#POV tips
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Note
Your first pride story was touching and all but you still married a man.
Yeah, bisexuals do that sometimes.
#thank god the first people i encountered in the queer community didn't have this shitty pov#because i spent 16 years feeling like an imposter in my ultra conservative christian community because i liked girls and boys#and if my first terrified forays into the queer community told me i was an imposter there as well#unless i performed my queerness to their specific liking I cant imagine how lost I would have felt#pro tip: if you're telling someone they can't be part of the family unless they deny a part of themselves#you are part of the problem#bisexual#lgbtq#queer#gatekeeping
333 notes
·
View notes
Text
Writing Notes: How to Choose POV

A Quick Guideline on Choosing POV
Refresher: Definitions
First-Person Singular: First-person singular narration uses the pronoun “I” and is the most commonly used form of first-person point of view. This style is perfect for character-driven novels and creates a close, immersive connection between the reader and the story. However, this type of narration limits the author and the reader to a single character’s experiences, feelings, and knowledge.
First-Person Plural: This first-person narration style utilizes the pronoun “we” and is less commonly used. It combines the intimacy associated with first-person with the flexibility of third-person omniscient. First-person plural can be effective when done well but can be tedious and is limited to the collective voice.
Second Person: Second person utilizes “you” for the narrator but is more commonly used in short stories. This style easily fosters close bonds between the readers and the characters as you start to feel as if they are you.
Third-Person Limited: Narration in third person limited relies on she/her, he/him, they/them, etc., pronouns as well as the character’s name. This point of view limits the author and reader to one character’s perspective allowing the writer to exercise the closeness of first-person singular through thoughts and feelings while also offering the broader perspective of third person.
Third-Person Omniscient: This type of narration also utilizes the character’s preferred personal pronouns and name and gives the narrator god-like storytelling abilities as they can reveal any character’s thoughts, go to any time or setting, know information the characters are unaware of, and comment on events in the past, present, and future. The degree to which these abilities are used is up to you. Third-person omniscient is popular among novelists with large casts and complex plots. However, this style can lead to too many shifts in perspective.
Tips for Choosing POV
You may find that you have a preferred point of view and then realize it’s not a good fit once you start writing your story. Many writers worry about finding their voice, but sometimes the story finds it for you. If you’re unsure which point of view to choose, consider these tips to help you pick.
Explore your options. You won’t know which POV to use unless you try them all. Try writing or rewriting a scene from your story in each POV to see which style fits your novel best.
Establish your POV. Once you’ve picked a style, stick to it and let your audience know which character they’re experiencing the story through.
Note limitations. POV will decide what information your character is privy to and thus determine their actions and opinions. Take time to review your work with your character’s limitations in mind to keep your writing accurate.
Don’t be afraid to change. If you find yourself drifting into another POV as your novel progresses, don’t shy away from revising your work into the best perspective for your story. It’s also important to note that some books shift from first to third to second, and it may benefit you to find examples of novels with varied narration to help you learn to master this style.
Source ⚜ More: Writing Notes & References ⚜ POV
#writing notes#on writing#pov#writing tips#writing advice#writeblr#writing basics#writing refresher#writing inspiration#creative writing#literature#writers on tumblr#writing prompt#poetry#poets on tumblr#spilled ink#dark academia#writing reference#light academia#studyblr#writing ideas#raphael kirchner#art nouveau#writing resources
152 notes
·
View notes
Text


#narutoedit#narutographic#oldanimeedit#dailynaruto#fyeahnaruto#allanimanga#dailyanime#fyanimegifs#naruto uzumaki#sasuke uchiha#naruto#i know naruto is just enjoying how sasuke wants a tip on climbing trees#but TBH here im thinking in narutos pov: hE BLUSHES OHOHOHO look at the faces he can make#im just so gay for them (im a woman)#land of waves arc
634 notes
·
View notes
Text
A Quick Guide on POVs and Tenses
First person
First person perspective uses I/my and typically also accompanies present tense:
"I walk over to see what’s happening"
However, it can be used with any tense. It is the closest you can get to the character—it tends to have unfiltered access to their thoughts, feelings, ideas, memories, etc. and is the most intimate. It goes great for stories that want to stay ‘in the moment’ and rely on lots of internal dialogue.
