#Solar Dynamics Observatory
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

Our Sun !
A main sequence star, emits a strong solar flare flashes in this image captured by NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory.
NASA/SDO
#art#cosmos#cosmic#universe#blast#space#sun#flare#solar flare#SDO#nasa#solar dynamics observatory#photography
59 notes
·
View notes
Text
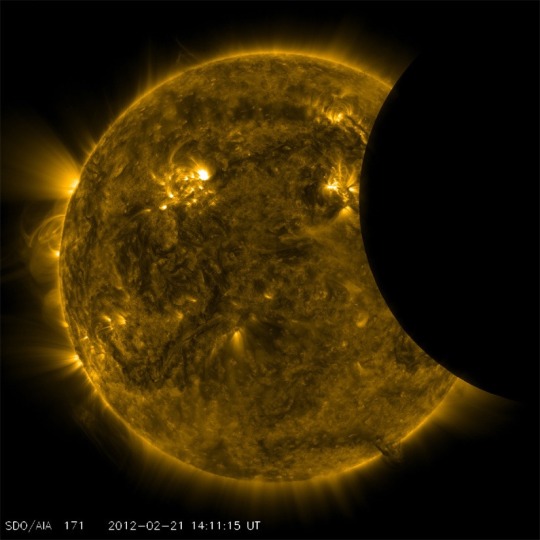

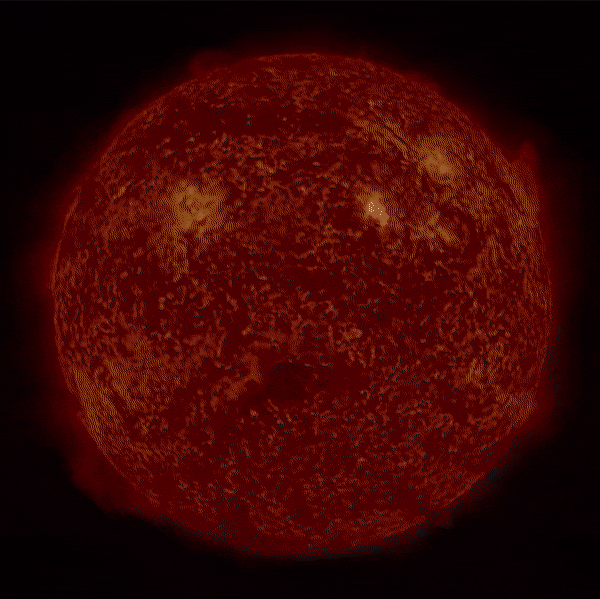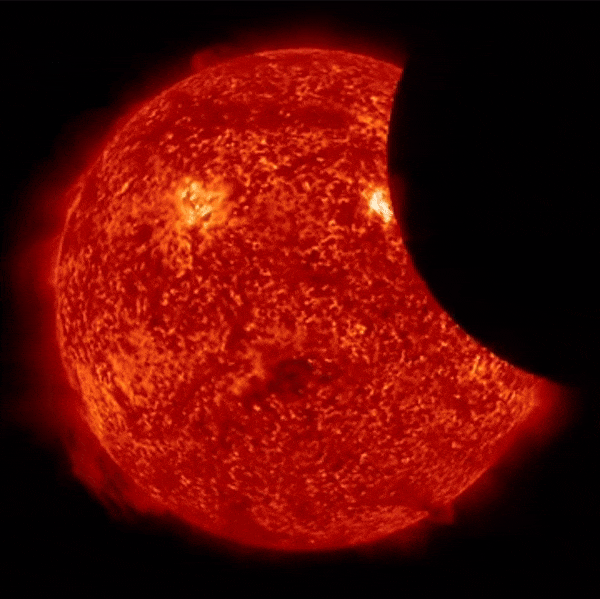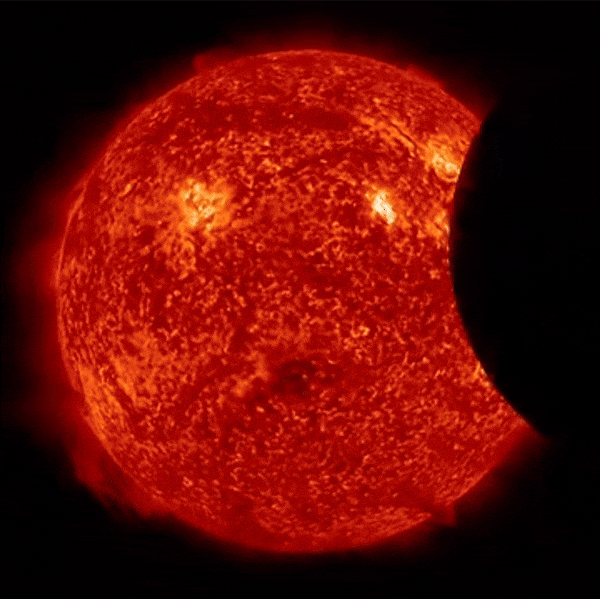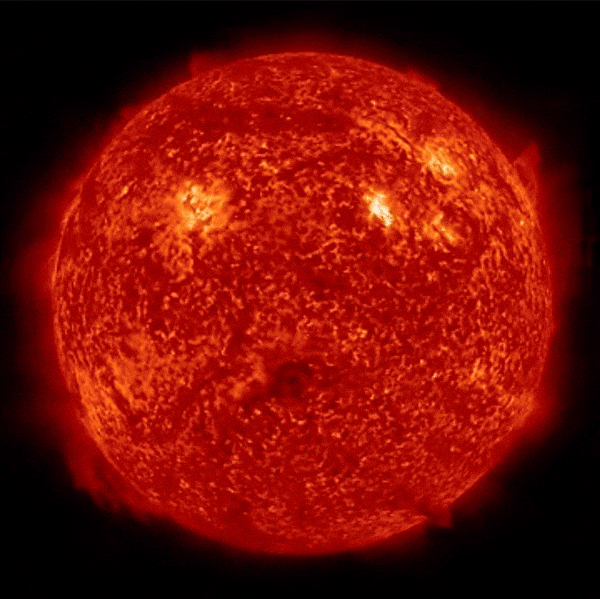
Partial Solar Eclipse Seen From Space
82 notes
·
View notes
Text

