#c. 5th century
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

A detail from the roman Kelenderis mosaic, showing a merchant ship in the harbor, ca. 5th century AD
129 notes
·
View notes
Photo

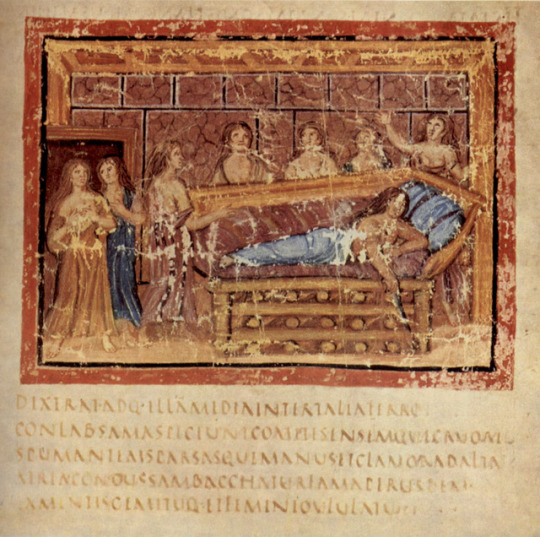
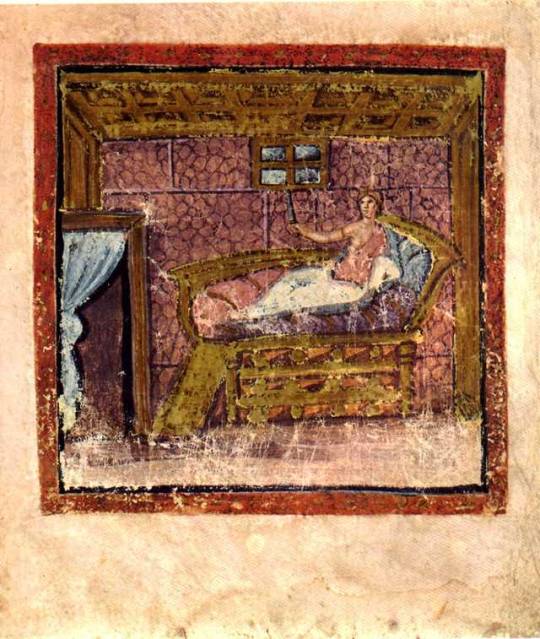
Vergil's Aeneid from the Vergilius Vaticanus illuminated manuscript kept in the collection of the Biblioteca apostolica Vaticana. MS lat. 3225. fol. 33 v; by the Master of the Vergilius Vaticanus; 5th century AD
#5th century#mdpearly#mdpancient#manuscript#illuminated manuscript#5th c. rome#rome#ancient rome#ancient manuscript
108 notes
·
View notes
Text
Grad school is a hell of my own making
#banging my head against a wall because everyone just assumes you know the reference letters for bible manuscripts#sorry stewe#i actually DONT know that A means Codex Alexandrinus#also#and why are we saying that an instrument from the medieval period existed in the time of aristophanes??????#there is no record of a bladder pipe prior to the 13th century and yet everyones like#'anyway this 5th c BCE comedian definitely is talking about this medieval instrument. ignore the fact that there is no other#evidence to support this and actually there is evidence to the contrary.'#and i have to be up early for my TA class that i literally do nothing for#i hate waking up early
0 notes
Text
Origins of Modern Greek folk sayings
NOTE: By "origins" here I do not mean absolute exact origin as this would be impossible to know. It rather signifies the likely first documented usage of the saying in the Greek literary heritage.
Ένα χελιδόνι (ή ένας κούκος) δεν φέρνει την άνοιξη. Meaning: A single swallow (or a single cuckoo) does not bring the spring. This is where the english idiom "one swallow does not a summer make" come from as well. Origin: Μία χελιδὼν ἔαρ οὐ ποιεἶ ( A single swallow does not create the spring) - Nicomachean Ethics, Aristotle (384 - 322 BC). Aristotle said this phrase inspired by one of Aesop's tales (620 - 564 BC).
Το ένα χέρι νίβει το άλλο. Meaning: Each hand washes the other. It exists in English as well as in other languages, spread through Latin "Manus manam lavat". Origin: ἁ δὲ χεὶρ τὰν χεῖρα νίζει - Epicharmus, 5th century BC.
Ό,τι σπείρεις θα θερίσεις. Meaning: You will reap what you sow. Widespread proverb. Origin: Εί κακά τις σπείραι κακά κέρδια αμήσειν (If one sows bad things, he will reap bad things) - Hesiod (~ 750 - 650 BC).
Κάλλιο να σε ζηλεύουνε παρά να σε λυπούνται Meaning: It's better to be envied than to be pitied by others. Origin: κρέσσον γὰρ οἰκτιρμοῦ φθόνος (for envy is better than pity) - Pindar, (~ 518 – 438 BC).
Έπαθε και έμαθε Meaning: He suffered so he learned Origin: τὸν πάθει μάθος (the suffering becomes a lesson) - Aeschylus (~ 525 - 455 BC)
Μη με συγχίζεις Meaning: Don't confound me, meaning "don't make me upset" Origin: μή μοι σύγχει - Homer (8th century BC)
Μη με σκοτίζεις Meaning: "Don't put me in the dark" meaning "don't annoy / bother me" Origin: Αποσκότησον με ("Get me out of the dark" AKA the notorious "Don't hide the sun and gtfo" line) - Diogenes to Alexander the Great
βίος αβίωτος Meaning: "Unlivable life", unbearable life Origin: Ἀβίωτον ζῶμεν βίον (We live an unlivable life) - Philemon (362 BC – c. 262 BC)
Ἐχει και του πουλιού το γάλα Meaning: "It even has the bird's milk" meaning it has anything you can imagine Origin: δώσομεν ὑμῖν γάλα τ᾽ ὀρνίθων (We will give you even the milk of birds / hens) - Aristophanes (446 - 386 BC)
Άει στον κόρακα Meaning: Go to the crow, an equivalent of "go to hell" Origin: ἔρρʼ ἐς κόρακας! (go to the crows) - standard phrase, frequently used by Aristophanes
Κάθε αρχή και δύσκολη Meaning: Every beginning is also difficult Origin: Αρχή δήπου παντός έργου χαλεπωτέρα (the beginning of every project is the hardest) - ancient saying
Η αλήθεια είναι πικρή Meaning: Truth is bitter Origin: ἔχει τι πικρὸν ὁ τῆς ἀληθείας λόγος (there is something bitter in the words of truth) - Demades (380 - 318 BC)
Η αλήθεια δεν κρύβεται Meaning: Truth cannot be hidden Origin: Ἀδύνατον τ' ἀληθές λαθεῖν (It is impossible to hide the true thing) - Menander (342 - 291 BC)
Φοβάται και την σκιά του Meaning: He's even afraid of his shadow (used when someone is afraid all the time) Origin: τὴν αὐτοῦ σκιὰν δέδοικεν (he's afraid of his own shadow) - Aristophanes (446 - 386 BC)
Καμιά δουλειά δεν είναι ντροπή Meaning: No job is shameful Origin: Έργον δ' ουδέν όνειδος - Hesiod (~ 750 - 650 BC)
Χτίζεις στην άμμο Meaning: You build in the sand, meaning you're doing something pointless, that will be ruined or over very soon. Origin: Εἰς ψάμμον οἰκοδομεῖς - Plutarch (46 - 119 AD)
#greece#ancient greek#modern greek#greek language#greek culture#languages#linguistics#langblr#language stuff#greek
291 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Kingdom of Abyssinia
The Kingdom of Abyssinia was founded in the 13th century CE and, transforming itself into the Ethiopian Empire via a series of military conquests, lasted until the 20th century CE. It was established by the kings of the Solomonid dynasty who, claiming descent from no less a figure than the Bible's King Solomon, would rule in an unbroken line throughout the state's long history. A Christian kingdom which spread the faith via military conquest and the establishment of churches and monasteries, its greatest threat came from the Muslim trading states of East Africa and southern Arabia and the migration of the Oromo people from the south. The combination of its rich Christian heritage, the cult of its emperors, and the geographical obstacles presented to invaders meant that the Ethiopian Empire would be one of only two African states never to be formally colonised by a European power.
Origins: Axum
The Ethiopian Highlands, with their reliable annual monsoon rainfall and fertile soil, had been successfully inhabited since the Stone Age. Agriculture and trade with Egypt, southern Arabia, and other African peoples ensured the rise of the powerful kingdom of Axum (also Aksum), which was founded in the 1st century CE. Flourishing from the 3rd to 6th century CE, and then surviving as a much smaller political entity into the 8th century CE, the Kingdom of Axum was the first sub-Saharan African state to officially adopt Christianity, c. 350 CE. Axum also created its own script, Ge'ez, which is still in use in Ethiopia today.
Across this Christian kingdom, churches were built, monasteries founded, and translations made of the Bible. The most important church was at Axum, the Church of Maryam Tsion, which, according to later Ethiopian medieval texts, housed the Ark of the Covenant. The Ark, meant to contain the original stone tablets of the Ten Commandments given by God to Moses, is supposed to be still there, but as nobody is ever allowed to see it, confirmation of its existence is difficult to achieve. The most important monastery in the Axum kingdom was at Debre Damo, founded by the 5th-century CE Byzantine ascetic Saint Aregawi, one of the celebrated Nine Saints who worked to spread Christianity in the region by establishing monasteries. The success of these endeavours meant that Christianity would continue to be practised in Ethiopia right into the 21st century CE.
The kingdom of Axum went into decline from the late 6th century CE, perhaps due to overuse of agricultural land, the incursion of western Bedja herders, and the increased competition for the Red Sea trade networks from Arab Muslims. The heartland of the Axum state shifted southwards while the city of Axum fared better than its namesake kingdom and has never lost its religious significance. In the 8th century CE, the Axumite port of Adulis was destroyed and the kingdom lost control of regional trade to the Muslims. It was the end of the state but not the culture.
Continue reading...
159 notes
·
View notes
Text

