#agriculture database
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Why Do Manufacturers Need Fertiliser Insights In Africa?
The agro and livestock products you see in the market are produced according to the needs of farmers and livestock owners. If you go to a farm dealer and ask for a specific type of seed or animal nutrition, the dealer will show multiple options. All manufacturers work according to market insights so you get multiple options.
Visit us - https://agnexus.africa/index.php/2024/11/25/why-do-manufacturers-need-fertiliser-insights-in-africa/
#agriculture research#agriculture database#agrodealers#agriculture consulting#market insights#agritrack
0 notes
Text
Flowering is a crucial biological process in angiosperms, impacting ecological balance and horticultural value. Despite extensive studies, the regulatory mechanisms of flowering genes remain incompletely understood due to the vast diversity among plant species. Previous research has focused on individual species or pathways, leaving a gap in comprehensive cross-species analyses. Based on these challenges, an in-depth study was necessary to compile and analyze flowering genes across a broad spectrum of plant species, to provide a unified platform for exploring flowering gene regulation and interactions. A recent study details the identification and comparative analysis of flowering genes from 837 angiosperm species, resulting in the creation of an extensive Plant Flowering-time Gene Database (PFGD).
Continue Reading.
#Science#Plants#Biology#Agriculture#Horticulture#Molecular Biology#Plant Flowering-time Gene Database#PFGD
47 notes
·
View notes
Text
Valeria Kogan, PhD, Founder and CEO of Fermata – Interview Series
New Post has been published on https://thedigitalinsider.com/valeria-kogan-phd-founder-and-ceo-of-fermata-interview-series/
Valeria Kogan, PhD, Founder and CEO of Fermata – Interview Series


Valeria Kogan, PhD, Founder and CEO of Fermata has been recognized as one of Forbes’ “30 Under 30” in 2022, Valeria is a serial entrepreneur with a proven track record in biotechnology and innovation. As the founder of Fermata and the biotech firm Smartomica, Valeria combines her scientific expertise with a visionary approach to transforming industries.
Fermata is a data science company revolutionizing agriculture with cutting-edge computer vision solutions. Its flagship platform, Croptimus™, provides 24/7 automated detection of pests and diseases, helping growers identify issues like powdery mildew, bud rot, and mosaic before they escalate. By reducing scouting time and minimizing crop loss, Fermata empowers farmers to focus on solutions and maximize yield, whether in controlled environments or outdoor settings.
What inspired you to transition from bioinformatics and cancer research to agriculture technology? How did your experience with Smartomica influence the founding of Fermata?
My transition from biotech to agriculture was pretty accidental. Friends of friends of mine who were tomato producers were looking for someone with experience in AI to brainstorm together on its applications in farming. It was the time when deep learning has just started and created a lot of buzz in the tech space – it also found immediate applications in the medical domain through computer vision in radiology. Everyone in my circle was talking about it, so when I saw what the farming guys showed me – plant health issues that can be detected visually and that need to be identified in real time – it immediately clicked. I had an idea to bring the knowledge from the medical space to agriculture which was a much less popular and digitized industry back then.
With a background in AI and biotech, what challenges did you face in adapting those technologies to agriculture?
I think in general anyone who comes with a digital product to a conservative industry faces the same level of resistance. However, it’s harder if you are an outsider. My approach was and is being humble and driven by the willingness to apply my company’s knowledge to help people, not to tell them what they are doing wrong and how we can help them do it in the right way. Through every conversation with growers, we learn and try to stay open-minded and not too attached to our technology while prioritizing the needs of the grower and adjusting our product accordingly.
Fermata focuses on reducing crop losses and pesticide use. What was the initial reception of this idea in the agricultural community, and how did you convince stakeholders to adopt AI-driven solutions?
The initial reception was that it was not possible. I can’t say that much has changed over the past 5 years! We see great support from the early adopters and a lot of concerns from the broader audience. We are lucky to have customers who believe in the technology and don’t just pay us money but become the showcases for the rest of the market. The best and only thing we can really do is let the product speak for itself.
How does Croptimus™ integrate multiple data sources, such as satellite imagery, sensors, and AI models, to provide actionable insights for growers?
Currently, we use only visual data from the cameras to analyze plant health and identify pests, diseases, nutrient problems, and other issues. However, with the new developments in the AI sector, we understand the benefits that additional data sources can bring to us both for higher detection quality and also for enabling predictive analytics. Currently, we only use climate data in some projects, but plan to expand beyond that in 2025.
What makes Fermata’s early pest and disease detection capabilities unique compared to other AgTech solutions?
There are several things that make us unique. First of all, over the past 5 years, we have collected an insane database of plant images both through our customers and with our own R&D facility where we infest the plants to collect additional data. We also used an internal labeling team which we very carefully trained. In combination with a broad network of agronomy experts from across the globe, this helped us to build a very high-quality dataset. A deep understanding of machine learning in combination with the product vision helped us create a useful and simple product on top of that.
AI and computer vision are advancing rapidly. How does Fermata ensure its technology stays ahead of the curve in this competitive landscape?
At Fermata, we follow a data-centric approach, ensuring high-quality and flexible data labeling by bringing together agronomists and data scientists. We invest in diverse datasets to keep our technology competitive and we also focus on solving specific problems and collaborate with partners when needed to remain the best at what we do.
You’ve emphasized sustainability as a key goal. How do you see Fermata’s technology impacting global efforts to reduce food waste and minimize environmental harm?
By helping farmers identify pests and diseases in time we help them prevent losses, minimize food waste, and reduce pesticide use. This is especially important in the current environment when the climate is changing. Many growers suffer from new pests or diseases that they have never seen in their regions before. Because of that, early detection and assistance in tuning the mitigation strategies is essential for them.
