#US law
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
#politics#political#us politics#donald trump#news#president trump#elon musk#american politics#jd vance#law#alexandria ocasio cortez#aoc#democratic#democratic party#democrat#democracy#house of representatives#sentate#congress#us law#american#america#us news#social security benefits#veterans affairs#veterans#healthcare#medicad#medicare#health care
560 notes
·
View notes
Text
More good things the Biden administration is doing: OSHA heat safety rules for workers
Remember when Texas and Florida passed laws preventing local and municipal governments from implementing their own heat safety rules and said that if heat is such a big problem, OSHA should make rules that apply to everyone? If not, NPR can remind you. OSHA has now accepted the challenge, moving much faster than they usually do:
OSHA National News Release U.S. Department of Labor July 2, 2024 Biden-Harris administration announces proposed rule to protect indoor, outdoor workers from extreme heat WASHINGTON – The U.S. Department of Labor has released a proposed rule with the goal of protecting millions of workers from the significant health risks of extreme heat. If finalized, the proposed rule would help protect approximately 36 million workers in indoor and outdoor work settings and substantially reduce heat injuries, illnesses, and deaths in the workplace. Heat is the leading cause of weather-related deaths in the U.S. Excessive workplace heat can lead to heat stroke and even death. While heat hazards impact workers in many industries, workers of color have a higher likelihood of working in jobs with hazardous heat exposure. “Every worker should come home safe and healthy at the end of the day, which is why the Biden-Harris administration is taking this significant step to protect workers from the dangers posed by extreme heat,” said Acting Secretary of Labor Julie Su. “As the most pro-worker administration in history, we are committed to ensuring that those doing difficult work in some of our economy’s most critical sectors are valued and kept safe in the workplace.” The proposed rule would require employers to develop an injury and illness prevention plan to control heat hazards in workplaces affected by excessive heat. Among other things, the plan would require employers to evaluate heat risks and — when heat increases risks to workers — implement requirements for drinking water, rest breaks and control of indoor heat. It would also require a plan to protect new or returning workers unaccustomed to working in high heat conditions. “Workers all over the country are passing out, suffering heat stroke and dying from heat exposure from just doing their jobs, and something must be done to protect them,” said Assistant Secretary for Occupational Safety and Health Douglas L. Parker. “Today’s proposal is an important next step in the process to receive public input to craft a ‘win-win’ final rule that protects workers while being practical and workable for employers.” Employers would also be required to provide training, have procedures to respond if a worker is experiencing signs and symptoms of a heat-related illness, and take immediate action to help a worker experiencing signs and symptoms of a heat emergency. The public is encouraged to submit written comments on the rule once it is published in the Federal Register. The agency also anticipates a public hearing after the close of the written comment period. More information will be available on submitting comments when the rule is published. In the interim, OSHA continues to direct significant existing outreach and enforcement resources to educate employers and workers and hold businesses accountable for violations of the Occupational Safety and Health Act’s general duty clause, 29 U.S.C. § 654(a)(1) and other applicable regulations. Record-breaking temperatures across the nation have increased the risks people face on-the-job, especially in summer months. Every year, dozens of workers die and thousands more suffer illnesses related to hazardous heat exposure that, sadly, are most often preventable. The agency continues to conduct heat-related inspections under its National Emphasis Program – Outdoor and Indoor Heat-Related Hazards, launched in 2022. The program inspects workplaces with the highest exposures to heat-related hazards proactively to prevent workers from suffering injury, illness or death needlessly. Since the launch, OSHA has conducted more than 5,000 federal heat-related inspections. In addition, the agency is prioritizing programmed inspections in agricultural industries that employ temporary, nonimmigrant H-2A workers for seasonal labor. These workers face unique vulnerabilities, including potential language barriers, less control over their living and working conditions, and possible lack of acclimatization, and are at high risk of hazardous heat exposure.