For those who are confused about the situation in Artsakh (part 1)
To anyone even remotely knowledgeable about the history of the region, the azerbaijani claims that Artsakh belongs or belonged to them, or that they are the natives of the land, sound not only incorrect but also hilariously pathetic. The earliest evidence of Artsakh’s ancient history dates back to the earliest stages of the Stone Age, specifically the Acheulean and subsequent periods (800,000 to 100,000 years ago). These include stone and bone tools found in the caves of Orvan-Msoz, Tsatsakhach, and Khoradzor. Excavations of settlements and tombs from the Bronze and Iron Ages (Stepanakert, Khojaly, Karkarjan, Amaras, Madagis, and the valleys of the Khachenaget and Ishkhanaget rivers) indicate that this area was part of the Kur-Araxes cultural system formed in the 4th-3rd millennia BC. The Kur and Arax are rivers in the Armenian Highlands; Arax is even considered the “mother river” of Armenia and is referred to as “Mother” in many Armenian poems and songs.
Artsakh was the northeastern boundary of the region where the Armenian people formed ethnically. This has been mentioned many times in the works of Strabo (64 or 63 BC – c. 24 AD, a Greek geographer, philosopher, and historian), Ptolemy (c. 100 - c. 170 AD, a renowned Greek geographer, astronomer, and mathematician), and many other non-Armenian geographers and historians. For over 3000 years, Artsakh has been inhabited by its natives, the Armenians.
You might ask, what do these historians write about the azerbaijanis? Well, nothing—because azeris did not exist back then and wouldn’t exist for at least the next 3000 years. How, then, could they have been the natives of the land?
Furthermore, aren’t azeris Muslim? In that case, how is it that right after Armenia adopted Christianity as its official religion—being the first nation to do so—many churches were built in Artsakh, not mosques, but churches? For example:
Gandzasar Monastery (4th century) and St. John the Baptist Church (1216-1238)
Dadivank (4th century) and Katoghike (9th-11th century)
Amaras Monastery (4th century)
St. George Church of Tzitzernavank (4th-5th century)
Gtichavank (4th-13th century)
Monastery of Apostle Yeghishe (Jrvtshtik) (5th century), Mataghis
Vankasar White Cross (5th century)
Kataro Monastery of Dizapayt and Holy Mother of God (5th century)
Mokhrenis Okht Drne Monastery (7th-17th century)
Kolatak St. Hakob Monastery (9th century)
Tsori Holy Savior (9th century)
Tsamakahogh St. Stephen (9th-10th century)
White Cross Monastery of Vank village, Hadrut (10th century)
Desert Monastery of Elisha Kusi, Chartar (12th century)
St. George Church of Jankatagh (12th century)
Khotavank (12th-13th century)
Holy Mother of God Nuns' Monastery of Karvachar (12th-13th century)
St. Savior Church of Poghosagomer (12th-13th century)
Shoshkavank Holy Mother of God of Msmena (13th century)
Horeka Monastery (13th century)
Kavakavank (14th century)
And many, many more. It pains me to tears to say that these churches, along with hundreds of others, are being destroyed by azeris to wipe out the evidence that Armenians lived there, pushing their false narrative that they are the natives of the land. Since the 2020 war, azerbaijani forces have destroyed over 570 Armenian cultural sites, with 3 to 4 monuments being demolished weekly—not to mention the desecration of both old and new Armenian graves.
So, the next time an azeri tries to argue that they are the natives of Artsakh and Armenia, just laugh at their faces. I’m sure I’ve got socks in the back of my drawer that are older than their “nation.”
#break the chain of ignorance#feel free to fact check what you read#history#artsakh is armenia#artsakh#armenia#world politics#world history#azeri crimes#turkish crimes#stop the genocide#armenian culture
197 notes
·
View notes
Text
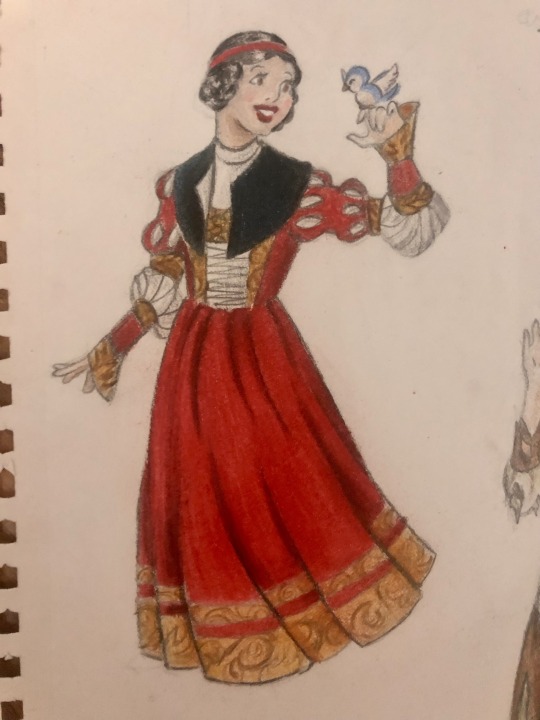
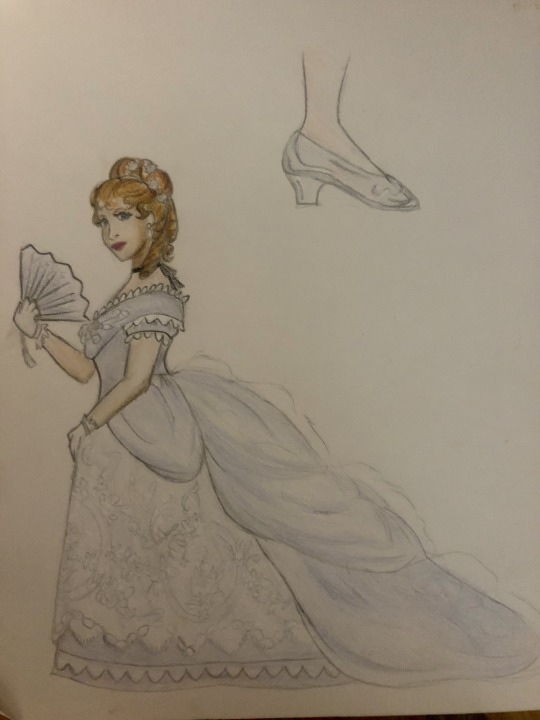
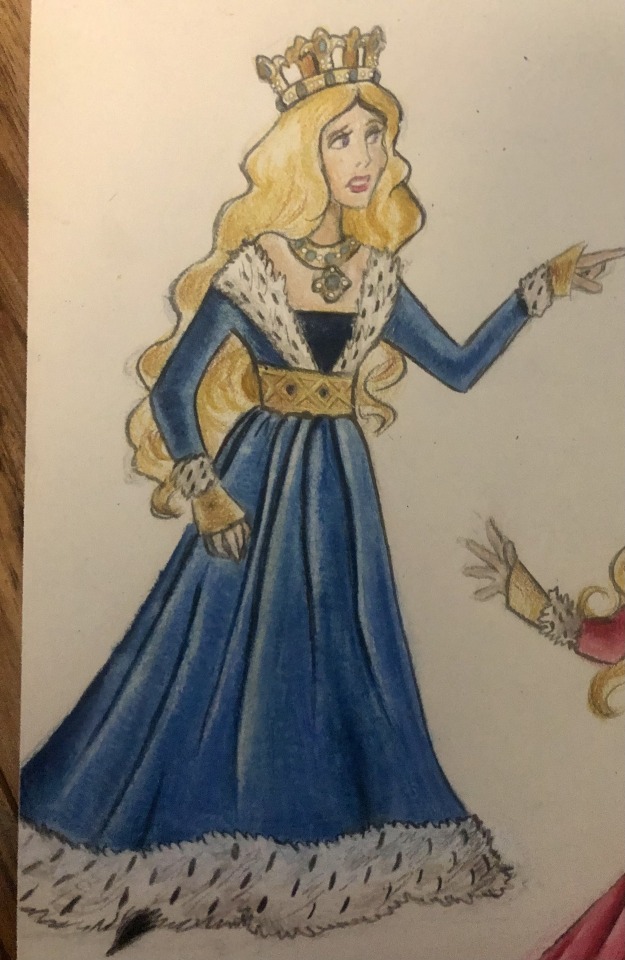
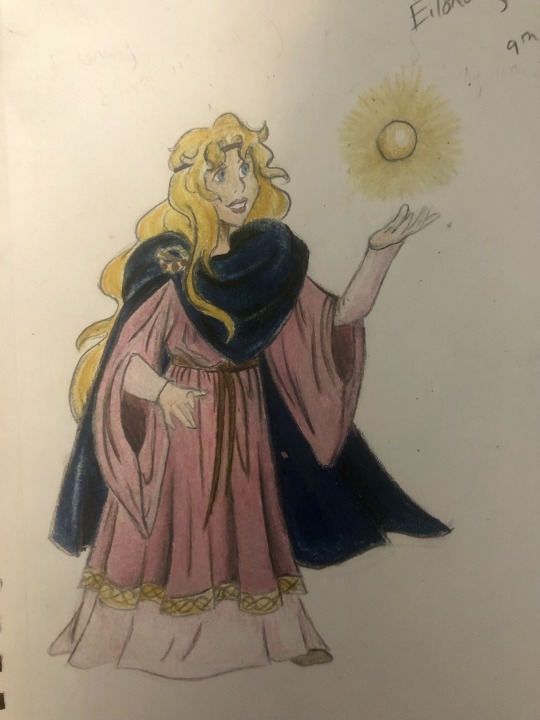
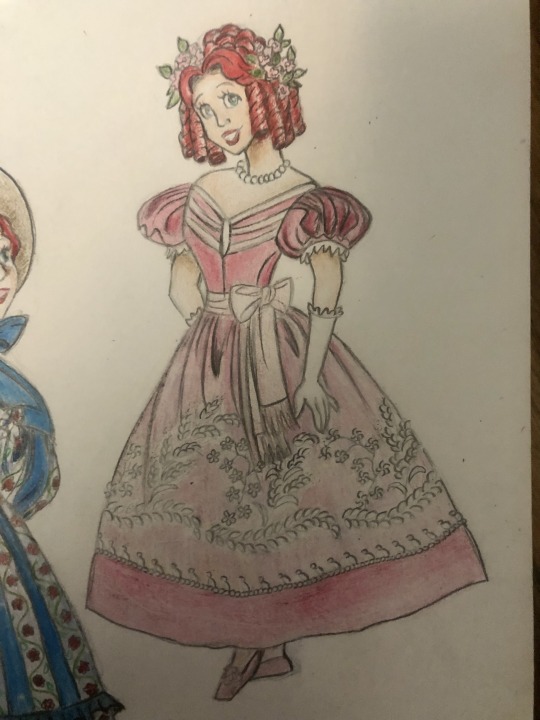
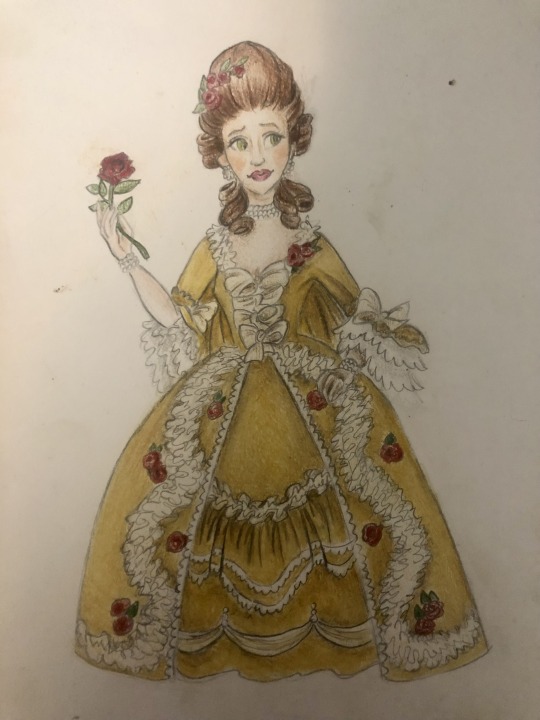
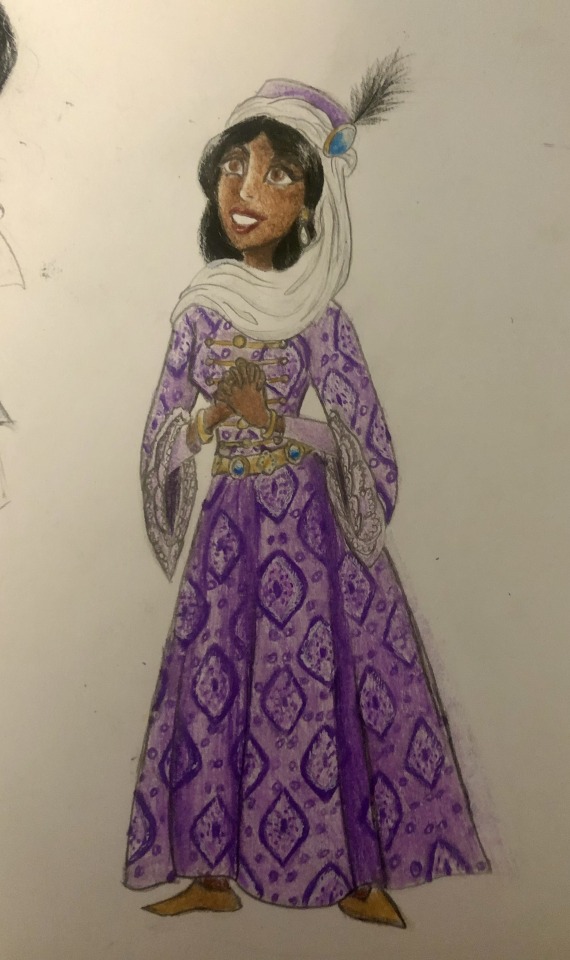
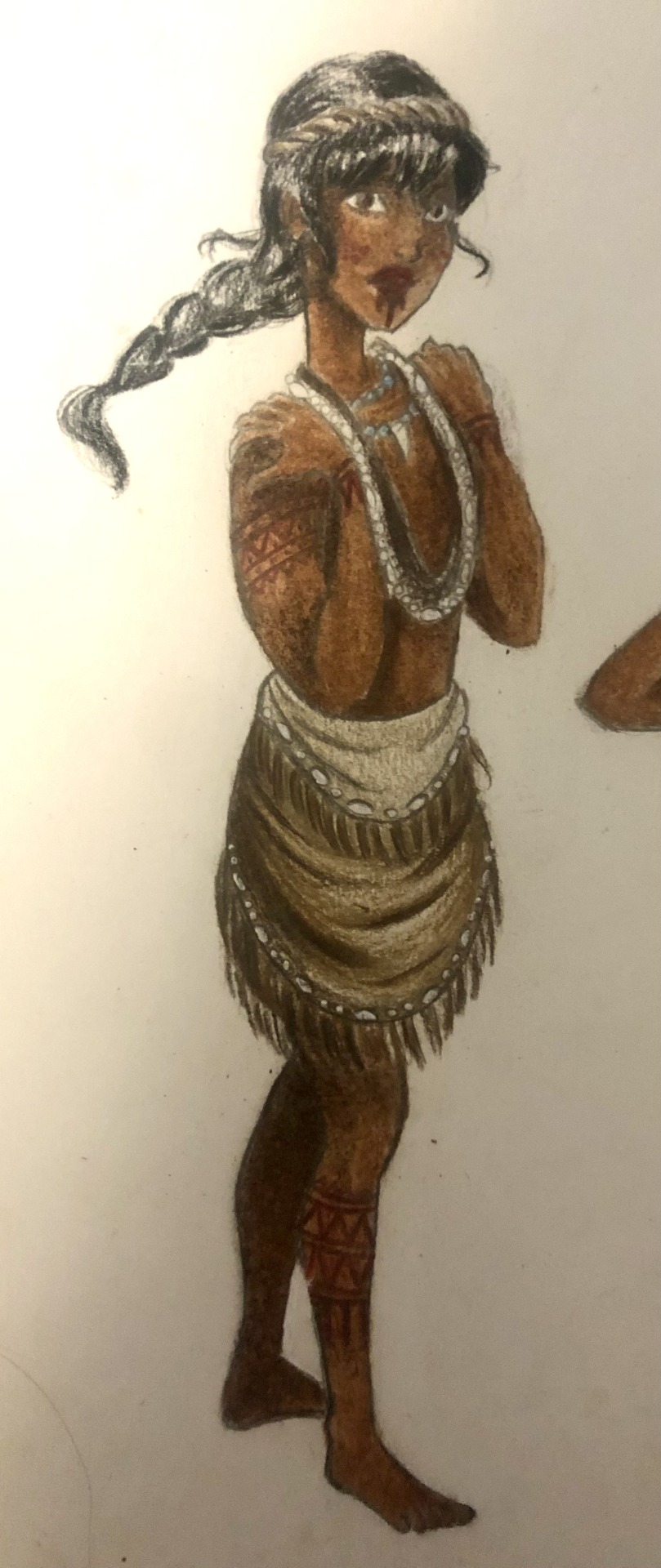
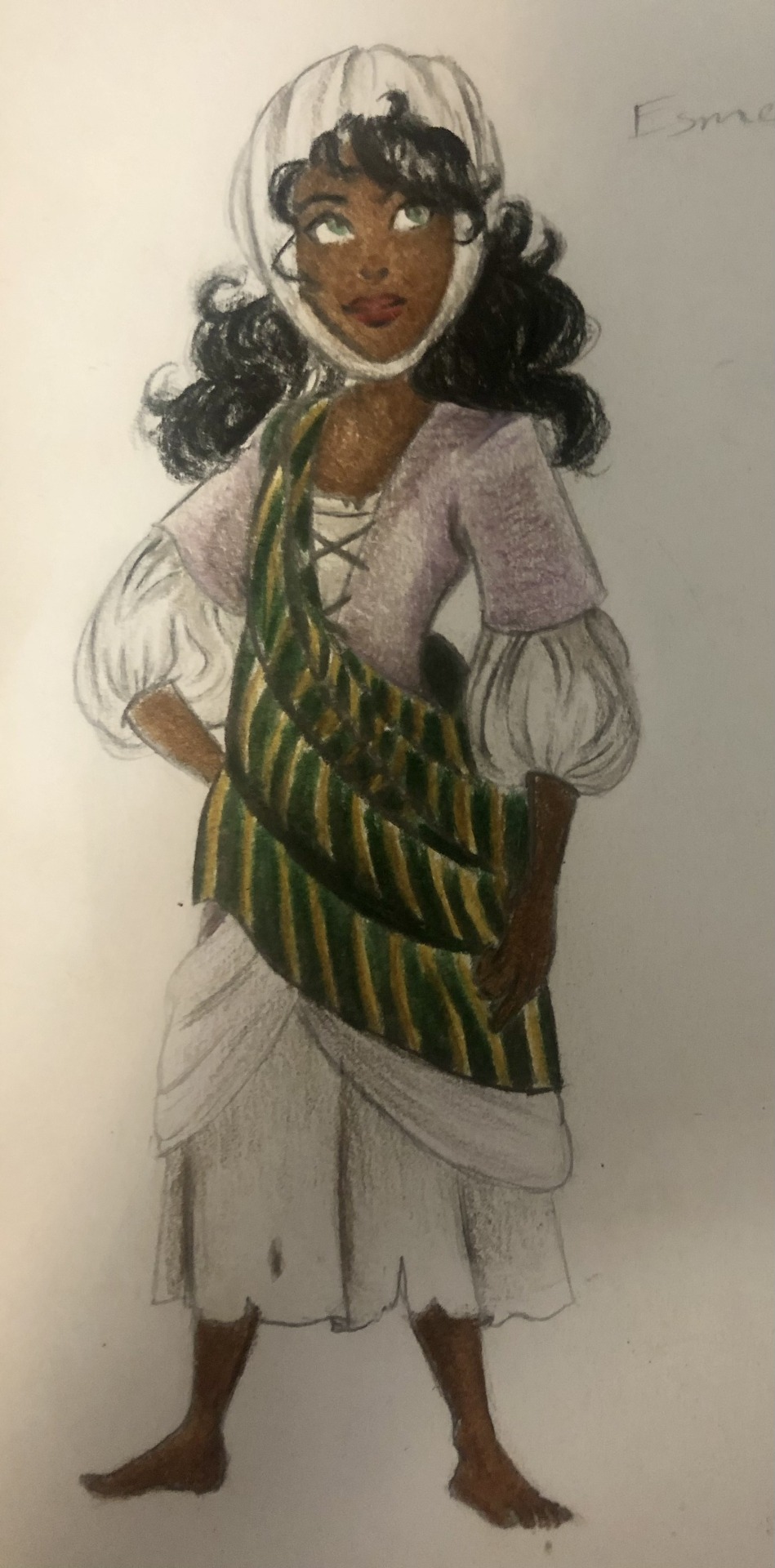
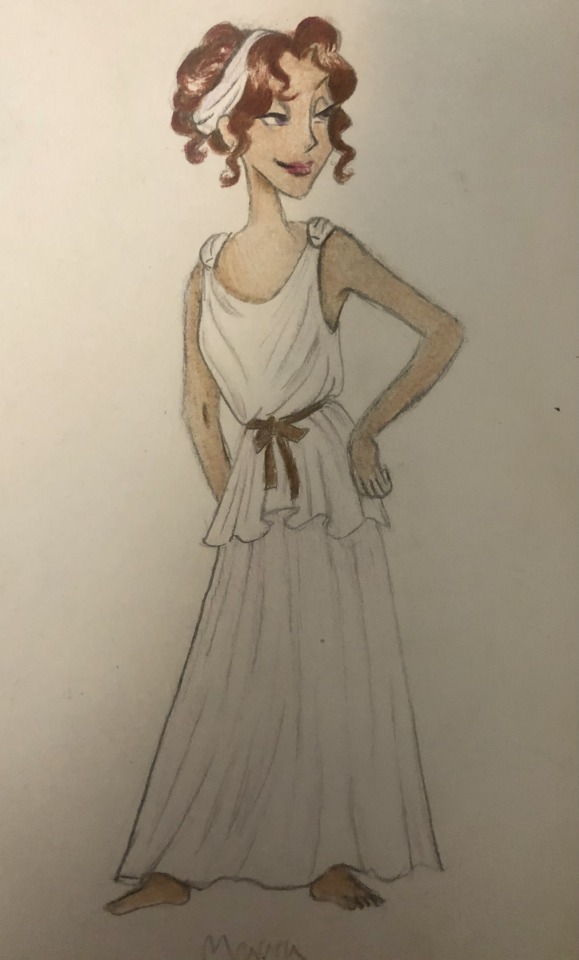
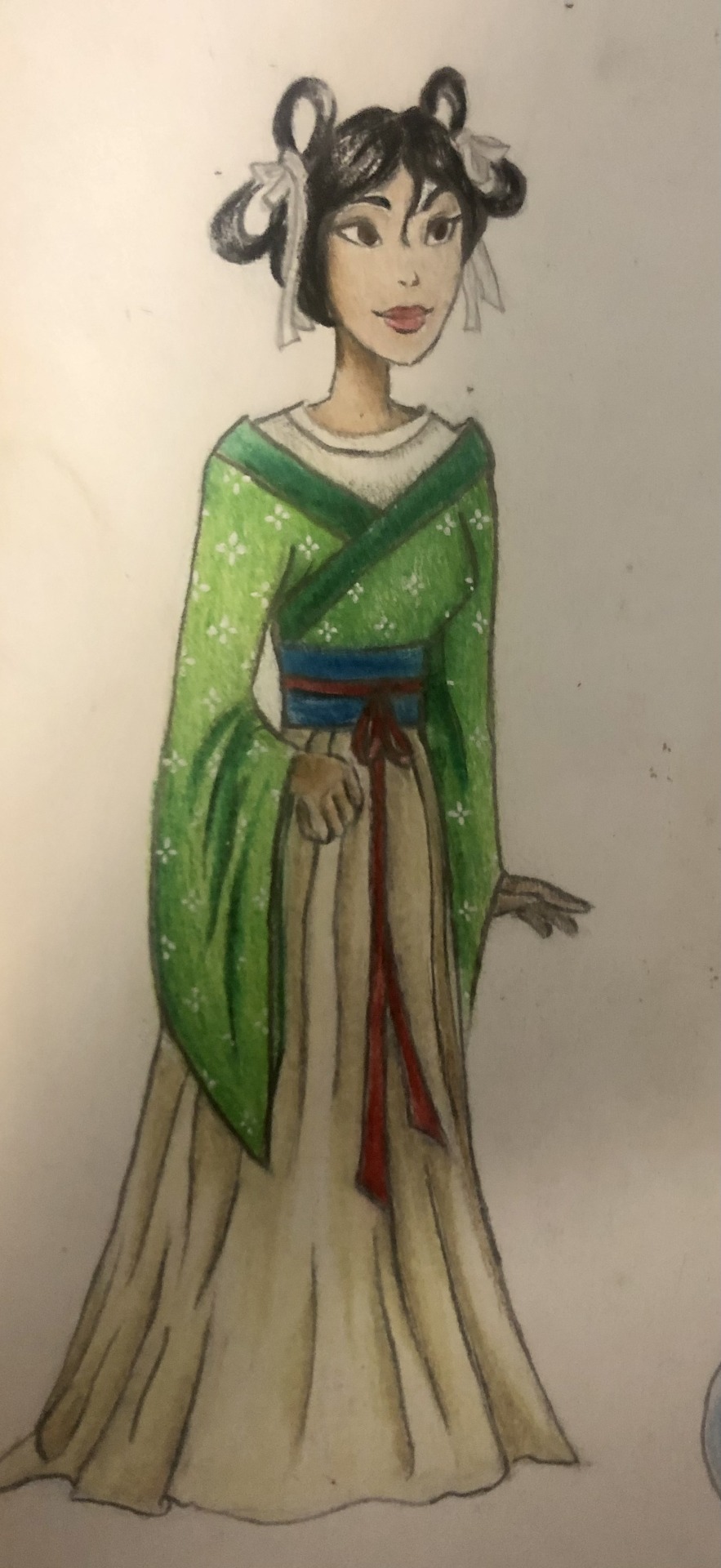
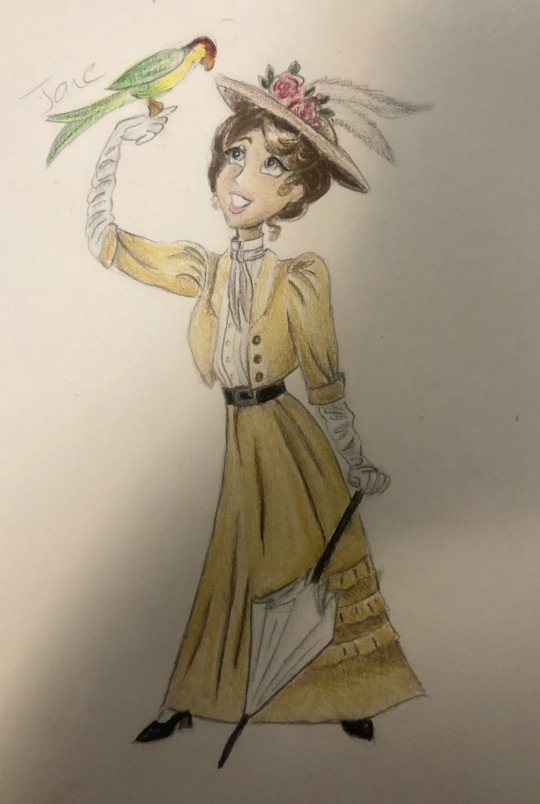
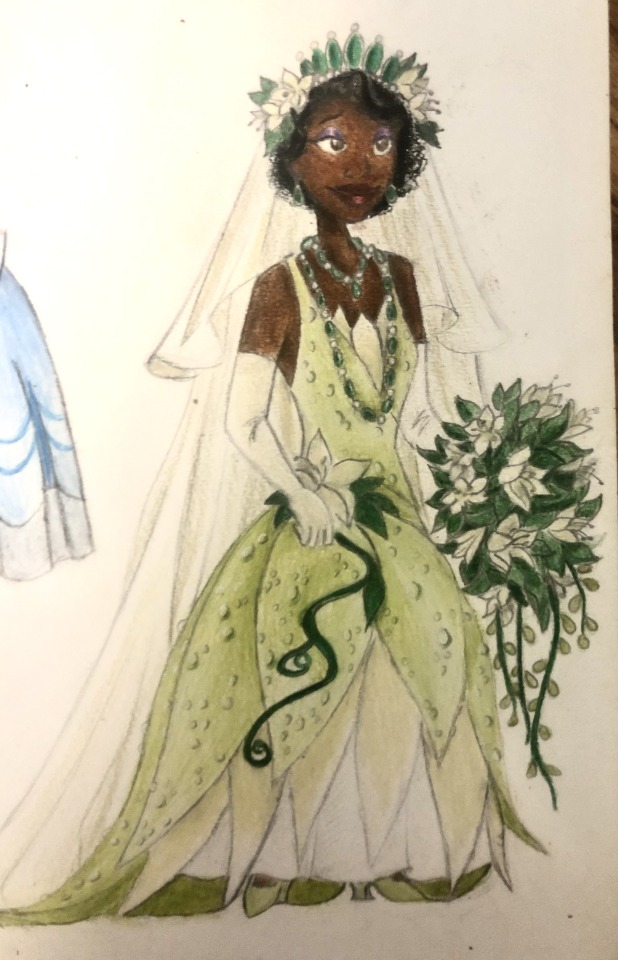
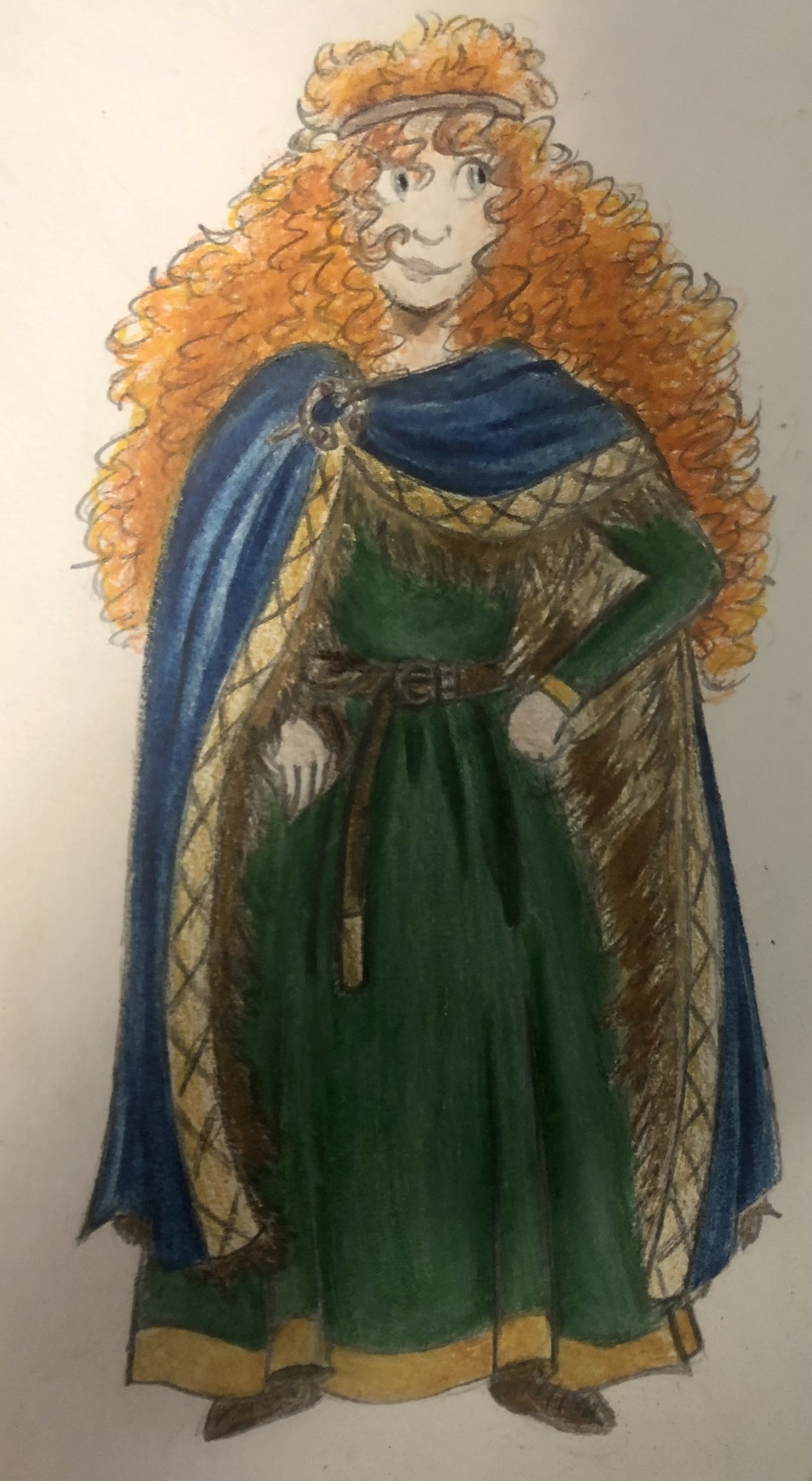
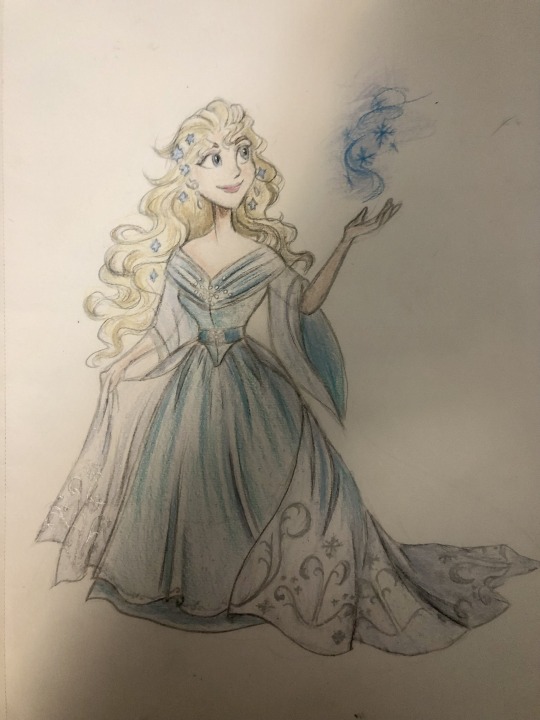
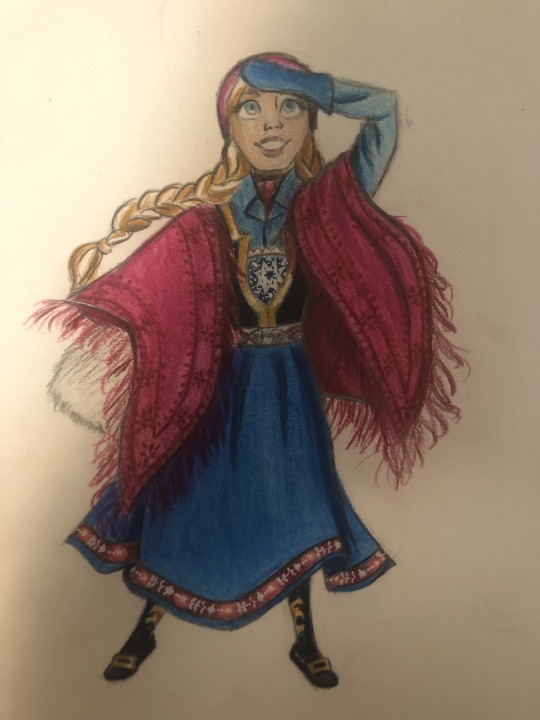
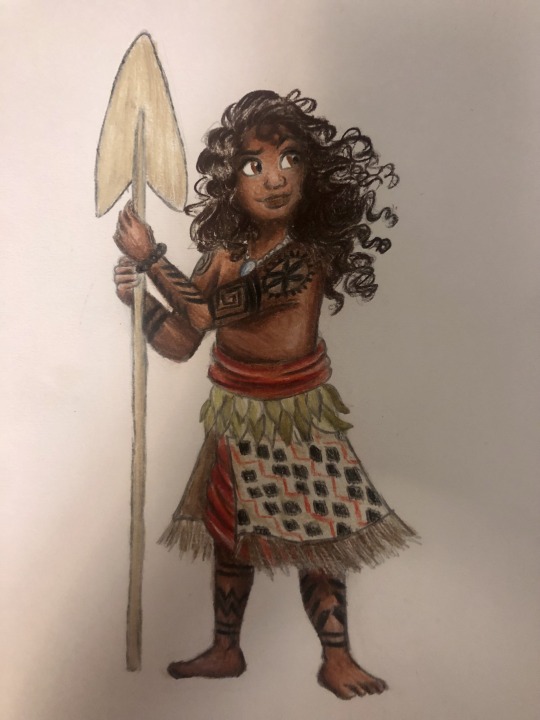


















