occur?
Calving occurs most frequently at the terminus (the end) of glaciers that extend into bodies of water like lakes, oceans, or fjords. It’s most common in polar regions, such as Greenland and Antarctica, where glaciers meet the sea. These environments allow ice chunks to break off and fall into the water, forming waves that can be incredibly powerful and far-reaching.
How Does Glacier Calving Happen?
Calving happens due to the natural movement of glaciers. As a glacier moves forward, driven by gravity, the ice at its edge becomes thinner and fractures. Over time, these fractures deepen, eventually causing large chunks of ice to break away. The forward motion pushes these ice chunks towards bodies of water, where they drop, creating an impactful and sudden splash.
The Science Behind Glacier Calving and Wave Formation
Ice Dynamics and Fracture Mechanics
The constant advance of glaciers creates stress along their edges, leading to cracks and fractures in the ice. When the ice reaches a critical fracture point, large sections break off. This detachment causes sudden displacement as the ice hits the water, creating waves that can be extremely powerful.
How Does Glacier Calving Generate Waves?
When an ice chunk detaches and crashes into the water, it displaces the water around it, creating a splash and powerful shockwaves. The size and intensity of the resulting wave depend on the size of the ice chunk. Larger ice pieces create more significant waves, capable of traveling far distances.
Wave Propagation in Glacier Fjords and Bays
Once a calving event occurs, the waves created by the impact move outward from the point of collision. In confined areas, like fjords or bays, these waves can be particularly intense. They bounce off rock walls, sometimes becoming even larger and more forceful, and can travel for kilometers, posing a danger to anything in their path.
The Impact of Calving Waves on Ecosystems and Human Activity
Environmental Impact: How Calving Waves Affect Marine Ecosystems
Calving waves can have a significant effect on local ecosystems. The waves stir up the seabed, displacing marine organisms and disturbing habitats. Over time, repeated calving events can also erode coastal areas, affecting both flora and fauna in the surrounding environment.
Human Implications: Why Calving Waves Are Dangerous
For people living in or near glacier regions, calving waves can pose severe risks. Fishing vessels, research ships, and tourist boats are especially vulnerable, as calving waves have capsized boats and caused substantial damage in the past. Coastal communities near glaciers or fjords may also feel the impact of these waves, making it important for ships and local authorities to remain vigilant.
Climate Change and Glacier Calving: A Connection with Global Implications
Climate change is accelerating glacier calving worldwide. Rising temperatures cause glaciers to melt and thin, making them more prone to calving events. This not only increases the frequency of calving but also contributes to global sea level rise as more ice melts and enters the ocean. Areas like Greenland and Antarctica, where calving is occurring at unprecedented rates, are contributing significantly to rising seas—a growing concern for coastal cities and communities worldwide.
Notable Glacier Calving Events and Their Massive Waves
To understand the sheer power of glacier calving, let’s look at some notable glaciers known for their spectacular calving events.
Jakobshavn Glacier, Greenland: One of the fastest-moving glaciers globally, Jakobshavn has witnessed some of the largest calving events on record. Chunks of ice as large as skyscrapers break off, creating waves that can be felt miles away.
Hubbard Glacier, Alaska: This Alaskan glacier is known for periodic large calving events that generate waves affecting cruise ships and other vessels in nearby fjords. This glacier’s movements attract scientists and tourists alike, both drawn by its power and potential risks.
Pine Island Glacier, Antarctica: As a significant contributor to ice loss in Antarctica, Pine Island Glacier’s calving events are substantial enough to be detected by seismometers thousands of miles away, showcasing the global scale of calving’s impact.
Fascination and Caution: Observing Glacier Calving Events
The Appeal of Glacier Tourism
For many tourists, witnessing a glacier calving event is a once-in-a-lifetime experience. The intense sound—often compared to a thunderous "crack" or "roar"—followed by a massive splash and radiating waves, creates a powerful, memorable scene. Locations such as Alaska, Greenland, and certain parts of Antarctica are popular destinations for this reason.
Safety Precautions for Viewing Glacier Calving Events
Despite their allure, calving events are highly unpredictable, and the waves they generate can be dangerous. Tourism operators and guides near glaciers must take strict precautions, maintaining safe distances from glaciers to ensure the safety of visitors. Special care is necessary for boats, as the waves can capsize small vessels that venture too close.
The Future of Glacier Calving and Its Impact on Sea Level Rise
As climate change continues to increase global temperatures, glaciers worldwide are expected to retreat and calve more frequently. This trend not only raises the likelihood of dangerous waves but also leads to long-term impacts, such as accelerated sea-level rise. Glacier calving events remind us of the urgent need to address climate change and mitigate its effects on our planet’s natural systems.
Conclusion: Glacier Calving as a Reminder of Nature’s Power
In summary, glacier calving is a breathtaking natural event and a powerful force with significant environmental, social, and scientific implications. From the thunderous crash of falling ice to the waves that ripple across fjords and bays, glacier calving captivates us while serving as a stark reminder of the interconnectedness of Earth’s natural systems. As climate change continues to reshape our world, glacier calving highlights the need to understand and preserve these fragile ice giants that are vital to our planet’s health and future.
