#Von Franz
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
“Nosferatu” (2024) and the Female Gothic Genre, Paganism and the Occult
The Gothic novel genre is deeply connected with female authors like Ann Radcliffe, Mary Shelley, Brontë sisters, Mary Robinson, and Charlotte Dacre, because it allowed them to explore themes that were “off limits” to women at the time (19th century) especially sexuality and women’s place in a patriarchal society. Hence the “Gothic female” genre was created, as a way for female authors and readers to digest their mixed feelings about these topics. This is the world Robert Eggers transports his audience in “Nosferatu” (2024).

This film checks every box of the Gothic genre: claustrophobic atmosphere, environment of fear, the threat of the supernatural, ruined buildings (usually from the Medieval ages), dreamlike states, nocturnal landscapes, demonic possession, blend of “high culture” and “low culture” (folklore), superstitious rituals, melancolia, melodrama, decay, fate, the macabre, the intrusion of the past into the present, stories of persecution, imprisonment and murder as metaphors for social conflict.
Indeed, the audience can’t analyze this story through contemporary lenses or bias, because it’s suppose to be an immersive experience into the Gothic genre and the Victorian era. The terms “gothic” and “romantic” exist in their historical context; “gothic” as in the literature genre (gothic novel), and “romantic” as in the 19th century artist movement (Romanticism).
No, this is not a story about grooming nor abuse... it can be, but not in the way many are interpreting it. Folks also need to let go of previous adaptations and their meanings, because this is Robert Eggers take on this story. And, it’s everything a remake (or retelling) should be, because its not a rehash, it’s a new interpretation of a old story, “Dracula”.
Robert Eggers tells us that the themes of sex and death are at the core of his story, it’s a “demon lover story”, and it’s Count Orlok and Ellen psychosexual connection that makes his adaptation different from the rest.
Ellen is our female gothic protagonist, and, like similar characters of the genre, she’s a persecuted heroine fleeing some a villainous outside force, personified by Count Orlok, the archetypal Death. Metaphorically, she’s a young woman haunted by her own mortality, by Death itself. She also has a sense of Doom looming over her, the heavy hand of Fate; can we outrun our destiny? “Providence!” Herr Knock screams throughout the film; as in a supernatural force, commonly God, guiding humanity destiny.

Ellen is no typical young woman, though. As she tells Von Franz, she had occult powers since childhood, being able to perceive glimpses of the future and suffering premonitions (knowing the contents of her Christmas gifts and when her mother would die). Her father called her “his little changeling girl”, as in the European folklore of human children kidnapped by supernatural creatures (fairies, demons, etc.) and a substitute being left in their place. Herr Knock also compares Ellen with a “sylph”, when he informs Thomas he’s to travel to Transylvania. “Sylphs” are air spirits from 16th century Germanic folklore and alchemy, a sort of nymph connected to air element in hermetic literature; throughout the centuries they have been culturally associated with fairies, too. We have two characters in the story connecting Ellen with a fairy-like creature. Interestingly enough we, the audience, see her floating in the opening scene.

“You are not for the living. You are not for human kind”, Orlok tells her, and calls her “enchantress”. Von Franz also said Ellen could have been a priestess of Isis had she been born in pagan times. Isis is one of the major Egyptian deities, considered the goddess of magic and healing. She was also connected with the Dead and funeral rites, since she was the sister-wife of Osiris, ruler of the Underworld. Pagan priestesses also entered trancelike states as Ellen “hysterical seizures” or “epilepsies” when communicating with the spiritual world, which is what Von Franz, the occult and alchemist student, recognizes in her. Ellen is a supernatural force, too.
Eggers Orlok was a sorcerer in life, a practitioner of Black Magic. He was one of the Solomonari, wizards from Romanian folklore, believed to be students of the Devil, who learned to ride dragons, and control beasts and the weather. In Eastern European tradition, the Solomonari were believed to be recruited among common folk and disguise themselves as beggars, Orlok is a Romanian nobleman who sought to achieve immortality, to conquer Death. As the abbess tells Thomas, the Devil preserved Orlok’s soul that his corpse may walk again in blasphemy, as a vampire feeding off the blood of the living and spreading plague.

However: who was it who awoke Orlok in “Nosferatu”? The Devil or Ellen?
At the prologue, we see Ellen crying and begging for companionship. She prays for a guardian angel, a spirit of comfort, a spirit of any celestial sphere, anything, to hear her call and come to her. She’s summoning some occult force and inviting it into her life. Orlok answers her call. And why is she doing this? She feels lonely, isolated and misunderstood by those around her. As she tells Von Franz, she’s no longer her father’s “little girl” and he recoils from her touch, because she’s no longer a child. As she grows older and enters womanhood, she starts to feel ostracized and put aside by 19th century society who has rigid gender expectations of her.

According to Orlok, it was Ellen who awoke him: “O’er centuries, a loathsome beast I lay within the darkest pit… ‘til you did wake me, enchantress, and stirred me from my grave. You are my affliction.” Which Ellen later confirms to Thomas: “I have brought this evil upon us” because she sought companionship and tenderness. This is a belief Von Franz also shares: it’s Ellen who “wills it”, and she’s the one who unleashed this plague upon the world.

This is very fitting with the Gothic female novel, where the supernatural connects with female societal status of this time period, generally women’s discontent with patriarchal society, difficult and unsatisfying maternal position (in “Nosferatu” we see this with Anne’s character, where she equals being pregnant with being drained of her life force) and their role within society (fear of entrapment in the domestic sphere, their bodies, marriage, childbirth, etc.).
Eggers’ Orlok is a combination of several Romanian folklore creatures, associated with vampirism: strigoi, moroi (these two are the “classic” vampires) and zburător (a ghost-like creature, usually handsome, and only visible to young women, attacks at night, usually newly-wed ladies and does “indecent” things with them). The influence of this legend in Ellen and Orlok story is evident.
Ellen tries to summon a spiritual companion in her teenage years, most likely when she reached puberty and her sexuality was starting to awake. A demon who’s a personification of appetite, devourance, sex and death is the one who answers her calling. They end up in a sexual spiritual connection, as Ellen experiences her sexual awakening with him, as shown in the prologue and later confirmed how Orlok took her as his lover. She also reveals to Thomas it was “sweet” and she “had never known such bliss” at first, until it turned into torture (seizures and nightmares), when her father found her laying unclothed and called her a sinner and it’s implied she might have been institutionalized, as she tells Von Franz. This episode might be a metaphor for masturbation and the historical shame associated with it. Hence her connection with Orlok being her “melancholy” (depression) and her “shame”, symbolic for the sexual urges 19th century society forced women to repress.
Count Orlok is the archetypal Death; which culminates with the “Death and the Maiden” motif at the end. This was a very popular Art History archetype around the so-called “Plague years” (14th to 16th century) in Europe, and it’s often connected with other motifs like “Danse Macabre” and “Memento Mori”. It has several meanings depending on the author intent, usually a reminder of our mortality, but also a meditation on sex and death, as in the French “la petite mort” (“little death”), the post-orgasm sensation, sexual release potentially causing temporary loss of consciousness (fainting) or dizziness. In the Medieval Ages, physicians believed orgasms could lead to death because they drained the “life force” from the body. This was when the term “petite mort” was created, and this belief persisted into the Renaissance and beyond. In “Nosferatu” this probably translates in the sexual pleasure that Orlok imprints on his victims as he drains their life force.
Ellen’s “hysterical seizures” miraculously stop once she meets and marries Thomas Hutter, our tragic romantic hero. This can also be a nod to Gothic Bildungsroman (“coming of age”) genre; where the female protagonists grow from adolescence to adulthood in the face of the impossibility of the supernatural, and come to the conclusion there’s a rational explanation. In Ellen’s case, it’s medical, as she’s diagnosed as a melancholic somnambulist hysteric (in another words, a depressive hyper-sexual sleepwalker).
At the beginning of the story, Ellen and Thomas are newly-weds fresh out of their honeymoon, which means sex (historically necessary to consummate marriages). With Thomas, Ellen is “free of her shame”, as she says so herself. Because, her sexuality is safely contained within marriage, as it’s socially acceptable. But Thomas dismisses her concerns about his well-being, and doesn’t believe her until he experiences the supernatural first-hand, having an homoerotic encounter with Orlok himself, which also causes him great shame. This is probably a Easter egg for Bram Stoker possible closet homosexuality and “Dracula” being a metaphor for that.