Thought I’d do a little art throwback with my own historically accurate (well mostly) takes on Disney princesses and heroines, which I did from 2021 to 2022! Included in this series are:
Snow White - early 16th century Germany (then part of the Holy Roman Empire)
Cinderella - late 1860s-early 1870s France
Aurora - mid 15th century France
Eilonwy - 8th-10th century (present day) Wales
Ariel - 1830s Mediterranean Europe (maybe Italy)
Belle - 1760s-1770s France
Jasmine - 16th century Arabian Peninsula during the Ottoman Empire
Pocahontas - 1607 Virginia, (present day) United States of America
Esmeralda - 1480s France (Romani garb)
Megara - Classical period of Ancient Greece (c. 5th-4th centuries BCE)
Mulan - Wei Dynasty China (386-535 AD)
Jane - 1900s England
Tiana - late 1920s New Orleans, Louisiana, USA
Rapunzel - 1790s-1800s Germany
Merida - 10th-11th century (present day) Scotland
Elsa - late 1830s-early 1840s Norway
Anna - same period as Elsa (duh)
Moana - ancient Polynesian Islands (c. 1st century BCE)
I had so much fun drawing these, as well as doing the research for each one! I actually drew most of the outfits each one wears (in their first movies) but they're waaaaay down further in my blog.
I'm planning to do a digital redo of these someday, as well as do my own historical spins on other characters I haven't done yet.
Which one is your favorite?
Commissions info
#my art#angie's scribbles#disney#disney princess#disney princesses#disney heroines#disney girls#disney ladies#historical disney#historically accurate disney#historical fashion#snow white#snow white and the seven dwarfs#snow white 1937#cinderella#cinderella 1950#princess aurora#aurora#sleeping beauty#sleeping beauty 1959#eilonwy#princess eilonwy#the black cauldron#ariel#the little mermaid#the little mermaid 1989#belle#beauty and the beast#beauty and the beast 1991#jasmine
269 notes
·
View notes
Text
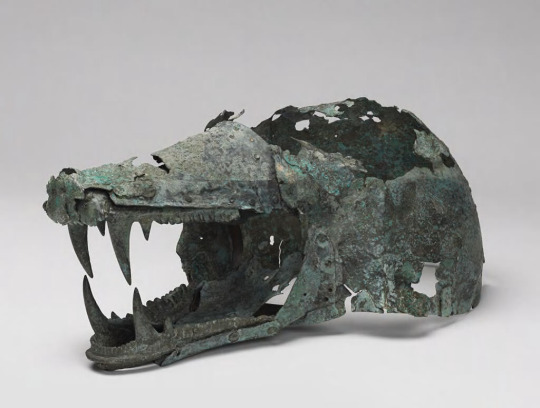