By understanding glacier calving, its causes, and its consequences, we not only gain insight into one of nature’s most spectacular displays but also increase our awareness of the urgent climate issues facing our planet today.
Go To The Power of Glacier Calving
#glacier calving#calving waves#glacier waves#environmental impact of glaciers#climate change glaciers#sea level rise#melting glaciers#Arctic glaciers#Antarctic icebergs#Greenland glaciers#glacier tourism#glacier ecosystems#glacial ice fracturing#marine ecosystems climate change#global warming impacts#glaciers and climate change#coastal erosion by glaciers#Pine Island Glacier#Jakobshavn Glacier#Hubbard Glacier Alaska#glacier safety measures#glacier calving events#polar science#fjord waves from glaciers#climate change impacts on ice#Youtube
0 notes
Text
"The coral reefs of south Sulawesi are some of the most diverse, colorful and vibrant in the world. At least, they used to be, until they were decimated by dynamite fishing in the 1990s.
As part of a team of coral reef ecologists based in Indonesia and the UK, we study the reefs around Pulau Bontosua, a small Indonesian island in south Sulawesi...
In many places around the world, damage like this might be described as irreparable. But at Pulau Bontosua, the story is different. Here, efforts by the Mars coral restoration program have brought back the coral and important ecosystem functions, as outlined by our new study, published in Current Biology. We found that within just four years, restored reefs grow at the same rate as nearby healthy reefs.
Speedy recovery
The transplanted corals grow remarkably quickly. Within a year, fragments have developed into proper colonies. After two years, they interlock branches with their neighbors. After just four years, they completely overgrow the reef star structures and restoration sites are barely distinguishable from nearby healthy reefs.
The combined growth of many corals generates a complex limestone (calcium carbonate) framework. This provides a habitat for marine life and protects nearby shorelines from storm damage by absorbing up to 97% of coastal wave energy.
We measured the overall growth of the reef framework by calculating its carbonate budget. That's the balance between limestone production (by calcifying corals and coralline algae) and erosion (by grazing sea urchins and fishes, for example). A healthy reef produces up to 20kg of reef structure per square meter per year, while a degraded reef is shrinking rather than growing as erosion exceeds limestone production. Therefore, overall reef growth gives an indication of reef health.
At Pulau Bontosua, our survey data shows that in the years following restoration, coral cover, coral colony sizes, and carbonate production rates tripled. Within four years, restored reefs were growing at the same speed as healthy reefs, and thereby provided the same important ecosystem functions...
Outcomes of any reef restoration project will depend on environmental conditions, natural coral larvae supply, restoration techniques and the effort invested in maintaining the project. This Indonesian project shows that when conditions are right and efforts are well placed, success is possible. Hopefully, this inspires further global efforts to restore functioning coral reefs and to recreate a climate in which they can thrive."
-via Phys.org, March 11, 2024
#coral#coral reef#marine life#marine biology#sea creatures#aquatic#environment#ecology#environmental news#environmental science#climate action#climate hope#ecosystem#conservation#endangered species#indonesia#sulawesi#good news#hope#overfishing#hopepunk#hope posting
6K notes
·
View notes
Text
The Devastating Impact of Fossil Fuels: Why We Need to Transition to Renewable Energy
Fossil fuels have been the primary source of energy for decades, but their use is causing significant harm to our planet. The burning of fossil fuels, such as coal, oil, and natural gas, is a major contributor to climate change, air pollution, and environmental degradation. In this blog post, we will explore the damage that fossil fuels are causing to the world and why it is important to…

View On WordPress
#Air pollution and its impact on global health: the role of fossil fuels#and geothermal power#fossil fuels#How the burning of fossil fuels is contributing to climate change#hydro#Renewable energy alternatives: solar#The economic costs of relying on non-renewable energy sources#The environmental damage caused by fossil fuel extraction and transportation#The harmful effects of fossil fuels on the environment and human health#The impact of oil spills on marine life and coastal ecosystems#The importance of reducing our carbon footprint through the use of renewable energy#The long-term benefits of investing in renewable energy for a sustainable future#Why transitioning to renewable energy is crucial for a sustainable future#wind
0 notes
Text
Coral reefs worldwide are in trouble. These ecosystems support a billion people and more than a quarter of marine species. Still, many have been damaged by unsustainable fishing and tourism, coastal construction, nutrient runoff, and climate change. Now, researchers have shown that broadcasting the sounds of healthy reefs is a way to encourage larval corals to repopulate degraded sites and help revitalize them.
Continue Reading.
446 notes
·
View notes
Text

The king eider (pronounced /ˈaɪ.dər/) (Somateria spectabilis) is a large sea duck that breeds along Northern Hemisphere Arctic coasts of northeast Europe, North America and Asia. The birds spend most of the year in coastal marine ecosystems at high latitudes, and migrate to Arctic tundra to breed in June and July. They lay four to seven eggs in a scrape on the ground lined with grass and down.