#biden harris administration#biden administration#osha#heat safety#worker safety#biden 2024#biden harris 2024#vote for democrats#vote blue#vote biden#us politics#us law
981 notes
·
View notes
Text
Public Domain Day 2025
Well another year another public domain day.
Europe and Similar (Life of Creator + 70)
Colette's Gigi
The Branting Monument, a statue of the Swedish Social Democratic leader Hjalmar Branting

[ID bstract sculpture featuring curved granite panels forming a semi-circular shape, with detailed relief carvings depicting scenes of workers and political figures. Front and center is Hjalmar Branting, a social democratic leader with his hand raised. The monument is surrounded by greenery in a park setting END ID]
The works of John Hilton
The works of writer and poet Cicely Fox Smith
Italian comic series Marmittone by Bruno Angoletta
The paintings of Frida Kahlo
New Zealand and Similar (Life of Creator + 50 years)
Valley of the Dolls by Jacqueline Susann
Kinsmen of the Dragon by Stanley Mullen
The Wind on the Moon by Eric Linklater
United States (95 years after publication)
What is public domain is anything published in the United States in 1929 such as.
Silly Symphonies - Skeleton Dance (im sure youve seen those dancing skeletons)
The Plowboy, first appearance of Horace Horsecoller
The first appearance of Popeye, the Sailor Man (was already public domain in other countries but now is public domain worldwide. trademark may still apply)
The song Singin' in the Rain
Ernest Hemingway's Farewell to Arms
Ellery Queen novels published that year
Un Chien Andalou, film co-written by Salvador Dali
Check some of these out on places like The Internet Archive and Project Gutenberg and maybe consider throwing them a few bucks, they do solid work.
132 notes
·
View notes
Text

URGENT! Stop KOSA!
Hey all, this is BáiYù and Sauce here with something that isn't necessarily SnaccPop related, but it's important nonetheless. For those of you who follow US politics, The Kids Online Safety Act passed the Senate yesterday and is moving forward.
This is bad news for everyone on the internet, even outside of the USA.
What is KOSA?
While it's officially known as "The Kids Online Safety Act," KOSA is an internet censorship masquerading as another "protect the children" bill, much in the same way SESTA/FOSTA claimed that it would stop illegal sex trafficking but instead hurt sex workers and their safety. KOSA was originally introduced by Sen. Edward Markey, D-Mass. and Bill Cassidy, R-La. as a way to update the 1998 Children’s Online Privacy Act, raising the age of consent for data collection to 16 among other things. You can read the original press release of KOSA here, while you can read the full updated text of the bill on the official USA Congress website.
You can read the following articles about KOSA here:
EFF: The Kids Online Safety Act is Still A Huge Danger to Our Rights Online
CyberScoop: Children’s online safety bills clear Senate hurdle despite strong civil liberties pushback
TeenVogue: The Kids Online Safety Act Would Harm LGBTQ+ Youth, Restrict Access to Information and Community
The quick TL;DR:
KOSA authorizes an individual state attorneys general to decide what might harm minors
Websites will likely preemptively remove and ban content to avoid upsetting state attorneys generals (this will likely be topics such as abortion, queerness, feminism, sexual content, and others)
In order for a platform to know which users are minors, they'll require a more invasive age and personal data verification method
Parents will be granted more surveillance tools to see what their children are doing on the web
KOSA is supported by Christofascists and those seeking to harm the LGBTQ+ community
If a website holding personally identifying information and government documents is hacked, that's a major cybersecurity breach waiting to happen
What Does This Mean?
You don't have to look far to see or hear about the violence being done to the neurodivergent and LGBTQ+ communities worldwide, who are oftentimes one and the same. Social media sites censoring discussion of these topics would stand to do even further harm to folks who lack access to local resources to understand themselves and the hardships they face; in addition, the fact that websites would likely store personally identifying information and government documents means the death of any notion of privacy.
Sex workers and those living in certain countries already are at risk of losing their ways of life, living in a reality where their online activities are closely surveilled; if KOSA officially becomes law, this will become a reality for many more people and endanger those at the fringes of society even worse than it already is.