etruscan era boar/wolf's head helm (?) c.6th-5th century BC//wolf jawsome costume hate c.21st century AD
...Although this object has been described previously as a helmet, perhaps used as part of a ritual, the interpretation of the object as a helmet depends greatly on the modern reconstruction (3). The closest comparanda for the upper part of the head are boar-head protomes on Etruscan chariots, which consist of the top section of boar heads, including the snout, eyes, ears, and sometimes crests, but not the lower jaws (4). These protomes covered the draft poles of chariots at the juncture of the pole and the main body of the chariot. It is possible that the eyes, top of the snout, and parts of the upper dome are ancient pieces from an Etruscan chariot, while other sections, such as the teeth, tongue, and nose piece, were added later to create a more cohesive piece...
Transform yourself into the wolf that has had a bad rap in all the stories with this Jawesome Wolf Hat. This cap has a soft-sculpted wolf head surrounding its normal structure. It is lined for comfort and has hook and loop fasteners to keep the head in shape. (You'll even find a secret pocket so you don't need to depend on pants to keep your cards in place!)
#this is the only way i will be presenting ancient artifacts from now on#also PLEASE read the harvard art museum article i linked. it's so interesting#tagamemnon#art history#queueusque tandem abutere catilina patientia nostra
426 notes
·
View notes
Text
Roughly 10 Cool Historical Queer Figures More People Should Know About
Part 1 - From Ancient Era to Early Modern Era
In spirit of Pride Month here's some snippets of queer history I think are interesting.
I've been working on a series of deep dives into interesting historical queer figures, but I haven't had the time to continue my list after the first entry about Julie d'Aubigny. I do want to continue with it, but I came to the realization that I will never have to time to do all the cool and interesting figures in depth, since there's too many, so I decided to do a list with brief descriptions about some of my favorite figures who are not that well known. Some of them are more well-known than others but I think they all deserve more acknowledgement.
I was able to trim down the number of figures to (roughly) 20, which was still too many for one post, so it's two posts now. They are in chronological order, so this part is set mostly before Victorian Era and the second part will be from Victorian Era onward.
This list is centered around western history (but not exclusively) because that's the history I'm most familiar with, though it's definitely not all white, since western history is not all white. I will be avoiding using modern labels, since they are rarely exactly applicable to history, rather I will present whatever we know about these figures' gender, sexuality and relationships. If there's information about what language they used about themselves, I will use that. Often we don't know their own thoughts, so I will need to do some educated guess work, but I will lean towards ambiguity whenever evidence is particularly unclear. If you are the type of person who gets angry with the mere suggestion there's a possibility that a historical gnc person might not have been cis, I encourage you to read my answers to related asks (here and here) first before sending me another identical ask. Try to at least bring some new arguments if you decide to waste my time with your trans erasure.
1. Khnumhotep and Niankhkhnum (latter half of 2400 BCE)
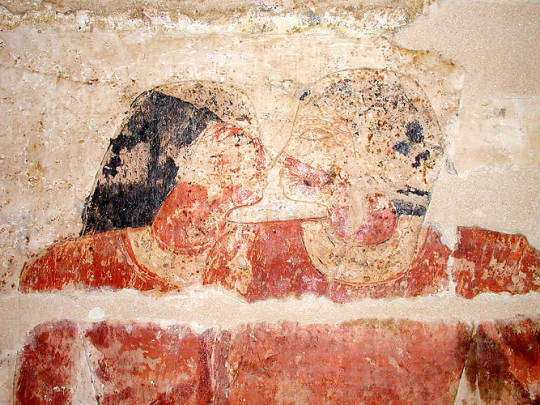

