#chinese god
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text





Macaque spent the whole season Big-Damn-Hero-ing and was NOT happy about it xD
#lmk season 5 spoilers#lmk spoilers#lmk season 5#lego monkie kid#lmk#macaque#liu'er mihou#six eared macaque#sun wukong#monkey king#qi xiaotian#mk#li jing#anyone else find it interesting that in english the 'macaque' part of his name comes first#but in chinese the 'six-ears' part comes first? so the way he's called by name in the different dubs has slightly different vibes#i can't quantify 'em tho :/ am not a vibeologist#Macaque was this season's biggest GOAT#like he's very petty about it but he cares about mk and swk SO. MUCH.#(well ok the petty is mostly aimed at swk)#which: fair#POV: everything is going to shit and you are currently the only celestial monkey NOT being re-traumatized or gaslight by celestial beings#macaque's gonna start rolling up to beach parties with a shirt that says:#I Saved The Monkey King's Arse Several Times And All I Got Was An Almost-Hand-Holding-Moment And This Stupid Shirt#MK NOOOOOOOOO#im a fucking wreck that's their KID. he's their BOY. their little BRO HE'S THEIR KID OKAY AND THEY LOVE HIM ENOUGH TO FISTFIGHT THE GODS#which i guess is a little easier since they can win those fights actually#not explicitly shadowpeach#but oh it is there. lurking. waiting to strike#lion king reference! :D
9K notes
·
View notes
Text
So You Want to Read More about Chinese Mythos: a rough list of primary sources
"How/Where can I learn more about Chinese mythology?" is a question I saw a lot on other sites, back when I was venturing outside of Shenmo novel booksphere and into IRL folk religions + general mythos, but had rarely found satisfying answers.
As such, this is my attempt at writing something past me will find useful.
(Built into it is the assumption that you can read Chinese, which I only realized after writing the post. I try to amend for it by adding links to existing translations, as well as links to digitalized Chinese versions when there doesn't seem to be one.)
The thing about all mythologies and legends is that they are 1) complicated, and 2) are products of their times. As such, it is very important to specify the "when" and "wheres" and "what are you looking for" when answering a question as broad as this.
-Do you want one or more "books with an overarching story"?
In that case, Journey to the West and Investiture of the Gods (Fengshen Yanyi) serve as good starting points, made more accessible for general readers by the fact that they both had English translations——Anthony C. Yu's JTTW translation is very good, Gu Zhizhong's FSYY one, not so much.
Crucially, they are both Ming vernacular novels. Though they are fictional works that are not on the same level of "seriousness" as actual religious scriptures, these books still took inspiration from the popular religion of their times, at a point where the blending of the Three Teachings (Buddhism, Daoism, Confucianism) had become truly mainstream.
And for FSYY specifically, the book had a huge influence on subsequent popular worship because of its "pantheon-building" aspect, to the point of some Daoists actually putting characters from the novel into their temples.
(Vernacular novels + operas being a medium for the spread of popular worship and popular fictional characters eventually being worshipped IRL is a thing in Ming-Qing China. Meir Shahar has a paper that goes into detail about the relationship between the two.)
After that, if you want to read other Shenmo novels, works that are much less well-written but may be more reflective of Ming folk religions at the time, check out Journey to the North/South/East (named as such bc of what basically amounted to a Ming print house marketing strategy) too.
-Do you want to know about the priestly Daoist side of things, the "how the deities are organized and worshipped in a somewhat more formal setting" vs "how the stories are told"?