2. Second person
Probably the least common—I’ve only ever seen it in fanfic and maybe a choose-your-own-adventure novel or two. This perspective uses you/your, and also tends to go with present tense.
“You walk over to the stall and survey the goods.”
It’s a really unique way of telling a story that brings the reader the closest to the action—however, it doesn’t have a lot of room for character development as it relies on fitting anyone who is reading it, leaving the POV ‘character’ a shell to be filled by the reader rather than its own character.
3. Third person omniscient
Third person perspectives are outside of the character. Typically they are joined with past-tense. They use pronouns he/she/they/his/hers/theirs, etc.
'Omniscient' means this narrator has full access to the knowledge of the narrative, as well as all the characters in it. It is a bit of an uncommon perspective, as it means the narrator can and will easily “head-hop” which can be a difficult technique to do well.
“He inhaled, staring icy daggers at Kate across from him. She knew instantly she had said the wrong thing, but had no idea how to take it back.”
(Notice how we’re both in the male character’s head, as well as Kate’s.)
This perspective keeps the readers at a distance, but allows them access to every character in the story. Beware, it can be difficult to build tension or keep secrets when using this perspective!
4. Third person limited/subjective
This perspective is probably the most common and my personal favourite. It has the same rules for third person, but instead of the narrator having full access to all the information, they only have access to the information the character they are following knows, or the thoughts/feelings they are having.
“He inhaled, staring icy daggers at Kate across from him. She had said the wrong thing, and now just looked back at him with big eyes, her mouth agape as she hesitated on what to say next.”
(Notice how in this example, Kate’s thoughts are only guessed at from our character’s POV. He doesn’t actually know what’s going on in her head, so neither does our narrator)
Third person limited is probably the most popular because it is really effective at being a very invisible way of telling story. As well, it’s great for building tension, keeping secrets, and can explore unique character perspective and miscommunication.
Tenses:
Present tense
Things are happening right now.
“I begin my walk to the store.”
“He says as he steps through the gate.”
“You follow a long path through the trees.”
2. Past tense
Things already happened.
“I began my walk to the store.”
“He said as he stepped through the gate.”
“You followed a long path through the trees.”
3. Future tense
Things will happen—things to come.
“I would begin my walk to the store.”
“He will say, stepping through the gate.”
“You will follow a long path through the trees.”
#writing#writers#writing tips#writing advice#writing inspiration#creative writing#writing community#books#film#filmmaking#screenwriting#novel writing#fanfiction#writeblr#povs and tenses#guide#character perspective
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
Juggling Multiple POVS (Writing Like A Movie)
At one point in a WIP, I had one character being held captive, two characters on a quest to bust them out, two characters racing to join the jailbreakers, four with no idea any of this is going on because they think they’re all dead, and then of those four, two split off on a side quest, and the remaining two also split off on various other tasks.
If you’re keeping track, that meant I had a book rotating between 6 different subplots and about 9 POVS at the absolute worst, and then about 4 subplots once characters finally reunited with each other.
It was… a lot.
Now this was never published so I don’t know how well it would have been received but it was a sequel and its predecessors received good feedback so I think I know what I’m doing.
—
When you’re committing to a book with Multiple POV, you’ve generally got two roads you can go down: predetermined narrators or ~cinematic~.
You can select a set number of characters to narrate regardless of how many exist in your ensemble cast, and no matter how many split off on their own subplots, those predetermined narrators will be keeping up with the story. These types of books tend to have shorter chapters and single narrators for chunks of chapters at a time with no cutting in between and fairly long breaks in between a character’s chunks of POV. Or, they have entire sections of book dedicated to them with clear markers between POVS.