Thomas’ main concern, throughout the story, is to fit into the patriarchal ideal of his genre, as a provider for his wife, and he aspires to be like his long-time friend, Friedrich Harding, the “perfect patriarch” with the perfect religious and dutiful wife, Anna, and their precious children. The Hardings are the perfect Victorian family; they are everything society expects them to be. Friedrich even chastises Ellen for her nature, and it’s clear he resents her for what she represents: “otherness” and “deviance” to societal norms.

However, soon enough, Ellen’s seizures return, symbolizing Thomas cannot sexually satisfy her. She’s “too ardent” as Harding calls her. “More! More!” She begs Thomas when they have sex to scorn Orlok. Not only her sexuality is too strong, but Thomas also shares with Friedrich his desire to wait to have children with Ellen because he wants to gain financial stability first. This in a time period when contraceptives weren’t widely spread, meaning abstinence.
Symbolically, Ellen’s seizures can also be connected with her fear of childbirth. Her “epilepsies” return while she’s staying in the Harding household, where they are children and Anna is pregnant. Children is what is expected of Ellen next, after all. But it’s sexual pleasure that Ellen seeks, and this causes her great shame and torment, because 19th century women weren’t suppose to known “such things”. “Sin! Sin! Sin!” as Ellen’s father screamed at her when he found her naked.

Fear of entrapment represented as Ellen tries to rip off her corset and “free herself”: this happens during one of her Orlok induced seizures.
As Robert Eggers tells us, Orlok both disgusts and attracts Ellen, she loves and hates him at the same time. He’s repulsive, rotten, animalistic and lustful, both literally and metaphorically. His character design is meant to invoke contradictory feelings in the audience: overall he’s foul and monstrous, but he appears almost handsome in some shots. This is intentional. Not only he’s a personification of Death, but of Ellen’s repressed sexuality by 19th century society. He represents the monstrous and dangerous female sexuality the Victorian era sought to contain. He’s the transgression and taboo theme in this Gothic story, as well: necrophilia. Which is probably Eggers “gotcha” moment to “vampire lovers” everywhere, as he forces his audience to confront their own bias.

Ellen herself is a medicalized character, as we see her being institutionalized, drugged, bound to her bed, forced to wear a corset to bed, and used as a scientific experiment by physicians. She’s not in control of her own body, and has little agency over it, overall. We see her being contained, literally and metaphorically, too. This is probably meant to symbolize women as a whole in 19th century Western European societies. The “disability of being female” is one major theme in Gothic female novels, after all.

And if Ellen unleashed Orlok unto the world and he’s connected with her what does this mean for this story? The obvious interpretation of the ending it’s Ellen sacrificing herself to save Wisburg from Nosferatu’s curse, like every other adaptation. But this appears to be somewhat disconnected from the overall themes of this particular retelling. Here, it’s Ellen who unleashed the curse, and only her can put an end to it.
We see Ellen summoning Orlok in two occasions: at the beginning and at the end of this tale. At first, she did it unconsciously, she dabbled with the occult and wasn’t aware of what she was inviting into her life. However, does this indicate Ellen has some degree of control over him? Orlok himself says she’s “his affliction”, and they are bound to one another. She’s not only a seer, she’s compared with a priestess of a Goddess associated with funeral rites and with the ability of resurrection and looking after the Dead (Isis). We can almost interpret her as a necromancer.
Here, we can have a different interpretation of Orlok unleashing a plague upon the society who ostracizes Ellen for her nature. Symbolically, he’s her reckoning, her vengeance upon society norms and expectations of gender. He’s the “plague carrier” and brings a “blood plague” transmitted by rats (symbolic of the Black Plague; the medieval ages terrorizing the modern world of science and rationality) upon Wisburg, and the “good Christians” who contain and shame “Pagan” Ellen.

Orlok’s most notorious victims are the Hardings, the perfect patriarchal Christian family model Ellen can never fit into; the patriarch Friedrich, the pregnant Anna and the two children. This also fits the Gothic female genre of the supernatural menace as a metaphor for women’s status in 19th century society. Ellen doesn’t want to be married to a patriarch like Friedrich, she doesn’t express any desire to become pregnant nor have children of her own. Consequently, we see Orlok killing all of these archetypes in the narrative.
Interestingly enough he spares Thomas and saves him for last when he should be his first victim once he arrives at Wisburg, because he’s the husband. However, Thomas is a character Ellen loves and cherishes, as he somewhat accepts her nature and represents her chance at a “normal life”. He’s also determined to save her from Death/Orlok, but is unable to. Symbolically, Ellen chooses death over conforming to gender norms and expectations.

However, we can’t forget Ellen’s supernatural nature, nor her connection with Orlok. She weds Death at the end, she’s no longer terrified of him, and she fulfills their covenant, and her dream premonition of marrying Death: “standing before me, all in black… was… Death. But I was so happy, so very happy. We exchanged vows, we embraced, and when we turned round, everyone was dead. Father… and… everyone. The stench of their bodies was horrible. And - But I never been so happy as that moment… as I held hands with Death.”
A “covenant” is a pact, both a religious and a occultist practice. This is a “blood covenant”, as their flesh becomes one and he drinks from her. “Blood is the life” is a quotation from the Bible, where “blood covenants” are also mentioned, because a “blood covenant” has the power to either destroy or redeem. For instance, Christ’s sacrifice redeemed humanity according to Christians. “Redemption” as Von Franz says, because only Ellen, like Christ, can redeem the habitants of Wisburg. He uses the expression “with Jove’s holy light” before dawn redemption will come to them: “Jove” is Jupiter, the “King of the skies”, and its energy neutralizes Saturn’s, connected with “melancholy” (depression).

However, that’s not what’s happening here, because Orlok is a servant of the Devil, and a literally un-dead “warlock”. So, what is Ellen pledging herself to here, exactly? Her covenant with Orlok has nothing to do with God or Jupiter, for these are forces of good, when Orlok is a force of evil and darkness.
Ellen also fulfills her role as “priestess of Isis” at the end, as she guides the un-dead Orlok to his physical death; like Isis, she resurrected him, and is now taking him into the Underworld with her. Because, like Orlok also told her, she’s “not for the living”, that’s her fate, the destiny she accepts at the end; she’s meant for Death, as Isis for Osiris.
“Our covenant is fulfilled. Your oath re-pledged.” Orlok tells her. But what was Ellen’s oath? We have to look into the prologue scene “You shall be one with me ever-eternally. Do you swear it?” And in the ending “As our spirits are one, so shall be our flesh. You are mine.” They fulfill their pact both in the physical and the spiritual worlds, and both make the ultimate blood sacrifice, by physically dying for “self-renunciation” is essential for blood covenants.
And a deity is always summoned to bless such a pact… but who was blessing this one? Ellen and Orlok indeed, died in the physical world, but are joined in the spiritual world forever, as decreed by their covenant, so where did their spirits go?

