#Renewable energy challenges
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

🌞 Empowering the Future with Renewable Energy Discover how innovations in renewable energy engineering are shaping a sustainable tomorrow. From harnessing solar power to overcoming challenges, we’re committed to creating a brighter, eco-friendly future. 🌍💡
#Renewable energy engineering#Solar photovoltaic technology#Wind energy advancements#Bioenergy innovations#Energy storage solutions#Renewable energy challenges#Algae-based biofuels
0 notes
Text
Electricity: An In-Depth Look at Why System Collapses Persist
The reliability and stability of electricity systems have become increasingly important as societies rely more on consistent power for everything from household appliances to critical infrastructure. However, despite advancements in technology and infrastructure, electricity systems continue to experience collapses that disrupt daily life and economic activities. This investigation delves into…
#aging infrastructure#cybersecurity threats#electricity systems#energy demand#grid failures#natural disasters#power grid resilience#power grid stability#regulatory challenges#renewable energy challenges#Touchaheart.com.ng
0 notes
Text
Beyond Hype: Tackling Real Challenges for a Thriving Renewable Energy Future
Renewable energy is no longer a futuristic dream, but a crucial part of the present. Yet, challenges remain. This article dives into the roadblocks hindering wider adoption and explores how we can move beyond non-performing aspects to unlock the full potential of clean energy sources.

0 notes
Text
Exploring the Science of Renewable Energy Technologies
Introduction These new renewable energy technologies are changing how we produce and consume energy. Where such technology is put into use, the harmful effects that alter the climate are significantly reduced. We at TechtoIO go deeper into the excellent science that drives these technologies, how they work, what their benefits are, and what we can expect in the future. Read to continue link..
#Science Explained#Tagsdecentralized energy systems#economic benefits of renewable energy#energy storage solutions#enewable energy technologies#environmental impact of renewable energy#geothermal energy#geothermal power#hydro energy#hydropower#renewable energy benefits#renewable energy challenges#renewable energy innovations#renewable energy policy#renewable energy research#renewable energy sources#smart grids#solar energy#solar panels#wind energy#wind turbines#business tech#trends#technology#tech news#science updates#science#nvidia drive#analysis#adobe cloud
1 note
·
View note
Text
I actually think Workers and Resources Soviet Republic needs a co-op mode. It's actually impossible to take care of everything in that game, you need a soviet. I'll take charge of steel and coal production, my comrade over there will oversee electrification, now this comrade, she's in charge of the bureau of urban planning and road building, and this other comrade places the tree props so that everything looks nice
#cosas mias#I wonder if you can actually make a carbon neutral 1970s Soviet Republic when you unlock renewable energies#would be so fun as a challenge
180 notes
·
View notes
Text




HAPPY NEW YEAR 2025
As we bid farewell to the past year and embrace the dawn of 2025, it's time to reflect on the opportunities and challenges that lie ahead. The start of a new year is a chance for fresh beginnings, setting goals, and making positive changes in our lives. Let's explore what the year 2025 has in store for us.
What Trends Will Shape 2025?
In the year 2025, we can expect to see significant advancements in technology, healthcare, sustainability, and more. With the rise of artificial intelligence, the Internet of Things, and renewable energy sources, the world is poised for a transformative year ahead. According to experts, the global economy is projected to grow by X% in 2025, driven by innovation and digitalization.
How Can You Make the Most of 2025?
To make the most of the opportunities that 2025 presents, it's essential to set clear goals, prioritize self-care, and stay adaptable in the face of change. Whether you're looking to advance your career, improve your health, or deepen your relationships, the key is to take proactive steps towards your aspirations. Studies show that people who set specific goals are X% more likely to achieve success compared to those who don't.
What Challenges Might Arise in 2025?
While the new year brings promise and excitement, it also comes with its own set of challenges. From geopolitical tensions to environmental concerns, individuals and communities will need to navigate various obstacles in 2025. It's crucial to stay informed, resilient, and proactive in addressing these challenges to create a better future for all.
How Can You Stay Positive and Resilient in 2025?
Staying positive and resilient in the face of adversity is key to thriving in 2025. Practicing mindfulness, cultivating a strong support network, and focusing on gratitude can help boost mental well-being and emotional resilience. Research shows that individuals who practice gratitude daily experience a X% increase in overall happiness and well-being.
As we embark on this new chapter, let's embrace the opportunities, overcome the challenges, and strive for a brighter future in 2025. Wishing you a happy and prosperous new year!
Welcome to a brand new year, full of endless possibilities and opportunities! As we step into 2025, it's the perfect time to reflect on the past year and set intentions for the year ahead. Whether you're looking to make big changes or simply want to embrace a fresh start, the new year is the perfect time to do so.
Setting Meaningful Goals
One of the best ways to kick off the new year is by setting meaningful goals for yourself. Take some time to think about what you want to achieve in the coming months and create a plan to make it happen. Whether it's focusing on personal growth, improving your health, or advancing in your career, setting goals can help you stay motivated and focused throughout the year.
Embracing Positive Changes
2025 is a blank canvas waiting to be filled with positive changes and new experiences. Embrace the opportunity to try new things, step out of your comfort zone, and challenge yourself to grow. Whether it's picking up a new hobby, traveling to a new destination, or making new friends, the new year is the perfect time to embrace change and welcome new opportunities into your life.
Practicing Gratitude
As you embark on this new year, don't forget to practice gratitude for all the blessings in your life. Take time each day to reflect on the things you are grateful for, whether it's your health, your loved ones, or the simple joys in life. Cultivating a mindset of gratitude can help you stay positive and focused on the good, even during challenging times.
Spreading Kindness
One of the best ways to make the world a better place in 2025 is by spreading kindness wherever you go. Whether it's a small act of kindness towards a stranger, volunteering in your community, or simply being there for a friend in need, every act of kindness has the power to make a difference. Let's make 2025 a year filled with compassion, empathy, and generosity towards others.
As you embark on this new year, remember that the possibilities are endless and the future is bright. Embrace the opportunities that come your way, stay true to yourself, and make 2025 a year to remember. Happy New Year!