393 notes
·
View notes
Text
Spectember 2024 #02: Swimming Swine
An anonymous submitter asked for a "buoyant ungulate that runs atop the sea":

Pontoporcus plotus is a 1.5m long (~5') amphibious pig descended from a feral population of domestic pigs left on a small tropical island. After inadvertently wreaking havoc on much of the local ecosystem, its ancestors eventually turned to a more marine-based lifestyle foraging along beaches and in coastal waters.
Naturally highly buoyant, Pontoporcus actually floats so well that it's mostly limited to the water's surface, unable to dive to any significant degree. But despite this it's a fairly good swimmer, using broad hooves with wide fleshy pads to paddle itself along in an aquatic trotting- or running-like gait.
It forages both on land and in the water, mainly eating soft vegetation and marine plants, but much like its ancestors it will also opportunistically feed on whatever smaller animals it can catch or scavenge. Its semi-prehensile trunk-like snout is used to grasp at food items, to probe and root around in soft sediment, and as a snorkel.
Its hairless skin is very susceptible to sunburn, but it secretes a thick oily red-brown substance (similar to modern hippo "blood sweat") that acts as a natural protective sunscreen.
These pigs are accomplished island-hoppers, regularly traversing the relatively shallow seas all along their island chain – but their natural flotation and long fat bodies also make them prime targets for large aquatic predators attacking from below, so these journeys tend to involve groups of Pontoporcus "running" along the sea surface aiming for their next destination as fast as they possibly can.
#spectember#spectember 2024#speculative evolution#pig#suidae#artiodactyla#ungulate#mammal#marine mammals#art#science illustration
234 notes
·
View notes
Text
Speed of Science🧬💻💌
I'm dating a STEM girlie and you're not (F1 Edition)



a/n: and im baaaaaacccckkkkk (like anyone even missed me lmao) with the long overdue request! life of a postgrad StEm girlie here and the struggle is really realll af. but besides that, I'm writing this down as a headcanon for the drivers requested on this poll i had posted long back here. I've always wondered how there's soo minimal povs/ocs where they are a scientific researcher, analyst, etc. sooo i dedicate this one to all the STEM F1 girlies out theree <33
alsoo quick shoutout to my girlieee @smoooothoperator for inspiring and motivating me to get back at writing!🥹🫶🏼 check out her lastest ongoing work 'What Was I Made For? ' its amazing and thats a FACT!! do check her works! its absolutely amazing❤️
check out my works: until i found you masterlist | other works
Scientific Art Illustrator - Charles Leclerc
As a Scientific Art Illustrator, you specialize in creating visually captivating and scientifically accurate illustrations that depict complex biological, astronomical, or technological subjects.
Charles first discovered you through your works at an exhibition where their stunning illustrations of Formula 1 cars caught his eye. Impressed by their attention to detail and artistic talent, they struck up a conversation about their mutual love for precision and creativity.
During a peaceful weekend afternoon, Charles suggests a spontaneous visit to a local art supply store. Excitedly exploring aisles stocked with vibrant paints, fine brushes, and specialized papers, the two of you engage in discussions about artistic techniques and innovative tools. Amidst laughter and shared enthusiasm for creativity, you bond over your mutual appreciation for the intricacies of art and science, making the afternoon a cherished memory of their shared passions.
After being away from home during race season, Charles always finds a framed series of sketches by you for the races you couldn't make it, capturing his most memorable racing moments. Each sketch is intricately detailed, depicting not only the speed and intensity of the races but also the emotions and determination etched on Charles' face. Touched by the thoughtful gesture, Charles hangs the sketches in his study, a constant reminder of your support and admiration for his passion.
...
Data Scientist - Lando Norris
A Data Scientist specializes in analyzing large volumes of data using statistical methods and machine learning techniques to extract insights and make data-driven decisions.
You and Lando first connected through a mutual fascination with racing data at a technology symposium focused on sports analytics. Your presentation on advanced predictive modelling in motorsports caught Lando's attention for its innovative approach to enhancing race strategies.
During a cosy evening at home, Lando playfully challenges you to a friendly data analysis competition using real-time telemetry from previous races. Their banter and shared excitement over dissecting racing data create a lighthearted and memorable bonding experience.
You two would watch old races and analyze historical racing data together, playfully debating optimal pit stop strategies and analyzing driver performance trends, their shared passion for racing and data fostering a deep connection and mutual admiration.
...

Oceanographer/Marine Biologist - Oscar Piastri
An Oceanographer or Marine Biologist studies marine life, ecosystems, and ocean processes to understand and protect marine environments and resources.
You and Oscar crossed paths during a research expedition to study coral reefs in a remote location. Your expertise in marine biology and passion for conservation impressed Oscar, sparking their connection.
Amidst the hectic F1 season, Oscar surprises you with a weekend getaway to a coastal retreat, where they explore tide pools and participate in a beach cleanup together, reaffirming their commitment to environmental stewardship.
You gave Oscar a custom-made charm bracelet featuring miniature charms of marine animals they've discussed during their beach walks and conservation talks. Each charm represents a meaningful moment in their relationship, from their first discussion about oceanography to their shared admiration for marine life. Oscar wears the bracelet during race weekends as a reminder of you and all the love and support you give, both on and off the track.
...