Though I won't recommend diving straight into the entire Daozang or Yunji Qiqian or some other books compiled in the Daoist text collections, I can think of a few "list of gods/immortals" type works, like Liexian Zhuan and Zhenling Weiye Tu.
Also, though it is much closer to the folk religion side than the organized Daoist side, the Yuan-Ming era Grand Compendium of the Three Religions' Deities, aka Sanjiao Soushen Daquan, is invaluable in understanding the origins and evolutions of certain popular deities.
(A quirk of historical Daoist scriptures is that they often come up with giant lists of gods that have never appeared in other prior texts, or enjoy any actual worship in temples.)
(The "organized/folk" divide is itself a dubious one, seeing how both state religion and "priestly" Daoism had channels to incorporate popular deities and practices into their systems. But if you are just looking at written materials, I feel like there is still a noticeable difference.)
Lastly, if you want to know more about Daoist immortal-hood and how to attain it: Ge Hong's Baopuzi (N & S. dynasty) and Zhonglv Chuandao Ji (late Tang/Five Dynasties) are both texts about external and internal alchemy with English translations.
-Do you want something older, more ancient, from Warring States and Qin-Han Era China?
Classics of Mountains and Seas, aka Shanhai Jing, is the way to go. It also reads like a bestiary-slash-fantastical cookbook, full of strange beasts, plants, kingdoms of unusual humanoids, and the occasional half-man, half-beast gods.
A later work, the Han-dynasty Huai Nan Zi, is an even denser read, being a collection of essays, but it's also where a lot of ancient legends like "Nvwa patches the sky" and "Chang'e steals the elixir of immortality" can be first found in bits and pieces.
Shenyi Jing might or might not be a Northern-Southern dynasties work masquerading as a Han one. It was written in a style that emulated the Classics of Mountains and Seas, and had some neat fantastic beasts and additional descriptions of gods/beasts mentioned in the previous 2 works.
-Do you have too much time on your hands, a willingness to get through lot of classical Chinese, and an obsession over yaoguais and ghosts?
Then it's time to flip open the encyclopedic folklore compendiums——Soushen Ji (N/S dynasty), You Yang Za Zu (Tang), Taiping Guangji (early Song), Yijian Zhi (Southern Song)...
Okay, to be honest, you probably can't read all of them from start to finish. I can't either. These aren't purely folklore compendiums, but giant encyclopedias collecting matters ranging from history and biography to medicine and geography, with specific sections on yaoguais, ghosts and "strange things that happened to someone".
As such, I recommend you only check the relevant sections and use the Full Text Search function well.
Pu Songling's Strange Tales from a Chinese Studios, aka Liaozhai Zhiyi, is in a similar vein, but a lot more entertaining and readable. Together with Yuewei Caotang Biji and Zi Buyu, they formed the "Big Three" of Qing dynasty folktale compendiums, all of which featured a lot of stories about fox spirits and ghosts.
Lastly...
The Yuan-Ming Zajus (a sort of folk opera) get an honorable mention. Apart from JTTW Zaju, an early, pre-novel version of the story that has very different characterization of SWK, there are also a few plays centered around Erlang (specifically, Zhao Erlang) and Nezha, such as "Erlang Drunkenly Shot the Demon-locking Mirror". Sadly, none of these had an English translation.
Because of the fragmented nature of Chinese mythos, you can always find some tidbits scattered inside history books like Zuo Zhuan or poetry collections like Qu Yuan's Chuci. Since they aren't really about mythology overall and are too numerous to cite, I do not include them in this post, but if you wanna go down even deeper in this already gigantic rabbit hole, it's a good thing to keep in mind.
#chinese mythology#chinese folklore#resources#mythology and folklore#journey to the west#investiture of the gods
2K notes
·
View notes
Photo
Neat