Khnumhotep and Niankhkhnum were ancient Egyptian royal servants, and possibly the first recorded gay couple in history known by name. They shared the title of Overseer of the Manicurists in the Palace of King Nyuserre Ini. They both had a wife and children, but they (along with their families) were buried together in a tomb. The tomb decorations show them similarly as other afterlife couples.
2. Marinos the Monk (c. 5th-8th century)
Marinos the Monk was born as Marina somewhere in eastern parts of Byzantine Empire, likely in the Levant. He was from a wealthy Christian family, possibly Coptic. Assigned female at birth his widowed father planned to marry him off and go to a monastery himself, but he convinced his father to take him with him dressed as a boy named Marinos. His father agreed and they were accepted as monks. After his father died many years later, he continued his life as a male presenting monk. Later he was accused of fathering an illegitimate child with a daughter of an innkeeper, which was not possible, but he didn't revoke the accusations, instead he begged for the abbot's forgiveness for "his sins". Marinos was banished from the monastery and became a beggar. For 10 years he raised his alleged illegitimate child as a father, until he was allowed to return to the monastery and do penance. Only after his death the abbot and the monks discovered his genitals and his inability to father children and were distraught for punishing an innocent man for 10 long years. The real father was discovered and along with the innkeeper and his daughter they all came to honor Marinos' grave and ask his forgiveness. He was canonized as a saint for his sacrificial selflessness, modesty and humility and honored across the Mediterranean from Ethiopia to France.
3. Mubārak and Muẓaffar al-Saqlabi (c. 10th - 11th century)
Mubārak and Muẓaffar were co-rulers of Taifa of Valencia in Muslim Spain. Al-Saqlabi means literally "of the Slavs", which in Al-Andalus was a general term for enslaved northern Europeans, as the two had been enslaved as children. They were in the service of another al-Saqlabi, a chief of police, and they worked they way up as civil servants till a local military coup in 1010, which resulted in them becoming the emirs of Taifa of Valencia. English language sources often describe them as "brothers" and "eunuchs", which gives the "historical gal pals" trope a concerning twist, but contemporary Muslim sources wrote fawningly about their passionate love, trust based on equality and mutual devotion. There was a popular genre of homoerotic poetry in the Islamic world at the time and poems in that genre were written about celebrating Mubārak and Muẓaffar's relationship. In 1018 Mubārak was killed in a riding accident and Muẓaffar shortly after in an uprising.
4. Eleno de Céspedes (1545 – died after 1589)
CW: genital inspection
Eleno was born in Andalusia, Spain, to an enslaved black Muslim woman and to a free Castillian peasant. He was assigned female at birth, given name Elena, and branded as a mulatto born to a slave. She was freed as a child and married to a stonemason at 15-16 years old. When pregnant, her husband left her and died a while later. Later Eleno testified that his intersex condition became externally visible, while he gave birth, and he became a man. He left his son to be raised by a friend and traveled around Spain. After he stabbed a pimp and ended up in jail, he started presenting as a man and openly courting women. Eventually he taught himself to be a surgeon with the help of a surgeon friend.
When he married María del Caño, his maleness was questioned and he was subjected to genital inspection multiple times and it was agreed by doctors that he had definitely male genitals, possibly also female genitals. After a year of marriage the couple was accused of sodomy. Eleno was tried by the Spanish Inquisition and subjected to more genital inspections, during which no penis was found. He claimed that his penis had been amputated after an injury. He defended himself in the trial by arguing that his intersex condition was natural and he had become a man after his pregnancy, so his marriage was legal. He was sentenced only for bigamy, since he had not confirmed that his husband was dead and punished as a male bigamist with 200 lashes and 10 years of public service to care for the poor in a public hospital. His fame attracted a lot of people wanting to be healed by him, which which was very embarrasing for the hospital so he was sent away and eventually exonerated from his charges.
7. Chevaliére d'Éon (1728-1810)

Charles d'Éon de Beaumont was born to a poor French noble family. In their 20s they became a government official and at 28 they joined the secret spy network of the king, Secret du Roi. They became a diplomat first in Russia and later in Britain while they used their position to spy for the king. Rumors circulated in London that they were secretly a woman. While in London they had a falling out with the French ambassador, accused him of attempted murder and published secret diplomatic correspondence. They were instead accused of libel and went into hiding. After the death of Louis XV in 1774 and the abolishment of Secret du Roi, d'Éon negotiated with the French government of the end of their exile in exchange for the rest of the secret documents he possessed. D'Éon took the name Charlotte, claimed she was in fact a cis woman - she had pretended to be man since a child so she could get the inheritance - and demanded the government to recognize her as such. When the king agreed and included funds for women's wardrobe, she agreed and returned to France in 1777. After that she helped rebels in the American War of Indepence - was not allowed to ]go and fight too, ghostwrote her not super reliable memoir, offered to lead a division of female soldiers against the Hasburgs in 1792 - was for some reason denied, attended fencing tournaments till 65 years old and settled down for the rest of her years with a widow, Mrs. Cole. After her death a surgeon reported that she had male primary sex characteristics, but fairly feminine secondary sex characteristics, like round breasts, which might suggest she had hormonal difference/was intersex in some way.
8. Public Universal Friend (1752-1819)

Public Universal Friend, or The Friend or PUF, was born as Jemima Wilkinson to Quaker parents in Rhodes Island, USA. Jemima contracted a disease in 1776, gained intense fever and almost died. The Friend claimed that she did die and God sent the Friend to occupy her body. The Friend didn't identify as man or a woman, and when asked about the Friend's gender, the Friend said "I am that I am". The Friend didn't want any gendered pronouns or gendered language to be used about the Friend. The Friend's pronouns, according to the writings of the Friend's followers, were "the Friend", "PUF" and possibly he. First recorded neo-pronouns perhaps? The Friend also dressed in androgynous/masculine manner.
The Friend started a bit cultish religious society disavowed by mainstream Quakers, The Society of Universal Friends, which I can only describe as chaotic good. The Friend first predicted a Day of Judgement would come in 1780 and when 1780 came and went, the Friend decided it was New England's Dark Day in 1780 and they had survived survived the Judgement Day so all was good then. The Friend preached for gender equality, free will, universal salvation (Jesus saved everyone and no one will go to hell) and abolition of slavery. The Friend persuaded any followers to free their slaves, which is probably the most chaotic good thing a potential cult leader can do with their influence over their followers, and several freed black people followed the Friend too. The Friend advocated for celibacy and was unfavorable towards marriage, but didn't think celibacy or rejection of marriage were necessary for everyone else, so it feels more like a personal preference. Many young unmarried women followed the Friend and some of them formed Faithful Sisterhood and took leadership positions among the Society.
The Society of Universal Friends tried to form a town for themselves around mid-1780s, till in 1799 the Friend was accused of blasphemy. The Friend successfully escaped the law two times. First the Friend, a skilled rider (what's a gender neutral version of horse girl?), escaped with a horse, then after an officer and an assistant tried to arrest the Friend at home, women of the house drove the men away. Third time 30 men surrounded the Friend's home at night, but a doctor convinced them that the Friend was in too poor health to move but would agree to appear at court. The Friend was cleared for all charges and even allowed to preach at the court.
9. Mary Jones (early 1800s–1853)
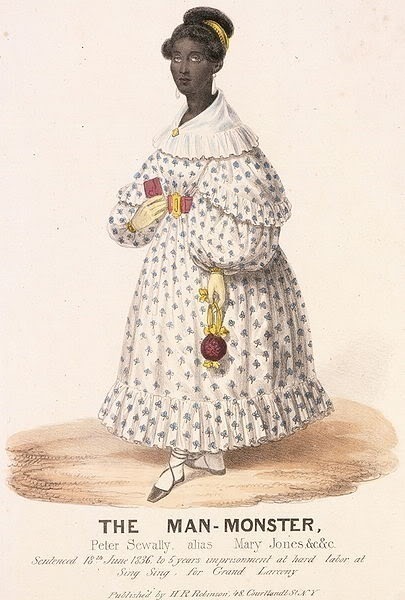

Mary Jones' origin is unknown, but she was an adult in 1836 in New York, USA. She was a free Black person, who preferred to present as a woman. She was sex worker by trade and used a prosthetic vagina. As a side hustle she would steel her customer's wallets, and usually they wouldn't tell anyone because it was 1830s and inter-racial sex and prostitution were illegal and everyone was repressed. Smart. Get your coin, girl. However after one of her more shameless customers discovered his wallet with 99 dollars inside had been replaced with a different man's empty wallet and contacted the police, she was arrested. The police discovered she had male genitals and when they searched her room they found several more stolen wallets. She appeared in court in her female presentation and when asked about her dress, she said that prostitutes she had worked with encouraged her to dress in women's clothing and said she looked better in them. They were right and she had since presented as a woman in her evening profession and among other Black people. She was convicted for grand larceny and sentenced to 5 years in prison. Later she continued to present as a woman and practice sex work, for which she was arrested for two more times.
10. George Sand (1804-1876)

George Sand was pen name of Amantine Lucile Aurore Dupin de Francueil, a French Romantic writer. Amantine was high-born with a countess as a grandmother. George wrote about themself with alternating masculine and feminine language, using feminine language when talking about his childhood, but masculine language often other times. Their friends also used both masculine and feminine terms about them. Victor Hugo for example said about them: "George Sand cannot determine whether she is male or female. I entertain a high regard for all my colleagues, but it is not my place to decide whether she is my sister or my brother." George preferred men's clothing in public, which was illegal for those seen as women without a permit, but they didn't ask for permissions. They alternated between masculine and feminine presentations. They were outspoken feminist, critic of the institution of marriage, committed republican and supporter of worker's rights. They were married at age 18, had two children and left their husband in 1831, but legally separated from him in 1835. They had many affairs with men and some with women, at least with actress Marie Dorval. Their most notable relationship was with Frédéric Chopin, but they fell out before Chopin's death.
#i will be absolutely writing in depth posts about some of these figures#the friend is 100% one of those i fucking love the friend that story is a gift that keeps giving#history#queer history#pride month#queer#lgbtq history#queer tag#trans history#gay history#sapphic history#lesbian history#intersex history
227 notes
·
View notes
Text
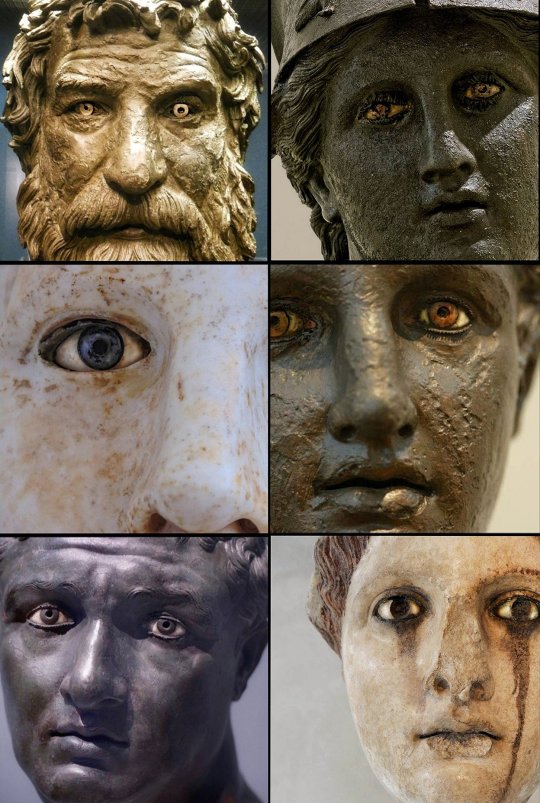

The piercing gaze of the ancient Greeks.
A collection of some famous Greek sculptures looking directly at...you
From left to right:
1) Antikythera Philosopher, 250 BCE
2) Athena of Piraeus, 4th century BCE
3) Head of Hygeia, 5th-4th cen. BCE
4) Antikythera Ephebe, 4th cent. BCE
5) Unknown man from Delos, c. 100
BCE
6) Head of a Goddess, 2nd cent. CE
📸 ArysPan
#dark academia#light academia#academia aesthetic#classical#academia#escapism#classic literature#books#books and libraries#architecture#greek#statue#sculpture#eyes#antikythera#Athena of Piraeus#Head of Hygeia#royal core#cottage core#aesthetic
2K notes
·
View notes
Text