Mechanical Engineer - Daniel Riccardo
You are a passionate Mechanical Engineer, specializing in advanced automotive design and performance optimization.
Daniel first encountered you at a technical conference organized by one of the team sponsors where you presented groundbreaking research on aerodynamic innovations that caught his attention.
Often, while you meticulously draft engineering schematics at their home office, he makes sure that you have your "engineering emergency kit" beside your workstation, which is a tray of snacks and their favourite coffee – ensuring they're fueled for their late-night brainstorming sessions. For when he's away for races, he stacks them up with small cute notes.
Before Daniel heads to a crucial race, you surprise him with a meticulously crafted miniature replica of his race car, complete with detailed decals and a personalized message of encouragement engraved on the base. Touched by the thoughtful gesture, Daniel proudly displays it in his motorhome, a reminder of the reader's unwavering support both on and off the track.
...

Statistician - George Russell
A Statistician specializes in collecting, analyzing, and interpreting numerical data to help organizations and individuals make informed decisions.
You and Russell first crossed paths during a university seminar on advanced statistical modeling in sports. Your insightful analysis of Formula 1 race data caught George's attention, sparking a lively discussion that led to mutual admiration for each other's analytical skills and shared passion for racing statistics.
During a particularly demanding race weekend, the reader surprises George with a meticulously prepared statistical analysis report highlighting his strengths and areas for improvement based on recent race data. This thoughtful gesture boosts George's confidence and motivation, showing the reader's support in his pursuit of excellence.
During a weekend getaway, you guys stumble upon a local go-kart track. George, always up for a challenge, suggests they have a friendly race. Knowing George's competitive spirit, you secretly calculate his optimal strategy and surprise him by winning with a perfectly executed last-minute overtaking maneuver. George is impressed by the your strategic thinking and playfulness, and they share a lighthearted and joyous moment celebrating their shared love for racing and friendly competition.
...

Astrophysicist - Logan Sargeant
An Astrophysicist studies the physical properties, behavior, and evolution of celestial objects such as stars, planets, galaxies, and the universe as a whole, using principles of physics and astronomy.
Logan and you first crossed paths during an expedition to study a rare astronomical event—a comet passing close to Earth. Both passionate about astrophysics, you found yourselves sharing a telescope at a remote observatory, marveling at the comet's beauty and discussing its celestial significance late into the night. Their shared awe and intellectual connection sparked a mutual admiration that grew into a deep bond over their shared passion for exploring the wonders of the cosmos.
During a quiet evening at home, Logan excitedly shows you a new telescope he acquired for stargazing during race weekends, expressing his eagerness to learn more about the cosmos together and sharing their enthusiasm for both racing and astrophysics in equal measure.
Before a critical race weekend, the reader surprises Logan with a personalized star chart that maps out the night sky above the upcoming race venue during the race weekend. Each star on the chart is marked with a heartfelt message of encouragement, reminding Logan of their unwavering support and belief in his abilities on and off the track. Touched by the thoughtful gesture, Logan treasures the star chart as a symbol of the reader's love and encouragement throughout his racing career.
...

Climate Scientist - Lance Stroll
A Climate Scientist studies climate patterns, environmental changes, and their impacts on Earth's ecosystems, using data analysis and modeling to understand and address global climate challenges.
Lance crossed paths with you at an eco-friendly racing event where Lance was advocating for sustainable practices in motorsport. Being a respected climate scientist, you caught Lance's attention with your insightful presentation on the environmental impact of racing and innovative solutions for reducing carbon footprints in the sport. Their shared passion for sustainability sparked an immediate connection and admiration for each other's dedication to making a positive impact on the environment.
One weekend, Lance surprises you with a homemade dinner featuring sustainably sourced ingredients, proudly showcasing his culinary skills while discussing ways to reduce your carbon footprint. His earnest commitment to sustainability and your shared vision for a healthier planet melts your heart, making this a cherished moment you both treasure.
You, being deeply involved in climate science, often spends late nights analyzing data or writing research papers. One evening, Lance bring him a cozy blanket and a mug of your favorite hot beverage, quietly sitting beside him as he works. You look up from your laptop, touched by his thoughtfulness, and pulls him into a warm embrace, grateful for his unwavering support and understanding of your demanding but vital work.
...
taglist: @lndonrris @thatgirlmj @lwstuff @dannyramirezwife-f1dump @moonypixel tysm for your suggestions! apologies on taking this long to write😅🫶🏼
a/n: hope y'all enjoyed reading this! this was my first time writing a headcanon and for f1 drivers beside charles and lando so hope i did justice to all.