#As we bid farewell to the past year and embrace the dawn of 2025#it's time to reflect on the opportunities and challenges that lie ahead. The start of a new year is a chance for fresh beginnings#setting goals#and making positive changes in our lives. Let's explore what the year 2025 has in store for us.#What Trends Will Shape 2025?#In the year 2025#we can expect to see significant advancements in technology#healthcare#sustainability#and more. With the rise of artificial intelligence#the Internet of Things#and renewable energy sources#the world is poised for a transformative year ahead. According to experts#the global economy is projected to grow by X% in 2025#driven by innovation and digitalization.#How Can You Make the Most of 2025?#To make the most of the opportunities that 2025 presents#it's essential to set clear goals#prioritize self-care#and stay adaptable in the face of change. Whether you're looking to advance your career#improve your health#or deepen your relationships#the key is to take proactive steps towards your aspirations. Studies show that people who set specific goals are X% more likely to achieve#What Challenges Might Arise in 2025?#While the new year brings promise and excitement#it also comes with its own set of challenges. From geopolitical tensions to environmental concerns#individuals and communities will need to navigate various obstacles in 2025. It's crucial to stay informed#resilient#and proactive in addressing these challenges to create a better future for all.#How Can You Stay Positive and Resilient in 2025?
0 notes
Text
Green Ammonia Market Statistics, Segment, Trends and Forecast to 2033
The Green Ammonia Market: A Sustainable Future for Agriculture and Energy
As the world pivots toward sustainable practices, the green ammonia market is gaining momentum as a crucial player in the transition to a low-carbon economy. But what exactly is green ammonia, and why is it so important? In this blog, we'll explore the green ammonia market, its applications, benefits, and the factors driving its growth.
Request Sample PDF Copy:https://wemarketresearch.com/reports/request-free-sample-pdf/green-ammonia-market/1359
What is Green Ammonia?
Green ammonia is ammonia produced using renewable energy sources, primarily through the electrolysis of water to generate hydrogen, which is then combined with nitrogen from the air. This process eliminates carbon emissions, setting green ammonia apart from traditional ammonia production, which relies heavily on fossil fuels.
Applications of Green Ammonia
Agriculture
One of the most significant applications of green ammonia is in agriculture. Ammonia is a key ingredient in fertilizers, and its sustainable production can help reduce the carbon footprint of farming. By using green ammonia, farmers can produce food more sustainably, supporting global food security while minimizing environmental impact.
Energy Storage
Green ammonia can also serve as an effective energy carrier. It can be synthesized when there is surplus renewable energy and later converted back into hydrogen or directly used in fuel cells. This capability makes it an attractive option for balancing supply and demand in renewable energy systems.
Shipping Fuel
The maritime industry is under increasing pressure to reduce emissions. Green ammonia has emerged as a potential zero-emission fuel for ships, helping to decarbonize one of the most challenging sectors in terms of greenhouse gas emissions.
Benefits of Green Ammonia
Environmental Impact
By eliminating carbon emissions during production, green ammonia significantly reduces the environmental impact associated with traditional ammonia. This aligns with global efforts to combat climate change and achieve sustainability goals.
Energy Security
Investing in green ammonia can enhance energy security. As countries strive to reduce their dependence on fossil fuels, green ammonia offers a renewable alternative that can be produced locally, minimizing reliance on imported fuels.
Economic Opportunities
The growth of the green ammonia market presents numerous economic opportunities, including job creation in renewable energy sectors, research and development, and new supply chain dynamics. As demand increases, investments in infrastructure and technology will drive innovation.
Factors Driving the Growth of the Green Ammonia Market
Regulatory Support
Governments worldwide are implementing policies and incentives to promote the adoption of green technologies. These regulations often include subsidies for renewable energy production and carbon pricing mechanisms, making green ammonia more competitive.
Rising Demand for Sustainable Solutions
With consumers and businesses becoming increasingly aware of their environmental impact, the demand for sustainable solutions is on the rise. Green ammonia aligns with this trend, providing an eco-friendly alternative to traditional ammonia.
Advancements in Technology
Ongoing advancements in electrolysis and ammonia synthesis technologies are making the production of green ammonia more efficient and cost-effective. As these technologies mature, they will further enhance the viability of green ammonia in various applications.
Conclusion
The green ammonia market represents a promising avenue for sustainable development across agriculture, energy, and transportation sectors. As technology advances and regulatory support strengthens, green ammonia is poised to become a cornerstone of the global transition to a greener economy. Investing in this market not only contributes to environmental preservation but also opens up new economic opportunities for innovation and growth.