Someone: Hey, are you a boy or a girl?
Guanyin: I’m whatever you perceive me as
Someone: No, I mean what’s between your legs?
Guanyin: The void
#I'll see myself out#I love that the wiki page uses both he/him and she/her pronouns for guanyin#guanyin#chinese god#buddhist god#shitpost#text post#lgbt#agender#babeyyyyy#gender is fake#send tweet#mythology#new fave god#am I allowed to tag non-human to this#I'm gonna#not liek there's a big fandom for it in the west#non-human#fei ren zai#观音#boss guan#bodhisattva guanyin
63 notes
·
View notes
Text












chinese fire art huohu火壶 (photographer: hunterwonder, KleinBlue)
#china#art#huohu#they have both women and men performancers amazing#sun wukong vibe definitely#or the god of fire zhurong who often shows herself as a woman in chinese mythology
608 notes
·
View notes
Text
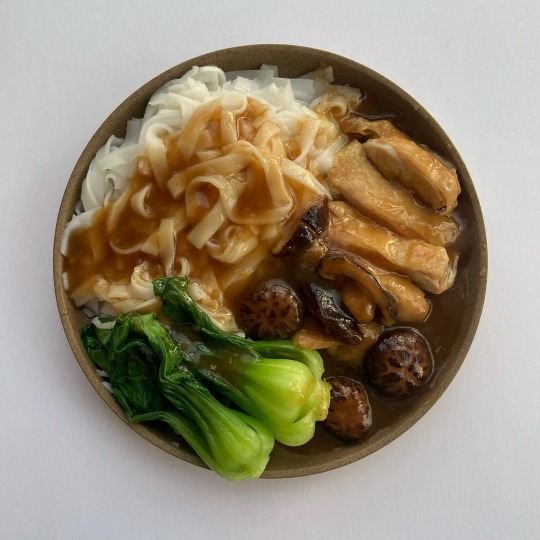
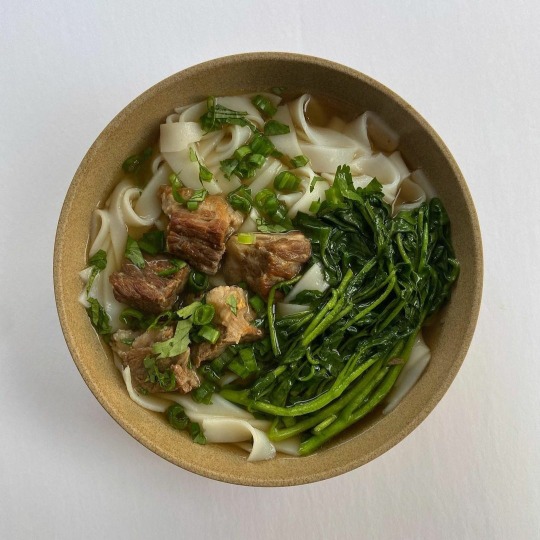
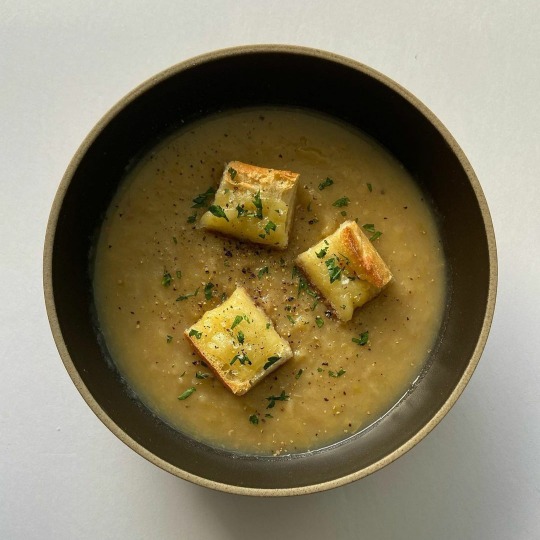
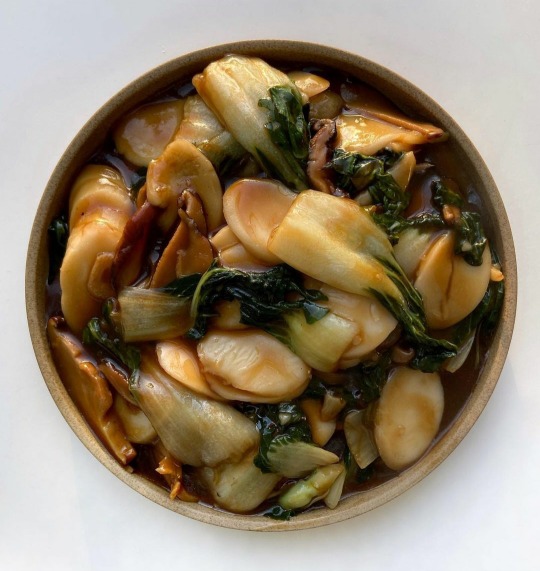
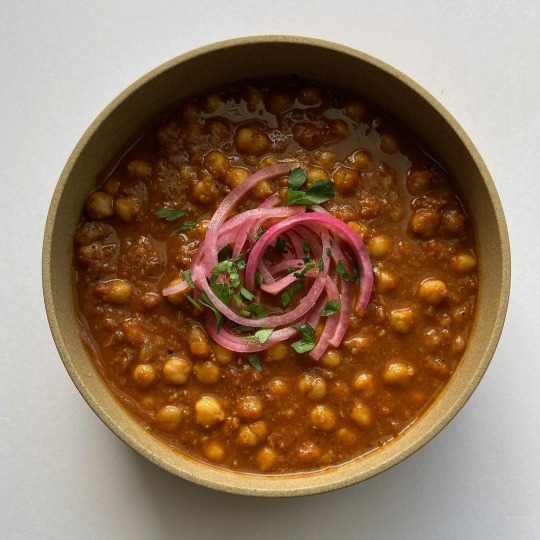






