#american journals
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Quote
I've always been torn between my appetite for people, the vanity and the agitation, and the desire to make myself the equal of these seas of forgetfulness, these unlimited silences that are like the enchantment of death. I have a taste for worldly vanities, my fellows, for faces but, out of step with this century, I have an example in myself which is the sea and anything in this world which resembles it. O sweetness of nights where all the stars sway and slide above the masts, and this silence in myself, this silence which finally frees me from everything.
Albert Camus, American Journals
#albert camus#camus#absurd#absurdism#american journals#people#vanity#desire#sea#silence#death#faces#world#night#stars#freedom
57 notes
·
View notes
Text




excerpts from American Journals by Albert Camus.
20 notes
·
View notes
Text
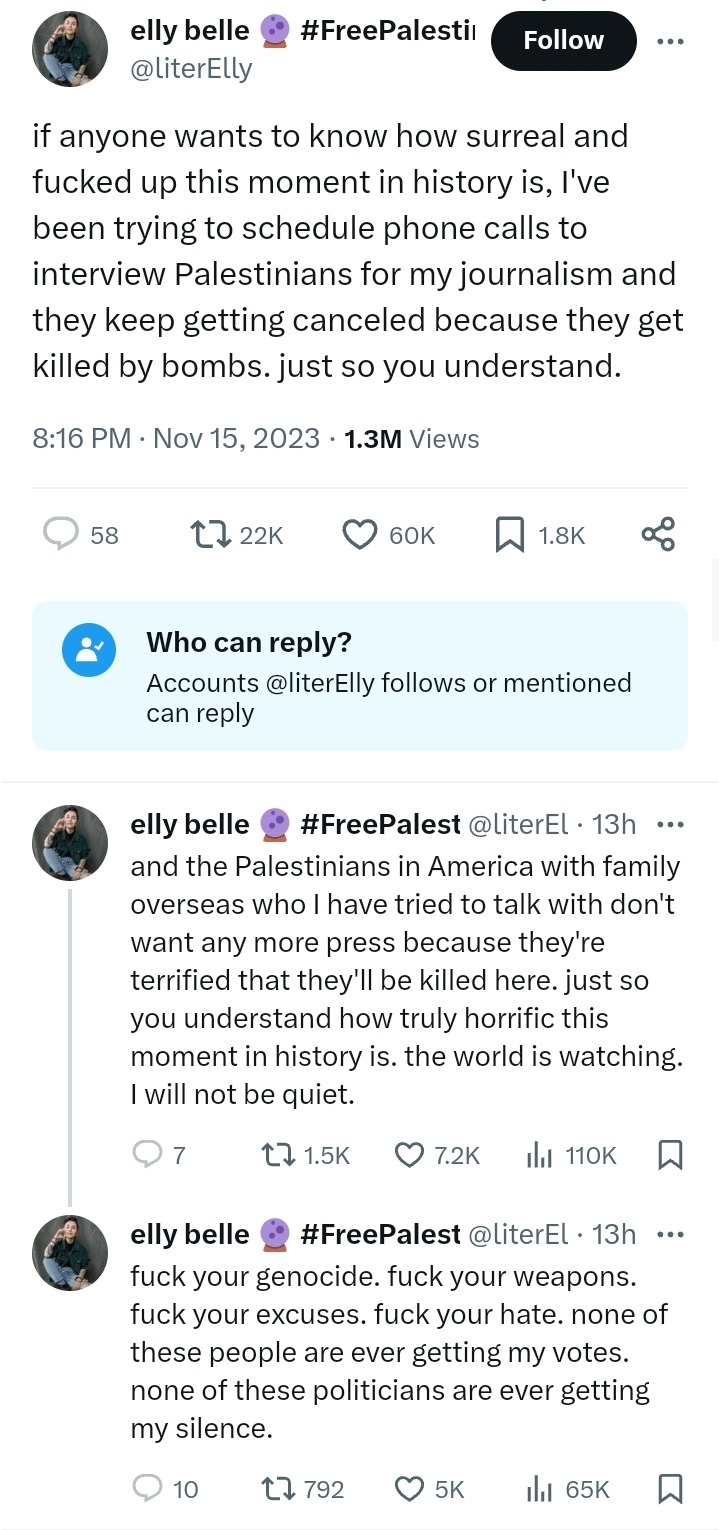
#this is like 9/11 all over again#gaza genocide#tw murder#tw death#ethnic cleansing#palestinian genocide#genocide joe#state terrorism#islamphobia#arab americans#media suppression#freedom of speech#human rights#us politics#white supremacy#journalism#free palestine#fascism#authoritarianism#knee of huss
11K notes
·
View notes
Text
‘— and I stood there, flooded with longing, electric, shivering.’
— Sylvia Plath, The Unabridged Journals of Sylvia Plath. July 1950s
#sylvia plath#the unabridged journals of sylvia plath#american literature#fragments#excerpts#on longing#on desire
2K notes
·
View notes
Text

