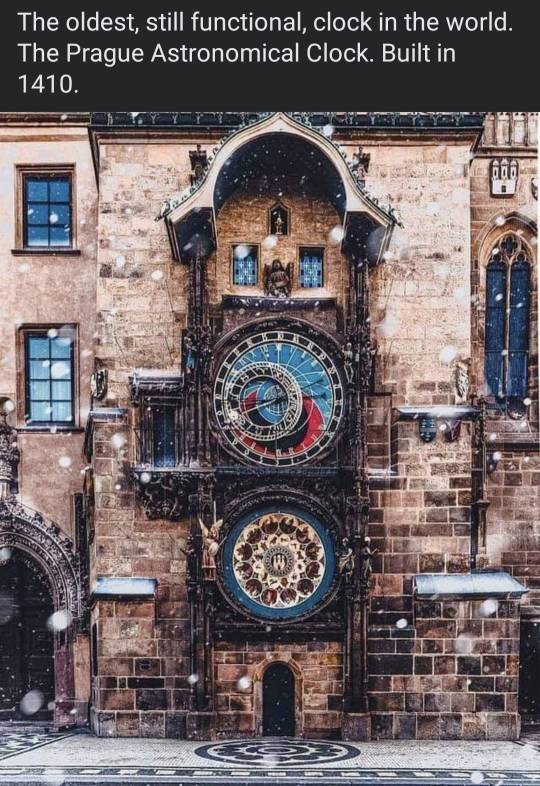
#astronomical stuff
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
For the first time in about a week, it isn’t densely cloudy and threatening to rain, so we decided to take a shot at seeing if we could catch Comet Tsuchinshan-ATLAS before it goes bye bye. We went out to a nice dark place with a clear view to the west, and man was it COLD. Not hardened for this weather yet. Got some lovely post sunset pictures, but not a glimpse of the comet, even with binoculars. So we decided to head home and try again tomorrow night, and wait 'til it’s darker. But on the way back we paused in our local industrial park, of all places, and I decided to see if my phone could see anything. Despite a nearby streetlight, the camera once again saw what I could not. Filtered through some very high thin clouds, which gives me hope that tomorrow might be better.

1 note
·
View note
Text

6K notes
·
View notes
Text
Hospitaller and knight trio doodles

@chao-mp3 I adore the joke in ur teutemp "good boy meme" art pls don't mind me reusing the joke🙏 (idk if that's a historically accurate thing but it's so in character for Gil to tell the highest higher up to shut up XDD)



*they're not related, this is just their weird ass trio dynamic

#hetalia#hws knights hospitaller#hws knights templar#hws teutonic knights#aph knights hospitaller#aph knights templar#aph teutonic knights#hws prussia#aph prussia#gilbert beilschmidt#hetalia fanart#hws fanart#aph fanart#historical hetalia#hetalia world stars#hetalia axis powers#Hannes' portrait is a reference to a painting by da vinci btw take ur guess#hard round brush w color jitter saved me fr#the * is there to make stuff clear in case this gets misinterpreted as me hcing them as brothers (I'm not btw)#hello fellow astronomers
139 notes
·
View notes
Text

#kandi thoughts#im so sorry ysf and winged y/n and my oc's and REALLY SORRY glitter and astronomer au and#glitter has a whole buncha stuff i wanna draw but#sobs#i wanna draw her roller rink and merch and gnnhhnhghg
375 notes
·
View notes
Text
Interesting tidbit from this Wikipedia article in light of today's episode (emphasis mine) :
Much of Newton's writing on alchemy may have been lost in a fire in his laboratory, so the true extent of his work in this area may have been larger than is currently known. Newton also suffered a nervous breakdown during his period of alchemical work.
Newton's writings suggest that one of the main goals of his alchemy may have been the discovery of the philosopher's stone (a material believed to turn base metals into gold), and perhaps to a lesser extent, the discovery of the highly coveted Elixir of Life. Newton reportedly believed that a Diana's Tree, an alchemical demonstration producing a dendritic "growth" of silver from solution, was evidence that metals "possessed a sort of life."
