#Wireless rf frequency
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Wireless rf frequency, digital audio mixer circuit programming, RFID capability
NT3H2111 Series 3.6 V 13.56 MHz Surface Mount RFID Transponder - XQFN-8
#Wireless & RF#RF Modules & Solutions RFID#NT3H2111W0FHKH#NXP#Wireless rf frequency#digital audio mixer circuit programming#RFID capability#rf control systems#Wireless detectors circuit#remote control#Digital rf modulator#demodulator
1 note
·
View note
Text
https://www.futureelectronics.com/p/semiconductors--wireless-rf--receiver-ics/clrc63201t-0fe-112-nxp-2283646
NXP, CLRC63201T/0FE,112, Wireless & RF Receiver ICs
CLRC632 Series Multiple Protocol Contactless Reader IC (MIFARE/I-CODE1) -SOIC-32
#NXP#CLRC63201T/0FE#112#Wireless & RF Receiver ICs#HDMI circuit#wireless RF circuit#RF radio frequency#AM FM receiver#HDMI receiver IR circuit#Phase locked loop#what is a FM receiver circuit#Phase lock loops#wireless Bluetooth receiver
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
https://www.futureelectronics.com/p/semiconductors--wireless-rf--rf-modules-solutions--gps/max-8q-0-u-blox-3122418
RF Modules, Digital rf modulator, Proprietary RF Module, Radio frequency module
MAX-8 Series 3.6 V u-blox 8 GNSS TCXO ROM Green 9.7x10.1 mm LCC Module
#u-blox#MAX-8Q-0#Wireless & RF#RF Modules & Solutions#GPS#Digital rf modulator#Proprietary RF Module#Radio frequency#USB Adapter#Bluetooth transmitter module#Balanced modulator#Demodulator#Bluetooth Accessories#Transceiver radio waves
1 note
·
View note
Text
https://www.futureelectronics.com/p/electromechanical--timing-devices--crystals/abs07-32-768khz-t-abracon-1392362
Logic clock, timing devices, quartz crystal, low-frequency crystal
ABS07 Series 32.768 kHz ±20 ppm 12.5 pF -40 to +85 °C SMT Low Profile Crystal
#Abracon#ABS07-32.768KHZ-T#Frequency Control & Timing Devices Crystals#logic clock#timing devices#quartz crystal#low-frequency#RF cable assemblies#Surface-mount crystal#Timing solutions#SMT low profile#Wireless timing system
1 note
·
View note
Text