Mania (active during the 5th to early 4th century BCE) served as the governor of Aeolis and led armies as a vassal of the Achaemenid Empire.
Her husband, Zenis of Dardanus, had governed Aeolis for the satrap (provincial governor) Pharnabazus II. When Zenis died of illness, Mania petitioned Pharnabazus, who had initially planned to appoint a man as her husband's successor. However, Mania sought the position for herself. According to Xenophon, she approached Pharnabazus with a large retinue and many gifts, both for him and to win favor with his concubines and the influential men at his court.
Her request was granted, and Mania became “mistress of the province”. She governed effectively and led successful military campaigns. She expanded her territory, capturing the cities of Larisa, Hamaxitos, and Kolonai with a force of Greek mercenaries. Mania also accompanied Pharnabazus twice in battle. Impressed by her abilities, he rewarded her and sometimes sought her counsel.
Polyaenus praised her as an exceptional general:
“She always went to battle drawn in a chariot; she gave out orders while in action, formed her lines, and rewarded every man who fought well, as she saw he deserved. And – what has scarcely happened to any general, except herself – she never suffered a defeat.”
Mania was over 40 years old (c.399 BCE) when she was murdered by her son-in-law Meidias, who reportedly claimed that “it was a disgraceful thing for a woman to be the ruler while he was in a private station.” Meidias also killed Mania’s 17-year-old son.
He then asked Pharnabazus to grant him control of the territory, but Pharnabazus rejected his gifts, stating that “he would not wish to live if he failed to avenge Mania.” Eventually, Mania’s cities were seized by the Spartan general Dercylidas. Meidias thus gained nothing in murdering Mania.
Here is the link to my Ko-Fi. Your support would be much appreciated!
Further reading:
Polyaenus, Stratagems in war
Xenophon, Hellenica
#mania#history#women in history#historyedit#women's history#ancient history#ancient world#warrior women#female generals#Achaemenid Empire#historical figures#4th century BCE#5th century BCE
128 notes
·
View notes
Text
sculptures* round 1 poll 9


face urn from the Pomeranian culture (7th-3rd century BC) found in Niestępowo:
propaganda: Okay, not sure if this counts as a sculpture but I love this old little urns with their faces. [check out more examples here!!]
zoomorphic vessel from the Lusatian culture (13th-5th c. BC) found in Gorszewice:
propaganda: Friend shaped
#archaeology#is this technically “polish art”? no. but what the hell#ty to the person(s) who submitted these#polls#sculptures#br3r1
117 notes
·
View notes
Text
Did the ancient Celts really paint themselves blue?
Part 2: Irish tattoos
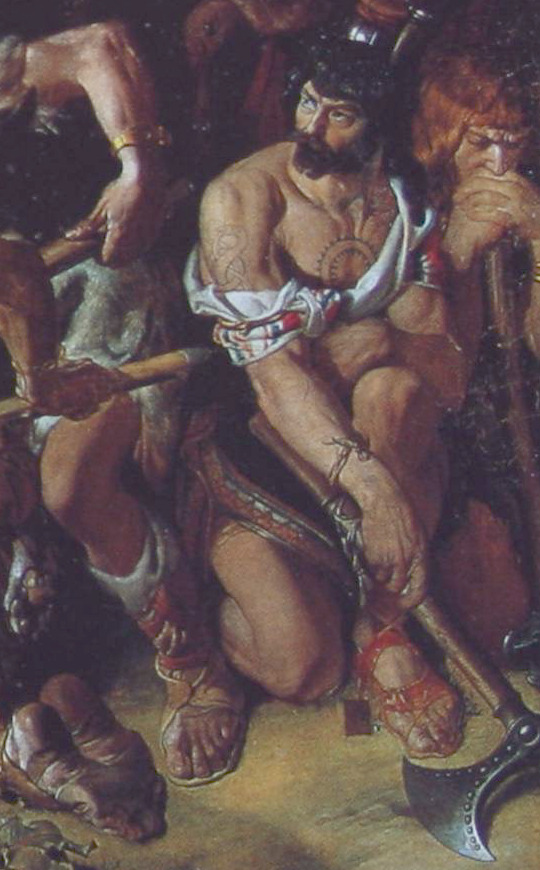
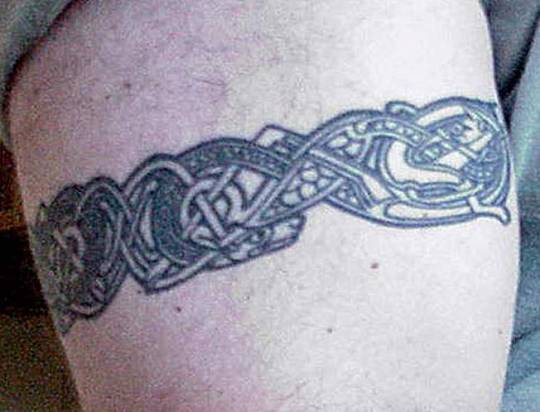




Clockwise from top left: Deirdre and Naoise from the Ulster Cycle by amylouioc, detail from The Marriage of Strongbow and Aoife by Daniel Maclise, a modern Celtic revival tattoo, Michael Flatley in a promotional image for the Irish step dance show 'Lord of the Dance'
This is my second post exploring the historical evidence for our modern belief that the ancient and medieval Insular Celts painted or tattooed themselves with blue pigment. In the first post, I discussed the fact that body paint seems to have been used by residents of Great Britain between approximately 50 BCE to 100 CE. In this post, I will examine the evidence for tattooing.
Once again, I am looking at sources pertaining to any ethnic group who lived in the British Isles, this time from the Roman Era to the early Middle Ages. The relevant text sources range from approximately 200 CE to 900 CE. I am including all British Isles cultures, because a) determining exactly which Insular culture various writers mean by terms like ‘Briton’, ‘Scot’, and ‘Pict’ is sometimes impossible and b) I don’t want to risk excluding any relevant evidence.
Continental Written Sources:
The earliest written source to mention tattoos in the British Isles is Herodian of Antioch’s History of the Roman Empire written circa 208 CE. In it, Herodian says of the Britons, "They tattoo their bodies with colored designs and drawings of all kinds of animals; for this reason they do not wear clothes, which would conceal the decorations on their bodies" (translation from MacQuarrie 1997). Herodian is probably reporting second-hand information given to him by soldiers who fought under Septimius Severus in Britain (MacQuarrie 1997) and shouldn't be considered a true primary source.
Also in the early 3rd century, Gaius Julius Solinus says in Collectanea Rerum Memorabilium 22.12, "regionem [Brittaniae] partim tenent barbari, quibus per artifices plagarum figuras iam inde a pueris variae animalium effigies incorporantur, inscriptisque visceribus hominis incremento pigmenti notae crescunt: nec quicquam mage patientiae loco nationes ferae ducunt, quam ut per memores cicatrices plurimum fuci artus bibant."
Translation: "The area [of Britain] is partly occupied by barbarians on whose bodies, from their childhood upwards, various forms of living creatures are represented by means of cunningly wrought marks: and when the flesh of the person has been deeply branded, then the marks of the pigment get larger as the man grows, and the barbaric nations regard it as the highest pitch of endurance to allow their limbs to drink in as much of the dye as possible through the scars which record this" (from MacQuarrie 1997).
This passage, like Herodian's, is clearly a description of tattooing, not body staining or painting. That said, I have no idea of tattoos actually work like this. I would think this would result in the adult having a faded, indistinct tattoo, but if anyone knows otherwise, please tell me.
The poet Claudian, writing in the early 5th c., is the first to specifically mention the Picts having tattoos (MacQuarrie 1997). In De Bello Gothico he says, "Venit & extremis legio praetenta Britannis,/ Quæ Scoto dat frena truci, ferroque notatas/ Perlegit exanimes Picto moriente figuras."
Translation: "The legion comes to make a trial of the most remote parts of Britain where it subdues the wild Scot and gazes on the iron-wrought figures on the face of the dying Pict" (from MacQuarrie 1997).
Last, and possibly least, of our Mediterranean sources is Isidore of Seville. In the early 7th c. he writes, "the Pictish race, their name derived from their body, which the efficient needle, with minute punctures, rubs in the juices squeezed from native plants so that it may bring these scars to its own fashion [. . .] The Scotti have their name from their own language by reason of [their] painted body, because they are marked by iron needles with dark coloring in the form of a marking of varying shapes." (translation from MacQuarrie 1997)
Isidore is the earliest writer to explicitly link the name 'Pict' to their 'painted' (Latin: pictus) i.e. tattooed bodies. Isidore probably borrowed information for his description from earlier writers like Claudian (MacQuarrie 1997).
In the 8th century, we have a source that definitely isn't Romans recycling old hearsay. In 786, a pair of papal legates visited the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms of Mercia and Northumbria (Story 1995). In their report to Pope Hadrian, the legates condemn pagans who have "superimposed most hideous cicatrices" (i.e gotten tattoos), likening the pagan practice to coloring oneself "with dirty spots". The location of the visit indicates that these are Anglo-Saxon tattoos rather than Celtic, but some scholars have suggested that the Anglo-Saxons might have adopted the practice from the Brittonic Celts (MacQuarrie 1997).
A gloss in the margin of the late 9th c. German manuscript Fulda Aa 2 defines Stingmata [sic] as "put pictures on the bodies as the Irish (Scotti) do." (translation from MacQuarrie 1997).

Fulda Aa 2 folio 43r The gloss is on the left underlined in white.
Irish Written Sources:
Irish texts that mention tattoos date to approximately 700-900 CE, although some of them have glosses that may be slightly later, and some of them cannot be precisely dated.
The first text source is a poem known in English as "The Caldron of Poesy," written in the early 8th c. (Breatnach 1981). The poem is purportedly the work of Amairgen, ollamh of the legendary Milesian kings. In the first stanza of the poem, he introduces himself saying, "I being white-kneed, blue-shanked, grey-bearded Amairgen." (translation from Breatnach 1981)

The text of the poem with interline glosses from Trinity College Dublin MS 1337/1
The word garrglas (blue-shanked) has a Middle Irish (c. 900-1200) gloss added by a later scribe, defining garrglas as: "a tattooed shank, or who has the blue tattooed shank" (Breatnach 1981).
Although Amairgen was a mythical figure, the position ollamh was not. An ollamh was the highest rank of poet in medieval Ireland, considered worthy of the same honor-price as a king (Carey 1997, Breatnach 1981). The fact that a man of such esteemed status introduces himself with the descriptor 'blue-shanked' suggests that tattoos were a respectable thing to have in early medieval Ireland.
The leg tattoos are also mentioned c. 900 CE in Cormac’s Glossary. It defines feirenn as "a thong which is about the calf of a man whence ‘a tattooed thong is tattooed about [the] calf’" (translation from MacQuarrie 1997)
The Irish legal text Uraicecht Becc, dated to the 9th or early 10th c., includes the word creccoire on a list of low-status occupations (Szacillo 2012, MacNeill 1924). A gloss defines it as: crechad glass ar na roscaib, a phrase which Szacillo interprets as meaning "making grey-blue sore (tattooing) on the eyes" (2012). This sounds rather strange, but another early Irish text clarifies it.
The Vita sancti Colmani abbatis de Land Elo written around the 8th-9th centuries (Szacillo 2012) contains the following episode:
On another time, St Colmán, looking upon his brother, who was the son of Beugne, saw that the lids of his eyes had been secretly painted with the hyacinth colour, as it was in the custom; and it was a great offence at St Colmán’s. He said to his brother: ‘May your eyes not see the light in your life (any more). And from that hour he was blind, seeing nothing until (his) death. (translation from Szacillo 2012).
The original Latin phrase describing what so offended St Colmán "palpebre oculorum illius latenter iacinto colore" does not contain the verb paint (pingo). It just says his eyelids were hyacinth (blue) colored. This passage together with the gloss from the Uraicecht Becc implies that there was a custom of tattooing people's eyelids blue in early medieval Ireland. A creccoire* was therefore a professional eyelid tattooer or a tattoo artist.
A possible third reference to tattooing the area around the eye is found in a list of Old Irish kennings. The kenning for the letter 'B' translates as 'Beauty of the eyebrow.' This kenning is glossed with the word crecad/creccad (McManus 1988). Crecad could be translated as cauterizing, branding, or tattooing (eDIL). McManus suggests "adornment (by tattooing) of the eyebrow" as a plausible interpretation of how crecad relates to the beauty of the eyebrow (1988). The precise date of this text is not known (McManus 1988), but Old Irish was used c. 600-900 CE, meaning this text is of a similar date to the other Irish references to tattoos.