Raising $10 million in Series A funding is a significant milestone. How will this funding accelerate Fermata’s vision, and what are your immediate priorities for growth?
We plan to use this money to grow from “The Eyes of Ag” to “The Brain of Ag” by integrating more data sources into our platform and broadening the list of products we offer beyond pests and diseases. Our immediate priorities include focusing on certain markets – Canada and the Netherlands, and tomato crops to get significant market share for the segment and then replicate it for the other regions and crops.
What role do you see emerging technologies, like robotics or IoT, playing in Fermata’s future innovations?
I believe that advancements in robotics and IoT will bring huge value to Fermata, because all these companies are our potential partners. We are looking forward to seeing both new ways to collect data as well as automated solutions to move through the facility and use fewer sensors and cameras to achieve the same goals.
What’s next for Fermata? Are there specific crops, regions, or technologies you are particularly excited to explore in the coming years?
In 2025 we will be focused on tomato producers mainly in Canada and the Netherlands, but following that we aim to expand our services to other vegetables like cucumbers and peppers, then strawberries and grapes. I hope that we will enter global markets with the new crops at the end of this year and in 2026. Regarding technologies, our plan is to go beyond pests and diseases into predicting the yield, assessing the efficiency of pollination, and many other exciting tasks where farmers will appreciate the help of AI.
Thank you for the great interview, readers who wish to learn more should visit Fermata.
#2022#2025#agriculture#Agtech#ai#AI models#amp#Analytics#applications#approach#background#biotech#biotechnology#Brain#Cameras#Canada#Cancer#CEO#climate#collaborate#Community#Companies#computer#Computer vision#crops#cutting#data#data science#data sources#Database
0 notes
Text
Explore These Exciting DSU Micro Project Ideas
Explore These Exciting DSU Micro Project Ideas Are you a student looking for an interesting micro project to work on? Developing small, self-contained projects is a great way to build your skills and showcase your abilities. At the Distributed Systems University (DSU), we offer a wide range of micro project topics that cover a variety of domains. In this blog post, we’ll explore some exciting DSU…
#3D modeling#agricultural domain knowledge#Android#API design#AR frameworks (ARKit#ARCore)#backend development#best micro project topics#BLOCKCHAIN#Blockchain architecture#Blockchain development#cloud functions#cloud integration#Computer vision#Cryptocurrency protocols#CRYPTOGRAPHY#CSS#data analysis#Data Mining#Data preprocessing#data structure micro project topics#Data Visualization#database integration#decentralized applications (dApps)#decentralized identity protocols#DEEP LEARNING#dialogue management#Distributed systems architecture#distributed systems design#dsu in project management
0 notes
Text
I don’t need brand name food so I’ll just get the cheapest one vs. all the cheap brands are probably sourced with like the most unsustainable and exploitative practices. FIGHT
#I know loads of name brands are also exploitative and unsustainable#but like the foods that are branded as sustainable are so expensive#and i don’t even know if they’re actually sustainable#and i don’t have the ability to buy local food all the time (no car)#and then It’s like woah is there actually any good choice or is it worthless because we need system wide change#and then It’s like what the fuck Can i do for system wide change#and like yeah i could look this up#and IVE tried#but that would be like a whole search for every single product I buy#and there’s not like an easy database for ‘is this food evil or not’ at least not as far as I can tell#Bc there’s so many different opinions on what’s the best thing for sustainable agriculture#and i want to take a class on this next year#but#it’s from 5-730 Pm#Ugh
0 notes
Text
Greenhouse, Indoor & CEA Growers/Consultants Database - Email List

View On WordPress
#agriculture#agritech#business leads#Cannabis#cannabis growers#cannabis tech#CEA#Email List#green house#horticulture#hydroponics#indoor farming#marketing database#targeted email list#vertical farming
0 notes
Text
https://eitpl.in/agriculture
Eitpl is a leading Agriculture software Development services, company in Kolkata provides Agricultural Statistics Database Management, Application Development, Database Management, Apps Development company in kolkata.
#Agriculture software Development company in Kolkata#Agricultural Statistics Database Management in kolkata#Agricultural Application Development in kolkata#Agricultural Database Management company in kolkata#Agricultural Apps Development company in kolkata#Agricultural satistics based software in kolkata#Agricultural database management in kolkata
0 notes
Text
Factors Responsible for a High Yield of Canola
A member of the Brassica family, canola is a cash crop grown widely for its oil, including both cooking oil and biofuel. Canola farming is a popular agricultural activity in several parts of the world, with Australia being the third largest exporter. Grown in all states and territories, canola is a vital oilseed crop in Australia. This crop is generally grown in rotation with other crops like wheat, barley, and pulses.
In this blog, we have discussed the
Factors Responsible for High Yield of Canola
1. Climatic Conditions: A cool-season crop, Australia’s climatic condition is well-suited for canola cultivation. Canola requires a moderate amount of rainfall and well-drained soils that are rich in organic matter. At the same time, canola requires a pH of 5.5 to 7.5 and is sown in autumn, from March to May, and harvested in a sprint from October to December.
2. Crop Varieties: Due to the availability of five distinct herbicide tolerance systems and two distinct canola breeding types, variety selection for canola is made more difficult (open-pollinated and hybrid). Each variety fits into farming systems differently.
3. Sowing Period: To increase canola yield in Western Australia, early sowing is the solution. In areas with low to moderate rainfall, canola is sown in April; in areas with heavy rainfall, it is sown in April and May. Depending on the area, some degree of frost danger must be tolerated to get maximum yields.