The easy example here is Heroes of Olympus that I believe had up to 4 narrators per book despite a main cast of about 8 characters depending on the book. The first two were 3-POV, for each of the 3 questers, and then once the whole party was together the POVS were determined by who split off into which groups. Rather infamously, in my opinion, the last book of the series did not give a POV to the two legacy characters and the former protagonist of the first series, which was… a choice. I think the point was that Riordan gave them their spotlight in book 4 and was passing the torch to the new batch for book 5, but for many of us, who had no idea we’d never get a POV of these two again, it was mighty disappointing.
These books also had no chapter titles and instead had banner-style chapters where you had NICO or PIPER in massive banners over the start of each chapter, which was also a choice as going without chapter titles (or even numbers, they’re in roman numerals) makes it a lot harder to search things up in books 500+ pages long.
Who narrates when is less determined by who the most important character of the chapter is, for the most part. It might be Hazel’s moment, but she’s not a narrator of this book, so it’s in Piper POV (or Nico’s forced coming out moment in Jason POV which I will never forgive Riordan for). It’s just a dice roll of whoever it lands on which can lead to some moments, like the Nico incident, that really should have been in Nico POV, but the structure of the story demanded otherwise.
I don’t really love this style of multiple POV. Personally, I think it’s rather inflexible and doesn’t take full advantage of what MPOV can do. But that’s personal opinion so here’s some strengths:
It doesn’t jump around as much and with a minimal set of narrators, it’s more streamlined. You know what to expect going in with no surprises
It forces the author to get creative within the bounds of the POV they’re stuck in
The extra time with a single narrator can be a solid guide rail through a complicated plot piece
—
Or, you can write a more ~cinematic~ MPOV. I don’t know the proper term for this, if it exists, but this style of MPOV is when you basically free-for-all. Anyone can narrate whenever the scene demands and this either grants you a book with short chapters, but one narrator per short chapter, or multiple narrators within a single chapter, as you’d film a movie or an episode of TV with multiple perspectives per set piece.
This isn’t a random grab-bag of narrators. It demands a lot of restraint. This kind of MPOV is entirely based on who is the most important character of the scene, or who’s POV would be the most interesting to view the scene through.
ENNS is written in cinematic MPOV, with a far smaller rotating cast than the WIP I mentioned at the top of this post. It starts out slow with the protagonist for the first two chapters as the only narrator, then mid-chapter 3, I give a cue that he’s going to be unable to narrate the next bit, and I switch to my deuteragonist. I don’t give banner headings. I don’t give my characters entire chapters because the POV structure demands it. I just start whichever POV with the narrator’s name within the first 1-3 sentences. If that means one character has an entire chapter to themselves, then at this point in the story, their arc is the most important thing to be focusing on.
In the WIP at the top of the post, it was book 3 of a series which gave me some freedom. Namely that most of those 9 POVs were established characters you’d already be familiar with. I wasn’t throwing my audience into the deep end with 9 strangers and demanding they try to keep up with 6 subplots of equally confusing and unknown characters.
Cinematic MPOV should rely less on “who hasn’t narrated in a while let’s give it to them” and more “who would be the most interesting narrator for this moment”. You could have a villain POV, a one-off that might never narrate again, or a tertiary character who isn’t doing the most action in the scene, but has the richest commentary on what’s going on.
It does demand restraint. If anyone can pick up the narrator hat, then you could find yourself splitting off into unnecessary subplots. Not every piece of the story must be told and letting readers imagine what’s going on behind closed doors is sometimes better than detailing it all out. I could give a captive or missing character some POVS, or I could let the audience anxiously stew with the rest of the cast wondering if they’re even still alive.