Kenning of the letter 'b' with gloss from TCD MS 1337/1
There is a sharp contrast between the association of tattoos with a venerated figure in 'The Caldron of Poesy', and their association with low-status work and divine punishment in the Uraicecht Becc and the Vita. This indicates that there was a shift in the cultural attitude towards tattoos in Ireland during the 7th-9th centuries. The fact that a Christian saint considered getting tattoos a big enough offense to punish his own brother with blindness suggests that tattooing might have been a pagan practice which gradually got pushed out by the Catholic Church. This timeline is consistent with the 786 CE report of the papal legates condemning the pagan practice of tattooing in Great Britain (MacQuarrie 1997).
There are some mentions of tattooing in Lebor Gabála Érenn, but the information largely appears to be borrowed from Isidore of Seville (MacQuarrie 1997). The fact that the writers of LGE just regurgitated Isidore's meager descriptions of Pictish and Scottish (ie Irish) tattooing without adding any details, such as the designs used or which parts of the body were tattooed, makes me think that Insular tattooing practices had passed out of living memory by the time the book was written in the 11th century.
*There is some etymological controversy over this term. Some have suggested that the Old Irish word for eyelid-tattooer should actually be crechaire. more info Even if this hypothesis is correct, and the scribe who wrote the gloss on creccoire mistook it for crechaire, this doesn't contradict my argument. The scribe clearly believed that eyelid-tattooer belonged on a list of low-status occupations.
Discussion:
Like Julius Cesar in the last post, Herodian of Antioch c. 208 CE makes some dubious claims of Celtic barbarism, stating that the Britons were: "Strangers to clothing, the Britons wear ornaments of iron at their waists and throats; considering iron a symbol of wealth, they value this metal as other barbarians value gold" (translation from MacQuarrie 1997). If the Britons wore nothing but iron jewelry, then why did they have brass torcs and 5,000 objects that look like they're meant to attach to fabric, Herodian?
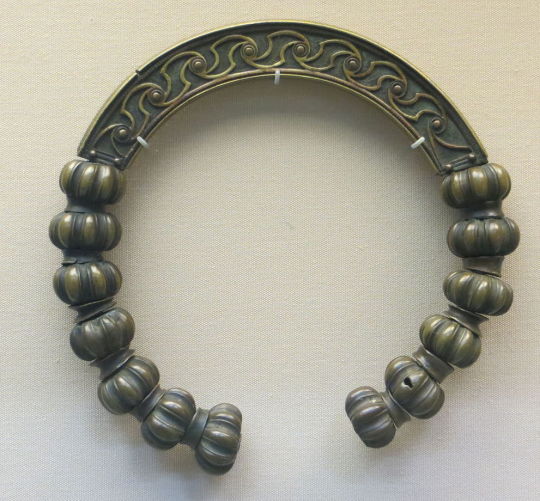
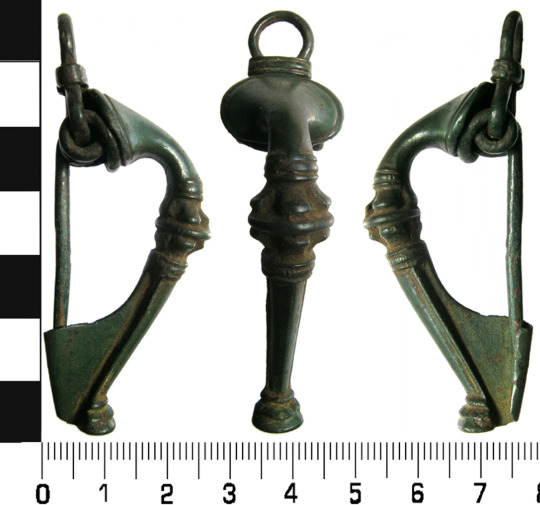


Brass torc from Lochar Moss, Scotland c. 50-200 CE. Romano-British trumpet brooch from Cumbria c. 75-175 CE. image from the Portable Antiquities Scheme.
Trumpet brooches are a Roman Era artifact invented in Britain, that were probably pinned to people's clothing. more info
Although Herodian and Solinus both make dubious claims, there are enough differences between them to indicate that they had 2 separate sources of information, and one was not just parroting the other. This combined with the fact that we have more-reliable sources from later centuries confirming the existence of tattoos in the British Isles makes it probable that there was at least a grain of truth to their claims of tattooing.
There is a common belief that the name Pict originated from the Latin pictus (painted), because the Picts had 'painted' or tattooed bodies. The Romans first used the name Pict to refer to inhabitants of Britain in 297 CE (Ware 2021), but the first mention of Pictish tattoos came in 402 CE (Carr 2005), and the first explicit statement that the name Pict was derived from the Picts' tattooed bodies came from Isidore of Seville c. 600 CE (MacQuarrie 1997). Unless someone can find an earlier source for this alleged etymology than Isidore, I am extremely skeptical of it.
Summary of the written evidence:
Some time between c. 79 CE (Pliny the Elder) and c. 208 CE (Herodian of Antioch) the practice of body art in Great Britain changed from staining or painting the skin to tattooing. Third century Celtic Briton tattoo designs depicted animals. Pictish tattoos are first mentioned in the 5th century.
The earliest mention of Irish tattoos comes from Isidore of Seville in the early 6th c., but since it seems to have been a pre-Christian practice, it likely started earlier. Irish tattoos of the 8-9th centuries were placed on the area around the eye and on the legs. They were a bluish color. The 8th c. Anglo-Saxons also had tattoos.
Tattooing in Ireland probably ended by the early 10th c., possibly because of Christian condemnation. Exactly when tattooing ended in Great Britain is unclear, but in the 12th c., William of Malmesbury describes it as a thing of the past (MacQuarrie 1997). None of these sources give much detail as to what the tattoos looked like.
The Archaeology of Insular Ink:
In spite of the fact that tattooing was a longer-lasting, more wide-spread practice in the British Isles than body painting, there is less archaeological evidence for it. This may be because the common tools used for tattooing, needles or blades for puncturing the skin, pigments to make the ink, and dishes to hold the ink, all had other common uses in the Middle Ages that could make an archaeologist overlook their use in tattooing. The same needle that was used to sew a tunic could also have been used to tattoo a leg (Carr 2005). A group of small, toothed bronze plates from a Romano-British site at Chalton, Hampshire might have been tattoo chisels (Carr 2005) or they might have been used to make stitching holes in leather (Cunliffe 1977).
Although the pigment used to make tattoos may be difficult to identify at archaeological sites, other lines of evidence might give us an idea of what it was. Although the written sources tell us that Irish tattoos were blue, the popular modern belief that woad was the source of the tattoo pigment is, in my opinion, extremely unlikely for a couple of reasons:
1) Blue pigment from woad doesn't seem to work as tattoo ink. The modern tattoo artists who have tried to use it have found that it burns out of the person's skin, leaving a scar with no trace of blue in it (Lambert 2004).
2) None of the historical sources actually mention tattooing with woad. Julius Cesar and Pliny the Elder mention something that might have been woad, but they were talking about body paint, not tattoos. (see previous post) Isidore of Seville claimed that the Picts were tattooing themselves with "juices squeezed from native plants", but even assuming that Isidore is a reliable source, you can't get blue from woad by just squeezing the juice out of it. In order to get blue out of woad, you have to first steep the leaves, then discard the leaves and add a base like ammonia to the vat (Carr 2005). The resulting dye vat is not something any knowledgeable person would describe as plant juice, so either Isidore had no idea what he was talking about, or he is talking about something other than blue pigment from woad.
In my opinion, the most likely pigment for early Irish and British tattoos is charcoal. Early tattoos found on mummies from Europe and Siberia all contain charcoal and no other colored pigment. These tattoos range in date from c. 3300 BCE (Ötzi the Iceman) to c. 300 CE (Oglakhty grave 4) (Samadelli et al 2015, Pankova 2013).
Despite the fact that charcoal is black, it tends to look blueish when used in tattoos (Pankova 2013). Even modern black ink tattoos that use carbon black pigment (which is effectively a purer form of charcoal) tend to look increasingly blue as they age.
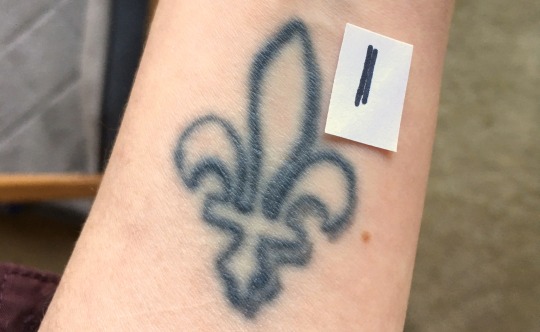
A 17-year-old tattoo in carbon black ink photographed with a swatch of black Sharpie on white printer paper.
The fact that charcoal-based tattoo inks continue to be used today, more than 5,000 years after the first charcoal tattoo was given, shows that charcoal is an effective, relatively safe tattoo pigment, unlike woad. Additionally, charcoal can be easily produced with wood fires, meaning it would have been a readily available material for tattoo artists in the early medieval British Isles. We would need more direct evidence, like a tattooed body from the British Isles, to confirm its use though.
As of June 2024, there have been at least 279 bog bodies* found in the British Isles (Ó Floinn 1995, Turner 1995, Cowie, Picken, Wallace 2011, Giles 2020, BBC 2024), a handful of which have made it into modern museum collections. Unfortunately, tattoos have not been found on any of them. (We don't have a full scientific analysis for the 2023 Bellaghy find yet though.)
*This number includes some finds from fens. It does not include the Cladh Hallan composite mummies.
Tattoos in period art?
It has been suggested that the man fight a beast on Book of Kells f. 130r may be naked and covered in tattoos (MacQuarrie 1997). However, Dress in Ireland author Mairead Dunlevy interprets this illustration as a man wearing a jacket and trews (Dunlevy 1989). Looking at some of the other figures in the Book of Kells, I agree with Dunlevy. F. 97v shows the same long, fitted sleeves and round neckline. F. 292r has long, fitted leg coverings, presumably trews, and also long sleeves. The interlace and dot motifs on f. 130r's legs may be embroidery. Embroidered garments were a status symbol in early medieval Ireland (Dunlevy 1989).
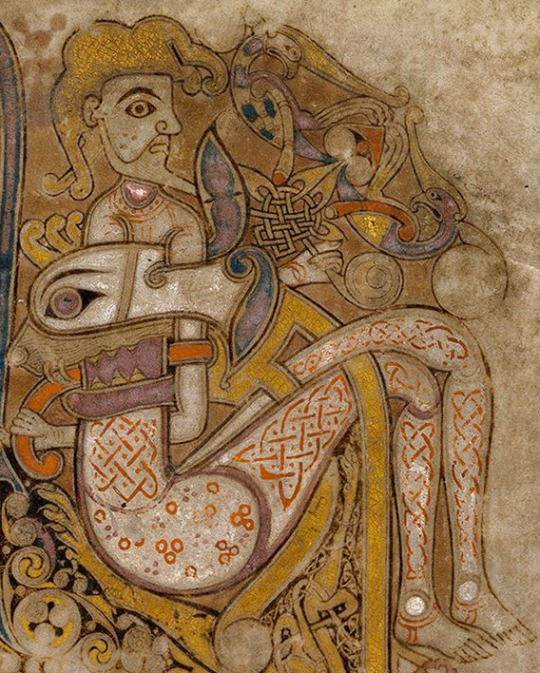

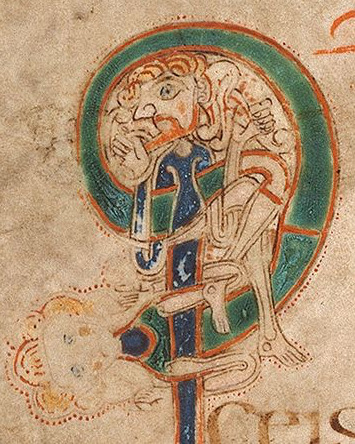

Left to right: Book of Kells folios 130r, 97v, 292r
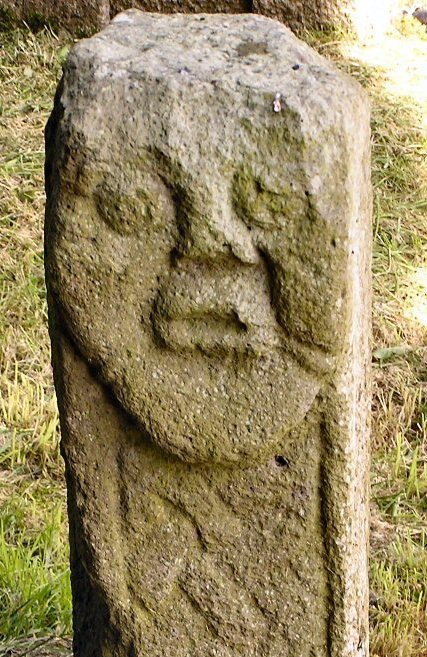
A couple of sculptures in County Fermanagh might sport depictions of Irish tattoos. The first, known as the Bishop stone, is in the Killadeas cemetery. It features a carved head with 2 marks on the left side of the face, a double line beside the mouth and a single line below the eye. These lines may represent tattoos.
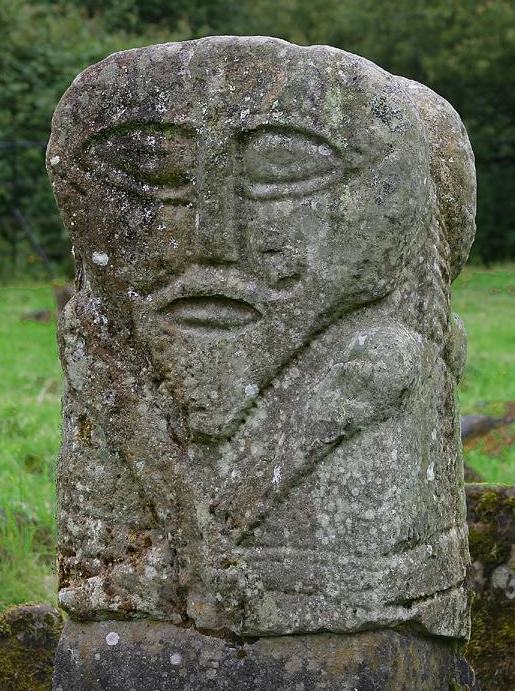