They are also surrounded by lilacs, their signature flower throughout the narrative, which symbolizes first love, yes, but also renewal and rebirth. Orlok conquered Death and immortality once before, because the Devil kept his soul. Now that Ellen is joined with him in spirit, what does this mean for her, and for them both?
#nosferatu 2024#Ellen Hutter 2024#friedrich harding#anna harding#Thomas Hutter 2024#Count Orlok 2024#von franz#lily rose depp#bill skargard#bill skarsgård#nicholas hoult#emma corrin#aaron taylor johnson#willem dafoe#ellen x orlok#orlok x ellen#robert eggers
702 notes
·
View notes
Text











Nosferatu (2024) dir. Robert Eggers
#nosferatu#nosferatu 2024#nosferatuedit#Bill Skarsgård#Count Orlok#Nicholas Hoult#Thomas Hutter#Prof. Albin Eberhart von Franz#von Franz#Willem Dafoe#Dracula#y#gif#mine
387 notes
·
View notes
Text
Ellen was on suicide watch and in the meantime Von Franz was like “indeed you are not of this cruel confusing world my redeeming angel ♥️ go be with death.”
meanwhile Van Helsing gets 4 heart attacks every single time Mina's sacrificial lamb complex flares up
375 notes
·
View notes
Text

Yeah….I loved this movie.
#nosferatu#nosferatu edit#nosferatu 2024#nosferatu film#nosferatu movie#robert eggers#vampire#vampires#text post meme#meme#memes#von franz#von franz nosferatu#albin eberhart von franz#willem dafoe#bill skarsgård#count orlok#ellen hutter#lily rose depp#horror#movies#nosferatu the vampyre#lol#funny#humor#meme humor#lol memes#vampyr#vampyre#macabre
198 notes
·
View notes
Text

#nosferatu#nosferatu 2024#nosferatu movie#willam dafoe#von franz#count orlok#ellen hutter#thomas hutter#horror#horror film#classic#cinema#twitter#tweet#fake tweets#shake my ass#best life#fuck you#fancy af#fire#burning building#maniac#maniacal laughter
160 notes
·
View notes
Text



Willem Dafoe as Von Franz in Robert Egger's Nosferatu (2024)
#willem dafoe#von franz#robert eggers#nosferatu#movies#cinema#films#demons#animal self#occult#spirituality#mysticism#shadow work#shadow#u
146 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Violence of Conformity: on Queerness, Shame, and Vampirism
As we all know, and as I feel I must express again - the metaphorical layers of Nosferatu (2024) consist of several complex, frequently intersecting social themes. Some of them, admittedly, exist a story or two below the surface-level discussions; but that makes them no less influential in regards to the primary plot, and they demand the viewer's exploration just the same.
This is especially true in regards to Eggers' approach to homoeroticism. Its presence within the film itself is unsurprising - implicit, or even explicit, expressions of queerness are a hallmark of gothic (and especially vampire) media. In the case of Nosferatu, this narrative vein provides an undercurrent to almost every aspect of the story; and, because I can't stop thinking about it, I'm making it everyone else's problem.
The Hutters are queer, biting is a metaphor, details under the cut.
To begin with, I must clarify that a queer reading of Nosferatu is not an external introduction. While that lens may be applied to any narrative, given a thorough enough discussion of gender roles, sexuality, and cultural context, it has always been a natural - if sometimes unspoken - component of gothic horror. Elements of it are observable in classics like Frankenstein (Shelley), The Picture of Dorian Gray (Wilde), and even detective fiction offshoots like The Hound of Baskervilles (Doyle), etc; and within the vampire subgenre, it is practically a requirement.
That, like many other things, may be ascribed to Lord Byron and his ever-enduring cultural legacy. In the year 1819, at the Villa Diodati in Switzerland, he challenged his illustrious group of friends to each write a ghost story; and while only two achieved any sort of prominence, that much was sufficient to alter the history of the horror genre. One of these was Mary Shelley's Frankenstein; the other was The Vampyre by Dr. Polidori.* As the title suggests, it was the first Western work of fiction that featured such a monster - and, in doing so, it set the blueprint for countless others to follow. Since then, the genre has been defined by the shape of the dark, hedonistic, and dangerous Lord Ruthven, who was unmistakably modelled after Byron himself.


As a character, Ruthven is confident, dominant, manipulative - and brooding, on occasion. His interpersonal approach is defined by a sort of hypnotizing, seductive, possessive, most certainly ill-advised allure. The overall impression is devilish; and that is indeed the point. Within the thematic framework of The Vampyre, Ruthven represents temptation of all kinds. He never hesitates to indulge himself; and so, once he is bored with cards and brothels, he has no qualms about fixating his appetites on Polidori's main character, Aubrey.
Their relationship is notably homoerotic. Despite - or, perhaps, even complemented by - Polidori's amateurish style, the text demonstrates a genuine, striking sensuality between them. In 1819, this easily fell in line with the rest of Lord Ruthven's characterization; and, following The Vampyre's a rapid rise to popularity, vampirism became a shorthand for any "sinful" - or, socially forbidden - sexual expression.
Given the numerous restrictions of the time, most of which persist today to a degree, this includes not merely abusive or incestuous, but also queer, interracial, and extramarital relations - as well as anything involving kink dynamics. From Ruthven, we get Carmilla (LeFanu), Dracula (Stoker + adaptations), and even relatively recent installments like Lestat (Rice).**


The premise of Nosferatu is no exception. One of the most famous cases of copyright infringement, and a triumphant testament to the historical/preservationist value of media piracy, Murnau's 1922 silent film survives - against explicit orders of the Stoker estate; and, being the literary bastard child of Dracula himself, Orlok maintains many of the same characteristics as his predecessor.
Among these is his implicit and classically vampiric queerness. Like the rest of the film, it is amplified in 2024 - and especially prominent in the first act, in which Thomas Hutter arrives to Orlok's castle.