5G 12dBi Magnetic Antenna with RG174 Cable
A 5G 12dBi magnetic antenna is a type of antenna designed to enhance the performance of 5G wireless communication devices, such as routers, hotspots, or modems. Let's break down the key features:
5G: 5G is the fifth generation of wireless technology, which offers faster data speeds, lower latency, and greater capacity compared to previous generations (4G, 3G, etc.). The antenna is specifically designed to work with 5G networks and devices.
12dBi Gain: The "12dBi" figure refers to the antenna's gain, which is a measure of how much the antenna can increase the power of the signal it receives or transmits. A higher gain indicates better signal reception and transmission capabilities. In this case, a 12dBi gain suggests that this antenna can significantly boost the signal strength.
Magnetic Antenna: The term "Magnetic Antenna" indicates that the antenna can be attached to metal surfaces using a magnetic base. This feature provides flexibility in terms of placement and allows for easy positioning on metallic surfaces, like the roof of a car or a metal housing for a 5G device.
Magnetic antennas are often used in mobile applications or in scenarios where temporary or flexible mounting is required. This type of antenna is convenient because it can be easily installed and removed, making it suitable for mobile installations or where drilling holes or more permanent mounting solutions are not practical.
#rf antenna#RF Antennas#RF Antenna at Best Price in India#RF antenna system#radio frequency antenna#Best RF Solution Provider#RF Antenna Suppliers#Manufacturer of RF Antenna#rf antenna manufacturers in india#RF Antenna Manufacturer#RF Antenna Exporters#RF Antenna Latest Price#Wireless HF Antenna#RF Antenna Companies in India#Wholesaler of RF Antenna#RF Antenna Amplifier#RF Antenna Module#2.45 GHz Antenna Module#High Performance RF#Antennas for LoRa and Sigfox#Omni-directional SMD antennas#3.3GHz RF Antennas#RF & Microwave Antenna Manufacturers#Antenna manufacturers in Canada#RF Antenna manufacturers & suppliers - India#RF Antenna made in India#India telecom rf antenna#2.4ghz & 5ghz antenna#multiband antenna#telecom rf antenna products
0 notes
Text
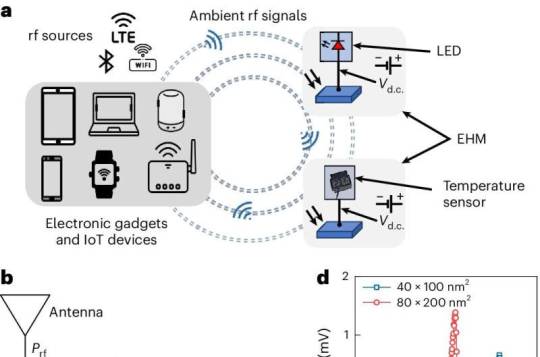
Battery-free technology can power electronic devices using ambient radiofrequency signals
Ubiquitous wireless technologies like Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and 5G rely on radio frequency (RF) signals to send and receive data. A new prototype of an energy harvesting module—developed by a team led by scientists from the National University of Singapore (NUS)—can now convert ambient or "waste" RF signals into direct current (DC) voltage. This can be used to power small electronic devices without the use of batteries. RF energy harvesting technologies, such as this, are essential as they reduce battery dependency, extend device lifetimes, minimize environmental impact, and enhance the feasibility of wireless sensor networks and IoT devices in remote areas where frequent battery replacement is impractical. However, RF energy harvesting technologies face challenges due to low ambient RF signal power (typically less than -20 dBm), where current rectifier technology either fails to operate or exhibits a low RF-to-DC conversion efficiency. While improving antenna efficiency and impedance matching can enhance performance, this also increases on-chip size, presenting obstacles to integration and miniaturization.
Read more.
43 notes
·
View notes
Text
Wireless-fidelity (“Wi-Fi”) is harmful due to radio-frequency radiation exposure, pulse-modulated RF carrying data, extremely low frequency (“ELF”) effect on the brain and the Wi-Fi memory effect in body tissues.
One of the unwanted effects of ELFs, Keith Cutter believes, is brainwave entrainment, where an external stimulus synchronises brainwaves with its frequency.
ELF refers to electromagnetic fields with frequencies between approximately 3 to 30Hz, which is the same range as our brains. Our brains operate within a range of frequencies, with different brainwave states corresponding to specific activities:
Delta Waves (0.5-4Hz): Associated with deep sleep, relaxation, and healing.
Theta Waves (4-8Hz): Linked to meditation, daydreaming, and increased creativity.
Alpha Waves (8-12Hz): Correspond to relaxation, closed eyes and decreased cortical activity.
Beta Waves (13-30Hz): Related to attention, mental activity and cognitive processing.
Gamma Waves (30-44Hz): Involved in sensory processing, working memory and higher-order cognitive functions.
Cutter is most concerned about ELFs at 10Hz from Wi-Fi and other sources.
In the presence of a persistent 10Hz signal, due to entrainment, the brain can shift toward that frequency. As noted above, at 10Hz the brain has decreased cortical activity.
Cortical activity refers to the electrical and chemical signals generated by neurons within the cerebral cortex, the outer layer of the brain responsible for, among other things, cognition.
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
Best Partner for Wireless Modules: A Comprehensive Antenna Selection Guide
n the field of wireless communication, antenna selection is crucial. It not only affects the coverage range and transmission quality of signals but also directly relates to the overall performance of the system. Among various wireless modules, finding the right antenna can maximize their potential, ensuring stable and efficient data transmission.
When designing wireless transceiver devices for RF systems, antenna design and selection are essential components. A high-quality antenna system can ensure optimal communication distances. Typically, the size of antennas of the same type is proportional to the wavelength of the RF signal; as signal strength increases, the number of required antennas also grows.
Antennae can be categorized as internal or external based on their installation location. Internal antennas are installed within the device, while external antennas are mounted outside.
In situations where space is limited or there are multiple frequency bands, antenna design becomes more complex. External antennas are usually standard products, allowing users to simply select the required frequency band without needing additional tuning, making them convenient and easy to use.