Why This Matters Outside of The USA
I previously mentioned SESTA/FOSTA, which passed and became US law in 2018. This bill enabled many of the anti-adult content attitudes that many popular websites are taking these days as well as the tightening of restrictions laid down by payment processors. Companies and sites hosted in the USA have to follow US laws even if they're accessible worldwide, meaning that folks overseas suffer as well.
What Can You Do?
If you're a US citizen, contact your Senators and tell them that you oppose KOSA. This can be as an email, letter, or phone call that you make to your state Senator.
For resources on how to do so, view the following links:
https://www.badinternetbills.com/#kosa
https://www.stopkosa.com/
https://linktr.ee/stopkosa
If you live outside of the US or cannot vote, the best thing you can do is sign the petition at the Stop KOSA website, alert your US friends about what's happening, and raise some noise.
Above all else, don’t panic. By staying informed by what’s going on, you can prepare for the legal battles ahead.
#stop KOSA#KOSA#censorship#us law#somethings wrong with sunny day jack#the groom of gallagher mansion#dachabo
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
92 notes
·
View notes
Text

The almost 222-year-old landmark precedent, as set forth by Chief Justice John Marshall on February 24, 1803, that “it is emphatically the province and duty of the judicial department to say what the law is.”
Marbury v. Madison, 1803
Quote carved in the halls of the SCOTUS.
#reddit#pics#gswindle76#1803#1800s#early 1800s#us law#us politics#chief justice john marshall#marbury v madison#scotus#quote#02/24#law#precedent
136 notes
·
View notes
Text
Made in the USA: Wage Theft, Fraud and Hidden Sweatshops
Unrolled twitter thread by derek guy (@dieworkwear)
4 Oct 24 • Read on X
ALT enabled on all images. Video has closed captions but is not transcribed.
Not trying to create a pile-on here. But let's talk about why something might still be made in unethical conditions even though it bears a "made in USA" tag. 🧵
The first thing to understand is that not all workers are covered by US labor laws. You might assume that workers get paid a minimum wage (after all, it says "minimum"). In fact, many garment workers in the US toil under what's known as the piecework system.
Piecework means you get paid not by the amount of time you work but the number of operations you complete. This system should be familiar to many of you. As a writer, I get paid per word. The pay is the same whether it takes me 100 or 10 hours to write a 1,000 word article.
My situation is fine bc I get paid enough to eat. But for a garment worker, the pay structure can be peanuts: three cents to sew a zipper or sleeve, five cents for a collar, and seven cents to prepare the top part of a skirt. These are real numbers for LA-based garment workers.
Piecework is how companies skirt minimum wage laws. Among labor organizers, the term "wage theft" refers to the difference between what a worker should have earned under min wage laws and what they actually earned through the piece rate system.
This system is incredibly common. A 2016 UCLA Labor Center study showed the median piece-rate worker in Los Angeles scrapes together $5.15 per hour—less than half the state’s mandated minimum wage. Labor conditions are also very bad: poor ventilation, dusty air, rats and mice.

A Federal Department of Labor investigation the same year found that 85 percent of Los Angeles garment factories were breaking labor laws. In 2016, these violations amounted to $1.3 million in back wages owed to 865 workers in a sample of 77 factories. This is wage theft.
In 2021, labor organizers won a fight to get piecework banned in California. But two years later, it's still incredibly common. I interviewed an LA-based garment worker who toils 12 hrs a day for $50. She sleeps in the corner of a kitchen. From my article in The Nation:

Currently, there's a new fight get piecework banned nationwide through the FABRC Act. I would link, but Twitter throttles threads that have outbound links, so I would prefer if you Google how you can support this legislation. Or follow @GarmentWorkerLA for more info.
The other reason why a "made in USA" tag may not mean much has to do with how the label is applied.
When you see this label inside your garment, what do you assume? Think about this before moving on to the next tweet.