4. Sowing Options: Due to the influence of delayed seeding on output and the availability of efficient post-emergence herbicide choices, a large percentage of canola fields are dry-seeded (depending on canola type). Plant emergence and plant density may be affected if furrow fills happens after dry sowing because plants won't be able to arise from too deep. Delaying selection will probably result in a produce penalty unless the season has already broken early. To calculate the amount of the yield penalty brought on by postponed sowing, use the links contained in the sowing window portion.
5. Sowing Rate and Depth: Even though lowering seeding rates can reduce costs; you need to ensure that target plant densities are achieved. To ensure yield potential, switching to earlier sowing is becoming more common to grow canola crops in challenging conditions, often with warm temperatures and drying soil.
6. Fertiliser: The gross margin of a canola crop may be lowered by excessive input costs or decreased returns, if there’s not enough fertiliser. Compared to other crops, canola has different nutritional requirements. Using some of the many tools (including software packages, mobile and online apps, information products, and professional services), a tailored fertiliser program can be developed. To outline the nitrogen strategy, consider the crop’s potential yield, soil test results, soil type, and rainfall information. To determine post-emergence rates, nitrogen is applied in split applications. It is necessary to check soil phosphorus status for maintenance rates at seeding. At the same time, canola requires more sulphur than wheat but is equally susceptible to micronutrient deficiencies like wheat. Therefore, you need to monitor the crop within the season and conduct tissue tests to identify micronutrient deficiencies. Conducting regular soil and tissue testing is necessary to develop fertiliser programs as per crop demand.
7. Weed Control: Western Australia canola varieties have several herbicide tolerance systems. To choose the herbicide tolerance system, consider the weed spectrum and weed resistance status, crop sequence, rainfall zone, and cost.
8. Insect Control: Although different insect species can infest canola crops, applying chemical insecticide is not always necessary. Monitoring the crops through the season, allowing response time to potentially damaging infestations is essential. Canola crops can reach damaging levels if it gets infested by turnip aphids, cabbage aphids, and green peach aphids.
9. Disease Control: Monitoring canola crops for disease during the growing season is important as it allows time to consider and implement management options. To complement other management strategies, fungicides can be used but cannot be relied on alone. Other options include seed dressing, fertiliser treatment, and foliar fungicides. However, the commercially sold seed comes with fungicide seed dressing. For canola growers, managing the fungal disease blackleg is an essential consideration for which growers need to utilise different strategies to reduce the loss of yield. There are other fungal and viral diseases that impact canola crops including powdery mildew, downy mildew, and more.
10. Harvest: For harvesting canola crops, two techniques are popularly used- direct harvesting and swathing. The key difference between swathing and harvesting methods is the cutting and drying time before harvest. While direct harvesting involves cutting and threshing the crop in a single pass with a combine harvester; swathing, on the other hand, involves cutting the crop and laying it in rows to dry for a few days before harvesting.
Wrapping Up,
Achieving high yields of canola in Australia requires managing various factors carefully that influence crop growth and productivity.
Now that we have discussed the factors that influence the high yield of canola crops in Australia, it will be easy for you as an agribusiness owner to venture into the canola plantation. If you require detailed insights into canola yield crops, contact us at KG2 Australia and we will provide you with personalised assistance.
#canola yield#canola crop#kg2 Australia#agribusiness#agriculture business#regenerative agriculture#Australian farmers#Farmer Database#direct marketing
0 notes
Text
The agency that carries out this "program" is called the Wildlife Services of the U.S. Department of Agriculture. I hate this agency with all the passion I can generate, and have ever since I learned about it and what it does 15 years ago. It exists to murder wildlife, particularly to benefit farmers and ranchers. Long ago, someone put handle on the agency, calling it the "gopher chokers." The name fits. I have done more than a fair amount of yelling to my dead representatives in Congress and senators to dismantle the agency or change its purpose and mission.
My favorite statistic. I don't remember the year, but let's just say 2014. In that year, Wildlife Services killed about 350,000 red-winged blackbirds. Why? They were eating sunflower seeds in sunflower farms. You'd think that a sunflower farmer should be taking that risk rather than causing us taxpayers to make his profit for him, right?
Other stats. We're starting to believe that beavers need to be returned to the wild to help us with floods and drought resistance. Wildlife Services killed 24,603 beavers in 2023. Other stats for death: 525 cardinals; 68,562 coyotes; 430 black bears; 17,109 mourning doves; 6,952 cattle egrets; 1,292 red foxes; 24,744 Canadian geese (even though they are protected by the Migratory Bird Treaty Act); 1,209 jackrabbits (four species of them); 1,981 possum; 905 robins. I could go on, but I'm going to puke. Here's the link to the chart.
Sorry about the length of this post, but it takes a while to describe pure evil.