some favourite bowls from alexacooksme's instagram 🥘
#god these look so good#alexacooksme#alexa fahlman#food#chinese food#indian food#recipes#soup#noodles#upl#the hits#fav plates
4K notes
·
View notes
Text

link
I can't properly put into words the amount of disgust that I feel seeing someone who looks like she could be my cousin fight for a genocidal occupational force like Israel but I will say this.
If you are Chinese, Korean, Japanese or any one of these Asian ethnicities that the West deem "acceptable" and you align yourselves with western-backed racial supremacy, you are making fools of yourselves. You have fallen prey to the myth of the "model minority" and you are suckers for it.
The premise of racial supremacy is based on exclusivity. And here's a dose of reality - the myth of the "model minority" is nothing but a tactic to placate you. To sow divide in the ranks of people of colour. To artificially manufacture another realm of racial supremacy in minorities so that you're distracted from how we all suffer under colonialism.
Did we all forget about the skyrocketing of sinophobia in the wake of the first COVID outbreak? The transformation of Chinese people into fiends with barbaric eating customs, poor hygiene, and mass conspiracy to infect the world with biological weapons?

link
What about the hate-crimes? The attacks in the street against anyone visibly asian? The rampant discrimination and ostracisation from society?

In 2020, Donald Trump referred to COVID-19 as "The Chinese Virus", "Kung-flu" at a campaign rally to raucous applause, a chilling echo of the times where fears of the "Yellow Peril" had the western world in a stranglehold.
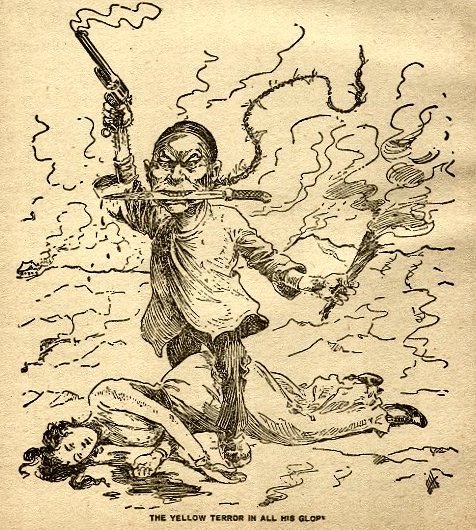


For all that Chinese people have been lauded as "prodigies" and "well-mannered workers", the moment our existence was incovenient, were were nothing more than another target. And although Chinese suffering then wasn't close to the scale of suffering that Palestinians now endure, we all received a reminder on what it was like to be in the world's crosshairs.
Now, in 2023, Biden dismisses death tolls as unreliable and remains proudly Zionist even after Netanyahu described the genocide Israel is inflicting upon Palestine as the "struggle between the children of light and the children of darkness, between humanity and the law of the jungle." At the same time, Palestinians are being compared to fleeing rats in a gesture of dehumanisation that mirrors how the Nazis portrayed Jews during the Holocaust.

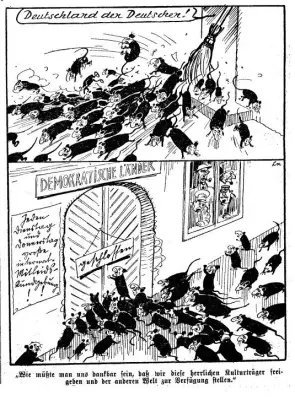
link
And let's not think Abigail's Jewishness will save her, not when it's been proven that Israel has administered contraceptives to Ethiopian Jewish immigrants without their consent. Racial supremacy is an exclusive club that never stops getting smaller, and there is nothing that you, as a minority, will ever be able to do to fit in. One day, you too will be a target and there'll be nothing you can do but blame yourself. After all - it's already happened.
So shame on Abigail. Truly. With the memory of knowing what it's like to be targeted for factors out of your control fresh in her mind, she happily fights to do the same to others. And that says more about her than I ever will be able to.
#this may be long winded and wordy but i had to get this off my chest#as a chinese-australian woman who does her best to be proud of her chinese heritage#this was a slap in the face#and ive tried lately to not inject my own voice into discussion about palestine bc i know there are people out there#who are more educated and more equipped with voices that need elevating more than mine do#but i think im allowed to talk about how enraged this made me#god.#free palestine#palestine#cw: mentions of sinophobia#colonialism
1K notes
·
View notes
Text