What are the main types of antennas?
External Antennas: These antennas can be classified into omnidirectional antennas and directional antennas based on the radiation pattern.
Internal Antennas: These antennas refer to antennas that can be placed inside devices.
Omnidirectional Antennas: These antennas radiate signals uniformly in the horizontal plane, making them suitable for applications that require 360-degree coverage, such as home Wi-Fi routers and mobile devices.
Directional Antennas: These antennas have a high emission and reception strength in one or more specific directions, while the strength is minimal or zero in others. Directional antennas are primarily used to enhance signal strength and improve interference resistance.
PCB Antennas: These antennas are directly printed on the circuit board and are suitable for devices with limited space, commonly used in small wireless modules and IoT devices.
FPC Antennas: FPC antennas are flexible printed circuit antennas that are lightweight, efficient, and easy to integrate.
Concealed Antennas: Designed for aesthetic purposes, concealed antennas can be hidden within devices or disguised as other objects, making them suitable for applications where appearance is important without compromising signal quality.
Antenna Selection Guide
When selecting the appropriate antenna for a communication module, it's essential to first determine whether to use an internal or external antenna based on the module's structure.

External Antennas: These antennas offer high gain, are less affected by the environment, and can save development time, but they may take up space and impact the product's aesthetics.
Internal Antennas: These have relatively high gain and are installed within the device, maintaining a clean and appealing exterior.
Sucker Antennas: These provide high gain and are easy to install and secure.
Copper Rod Sucker Antennas: Made from large-diameter pure copper radiators, these are highly efficient with a wide bandwidth.
Rubber Rod Antennas: Offer moderate gain at a low cost.
Fiberglass Antennas: Suitable for harsh environments and ideal for long-distance signal