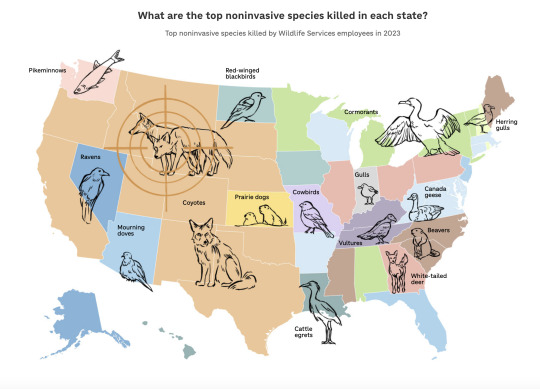
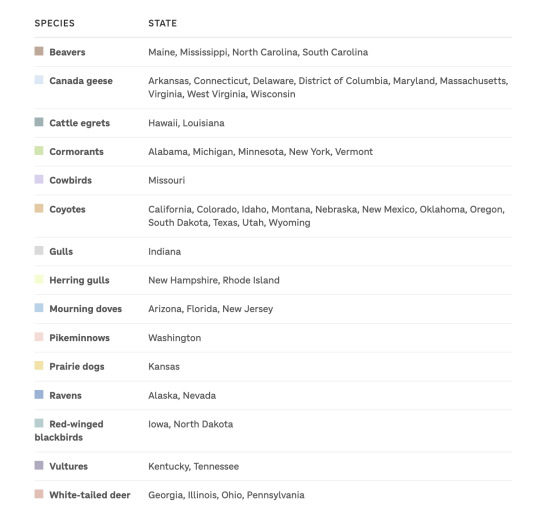

Excerpt from this story from NPR:
The United States Department of Agriculture's [USDA’s] Wildlife Services program is a holdover from the 1930s, when Congress gave the federal government broad authority to kill wildlife at the request of private landowners. In that era, government-sponsored extermination programs for native wild animals, like wolves and grizzly bears, were common.
After the Endangered Species Act was passed in 1973, federal agencies were required to change course and start helping some of those wild animal populations recover. But today, Wildlife Services employees still kill hundreds of thousands of noninvasive animals a year, data from the agency shows. Even species considered threatened under the Endangered Species Act, like grizzly bears, are not exempt. So long as livestock or human life are threatened, federal rules allow Wildlife Services to kill those animals, too.
Conservationist groups have long protested the program, saying the government is killing animals at the request of private livestock owners without first presenting enough evidence to show that the management methods aren’t harming the environment, as federal law requires.
“One of the biggest issues that comes up with Wildlife Services, and where we've beaten them in court multiple times in multiple states, is the controversy of the science,” said Lizzy Pennock, an attorney for the nonprofit WildEarth Guardians. “We need to get out of the framework of the 1800s and 1900s where it's like, kill any carnivores that might be inconvenient.”
Wildlife Services officials say that with the exception of invasive species, employees only kill wild animals that attack livestock or cause damage. But data obtained by NPR indicates the program often kills native wildlife that didn’t kill or injure livestock.
NPR obtained and digitized thousands of Wildlife Services work orders from Montana, created from 2019 through 2022, and built a database that shows that the program’s employees frequently kill native wild animals without evidence of livestock loss. The documents reveal that during those three years, employees killed approximately 11,000 wild animals on Montana properties where no wildlife was recorded as responsible for killing or injuring any livestock. In those cases, only a "threat" from those wild animals was logged in the records.
The agency frequently used helicopters and planes to shoot large numbers of wild animals at a time, the documents show, a method activists consider cruel and scientists say can lead to local eradications.
Although some livestock organizations financially support part of Wildlife Services' work, individual livestock owners do not pay a fee when federal employees come to their properties. Employees are allowed to kill wild animals on those private areas as well as on public land, like state forests and parks.
“That’s a bloodbath,” said Collette Adkins, a lawyer who leads the Carnivore Conservation program at the Center for Biological Diversity. “That just seems like yahoos with rifles killing everything they see that moves. It’s horrible to imagine the amount of suffering involved there.”
“Of all wildlife encountered in FY 2023, Wildlife Services lethally removed 5.14%, or approximately 1.45 million, from areas where damage was occurring. Invasive species accounted for 74.2% (1,079,279) of the wildlife lethally removed,” a representative wrote.
An NPR analysis of those reports shows that Wildlife Services killed more than 370,000 noninvasive animals across the country in the 2023 fiscal year. And over the past nine years, Wildlife Services killed 30 threatened grizzly bears and at least 1,500 gray wolves in states where they were otherwise supposed to receive protection under the Endangered Species Act, like in Minnesota and Wisconsin.
But the reports don’t reveal the names of the livestock owners that use Wildlife Services. That’s to protect the privacy of people in the agriculture industry, the agency has said. Wildlife Services also doesn’t disclose in those reports how many wild animals were killed by federal employees on public land.
20 notes
·
View notes
Text

35 Bottles From the 18th Century Filled with Cherries Found at George Washington’s Mount Vernon
The story of a six-year-old George Washington chopping down a cherry tree may be a myth, but archeologists excavating Mount Vernon, the home of the United States’ first president, made the very real discovery of 35 glass bottles filled with cherries and berries.
The bottles were found in five storage pits in the mansion’s cellar, with 29 of them intact and containing “perfectly preserved cherries and berries, likely gooseberries or currants,” according to a news release from George Washington’s Mount Vernon on Thursday.
Crews unearthed the 18th-century bottles during the ongoing $40 million revitalization project launched last year at Mount Vernon, Virginia.
The bottles were extracted from the pits and refrigerated, and are expected to undergo scientific analysis, the release states.
The slowly drying bottles, “composed of materials and foodstuffs that are likely 250 years old,” will be sent from Mount Vernon’s archaeology lab to an off-site location for conservation, according to the release.
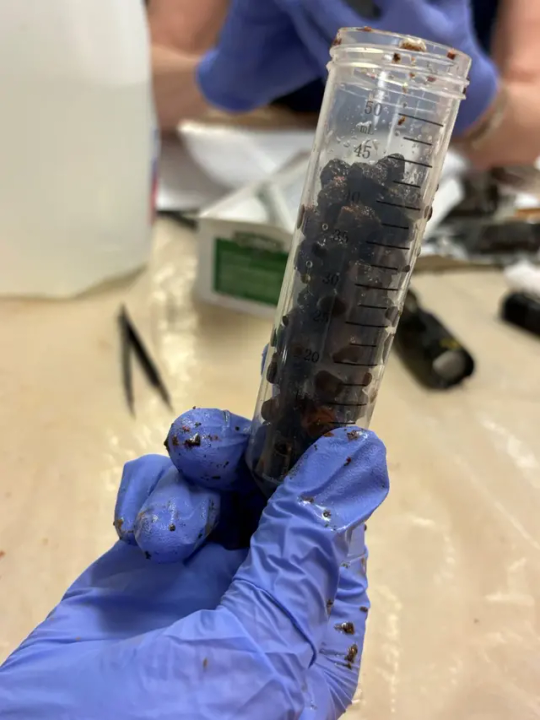


The latest discovery comes after the recent find of two intact European-manufactured glass bottles, also from the 18th century, filled with liquid, cherries and pits in the same cellar, according to the organization.