Venus transit from Solar Dynamics Observatory.
(Image credit: NASA)
25 notes
·
View notes
Video
NASA’s NuSTAR Telescope Reveals Hidden Light Shows on the Sun by NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center Via Flickr: Even on a sunny day, human eyes can’t see all the light our nearest star gives off. A new image displays some of this hidden light, including the high-energy X-rays emitted by the hottest material in the Sun’s atmosphere, as observed by NASA’s Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array (NuSTAR). While the observatory typically studies objects outside our solar system – like massive black holes and collapsed stars – it has also provided astronomers with insights about our Sun. In this composite image, NuSTAR data is represented as blue and is overlaid with observations by the X-ray Telescope (XRT) on the Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency’s Hinode mission, represented as green, and the Atmospheric Imaging Assembly (AIA) on NASA’s Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO), represented as red. NuSTAR’s relatively small field of view means it can’t see the entire Sun from its position in Earth orbit, so the observatory’s view of the Sun is actually a mosaic of 25 images, taken in June 2022. The high-energy X-rays observed by NuSTAR appear at only a few locations in the Sun’s atmosphere. By contrast, Hinode’s XRT detects low-energy X-rays, and SDO’s AIA detects ultraviolet light – wavelengths that are emitted across the entire face of the Sun. Image Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/JAXA #nasa #marshallspaceflightcenter #msfc #heliophysics #sun #space #solar #observation #star #astronomy #science #hinode #SDO #SolarDynamicsObservatory #NuSTAR Read More More about NuSTAR More about Solar Dynamics Observatory More about Hinode NASA Media Usage Guidelines
#NASA#NASA's#Marshall#Space#Flight#Center#Heliophysics#Sun#Hinode#NuSTAR#SDO#Solar Dynamics Observatory#Goddard Space Flight Center#GSFC#flickr
4 notes
·
View notes
Photo
[source]