Post-mortem study of a collapsed lung from the American College of Chest Physicians, 1944
#my post#medical#xray#lungs#medical history#american college of chest physicians#1940s#collapsed lung#b&w#medical journal#pneumothorax
315 notes
·
View notes
Text

poetry scan from my journal + found images, layered and printed on lined paper
#s0larize#my art#art journal#mixed media art#mixed media#art print#printmaking#southern gothic#grunge#grunge aesthetic#nostalgiacore#memorycore#midwest gothic#americancore#nostalgia#collage art#word collage#poetry collage#my poetry#love poems#american gothic#grunge art
555 notes
·
View notes
Text
How to shatter the class solidarity of the ruling class

I'm touring my new, nationally bestselling novel The Bezzle! Catch me WEDNESDAY (Apr 11) at UCLA, then Chicago (Apr 17), Torino (Apr 21) Marin County (Apr 27), Winnipeg (May 2), Calgary (May 3), Vancouver (May 4), and beyond!

Audre Lorde counsels us that "The Master's Tools Will Never Dismantle the Master's House," while MLK said "the law cannot make a man love me, but it can restrain him from lynching me." Somewhere between replacing the system and using the system lies a pragmatic – if easily derailed – course.
Lorde is telling us that a rotten system can't be redeemed by using its own chosen reform mechanisms. King's telling us that unless we live, we can't fight – so anything within the system that makes it easier for your comrades to fight on can hasten the end of the system.
Take the problems of journalism. One old model of journalism funding involved wealthy newspaper families profiting handsomely by selling local appliance store owners the right to reach the townspeople who wanted to read sports-scores. These families expressed their patrician love of their town by peeling off some of those profits to pay reporters to sit through municipal council meetings or even travel overseas and get shot at.
In retrospect, this wasn't ever going to be a stable arrangement. It relied on both the inconstant generosity of newspaper barons and the absence of a superior way to show washing-machine ads to people who might want to buy washing machines. Neither of these were good long-term bets. Not only were newspaper barons easily distracted from their sense of patrician duty (especially when their own power was called into question), but there were lots of better ways to connect buyers and sellers lurking in potentia.
All of this was grossly exacerbated by tech monopolies. Tech barons aren't smarter or more evil than newspaper barons, but they have better tools, and so now they take 51 cents out of every ad dollar and 30 cents out of ever subscriber dollar and they refuse to deliver the news to users who explicitly requested it, unless the news company pays them a bribe to "boost" their posts:
https://www.eff.org/deeplinks/2023/04/saving-news-big-tech
The news is important, and people sign up to make, digest, and discuss the news for many non-economic reasons, which means that the news continues to struggle along, despite all the economic impediments and the vulture capitalists and tech monopolists who fight one another for which one will get to take the biggest bite out of the press. We've got outstanding nonprofit news outlets like Propublica, journalist-owned outlets like 404 Media, and crowdfunded reporters like Molly White (and winner-take-all outlets like the New York Times).
But as Hamilton Nolan points out, "that pot of money…is only large enough to produce a small fraction of the journalism that was being produced in past generations":
https://www.hamiltonnolan.com/p/what-will-replace-advertising-revenue
For Nolan, "public funding of journalism is the only way to fix this…If we accept that journalism is not just a business or a form of entertainment but a public good, then funding it with public money makes perfect sense":
https://www.hamiltonnolan.com/p/public-funding-of-journalism-is-the
Having grown up in Canada – under the CBC – and then lived for a quarter of my life in the UK – under the BBC – I am very enthusiastic about Nolan's solution. There are obvious problems with publicly funded journalism, like the politicization of news coverage:
https://www.theguardian.com/media/2023/jan/24/panel-approving-richard-sharp-as-bbc-chair-included-tory-party-donor
And the transformation of the funding into a cheap political football:
https://www.cbc.ca/news/politics/poilievre-defund-cbc-change-law-1.6810434