External Directional Antennas
Typically used in environments with long communication distances, small signal coverage areas, and high target density.
Panel Antennas have high efficiency, are compact, and easy to install, while considering the impact of gain and radiation area Yagi Antennas offer very high gain, are slightly larger, and have strong directionality, making them suitable for long-distance signal transmission; however, attention must be paid to the antenna's orientation during use
Internal Antenna Selection
Most internal antennas are affected by environmental factors and may require custom design or impedance matching
Spring Antennas are cost-effective but have low gain and narrow bandwidth, often requiring tuning for good matching when installed Ceramic Patch Antennas occupy minimal space and perform well, but have a narrow bandwidth
For details, please click:https://www.nicerf.com/products/ Or click:https://nicerf.en.alibaba.com/productlist.html?spm=a2700.shop_index.88.4.1fec2b006JKUsd For consultation, please contact NiceRF (Email: [email protected]).
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Wireless Keyboards are good?
In today's fast-paced digital world, efficiency and convenience are paramount. As technology continues to evolve, so do the tools we use to interact with it. One such tool that has seen significant advancements in recent years is the humble keyboard. While traditional wired keyboards have been the standard for decades, wireless keyboards are gaining popularity for their flexibility, mobility, and overall user experience.
Wireless keyboards, as the name suggests, operate without the need for physical cables connecting them to a computer or other devices. Instead, they utilize wireless technologies such as Bluetooth or RF (radio frequency) to communicate with the device they are paired with. This simple yet powerful innovation has revolutionized the way we interact with our computers, tablets, and even smartphones. Here are several reasons why wireless keyboards are a good choice for modern users:
Enhanced Mobility:
Perhaps the most obvious advantage of wireless keyboards is their freedom of movement. Without being tethered to a device by a cable, users can position their keyboard wherever they find most comfortable, whether it's on a desk, in their lap, or even across the room. This flexibility is especially beneficial for those who frequently switch between devices or work in unconventional settings.
Clean and Clutter-Free Setup:
Say goodbye to tangled cables cluttering your workspace. Wireless keyboards eliminate the need for unsightly wires, creating a cleaner and more organized environment. This not only improves the aesthetic appeal of your workspace but also reduces the risk of accidents such as tripping over cables or inadvertently pulling devices off the desk.
Versatility:
Wireless keyboards are compatible with a wide range of devices, including desktop computers, laptops, tablets, and smartphones. This versatility allows users to easily switch between devices without having to invest in multiple keyboards or adapters. Whether you're typing up a document on your computer or responding to emails on your tablet, a wireless keyboard provides a seamless typing experience across all your devices.
Easy Setup and Installation:
Setting up a wireless keyboard is a breeze. Most modern devices feature plug-and-play functionality, meaning they can be paired with your device with just the push of a button. There's no need to fuss with drivers or software installations—simply turn on your keyboard, pair it with your device, and you're ready to start typing. A few keyboards accompany extra elements or adjustable settings. If you lost a dongle you can check how to do pairing without a dongle.
Compact and Portable:
Many wireless keyboards are designed to be slim and lightweight, making them ideal for users on the go. Whether you're a frequent traveler or simply prefer to work in different locations throughout the day, a wireless keyboard can easily slip into your bag or backpack, allowing you to take your productivity with you wherever you go.
Improved Ergonomics:
Some wireless keyboards are ergonomically designed to provide greater comfort during extended typing sessions. Features such as split key layouts, adjustable tilt angles, and wrist rests can help reduce strain and fatigue, promoting healthier typing habits in the long run.
Customization Options:
Many wireless keyboards offer customizable features such as programmable keys, backlighting, and multimedia controls, allowing users to tailor their typing experience to suit their individual preferences and workflow.
While wireless keyboards offer numerous advantages, it's important to consider potential drawbacks as well. Battery life, connectivity issues, and compatibility concerns are factors that users should be mindful of when choosing a wireless keyboard. Additionally, some users may prefer the tactile feedback and reliability of traditional mechanical keyboards.
In conclusion, wireless keyboards are an excellent choice for users seeking convenience, flexibility, and enhanced productivity in their computing experience. With their wireless connectivity, sleek design, and versatile functionality, wireless keyboards are well-suited to meet the demands of today's modern lifestyles. Whether you're a busy professional, a student on the go, or simply someone who values simplicity and ease of use, a wireless keyboard is sure to enhance your typing experience.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Ensuring Regulatory Compliance for Wireless Devices
Regulatory Framework
Regulatory compliance for wireless devices is governed by various national and international authorities. In the United States, the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) plays a pivotal role in setting and enforcing regulations related to wireless devices. The FCC establishes guidelines for electromagnetic compatibility, radio frequency emissions, and more, to prevent interference and protect consumers.
Wireless Standards