#apparently apocryphal accounts say his dog started the fire and he lost 20 years of research#also apparently he did a lot of like. biblical studies of the apocalypse. so im less surprised they chose to have a case about him now#also also. the great fire of london was 1666.#did the fucking royal society of astronomers burn it down to stop the bubonic plague that was apparently supernatural here?#not astronomers sorry. my minds still on halley#the magnus protocol#tmagp spoilers#my magnus protocol stuff#original post#19 hard reset#queue cause i'll be at work when the episode airs#magnus protocol speculation/analysis
126 notes
·
View notes
Text

They are discussing
#okokok fr fr im done ;;;;;;w;;;;;;;#(im not)#(Ill only sorta shut up as im very busy with work stuff and also playing bo:potl)#ill probably still not shut up tho#nine sols#oc art#[Tolbi]#Tolbi's more of an astronomer at heart and studies other varying facets of science in their spare time
83 notes
·
View notes
Text
Sometimes I see the way certain people in a fandom treat a ‘tough love but well meaning and trying his best in the only way he knows how’ Dad and I can only think “You have a horrid relationship with your father, don’t you? 🫵👁️👁️”
#self projection is a very real thing and most of the time it’s silly fun but sometimes your blowing up a character when you really-#should be blowing up your father; I’m just saying.#the amount of times I’ve seen a dad who doesn’t understand his kid and unintentionally hurts them but grows to try and understand them but-#then the fandom wants that guy DEAD is ASTRONOMICAL.#this was spurred on from the fact I was thinking about Norman’s Dad in Paranorman. Yeah he’s tough love but the movie says it outright;#the reason he acted like that is because he’s scared for Norman. he doesn’t understand him and when people don’t understand something they-#get scared and mad. and even though he was shown to get upset note that he NEVER hurt Norman and buys him weird zombie/horror stuff because-#despite not understanding him and wishing he was ‘normal’ he still loves him! and he accepts his weirdness by the end of the movie in his-#own weird emotionally stunted way!#ignore this entire rant I just have so many emotions about dads who don’t understand but try their best regardless OUGH#prince rambles in this chilies tonight#fandom
37 notes
·
View notes
Text


I discovered these paintings by James McNeill Whistler recently, Nocturne in Black and Gold: Falling Rocket (top) and Nocturne in Black and Gold: The Firewheel (bottom). I’m sharing them because they make me think of Nevermoor, as so many things do.
With paintings, a nocturne refers to the depiction of night. This is derived from the musical term, where a nocturne refers to a musical piece that is “inspired by, or evocative of, the night.” These both just come from the fact that “nocturne” essentially means “of the night”.
On a basic level, this just reminds me of Nevermoor by the aesthetics. The dreamy nighttime setting strikes me the most, but also the sparks of yellow fire that make me think of Wunder. Think of how many important scenes happen at night- Morrigan on Eventide, the Museum of Stolen Moments, and the Hollowpox in Courage Square. But the concept has me thinking, obviously, about the Wundrous Art of Nocturne. The only songs we know are Morrigan and Squall’s, who both chose nursery rhymes as their Nocture. Their choices make me think of lullabies, sung at night… and there’s lots to think about with that.
#does anyone else see or understand my vision…..#nevermoor#nevermoor in the wild#another post from my drafts cuz I feel bad I have no art to share#only art history classes I actually took was animation history and then ancient and medieval so most of my info or knowledge from#anything later relies on me looking it up and seeing what research and info is online and etc etc etc#anyways. love whenever magic (of the wundrous arts variety) in nevermoor is compared to art or the process of making art. <333#I need to make a Pinterest / some other sort of site where I can share everything visually that reminds me of nevermoor. but also filterabl#and also where I can add notes for why different stuff makes me think of nevermoor or what I associate it with…..#bc I’m often sharing architecture in the discord but I also am always bookmarking clothes and stuff that I don’t share lol#I saw two clocks the other day at a history museum and also an alway thinking abt the Prague astronomical clock so my brain is always like:#‘wow just like the skyfaced clock :) nevermoor :)#circling back if anyone knows some sort of site like Pinterest where you can have bunch of images with notes and also filter between#different attributes pls lmk. I’m not a coder so I can’t think how to make smthn like that myself lol#I started this post like a month ago that’s why I don’t have anything better to say besides ending with ‘much to think about’ lol
50 notes
·
View notes
Text
In case no one’s told you, you’re made of big bang stuff.
Sure, we often hear about being made of star stuff—how the carbon and oxygen in us were forged in the hearts of stars. But remember, the hydrogen atoms that make up most of you were born in the first two minutes of the universe’s existence.
The hydrogen that is a part of you -- that is you -- was formed in that primordial soup, 13.8 billion years ago. A part of you was there; at the start of it all.