But the worst version of those problems is still better than the best version of the private-equity-funded model of news production.
But Nolan notes the emergence of a new form of hedge fund news, one that is awfully promising, and also terribly fraught: Hunterbrook Media, an investigative news outlet owned by short-sellers who pay journalists to research and publish damning reports on companies they hold a short position on:
https://hntrbrk.com/
For those of you who are blissfully distant from the machinations of the financial markets, "short selling" is a wager that a company's stock price will go down. A gambler who takes a short position on a company's stock can make a lot of money if the company stumbles or fails altogether (but if the company does well, the short can suffer literally unlimited losses).
Shorts have historically paid analysts to dig into companies and uncover the sins hidden on their balance-sheets, but as Matt Levine points out, journalists work for a fraction of the price of analysts and are at least as good at uncovering dirt as MBAs are:
https://www.bloomberg.com/opinion/articles/2024-04-02/a-hedge-fund-that-s-also-a-newspaper
What's more, shorts who discover dirt on a company still need to convince journalists to publicize their findings and trigger the sell-off that makes their short position pay off. Shorts who own a muckraking journalistic operation can skip this step: they are the journalists.
There's a way in which this is sheer genius. Well-funded shorts who don't care about the news per se can still be motivated into funding freely available, high-quality investigative journalism about corporate malfeasance (notoriously, one of the least attractive forms of journalism for advertisers). They can pay journalists top dollar – even bid against each other for the most talented journalists – and supply them with all the tools they need to ply their trade. A short won't ever try the kind of bullshit the owners of Vice pulled, paying themselves millions while their journalists lose access to Lexisnexis or the PACER database:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/02/24/anti-posse/#when-you-absolutely-positively-dont-give-a-solitary-single-fuck
The shorts whose journalists are best equipped stand to make the most money. What's not to like?
Well, the issue here is whether the ruling class's sense of solidarity is stronger than its greed. The wealthy have historically oscillated between real solidarity (think of the ultrawealthy lobbying to support bipartisan votes for tax cuts and bailouts) and "war of all against all" (as when wealthy colonizers dragged their countries into WWI after the supply of countries to steal ran out).
After all, the reason companies engage in the scams that shorts reveal is that they are profitable. "Behind every great fortune is a great crime," and that's just great. You don't win the game when you get into heaven, you win it when you get into the Forbes Rich List.
Take monopolies: investors like the upside of backing an upstart company that gobbles up some staid industry's margins – Amazon vs publishing, say, or Uber vs taxis. But while there's a lot of upside in that move, there's also a lot of risk: most companies that set out to "disrupt" an industry sink, taking their investors' capital down with them.
Contrast that with monopolies: backing a company that merges with its rivals and buys every small company that might someday grow large is a sure thing. Shriven of "wasteful competition," a company can lower quality, raise prices, capture its regulators, screw its workers and suppliers and laugh all the way to Davos. A big enough company can ignore the complaints of those workers, customers and regulators. They're not just too big to fail. They're not just too big to jail. They're too big to care:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/04/04/teach-me-how-to-shruggie/#kagi
Would-be monopolists are stuck in a high-stakes Prisoner's Dilemma. If they cooperate, they can screw over everyone else and get unimaginably rich. But if one party defects, they can raid the monopolist's margins, short its stock, and snitch to its regulators.