Compliance with established wireless standards is fundamental to ensuring device interoperability and safety. Two widely recognized standards organizations are the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) and the Wi-Fi Alliance. Devices must meet these standards to ensure that they can effectively connect to wireless networks and function correctly.
Radio Frequency (RF) Emissions
One of the primary concerns in wireless device compliance is the emission of radio frequency signals. Wireless devices must not emit harmful interference that can disrupt other wireless networks or devices. Manufacturers are required to conduct extensive testing to ensure their products conform to permissible RF emissions limits.
Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC)
EMC compliance is crucial to prevent electromagnetic interference between wireless devices and other electronic equipment. Compliance ensures that wireless devices can coexist harmoniously with other electronic devices, enhancing user experience and preventing conflicts.
SAR (Specific Absorption Rate)
SAR measures the amount of radio frequency energy absorbed by the human body when using a wireless device. To protect users from excessive exposure to radio waves, regulatory bodies establish maximum SAR limits. Manufacturers must test and disclose the SAR levels of their products, enabling consumers to make informed choices.
Product Labeling and Certification
Regulatory compliance often requires manufacturers to obtain certification for their wireless devices. These certifications, such as FCC, CE (for European markets), or other regional certifications, demonstrate that a product meets all relevant safety and performance standards. Labeling on the device indicates its compliance status, ANATEL Certification for Brazil allowing consumers to identify certified products easily.
Security and Privacy Compliance
As wireless devices collect and transmit sensitive data, ensuring data security and privacy is a critical aspect of regulatory compliance. Regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe and various data protection laws worldwide mandate that manufacturers take appropriate measures to safeguard user data.
Over-the-Air (OTA) Updates
OTA updates are crucial for maintaining the security and functionality of wireless devices. Manufacturers must design their devices to facilitate secure and regular updates, ensuring that vulnerabilities are promptly addressed.
User Education
Compliance isn't solely the responsibility of manufacturers and regulators; consumers play a vital role. Users should stay informed about the regulatory requirements for their wireless devices, including firmware updates and proper usage. Understanding the potential risks and best practices can enhance the overall safety and performance of these devices.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Freedom of Wireless Mice: Unleash Your Productivity
In a world where technology continually strives for convenience and efficiency, wireless mice have become indispensable tools for many individuals. Whether you're a professional, a gamer, or simply someone who values a clutter-free workspace, wireless mice offer a liberating experience. In this blog post, we'll explore the benefits, technology, and considerations surrounding wireless mice.
The Advantages of Wireless Mice
No More Tangled Wires: Perhaps the most apparent advantage of wireless mice is their freedom from tangled cables. This means you can say goodbye to the hassle of untangling cords or worrying about tripping over them. A clutter-free desk promotes a more organized and stress-free work environment.

Enhanced Mobility: Wireless mice allow you to work or play from various positions without being tethered to your computer. Whether you're giving a presentation, lounging on the couch, or using your computer for a home theater setup, wireless mice offer the freedom to control your device from a distance.

Reduced Desk Clutter: With no cords to worry about, your workspace will look cleaner and more organized. This can lead to increased productivity and a sense of calm while working or gaming.

Travel-Friendly: Wireless mice are typically smaller and lighter than their wired counterparts, making them easy to carry around in your laptop bag or backpack. This portability is especially convenient for travelers or those who frequently work on the go.

Precision and Performance: Modern wireless mice offer the same level of precision and performance as wired mice. Many wireless models feature advanced sensors and customizable settings, ensuring a seamless and responsive experience.

Wireless Mouse Technology
Radio Frequency (RF) and Bluetooth: Most wireless mice use either RF or Bluetooth technology to communicate with the computer. RF mice come with a USB receiver that plugs into your computer, while Bluetooth mice connect directly to your device without the need for a dongle. Bluetooth mice are more versatile as they can connect to multiple devices simultaneously.

Battery Life: Wireless mice are powered by batteries, which can be either disposable or rechargeable. Battery life varies among models, but many wireless mice can last several months on a single charge or a set of batteries.

Lag and Interference: In the past, wireless mice were criticized for lag and interference issues. However, modern wireless technology has largely overcome these problems, providing a seamless and responsive experience for users.