Venus and the Triply Ultraviolet Sun
Credits: NASA, SDO, Peter L. Dove
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
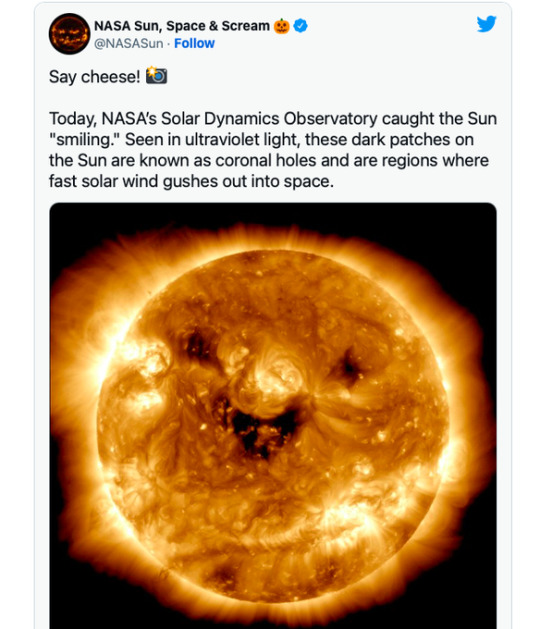
A little something to "brighten" your day!
1 note
·
View note
Text



1 note
·
View note
Video
youtube
133 Days on the Sun
0 notes
Text
Do You Love the Color of the Sun?

Get dazzled by the true spectrum of solar beauty. From fiery reds to cool blues, explore the vibrant hues of the Sun in a mesmerizing color order. The images used to make this gradient come from our Solar Dynamics Observatory. Taken in a variety of wavelengths, they give scientists a wealth of data about the Sun. Don't miss the total solar eclipse crossing North America on April 8, 2024. (It's the last one for 20 years!) Set a reminder to watch with us.
37K notes
·
View notes
Text
NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory Discovers Massive Sunspot with Potential for Solar Flares
NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory Discovers Massive Sunspot with Potential for #SolarFlares. @neosciencehub #NASA #SDO #SunspotDiscovery #SpaceWeather #EarthImpact #SpaceScience #Astronomy #SolarObservation #SolarPhenomena #SolarDynamics #Astrophysics
In a groundbreaking discovery, NASA’s Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO) has illuminated a colossal sunspot on the surface of the Sun, harboring energy capable of unleashing M-class solar flares. This development comes as the peak of solar cycle 25 approaches, marked by a surge in solar activities such as coronal mass ejections (CMEs), solar flares, and storms. The identified sunspot, named…

View On WordPress
#Coronal Mass Ejections (CMEs)#Earth-directed flares#featured#M-class solar flares#nasa#Solar activity#Solar cycle 25#Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO)#Solar flares#Solar observation#Solar phenomena#space#Space science#Space weather#Sun&039;s energy#Sunspot Complex AR3490-91-92#Technological impact of solar flares
0 notes
Photo

2024 September 2
A Triangular Prominence Hovers Over the Sun Image Credit & Copyright: Andrea Vanoni
Explanation: Why is there a triangle hovering over the Sun? Although the shape is unusual, the type of structure is not: it is part of an evolving solar prominence. Looping magnetic fields on the Sun channel the flow of energetic particles, sometimes holding glowing gaseous structures aloft for months. A prominence glows brightly because it contains particularly hot, dense, or opaque solar plasma. The surprising triangular structure occurred last week. Larger than our Earth, the iconic prominence was imaged by several solar photographers and documented by NASA's Solar Dynamic Observatory to form and violently dissipate in about a day. The featured image was captured in a color of red light emitted strongly by hydrogen. Below, solar fibrils carpet the Sun's chromosphere, while the background sky is so faint in comparison that no stars are visible. Our Sun's surface has been quite active this year.
∞ Source: apod.nasa.gov/apod/ap240902.html
235 notes
·
View notes
Text
WHY IS EVERYTHING IN SPACE ALWAYS MOVING??
Blog#434
Saturday, September 7th, 2024.
Welcome back,
Have you ever wondered why everything in the universe seems to be in constant motion? From our planet's orbit around the sun to the rotation of galaxies, nothing in space stands still. But what drives this cosmic dance?
The story of movement in the universe begins at the very dawn of time, with the Big Bang. According to Edward Gomez, an astrophysicist and the education director at Las Cumbres Observatory, the universe started expanding outward from an infinitely dense point.