i'm being wanting to read some good domestic bliss, sweet, adorable and lovey dovey blurbs, fics of lando (i talked abt it here) soo maybe i'll work on some drafts at some point cause i'm currently in the middle of project work of my masters degree soo don't know when i'll be posting soo until next time, see yaaa and going back to read mode 👋💓✨️
check out my works: until i found you masterlist | other works
#f1 x reader#f1 headcanons#charles leclerc#charles leclerc x reader#lando norris#lando norris x reader#oscar piastri#oscar piastri x reader#daniel ricciardo#daniel ricciardo x reader#george russell#george russel x reader#logan sargeant#logan sargent x reader#lance stroll#lance stroll x reader#f1 driver x you#f1 driver x reader#formula one
316 notes
·
View notes
Text
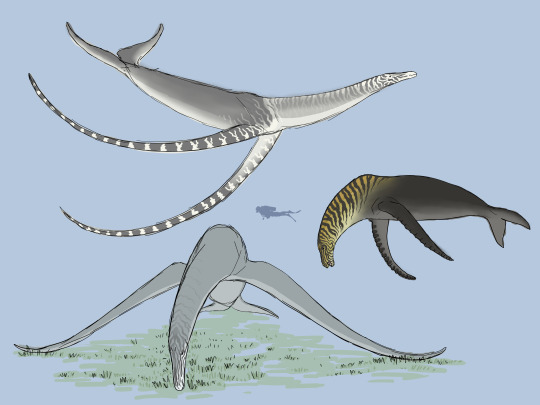
Some sketchy concept stuff that I'm posting because I liked it but couldn't be bothered to refine it into an actual artwork.
These submarine behemoths are the Mermares (Clade Euhippocampiformes), secondarily aquatic descendants of the domestic donkey. The group first appeared around 29 million years post-cataclysm, in the late Nerian stage of the Diluvian period. They evolved from an animal called the Seabra, a descendant of the Donkey which adapted to exploit a niche with, thus far, zero competition - that of a large marine herbivore.
On earth, marine ecosystems are notable for the distinct lack of vascular plant life, a condition caused by a number of factors - most notably the osmotic stress caused by the saltwater. Most photosynthesis is carried out by algae. On Spero, however, things are different. Because Spero's oceans were generated relatively recently, from extraterrestrial ice particles, there just hasn't been enough time for erosion and the water cycle to deposit dissolved minerals in the water. As a result, Spero's seas are made of freshwater - a much more tolerable condition for most plants, and thus the diversity of marine vascular plants is much, much higher than on earth. Also, due to the flatness of the flooded landscape and lack of any real tectonic features, enormous swathes of the seabed lie within the photic zone, less than 200 meters from the surface. Thus, endless expanses of marine grasslands - the "seagrass prairies" - extend from the shore, often for hundreds of miles before the water finally gets too deep for photosynthesis to occur.
All of this plant life is an extremely attractive prospect for herbivores, and it was likely what drew the ancestral Seabra to forage in shallow coastal meadows in the first place. But as the oceans got deeper and life adapted, the Seabra had to adapt in kind - their hind legs rotated backwards to act as a pair of propulsive flukes, their forelimbs developed into steering flippers, and their nostrils retreated to sit on their foreheads.
One notable feature of the Mermares is hyperphalangy, a condition where the fingers have too many bones. It's very common in large marine tetrapods in Earth's history - whales and dolphins, Ichthyosaurs, Plesiosaurs, and Mosasaurs all exhibited hypoerphalangy to some degree - and seems to be associated with the specialization of the limbs into flippers. We would expect to see similar patterns in marine lineages on Spero. What's unique about the Mermares, however, is the sheer number of extra phalanges in the finger; at least fifteen in the shorter-finned species, and more than thirty in the longest-finned forms. And because Mermares - being equids - only possess one digit per limb, the result is a single long chain of flat, squarish bones which, in some cases, can reach over forty feet long - the longest arms ever to exist.
These ridiculous appendages produce a lot of drag and are merely adequate for steering and stabilization. So why do the Mermares have them?
The answer is that they're weapons. And particularly devastating ones, at that.
Mermares use their flagellating flippers as bludgeons, against both predators and conspecifics. The flippers are connected to powerful neck muscles and can be swung forward with impressive force; combined with a well-timed twisting of the giant horse's torso, the huge flippers can impact hard enough to shatter bone and pulverize flesh. The flippers themselves do not escape unscathed, and older individuals often have scarred or mangled flipper-tips from numerous battles over the years; but it's a small price to pay for survival.
When not being used against their enemies, the flippers may be folded back against the sides of the animal to reduce drag, or used as props to keep the animal's belly up off the seabed when feeding. Mermares spend up to 18 hours per day grazing, using their long neck to crop aquatic grasses and other vegetation in a wide arc without moving their bodies and occasionally dipping up to the surface to breathe. Mermares are keystone species in the seagrass prairies; as hindgut fermenters, they are not as efficient at processing plant matter as ruminants like goats, and produce large amounts of nutrient-rich dung which acts as fertilizer for the meadows and helps keep the environment productive. The dung also acts as food for a variety of fish and invertebrates.
Let's look at some of the Mermare's diversity, shall we?