The Federal Trade Commission has pretty strict rules on who gets to apply that label. For clothes, the item has to be cut and sewn in the US using materials that were made in the US. The FTC tries to match its rules with the common understanding of what "made in US" means.
If you're a giant company like Levi's or LL Bean, you may have lawyers who are advising you on these rules. This is why you see labels like "imported," which means the item was made abroad. Or "made in the US from imported materials" when they can't meet the MiUSA standard.
But it's incredibly common for companies to violate FTC rules. In 2022, the FTC fined the pro-Trump brand Lions Not Sheep $211k for labeling their t-shirts "made in USA" when the shirts were actually imported from China and other countries.
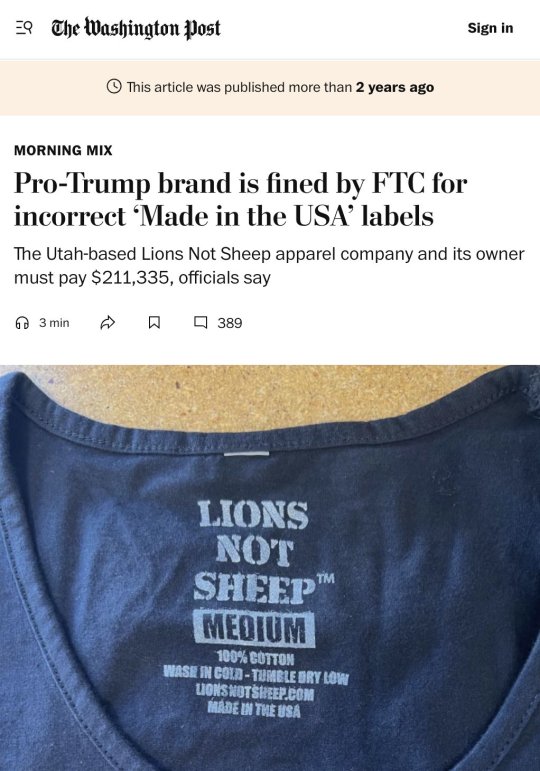
The company was basically importing blanks from China, ripping out the "made in China" label, screen printing the shirt in the US, and then applying a new screen-printed "made in US" label. CEO Sean Whalen claimed he was being persecuted for his pro-Trump views.
But the whole thing started bc Whalen made a video about how his customers are price sensitive, so he imports blanks from China. That's what kicked off the FTC investigation. So while this mislabeling is common, it's hard to get caught unless you make a video about your crimes.
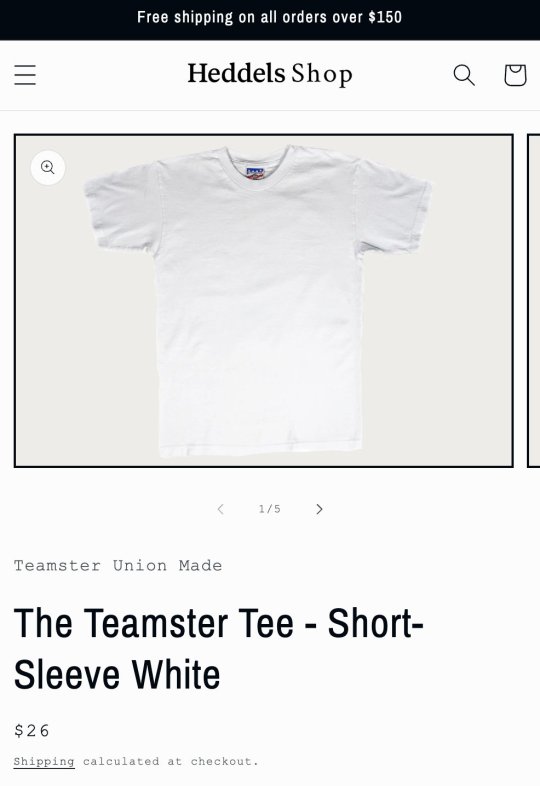
The truth is that making a t-shirt in the USA according to FTC standards will result in a relatively expensive garment. Heddels and Velva Sheen both produce shirts in the US from US grown cotton. The first is $26; second is $90 for a two-pack.