#affirmations#astronomy#another reason I want to be an astronomer#big bang#you are star stuff#but you are also big bang stuff#crwn's academic
27 notes
·
View notes
Photo










[concept-dump] Space-au - (main(?) Antagonist) Skal, enemy of sun and mentor to iron
#spaceau#tf2 space au#gordon freeman#ironstar gordon#skal the chimera#my ocs#myart#yes theres homoerotic tension yes youre reading that right#skal was initially a one-off antagonist to 100years ago/pre-team sol and boone#but i decided to keep him alive and he somehow got involved with gordon and now theres so much stuff between them aksdjhad#skal helps indirectly shape gordon into his own person while gordon breaks skal down from his skyhigh ego#human helps alien accept he's not human and thats okay while alien helps human accept he's only human and thats okay#you dunno what they do to my brain was possessed by them the whole ass move#he also changes the most throughout the whole story like visually i mean x'D this is all the same guy i swear#he's just veeeeeeeeeery old and goes through a lotta ego death jkhfdsfd#he's originally an outcast astronomer from the 1500s#turns into a deranged alchemist who figures out how to eat celestial cores in order to make himself into a star#yknow how it is khsjdffsd#anyway i told my friend about skal and they said he reminded them of an owlhouse character#and now ive watched the show and im lookin back on this guy and im sdjfkhfsgd yeah yeah he does have that vibe#also he's dutch and his voiceclaim his sigma(overwatch) bc that guy was squandered and i love his voice still#a lot of these pics are panels from a lil voiceline compilation thing i didnt finish kjhdsfsk#maybe ill post it if i can finish editting it
444 notes
·
View notes
Text



"The outer reaches of space remain unexplored by humankind to this day, but its greed is relentless. We grasp and yearn and hunger for knowledge— answers to questions we cry out into the endless void expecting to understand, expecting the stars to respond. The stars will not, but one day something else will— and we will not like what it has to say." — Rome Solomon, Beyond the Exosphere (1965)
taglist (opt in/out): @shellibisshe, @florbelles, @ncytiri, @hibernationsuit, @stars-of-the-heart, @vvanessaives, @katsigian, @radioactiveshitstorm, @estevnys, @adelaidedrubman, @celticwoman, @rindemption, @carlosoliveiraa, @noirapocalypto, @dickytwister, @killerspinal, @euryalex, @ri-a-rose, @velocitic, @thedeadthree
#obscura#edit:rome#nuclearocs#nuclearedits#ok so. ok hi. red and i made a new universe hi. sorry. morris quincy victor and eleanor belong to them the rest belong to meee :3#the pictures i used are basically the patron saints of their occupation / line of work! so that's not what they look like#anyway it's a mix of paranormal stuff + lovecraftian horror + sort of zombies :^)#they're like. the domains of lucifer (demons) behemoth (zombies) and leviathan (the eldritch horrors that happen in space and oceans)#who are like. the three evils that torment the mortal realm#it's all in a historical setting kind of parallel to our world? so a bunch of historic events are the same but it's like#a little bit more advanced with technology but at the same time it's not. it's Just A Little Different y'know#rome's sister went to space for a mission and just straight up went missing which prompts him to become an astronomer#and he's the first one to start speculating the existence of leviathan as eldritch god#morris is a technician at the academy who has an angel stuck in his computer#eve is a nun and herbalist who witnesses the influence of behemoth firsthand through some sick travelers#that she and the other nuns of her convent take care of#anatoly and quincy are both from different space missions who end up as the only survivors who are not basically a plant#the other two survivors have secretly been replaced with some sort of parasites. annihilation style if you've seen that movie#eleanor is a demonologist and works together with her brother victor who's her cameraman#clarence is a blind psychic who lost her sight because of an angel trying to warn her and in return got her psychic abilities#and lazarus is one of the two most famous demonologists in the world but his wife (the other one) passed away#so now he's alone and since he's not from an upper class family like his wife was he's not all that loved as she was#there's a lot going on but it's SO fucking fun to work on so far. feel free to send any asks i would love to explain more :^)#if you've made it this far also hi i love you. kiss for you
50 notes
·
View notes
Text

ENTANGLEMENT | Part I, Chapter I
A Portal/Half Life Universe Fic from Chell's Perspective Rating: Explicit Overall Word Count: 10,730 Chapters: 1/20 Where to Read: AO3 | Google Drive | // ?UN?/KN@?#WN
SYNOPSIS
Location Unknown, Michigan, USA. Aperture released her, set her free. That ought to have been the end of it. But cast out into a world rendered unrecognizable after a mass extinction level event, Chell is forced to fend for herself, navigating a war-torn world in the aftermath of the seven hour war that devastated the states in a bygone era. Mere days into her newfound experience on the surface, Chell finds bizarre technology inside a Michigan radio tower, discovering that the same interdimensional forces that started the war were still around, scouring the area in search of technology from the facility she hoped to never see again — Aperture Science. With no choice but to go back to the facility to deliver a dire warning, Chell tightropes on the cusp of two worlds, unaware of the consequences of pursuing the past and surviving an uncertain future alongside an unlikely ally.