#The Green Ammonia Market: A Sustainable Future for Agriculture and Energy#As the world pivots toward sustainable practices#the green ammonia market is gaining momentum as a crucial player in the transition to a low-carbon economy. But what exactly is green ammon#and why is it so important? In this blog#we'll explore the green ammonia market#its applications#benefits#and the factors driving its growth.#Request Sample PDF Copy:https://wemarketresearch.com/reports/request-free-sample-pdf/green-ammonia-market/1359#What is Green Ammonia?#Green ammonia is ammonia produced using renewable energy sources#primarily through the electrolysis of water to generate hydrogen#which is then combined with nitrogen from the air. This process eliminates carbon emissions#setting green ammonia apart from traditional ammonia production#which relies heavily on fossil fuels.#Applications of Green Ammonia#Agriculture#One of the most significant applications of green ammonia is in agriculture. Ammonia is a key ingredient in fertilizers#and its sustainable production can help reduce the carbon footprint of farming. By using green ammonia#farmers can produce food more sustainably#supporting global food security while minimizing environmental impact.#Energy Storage#Green ammonia can also serve as an effective energy carrier. It can be synthesized when there is surplus renewable energy and later convert#Shipping Fuel#The maritime industry is under increasing pressure to reduce emissions. Green ammonia has emerged as a potential zero-emission fuel for shi#helping to decarbonize one of the most challenging sectors in terms of greenhouse gas emissions.#Benefits of Green Ammonia#Environmental Impact#By eliminating carbon emissions during production#green ammonia significantly reduces the environmental impact associated with traditional ammonia. This aligns with global efforts to combat
0 notes
Text
dahabminers.com
#Bitcoin Mining#Cryptocurrency Mining#Blockchain Technology#Mining Hardware#ASIC Miners#GPU Mining#Mining Profitability#Renewable Energy for Mining#Crypto Economics#Decentralization#Mining Pools#Hashrate#Mining Algorithms#Proof of Work (PoW)#Bitcoin Economics#Crypto Market Trends#Mining Challenges#Green Energy Solutions#Mining Security#Crypto Regulatory News
0 notes
Text
Turning Waste into Power: How Kenyan Tea Farmers are Benefiting from Tea Clippings Gasification
A Deeside-based waste-to-energy company has unveiled its role on a project that will use waste tea clippings to make greener power for Kenyan farmers. l-r: Emily Mutindi Mutua of IITA, Paul Willacy of CSS, Niel Schulz from United Nations Industrial Development Organization, and Aarti Shah of IITA at a tea plantation in Limuru highlands, Kenya. (Photo credit: CSS) Kenya produces £1bn of tea per…
#Agricultural Innovation#aquaculture#biochar in farming#biomass for energy#carbon capture in farming#carbon footprint reduction#circular economy in agriculture#Compact Syngas Solutions#emissions reduction#energy challenges in tea farming#energy security in agriculture#energy shortages in Kenya#energy-efficient farming#gasification technology#global tea brands sustainability#green energy for farmers#hydrogen from gasification#improving crop yields#Kenya Climate Innovation Center#Kenya tea factories#Kenyan tea industry#methane fuel#power solutions for farmers#renewable energy in Kenya#renewable energy solutions#Scope 3 emissions reduction#soil fertility improvement#sustainable energy#sustainable tea farming#syngas production
0 notes
Text
Jamshedpur Engineer Soumya Deep Claims Breakthrough In Flywheel Energy Storage
Saumya Deep’s Patent Challenges Conventional Thermodynamics Laws Invention promises increased efficiency for renewable energy storage systems. JAMSHEDPUR – Saumya Deep, who is a mechanical engineer and school administrator, recently made an exciting announcement about a potentially revolutionary invention in flywheel energy storage technology. Deep’s patent, titled "A Process to Make Over Unity…
#A.P.J. Abdul Kalam Recognition#जनजीवन#Flywheel Energy Storage#Green Energy Technology#Jamshedpur Engineering Innovation#Jamshedpur Scientific Developments#Life#Over Unity Efficiency Claims#Patent Office Kolkata#Renewable Energy Breakthroughs#Saumya Deep Inventor#Thermodynamics Challenges
0 notes
Text
Dive into the future of Indian renewable energy stocks with this insightful blog. Discover how green energy is reshaping the investment landscape in India.
For more such blogs: Visit our blog site today: https://tradingbells.com/blogs And for Financial Advice reach us at: https://tradingbells.com/ Phone: +91 932 953 6100
#renewable energy#Indian Renewable Energy Stocks#investment opportunities#challenges#stock market trading#stock market
0 notes
Text
Navigating India's Renewable Energy Landscape: A Study on NPAs in RE Projects | Eninrac Reports
Exploring India's Renewable Energy Financing: Challenges & NPAs. Debt for 1.3GW RTC Project and Lender Dynamics.

0 notes
Text
The Future of Renewable Energy: Innovations and Trends
Introduction
The need for sustainable energy solutions has reached an unprecedented level of importance.. As global demand for energy continues to rise, the need for renewable energy sources becomes increasingly urgent. Renewable energy not only offers a cleaner alternative to fossil fuels but also promises to meet our energy needs sustainably. In this article, we at TechtoIO explore the future of renewable energy, focusing on the latest innovations and trends driving this vital sector forward. Read to continue link
#Innovation Insights#Tagsenergy storage solutions#future of renewable energy#green hydrogen#grid modernization#hydrogen energy#microgrids#renewable energy#renewable energy benefits#renewable energy challenges#renewable energy future#renewable energy innovations#renewable energy investment#renewable energy landscape#renewable energy policies#renewable energy technologies#renewable energy trends#solar technology#sustainable energy solutions#Best Fitness Gadgets to Boost Your Workout Routine#Technology#Science#business tech#Adobe cloud#Trends#Nvidia Drive#Analysis#Tech news#Science updates#Digital advancements
1 note
·
View note
Text
Flowing Forward: Nepal's Hydroelectric Future Enhanced by Innovative Energy Storage
Australia’s Hornsdale Power Reserve, a powerhouse in energy storage, boasts one of the country’s largest units, capable of reserving up to 150 MW in its advanced lithium-ion batteries. On the other side of the globe, the Bath County Pumped Storage Station in Virginia, USA, stands as a venerable giant in pumped hydro storage, operating since 1985. This monumental project strategically utilizes two…

View On WordPress
#ADELE#Australia&039;s Hornsdale Power Reserve#Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS)#Compressed Air Energy Storage (CAES)#energy storage#Energy Storage System (ESS)#Grid Stability#lithium-ion batteries#Nepal&039;s Hydroelectric Challenge#Pumped Hydro Storage#Renewable Energy Integration
0 notes
Text
Challenge: Autonomous Platform for Maintenance Operations in Solar Plants - Technology Org
New Post has been published on https://thedigitalinsider.com/challenge-autonomous-platform-for-maintenance-operations-in-solar-plants-technology-org/
Challenge: Autonomous Platform for Maintenance Operations in Solar Plants - Technology Org


How can we automate maintenance operations systems in solar plants to make harnessing renewable energy more efficient?
A2A, the Seeker of this Challenge, is looking to automate more of the maintenance operations related to the correct functioning of solar photovoltaic (PV) plants. Solvers are asked to create a detailed document about your plans or inform A2A about a system capable of bringing together as many maintenance operations as possible – including both extended and detail operations.
To continue to improve the overall efficiency of A2A’s PV plants, this Challenge asks Solvers to design a layout that will leverage a combination of hardware and software to create an automatic/autonomous system or platform capable of minimizing manual intervention, to become more cost-effective and reliable.