It's true that there's a clear incentive for hedge-fund managers to fund investigative journalism into other hedge-fund managers' portfolio companies. But it would be even more profitable for both of those hedgies to join forces and collude to screw the rest of us over. So long as they mistrust each other, we might see some benefit from that adversarial relationship. But the point of the 0.1% is that there aren't very many of them. The Aspen Institute can rent a hall that will hold an appreciable fraction of that crowd. They buy their private jets and bespoke suits and powdered rhino horn from the same exclusive sellers. Their kids go to the same elite schools. They know each other, and they have every opportunity to get drunk together at a charity ball or a society wedding and cook up a plan to join forces.
This is the problem at the core of "mechanism design" grounded in "rational self-interest." If you try to create a system where people do the right thing because they're selfish assholes, you normalize being a selfish asshole. Eventually, the selfish assholes form a cozy little League of Selfish Assholes and turn on the rest of us.
Appeals to morality don't work on unethical people, but appeals to immorality crowds out ethics. Take the ancient split between "free software" (software that is designed to maximize the freedom of the people who use it) and "open source software" (identical to free software, but promoted as a better way to make robust code through transparency and peer review).
Over the years, open source – an appeal to your own selfish need for better code – triumphed over free software, and its appeal to the ethics of a world of "software freedom." But it turns out that while the difference between "open" and "free" was once mere semantics, it's fully possible to decouple the two. Today, we have lots of "open source": you can see the code that Google, Microsoft, Apple and Facebook uses, and even contribute your labor to it for free. But you can't actually decide how the software you write works, because it all takes a loop through Google, Microsoft, Apple or Facebook's servers, and only those trillion-dollar tech monopolists have the software freedom to determine how those servers work:
https://pluralistic.net/2020/05/04/which-side-are-you-on/#tivoization-and-beyond
That's ruling class solidarity. The Big Tech firms have hidden a myriad of sins beneath their bafflegab and balance-sheets. These (as yet) undiscovered scams constitute a "bezzle," which JK Galbraith defined as "the magic interval when a confidence trickster knows he has the money he has appropriated but the victim does not yet understand that he has lost it."
The purpose of Hunterbrook is to discover and destroy bezzles, hastening the moment of realization that the wealth we all feel in a world of seemingly orderly technology is really an illusion. Hunterbrook certainly has its pick of bezzles to choose from, because we are living in a Golden Age of the Bezzle.
Which is why I titled my new novel The Bezzle. It's a tale of high-tech finance scams, starring my two-fisted forensic accountant Marty Hench, and in this volume, Hench is called upon to unwind a predatory prison-tech scam that victimizes the most vulnerable people in America – our army of prisoners – and their families:
https://us.macmillan.com/books/9781250865878/thebezzle
The scheme I fictionalize in The Bezzle is very real. Prison-tech monopolists like Securus and Viapath bribe prison officials to abolish calls, in-person visits, mail and parcels, then they supply prisoners with "free" tablets where they pay hugely inflated rates to receive mail, speak to their families, and access ebooks, distance education and other electronic media:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/04/02/captive-customers/#guillotine-watch
But a group of activists have cornered these high-tech predators, run them to ground and driven them to the brink of extinction, and they've done it using "the master's tools" – with appeals to regulators and the finance sector itself.
Writing for The Appeal, Dana Floberg and Morgan Duckett describe the campaign they waged with Worth Rises to bankrupt the prison-tech sector:
https://theappeal.org/securus-bankruptcy-prison-telecom-industry/
Here's the headline figure: Securus is $1.8 billion in debt, and it has eight months to find a financier or it will go bust. What's more, all the creditors it might reasonably approach have rejected its overtures, and its bonds have been downrated to junk status. It's a dead duck.