Considerations When Choosing a Wireless Mouse
Ergonomics: Choose a wireless mouse that fits comfortably in your hand. Ergonomics are crucial for long-term comfort, especially if you use the mouse extensively for work or gaming.
DPI (Dots Per Inch): Higher DPI mice offer more precise control. If you're a gamer or a graphic designer, look for a mouse with adjustable DPI settings to tailor the sensitivity to your needs.
Battery Life: Consider whether you prefer a mouse with disposable batteries or a rechargeable one. Rechargeable mice can be more cost-effective and eco-friendly in the long run.
Additional Features: Some wireless mice come with additional features like customizable buttons, RGB lighting, and extra programmable functions. Think about what features will enhance your workflow or gaming experience.
Conclusion
Wireless mice have come a long way in terms of performance, reliability, and convenience. They offer a liberating experience, freeing you from the constraints of wired peripherals. Whether you're a professional looking for a clutter-free workspace or a gamer seeking precision and flexibility, a wireless mouse might be the perfect addition to your tech arsenal. So, why not break free from the wires and unlock your full potential with a wireless mouse today?
#wireless mouse#computer accessories#computing#computers and technology#mouse#networking#reliability#ergonomics#radio#radiology#precision scales analytical/laboratory scales
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
SDR Research
Tools
GQRX - Spectrum Analyzer
RFanalyzer - Spectrum Analyzer for Android
Universal Radio Hacker - Investigate Wireless Protocols like a boss
ooktools - On-off keying is used extensively in IoT projects
fldigi - I'm not a big fan of fldigi, but its there for when you need to demodulate a common signal
Tools for more specialty purposes
Salamandra is a tool to find spy microphones
rpitx is a RF transmitter for Raspberry PI
Tactics
You don't need to learn DSP, or get your Ham license to explore radio signals. I didn't. You could even explore interesting signals such as vehicle key fobs without learning either, but learning these things will increase your understanding of signals and aid in your ability to go beyond the limitations of your tools.
Digital Signal Processing
The Scientist and Engineer's Guide to DSP was my introduction to DSP and I highly recommend it. Its free online and can be purchased in physical form.
Think DSP in Python is on my todo list. Also free online can can be purchased in physical form.
HAM Radio
Though I haven't taken the test yet. Covid was a major interruption in my plans, and I also plan to pass all 3 tests in one day. Using my personal test taking process, I would first start by reading No-Nonsense Study Guides.
Then take a pretest. Its important that you read all of the material before you take a pre-test as the goal is to retain knowledge, not just memorize a test. Most of the study should be reading/practicing the material, with few pre-tests as self assessments.
There are plenty of apps on Android (and I imagine IOS) that you can use. You need to get 74% to pass the exam, but I always shoot for 90%. If you get 90% on the pre-test, then move on to taking the actual exam.
If you didn't get 90% on the pre-test. The pre-test should be able to break down your score across various sections. Note the sections you're weakest in. From here, I would recommend switching over to the ARRL study guide as they are more detailed and only study the sections you're weakest end. When you complete all those sections, then take another pre-test and repeat until you're ready to take the exam.
Techniques
Accuracy
Radio is a science, but the tools that we can afford as hobbyists are not accurate. The three issues I face is drift, noise, and clock.
Drift occurs typically from your SDR getting hot and is a problem that grows across the session. To counter drift, you'll need to recalibrate your SDR to a Nation Weather Radio station. Find the frequency used in your area and tune to that frequency. You'll notice that you're probably a little off, this is the fault of your SDR not the National Weather Radio station. Set the offset of your SDR until your frequency of the station matches the one advertised. You'll then want to bookmark this frequency and check back to it every hour to insure that your SDR hasn't drifted.
Noise can interfere with interpreting weak signals (either distant, low powered, or both). To reduce noise and improve your signal collection, I'd suggest these guides for reducing on-site noise sources and external noise sources.
Signal Identification
Most signals are standardized or frequently used that dont require extensive analysis, but just identification.
The Signal Identification Wiki is a great place to start, and if that doesn't work, check out the sub-reddit r/signalidentification
This is an archived site that has a collection of digital signals that you could test your demodulation tools with.
Signal Analysis
Signal analysis is for those proprietary signals. As always, remember your ABC's.

Radio signals are fleeting. If you don't capture them, they may not repeat themselves. Don't worry about demodulating them at first. Capture the signals, and you can demodulate them at any time later.
Even if you're not able to record IQ data, for example you're listening to someone else's remote radio (there are a lot around the world on the internet), recording the audio which can be analyzed by tools such as fldigi.
I should add a lot more stuff here in the future.
The Signal Identification Wiki is a great place to start, and if that doesn't work, check out the sub-reddit r/signalidentification
This is an archived site that has a collection of digital signals that you could test your demodulation tools with.
Other Techniques
Using ooktools
NCC's RF testing Methodology
Wireless DoorBell Ringer and another Doorbell hack
Learn Morse Code
Project Ideas
Passive Radar with SDR
TDOA Transmitter Localization with RTL-SDRs
Other Links
No SDR, no problem! Use other people's radios with GlobalTuners.
#radio#signals#radio transmissions#sdr#ham radio#DSP#digital signal processing#signal analysis#technology
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Enhancing Innovation with RF Microelectronics and PCB Assembly in Silicon Valley
Silicon Valley stands as a global hub of technological innovation, driving advancements in various fields, including RF microelectronics and PCB assembly. At Absolute EMS, we offer cutting-edge solutions that integrate advanced manufacturing techniques to support the demands of modern industries.