FANGS OF FORTUNE 大梦归离 (2024) ep. 21
#fangs of fortune#xu zhenxuan#ying lei#cdrama#userdramas#clairedaring#belleparkgif#cdramaedit#dailyasiandramas#asiandramasource#chinese drama#userstorge#lextag#samblr#userginpotts#userkimchi#udeokmis#tuserkimmie#syaring#natahjikio#tuservic#bai jiu be testing his patience 😂😂😂#aaaahh little mountain god u cutieeee
326 notes
·
View notes
Photo


@rateater2000 you. i like the way you think >:)
now all four of them be stylin (they’re not completely the same, if that’s what you were expecting, but I wanted to give them a little ✨flair✨)
#i had to give donnie some kind of dragon detail. like its unacceptable NOT to#and leos lightning detail is more greek-reminiscent than chinese or japanese like the others but...cmon. its too perfect#last but not least mikey gets multiple color privileges#leo got a crumb with his yellow accent but beyond that? just mikey#rottmnt#mutant manhunt au#god i love designing cool outfits#rottmnt mikey#rottmnt leo#rottmnt donnie#kinda rottmnt raph?#my art
4K notes
·
View notes
Text


Photographer: IG: amamiya_shion9

0 notes
Text






Xu Zhen Xuan as Ying Lei FANGS OF FORTUNE 大梦归离 (2024) dir. Edward Guo, Luo Luo, Wei Nan
#fangs of fortune#cdrama#cdramaedit#the story of mystics#大梦归离#cdramasource#dailyasiandramas#xu zhenxuan#chinese drama#xu zhen xuan#fangsoffortuneedit#fofedit#fof: 1.14#.gif#my favorite little mountain god ✨
187 notes
·
View notes
Text
One nerd's musing about Chinese religion and "respect"
-I try to stay away from fandom discourse, but, much like how you can smell the stench from a dumpster fire without walking into said dumpster fire, I've noticed something that seemed to come up a lot in western JTTW + adjacent fandoms: "respect Chinese religion".
-Usually as a reason for why you shouldn't ship a character, because of fucking course it's shipping discourse too.
-And my first reaction is "Man, you are taking Chinese religion too darn seriously, more than people who are born and raised in China."
-My second reaction is "I mean, most of us are atheist/agnostic by default anyways, with a good number of what I'd call 'atheist/agnostics with superstitions': people who said they were not religious, yet believed in Fengshui or divinations and burnt incense at temples for good luck."
-My third reaction: "But why do I get the feeling that when you mention 'Respect', you are thinking about something completely different?"
-Then I reread an essay from Anthony C. Yu, "Religion and Literature in China: The "Obscure Way" of Journey to the West", and the metaphorical lightbulb just lit up over my head.