Drepanarion (center right) One of the smaller Mermares, Drepanarion nonetheless grows to nearly 12 meters (39 feet) long. It is immediately recognizable by the bold black-and-yellow striping on the heads and necks of the stallions, and by the tall, narrow nuchal crest which extends from the withers and makes the stocky body look even more powerful. Unlike most other Mermares, which live in small groups of less than ten individuals, Drepanarion can be found in herds of over a hundred in the seagrass prairies of the Savanian (41 - 50 million years post-cataclysm). These nomadic throngs graze patches of seagrass nearly to the roots before moving on, giving the ecosystem time to regrow before returning in a few years' time. Drepanarion exhibits the most extreme sexual dimorphism of any Mermare, with stallions being both larger and more brightly coloured than mares; during the annual rut, males will fight each other in brutal bludgeoning matches to establish dominance and secure mates. To this end, they have some of the most extreme flipper anatomy of any Mermare; though not especially long (indeed, they have the shortest flippers of any derived genera), each phalanx bone has a protruding bony tubercle on the anterior edge which extends into a keratinous knob. These knobs both protect the flipper during combat and focus the force of the blow into a smaller area, dealing more damage.
Hipposeidon (bottom left) First appearing in the early Imberian (50 million years post-cataclysm), Hipposeidon is the largest of all Mermares and, indeed, the largest animal ever to exist on Spero, with stallions regularly reaching over 24 meters (80 feet) long (mares are slightly smaller). Extremely large specimens may even reach 30 meters (100 feet), although this is rare. This ludicrous size - nearly rivaling even the mighty Blue Whale of Earth - is possible only due to the sheer abundance of its food. Hipposeidon appears at the height of the seagrass prairie's extent, and can pack away almost 900 kilograms (1900 pounds) of seagrass per day. This superlative food requirement has important consequences for Hipposeidon's behaviour; this animal is migratory. Seagrass prairies are extremely productive ecosystems, but nonetheless Spero is a seasonal world; as the summer growth gives way to the winter die-back, the greatest of the Mermares must migrate across the equator to seek out a continuous food source to fuel its immense bulk. In this way Hipposeidon experiences a perpetual summer, interrupted only by the biannual migration from north to south and back again. Female Hipposeidon are pregnant for about one year, timing the birth of the single large foal with arrival to the feeding grounds; the six-meter-long foal enjoys a long childhood nursing and playing in shallow summer waters, gathering strength before making the long swim across the barren tropical zone to pastures new.
Bathypegasus (top left) The last and possibly the weirdest of the great Mermares, Bathypegasus is the only member of the clade which is not a grazer. Instead, it is a specialist feeder on pelagic, free-floating ferns. These ferns are a seasonal bounty, growing in huge numbers in the tropical summers of the late Imberian (60 million years post-cataclysm), where the planetary ring system shades out large portions of the planet for half the year. A close relative of Hipposeidon, Bathypegasus has left its ties to the seabed behind, becoming a fast, powerful swimmer which spends most of its life far above the sea floor. Its flippers have adapted to be even more ludicrously long - the longest forearms of any animal, ever, with each one measuring nearly 14 meters (45 feet) in length and each containing at least 35 individual bones. No longer used to prop the animal up off the seabed, these whiplike flippers are narrow and streamlined and can be whipped through the water at speeds of nearly 20 meters per second (that's over 40 mph) - the most extreme weaponry of any Mermare, and used to great effect against predators. Bathypegasus, like Hipposeidon, is migratory, following the blooms of pelagic ferns across Spero's oceans. Thanks to this midwater diet it is the only genus of Mermare to survive past the mid-Imberian extinction, when rising sea levels and steepening coastal slopes caused the seagrass prairies to disappear. Bathypegasus finally died out in the Ultimoxerian stage, around 75 million years post-cataclysm, the last and weirdest of the giant marine horses.
#spec bio#spec evo#speculative biology#speculative evolution#Vicis Aeternum#Spero#seed world#equid#donkey#they're like if a whale and a horse had a baby and that baby was somehow also a diplodocus
867 notes
·
View notes
Text

Learn About Nurseries of the Marine World in the La Jolla Peninsula & Torrey Pines State Reserve! Bird Life, Aquatic Marine Species, Baby animals, Ospreys, Whales, Dolphins, and the beautiful turquoise teal blue Pacific Ocean: Live Now On YouTube!
youtube
#youtube#southern california#california#beach#travel#la jolla#san diego#north county san diego#ocean#socal#Marine LIfe#Marine Biology#Ecology#Ecosystem#Wildlife#Osprey#Ospreys#Osprey Nest#Nature#Coastal Wildlife#Aquatic Wildlife#Nature Study#Earth Science
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
Unveiling the Secrets of Life Below Water: Goal 14 for a Sustainable Future

In our journey towards achieving a sustainable future, Goal 14 of the United Nations' Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) plays a pivotal role. Life Below Water, as it is commonly referred to, focuses on the preservation and sustainable use of oceans, seas, and marine resources. With this goal, the international community aims to safeguard marine ecosystems, mitigate the impacts of human activities, and promote sustainable livelihoods for coastal communities. This article delves into the significance of Goal 14, explores the challenges faced, and highlights the initiatives that can help us ensure a healthier and more vibrant life below water.
Understanding the Importance of Goal 14
The Earth's oceans are vast and cover more than 70% of the planet's surface. They are teeming with life and harbor a remarkable diversity of species and ecosystems. From the mesmerizing coral reefs to the mysterious depths of the abyss, the oceans are a treasure trove of biodiversity, supporting millions of species, including plants, animals, and microorganisms.