In some books I’ve read, the deliberate choice to not let readers see into the mind of a character as they make important decisions, left on the outs with their friend or lover or relative, is maddeningly entertaining. They won’t explain themselves to the people who care about them, and they won’t explain themselves to the audience, either.
Or, you can let a side character have the spotlight for a scene or two as we see our favorites through their eyes, possibly in a way they’ve never been depicted before. A’s lover B might describe them as strong and brash. A’s old rival C might describe those same actions completely differently.
—
In terms of who narrates when, like the 9-POV monster I had going, I had key moments of every POV that had to hit the book's physical layout at specific times. Like episodes of TV, I needed certain scenes and moments and reveals to fit within specific chapters, not dangling off on either end.
I had to remember the time scale that all of this was happening on so every scene that was meant to happen simultaneously actually read like it was all going on at once. I had some chapters with the “A” group of narrators, then skipped them for a chapter for the “B” group of narrators for their scenes. Keeping the pacing as frenetic as it needed to be wasn’t easy, but if you can pull it off, I think it can be quite entertaining.
Some things to keep in mind with MPOV:
Don’t retread the same scenes or conversations. I read a fanfic a very long time ago that had I think 10 different takes on one character’s death with the dialogue copy-pasted over and over again and it was exhausting. If you want to have a character reflect on a previous scene, pull the specific lines as they remember them.
Unless messing up the timeline is the point of the story or you make it very clear that a scene happens before the present, don’t let POVs muck up the continuity. If plot happens on a Wednesday and the next scene is more important plot that happens that previous Tuesday, you might confuse your readers on when everything is meant to be happening.
Sometimes not knowing is better. Prequels tend to fail because whatever fans imagined happening is way better than what the writers explicitly show happening. Practice restraint.
Unless your story is paced very slowly, try not to have POVS butt up right against each other every time. In an action set piece, everything happens in sequence with zero black space between them. But a whole book with zero room to breathe can get tiring to read. Books with a single narrator have scene breaks and mini time skips, not every single part of your characters’ day has to be detailed.
If you don’t have banners, make it clear as quickly as possible who the new narrator is. Eventually, if your narration is distinct enough for each character, you can go a paragraph or two and your audience will know who it is anyway just based on how they think.
If these are all unknown characters, try to hop around minimally at first until you establish a clear protagonist, otherwise your readers might get lost on who the focus of the story is meant to be and lose which character is doing or thinking what.
*ETA: I forgot: typically with multiple narrators for a single “group”, like two characters stuck on a side quest together, I try to flip-flop their POVS. For example, if I have D and E with a whole chapter to themselves, the POV structure would go D E D E. To my eyes, it looks better, as they have equal share of the action. I try very hard to not let any one narrator have back-to-back POVS unless the narrative demands otherwise. But that’s just me.
—
This is personal opinion on what I think works. If you’re struggling on maintaining pacing or clarity with your ensemble cast, consider the above points. Hope this helps!
#writing#writing advice#writing resources#writing a book#writing tips#writing tools#writeblr#book formatting#pov#multiple pov#story structure
134 notes
·
View notes
Text

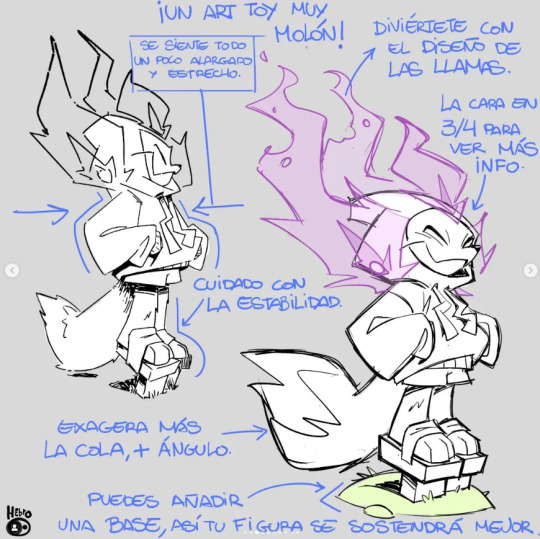






Character Design Reviews with notes of improvement
Daniel Fernández Casas aka @hebrocharacterdesign (GHP) -Give his permission-
Portfolio || Instagram
#reference#tutorial#art#art reference#concept art#animation#anatomy#illustration#artist#poses#dynamic#action line#pov#angles#character design#character designer#spa studios#tips
56 notes
·
View notes
Note
Hi!! I love your art!! Please tell us more about your OC 🥲 💕 Also what equipment do you use? Any good (kind of affordable) tablet/computer/software/brush recs for someone who wants to get into digital art!!