(Everything below applies more to Daoism + associated folk religions, but by the time most classic Chinese vernacular novels were written, the blending of the three religions had become well and truly mainstream.)
(The conception of gods differs from dynasty to dynasty. What I'm describing here is mostly based on Ming and Qing ones; if you went back to Han or pre-Qin times, most of these would not apply.)
(I am one of the "atheist/agnostic by default" people. I just have an interest in this kind of stuff. I am also just one Chinese person, and an actual Daoist/Buddhist/Religion Studies researcher would probably have a lot more valuable information and perspective to offer when it comes to contemporary practices and worship. Like any people on the internet: take my words with a grain of salt.)
-Even in the past, when society was far less secularized, Chinese gods are not omniscient, perfect beings whose worship is a solemn, humorless affair. Some's worship are Serious Business, but that has more to do with the sort of gods they are and the patronage they enjoy, not godhood in and of itself.
-And even the ones that you are supposed to "treat seriously" are still very human. To use an analogy I've used plenty of times before: you respect and fear them in the same way you'd respect and fear an emperor's official, or the emperor himself, because if you don't, you are not gonna like the consequences.
-However, unlike Jesus, the emperor & his officials were capable of being temperamental, flawed, or an outright asshole, divine or not. Ideally, they wouldn't be, and if you were one of the "serious" believers——people who actually got an official permit, became ordained clergy, and went to live in a temple, you were unlikely to think of your gods in that manner.
-But it wasn't a complete, utter impossibility. The lower you go in the pantheon, the closer you get to popular religion, the less "serious" the gods and their worship become. By that, I mean general attitude, not sincerity of faith. You still shouldn't be rude to them, but, well, they are more likely to take a joke in stride, or participate in the "vulgar" pleasures of commoners because they weren't as bound to Confucian moral standards or religious disciplines.
-To stretch the same analogy further: you should still respect your village head, they could still give your ass a good spanking for being a disrespectful brat, but you were not obligated to get on your knees and kowtow to them like you would do in front of a provincial magistrate, the emperor's minister, or the emperor himself, nor did they have the power to chop your head off just because you were rude.
-On the other hand, the emperor would never visit a random peasant just to help them fix their broken plow or treat them to a nice meal, but your village head could, and your relationship would probably be warmer and a lot more personal as a result.
-Your respect for them was more likely to stem from the things they actually did for you and the village as a whole, instead of something owed to this distant, powerful authority you might never get to see in your lifetime, but could change its course with a single stroke of a brush.
-Now exchange "village head" for your run-of-the-mill Tudis and Chenghuangs and friendly neighborhood spirits (because yes, people worshipped yaoguais for the exact same reasons), emperor + his officials for the Celestial Bureaucracy, and you'd have a basic idea of how Chinese religions worked on the ground level.
-This is far from absolute: maybe your village head was a spiteful old bastard who loved bullying his juniors, maybe your regional magistrate was an honest, upright man who could enjoy a good drink and a good laugh, maybe the emperor was a lenient one and wouldn't chop your head off for petty offenses. But their general degree of power over you and the closeness of your relationships still apply.
-Complicating the matter further, some folk gods (like Wutong) were worshipped not because they brought blessings, but because they were the divine equivalent of gangsters running a protection racket: you basically bribed them with offerings so they'd leave you alone and not wreck your shit. Famous people who died violently and were posthumously deified often fell into this category——shockingly enough, Guan Yu used to be one such god!
-Yeah, kinda like how your average guy could become an official through the imperial examinations, so could humans become gods through posthumous worship, or cultivate themselves into immortals and Enlightened beings.
-Some immortals aren't qualified for, or interested in a position in the Celestial Bureaucracy——they are the equivalent of your hermits, your cloistered Daoist priests, your common literati who kept trying and failing the exams. But some do get a job offer and gladly take it.
-Anyways, back to my original point: that's why it's so absurd when people pull the "Respect Chinese Religion1!!1!" card and immediately follow up with "Would you do X to Jesus?"