“Now we know those bottles were just the beginning of this blockbuster discovery,” Mount Vernon President and CEO Doug Bradburn said in a statement.
Bradburn referred to the discoveries as “an unprecedented find,” adding that “nothing of this scale and significance has ever been excavated in North America.”



“The bottles and contents are a testament to the knowledge and skill of the enslaved people who managed the food preparations from tree to table,” said Jason Boroughs, Mount Vernon principal archaeologist.
The bottles may have been forgotten when Washington left Mount Vernon to take command of the Continental Army, according to Bradburn.
“These artifacts likely haven’t seen the light of day since before the American Revolution,” he said. “It’s so appropriate that these bottles have been unearthed shortly before the 250th anniversary of the United States.”




Bradburn added that the organization’s team is hopeful the cherry pits may be viable for future germination.
Mount Vernon partnered with the US Department of Agriculture’s Agricultural Research Service to analyze the bottles’ contents.
In the early stages of analysis, researchers identified 54 cherry pits and 23 stems, suggesting the bottles were likely full of cherries at one point, according to the release.
“The cherries likely are of a tart variety, which has a more acidic composition that may have aided in preservation,” the release states.
The cherries are likely candidates for DNA extraction, which could help researchers compare them against a database to identify their exact species, according to the release.
By Ashley R. Williams.

#35 Bottles From the 18th Century Filled with Cherries Found at George Washington’s Mount Vernon#mount vernon#George Washington#glass#glass bottles#18th-century bottles#ancient artifacts#archeology#archeolgst#history#history news
37 notes
·
View notes
Text
What Are The Advantages Of Agriculture Database?
Agro-industry includes farmers, agro-product manufacturers, and agriculture data companies. Out of the three, data firms play a central role in shaping the agro-industry. If you make a pyramid of agro-industry, you will find that the farming community is at the receiving end and the manufacturers are at the top. Data firms connect farmers and manufacturers.
Visit us - https://agnexusafrica.livejournal.com/1434.html?newpost=1
0 notes
Note
📂HEADCANONS
YEAH
Trying to think of ones I haven’t already talked about A Lot
Murderbot describes Preservation as "a complicated barter system" because it doesn't really have the words or concepts to parse what it's looking at: primarily a gift economy. An economy with a robust central government that does a lot of distribution of primary resources, and a social logic based more on providing than consuming. Farmers and agriculture techs don't produce food to then trade to other people, they produce food that's then re-distributed to everyone as needed by a central organization, and the farmers and ag-techs are given what they need and want by others who, y'know, eat food and express gratitude for Having Food. People don't trade for health care, doctors provide health care to whoever needs it because that's what they've trained and chosen to do and are given what they need by others for their service in providing health care.
Pin-Lee doesn't tend to have a lot to trade but she is a lawyer who keeps things functioning between Preservation and the Corporates, does the legal work that allows Preservation citizens to safely travel, and helps to maintain the contracts that prevent other more opportunistic planets fromtaking advantage of them. She provides this service to the planet and gets what she needs from other people who provide other services. Gurathin helps to maintain the university's database infrastructure, when he's getting coffee he doesn't need to offer to like, make a database for the coffeeshop, it's just understood that he's providing a service to society and partaking in another service to society. Arada and Ratthi are research biologists and their work is only tangentially productive to The Planet but I'm sure there's a public outreach or education aspect that's expected of a lot of researchers - learning without sharing what you're learning is socially unfair, even if their lectures are mostly only attended by students who are told by their teachers to go watch them. But it's kind of understood that by being an adult in the world, you are doing something that contributes to society and to others in some way, and as such are entitled to having your needs met as well.
It's a reciprocity-based logic of actions rather than commodity exchange, and honestly it works because 1) Preservation's population is relatively small, 2) there is a lot of bureaucratic organization work making sure everyone is getting what they need, the government is SO many committees 3) a whole lot of labor is done by machines (non-sentient robots) and bots (sentient robots). The reliance on bot labor is absolutely gonna be something Preservation has to think more about.
Citizens also every once in a while on rotation get called for a kind of labor tax akin to the way jury duty works, where every couple of months you have to put in a day working in the central town food court washing dishes or something. There are also Perks offered for jobs that might be a harder sell for people to do, like premium station housing.
Straight-up money that comes into the station from outsystem trade and travel mostly gets re-invested in supporting Preservation travelers off-planet into societies that do use money (like PresAux's ASR survey), or buying materials or machines that are hard to make locally (like ag-bots, or some spaceship or station parts for repairs).
However where barter comes in is on a more interpersonal one-on-one level, more similar to commissions. You grow a lot of carrots while my grapefruit tree is producing a lot more fruit than I could possibly eat, want to trade? You make ceramics as your primary Work, I'll trade you something if you make me something specific I have in mind. Can you help me fix my roof? I'll get you some good wood when the lumber trees are mature next year. Developing skills for these kind of interpersonal more-specialized trades is a significant motivation, too. And different skills and jobs inevitably attract more status and impressiveness than others. But it's not barter exactly so much as reciprocity, a strong culture of civic duty, and a highly organized government.