for tablets, i've been using huion's inspiroy H1161 for about 4 years now, and i previously used a monoprice tablet (i have a quick review & comparison of it with wacom here). there are tablets with and without displays, and even if you're interested in a display tablet, i'd still recommend starting with a basic drawing tablet just to get used to things and see how you like it. i've found that i personally don't like drawing on display tablets, which is great bc display tablets are expensive
for art programs, you can start with free programs to get used to things (like krita, firealpaca, etc--i haven't used them myself so i don't have personal recs) or paid programs like paint tool sai (my old favorite) or clip studio paint (which i use currently, and they run sales periodically so you can get it at a discount)
out of the paid programs, paint tool sai is more approachable and beginner friendly. clip studio paint can be pretty intimidating as a first-time art program, was intimidating to me when i first got it, and i'm still learning new things about it. what really led me to switch from sai to csp though is the 3d model support (which is what lets me make these) and the expansive asset library (which has brushes, 3d models, textures, auto functions, etc). some assets are paid, but plenty are free, and csp occasionally gives away "clippy" that you can use to buy paid assets
and about radri, aw thank you for asking! hmm, idk what to say that hasn't been said... she's just really shy and afraid and cringe but in kind of a cute way (to me). i just think it's funny for her to have such a terrifying reputation and then you meet her in person and she's struggling to catch the innkeeper's attention to book a room
#sovo answers#pov you're an assassin trying to strike up a ''i'm going to kill you >:)'' conversation with her but she keeps slipping away#and avoiding eye contact bc she's afraid you're going to ask her for directions and she does Not want the pressure of answering#and when you're finally like 'i'm TRYING to kill you!!' she gives a sigh of visible relief before absolutely murdering you#art tips#radri of candlekeep
44 notes
·
View notes
Text



The Gold
#satosugu#jjk#jujutsu kaisen#jjk season 2#geto suguru#gojo satoru#comic#um pro tip if you don’t want to cry#don’t listen to phoebe bridgers on repeat while reading satosugu fics :)))#I recently read the fix it time travel one and uhh#I’m not okay#this is geto pov btw I don’t think it makes sense otherwise#and I misspelled lose ;( I am but a tiny non native and every so often it hits me in the face
371 notes
·
View notes
Text
Writing Advice: Third Person Point of View - The Problem with Head-Hopping
A personal pet peeve in fanfic—and even some published books, unfortunately—is an author head-hopping.
I understand that not everyone learned about writing point of view in primary school, and many fanfic writers are new to writing and might not even realize they're writing head-hopping.
So, this post is an educational means for those who are interested in learning how to improve their writing.
I'm going to give a quick overview of point of view, a breakdown of third person point of view, and how to spot head-hopping in your writing.
What Is Point of View?
Point of view (POV) is the perspective (voice) from which a story is narrated.
There are three POVs.
First person
Second person
Third person
Third Person: Limited vs. Omniscient
In third person POV, the author is narrating the story through third-person pronouns (she, he, they).
Third person POV is subdivided into two categories: third person limited and third person omniscient.
Third Person Limited
In third person limited, the narrator is an external observer who knows the thoughts and feelings of ONE character at a time.