It is evident from his earlier characterization that Thomas is a repressive type. More so than Aubrey or Jonathan Harker, he keeps his head down, obstinately ignoring the web of fears that shape his daily existence; and it is a monster's narrative duty to expose and realize every single one.
Granted, social circumstances do play a role in this situation. Aubrey has wealth and status; Jonathan Harker has friends and a stable, loving marriage; and Thomas Hutter has neither of those things. Without the benefit of money or community, he lives within a world that is almost as restrictive as Ellen's. His personality is defined by his similarly desperate desire for respect; and his behaviour throughout the film is informed by that underlying pattern. It manifests, most prominently, as a near-compulsive, yet formulaic, adherence to social expectations. He chases after a promotion, marries, gives his wife flowers she didn't want - and, in the same breath, dismisses her "childish fantasies", not out of any malicious intent, but simply because it is supposed to be his duty as a man and husband. It is a destructive cycle of indignity and overcompensation - and I believe it is essential to acknowledge that it's motivated, in great part, by his financial insecurity. As a self-described "pauper," Thomas is anxious to prove himself to his ruthless, unforgiving society - because if he does not, he runs a very real risk of losing even the few comforts he has managed to scrape together.
This threat of destitution is an act of violence. Implicitly, constantly, in consequence of daring to exist, Thomas is being held hostage - unless he conforms.
His sojourn at Orlok's castle is, therefore, peppered with evidence of his superstitions, his social class, and his weakness. Orlok - whom he eventually finds slumbering in the dungeon, the symbolic core of the building itself - is its culmination. What Thomas sees after opening the casket is a nude man, always and never dead, who is trying to take away his wife and imprison him, like a damsel, in a castle. He is horrified; and the implication is blatant. In context with everything else, the deeply sensual, lingering brutality of Orlok's attack is symbolic of the one last thing that Thomas is repressing - and has been for so long that facing it is unthinkable. Still, he can do nothing to resist Orlok - who pushes him to annul his heterosexual marriage, subdues him, bites him; and drinks from him, night after night.

Even during daylight, Thomas fails to destroy his tormentor. In the story sense, he cannot do it because Orlok is a vampire; on the symbolic level, we understand that he cannot kill his own nature.
It goes without saying that this experience is violent; it is both grotesque and shockingly, blatantly lewd. It is traumatic. It is euphoric. It is a form of sexual assault, as far as the biting - a naturally penetrative act - is concerned; and, crucially, it is also Thomas' own repressed desire forcing him to know it. His fear and self-disgust are made flesh in Orlok. Unwanted Desire versus Unwanted Advances; it is a classic gothic paradox - and, in the end, he is unable to accept it. He flees, back to Ellen and the familiar comfort of repression.
Curiously, Ellen herself - who is also distinctly queercoded - presents a depiction of an alternate path.
Like Thomas, she begins the film rigidly repressed and doing her utmost to conform to the established heterosexual social standards. The most prominent factors behind Ellen's oppression are ableism and misogyny - both rooted in things she cannot possibly hide. Her seizures are extremely noticeable to say the least, her neurodivergence affects every conversation she has with the people around her, and all of them perceive her as a woman first and a person never. As the film goes on, it becomes increasingly clear that this emulation of a happy marriage requires constant and agonizing effort to sustain; but while she is also blatantly queercoded, and this queerness definitely contributes to the way she is treated (e.g. by Harding, who views her as a threat to his own marriage), her struggle in maintaining her union with Thomas is not necessarily rooted in a lack of sexual attraction.
The issue is, rather, its "inappropriate" manifestation. Ellen is sexually dominant. Her desires are carnal (and, as the original script implies, mildly sadistic). In a society that expects women to be both innocent and submissive, limits their financial opportunities, and threatens the nonconforming with institutionalization or abandonment, she is caged.
Unlike Thomas, she is aware of that and resents it accordingly - which is not to say that she doesn't feel overwhelming guilt in regards to her sexual inclinations. She absolutely does; and it is interesting to note here that her own pain, in this case, manifests as attacks on her husband and Anna.

This is the part of the story that actively deals with Ellen's queerness. It is evident that she has lived her entire life with the idea that such feelings themselves are sinful; her desires are already unacceptable, even within the sanctity of a heterosexual marriage - thus, actively pursuing another woman would be monstrous. In this interaction, however subtle or unspoken (and, on Anna's part, likely unrecognized), Ellen perceives herself as an aggressor. This is the reason her friend is attacked directly after they share a private, tender moment together - true to the classic gothic vampire tradition, Orlok is, consistently, the direct manifestation of Ellen's shame. He drinks from Anna's breast (the characteristic bite notably favoured by Carmilla - the original lesbian vampire); he destroys the Hardings' perfect nuclear family; and Friedrich Harding blames Ellen and her "fairy ways." Symbolically, their suffering is her punishment - both for feeling a brief moment of queer affection (guilt, fear - direct, setting-driven), and for refusing to indulge it (self-acceptance, rebellion - metaphorical, represented by Orlok).
Still, despite her fear and guilt, Ellen knows that she has done nothing wrong by following her "nature." Her queerness is inherent to her - much like her disability, or her psychic gift; and it is no accident that, among the human characters, the latter is only truly identified by the remarkably eccentric, disgraced, flamboyant, cat-loving, unmarried, bohemian Von Franz. Even though he might be better-adjusted to their surrounding society than her, he still decidedly exists on its outskirts. There is a familiarity of recognition between them, as well as the particular dynamic of a fresh and uncertain fear vs a resigned bitterness that alludes to an interaction between two different queer generations. Even as he is unable to promise her a happy ending, he confirms that she was meant for greater things than the world around them would allow; and that, in my opinion, marks a turning point.
Prior to her conversation with Von Franz, the only validation Ellen has ever received was from Orlok - which posed a moral complication. He was and is a monster, and as such, she believed him to be, fundamentally, a "deceiver." Because of this, she could not bring herself to entirely accept what he was saying; but, conveniently, Von Franz provides an alternate opinion. He stresses that her gift is not only powerful, natural, and inevitable, but also inherently beautiful and sacred.
This is a drastic shift from the way Ellen is normally perceived by humanity. The story consistently demonstrates that the other characters dismiss, infantilize, or condemn her out of turn; however, in this new philosophical context, her night of passion with Orlok - or, the city's only hope for salvation - becomes a supremely important, adult, and holy act. In a spiritual sense, it is equivalent to a marriage; and the film frames it as such.

Like a father, Von Franz gives her away. Despite his well-established monstrosity, Orlok is tender with her to the point of reverence; and she pulls him close - as unnecessary or selfish as that may be. It is, after all, a metaphor. By embracing the Vampire, Ellen embraces the physical representation of everything she had once considered ugly in herself. In regards to her queerness (as well as her psychic power/neurodivergence/disability/personhood), it is a triumphant moment of self-acceptance.
Ellen's arc therefore ends in sublimation. Meanwhile, Thomas is left behind; over the course of the film, he has been unable to let go of the structures that have directed his thinking and behaviour throughout his life - and yet, at the same time, he has also seen them fail, over and over. Knock betrays him, Sievers is out of his depth; Thomas himself cannot be a hero, and Harding - his glittering ideal - crumbles, consumed by grief and madness. The finale, therefore, leaves him on a precipice.