-Um, there are a lot of things you can do with Chinese gods that I'm pretty sure you can't do with Jesus. Like worshipping him side by side with Buddha and Confucius (Lao Tzu). Or inviting him to possess you and drink copious amount of alcohol (Tang-ki mediums in SEA). Or genderbend him into a woman over the course of several centuries because folks just like that version of Jesus better (Guan Yin/Avalokitesvara).
-But most importantly, Chinese religions are kinda a "free market" where you could pick and choose between gods, based on their vicinity to you and how efficient they were at answering prayers. You respect them because they'll help you out, you aren't an asshole and know your manners, and pissing them off is a bad idea in general, not because they are some omnipotent, perfect beings who demand exclusive and total reverence.
-A lot of the worship was also, well, very "practical" and almost transactional in nature: leave offerings to Great Immortal Hu, and he doesn't steal your imperial seal while you aren't looking. Perform the rites right and meditate on a Thunder General's visage, and you can temporarily channel said deity's power. Get this talisman for your kids at Bixia Yuanjun's temple, and they'll be protected from smallpox.
-"Faith alone" or "Scripture alone" is seldom the reason people worship popular deities. Even the obsession with afterlife wasn't about the eternal destination of your soul, and more about reducing the potential duration of the prison sentence for you and your loved ones so you can move on faster and reincarnate into a better life.
-Also, there isn't a single "canon" of scriptures. Many popular gods don't show up in Daoist literature until much later. Daoist scriptures often came up with their own gigantic pantheons, full of gods no one had heard of prior to said book, or enjoyed no worship in temples whatsoever.
-In the same way famous dead people could become gods via worship, famous fictional characters could, too, become gods of folk religion——FSYY's pantheon was very influential on popular worship, but that doesn't mean you should take the novels as actual scriptures.
-Like, God-Demon novels are to orthodox Daoism/Buddhism what the Divine Comedy is to medieval Christian doctrines, except no priests had actually built a Church of Saint Beatrice, while Daoists did put FSYY characters into their temples. By their very nature, the worship that stemmed from these books is not on the same level of "seriousness" as, say, the Tiantai school of Buddhism and their veneration of the Lotus Sutra.
-At the risk of being guilty of the same insertion of Christianity where it doesn't belong: You don't cite Dante's Inferno in a theological debate, nor would any self-respecting pastor preach it to churchgoers on a Sunday.
-Similarly, you don't use JTTW or FSYY as your sole evidence for why something is "disrespectful to Chinese religion/tradition" when many practitioners of said religions won't treat them as anything more than fantasy novels.
-In fact, let's use Tripitaka as an example. The historical Xuanzang was an extraordinarily talented, faithful, and determined monk. In JTTW, he was a caricature of a Confucian scholar in a Buddhist kasaya and served the same narrative function as Princess Peach in a Mario game.
-Does the presence of satire alone make JTTW anti-Buddhist, or its religious allegories less poignant? I'd say no. Should you take it as seriously as actual Buddhist sutras, when the book didn't even take itself 100% seriously? Also no.
-To expand further on the idea of "seriousness": even outside of vernacular novels, practitioners are not beholden to a universal set of strict religious laws and taboos.
-Both Daoism and Buddhism had what we called "cloistered" and "non-cloistered" adherents; only the former needed to follow their religious laws and (usually) took a vow of celibacy.
-Certain paths of Daoist cultivation allow for alcohol and sexual activities (thanks @ruibaozha for the info), and some immortals, like Lv Dongbin, had a well-established "playboy" reputation in folklore.
-Though it was rarer for Buddhism and very misunderstood, esoteric variants of it did utilize sexual imageries and sex. And, again, most of the above would not apply if you weren't among the cloistered and ordained clergy.
-Furthermore, not even the worship of gods is mandatory! You could just be a Daoist who was really into internal alchemy, cultivating your body and mind in order to prolong your lifespan and, ideally, attain immortality.
-This idea of "respect" as…for a lack of better words, No Fun & R18 Stuff Allowed, you must treat all divinity with fearful reverence and put yourself completely at their mercy, is NOT the norm in Chinese religious traditions.
-There are different degrees and types of respect, and not every god is supposed to be treated like the Supreme Heavenly Emperor himself during an imperial ceremony; the gods are capable of cracking a joke, and so are we!
TL;DR: Religions are complicated, and you aren't respecting Chinese religions by acting like a stereotypical Puritan over popular Chinese deities and their fictional portrayals.
#chinese religion#chinese mythology#chinese folklore#fandom discourse#journey to the west#xiyouji#investiture of the gods#fengshen yanyi
1K notes
·
View notes
Text