This is a Prize Challenge which requires a written proposal to be submitted. Awards will be contingent upon the theoretical evaluation of the proposal by A2A. For this Prize Challenge, Solvers are required to transfer all rights to the Intellectual Property (IP) in their proposed solution, to be awarded. A2A is willing to consider non-exclusive IP rights for a partial award.
Submissions to this Challenge must be received by 11:59 PM (US Eastern Time) on December 01st, 2023.
Source: Wazoku
You can offer your link to a page which is relevant to the topic of this post.
#2023#challenge#Competitions#december#Design#efficiency#energy#Energy & fuel news#Fundamental physics news#Hardware#how#intellectual property#layout#Link#photovoltaics#plants#pm#renewable#renewable energy#Software#Solar#solar plants#technology#time#transfer
0 notes
Text
The future of food in a changing climate

Written by: Jagriti Shahi, Business Analyst at Global Launch Base
Introduction
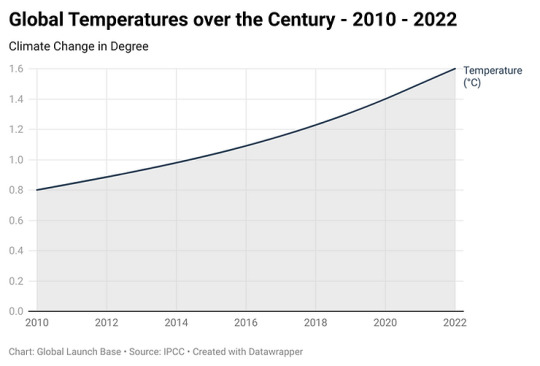
Figure 1: Global Temperature over the Century
This data shows that global temperatures have been rising steadily over the past few decades. The rate of warming is expected to accelerate in the coming years, if we do not take action to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) has warned that if we do not take action to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, global temperatures could rise by as much as 5.2 degrees Celsius by the end of the century. This would have devastating consequences for the planet, including more extreme weather events, rising sea levels, and mass extinctions. The data is clear that we are facing a serious challenge, and we need to take action now to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and mitigate the effects of climate change.
Climate Change and Food Production
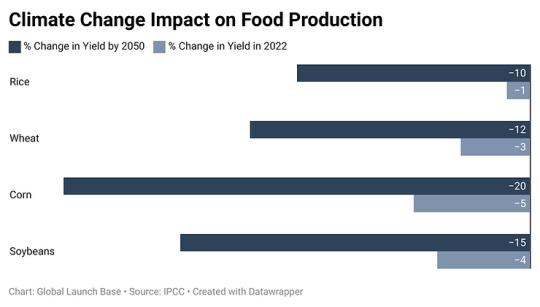
Figure 2: Climate Change Impact on Food Production
This data shows that the % change in yield of different crops by 2050 is already starting to be felt in 2022. For example, rice yields are already 1% lower in 2022 than they were in 2020. This is likely due to the combination of climate change and other factors, such as pests and diseases.
The trend is expected to continue in the coming years, as climate change continues to impact crop yields. This could have a serious impact on food security, as it will make it more difficult to produce enough food to feed the world's growing population.
The intricate relationship between climate change and food production is reshaping agricultural landscapes, challenging traditional practices, and compelling us to explore innovative solutions to ensure global food security. In this article, we delve into the intricate interplay between climate change and food production, highlighting the challenges faced and the potential pathways toward a more resilient future.
Altered Growing Conditions: One of the most immediate and palpable impacts of climate change on food production is the alteration of growing conditions. Rising global temperatures influence the length of growing seasons and shift the geographic suitability of certain crops. In some regions, this leads to reduced yields, as crops may experience stress due to excessive heat, prolonged droughts, or erratic precipitation patterns. Conversely, other areas might witness extended growing seasons, presenting opportunities to cultivate new varieties of crops.
Increased Pest and Disease Pressure: As the climate warms, pests and diseases that were once constrained by temperature limitations are expanding their ranges, posing significant threats to crops and livestock. The increased prevalence of pests can lead to reduced yields and necessitate more intensive use of pesticides, raising environmental concerns and potentially compromising food safety.
Water Scarcity and Agricultural Droughts: Climate change exacerbates water scarcity, a critical factor in agricultural productivity. Changing precipitation patterns and the intensification of droughts can jeopardize water availability for irrigation, which is essential for many crops. This can force farmers to compete for limited water resources, driving up costs and reducing overall agricultural output.
Impacts on Livestock Production: Livestock farming, a vital component of global food systems, is also vulnerable to the effects of climate change. Heat stress can lead to reduced livestock productivity, affecting meat and milk production. Moreover, changing forage availability due to altered precipitation patterns can challenge livestock feed supply, leading to increased costs for farmers.
Soil Degradation and Erosion: Climate change can exacerbate soil degradation and erosion, undermining agricultural sustainability. Intense rainfall events can lead to soil erosion, stripping away fertile topsoil and diminishing its ability to support crop growth. Soil degradation impacts soil structure, nutrient content, and water-holding capacity, posing a significant threat to long-term food security.
Adaptation and Mitigation Strategies: To address these challenges, a combination of adaptation and mitigation strategies is required.
Adaptation: Farmers can adopt climate-resilient practices such as crop diversification, agroforestry, and improved water management. Planting diverse crop varieties can spread risk and enhance resilience to changing conditions. Agroforestry systems, which combine trees with crops or livestock, can stabilize soil, conserve water, and provide additional income sources. Implementing efficient irrigation techniques and rainwater harvesting can help manage water scarcity.
Mitigation: Mitigating climate change through the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions is a critical step toward safeguarding food production. Sustainable land management, reforestation, and the adoption of renewable energy sources can contribute to lowering emissions from the agricultural sector.
7. Technological Innovations: Advancements in technology hold promise for enhancing climate resilience in food production. Precision agriculture utilizes data-driven approaches to optimize resource use, monitor crop health, and reduce waste. Climate-resilient crop varieties developed through traditional breeding or genetic modification can enhance yields under changing conditions.