It is a classic moment of deliberation - epitomized, perhaps, by The Matrix (Wachowski Sisters, 1999), in its iconic "red pill/blue pill" scene. As much as the interpretation of it has been twisted over the years, the fundamental, intentional meaning of it is inherently queer; it is about weighing the danger and value of awareness against the meaningless bliss of ignorance. These narrative points are most frequently framed as a beginning - but for Thomas, that is how the movie ends.
He could return to the prison of his daily existence, repress everything he truly feels once more, and suffocate himself in a stranger's life. Before him, Ellen and Orlok depart into a "sea of fog" - an unknown, terrifying, beautiful alternative. It is a promise of freedom and a guarantee of struggle. He sees an example of what he could become, in them and in Von Franz. Their society - and ours, to a degree - is unforgiving of deviation, yes, but the story has also forced him to recognize that acquiescence is not the only option; nor is it actually enough to protect him or his loved ones. Within an oppressive society, safety is always subject to an implicit transaction; and as the finale of Nosferatu makes painfully clear - Orlok may have been in covenant with the Devil, but Harding is the one who sold his soul. The question, now, is whether or not Thomas can bring himself to ignore that.
I know what I would personally wish for him - a full and vibrant life, somewhere on the edges of polite society, that allows him to delve into the eccentricities he never knew he had. He could get into the occult himself; maybe even meet a dashing vampire hunter who would sweep him off his feet and shock his lingering sensibilities every morning (and if the man's a cowboy, even better). However, the point is that we do not know what he will do or what will happen. A life is always in flux. Regardless of our circumstances, there are still a few things we get to choose for ourselves, and a precipice is also sometimes an opportunity for a leap of faith.
I hope, most affectionately, that Thomas Hutter jumps off a cliff.
*POLIDORI - Dr. John William Polidori, who may indeed be considered the creator of the modern vampire genre, graduated from Ampleforth College in 1815 with a thesis on sleepwalking. It's not exactly relevant; but, in the context of Nosferatu, rather apt. I would've really liked to see his thoughts on it, seeing as it's such a perfect intersection.
**LESTAT - being blond, Lestat does stand out from the primary archetype in the visual sense; but the current discussion is more in the realm of personality.
#`nosferatu#nosferatu 2024#nosferatu (2024)#thomas hutter#ellen hutter#count orlok#friedrich harding#anna harding#von franz#willem dafoe#lily rose depp#nicholas hoult#bill skarsgård#vampires#vampirism#dracula#carmilla#gothic horror#horror film#horror film analysis#nosferatu meta#queercoding#literature#film#queer fiction#queer lens#vampire#gothic romance#emma corrin#aaron taylor johnson
126 notes
·
View notes
Note
Jonathan harker voice: me and my friends wouldve staked that old cadaverous bastard i can tell you that
Honestly, it just makes me want a scene where Old Man Thomas Hutter comes across the Drac Attack Pack. Still with Von Franz' 'sHe HaS tO dIe To ReDeEm Us!' speech in his head decades later. Somehow he catches wind of the Dracula situation.
And Van Helsing and the Suitors' sworn euthanasia pact.
And Mina counting down the nights until she has to die over her being attacked.
And Jonathan sharpening his knife, prepared to kill the Count and/or anyone else who dares to get within harming distance of his wife.
Deja vu hits.
For reasons Jonathan cannot understand but does not question, a sullen old man passes a parcel into his hands.
"Do not deplete your cache of arms with parsing them out too thin. I am old. Your love, she will make more use of it now. On whoever she need use it on."
Jonathan unwraps the gun and its ammunition. Stunningly, it is already a sacred thing, the bullets and weapon long since blessed.
Much later, after the adventure is over, Van Helsing will bring up a strange encounter with a man far older than himself. A German of so much grim gravity.
"He asks of me, 'Do you know of a man called Von Franz?' I tell him yes, the name is most familiar. A sadly shunned man of scientific and occult learning. I studied his old papers.' The old man, he nods. 'I thought as much,' he says. Then he leans upon his cane until he is low enough to meet my eye. 'If you return from the mountains and that girl does not, I shall introduce you to him myself.'"
Jonathan feigns shock well enough. And saves a grim and private smile for himself later.
#I love this show*#*my imaginary crossovers#jonathan harker#dracula#thomas hutter#nosferatu#nosferatu 2024#abraham van helsing#von franz
123 notes
·
View notes
Text
guys
I know this is the monsterfucker website
but please
I need you to look me in the eyes and tell me that Nosferatu wasn't a tale of sexual liberation
I need you to tell me that we watched the same movie about sexual abuse, victim blaming, grooming and self-blame
please
#please for the love of god#theres so many horrendous takes ive seen elsewhere its making me lose it#nosferatu#orlok#robert eggers#nosferatu 2024#eggers#ellen hutter#count orlok#thomas hutter#wilhelm sievers#sievers#von franz#professor albin eberhart von franz#professor von franz#albin eberhart von franz
71 notes
·
View notes
Text








Nosferatu (2024)
#nosferatu#nosferatu 2024#ellen hutter#lily rose depp#thomas hutter#nicholas hoult#von franz#willem dafoe#count orlok#bill skarsgård
95 notes
·
View notes
Text
thomas this, count orlok that, the ACTUAL hottest man in the film is professor von franz
#nosferatu#nosferatu 2024#robert eggers#film#von franz#willem dafoe#nicolas hoult#bill skarsgård#count orlok#thomas hutter#ivy.txt
84 notes
·
View notes
Text
"Priestess of Isis", "Enchantress" and "Sylph": Occult References in Ellen Hutter’s character in “Nosferatu” (2024)
In another post I analyzed Ellen Hutter’s character in the 2024 adaptation of “Nosferatu” through literary lenses of the Gothic female genre. Now, I want to dwell on her occult and mystical symbolism, and how this translates in her connection with Count Orlok, the undead demon of the story, who’s bound to her. But how and why? And what exactly is she in this story?
“In heathen times you might have been a great priestess of Isis.”
Von Franz tells this to Ellen in their last scene together, because he recognizes her spiritual power and ability to communicate with the spiritual world. Her “hysterical fits” and “epilepsies” also mirror the trance-like states of Pagan priestesses. She inhabits the “borderland”, a peripheral area, a portal between the two worlds: the physical (matter) and the spiritual.

“The pupil is expanded. It does not contract naturally to the light. […] A second sight. She’s no longer here. […] She communes now with another realm.”

“Somnambulists afflicted with these perversions [hysterics and lunatics] oft possess a gift: a sight into the borderland. […] I believe she has always been highly conductive to cosmic forces, uniquely so.”
Von Franz says demons usually obsess over “those whose lower animal functions dominate”, because they like them and seek them out. He elaborates: hysterics and lunatics. However, he says this before he actually gets to know Ellen, and he quickly realizes that’s not the case here. Because Ellen is the one who awoke Orlok from his centuries old sleep. Which is confirmed by three characters in the narrative: Orlok, Ellen herself and Von Franz.
O’er centuries, a loathsome beast I lay within the darkest pit… ‘til you did wake me, enchantress, and stirred me from my grave. You are my affliction.

Which leads me to the next topic:
Why Isis, of all deities?
Isis and Osiris
Isis is one of the major Egyptian deities. She’s more commonly known for her role as “Mother Goddess” of Horus, the Sun god. Isis had mighty magical powers, greater than that of all other gods, she governed the natural world, healing and wield power over Fate itself.
“Destiny!” Ellen cries out to Anna, while looking at the sea. “Providence!” Herr Knock screams throughout the narrative. “You run in vain! You cannot out-run your destiny!” Von Franz laughs in religious fervor as Thomas tries to save Ellen.
Isis is also connected with the themes of death, sex and rebirth in Egyptian cosmology, due to the myth of Isis and Osiris; which are also the core themes of Robert Eggers’ adaptation of “Dracula/Nosferatu”, so it’s not coincidental.
The “Osiris Myth” is one of the major surviving pieces of Egyptian mythology. It’s a ancient tale, with its early versions dating back to the 5th Dynasty (c. 24th century B.C.). It has known several adaptations throughout Egyptian history. The most complete version is in “The Moralia” by the 1st-century scholar Plutarch of Chaeronea, a collection of essays about Greco-Roman culture; that became very popular during the Renaissance era (14-16th centuries) and the Enlightenment period (18th century) in Europe.
Isis and Osiris were brothers, and according to Ancient Egyptian religion, they were in love with one another before they were born, and enjoyed each other in the dark before they came into the world. They eventually married.
Osiris had two facets as a God: in life, he was the God of fertility, agriculture, and vegetation, being considered a “Shepherd God”; in death, he was the God of the Underworld, the judge and Lord of Dead, the afterlife and resurrection. The pharaohs of Ancient Egypt were associated with Osiris in death, because as he rose from the dead, so would they unite with him and gain eternal life through imitative magic. Which appears to be the whole deal between Orlok and Herr Knock in “Nosferatu”, as Knock seeks to gain immortality like Orlok, by serving him.
On Earth, Osiris was believed to take on the form of a bull (the sacred bull Apis). What I find interesting here is that in both the 2016 script and the 2023 script of “Nosferatu”, Orlok’s physicality is actually compared to a bull:


Osiris became king of Egypt, and taught the people how to farm and live peacefully in their villages; he had a reputation for being a powerful and wise king, loved and respected by the Egyptian people. We don’t know exactly how Eggers’ Orlok was in life, other than him being a Romanian or Hungarian nobleman and a Solomonar sorcerer who sought to achieve immortality. But if we go by Vlad III (Drakule or Dracula, the infamous “Vlad the Impaler”) biography, he’s actually considered a Romanian national hero because he defended the Romanian people from foreigner invaders (Germanics and Turks, mostly). Just throwing this out there, because it’s unsure if this is intentional or not.
Osiris and Isis had a brother, Seth (or Typhon in Plutarch essays), the God of deserts, storms, disorder and violence, who murdered Osiris to take his throne. He tricked Osiris into climbing into a wooden chest/coffin, shut the lid, sealed it shut, and threw it down the Nile River, knowing Osiris would never be able to survive. In some versions, it’s said Seth cut Osiris body into pieces and scattered them throughout Egypt. Interestingly enough, there’s a similar legend associated with Vlad the Impaler, who died in battle against the Ottomans, and, according to Leonardo Botta, the Milanese ambassador in Buda(pest), Vlad’s enemies cut his corpse into pieces, too. and his remains were never found.


Isis is the epitome of the mourning widow in this myth, as she mourns Osiris’ death deeply. Here enters the symbolism of the lilacs in "Nosferatu", the symbolic flowers of Ellen and Orlok: in the Victorian era, they were associated with widows because they represented a memento of a deceased lover.
Can this also be a nod to “Bram Stoker’s Dracula” (1992) by Francis Ford Coppola? Where Dracula himself is the grieving widower because Elisabeta commits suicide? In the 1992 adaptation, Mina also speaks of “flowers of such frailty and beauty as to be found nowhere else”. What flowers is Mina talking about? It’s unclear, but Lilacs are native flowers to the Balkans, after all.
Isis sought for Osiris’ mangled body and with help of tree other Gods (Nepthys, Thoth and Anubis), they sew Osiris’ body back together, and then wrapped it head to toe in strips of linen, creating a mummy. Interestingly enough, Orlok’s corpse appears almost mummified at the end of the story.

In the Osiris myth, Isis uses powerful magic (incantations and magic spells) to bring her dead lover back to life; similar to Ellen who resurrects Orlok with her summoning prayer. In one version, this happened on a night of the full moon; in “Nosferatu” (2024) we also have a full moon connected to Ellen and Orlok, in the prologue, when he reveals his rotten corpse to her:

According to Ancient Egyptian funerary texts, it’s Isis sorrow, sexual desire and anger that empower her magic to be able to bring Osiris back to life. When Ellen prays for a companion of “any celestial sphere” in the prologue, she’s crying (sorrow), she’s upset because her father recoils from her now that’s she’s no longer a child (anger) and she’s in her teenage years/puberty (sexual desire). Like Isis with Osiris, it’s the combination of these emotions that power her magic to unconsciously resurrect Orlok.
However, Osiris can’t remain among the living, because he has to return to the Underworld and become King of the Afterlife. But before he goes, Osiris and Isis conceive Horus, the God of the sun and the sky, who will restore peace and order to the universe. In “Nosferatu” (2024), Von Franz says that “with Jove’s holy light” before dawn, redemption will come to the people of Wisburg and the curse of Nosferatu will be vanquished. “Jove” is Jupiter, the “King of the skies”, who’s connected with the Egyptian Horus. Horus and Ra are often merged together in Ancient Egyptian religion, making Isis and Osiris the metaphorical parents of the Sun.

In “Nosferatu” (2024), as Orlok and Ellen complete their covenant, consummate their wedding and he drinks from her, the sun is also the metaphorical result of their union. As dawn breaks, the sunlight vanquishes them both from the physical world, as they both die in the material realm.

After being buried by Isis, Osiris goes into the Underworld to rule over it. And from then on, Isis herself is also associated with funeral rites, as she would guide the souls of the dead, helping them entering the afterlife. Through her magic, Isis helped resurrecting the souls of the dead, as she did with Osiris, acting as a mother to the deceased, providing protection and nourishment.

At the end of "Nosferatu" (2024) we see Ellen fulfilling her role as “priestess of Isis” (or as Isis herself?), as the Goddess of healing, who ends the blood plague in Wisburg, but also guides her dead lover Orlok/Osiris with her into the Underworld... where he'll rule as king? Unclear.
Since we are discussing the Egyptian Gods, I have to mention Greta the Cat, Ellen’s domestic cat. Her name is an obvious homage to Greta Schröder, the actress who played Ellen Hutter in the original 1922 “Nosferatu”. Indeed, cats are predators to rats, however, the Egyptian Goddess Bastet is considered to be Isis’ daughter. She's the "cat goddess" for cats were considered sacred in Ancient Egypt. Bastet was associated with sun gods like Horus and Ra. Bastet was the goddess of pregnancy, childbirh, and protection against contagious diseases and evil spirits.
Enchantress
Orlok calls Ellen “enchantress”, but what does this mean? “Enchantress” is not only a female archetype, but has root in historical realities. Enchantresses were practitioners of feminine magic: oracles, healers, herbalists, midwives and shamanic shapeshifters. They were what’s commonly known as “witches”. These female magicians studied and practiced their art in goddess temples, mystery schools, alchemy schools and hedge schools.
The alchemists of the Middle-ages studied these dynastic lineages of “wise women”, and they had several names: enchantresses, chantresses, encantrices, or incantrix. Many physicians who founded "medicine" and "science" studied these wise women, mainly healers and their use of medicinal plants and herbs.
Ellen’s character appears to fit that of a “incantrix”. Women who used words, incantations, songs, spells and prayers to shape reality. It’s the priestess of an old religion (as Von Franz also calls her); gifted with magic power and authority to command the elements or the body by the power of their word.

Heptagrams
Orlok seal (or sigil) meaning has already been widely discussed by others (symbols of Ancient Dacian religion, mainly the figure of Zalmoxis), but what I want to mention here is the heptagram itself, the seven-pointed star. Heptagrams have several occult meanings, including warding off evil which, for obvious reasons, doesn’t fit Orlok’s character. It has meaning in Alchemy, too, as representative of the seven planets and seven substances.

The heptagram, however, is used by Aleister Crowley in his occult system Thelema (from Ancient Egyptian text) to represent a goddess/archetype: Babalon, which is also connected with Isis, Nuit, Lilith, Kali, among other goddesses and deities. At its core, it’s a goddess of female empowerment and liberation, of divine feminine. According to this occult belief, Babalon has several manifestations (sort of incarnation) and is a spiritual gateway to wisdom and enlightenment through chaos and female sexuality.