This expansion set everything in motion, imprinting movement into the very fabric of the cosmos. As Carol Christian, an astrophysicist and outreach project scientist for the Hubble Space Telescope, explains, "The beginning was movement, and so movement has been built into the universe from the very beginning."
While the universe’s expansion mainly affects vast distances, it’s not just about objects moving through space; it’s also about the space between them growing larger. On smaller scales, however, rotation plays a key role in how objects behave.

This spinning motion is a fundamental aspect of the universe, evident in everything from the tiniest particles to massive galaxies.
So, why does everything spin? The answer lies in a concept called angular momentum. When two objects in space come close to each other, their mutual gravitational pull often causes them to orbit one another, rather than colliding or drifting apart. This effect is responsible for the rotational motion we observe in celestial bodies.

Edward Gomez likens the formation of our solar system to making a pizza: as you spin the dough, it flattens into a disc. Similarly, the solar system began as a spinning mass of gas and dust, which eventually coalesced into the sun and planets. Angular momentum ensured that this spinning never ceased, and it's why the planets continue to orbit the sun today.
Interestingly, galaxies don't spin the way you might expect based on visible matter alone. Instead, they rotate as if they were solid objects, a phenomenon that puzzled scientists until the discovery of dark matter. This mysterious substance, which doesn’t interact with light, exerts gravitational forces that influence the motion of galaxies, adding another layer to the complexity of cosmic movement.

In the grand scheme of things, motion is not just a characteristic of the universe—it’s a fundamental ingredient. As Gomez eloquently puts it, motion shows that "the universe is alive—not in the sense of being conscious, but things are happening." Chemical and physical reactions drive the cosmic machinery, and at the heart of it all is motion, the most basic form of energy.
This never-ending movement reminds us that the universe is an active, dynamic place, constantly evolving and shifting. And while we may not be able to see all the forces at play, the dance of the cosmos continues, driven by the invisible threads of gravity, dark matter, and angular momentum.
Originally published on https://www-moneycontrol-com
COMING UP!!
(Wednesday, September 11th, 2024)
"WHAT HAPPENS IF WE MOVE AT THE SPEED OF LIGHT????"
#astronomy#outer space#alternate universe#astrophysics#universe#spacecraft#white universe#space#parallel universe#astrophotography
106 notes
·
View notes
Text

The bright flash of a solar flare captured by NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory.
Dazzling images of the sun
(Image credit: NASA)

Active regions of the sun are shown with X-Ray imaging taken by the NuSTAR telescope.
#nasa#photographer#sun#space#astronomy#science#solar flare#nature#nasa's solar dynamics observatory#nustar telescope#x-ray image
25 notes
·
View notes
Text

Did You Know: If Superman flew to the Sun from Earth at the speed of light—186,000 miles (300,000 km) per second—it would take him more than eight minutes to get there because the Sun is about 93 million miles (150 million km) away. Credit: NASA Solar Dynamics Observatory.
72 notes
·
View notes
Text
Solar Filament Eruption

From Earth, we rarely glimpse the violent flows of our home star. Here, a filament erupts from the photosphere creating a coronal mass ejection, captured in ultraviolet wavelengths by the Solar Dynamics Observatory. (Image credit: NASA/GSFC/SDO; via APOD) Read the full article
#coronalmassejection#fluiddynamics#magneticfield#magnetohydrodynamics#NASASDO#physics#plasma#science#solardynamics#sun
132 notes
·
View notes
Text

Active regions on the Sun combined to look something like a jack-o-lantern’s face on Oct. 8, 2014. The image was captured by NASA’s Solar Dynamics Observatory, or SDO, which watches the Sun at all times from its orbit in space. The active regions in this image appear brighter because those are areas that emit more light and energy. They are markers of an intense and complex set of magnetic fields hovering in the Sun’s atmosphere, the corona. This image blends together two sets of extreme ultraviolet wavelengths at 171 and 193 Ångströms, typically colorized in gold and yellow, to create a Halloween-like appearance. Image description: The Sun is surrounded by a plain black background. Bursts of light from active regions create the shape of a jack-o-lantern’s face – including glowing golden eyes and a mouth. Credit: NASA/SDO
#halloween#sun#nasa#sol#aesthetic#indie#grunge#universe#space#alternative#universo#stars#vintage#aesthetics
192 notes
·
View notes