8. Policy and International Cooperation: Global efforts are indispensable in addressing the complex challenges posed by climate change and food production. International agreements and policies can incentivize sustainable agricultural practices, support smallholder farmers, and promote technology transfer. Investment in research and development can drive innovation and provide farmers with the tools they need to adapt to changing conditions.
Key players in the market:
Impossible Foods: Impossible Foods is a food technology company that makes plant-based meat products that are indistinguishable from real meat. Impossible Foods' products use less water, land, and energy than traditional meat, and they emit significantly fewer greenhouse gasses.
Danone: Danone is a food and beverage company that has set a goal of becoming carbon neutral by 2050. Danone is working to reduce its greenhouse gas emissions across its entire value chain, from the farm to the fork.
Innovative Agricultural Practices
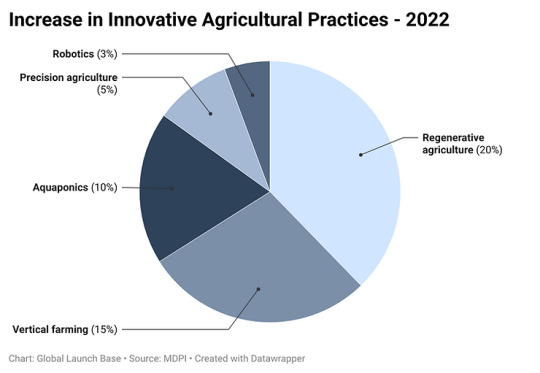
Figure 3: Increase in Innovative Agricultural Practices
This data shows that there is a growing interest in innovative agricultural practices. This is likely due to the increasing awareness of the environmental impact of traditional agriculture and the need for more sustainable food production methods.
Innovative Agricultural Practices: Navigating the Future of Sustainable Food Production
In a world where climate change and environmental degradation pose unprecedented challenges to traditional agricultural practices, innovation emerges as a beacon of hope. Innovative agricultural practices are essential not only for meeting the growing global demand for food but also for ensuring the long-term sustainability of our planet. In this article, we explore a spectrum of groundbreaking techniques that are transforming the way we cultivate crops, rear livestock, and manage natural resources.
Agroecology: Harmonizing Nature and Agriculture: Agroecology is a holistic approach that seeks to mimic natural ecosystems within agricultural systems. By fostering biodiversity, enhancing soil health, and minimizing external inputs, agroecological practices promote resilient and sustainable food production. Techniques such as intercropping, cover cropping, and crop rotation reduce the reliance on synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, mitigating the environmental impact of conventional agriculture.
Precision Agriculture: Merging Technology and Farming: Precision agriculture leverages cutting-edge technologies, including GPS, remote sensing, and data analytics, to optimize resource utilization and enhance productivity. By precisely mapping variations in soil and crop conditions, farmers can tailor irrigation, fertilization, and pest control measures, minimizing waste and maximizing yields. Drones, sensors, and automated machinery further streamline operations and minimize environmental footprint.
Vertical Farming and Hydroponics: Farming in Tight Spaces: Vertical farming and hydroponics redefine the boundaries of traditional agriculture by enabling food production in urban environments and underutilized spaces. Vertical farms stack crops in vertical layers, utilizing artificial lighting and controlled environments to optimize growth. Hydroponics, a soilless cultivation method, delivers water and nutrients directly to plant roots, reducing water usage and enabling year-round production.
Conservation Tillage and No-Till Farming: Preserving Soil Health: Conventional tillage practices disrupt soil structure and contribute to erosion, compaction, and carbon loss. Conservation tillage and no-till farming minimize soil disturbance, maintaining soil structure and organic matter. This enhances water retention, reduces erosion, and sequesters carbon, making farms more resilient to extreme weather events and contributing to climate change mitigation.
Aquaponics: Symbiotic Aquaculture and Hydroponics: Aquaponics integrates aquaculture (fish farming) and hydroponics in a mutually beneficial system. The fish waste provides nutrients for hydroponically grown plants, which, in turn, filter and purify the water for the fish. This closed-loop system conserves water, eliminates the need for synthetic fertilizers, and yields both protein and vegetables.
Controlled Environment Agriculture: Climate-Proofing Crop Production: Controlled environment agriculture (CEA) encompasses greenhouse and indoor farming, allowing year-round cultivation of crops under precisely managed conditions. CEA protects plants from extreme weather, pests, and diseases while optimizing resource efficiency. High-tech greenhouses use advanced climate control systems, enabling growers to fine-tune temperature, humidity, and light levels for optimal plant growth.
Permaculture: Designing Sustainable Ecosystems: Permaculture draws inspiration from natural ecosystems to create self-sustaining and regenerative agricultural systems. By integrating diverse plant and animal species, permaculture designs promote ecological harmony, resilience, and long-term productivity. Food forests, which emulate natural forests with layers of edible plants, exemplify permaculture principles and provide a wide array of harvestable foods.
Urban Agriculture: Nourishing Cities Locally: Urban agriculture transforms urban landscapes into productive spaces, mitigating the environmental impact of food transportation and enhancing food security. Rooftop gardens, community plots, and vertical farms bring fresh produce to city dwellers while fostering a sense of community and reconnecting people with their food sources.
Key players in the market:
Ceres Imaging: Ceres Imaging uses satellite imagery and artificial intelligence to help farmers make more informed decisions about their crops. Ceres Imaging's products can help farmers to identify pests and diseases early on, optimize their irrigation practices, and improve their yields.
AeroFarms: AeroFarms' vertical farms are located in urban areas, which helps to reduce the company's carbon footprint. AeroFarms also uses recycled materials in its farms and packaging, and it is committed to reducing its environmental impact.
Resilient Crop Varieties
The development of climate-resilient crop varieties through breeding and genetic modification is crucial. Scientists are working on crops that can withstand higher temperatures, require less water, and exhibit resistance to pests and diseases. Gene editing techniques like CRISPR-Cas9 offer precise methods to enhance desired traits, potentially revolutionizing crop production. However, careful consideration of ethical and environmental implications is essential in adopting such technologies.