It's finally here!! A former roleplay thread with @sarcasticgaypotato turned novel, this story follows the events of Half Life 2: Episode 2, and is an inspired continuation of the ending of Half Life: Alyx from the perspective of everyone's favorite Aperture-dwelling characters. Chell, whose mission is to protect Aperture technology from getting in the hands of the Combine, must also act as GLaDOS's protector and keep her safe. GLaDOS, on the other hand, has to figure out the complicated ways of the world from a new perspective - literally. This story is friendly to those who don't know Half-Life lore, and a treat for those who do! This story is a close-to-canon survival novel fic with ChellDOS as a major focus. Full of survival, interactive elements, complicated feelings, and a beautiful slow burn robot/human love story. <3
#portal 2#half life#chell#GLaDOS#ChellDOS#I CAN FINALLY SCREAM ABOUT THIS OMMMGG#nearly a fucking DECADE LATER AHHHH#words cannot explain how excited I am to finally release this project into the masses I could explode#Chell was my first muse my first comfort character my first love#this rp to novel that me and sarcastic worked on for ages is without a doubt the most research I have done for a story EVER in my life#and I love the absolute most out of everything I've written#I have been wanting to write ChellDOS fanfiction for a very long time#and while I've done rp stuff#I wanted my first ChellDOS fic to be so fucking astronomical#I'm finally satisfied#and I hope you all love this story too! thank you all for reading <3
47 notes
·
View notes
Note
12 yo iztea art reveal!!!










i was so full of swag you couldn't even fathom
#anon i literally have a folder in my home with drawings from when i was 12/13 how did you know#god the cringe levels are astronomical but this is just how 2014/15 was#i dont have words the type of stuff i used to draw always makes me laugh#THAT ANGELS CAN FLY QYOTE IS JUST TAKING MEEE OUTTTRTTT#I THOUGHT IT WAS SOOOO DEEP BNSHDJBFIS#it REEKS of basic tumblr white girl#i didn't even have tumblr back then mind you#there's more but some of them are just TOO cringe to show#ask iztea
69 notes
·
View notes
Text

#flags#usa#astronomy photography#funny post#funny stuff#funny shit#moon#moon landing#us flag#man on the moon#astrography#astronomers#astro notes#astrophotography#astronomy#lunar#hahaha#nasa picture of the day#nasa photos#nasawebb
58 notes
·
View notes
Text
Me: (staring at my plans for how to get the right characters in the right place for the climax) This feels contrived. >:(
My brain: You need to have some reasonable adults allow some main character kids to accompany them into a dangerous situation to help save the world, you're giving it your best shot. Besides, this whole series is contrived, the audience will probably be willing to suspend their disbelief as long as you stick to the rule of cool and reasonably steady logic. It's a genre staple that the kids/teens who should technically be too young and inexperienced help out with this stuff, it's fine.
#my life#my writing#the divine madness continues#Got a Light?#rwby#listen - I recognize that the standards for this stuff in this fandom are relatively low#but my own standards for my own writing are astronomical at all times and I am Suffering
16 notes
·
View notes
Text
Hello there, I am a space nerd, a fact I’m sure no one guessed from the fact that I go by Stars on the internet. I am here to explain how the moon works, because I think it’s cool and also something that most people don't know. This is mostly an infodump just for fun, but may also be vaguely useful for artists, writers & stargazers.
By “how the moon works,” I mean that although pretty much everyone knows about the moon’s phases, not everyone really gets how they affect things like when & where the moon is in the sky. See: the common idea that the sun is in the sky in the day, and the moon is in the sky at night. You know this isn’t strictly true if you’ve ever seen the moon in the sky in the daytime, but do you know how it actually works? If I gave you a moon phase and a time of day, would you be able to tell me whether the moon was in the sky or not?
I am here to (hopefully) explain how you can do that! With scribbly diagrams! Please join me under the readmore if you would like to come to my TED talk.
First of all, to avoid any accidental curse-of-knowledge assumptions on my part, let me define some terms!