Here's an example from R.F. Kuang's, The Poppy War, page 341:
The Cike were stretched to their limit, especially Rin. Each moment not spent on an operation was spent on patrol. And when she was off duty, she trained with Altan.
Note that this paragraph—the entire book, actually—is from Rin's POV. We have access to Rin's feelings, thoughts, and observations throughout the book, while also seeing how other characters are acting.
But we are only in Rin's head. We do not have access to the thoughts and feelings of other characters. This is third person limited POV.
Third Person Omniscient
In third person omniscient, the narrator is an all-knowing observer who has access to the thoughts, feelings, and experiences of ALL characters in the story.
Here's an example from Jane Austen's, Pride and Prejudice, page 104:
As they drove to Mr. Gardiner’s door, Jane was at a drawing-room window watching their arrival; when they entered the passage she was there to welcome them, and Elizabeth, looking earnestly in her face, was pleased to see it healthful and lovely as ever.
Notice how we have access to both Jane and Elizabeth's 1) physical locations, and 2) thoughts. Even though Elizabeth is in a carriage and Jane is inside a house, the narrator is all-knowing and can narrate both of them at the same time.
The problem I see from many fanfic writers: they attempt to write in third person omniscient when they're actually writing shoddy third person limited, constantly switching between the POVs of multiple characters.
This is called head-hopping.
Head-Hopping vs. Omniscient
Head-hopping is when an author shifts between the POVs of multiple characters without a scene break. Meaning, the author is inside Character A's head but abruptly—and randomly—shares the thoughts, feelings, and/or observations of Character B.
Here's an example:
Kathy arrived at the cafe in hopes of showing Brittany her completed sweater. It was the first time she had knitted and she was eager to share her hard work with her best friend. Brittany took one look at the sweater and cringed. She hated it, but she didn't want to hurt Kathy's feelings. She didn't know what to say.
In this example, we are inside both Kathy and Brittany's heads. Both characters have distinctive voices, and because of this, the narration of the story is inconsistent.
It's jarring to read, and pulls you out of the story.
Here's the same example written through omniscient POV:
Kathy arrived at the cafe with the intent to show Brittany her completed sweater. After hours of hard work, the opinion of her best friend was important. At Kathy's approach, Brittany observed the sweater in her friend's hand and wrinkled her nose. The sweater was hideous.
In this example, we are inside the head of the narrator. The narrator is telling the story through its voice, rather than the individual voices of Kathy and Brittany.
Remember: Omniscient means the reader is inside the NARRATOR's head, not the characters'.
The Scene Break to Denote POV Switch
Back to my definition of head-hopping: Head-hopping occurs when a writer suddenly switches POV without a scene break.
Like the first example of Kathy and Brittany—there is no scene break between their thoughts. If the author wanted to write from both Kathy and Brittany's perspective, the author would have to include a physical break to alert the reader to a switch in POV. See below:
Kathy arrived at the cafe in hopes of showing Brittany her completed sweater. It was the first time she had knitted and she was eager to share her hard work with her best friend. ~~~~~~~~~~ Brittany took one look at the sweater and cringed. She hated it, but she didn't want to hurt Kathy's feelings. She didn't know what to say.
The squiggly lines demonstrate a switch in POV, and the scene would then continue in Brittany's POV. [Please note that a single paragraph space (as seen in the first example of Kathy and Brittany) is not a scene break. It is a paragraph break, and therefore cannot be used to demonstrate a switch in POV.]
You can write multiple POVS throughout a story. These will all be in third person limited POVs.
For example, each chapter in Rick Riordan's Heroes of Olympus series is dedicated to ONE character. Throughout that chapter, the reader is inside the head—reading the thoughts, feelings, and observations—of that singular character.
Individual chapters can also have multiple POVs (again, these are third person limited POVs). These are denoted by a divider or additional paragraph space.
For example, Timothy Zahn's Thrawn switches between the POVs of multiple characters in each chapter. The switch between his characters' POV is shown by an additional paragraph space.