#trying to figure out So Hard how a spacefaring multiplanetary no-money barter society works#asks#elexuscal#next one will be more fun I promise
57 notes
·
View notes
Text
ApertureData Secures $8.25M Seed Funding and Launches ApertureDB Cloud to Revolutionize Multimodal AI
New Post has been published on https://thedigitalinsider.com/aperturedata-secures-8-25m-seed-funding-and-launches-aperturedb-cloud-to-revolutionize-multimodal-ai/
ApertureData Secures $8.25M Seed Funding and Launches ApertureDB Cloud to Revolutionize Multimodal AI
ApertureData, a company at the forefront of multimodal AI data management, has raised $8.25 million in an oversubscribed seed round to drive the development and expansion of its groundbreaking platform, ApertureDB. The round was led by TQ Ventures with participation from Westwave Capital, Interwoven Ventures, and a number of angel investors. The funding will allow ApertureData to scale its operations and launch its new cloud-based service, ApertureDB Cloud, a tool designed to simplify and accelerate the management of multimodal data, which includes images, videos, text, and related metadata.
Addressing the Multimodal Data Crisis
The growth of AI has led to an explosion in the generation of multimodal data across industries such as e-commerce, healthcare, retail, agriculture, and visual inspection. Despite this growth, most organizations struggle to effectively manage and utilize this data. This inefficiency often hampers AI development, leading to longer project timelines and lower returns on investment.
ApertureData’s flagship product, ApertureDB, addresses this challenge head-on. It provides a unified database platform specifically built for managing large-scale multimodal data, which includes images, videos, documents, and their associated metadata. Unlike traditional databases focused on textual data, ApertureDB integrates graph and vector search capabilities, allowing businesses to streamline their AI workflows and significantly reduce the time spent on data preparation and management.
The Launch of ApertureDB Cloud
ApertureDB Cloud, the company’s new cloud-based platform, extends the power of ApertureDB, making it easier for enterprises to access and deploy their multimodal AI solutions without complex infrastructure setups. Users can now manage vast datasets with just a few clicks, utilizing ApertureDB Cloud’s advanced graph-vector search capabilities and seamless integration with AI applications. The platform offers a unified data layer that centralizes all relevant data types and metadata, providing fast and efficient querying and retrieval, which is crucial for AI development.
With the launch of ApertureDB Cloud, organizations can now try the platform with a risk-free 30-day trial, making it accessible for AI teams looking to streamline their data operations and scale their AI models.
A Game-Changer for AI and Machine Learning Pipelines
ApertureDB is designed to solve some of the biggest bottlenecks in AI development. By unifying multimodal data management, the platform offers several advantages, including:
35x faster dataset creation compared to traditional data integrations, speeding up AI project timelines.
63% reduction in network transfer of large visual data, improving operational efficiency.
Integrated vector similarity search and advanced graph search capabilities for complex data handling.
These features allow organizations to efficiently manage massive datasets, reducing the time spent on manual data preparation from months to just a few days. The platform is already deployed across multiple industries, from retail and e-commerce to biotechnology and generative AI startups. For instance, a major home furnishings retailer is using ApertureDB to manage product images and metadata, optimizing their recommendation systems and customer insights.
In the biotech sector, ApertureDB is helping AI-driven medical imaging and visual inspection applications, providing seamless access to large volumes of multimodal data.
Backed by Leading Investors
The $8.25 million seed round backing ApertureData was led by TQ Ventures, a New York-based venture capital firm focused on software businesses and technology-driven startups. According to Andrew Marks, General Partner at TQ Ventures, ApertureData is uniquely positioned to be a foundational player in the emerging AI landscape:
“ApertureData has steadily built an amazing business with a wide view on the tech stack. They knew early on that traditional databases, which are geared toward textual data, would be insufficient for managing more complex multimodal data. The quantum of multimodal data and the desire to leverage it for analysis and machine learning is likely to explode over the coming decade as we are already seeing with the growth in use cases for generative and multimodal AI. And so, the work ApertureData is doing today will be foundational towards building the best infrastructure for emerging multimodal AI applications across various industries.”
TQ Ventures, founded in 2018, has a portfolio of over 80 investments and $1 billion under management, giving ApertureData access to a broad network of resources and expertise.
Also participating in the round were Westwave Capital, a pre-seed and seed-stage enterprise investor with a focus on AI, robotics, and analytics, and Interwoven Ventures, a firm specializing in early-stage investments in AI, robotics, and healthcare technology. Both investors bring significant operational experience and industry knowledge to help ApertureData scale and refine its platform for the future of multimodal AI.
Expanding Use Cases for Multimodal Data
ApertureDB’s potential spans a wide range of applications, as industries increasingly generate multimodal data and look for ways to turn this data into actionable insights. The platform’s unique ability to integrate knowledge graphs and multimodal data search functions makes it ideal for AI-driven tasks in e-commerce, agriculture, healthcare, and beyond.
For example, in smart retail, ApertureDB allows retailers to use customer data, images, and metadata to deliver personalized product recommendations and improve the customer experience. In smart agriculture, the platform helps farmers analyze images and geolocation data to optimize farming practices. Medical imaging companies leverage ApertureDB’s ability to handle large multimodal medical datasets, facilitating advanced AI-driven diagnostics.
The Road Ahead for ApertureData
With its newly secured funding, ApertureData plans to scale production deployments, enhance its platform’s user experience, and integrate more ecosystem solutions to cater to various AI and machine learning workflows. The company is also looking to expand its marketing and sales efforts, positioning itself as a leader in multimodal AI data management.