The Power of RF Microelectronics in Silicon Valley
RF (Radio Frequency) microelectronics is revolutionizing industries like telecommunications, aerospace, and IoT. With a surge in wireless applications, the need for precision, reliability, and scalability in RF microelectronic design and manufacturing has grown exponentially.
Absolute EMS specializes in:
Developing RF microelectronic components that enhance signal integrity.
Customizing designs to meet unique client requirements.
Ensuring optimal performance through rigorous testing and validation processes.
Our Silicon Valley facility combines expertise with state-of-the-art equipment to provide unparalleled RF microelectronics manufacturing services.
PCB Assembly and System Integration
Printed Circuit Board (PCB) assembly is at the core of any electronic device, connecting intricate components into a functional system. Absolute EMS is a trusted partner for high-quality PCB assembly and seamless system integration.
Our services include:
Prototype Development: Rapid prototyping for quick iterations and reduced time to market.
Advanced Assembly Techniques: Including SMT (Surface Mount Technology) and Through-Hole Assembly.
System Integration: Combining hardware and software components into a cohesive product.
We adhere to stringent quality standards, ensuring your products meet industry certifications and exceed performance expectations.
Why Choose Absolute EMS?
Expertise in Silicon Valley: We leverage the innovative spirit and resources of Silicon Valley to deliver world-class solutions.
Tailored Solutions: Our team collaborates closely with clients to design and produce customized RF microelectronics and PCB assemblies.
End-to-End Capabilities: From design and prototyping to final system integration, we manage the entire manufacturing process.
Quality Assurance: Advanced inspection technologies, including 3D solder paste and optical inspection, ensure precision and reliability.
Empowering the Future
With a strong focus on innovation and customer satisfaction, Absolute EMS is committed to driving advancements in RF microelectronics and PCB assembly. Whether you're launching a next-generation IoT device or developing mission-critical aerospace systems, our expertise and dedication position us as a premier partner in Silicon Valley.
Ready to elevate your manufacturing process? Contact Absolute EMS today to discover how we can help bring your vision to life.
0 notes
Text
The Hazards of Drone Technology and Its Impact on Others
As the drone sector has experienced significant growth, certain individuals and groups worldwide have begun to utilize drones for harmful intentions. Many of us have encountered news stories detailing the misuse of drones and have questioned whether effective anti-drone technologies exist to counteract these actions. The reality is that such technologies have been available for years in military applications, yet the pressing issue remains how to implement them legally in non-combat environments without causing collateral damage.
A variety of companies focused on anti-drone technologies have reacted to reports concerning troublesome drones by marketing their offerings. They have developed an array of products, such as anti-drone rifles, shotgun ammunition designed for drone interception, trained raptors, net guns, laser systems, missile launchers, radio signal disruptors, and GPS spoofing tools. Some of these technologies can pose considerable disruptions to individuals, especially those piloting manned aircraft or vehicles that depend on GPS navigation, as well as users of wireless technologies like Wi-Fi.