As the world grapples with the uncertainties of a changing climate, ensuring a steady and nutritious food supply has become a paramount challenge. Resilient crop varieties, born from innovative breeding techniques and scientific advancements, offer a glimmer of hope in the face of shifting weather patterns, changing pest dynamics, and dwindling natural resources. In this article, we delve into the significance of resilient crop varieties and the transformative potential they hold for securing global food security.
1. The Need for Resilience
Traditional crop varieties, often developed for specific regions and historical climatic conditions, are increasingly vulnerable to the unpredictable and extreme weather events wrought by climate change. Droughts, floods, heatwaves, and new pest and disease pressures threaten agricultural productivity and food availability. Resilient crop varieties possess traits that enable them to withstand and recover from these challenges, ensuring a consistent supply of food even in the face of adversity.
2. Breeding for Resilience
The art and science of breeding resilient crop varieties involve a combination of classical breeding methods and cutting-edge technologies. Plant breeders select and cross plants with desirable traits, such as drought tolerance, disease resistance, and improved nutrient uptake. Advancements in molecular biology, genetic mapping, and gene editing techniques like CRISPR-Cas9 enable scientists to precisely manipulate plant genomes, accelerating the development of resilient varieties.
3. Drought-Resistant Varieties
Drought is a major concern for agricultural regions worldwide. Resilient crop varieties with enhanced water-use efficiency and deep root systems can thrive with limited water availability. Genetic modifications that control stomatal opening and closing, reducing water loss through transpiration, are being explored to confer drought tolerance.
4. Disease and Pest Resistance
Pests and diseases can devastate crop yields, leading to food shortages and economic losses. Resilient crop varieties can be engineered with natural pest repellents, reducing the need for chemical pesticides. Genetic markers linked to disease-resistance genes are identified to expedite breeding efforts, resulting in more robust crops.
5. Heat and Cold Tolerance
Extreme temperatures, whether scorching heat or chilling cold, disrupt plant metabolism and growth. Resilient crop varieties can be developed with genetic traits that enable them to thrive in temperature extremes. Heat-tolerant crops might possess heat-shock proteins that protect cellular structures, while cold-tolerant crops could have antifreeze proteins that prevent ice-crystal formation.
6. Salinity and Soil Adaptation
As sea levels rise and agricultural lands become salinized, crops need to tolerate higher levels of salt in the soil. Resilient crop varieties can be bred to thrive in saline conditions, ensuring continued food production on affected lands. Breeding for improved nutrient uptake and utilization also contributes to healthier plants and improved yields.
7. Biodiversity and Resilience
Maintaining a diverse array of crop varieties is essential for building resilience. Traditional and heirloom varieties often possess unique traits that can be crucial for adaptation. Initiatives to conserve and promote local crop diversity are essential for safeguarding food security in a changing world.
8. Ethical and Environmental Considerations
While resilient crop varieties hold immense promise, ethical and environmental considerations must guide their development and deployment. Ensuring that genetic modifications do not inadvertently harm ecosystems or reduce genetic diversity is a critical aspect of responsible breeding practices.
Key players in the market:
Monsanto: Monsanto is a multinational agricultural biotechnology corporation that develops and markets crop seeds, herbicides, and other agricultural products. Monsanto has a portfolio of resilient crop varieties that are tolerant to a variety of abiotic stresses, as well as some biotic stresses, such as pests and diseases.
Seminis: Seminis is a subsidiary of Bayer CropScience that develops and markets crop seeds. Seminis has a portfolio of resilient crop varieties that are tolerant to a variety of abiotic stresses, such as drought, heat, and salinity.
Sustainable Resource Management
Sustainable management of natural resources is pivotal to food security in a changing climate. Efficient water management, such as rainwater harvesting and drip irrigation, conserves water and ensures its availability during dry spells. Soil health restoration through techniques like cover cropping and reduced tillage enhances soil's capacity to retain water and nutrients. Integrated pest management minimizes chemical use and maintains a balance between pests and their natural predators.
Resilience Through Resource Efficiency: Sustainable resource management serves as a cornerstone for building resilience in the face of climate-related uncertainties. Efficient utilization of resources, such as water, energy, and soil, is paramount to ensure that food systems remain productive and adaptable. Through water-efficient irrigation methods, reduced energy consumption, and soil health enhancement, sustainable practices bolster the capacity of agricultural systems to weather the impacts of altered climatic conditions.
Water: A Precious Commodity: In a changing climate, water scarcity and variability become magnified challenges for agricultural production. Sustainable resource management involves optimizing water use through techniques like drip irrigation, rainwater harvesting, and integrated water management systems. By safeguarding water sources, improving distribution, and minimizing wastage, we ensure a consistent supply of this invaluable resource to sustain food production.
Soil Health and Carbon Sequestration: Healthy soils play a pivotal role in both climate mitigation and adaptation. Sustainable resource management practices prioritize soil health through reduced tillage, cover cropping, and organic matter enrichment. These strategies not only enhance soil fertility and water retention but also contribute to carbon sequestration, mitigating the atmospheric buildup of greenhouse gasses.
Biodiversity Conservation for Resilient Ecosystems: Preserving biodiversity within agricultural landscapes is central to sustainable resource management. Diverse ecosystems are more resilient to climatic fluctuations and provide natural pest control, pollination services, and soil fertility. Agroecological approaches, such as crop rotation, agroforestry, and maintaining habitat corridors, support diverse species and foster ecosystem health.
Circular Economy and Waste Reduction: A circular economy approach within food systems minimizes waste and resource depletion. Sustainable resource management encourages reducing food waste, adopting efficient packaging, and promoting composting or recycling of organic matter. By embracing a circular mindset, we reduce the burden on landfills, conserve resources, and limit the environmental footprint of food production and consumption.
Renewable Energy Integration: As we envision a climate-resilient food future, the integration of renewable energy sources into agricultural operations becomes essential. Sustainable resource management emphasizes transitioning from fossil fuels to renewable energy to power irrigation, processing, and distribution systems. Solar panels, wind turbines, and biogas facilities contribute to reducing emissions and enhancing overall sustainability.