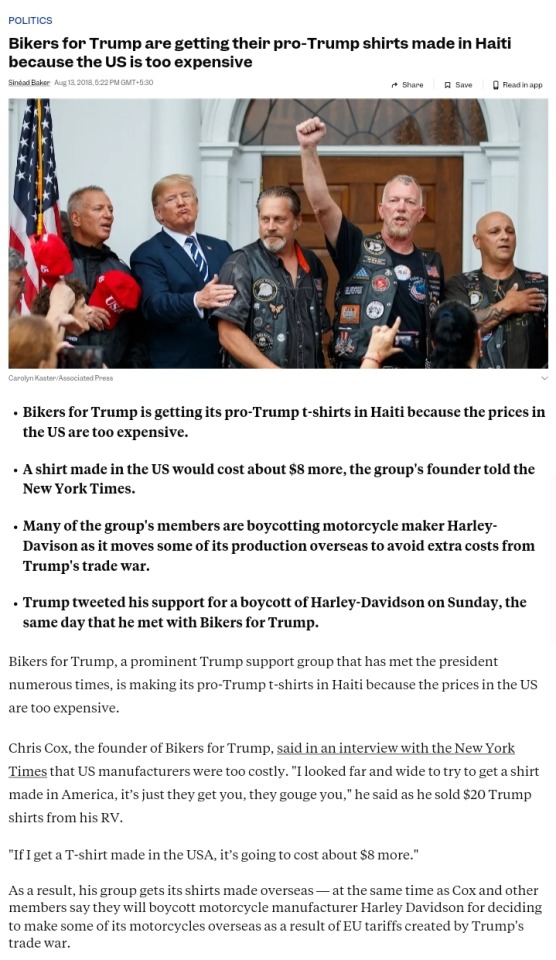
Once you add things such as screenprinting—or if you want a more unique cut and not just basic blanks—the costs go up. This is why Bikers for Trump sourced their merch from Haiti. They knew their customers would not pay an extra $8 for true made-in-USA production.
Today, there are countless companies that make merch for other organizations. They source their t-shirts from a variety of places—some made in the US, most not—and then screenprint a design and fulfill orders. This way, the other org doesn't have to do any work but marketing.
When you see a screenprinted t-shirt for $20, ask yourself: Where was the material grown? Where were the yarns spun? Where was the cutting, sewing, and finishing performed? Where was the screenprinted done? What were the wages and labor conditions along these steps?
I'm not a nationalist, so I don't prioritize American jobs over foreign ones. But I do care about fair wages and labor protections. Just because something was made abroad doesn't mean it was made in a sweatshop. Just because it was made in the US doesn't mean fair wages.

Paying more for a garment is also no guarantee of ethical manufacturing. But when the price of a garment is so low, you leave little on the table for workers. Just because you see a $20 t-shirt that says "made in USA" doesn't mean it was made fairly.
Please don't harass the person who posted that original tweet. My intention is not to cause harm or stress for anyone. Only to help shed light on what goes into garment manufacturing, fair labor, and labeling. Hopefully, you will consider these issues when shopping.
For the inevitable question: "How do I make sure my clothes were made ethically?" This is very difficult to answer in a thread. My simplest answer is that we should elect pro-worker politicians, fight for pro-labor laws, and empower unions so workers can advocate for themselves.

--------------------End----------------------
TL; DR: Doesn't matter if it's the US, if it's not union it's probably a sweatshop. And not all merch is priced high because of fair labour conditions (looking at Taylor Swift and Beyoncé). Look for supply chain transparency.