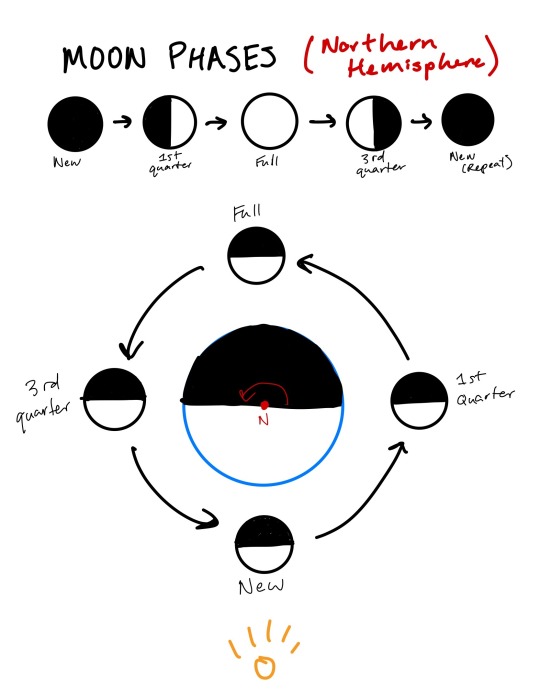
First off, the phases of the moon, which you probably know most of, but bear with me. A “full moon” is when the moon is fully illuminated and appears as a circle in the sky. A “gibbous moon” is when the moon is more than half full, but not completely full—it appears large and roundish, but not a circle (not everyone knows the name for this one). A “half moon” is when the moon is half illuminated and appears as a semicircle—this one has some other names that I’ll get to in a second. A “crescent moon” is when the moon is less than half illuminated and appears as a concave curve. A “new moon” is when the moon is completely dark from Earth’s perspective and can’t be seen in the sky.
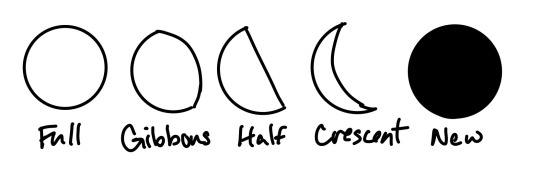
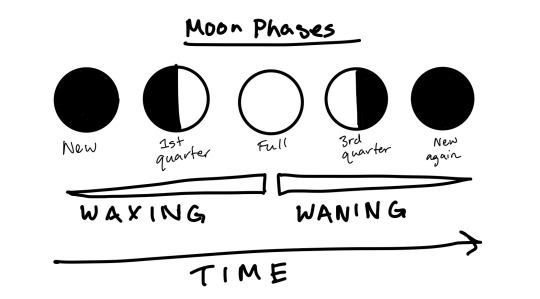
Also, “waxing” is when the moon is transitioning from new to full, or getting bigger in the sky, and “waning” is when the moon is transitioning from full to new, or getting smaller in the sky.
Speaking of “half moon,” I frequently confuse friends by calling this a “first quarter” or a “third quarter” moon. Those names refer not to the illumination of the moon but to the full cycle of phases. If you think of the moon phases as split into four quarters, starting from zero at a new moon, then halfway to full is 1/4, full is 1/2, halfway back to new is 3/4, and then we’ve reached the end/beginning of the cycle with another new moon. So one of the half moons is a first quarter moon, and the other (with the other half illuminated) is a third quarter moon.
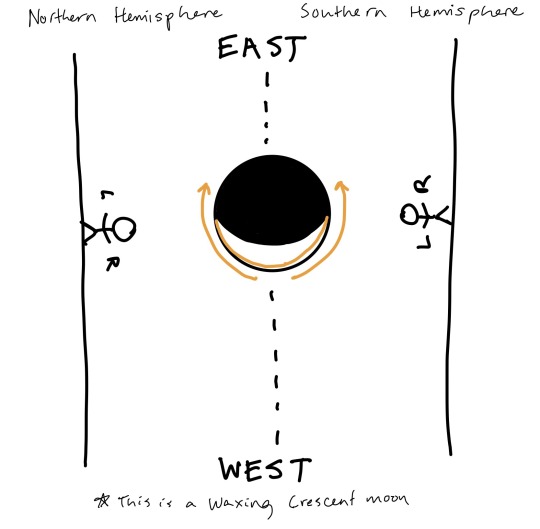
This is where I have to add a disclaimer—I am in the northern hemisphere, and I am familiar with astronomy in the northern hemisphere. If you are in the southern hemisphere, to you, I am looking at the moon “upside down.” Yes, really. If you’re using my diagrams, flip them upside down. I’ll try to be clear when I’m talking about stuff that flips between the hemispheres, but it’s something that I struggle to wrap my head around too, so apologies if I’m confusing or miss something.
So, here’s a diagram of the moon phases to show you the difference between first and third quarter moons, but if you’re in the southern hemisphere, please flip it over to see what they would look like for you. (The chronological order still goes in the same direction as the arrow, the moon itself is just the other way in the sky.)