Localized Food Systems and Resilient Communities: Sustainable resource management advocates for the development of localized food systems that prioritize regional resilience. By supporting small-scale farmers, community gardens, and farmers' markets, we enhance local food security and reduce the carbon footprint associated with long-distance transportation.
Policy, Collaboration, and Global Action: Effective sustainable resource management requires a collaborative effort encompassing policymakers, researchers, industries, and consumers. Governments can incentivize sustainable practices through policies, subsidies, and regulations. International cooperation is vital to share knowledge, innovations, and best practices, ensuring a collective response to the global challenge of climate change.
Key players in the market:
Veolia: Veolia is a French multinational water, waste management and energy services company. Veolia has a long history of sustainable resource management, and it is one of the world's leaders in the field. Veolia's water treatment plants are some of the most efficient in the world, and the company is also a leader in waste recycling and energy recovery.
Ecolab: Ecolab is an American multinational provider of water, hygiene and energy technologies and services. Ecolab is a leader in sustainable resource management, and the company has a number of programs and initiatives in place to reduce its environmental impact. Ecolab's water conservation programs have helped to save billions of gallons of water, and the company's energy efficiency programs have helped to reduce its energy consumption by millions of kilowatt-hours.
Climate-Resilient Livestock Farming
Livestock production is another area greatly affected by climate change. Heat stress reduces livestock productivity, and changing grazing patterns impact feed availability. Transitioning towards climate-resilient livestock farming involves improving animal genetics, optimizing feed formulations, and implementing better shelter and cooling systems. Alternative protein sources like insect farming and lab-grown meat might also play a significant role in ensuring a sustainable and climate-resilient protein supply.
Adapting to Changing Conditions: Climate-resilient livestock farming entails embracing adaptable practices that mitigate the impact of a changing climate on animal health, productivity, and well-being. Heat stress, a growing concern due to rising temperatures, can lead to decreased feed intake, reduced reproductive efficiency, and overall livestock productivity. Employing cooling measures such as shade structures, misting systems, and proper ventilation helps mitigate heat stress and maintain optimal livestock conditions.
Improved Breeding for Resilience: Selecting and breeding animals for climate resilience is a key facet of climate-resilient livestock farming. Breeding programs aim to develop livestock varieties that are better equipped to withstand heat stress, disease outbreaks, and changing feed availability. Genetic traits that confer heat tolerance, disease resistance, and efficient nutrient utilization contribute to animals better suited for a changing climate.
Sustainable Feed Sourcing: Climate-resilient livestock farming integrates sustainable feed sourcing practices to ensure the long-term availability of nutritious and environmentally friendly animal diets. Livestock production is a significant contributor to deforestation and land degradation, often driven by the demand for animal feed crops. Transitioning to alternative feed sources, such as algae, insect-based protein, and agroforestry byproducts, minimizes environmental impact while ensuring adequate nutrition for animals.
Precision Livestock Management: Advances in technology play a pivotal role in climate-resilient livestock farming through precision livestock management. Sensors, data analytics, and artificial intelligence enable real-time monitoring of animal health, behavior, and productivity. This data-driven approach enhances disease detection, facilitates targeted interventions, and optimizes resource utilization, contributing to both economic efficiency and animal welfare.
Agroecological Integration: Integrating livestock into agroecological systems fosters synergy between animal and crop production. Agroforestry, where livestock graze in wooded areas, enhances feed availability, carbon sequestration, and biodiversity. Rotational grazing, which involves moving animals between different pastures, prevents overgrazing, improves soil health, and enhances forage quality.
Alternative Livestock Systems: Exploring alternative livestock systems offers a promising avenue for climate resilience. Silvopasture combines trees with pasture, providing shade, forage, and carbon sequestration potential. Aquaculture and integrated fish-farming systems can complement traditional livestock production, diversifying income sources and protein supply.
Community Engagement and Knowledge Sharing: Climate-resilient livestock farming thrives in a collaborative environment where farmers, researchers, and communities exchange knowledge and best practices. Farmers' networks, extension services, and capacity-building initiatives facilitate the dissemination of climate-resilient techniques and encourage collective adaptation to changing conditions.
Policy Support and Incentives: Effective policies and incentives play a pivotal role in fostering climate-resilient livestock farming. Government support for research and development, funding for sustainable practices, and market incentives for climate-resilient products incentivize farmers to adopt and invest in these strategies.
Key players in the market:
Alltech: Alltech is a global animal nutrition company that develops and markets products and services for livestock producers. Alltech has a program called Alltech Climate Challenge that helps livestock producers reduce their environmental impact. Alltech Climate Challenge provides farmers with training on climate-friendly livestock farming practices, such as methane mitigation and water conservation.
Zoetis: Zoetis is a global animal health company that develops and markets products and services for livestock producers. Zoetis has a program called Zoetis Sustainable Agriculture that helps livestock producers improve their environmental performance. Zoetis Sustainable Agriculture provides farmers with training on sustainable livestock farming practices, such as reducing antibiotic use and improving manure management.
Reducing Food Waste and Loss
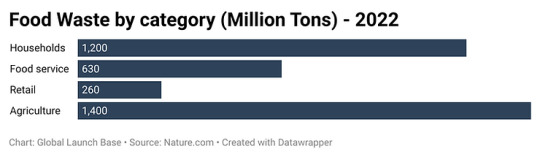
Figure 4: Food Waste by Category
This data shows that food waste is a major problem worldwide. It is estimated that one-third of all food produced for human consumption is wasted. This waste has a significant environmental impact, as it contributes to climate change, water pollution, and land degradation. Households are the biggest contributors to food waste, followed by food service and retail. Agriculture also contributes a significant amount of food waste, but this is often due to factors beyond human control, such as crop losses due to pests and diseases.
The Scale of the Challenge: Food waste and loss constitute a staggering paradox in a world where millions go hungry. According to the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), approximately one-third of all food produced for human consumption is lost or wasted annually. In a changing climate, this inefficiency takes on heightened significance, given the increased strain on agricultural resources and the urgent need to maximize production.
Climate Impacts and Food Loss: The impacts of climate change, including extreme weather events, temperature fluctuations, and altered growing seasons, exacerbate the problem of food waste and loss. Disrupted supply chains, reduced crop yields, and increased pest and disease pressures contribute to losses at every stage of the food system, from production to consumption.