Even better is how this happened. Securus's debt problems started with its acquisition, a leveraged buyout by Platinum Equity, who borrowed heavily against the firm and then looted it with bogus "management fees" that meant that the debt continued to grow, despite Securus's $700m in annual revenue from America's prisoners. Platinum was just the last in a long line of PE companies that loaded up Securus with debt and merged it with its competitors, who were also mortgaged to make profits for other private equity funds.
For years, Securus and Platinum were able to service their debt and roll it over when it came due. But after Worth Rises got NYC to pass a law making jail calls free, creditors started to back away from Securus. It's one thing for Securus to charge $18 for a local call from a prison when it's splitting the money with the city jail system. But when that $18 needs to be paid by the city, they're going to demand much lower prices. To make things worse for Securus, prison reformers got similar laws passed in San Francisco and in Connecticut.
Securus tried to outrun its problems by gobbling up one of its major rivals, Icsolutions, but Worth Rises and its coalition convinced regulators at the FCC to block the merger. Securus abandoned the deal:
https://worthrises.org/blogpost/securusmerger
Then, Worth Rises targeted Platinum Equity, going after the pension funds and other investors whose capital Platinum used to keep Securus going. The massive negative press campaign led to eight-figure disinvestments:
https://www.latimes.com/business/story/2019-09-05/la-fi-tom-gores-securus-prison-phone-mass-incarceration
Now, Securus's debt became "distressed," trading at $0.47 on the dollar. A brief, covid-fueled reprieve gave Securus a temporary lifeline, as prisoners' families were barred from in-person visits and had to pay Securus's rates to talk to their incarcerated loved ones. But after lockdown, Securus's troubles picked up right where they left off.
They targeted Platinum's founder, Tom Gores, who papered over his bloody fortune by styling himself as a philanthropist and sports-team owner. After a campaign by Worth Rises and Color of Change, Gores was kicked off the Los Angeles County Museum of Art board. When Gores tried to flip Securus to a SPAC – the same scam Trump pulled with Truth Social – the negative publicity about Securus's unsound morals and financials killed the deal:
https://twitter.com/WorthRises/status/1578034977828384769
Meanwhile, more states and cities are making prisoners' communications free, further worsening Securus's finances:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/02/14/minnesota-nice/#shitty-technology-adoption-curve
Congress passed the Martha Wright-Reed Just and Reasonable Communications Act, giving the FCC the power to regulate the price of federal prisoners' communications. Securus's debt prices tumbled further:
https://www.govtrack.us/congress/bills/117/s1541
Securus's debts were coming due: it owes $1.3b in 2024, and hundreds of millions more in 2025. Platinum has promised a $400m cash infusion, but that didn't sway S&P Global, a bond-rating agency that re-rated Securus's bonds as "CCC" (compare with "AAA"). Moody's concurred. Now, Securus is stuck selling junk-bonds:
https://www.govtrack.us/congress/bills/117/s1541
The company's creditors have given Securus an eight-month runway to find a new lender before they force it into bankruptcy. The company's debt is trading at $0.08 on the dollar.
Securus's major competitor is Viapath (prison tech is a duopoly). Viapath is also debt-burdened and desperate, thanks to a parallel campaign by Worth Rises, and has tried all of Securus's tricks, and failed:
https://pestakeholder.org/news/american-securities-fails-to-sell-prison-telecom-company-viapath/
Viapath's debts are due next year, and if Securus tanks, no one in their right mind will give Viapath a dime. They're the walking dead.
Worth Rise's brilliant guerrilla warfare against prison-tech and its private equity backers are a master class in using the master's tools to dismantle the master's house. The finance sector isn't a friend of justice or working people, but sometimes it can be used tactically against financialization itself. To paraphrase MLK, "finance can't make a corporation love you, but it can stop a corporation from destroying you."
Yes, the ruling class finds solidarity at the most unexpected moments, and yes, it's easy for appeals to greed to institutionalize greediness. But whether it's funding unbezzling journalism through short selling, or freeing prisons by brandishing their cooked balance-sheets in the faces of bond-rating agencies, there's a lot of good we can do on the way to dismantling the system.