The fun trick I was taught to remember which way the cycle goes is “light from the right.” (Southern hemisphere people, you’ll have to flip this one.) Light, or shadow, moves from the right edge of the moon to the left. So if the moon is a crescent and the right edge is lit up, it’s waxing, or moving towards full. If the moon is a gibbous with a dark right edge, it’s just past full and will be waning towards the third quarter over the next few days. If you look at the diagram above (and imagine the crescent and gibbous phases transitioning in between), this might be easier to imagine.
Like I said, for the southern hemisphere this would actually be “light from the left.” If you’re near the equator and the moon is overhead, you could use “light from the west,” because that’s secretly the real rule. Another thing that’s useful to know for stargazing—the moon, sun and planets follow a path in the sky called the ecliptic, which is roughly over the equator. (Not exactly—it wiggles around relative to earth’s surface, because of the tilt of the earth’s axis that causes the seasons, but it stays near the equator.) If you’re standing in the northern hemisphere, the equator is south of you, so the ecliptic is also in the southern part of the sky. When you look at the moon, it will always be in the south, so the west-facing side of the moon will always be to your right. Likewise, if you’re in the southern hemisphere, the moon (and sun, and planets) will always appear in the northern half of the sky, so west will be to your left. Light moves across the moon’s surface from the west to the east.
Now you can impress people by looking at the moon and saying, “Oh look, what a lovely waxing gibbous!” (I don’t actually know if the is impressive, but I do it all the time. For bonus points, get an app on your phone that tells you the phase of the moon and check it frequently so you can plan when to stargaze. Then you can casually mention that the moon will be full in a couple days when it’s not even in the sky, and maybe people will think you’re a werewolf.)
Now that I’ve explained the moon’s phases, I get to explain how they’re related to the time and place that the moon is in the sky. See, most people (I assume) don’t think twice about things like, say, a book describing a crescent moon in the sky overhead at midnight. But that actually can’t happen! And it has to do with the moon’s position in the 3D solar system, and how that maps onto our sky. This is kind of hard for me to explain without a lot of 3D hand gestures and pointing at the sky, but I’m gonna do my best to show it in two dimensions.
So, most people probably know that the moon’s phases are caused by the sun’s light illuminating half of the moon, and since the relative positions of the moon, sun & earth change throughout the month, the half that’s illuminated moves around the moon and changes how it looks from our viewpoint. So, a very basic rule: the side of the moon that’s illuminated is the side that’s facing the sun.
So, when the moon is full, that’s because the side that faces us is also facing the sun. This means the sun is directly opposite the moon. Here’s a very scientific diagram:
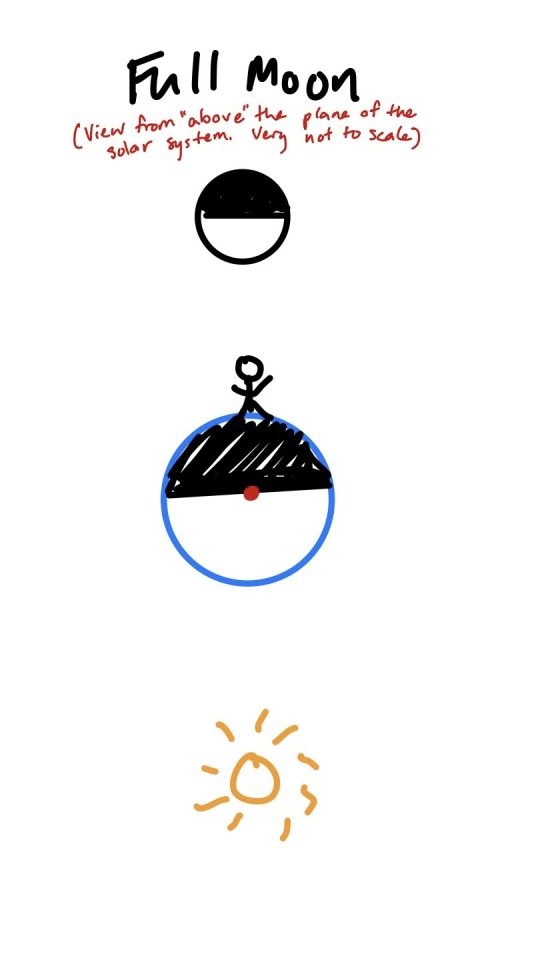
In case it’s not clear, this is a “top-down” view of the solar system where the moon, earth and sun are all in the same plane (in this case it doesn’t matter if we’re looking at the north or south pole, the positions would look the same). It’s also obviously not to scale and very simplified, but the point is to demonstrate that the moon is opposite the earth from the sun.*
The little person on the earth is of course spinning around as the earth rotates once per day. But at this point in the lunar month, you can see that when they are on the side of the earth where they can see the moon, they are also on the side facing away from the sun. When the moon is full or close to full, it’s opposite the sun—it rises around sunset, sets around sunrise, and is at its peak in the sky around midnight. This is how lots of people tend to think of the moon rising and setting, but it’s only true when the moon is close to full!