Vishakha Gupta, CEO of ApertureData, envisions a future where the demand for multimodal AI will continue to surge:
“The increasing adoption of multimodal data in powering advanced AI experiences, including multimodal chatbots and computer vision systems, has created a significant market opportunity. As more companies look to leverage multimodality, the demand for efficient management solutions like ApertureDB is expected to grow.”
Co-founded by Vishakha Gupta and Luis Remis, both former researchers at Intel Labs with deep expertise in AI and data infrastructure, ApertureData has grown quickly in response to the needs of the modern AI landscape. Their firsthand experience with managing large datasets of visual data inspired the creation of ApertureDB, a tool that is transforming how companies handle AI and machine learning pipelines.
As enterprises increasingly look to multimodal data to drive AI innovations, ApertureData is poised to lead the charge by providing the critical infrastructure needed to handle the vast, complex datasets of the future. The company’s platform is set to play a vital role in the next generation of AI innovations, helping companies turn data into competitive advantage.
#adoption#agriculture#ai#AI development#AI models#amazing#Analysis#Analytics#ApertureData#applications#billion#biotech#biotechnology#Building#Business#CEO#challenge#chatbots#Cloud#Commerce#Companies#computer#Computer vision#critical infrastructure#customer data#customer experience#data#Data Management#data preparation#Database
0 notes
Text
In a rare case, a black bear in Connecticut has tested positive for rabies, sparking a warning from state wildlife officials.
The bear was a wild female adult discovered in Canton, Connecticut, in February 2023. Like other bears, it should have been hibernating during the winter months. However, due to mobility issues on the left side of its body, the bear was seen falling over, lying down, and not responding to human presence, according to a new paper in the journal Microbiology Resource Announcements.
The bear was observed for 24 hours before being euthanized by a Connecticut conservation officer. Its body was taken to the Connecticut Veterinary Medical Diagnostic Laboratory (CVMDL) at the Unversity of Connecticut's College of Agriculture, Health and Natural Resources for a post-mortem.
After the CVMDL sequenced the bear's brain tissue during the necropsy, they discovered that it was infected with rabies. This was only the second bear the lab had encountered with the virus.
The Connecticut Department of Energy and Environmental Protection (DEEP) has advised the public to avoid any animal that "appears to be distressed, which may include symptoms like stumbling, staggering, walking in circles, dragging a limb or the hind end, or otherwise acting strangely," according to a statement from the University of Connecticut.
Rabies is a viral disease that affects the central nervous system of mammals, causing the inflammation of the brain. The virus is typically transmitted through the saliva of infected animals via bites, scratches, or even mucous membranes and open wounds. It is almost always fatal once symptoms appear, which generally manifest after around 2–3 months and can initially include fever, headache and weakness, progressing to agitation, anxiety, hallucinations, a fear of water, excessive salivation, and lack of coordination.
If an animal displays neurological symptoms, such as stumbling and falling over, then scientists will first test for rabies. If the test comes back positive, CVMDL does not proceed with a full necropsy to protect staff.
"We rule out rabies because we don't want to do a necropsy that could expose people unnecessarily," Guillermo Risatti, CVMDL director and professor at the University of Connecticut, said in the statement. "So, once we detect rabies, that's it. We don't do anything else with the carcass."
The CVMDL scientists sequenced the entire genome of the rabies virus found inside the bear to compare it with a gene bank of other sequences from animals infected with rabies across the world. They found that the virus in the bear—which was the only bear sample on the whole database—most closely resembled a virus sequence from a raccoon in New England.
By comparing these strains of rabies, scientists can investigate how the virus spreads between animals in certain areas.
"That's the value—to see what the virus looks like and be able to distinguish a new virus coming into the area," Risatti said. "All of the sequencing is done by us, here in house. So that is the value. We have created a sequencing lab inside a diagnostic lab that is allowing us to dig more into what is going on."
Only 1 to 3 cases are reported in humans in the United States annually. If a human contracts rabies, they need to receive post-exposure prophylaxis as soon as possible, which can be up to 100 percent effective at preventing the disease. Around 60,000 people receive this post-exposure prophylaxis in the U.S. every year.
Humans most at risk are those living in areas where wildlife that commonly contract rabies, including bats, raccoons, skunks, and foxes, are common. While this case of rabies in a bear is rare, it may become more common in the future, as sightings of black bears in Connecticut have increased lately.
Nine bears were submitted to the CVMDL for testing in 2023 alone, compared to seven between 2019 and 2022.
The DEEP advises calling the local animal control officer or police department if you spot a potentially rabid animal, staying well clear of it, and definitely not attempting to pick it up.
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
The players in my Cyberpunk: Red game don't know it, but yesterday, they met one of the greatest hustlers in the city.
So, some edgerunners were auctioning off some data recovered from an old facility. It used to belong to the corporation my players work for, and they were going to buy it back to keep anyone else from taking the designs, starting up manufacturing, and selling their company's products.
The data being sold were blueprints for a couple kinds of agricultural drones, and a genomic database that ranged from company GMOs to unmodified wild and domesticated plants and animals. The auction ended up being between the PCs, another corporation, and a freelancer representing locals who wanted the bots to help with urban farming efforts. The freelance guy told the PCs that, if they let him have a non-commercial license for the bots, he'd tell them what the other corpo was after and how to stop him from bidding half a million. They agreed, and he pointed out to them that the genomic database included crocus sativus, the plant that saffron came from before it went extinct. The other corpo is from a food company. All he wants is the one plant.