#sweatshops#fashion#american sweatshop#chappell roan merch#sweatshirt#chappell roan#merchandise#made in usa#garment industry#fast fashion#worker rights#labour rights#labour unions#capitalism#worker exploitation#us politics#us law#knee of huss
133 notes
·
View notes
Text
119th Congress Begins
Happy New Years! We've had a little bit of down time, but now things are going to pick back up because the next congressional session, the 119th Congress, is starting up and are already discussing passing harmful and controversial bills that threaten voting rights, the LGBTQ+, immigrants, and many more people. So, now is when we support our neighbors and communities and participate in local and national movements to try to fight back against such bills and try to stop them.
Also Blackburn and Blumenthal are already talking about reintroducing KOSA, which will once again probably have another up-hill battle and will face heavy opposition. In 2024, several advocates against KOSA said that it likely would've passed if it had not been for our calls and heavy push-back. This is momentum we need to maintain, not only for this bill, but others.
All this is to essential say we know what's coming and we know we have to work hard to push back and protect each other.
68 notes
·
View notes
Text

(Source)
Chevron deference was a legal doctrine where the US judicial system was required to defer to an executive agency's interpretation of ambiguous laws. Effectively, this meant that federal agencies were able to address loopholes in laws Congress had passed (e.g. banning toxic waste dumping in weird legal ways).
This morning, the Supreme Court overturned Chevron and stated that the judicial system should have that power instead of the federal agencies.
116 notes
·
View notes
Text

imagine having to find a legal loophole to send a man like donald trump to jail
#imagine having to find a legal loophole to send a man like donald trump to jail#us law#us lawmakers#donald trump#anti donald trump#fuck trump#trump#new york state#loophole#jeffrey epstein#epstein island#epstein files#epstein#mossad#anti elon musk#elon musk#hillary clinton#bill clinton#blue maga#maga 2024#maga morons#fuck maga#maga cult#maga#usa is a terrorist state#usa is funding genocide#usa politics#usa news#usa#american indian
44 notes
·
View notes
Text

#former secretary of labor#politics#us politics#political#donald trump#news#president trump#elon musk#american politics#jd vance#law#labor secretary#labor#government#us news#us law#robert reich#amazon#jeff bezos
98 notes
·
View notes
Text
My hospital has stopped supplying hormones to transgender people underneath 19. They're a children's hospital, they are FOR people under 19.
This doesn't affect me very severely. They sent out one last 6-month supply. I will be 19 in a little over 6 months.
Still, they're kneeling for him. And I am so. fucking. scared.
27 notes
·
View notes
Text
Trump’s New Order: A Dangerous Power Grab That Could Impact Your Future
Have you heard about the latest executive order signed by President Trump? It’s a big one, and it’s something you should definitely pay attention to. In a move that has shocked many, Trump just signed an order saying that only the President or the Attorney General can interpret the law. This means federal regulators and agencies—like the EPA, FDA, and FCC—can no longer make their own calls on what laws mean. Instead, they’ll have to listen directly to Trump and his team.
Why Does This Matter to You?
Okay, so what’s the big deal? For starters, this is a huge shift in how the government operates. It takes away the independence of agencies that protect things like our environment, public health, and consumer rights. Imagine if the FDA could no longer make decisions without asking Trump first—things like the safety of the food you eat or the medicine you rely on could be at risk. This is the kind of power grab that could lead to decisions being made with no accountability to you or anyone else.
The Bigger Picture
This is more than just an isolated executive order—it’s a fundamental attack on the structure of U.S. governance. By stripping regulatory agencies of their independence, Trump is consolidating power within the Executive Branch, weakening the ability of agencies to act without direct presidential influence. Critics argue that this undermines democratic principles and shifts the nation closer to an authoritarian regime. The fear is that such moves could lead to a future where the President can unilaterally dictate policy, ignoring judicial oversight and stifling any dissenting voices in the government.
What’s at Stake?
Democratic accountability: The order bypasses the democratic checks that typically ensure elected officials are held accountable for their decisions.
Environmental and consumer protections: With agencies like the EPA and FDA now directly under the control of the White House, the potential for deregulation in sensitive areas like public health, safety, and the environment increases dramatically.