If that doesn’t make sense, here’s a diagram of when the moon is at the opposite point in its cycle, a new moon:
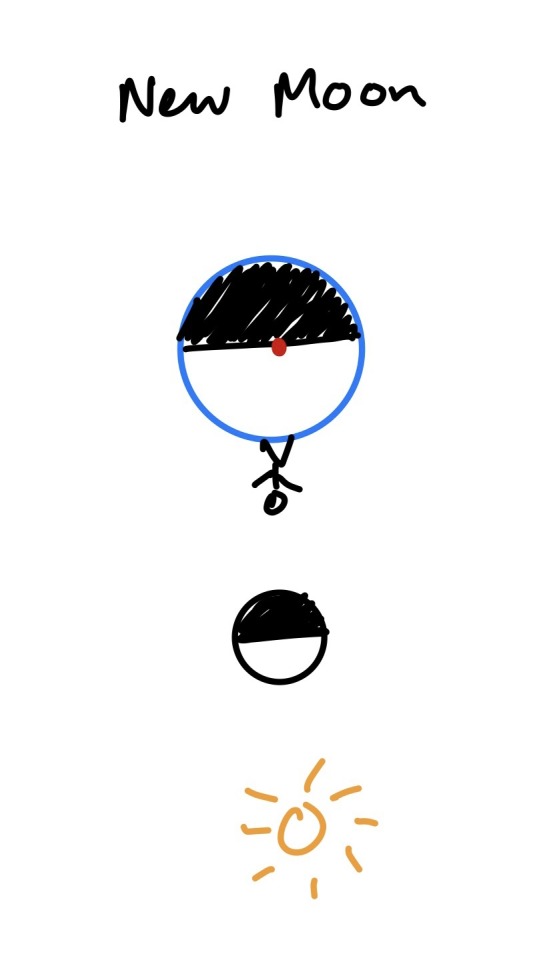
When the moon is new, the side that faces the earth is dark, which means the opposite side is facing the sun. The moon is on the same side of earth as the sun is. The little person spinning around the earth won’t see the moon in the night sky, because the moon is close to the sun in the sky,* and it’s actually rising in the morning and setting in the evening at this time of the month! You can’t easily see the moon when it’s new, but it might be visible a few days before or after this as a crescent. You’ll only see a crescent moon in the sky during the day, or close to dawn/dusk—it will be close above the horizon where the sun has just set or is about to rise. (The light edge faces the sun, so if it’s near the horizon in twilight sometimes it will look like the light edge is actually pointing down, with the tips of the crescent pointing up in the sky.)
*A side note on eclipses: My diagram is oversimplified! The moon, earth and sun aren’t actually all in the same plane all the time, they’re slightly misaligned. So even when I say the moon and sun are “directly” opposite each other, or aligned, they aren’t lined up perfectly enough to cast shadows on each other most of the time. When they do line up perfectly at the right time, that’s when you get a solar eclipse (when the moon is new) or lunar eclipse (when the moon is full).
Okay, so when the moon is full it’s in the sky at night, and when the moon is new it’s in the sky during the day. What about in between? This is where it gets a little confusing, especially for those of you in the southern hemisphere, who are going to have to flip everything I say. Apologies in advance, but it kind of hurts my head even to explain how this works in my own half of the sky.
So, when the moon is half-full, at the first quarter and third quarter of the phase cycle I explained above, the sun’s light is coming (from our perspective) from the side. The moon is ninety degrees away in its orbit from full or new, and the sun’s light is effectively perpendicular to our viewpoint, instead of parallel. This time it matters which way we’re looking, so these are a top-down view from the northern-hemisphere side. If you’re in the southern hemisphere, I think you can flip which is the first & third quarter to make this accurate.
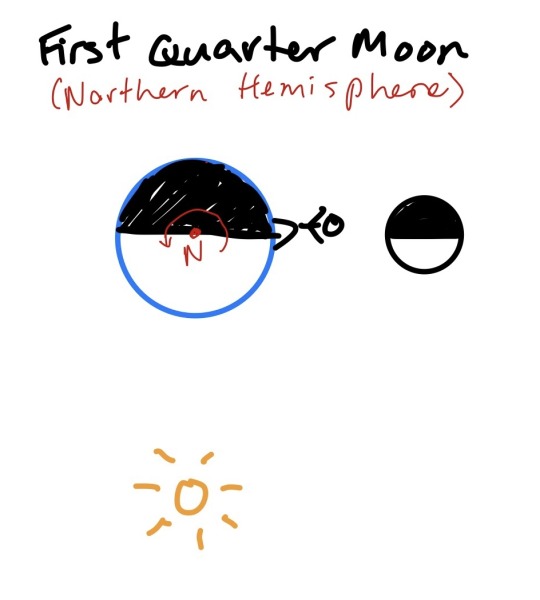

As you can see, when our little person is spinning around the globe, they’re going to be seeing the moon high in the sky right around the line between night and day. From a northern perspective, the earth spins counter-clockwise (vice versa from the south), so if you picture the person spinning around their little earth, you can see that the first quarter moon is going to be visible when they’re spinning from light to dark (sunset) and the third quarter moon is going to be visible when they’re spinning from dark to light (sunrise).