How Some Anti-drone Technologies Can Endanger Others
There have been occasions where airport management did not align their evaluations and demonstrations with the Federal Aviation Administration beforehand. It is essential for federally funded airports to comprehend that the FAA has not sanctioned any airport to perform drone detection or countermeasure assessments unless they are part of the FAA’s drone detection program through the CRDA. Airports that permit these assessments risk violating their grant assurances. Additionally, the letter emphasizes that unauthorized drone detection and countermeasure implementations could result in numerous issues, such as electromagnetic and radio frequency (RF) interference, which can adversely affect flight safety and air traffic management.
Additionally, the American Radio Relay Alliance has communicated a warning to the FCC about the presence of video transmitters on the market that operate between 1010 and 1280 MHz, capable of transmitting at levels up to six times the legal limit. "The most pressing issue is the potential for these devices to interfere with the auxiliary targeting/transponder system utilized in air traffic control." It is important to note that one of the frequencies mentioned is legally available for amateur radio operations, while the others are not. This creates a scenario where individuals might acquire this equipment and use it on frequencies that are prohibited. What equipment is known to function within this frequency spectrum?
Counter-drone systems and the Fourth Amendment
The populace is entitled to security in their persons, homes, papers, and possessions against unreasonable searches and seizures. A warrant may only be granted based on probable cause, which must be established by an oath or declaration, and must clearly specify the area to be searched as well as the individuals or items to be confiscated.
Do drone jammers work?
It is correct that the use of jamming devices against drones is prohibited for all individuals, except for designated federal agencies. Drones share radio frequencies with numerous other technologies, such as Bluetooth and Wi-Fi. Therefore, the act of jamming drones could also interfere with the radio communications of others in the vicinity, rendering it highly illegal.
0 notes
Text

GSM 15dBi Yagi Antenna with RG58 Cable (L-10CM) + N (F) St. Connector
ETEILY Manufactures Yagi Antennas with good performance that comes handy, suitably working in all environment conditions.Our directional antennas are both suited for domestic as well as commercial applications.
Robust Mechanical design
High Gain
Good Signal Reception
Better Signal to Noise ratio
#Yagi–Uda antenna#Yagi antenna#Yagi beam antenna#rf antenna#RF Antennas#RF Antenna at Best Price in India#RF antenna system#radio frequency antenna#Best RF Solution Provider#RF Antenna Suppliers#Manufacturer of RF Antenna#rf antenna manufacturers in india#RF Antenna Manufacturer#RF Antenna Exporters#RF Antenna Latest Price#Wireless HF Antenna#RF Antenna Companies in India#Wholesaler of RF Antenna#RF Antenna Amplifier#RF Antenna Module#2.45 GHz Antenna Module#High Performance RF#Antennas for LoRa and Sigfox#Omni-directional SMD antennas#3.3GHz RF Antennas#RF & Microwave Antenna Manufacturers#Antenna manufacturers in Canada#RF Antenna manufacturers & suppliers - India#RF Antenna made in India#India telecom rf antenna
0 notes
Text
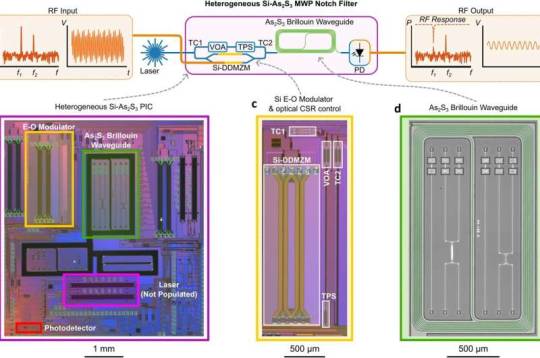
Photonic chip that 'fits together like Lego' opens door to semiconductor industry
Researchers at the University of Sydney Nano Institute have invented a compact silicon semiconductor chip that integrates electronics with photonic, or light, components. The new technology significantly expands radio-frequency (RF) bandwidth and the ability to accurately control information flowing through the unit. Expanded bandwidth means more information can flow through the chip and the inclusion of photonics allows for advanced filter controls, creating a versatile new semiconductor device. Researchers expect the chip will have applications in advanced radar, satellite systems, wireless networks and the roll-out of 6G and 7G telecommunications and also open the door to advanced sovereign manufacturing. It could also assist in the creation of high-tech value-add factories at places like Western Sydney's Aerotropolis precinct.
Read more.
11 notes
·
View notes