In “Nosferatu” (2024), when Ellen and Thomas are returning home, there’s a man in the streets rambling bits from the “Book of Revelations” (Apocalipse) from the Bible: “And I saw a beast rising out of the sea, owith ten horns and seven heads, with ten diadems on its horns and blasphemous names on its heads.” (Revelations, 13:1).
Indeed this passage is about Orlok arrival and how he’ll spread plague among the town. However, we have a character in the “Book of Revelations” which is connected to all of this: the Whore of Babylon, the “Mother of Prostitutes and All Abominations of the Earth”, and she rides this Beast, which is the same as Crowley’s Babalon. What Crowley did was a positive reinterpretation of this biblical figure, symbolizing liberated female sexuality by embracing the powers of the Divine Harlot.
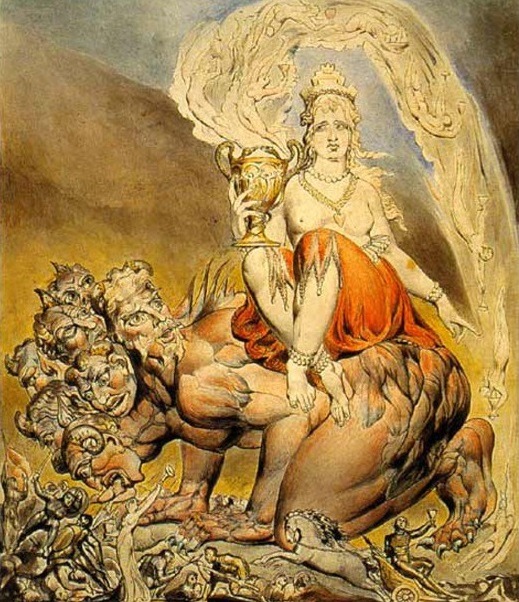


Also known as the “Scarlet Woman” and “Great Mother”, this complex and mysterious figure was established in 1904 in “The Book of Law”, however her roots are far older, and can be found in the Enochian tradition, a magical system by John Dee and Edward Kelly, dated from the late 16th century. In the 2016 script of “Nosferatu”, Orlok spoke Enochian, so it’s clear Robert Eggers is very much aware of all of this.
Initiatrix, Creator and Destroyer, Babalon is the “Great Mother” because she represents matter, Mother Earth. Like Isis, she’s the Archetypical Mother, the Womb, the Great Sea and the Divine Blood itself. According to Crowley, the “whore/harlot” facet is about enjoying sex without the burden of reproduction; and the “mother of abominations” connects with destruction like natural catastrophes, plagues, etc. She’s the ruler of the cosmological sphere and both good and evil (as evil as elemental forces can be or are considered as).
Crowley is a man who was born and raised in the Victorian era where sexuality was to be silenced and repressed, which provides context to his occultist beliefs and his “sex magick” theories. Victorian physicians and scientists were obsessed with classification of sexual perversions, too. “Hysteria” being one example among many. Which is the historical context for Eggers adaptation of “Nosferatu”/“Dracula”, so these references are quite fitting.
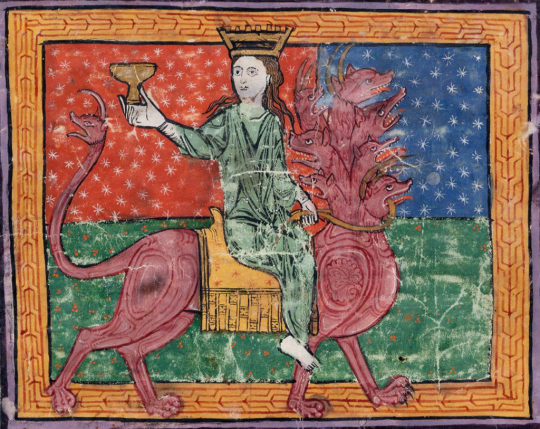

According to the Thelema, Babalon is the “Sacred Whore”, and her primary symbol is the Chalice or Graal (symbolic womb). She’s a consort to the Beast, who has seven heads, which is symbolically represented in her heptagram sigil. Crowley described her: “She rides astride the Beast; in her left hand she holds the reins, representing the passion which unites them. In her right she holds aloft the cup, the Holy Grail aflame with love and death. In this cup are mingled the elements of the sacrament of the Aeon”.
To Crowley these were not actual beings but titles/archetypes (sort of speak) in his Sex Magick beliefs: the “Scarlet Woman” is the High Priestess, and the “Beast” is the Hierophant. This fits Ellen (the priestess) and Orlok (warlock, black sorcerer) in “Nosferatu” (2024). The “Scarlet Woman” is a gateway to both the moon and the sun, and we see both associated with Ellen.
Orlok is described as a “beast” several times in the film, including by himself and by Von Franz, who also mentions Ellen’s “dark bond with beast”, and how she gave her love to the beast: "and lo the maiden fair did offer up her love unto the beast, in close embrace until the first cock crow, her willing sacrifice thus broke the curse and freed them from the plague of Nosferatu."
Orlok says Ellen’s passion is bound to him, like Babalon’s passion is united with the Beast. Babalon as “mother of abominations” also fits with how Ellen unleashed Orlok and his blood plague onto the world, bringing destruction and apocalypse.

Your passion is bound to me. […] I cannot be sated without you. […] Remember how once we were? A moment. Remember?
Thelemic followers of the Beast have been trying to call into being an older, more primeval, female force that is lacking in the Modern Age. Interestingly enough, this was the reason why Orlok became interested in Ellen in the 2016 script (which was later changed, because in the 2023 version it’s Ellen who summons Orlok): “I have sought a creature from the depths. A Eve that remembers her Eden. You are such one.” Both Crowley but more notoriously Jack Parsons have tried a bunch of incantations to conjure Babalon into being.
Oddly enough, the conjuring ritual we see Herr Knock performing at the beginning of “Nosferatu” (2024) is very similar to one of the incantations of Babalon performed by Jack Parsons: Air dagger, blood and channeling of windstorms and the Air element, over a heptagram. He also compares Ellen to a sylph; a nymph of the air element from alchemy and hermetic literature. We are told by Von Franz this is Solomonari sorcery, but is it really?

In Ophidian Thelema, Babalon is the Goddess of magick (“Heka”), of the Liberation of the Spirit (ecstasy), of the Liminal Point, of the Underworld, of Vengeance and of the Principles of Life. Their priestesses use the female body (vulva and womb) to channel their power during their magic rituals. This is similar to Ellen’s “hysterical fits” when she’s communicating with Orlok in the spiritual world, especially since “hysteria” was considered a disease caused by “wandering womb”. In the film, we also see Ellen's womb being talked about between Von Franz and Dr. Sievers during her examination, when they say her menstruation is liberal and she has too much blood in her.