If you'd like an essay-formatted version of this post to read or share, here's a link to it on pluralistic.net, my surveillance-free, ad-free, tracker-free blog:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/04/08/money-talks/#bullshit-walks

Image: KMJ (modified) https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Boerse_01_KMJ.jpg
CC BY-SA 3.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/deed.en
#pluralistic#shorts#short sellers#news#private equity#private prisons#securus#prison profiteers#the bezzle#anything that cant go on forever eventually stop#steins law#hamilton nolan#Platinum Equity#American Securities#viapath#global tellink#debt#jpay#worth rises#insurance#spacs#fcc#bond rating#moodys#the appeal#saving the news from big tech#hunterbrook media#journalism
805 notes
·
View notes
Text


It's (D)ifferent
#donald trump#trump#musk#elon musk#president trump#president donald trump#trump 2024#presidential election#elections#election 2024#us elections#captain america#politics#us politics#american politics#vote trump#new york times#media#press#journalism
176 notes
·
View notes
Text
“I feel profoundly alone, cut off, unattractive... I feel unloveable. But I respect that unloveable soldier — struggling to survive, struggling to be honest, just, honourable. I respect myself.”
— Susan Sontag, As Consciousness is Harnessed to Flesh: Journals and Notebooks, 1964-1980.

— Diane Arbus, “Susan Sontag alone on a bed. N.Y.C.𝟣𝟫𝟨𝟧.”
#susan sontag#diane arbus#female gaze#female artists#american literature#nyc#photography#art#b&w#female photographers#quote#literary quotes#literature#american writer#writers#spilled ink#spilled feelings#deep thoughts#feminism#poetry#journal#writing#academia#words#beautiful quote#self image#inspiring quotes#sapphic#love#w
243 notes
·
View notes
Text
Trump’s Trial Violated Due Process
Trump was denied notice of the charges, meaningful opportunity to respond and proof of all elements.
By
David B. Rivkin Jr. and Elizabeth Price Foley
Wall Street Journal
Whether you love, hate or merely tolerate Donald Trump, you should care about due process, which is fundamental to the rule of law. New York’s trial of Mr. Trump violated basic due-process principles.
“No principle of procedural due process is more clearly established than that notice of the specific charge,” the Supreme Court stated in Cole v. Arkansas (1948), “and a chance to be heard in a trial of the issues raised by that charge, if desired, [is] among the constitutional rights of every accused in a criminal proceeding in all courts, state or federal.” In in re Winship (1970), the justices affirmed that “the Due Process Clause protects the accused against conviction except upon proof beyond a reasonable doubt of every fact necessary to constitute the crime with which he is charged.” These three due-process precepts—notice, meaningful opportunity to defend, and proof of all elements—were absent in Mr. Trump’s trial.
The state offense with which Mr. Trump was indicted, “falsifying business records,” requires proof of an “intent to defraud.” To elevate this misdemeanor to a felony, the statute requires proof of “intent to commit another crime.” In People v. Bloomfield (2006), the state’s highest court observed that “intent to commit another crime” is an indispensable element of the felony offense.
New York courts have concluded that the accused need not be convicted of the other crime since an “intent to commit” it is sufficient to satisfy the statute. But because that intent is, in the words of Winship, “a fact necessary to constitute the crime,” it is an element of felony falsification. Due process requires that the defendant receive timely notice of the other crime he allegedly intended to commit. It also requires that he have opportunity to defend against that accusation and that prosecutors prove beyond a reasonable doubt his intent to commit it.
Mr. Trump’s indictment didn’t specify the other crime he allegedly intended to commit. Prosecutors didn’t do so during the trial either. Only after the evidentiary phase of the trial did Judge Juan Merchan reveal that the other crime was Section 17-152 of New York’s election law, which makes it a misdemeanor to engage in a conspiracy “to promote or prevent the election of any person to a public office by unlawful means.”