So, the PCs cut a deal where they let him buy the one item out of the database. They didn't have to try to outbid him to keep the GMOs in company hands, and he didn't have to buy the whole goddamn thing, once he knew they knew and the whole plan to be sneaky about it went out the window.
Nice deal, right?
They don't know this, but the only reason the other corpo was even at the auction is because the freelance guy told him where he could get his hands on the genetic code for saffron in exchange for 5,000 kilos of kibble, and another 5,000 if he could keep the original owner from bidding too hard on it.
So now, in exchange for exactly $0, his clients have a year's supply of preserved food and a manufacturing license for autonomous pest control bots.
Ladies and gentlemen, meet Gary Klemp, greatest freelance executive in Night City.
27 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Rise of B2B Marketplaces
B2B marketplaces serve as digital meeting points for buyers and sellers. Over the last decade, they have gained traction due to the convenience, speed, and efficiency they offer to businesses looking to trade internationally. Traditional methods of sourcing and procurement, involving in-person meetings, trade shows, or middlemen, are increasingly being replaced by digital platforms like TradeKey.
TradeKey, launched in 2006, is one of the pioneers in the B2B online space, providing a platform where manufacturers, suppliers, importers, and exporters can interact seamlessly. The platform caters to various industries, including electronics, machinery, agriculture, textiles, chemicals, and more. With its headquarters in Saudi Arabia, TradeKey has a strong presence globally, particularly in emerging markets across Asia, the Middle East, and Africa.
TradeKey’s Unique Selling Proposition (USP)
What sets TradeKey apart from other B2B platforms is its focus on trust and verification. Given the rise of fraudulent activity and scams in international trade, buyers and sellers alike require a platform that ensures safety and reliability. TradeKey addresses this need through its Verified Buyers Database, a unique feature that guarantees that the buyers listed on the platform have undergone a rigorous verification process. This verification process helps in minimizing the risk of fraud and instills confidence in businesses using the platform.
This Verified Buyers Database is particularly valuable for suppliers and exporters looking to tap into global markets without the fear of encountering fake buyers or fraudulent transactions. TradeKey’s platform also allows businesses to verify potential buyers, ensuring that both parties involved in a transaction can trust each other, which is a significant advantage in today's interconnected global trade environment.
Navigating TradeKey: Key Features and Benefits
Global Reach and Industry Focus: TradeKey’s platform is vast, covering more than 9 million registered users from 240 countries. Its global network spans a wide array of industries, allowing businesses to find partners from virtually any sector. The platform's design allows suppliers and buyers to search for products based on industry categories, making it easier to find the right match.
Verified Buyers and Suppliers: As mentioned earlier, TradeKey’s verification system is one of its most crucial aspects. By focusing on transparency, the platform enhances trust among users. Verified buyers and suppliers can negotiate with greater confidence, reducing the risk of scams or unreliable business deals. This feature is particularly beneficial for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), which may lack the resources to conduct extensive background checks on potential partners.
Trade Shows and RFQs: TradeKey provides access to global virtual trade shows, allowing businesses to showcase their products to a global audience without the costs associated with physical participation. Additionally, businesses can post Request for Quotations (RFQs), making it easy to receive proposals from multiple suppliers or manufacturers. This feature streamlines the procurement process, especially for buyers looking to compare offers and select the best deal.
Digital Marketing and Branding Support: Beyond merely connecting buyers and suppliers, TradeKey also offers digital marketing and branding solutions. The platform provides tools to help businesses optimize their listings, making them more visible to potential buyers. Through effective SEO techniques, businesses can ensure their products appear at the top of search results, increasing visibility and lead generation.
Buyer and Seller Communication Tools: Communication is key in B2B transactions, and TradeKey has built-in communication tools that allow for direct messaging, inquiries, and real-time negotiations between buyers and sellers. This reduces the time typically involved in email exchanges or delayed responses, helping to speed up decision-making and order placement.
Market Insights and Analytics: TradeKey also offers access to valuable market data and analytics, which can guide businesses in making informed decisions. By understanding market trends, buyer preferences, and pricing strategies, businesses can fine-tune their offerings and enhance their competitiveness in the global market.
Security and Trust: Overcoming B2B Fraud
One of the biggest challenges in the B2B space is the prevalence of scams and fraud. Many businesses, especially smaller ones, are wary of international trade due to the risk of dealing with unknown or unverified parties. TradeKey addresses these concerns by offering TradeKey GoldKey Membership and TradeKey TrustPass Membership, which provide additional layers of security and credibility for businesses. These memberships allow companies to display their verified status, making them more attractive to potential buyers.
TradeKey also actively educates its users about B2B safety, offering guides on how to avoid scams, identify red flags, and ensure secure payment methods. The platform's dedication to transparency and security has made it a trusted name in the industry, particularly among SMEs looking to expand globally.
The Role of TradeKey in Global Business Growth
In the context of the global supply chain, TradeKey has become a significant facilitator of cross-border trade. Its role is particularly important for businesses in developing regions, where access to global markets might otherwise be limited. By providing a safe, efficient, and user-friendly platform, TradeKey is not only helping businesses find international buyers and suppliers but also contributing to global economic growth by fostering trade partnerships.
Conclusion
As the world becomes increasingly connected, platforms like TradeKey will continue to play a vital role in enabling international trade. With its focus on trust, verification, and ease of use, TradeKey has positioned itself as a go-to platform for businesses looking to expand their global footprint. Whether you are a buyer seeking reliable suppliers or a seller aiming to reach new markets, TradeKey offers the tools, resources, and support needed to succeed in today’s competitive B2B landscape.
By emphasizing security and fostering transparency, TradeKey ensures that businesses can engage in global trade with confidence, making it an invaluable resource in the modern business world
3 notes
·
View notes