The second sculpture is the Janus figure on Boa Island. (So named because it has 2 faces; it's not Roman.) It has marks under the right eye and extending from the corner of the left eye that may be tattoos.
I cannot find a definitive date for the Bishop stone head, but it bears a strong resemblance to the nearby White Island church figures. The White Island figures are stylistically dated to the 9th-10th centuries and may come from a church that was destroyed by Vikings in 837 CE (Halpin and Newman 2006, Lowry-Corry 1959). The Janus figure is believed to be Iron Age or early medieval (Halpin and Newman 2006).
Conclusions:
Despite the fact that tattooing as a custom in the British Isles lasted for more than 500 years and was practiced by at least 3 different cultures, written sources remain our only solid evidence for it. With only a dozen sources, some of which probably copied each other, to cover this time span, there are huge gaps in our knowledge. The 4th century Picts may not have had the same tattoo designs, placements or reasons for getting tattooed as the 8th c. Irish or Anglo-Saxons. These sources only give us fragments of information on who got tattooed, where the tattoos were placed, what they looked like, how the tattoos were done, and why people got tattooed. Further complicating our limited information is the fact that most of the text sources come from foreigners and/or people who were prejudiced against tattooing, which calls their accuracy into question.
'The Cauldron of Posey' is one source that provides some detail while not showing prejudice against tattoos. The author of the poem was probably Christian, but the poem appears to have been written at a time when Pagan practices were still tolerated in Ireland. I have a complete translation of the poem along with a longer discussion of religious elements here.
Leave me a tip?
Bibliography:
BBC (2024). Bellaghy bog body: Human remains are 2,000 years old https://www.bbc.com/news/uk-northern-ireland-68092307
Breatnach, L. (1981). The Cauldron of Poesy. Ériu, 32(1981), 45-93. https://www.jstor.org/stable/30007454
Carey, J. (1997). The Three Things Required of a Poet. Ériu, 48(1997), 41-58. https://www.jstor.org/stable/30007956
Carr, Gillian. (2005). Woad, Tattooing and Identity in Later Iron Age and Early Roman Britain. Oxford Journal of Archaeology 24(3), 273–292. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-0092.2005.00236.x
Cowie, T., Pickin, J. and Wallace, T. (2011). Bog bodies from Scotland: old finds, new records. Journal of Wetland Archaeology 10(1): 1–45.
Cunliffe, B. (1977) The Romano-British Village at Chalton, Hants. Proceedings of the Hampshire Field Club and Archaeological Society, 33(1977), 45-67.
Dunlevy, Mairead (1989). Dress in Ireland. B. T. Batsford LTD, London.
eDIL s.v. crechad https://dil.ie/12794
Giles, Melanie. (2020). Bog Bodies Face to face with the past. Manchester University Press, Manchester. https://library.oapen.org/viewer/web/viewer.html?file=/bitstream/handle/20.500.12657/46717/9781526150196_fullhl.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y
Halpin, A., Newman, C. (2006). Ireland: An Oxford Archaeological Guide to Sites from Earliest Times to AD 1600. Oxford University Press, Oxford. https://archive.org/details/irelandoxfordarc0000halp/page/n3/mode/2up
Hoecherl, M. (2016). Controlling Colours: Function and Meaning of Colour in the British Iron Age. Archaeopress Publishing LTD, Oxford. https://www.google.com/books/edition/Controlling_Colours/WRteEAAAQBAJ?hl=en&gbpv=0
Lambert, S. K. (2004). The Problem of the Woad. Dunsgathan.net. https://dunsgathan.net/essays/woad.htm
Lowry-Corry, D. (1959). A Newly Discovered Statue at the Church on White Island, County Fermanagh. Ulster Journal of Archaeology, 22(1959), 59-66. https://www.jstor.org/stable/20567530
MacQuarrie, Charles. (1997). Insular Celtic tattooing: History, myth and metaphor. Etudes Celtiques, 33, 159-189. https://doi.org/10.3406/ecelt.1997.2117
McManus, D. (1988). Irish Letter-Names and Their Kennings. Ériu, 39(1988), 127-168. https://www.jstor.org/stable/30024135
Ó Floinn, R. (1995). Recent research into Irish bog bodies. In R. C. Turner and R. G. Scaife (eds) Bog Bodies: New Discoveries and New Perspectives (p. 137–45). British Museum Press, London. ISBN: 9780714123059
Pankova, S. (2013). One More Culture with Ancient Tattoo Tradition in Southern Siberia: Tattoos on a Mummy from the Oglakhty Burial Ground, 3rd-4th century AD. Zurich Studies in Archaeology, 9(2013), 75-86.
Samadelli, M., Melisc, M., Miccolic, M., Vigld, E.E., Zinka, A.R. (2015). Complete mapping of the tattoos of the 5300-year-old Tyrolean Iceman. Journal of Cultural Heritage, 16(2015), 753–758.
Story, Joanna (1995). Charlemagne and Northumbria : the in
fluence of Francia on Northumbrian politics in the later eighth and early ninth centuries. [Doctoral Thesis]. Durham University. http://etheses.dur.ac.uk/1460/
Szacillo, J. (2012). Irish hagiography and its dating: a study of the O'Donohue group of Irish saints' lives. [Doctoral Thesis]. Queen's University Belfast.
Turner, R.C. (1995). Resent Research into British Bog Bodies. In R. C. Turner and R. G. Scaife (eds) Bog Bodies: New Discoveries and New Perspectives (p. 221–34). British Museum Press, London. ISBN: 9780714123059
Ware, C. (2021). A Literary Commentary on Panegyrici Latini VI(7) An Oration Delivered Before the Emperor Constantine in Trier, ca. AD 310. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. https://www.google.com/books/edition/A_Literary_Commentary_on_Panegyrici_Lati/oEwMEAAAQBAJ?hl=en&gbpv=0
#early medieval#roman era#pict#tattoos#ancient celts#apologies to people who wanted a shorter post#archaeology#art#anecdotes and observations#statutes and laws#irish history#gaelic ireland#medieval ireland#anglo saxon#insular celts#romano british
102 notes
·
View notes
Text
Medieval Hermitage atop Katskhi Pillar, in Georgia (South Caucasus), c. 800-900 CE: this church was built during the Middle Ages, and it sits atop an enormous limestone column that has been venerated as a "Pillar of Life" for thousands of years

Known as Katskhi Pillar (or Katskhis Sveti), this giant block of limestone is located in western Georgia (the country, not the state), about 10km from the town of Chiatura.
The church that stands atop Katskhi Pillar was originally constructed during the 9th-10th centuries CE. It was long used as a hermitage for Stylites, who are sometimes referred to as "Pillar Saints" -- Christian ascetics who lived, prayed, and fasted atop pillars, often in total isolation, in an effort to bring themselves closer to God. The Stylite tradition originated in Syria during the 5th century CE, when a hermit known as Simeon the Elder purportedly climbed up onto a pillar and then stayed there for nearly 40 years, giving rise (no pun intended) to Christian Stylitism.
Stylitism managed to survive for about 1,000 years after its inception, but it began to die out during the late Middle Ages, and by the end of the 16th century, it had essentially gone extinct.

Researchers don't really know how the monks who built this Medieval church originally gained access to the top of Katskhi Pillar, or how they were able to transport their building materials up to the top of the column. Evidence suggests that there were still monks/Stylites living atop Katskhi Pillar up until the 1400s, but the site was abandoned shortly thereafter. Georgia fell under Ottoman rule during the same period, but it's unclear whether or not that may have played a role in the abandonment of the site.
The hermitage at the top of Katskhi Pillar lay abandoned for nearly 500 years after that; no one was able to reach the top of the pillar, and very little was known about the ruins that lay scattered at the top, as knowledge of the site's origin/history was gradually lost over time. There are many local legends that ultimately arose in order to fill in those blanks.
The abandoned hermitage was not visited again until July 29th, 1944, when a mountaineer finally ascended to the top of the column with a small team of researchers, and the group was able to perform the first archaeological survey of the ruins. They found that the structure included three hermit cells, a chapel, a wine cellar, and a small crypt; within the crypt lay a single set of human remains, likely belonging to one of the monks who had inhabited the site during the Middle Ages.
A metal ladder (the "stairway to Heaven") was ultimately installed into the side of the pillar in order to make it easier for both researchers and tourists to gain access to the ruins.

The hermitage at the top of Katskhi Pillar actually became active again in the early 1990's, when a small group of monks attempted to revive the Stylite tradition. A Georgian Orthodox monk named Maxime Qavtaradze then lived alone at the top of Katskhi Pillar for almost 20 years, beginning in 1995 and ending with his death in 2014. He is now buried at the base of the pillar.
The hermitage is no longer accessible to the public, and it's currently uninhabited, but it is still visited by local monks, who regularly climb up to the church at the top of the pillar in order to pray. There is also an active monastery complex at the base of the pillar, where a temple known as the Church of the Simeon Stylites is located.
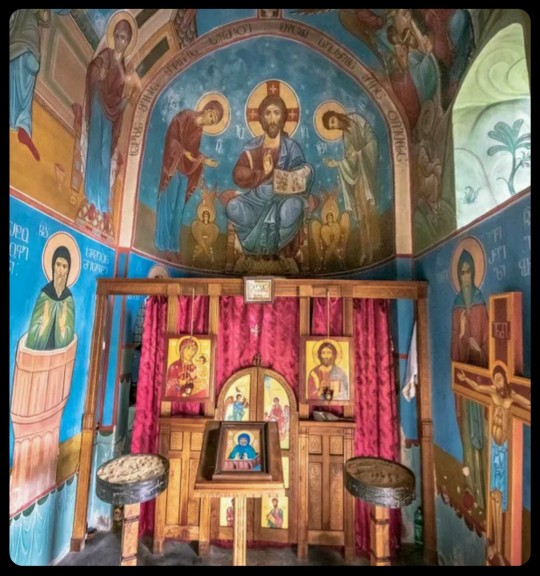

The Church of the Simeon Stylites: this church is located within an active monastery complex that has been built at the base of the pillar; several frescoes and religious icons decorate the walls of the church, and a small shrine containing a 6th century cross is located in the center
There are many lingering questions about the history of Katskhi Pillar, particularly during the pre-Christian era. There is at least some evidence suggesting that it was once the site of votive offerings to pagan deities, as a series of pre-Christian idols have been found buried in the areas that surround the pillar. According to local tradition, the pillar itself was once venerated by the pagan societies that inhabited the area, but it's difficult to determine whether or not those claims may simply be part of the mythos that surrounds Katskhi Pillar, particularly given its mysterious reputation.

Sources & More Info:
BBC: Georgia's Daring, Death-Defying Pilgrimage
CNN: Katskhi Pillar, the Extraordinary Church where Daring Monks Climb Closer to God
Radio Free Europe: Georgian Monk Renews Tradition, Lives Atop Pillar
Architecture and Asceticism (Ch. 4): Stylitism as a Cultural Trend Between Syria and Georgia
Research Publication from the Georgian National Museum: Katskhi Pillar
Journal of Nomads: Katskhi Pillar, the Most Incredible Cliff Church in the World
Georgian Journal: Georgia's Katskhi Pillar Among World's 20 Wonderfully Serene and Secluded Places
#archaeology#history#anthropology#artifacts#medieval architecture#medieval church#Stylites#asceticism#georgia#sakartvelo#katskhi pillar#religion#travel#monastery#paganism#caucasus#christianity#strange places#ruins#medieval europe#weird history
514 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Iris
Iris is the goddess of rainbows and an important messenger between the gods and humans in Greek mythology. She was most commonly portrayed as the personal messenger of Hera. Iris was the daughter of the Titans Thaumas and Electra and the sister of the fearsome Harpies. Common epithets include "golden-winged Iris", "swift Iris", or "swift-footed Iris."
Birth & Family
As mentioned in the Theogony by Hesiod (c. 700 BCE), Iris was the daughter of the Titans Thaumas and Electra and the sister of the Harpies (half-woman, half-bird creatures). Although not mentioned in Hesiod's Theogony, other writers like Nonnus (c. 5th century CE) and Alcaeus (c. 625/620-580 BCE) state that Iris was married to Zephyrus, the West Wind and that they had Pothos (the god of yearning and desire) together. Some sources also list Eros as being their son.
Continue reading...
119 notes
·
View notes
Text

howling wolf figurine, Southern Siberia, c. 5th-3rd century BCE, wood with shell inlays
currently in the collection of the Cleveland Museum of Art (Cleveland, Ohio, USA), accession no. 1986.26
811 notes
·
View notes