To recap, the prosecution involved (1) a misdemeanor elevated to a felony based on an “intent to commit another crime,” (2) an indictment and trial that failed to specify, or present evidence establishing, another crime the defendant intended to commit, and (3) a jury instruction that the other crime was one that necessitated further proof of “unlawful means.” It’s a Russian-nesting-doll theory of criminality: The charged crime hinged on the intent to commit another, unspecified crime, which in turn hinged on the actual commission of yet another unspecified offense.
To make matters worse, Judge Merchan instructed the jury: “Although you must conclude unanimously that the defendant conspired to promote or prevent the election of any person to a public office by unlawful means, you need not be unanimous as to what those unlawful means were.”
Due process demands that felony verdicts be unanimous, but in Schad v. Arizona (1991), a murder case, the high court indicated that there need not be unanimity regarding the means by which a crime is committed. But a plurality opinion by Justice David Souter cautioned that if the available means of committing a crime are so capacious that the accused is not “in a position to understand with some specificity the legal basis of the charge against him,” due process will be violated. “Nothing in our history suggests that the Due Process Clause would permit a State to convict anyone under a charge of ‘Crime’ so generic that any combination of jury findings of embezzlement, reckless driving, murder, burglary, tax evasion, or littering, for example, would suffice for conviction,” Justice Souter wrote.
Justice Antonin Scalia concurred, observing that “one can conceive of novel ‘umbrella’ crimes (a felony consisting of either robbery or failure to file a tax return) where permitting a 6-to-6 verdict would seem contrary to due process.” Four dissenting justices argued that the In re Winship precedent requires unanimity regarding all elements of a crime, including the means by which it’s committed.
All nine justices in Schad, then, believed unanimity is required to convict when the means by which a crime can be committed are so broad that the accused doesn’t receive fair notice of the basis of the charge. New York’s election law requires that the violation occur “by unlawful means,” so any “unlawful” act—including, in Scalia’s example, either robbery of failure to file a tax return—can qualify. That’s clearly overbroad. Thus, Judge Merchan’s instruction that the jury “need not be unanimous as to what those unlawful means were” was unconstitutional.
That isn’t all. Judge Merchan hand-selected three laws—federal election law, falsification of “other” business records and “violation of tax laws”—as the “unlawful means” by which state election law was violated. Mr. Trump received no notice of any of these offenses, and the prosecutor briefly alluded only to federal election law, during the trial. Mr. Trump tried to call former Federal Election Commission Chairman Brad Smith to explain why this law wasn’t violated, but Judge Merchan ruled Mr. Smith couldn’t testify on whether Mr. Trump’s conduct “does or does not constitute a violation” of federal election law, denying him a meaningful opportunity to be heard.
Judge Merchan’s second “unlawful” means, falsification of other business records, is circular: A misdemeanor becomes a felony if one falsifies business records by falsifying business records. Further, the prosecution never alleged or provided evidence that Mr. Trump falsified “other” business records. The prosecutors likewise neither alleged nor offered evidence that Mr. Trump had violated tax laws, Judge Merchan’s third predicate.
Mr. Trump, like all criminal defendants, was entitled to due process. The Constitution demands that higher courts throw out the verdict against him. That takes time, however, and is unlikely to occur before the election. That unfortunate reality will widen America’s political divide and fuel the suspicion that Mr. Trump’s prosecution wasn’t about enforcing the law but wounding a presidential candidate for the benefit of his opponent.
Mr. Rivkin served at the Justice Department and the White House Counsel’s Office during the Reagan and George H.W. Bush Administrations. Ms. Foley is a professor of constitutional law at Florida International University College of Law. Both practice appellate and constitutional law in Washington.
#Wall Street Journal#trump#president trump#america first#americans first#repost#trump 2024#donald trump
348 notes
·
View notes
Text