Beyond their ecological significance, the oceans play a crucial role in regulating the Earth's climate. They act as a massive heat sink, absorbing a significant amount of the sun's energy and distributing it across the planet. Additionally, oceans play a vital role in the water cycle, facilitating the evaporation of water, which then falls as precipitation and sustains terrestrial ecosystems.
The oceans are not only important for the environment but also for human societies. They provide sustenance to millions of people around the world. Fishing, both for subsistence and commercial purposes, is a primary source of livelihood for coastal communities. The oceans also support economic activities such as tourism, shipping, and offshore industries, contributing significantly to global economies.
However, the delicate balance of marine ecosystems is under threat due to various human activities. Overfishing, driven by unsustainable practices and the demand for seafood, has led to the depletion of fish stocks worldwide. Large-scale industrial fishing, with destructive methods such as bottom trawling, threatens not only the targeted species but also the entire marine food web.
Marine pollution is another significant challenge faced by the oceans. Pollution from land-based sources, including plastic waste, chemicals, oil spills, and agricultural runoff, finds its way into the marine environment, causing severe harm to marine life and ecosystems. The accumulation of plastic debris in the oceans has reached alarming levels, forming giant garbage patches and causing entanglement and ingestion by marine organisms.
Habitat destruction and degradation are also taking a toll on marine ecosystems. Destructive practices such as coral reef destruction, coastal development, and the destruction of mangroves and seagrass beds result in the loss of critical habitats and the disruption of delicate ecological relationships. These habitats serve as nurseries and breeding grounds for many species, and their loss has far-reaching consequences for marine biodiversity.
Furthermore, climate change poses one of the most significant threats to life below water. Rising sea temperatures, ocean acidification, and sea-level rise are already impacting marine ecosystems. Corals, which are vital for the survival of countless marine species, are particularly vulnerable to rising temperatures and increased ocean acidity, leading to coral bleaching events and the degradation of coral reefs.
In recognition of the urgent need to protect and sustainably manage marine resources, Goal 14 of the United Nations' Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) was established. Also known as Life Below Water, this goal aims to ensure the conservation and sustainable use of the oceans, seas, and marine resources for present and future generations.
Goal 14 encompasses various targets and indicators to guide efforts towards sustainable ocean management. One of the key focuses is the protection and restoration of coral reefs, which are among the most diverse and valuable ecosystems on Earth. Coral reefs provide habitat for numerous species, protect coastlines from erosion, and support vibrant tourism industries. By implementing measures to reduce coral bleaching, enhance reef resilience, and combat destructive practices, Goal 14 seeks to safeguard these vital ecosystems.
Another critical aspect of Goal 14 is the reduction of marine pollution. It calls for the prevention and significant reduction of marine debris, particularly plastic waste. Efforts are being made to promote better waste management systems, recycling and reusing plastics, and raising awareness about the detrimental effects of single-use plastics. Innovative technologies for ocean cleanup are also being developed to tackle existing pollution.
To address the issue of overfishing, Goal 14 emphasizes the need to restore fish stocks to sustainable levels. This involves implementing science-based management plans, combating illegal, unreported, and unregulated fishing, and promoting responsible fishing practices. Creating marine protected areas and adopting ecosystem-based management approaches can help protect critical habitats and ensure the long-term viability of fisheries.
Furthermore, Goal 14 acknowledges the urgent need to address ocean acidification, which poses a grave risk to marine organisms. By reducing carbon dioxide emissions and taking steps to enhance the resilience of marine ecosystems, such as protecting mangroves and seagrass beds, this goal aims to mitigate the impacts of ocean acidification and ensure the survival of vulnerable species.
Achieving Goal 14 requires a collaborative effort from governments, businesses, civil society organizations, and individuals worldwide. International cooperation is crucial to strengthen governance frameworks, regulate resource exploitation, combat illegal fishing, and promote sustainable practices. By taking collective action and embracing sustainable approaches, we can secure a healthier and more vibrant future for life below water.
Challenges and Threats to Life Below Water
The life below water faces a multitude of challenges that require immediate attention and concerted efforts. Overfishing, driven by unsustainable practices and illegal, unreported, and unregulated fishing, has led to a decline in fish stocks worldwide. The loss of biodiversity affects not only marine ecosystems but also the communities that depend on them for food security and economic opportunities.
Marine pollution poses another significant threat. Plastic waste, chemicals, oil spills, and other pollutants contaminate the oceans, harming marine life and ecosystems. The accumulation of plastic debris, in particular, has gained global attention due to its devastating impact on marine organisms and the potential consequences for human health through the food chain.
Ocean acidification, caused by the absorption of excess carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, poses a grave risk to marine organisms such as corals, shellfish, and plankton. Acidic waters can hinder the growth and survival of these organisms, disrupting the entire marine food web and impacting the livelihoods of coastal communities.
Initiatives and Solutions for a Sustainable Life Below Water
Achieving Goal 14 requires a comprehensive approach involving governments, businesses, civil society, and individuals. Several initiatives and solutions have emerged to address the challenges faced by life below water:
Sustainable Fisheries Management: Implementing science-based management plans, promoting responsible fishing practices, and combating illegal fishing are crucial steps towards replenishing fish stocks and ensuring the long-term sustainability of fisheries. Tools like marine protected areas and ecosystem-based management help preserve critical habitats and protect biodiversity.