Legal independence: The judiciary, which has traditionally interpreted laws impartially, now risks being sidelined as Trump consolidates more control over the legal landscape.
So, What’s the Real Impact?
By giving Trump and the Attorney General the ultimate say in how laws are interpreted, this order weakens the role of other branches of government. It means that things like environmental protection, health standards, and even internet regulations could become whatever Trump decides they should be—without oversight or checks from independent agencies or even the courts. This could hurt future generations by opening the door for more harmful policies that prioritize money over people.
But What Can You Do About It?
Stay woke: It’s time to get informed. The more you know about what’s happening in politics, the better you can help shape the future. This move from Trump is just the latest in a series of actions that show how much power the Executive Branch is trying to take.
Speak up: Your voice matters. This is your future we’re talking about, so don’t sit back and let these decisions slide. Stay active, share what you know, and make sure the people around you understand what’s at stake.
Vote: Seriously. This is why voting is so important. You want to make sure that the people making the decisions in Washington have your best interests at heart.
This isn’t just about some old executive order. It’s about the future of democracy, accountability, and fairness. So, pay attention. This is your country, your future. Let’s make sure we’re all in the driver’s seat.
#president trump#trump is a threat to democracy#trump administration#donald trump#trump#america#us law#us politics#politics#elon musk#project 2025
22 notes
·
View notes
Text
Does anyone else watch LegalEagle too? I started watching years ago, but now his coverage of all the fucked up shit trump is doing is soo good
20 notes
·
View notes
Text
Well, here it comes, a filing at the Republican-controlled Sixth US Circuit Court of Appeals that could lead to the overturn of the rights to same-sex marriage, birth control, even the right to have same-sexy-sextimes in the privacy of one’s own home, courtesy of Apostolic Christian Kentucky court clerk Kim Davis and her designated-hate-group law firm, Liberty Counsel.
Yes, it’s THAT lady again, the one the hair who’s been pitching one long legal fit since 2015, starting when she refused to sign marriage certificates for gay couples after Obergefell v. Hodges made same-sex marriage the law of the land, moaning that it would violate her right to religious expression to have her Godly Christian signature on such sinful paperwork.
The couples sued her for being a flagrant asshole who denied them their rights, and a jury agreed with them. Davis appealed to the Supreme Court, back in the saner days of old (2020 and before), they didn’t want to hear it.
Nevertheless, Justice Clarence “RV” Thomas took the opportunity to write a whole unsolicited statement about how the victim here wasn’t nice couples in love trying to get married like they were legally allowed to do, but poor Kim Davis, because now everybody thinks she’s a bigot instead of decent, good, and honorable, and that makes her sad. How dare Obergefell have not considered the right of Christian moral scolds to butt into everybody’s private life and make scenes, the way God intended?
[ ]
So now Davis and Liberty Counsel have an in, using Thomas’s statement to take their legal spanking to the 6th Circuit as being UGH SO UNFAIR to Davis as an oppressed bigot-American. Also while the 6th Circuit is at it, Davis thinks they should “reconsider all of th[e] Court’s substantive due process precedents, including Griswold [v. Connecticut], Lawrence [v. Texas], and Obergefell”, maybe the 6th Circuit could have a talk with the manager?
[ ]
But guffaw, Liberty Counsel is never happy! Not for nothing the Southern Poverty Law Center designates them as a hate group! Their lawyers Mat (one ‘T’) Staver and Matt Barber have opined many times that gay sex is so ew yuck icky that we should all have an entire civil war about it. In 2019 Liberty Counsel was publicly mad that gay people were included in the federal Justice for Victims of Lynching Act, lest you think they aren’t deadly serious about wanting to kill people.
That’s a goal that also tops on Project 2025’s wish list, that plus labeling content with LGBTQ people in it as pornography, making “pornographers” register as sex offenders, and that sex offenders should get the death penalty. And like Davis, Project 2025 would also like to throw out the Comstock Act and have the FBI spend their time searching people’s mail for suspected “abortifacients.”
51 notes
·
View notes