Evan Peters the man that you are
#evan peters#actor#evan peters hot#american horror story#america#evan peters ahs#evan peters is my love#evan peters fandom#— ֢ ׄ ୨୧ ࡛ mel's journal
129 notes
·
View notes
Text

Friendly reminder that:
#angelcore is NOT for nsfw or coquette posts. It's an ethereal aesthetic that's usually related to the angelkin community. So your Lana del Rey gifs and edits of pornstars don't fit here.
#coquette is NOT for nsfw. It's a tag for teen/young girls and celebrating feminity and girlhood
#morute is NOT for nsfw or coquette posts. It's an aesthetic that mixes delicate and cute elements with morbid and creepy ones. And it's sometimes used as a coping mechanism.
#lolita fashion / #sweet lolita is NOT for nsfw or coquette posts. these are a type of japanese fashion, not your "daddy's good girl" fantasy.
#nymphet / #nymphette is NOT for nsfw. It's a fashion style/coquette aesthetic and the name comes from a novel about pedophilia. So you don't wanna mix it with your "daddy's good girl" fantasy.
If knowing all of this you still post your "dumb whore" and "r*pe kink" stuff under this tags, you're a disgusting asshole and we don't want you here ♡

#im sorry for the tags but you know who is this directed for#girlblogging#girl blogger#girlblogger#coquette#dollette#manic pixie dream girl#girlhood#this is what makes us girls#nymph3t#just girly thoughts#angelic#angelcore#morute#morute aesthetic#american lolita#sweet lolita#† journal
130 notes
·
View notes
Text

❀ 𝐉𝐨𝐚𝐧 𝐃𝐢𝐝𝐢𝐨𝐧 ❀
#joan didion#american writer#writer#american author#journalism#1960s#60s#sixties#60s icons#photography#black and white photography#1970s#70s#seventies#new journalism#60s women#literature
90 notes
·
View notes
Text

captain hook and peter pan's shadow
okay so hear me out. I had a weird dream a few months back about hook suddenly waking up on a ship and everyone else is dead. decaying. dismembered and disassembled. for some reason, the blood on the floors is still wet. an absolute nightmare of a time. the only other person in neverland who isn't a corpse is the shadow of peter pan, who, over time, has slowly come into form as a vaguely fashionable adult since there's nothing tying it to the body of a youth that refuses to grow up (since he was originally nothing but a shadow, he will remain forever shadowless tho)
('One day, Peter decided he didn't need a shadow, that it was more fun to sneak up on people without giving them a chance to notice, and I was left to do whatever I wanted. Eventually I started to care, to feel, and from there I became what I am now.')
it was. some kind of murder mystery, where it's very clearly peter who committed the murders, but hook and the shadow go about trying to figure out the events leading up to it. as one does!
#anyway if it was not clear. brom's peter had a huge visual influence on me as a teenager. and i also enjoyed american mcgee's alice#drawing tag#im obsessed with peter pan ngl i read academic texts and journals abt the narrative for fun#its just fun to read about. and also the original texts and stories are fun to read too
496 notes
·
View notes
Text
and heres a tate journal page version !


#ahs fandom#tate langdon#violet and tate#ahs tate#ahs murder house#ahs#american horror story#nirvana#tate langdon journal page#tate langdon journal#tate langdon scrapbook#tate langdon vibe#tate langdon ahs#tate langdon american horror story#tate langdon ahs murder house#Spotify
54 notes
·
View notes
Text
I hate his personnality, but damn Patrick Bateman is so hot ᡣ𐭩

#coquette#dolette#female hysteria#female manipulator#female urge#femcel#feminism#im just a girl#just girly posts#lana del ray aesthetic#american psycho#patrick bateman#vanilla girl#girl interrupted#girlblogging#hell is a teenage girl#tumblr girls#just girly things#girlhood#this is a girlblog#feminine urge#fuck incels#girl interupted syndrome#feminine sissy#the virgin suicides#dark urge#ultraviolence#crush#murder drones lizzy#journal
63 notes
·
View notes