Marine Pollution Prevention: Reducing plastic pollution and other sources of marine debris is vital. This can be achieved through improved waste management systems, recycling and reusing plastics, and raising awareness about the consequences of single-use plastics. Additionally, promoting the use of biodegradable alternatives and supporting innovative technologies for ocean cleanup can help mitigate the impact of existing pollution.
Climate Change Mitigation and Adaptation: Addressing climate change is fundamental to preserving life below water. Transitioning to renewable energy sources, reducing greenhouse gas emissions, and promoting sustainable coastal development are essential steps in mitigating the impacts of climate change on marine ecosystems. Additionally, enhancing the resilience of coastal communities through measures such as mangrove restoration, coastal protection, and sustainable tourism can aid adaptation efforts.
International Cooperation and Governance: Collaboration among nations is crucial for the effective implementation of Goal 14. Strengthening international frameworks, such as the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS), and promoting regional cooperation can help combat illegal fishing, regulate resource exploitation, and ensure the sustainable use of marine resources.
Conclusion
Preserving life below water is not only crucial for the health of our oceans but also for the overall well-being of our planet. Goal 14 provides a roadmap for sustainable ocean management, aiming to conserve marine biodiversity, mitigate pollution, and promote the sustainable use of marine resources. By taking action at individual, local, and global levels, we can make a significant difference in ensuring a healthier and more vibrant future for life below water. Let us join hands and work together to safeguard the oceans for generations to come.
#Sustainable management of marine resources#Conserving marine biodiversity#Protecting coral reefs and marine ecosystems#Sustainable fishing practices for life below water#Reducing marine pollution for a healthier ocean#Restoring fish stocks for sustainable fisheries#Addressing the threats of overfishing#Combating illegal fishing activities#Preserving the delicate balance of marine ecosystems#Tackling plastic pollution in the oceans#Solutions for ocean acidification#Climate change impact on life below water#Sustainable tourism and the oceans#Promoting responsible coastal development#Achieving United Nations' Goal 14 for a sustainable future#Enhancing resilience of coastal communities#Sustainable livelihoods for coastal populations#Importance of ocean conservation and sustainability#Preserving marine habitats and species diversity#Ecosystem-based management for marine resources#Strengthening international cooperation for Goal 14#Achieving sustainable development through Goal 14#Role of marine protected areas in conservation#Long-term viability of marine ecosystems#Promoting sustainable shipping practices#Economic benefits of sustainable ocean management#Balancing human activities with marine conservation#The significance of Goal 14 in the SDGs#Ensuring a vibrant future for life below water#Global initiatives for the protection of marine environments
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
💙🦈 WORLD SHARK AWARENESS DAY!! 💙🦈

Did you know??
Sharks, one of our planet’s oldest species with fossils dating back over 400 million years, have played a pivotal role in marine ecosystems far longer than we have existed on Earth.
Deemed a keystone species, sharks exert such a profound influence on their habitats that their absence would dramatically alter the entire ecosystem. As apex predators, they stand at the pinnacle of the food chain, crucially maintaining the balance of marine life by regulating prey populations. Sharks control species abundance, distribution, and diversity, which reciprocally affects the health of marine habitats.
Organizations worldwide, like the Shark Conservation Fund, are striving to protect sharks directly. Others, such as Blue Ventures and Saving the Blue, indirectly work towards their protection by safeguarding marine habitats and engaging coastal communities.
#world shark awareness day#world shark awareness#shark awareness day#shark awareness#july 14#shark blog#sharks#shark post#advocacy for sharks#respect the locals#save the sharks#protect sharks#protect the ocean#protect the earth#protect the environment#protect the planet#shark advocate#shark importantance#sharks are important#ocean#marine life#protect marine life#marine life advocate#marine life blog
93 notes
·
View notes
Text
🎉Happy World Ocean Day! We’ve got some good news to share!🎉
Some of California’s most important coastal habitats—kelp forests, eelgrass meadows, and oyster beds—are being protected and restored! A bill (AB1407) authored by Assemblymember Dawn Addis and co-sponsored by the Aquarium and The Nature Conservancy is moving ahead! …but what does that mean? 🤔

Kelp, eelgrass, and oyster beds—oh my!—are homes for animals, strengthen coasts against storms, and even capture carbon dioxide. They’re basically superheroes of the sea. 🦸🏽♀️🌊
But these heroic homes are under attack! Our terrific trio are threatened by sinister super villains like pollution, overharvesting, climate change, and habitat loss. 🦹🏽
Yet there’s hope! A massive coastal restoration policy is being proposed for approval and it’ll set goals to conserve and rebuild these excellent ecosystems. Supporting policy to protect the ocean means that together we can be heroes and ensure a healthy future for sea life and future generations of marine stewards. 🌊💙🌊
#monterey bay aquarium#shellebrating world ocean day#look out in the sea#its a seabird its a seaplane no its super ecosystems!
1K notes
·
View notes