Bonus fun trick: If you remember the rule of “light from the right” in the northern hemisphere and how that determines the order of the phases, and look at these diagrams again, you can figure out which direction the moon orbits the earth from this viewpoint. (This is, in fact, the only way I can remember which direction the moon orbits the earth, despite being far more complicated than just memorizing it. If you’d like to make a game of it, I’ll put the answer at the bottom of the post).
Remembering how this looks from this top-down floating-above-the-earth perspective is hard, but you don’t really have to. I only explained it so it would make sense when I went back to my earlier visualization, from when I was explaining how “light from the right” works. I’m a very spatial learner, and I like picturing things relative to my own body, so this is how I remember when the different phases of the moon appear in the sky:
Imagine you’re standing, facing the ecliptic, where the sun and the moon travel through the sky. In the northern hemisphere, you’re facing south, with east to your left and west to your right. Imagine that the sun has just set, falling beneath the horizon to your right. Imagine that the moon is full, and hopefully I’ve explained well enough that now you know where it will be—cresting the horizon at your left. Imagine the opposite too—the sun is rising in the east at your left, as the full moon sinks in the west at your right. The new moon’s position, if you’d like to visualize that, is effectively the same as the sun.
Now, the difference between the two half-moons. Light comes from the west—in the northern hemisphere, your right—so when the right half is illuminated, it’s the first quarter of the lunar month, waxing to full, and when the left half is illuminated, it’s the third quarter, waning to new. One is high at dusk and one is high at dawn. Which is which?
You’re facing south. Picture a first quarter moon, right side lit up, at its peak in the southern sky. The light side is always facing the sun. Where is the sun? It must be to your right, touching the horizon in the west, setting. The first quarter moon is in the sky before, during and after dusk.
Picture a third quarter moon, left side lit up, at its peak. The light side faces the sun. The sun is to your left, touching the horizon in the east, rising. The third quarter moon is in the sky before, during and after dawn.
When I imagine this, I’m standing on my back porch, where I often go outside and stargaze. My telescope is small and one of the few things it can see with any detail is the moon. I want to be able to look at the moon just after dark, without having to stay up too late—and this memory device, of facing south and imagining the sun at my right hand to the west, is how I remember that the first quarter is the best time for me to observe the moon. It will be high in the sky at sunset, easy for me to see over the houses and trees.
If you remember that the moon waxes and wanes from the west (right in the north, left in the south), then you can fill in all the gradations of crescent and gibbous moon between the four main quarters. (As an example, if I wait a few days past first quarter to go outside and look at the moon, it’s waxed into a gibbous moon and it rises later in the evening, peaking in the sky closer to midnight. Another example: a waxing crescent is between a new moon and first quarter, so it will trail behind the sun and be above the horizon in the southwest at sunset.)
I hope that all of this makes sense and is useful to someone, whether for figuring out when you can observe the moon and where in the sky to look, or for thinking about how to place it in the sky in your writing and art. If nothing else, I hope I have brought you entertainment, and/or ruined the way the moon works in Minecraft for you forever. (It rises and sets directly opposite the sun!! Even when it’s a new moon!!! Light doesn’t work like that!!)
And finally, if you were trying to guess, the moon orbits the earth counter-clockwise if you’re looking down from the northern side.
#stars has thoughts#space#the moon#amateur astronomy#thank you for coming to my ted talk#and thanks discord friends for saying 'write the moon infodump post!!'#when i was like 'i wonder if i should write a moon infodump post'#i am a humble space nerd slash backyard astronomer with a 4inch scope#but explaining how i visualize and remember space stuff in simple terms is one of my favorite things to do ever#i could do a bunch of other posts about stuff like this. why venus is the morning star. how telescopes work (explain it like i'm 5 edition)#perhaps i will#undescribed#(i will try to come back with image descriptions later but i have already done all the explaining of visual concepts with words#that i can manage today. apologies)
72 notes
·
View notes