Farm-Level Strategies: At the production level, climate-resilient agricultural practices are essential in minimizing food loss. Crop diversification, improved storage facilities, and effective pest management contribute to preserving harvests. Climate-smart irrigation and water management systems ensure that water resources are used efficiently, reducing losses due to drought-related crop failures.
Post-Harvest Innovations: Innovations in post-harvest technologies play a pivotal role in reducing food loss. Cold storage, modified atmosphere packaging, and controlled atmosphere storage systems extend the shelf life of perishable goods. Solar drying and value-addition techniques enable smallholder farmers to process excess produce into value-added products, minimizing waste and increasing income.
Efficient Distribution and Supply Chains: Efficient distribution and supply chains are central to addressing food waste. Improving transportation infrastructure, embracing digital solutions for real-time inventory management, and facilitating coordination between producers, distributors, and retailers can prevent perishable goods from spoiling before reaching consumers.
Consumer Behavior and Awareness: Shifting consumer behavior towards responsible consumption is essential in curbing food waste. Education campaigns, labeling initiatives, and community-driven efforts raise awareness about the consequences of wasting food and empower individuals to make conscious choices.
Food Rescue and Redistribution: Food rescue organizations and surplus food redistribution networks salvage edible food that would otherwise be discarded. These initiatives divert surplus produce from landfills to those in need, addressing both food waste and food insecurity simultaneously.
Policy and Industry Leadership: Government policies and private sector initiatives play a crucial role in reducing food waste and loss. Regulatory measures, tax incentives, and industry commitments to zero-waste goals drive systemic change across the food supply chain.
Key players in the market:
Too Good To Go: Too Good To Go is a Danish company that has developed an app that connects consumers with businesses that have surplus food. Businesses can list their surplus food on the app, and consumers can purchase it at a discounted price. Too Good To Go has helped to prevent millions of meals from being wasted.
RapidPricer: RapidPricer is an AI-powered pricing platform that helps retailers automate their pricing and promotions. The platform uses deep learning algorithms and machine vision to dynamically price products to match their real-time value based on competition, product lifecycle, and market conditions. With deep expertise in retail pricing, RapidPricer computes merchandising actions for real-time execution in a retail environment.
Policy and Global Cooperation
Mitigating the impact of climate change on food production requires global cooperation and effective policy measures. International agreements and frameworks can promote sustainable agriculture, support smallholder farmers, and facilitate technology transfer to developing countries. Financial incentives, subsidies for sustainable practices, and research funding can drive innovation and promote the adoption of climate-resilient technologies. 1. Policy as a Catalyst for Change Sound and visionary policies are the cornerstone of a resilient food system. Governments play a pivotal role in shaping the trajectory of food production, distribution, and consumption through regulations, incentives, and strategic planning. Policies that promote climate-resilient agriculture, sustainable resource management, and reduced food waste set the stage for a more secure and sustainable food future. 2. Climate-Smart Agriculture Policies Climate-smart agricultural policies harness innovative approaches to enhance productivity, mitigate climate impacts, and reduce emissions. By incentivizing the adoption of climate-resilient practices, such as crop diversification, agroforestry, and improved irrigation, governments foster adaptive capacity and mitigate the vulnerabilities of agriculture to a changing climate. 3. Research and Innovation Funding Government funding for research and innovation accelerates the development and adoption of climate-resilient agricultural technologies and practices. Support for breeding drought-tolerant crops, developing efficient irrigation systems, and advancing precision agriculture empowers farmers to overcome the challenges posed by climate change. 4. International Agreements and Frameworks The global nature of climate change demands international collaboration. Agreements like the Paris Agreement underscore the commitment of nations to combat climate change and lay the groundwork for coordinated efforts in the agricultural sector. Frameworks for technology transfer, capacity-building, and financial support ensure that countries with varying levels of resources can participate in climate-resilient food production. 5. Sustainable Trade and Supply Chain Policies International trade and supply chains are integral to global food security. Policies that promote sustainable trade practices, reduce trade barriers and ensure equitable access to markets contribute to stable food supplies and price stability, benefiting both producers and consumers. 6. Strengthening Smallholder Resilience Policies that specifically target smallholder farmers, who are often the most vulnerable to climate impacts, play a vital role in enhancing food security. Financial support, access to credit, and extension services empower smallholders to adopt climate-resilient practices and diversify their livelihoods. 7. Public-Private Partnerships Collaboration between governments, private sector entities, and civil society organizations amplifies the impact of climate-resilient policies. Public-private partnerships drive innovation, leverage resources, and facilitate knowledge exchange, ensuring that policies are implemented effectively and that a wide array of stakeholders are engaged. 8. Education and Consumer Awareness Policies that promote consumer education and awareness campaigns raise consciousness about sustainable consumption practices. Clear labeling, educational initiatives, and public awareness campaigns inform consumers about the environmental and social impacts of their food choices, influencing demand and driving market shifts.
Conclusion
The future of food in a changing climate is a complex challenge that demands immediate attention and collaborative efforts. Innovations in agriculture, sustainable resource management, and climate-resilient practices offer hope for ensuring food security for a growing global population. By embracing new technologies, promoting sustainable practices, and fostering international cooperation, we can navigate the challenges presented by a changing climate and build a more resilient and secure food future for generations to come. ------------------------------------ Global Launch Base helps international startups expand in India. Our services include market research, validation through surveys, developing a network, building partnerships, fundraising, and strategy revenue growth. Get in touch to learn more about us. Contact Info: Website: www.globallaunchbase.com LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/globallaunchbase/ Email: [email protected]
#Climate change#Food security#Sustainable agriculture#Climate-resilient farming#Adaptation strategies#Agricultural innovation#Climate-smart technologies#Global food systems#Environmental impact#Crop diversity#Resource management#Food supply chain#Resilient livestock farming#Circular economy#Policy initiatives#Smallholder resilience#Sustainable sourcing#Climate challenges#Food waste reduction#Renewable energy integration
0 notes