The “liberation of spirit” is in the form of a Serpent, which manifests in the flesh. This notion was present in the “Book of Law”, where its said there’s the dove, and there’s the serpent, and a choice must be made. While the dove represents religion, the serpent represents the spirit. In one scene, Ellen says Orlok is like a serpent in her body; and he replies it’s not him, but her own nature, a nature she denies. Babalon says “my vocation is the serpent.”
The priestesses of Babalon are also in control of their “trances” when they access the spiritual world. In “Nosferatu” (2024) there’s a interesting scene between Ellen and Thomas (the infamous sex scene), when Ellen “comes back” from her transe when he says he’ll call for Dr. Sievers. Does this indicate Ellen is actually in control of her trance-like states?
Babalon is the guardian of the Seven Principles of the Underworld, a place of darkness and transformation. Orlok tells Ellen in the prologue “you are not for the living. You are not for human kind.” Babalon is also the goddess of the liminal point, who can access other realms. As Goddess of vengeance, Babalon punishes when life is out of balance, and exerts violence and corruption upon those who are in the wrong. Ellen unleashes Orlok onto the world, and we can interpret him bringing plague into Wisburg as Ellen’s reckoning against a society that ostracizes her and will never accept her.

All rites and initiations of the Underworld Goddesses include rites of sex and death. Which is what we see with Ellen at the end of “Nosferatu” (2024). By Thelemic occult tradition, she, the manifestation of Babalon, has sex with the Beast (Orlok), “representing the passion which unites them” and her womb (Holy Grail; cup) is “aflame with love and death” (sexual climax, orgasm, with an un-dead vampire).
I will work the work of wickedness; I will kill my heart; I will be loud and adulterous; I will be covered with jewels and rich garments; I will be shameless before all men; I will, for token thereof, will freely prostitute my body to the lusts of each and every living creature that shall desire it; I claim the Mystery of Mysteries, BABALON the Great, and the Number 156, and the robe of the Woman of Whoredomes and the Cup of Abomination. “The Great Beast: The Life of Aleister Crowley”, John Symonds, 2016

Orlok being the Beast and Ellen the manifestation of Babalon explains why she’s promise to him in the narrative, and was never meant to marry Thomas: in Thelemic tradition, the Beast is the consort of Babalon, after all. Orlok's interest in Ellen isn't predatory for its own sake; he sees her as his rightful and fated spiritual consort, which fits the "bride of Dracula" theme of the Bram Stoker original story.
This probably also mirrors the 1992 adaptation by Francis Ford Coppola, where Van Helsing calls Lucy the “Devil’s concubine”: "Hear me out, young man. Lucy is not a random victim attacked by mere accident. Do you understand? No. She is a willing recruit, a breathless follower, a wanton follower. I dare say, a devoted disciple. She is the devil's concubine! Do you understand me? Yet, we may still save her precious soul." In this adaptation, Lucy is full Crowley and Parsons “Scarlett Woman”, with red garments and red hair.


Orlok also gives Ellen three nights to accept him/her nature and complete their covenant. Some are mistakenly associating this with Jesus Christ. These “three days” are possibly connected with another Goddess associated with Babalon: Inanna (or Ishtar), the ancient Mesopotamian Goddess of love, war, fertility, sensuality and divine law. The most famous myth about this deity is her descent into the Underworld, where she spends three days and three nights dead, until she re-ascends (rebirth).
Ellen also goes through the “Myth of Inanna” in “Nosferatu” (2024), which is the theme of the heroine descending into the “Underworld”, to suffer, to be stripped bare, to die, and to be reborn in the aftermath. This is the primal Shamanic crisis. Ellen also goes through three days and nights of suffering and death (witnessing her friends and the townsfolk of Wisburg dying by the blood plague) until she joins Orlok and is reborn.
Ellen and Orlok are involved in sex magick, at the end, clearly. But with what purpose? Sex magick to Crowley has several purposes and strong creative power, conjuring, invocation, etc. He believed deliberate acts of sexual transgression were a radical form of super-human power that promised to explode the narrow boundaries of Western Christian society and open the way for a whole new era of human history. Which is probably what’s happening here? A symbolic ending to the sexually repressed Victorian era as Western societies moved toward a more open-minded and accepting view of sexuality? Or it’s Ellen reborn as a Goddess of the Underworld (return to spiritual state), after going through a initiation rite of sex and death, as she breaks free from her human form? Or both?
Or it can be a nod to Crowley idea of sex magick to unleash supreme creative power to generate a godlike child? This can mirror the Osiris and Isis myth, of Horus (the Sun) as their metaphorical child, like it is for Ellen and Orlok here, as the end result of their union.
Alchemy
Alchemy, at its core, is the transmutation of base materials (lead, etc.) into noble materials (gold), and the pursuit of immortality (“philosopher’s stone”). Occultists reinterpreted this as a spiritual quest of self-transformation, purification and regeneration of the human soul. Hence physical death being seen as a gateway to another life (rebirth); which is the symbolism of the final scene of “Nosferatu” (2024).

Both Ellen and Orlok evolve from a diseased and corruptive state (physical world) into regenerative and perfect state (spiritual world), after being purified by fire (the Sun). Their old selves are empty shells, as their spirits ascend. This also finds parallel in the myth of Isis and Osiris, as they both went from “daemons” to Gods in the Plutarch essay.
And this also finds parallel in the 1992 adaptation when Vlad/Dracula ascends to the Heavens and is reunited with Elisabeta’s soul. Is this intentional? Are we dealing with reincarnation themes in Eggers' adaptation, as well? According to occultists both Babalon and the Beast have had many manifestations (reincarnations) in the physical world throughout the centuries, after all.

Orlok asking Ellen to remember their shared past, is also an interesting nod to Vlad and Mina in the Coppola's adaptation (their OST is called "Love Remembered"): "I have crossed oceans of time to find you." and “I have sought a creature from the depths. A Eve that remembers her Eden. You are such one.” in the 2016 "Nosferatu" script. Which didn't change all that much in 2023, except we don't have an actual explanation for Orlok interest in Ellen, other than her waking him from his centuries old sleep (resurrection).
#nosferatu 2024#robert eggers#ellen hutter#count orlok#lily rose depp#bill skargard#von franz#dr sievers#ellen x orlok#orlok x ellen
270 notes
·
View notes
Text



von Franz + Cats
for @robinsnest2111
60 notes
·
View notes
Text



Aaron with Willem Dafoe, Nicholas Hoult & Emma Corrin - LA premiere Nosferatu
#aaron taylor-johnson#aaron taylor johnson#aarontaylorjohnson#nosferatu premiere#nosferatu 2024#friedrich harding#willem dafoe#nicholas hoult#emma corrin#von franz#thomas hutter#anna harding#atja#los angeles
73 notes
·
View notes
Text
I had an absolutely hilarious dream in which Von Franz’ solution to getting rid of all the plague rats was to hire the Pied Piper and as soon as he showed up and started playing his pipe, every single rat began dancing in a sort of conga line, but what made it even better was the fact that Orlok was also compulsively dancing
Ellen and Thomas peered out of the window in the middle of the night to find a long line of rats boogieing down the street and in the midst of it all was Orlok, who shouted “Ellen, save me! I can’t stop!” as he waltzed past
And just to truly top it all off, the song the Pied Piper was playing just happened to be Rasputin by Boney M
#nosferatu#nosferatu 2024#Ellen hutter#Thomas hutter#count Orlok#von franz#pied piper#plague rats#oddly enough this is probably the most coherent dream I’ve ever had#dream journal
47 notes
·
View notes
Text

Robert Eggers’ Nosferatu (2024) [script].
#robert eggers#nosferatu#script#ellen hutter#von franz#albin eberhart von franz#carl jung would’ve loved him.#posting this for my own reference; ..is it too early?
41 notes
·
View notes