#fangs of fortune#大梦归离#tian jiarui#xu zhenxuan#zhou yichen#li lun#cdramaedit#cdrama#chinese drama#noonas gifs#none of my kinks are in these gifs#jesus god#noonas fof
203 notes
·
View notes
Text
Erlang Shen—A Playful Free Spirit Pt. 2
If you think Erlang Shen is just a stoic, no-nonsense warrior god, you're definitely missing out. One of the most fascinating quirks about him in Chinese mythology is his adaptability and love for transformation, especially into a woman, to mess with people. He fully commits to those roles, playing with assumptions about gender and appearance, letting others trip over their own indoctrinated misconceptions.

The most well-known example is from The Investiture of the Gods. Erlang is tasked with protecting a prince from an assassination. Instead of just standing guard, he turns a melon into the prince and transforms himself into a beautiful concubine. The assassin, thinking he's succeeded after beheading the “prince,” quickly turns his attention to the “concubine” who's begging for mercy. Caught up in lust, the assassin lets his guard down, and that's when Erlang strikes, back into his true form with the assassin dangling under his arm, still dazed and confused.
This is by no means the only account of Erlang's gender-bending transformations. In JTTW, he and Sun Wukong engage in an iconic shape-shifting duel, each transformation designed to one-up the other. When Wukong turns into a creature, Erlang counters by transforming into its natural predator. In the folk version (similar style to the headless monk song in Black Myth: Wukong) of Havoc in Heaven, Erlang ups the ante by transforming into a young widow and even delivers a four-minute soliloquy mourning her lost husband, unfortunate miscarriage, and harsh in-laws. Wukong is unfazed and transforms into the flirtatious brother-in-law, teasing the young widow and grabbing her foot (a scandalous act for that time). Startled, Erlang drops the act and chides Wukong for his lewdness. It seems less like a serious battle but more like a courting game playful test of boundaries, each trying to throw the other off balance.
Erlang also plays with gender expectations and power dynamics outside of battles. In a 12th-century collection of strange tales (《夷坚志》), a strong laborer named Cai Qi stumbles across a handsome young man by a bridge late at night. A bit tipsy and opportunistic, Cai Qi grips the young man, intending to take advantage of him. The young man is actually Erlang Shen on a casual trip in the mortal world. Instead of confronting Cai Qi directly, which would’ve been very easy for a god, Erlang plays along, pretending to be overpowered and offering a silver wine vessel as a bribe to plea himself out of the harassment. Cai Qi, thrilled with the windfall, takes the silver home, only to discover the next day that the public storehouse is missing silver. He realizes too late that Erlang has his presumptuousness and greed lead him into trouble.

This playful trickery makes its way into modern retellings as well. In the 2003 animated series The Legend of Nezha, Erlang Shen pulls another gender-bending transformation during a playful match with Nezha. After stealing Nezha’s weapon, the Red Armillary Sash (混天绫), Erlang transforms into a woman crying by the river, conspicuously draped in the sash and calling for help from Nezha. Seeing through Erlang's shenanigan, Nezha demands his weapon back. Erlang feigns innocence and tells Nezha to go take her clothes himself, taunting, “What kind of hero robs a woman’s clothes in broad daylight?” Flustered, Nezha concedes the win and asks Erlang to transform into anything else. Erlang laughs, tosses back the sash, and calls for another rematch.
While quite a few gods and yaoguais in Chinese mythology use transformation as a disguise, Erlang Shen takes it further by leaning into the roles spontaneously to confuse, distract, and tease, playing with both gender and power dynamics. His transformations aren't just about hiding or escaping—they're about flipping the script and catching others off guard. As the god who tames the water, true to form, Erlang is adaptive, pragmatic, and fluid.
“Naturally fond of roaming free, with transformations that follow no fixed pattern.” —Indeed.
#erlang shen#yang jian#chinese mythology#journey to the west#black myth wukong#sun wukong#investiture of the gods#nezha
212 notes
·
View notes
Text




“From now on, you are my man. I will provide you with the best food and drinks, and give you whatever you want. I will never leave or forsake you.“
Uncensored wuxia BL Meet You At The Blossom (2024)
#meet you at the blossom#huaibao#huaien x xiaobao#zongzheng huaien x jin xiaobao#花开有时颓靡无声#huaibaoheartbeat#chinese bl#myatbedit#mygifs#mine#mjtag#userjap#userspicy#usersasa#rinblr#raeblr#tusermona#sandushengshou#userinahochi#userspring#cdramaedit#cdrama#so thirsty my god
324 notes
·
View notes
Text













wuxia and xianxia aesthetics in chinese costume drama (guzhuang drama) | actor cheng yi 成毅 (real name fu shiqi傅诗淇)
#china#fashion#drama#chinese fashion#guzhuang#costume drama#cheng yi is like the one of the best actors for the main role of chinese wuxia drama#his martial arts scenes are excellent#while his performance is subtle and the feelings are strong#and he is the god of vibe omg#he may not be the most good looking one#but his acting is always mesmerizing#no wonder they always give him high quality wuxia or xianxia scripts#cheng yi#hanfu
251 notes
·
View notes