Why Should You Care about Head-Hopping?
If writing head-hopping makes you happy, then keep at it. It's fanfic, and most readers are so desperate for content they don't care.
But, if you're interested in improving your writing, here are a few reasons why head-hopping is problematic:
It's jarring to the reader, and takes them out of the story. Frequent head-hopping can confuse readers as they struggle to keep track of whose perspective they are currently experiencing. It disrupts the flow of the narrative and can make it challenging for readers to form a strong connection with any one character.
It makes it harder for readers to truly immerse themselves in your story. Consistent use of a single POV allows readers to immerse themselves in the story's world through the eyes of a specific character. Head-hopping disrupts this immersion by constantly pulling readers out of one character's perspective and into another's.
It hinders character development. When the narrative constantly shifts between characters, there may not be enough time or focus on any one character's growth and development.
It takes away the emotional impact of the scene. Head-hopping can prevent readers from fully empathizing with or understanding any particular character's emotions, motivations, and inner conflicts.
Even well-established authors struggle to write omniscient without head-hopping. It's a nuanced subject that can be confusing to understand and difficult to overcome.
Again, this post is simply to inform writers about third person point of view and the subtle differences between its subdivisions. It’s not an attack on fanfic writers.
#writing advice#writing tips#writing fanfic#point of view#third person pov#omniscient pov#head-hopping#limited pov
171 notes
·
View notes
Text
Writing Notes: Point of View
Point of view (POV) - the position from which the events of a story are observed.
The author establishes point of view through the use of characters, dialogue, actions, setting, and events.
Authors rarely speak in their own voices. Instead, they assume a particular persona and adopt a "voice" that enables them to narrate their stories and novels. This voice is called point of view.
4 Common Points of View
1. Omniscient 2. Limited Omniscient:
Major character
Minor character
3. Objective 4. First Person:
Major character
Minor character
OMNISCIENT
The story is told in the third person ("he," "she," "it") by a narrator who knows everything about the characters, actions, and events.
The narrator is able to move in time and place, to shift from character to character, and to reveal or conceal as little or as much as he or she pleases.
This type of narrator is "all knowing."
Example from "Godfather Death:"
"He ought to have remembered his godfather's warning."
The narrator has unlimited knowledge, even knowing the mind of Death, and he comments on and evaluates the doctor as he is dying.
LIMITED OMNISCIENT
The story is also told in the third person, but only from the viewpoint of a single character, whether a major or minor one.
The author selects which character to see through, and the narrator is confined to knowing only the thoughts and actions of that character.
Such a character is the "lens" through which events pass in the story.
Example from Gustave Flaubert's Madame Bovary:
"Charles went upstairs to see the patient. He found him in bed, seating under blankets, his nightcap lying where he had flung it....The fracture was a simple one, without complications of any kind. Charles couldn't have wished for anything easier. Then he recalled his teachers' bedside manner in accident cases, and proceeded to cheer up his patient...."
It is only through Charlie's eyes that readers "see" and learn about the patient.
OBJECTIVE
The story is told in third person, but the narrator does not enter the mind of any character.
The narrator objectively describes events from the outside.
The reader is left to infer the character's inner thoughts and feelings.
The narrator knows which details to use to communicate deep meaning.
Example from Dashiell Hammett's the Maltese Falcon:
"Spade's thick fingers made a cigarette with deliberate care, sifting a measured quantity of tan flakes down into curved paper, spreading the flakes so that they lay equal at the ends with a slight depression in the middle...."
Readers must infer that Spade is deliberate, cool, efficient, and painstaking during a crisis; the author never uses those adjectives to describe Spade.
FIRST PERSON
The story is told in first person ("I"), through the thoughts and feelings of the narrator, not anyone else's.
What reaches the reader is subjective.
So, more important than whether the narrator is a major or minor character is the narrator's reliability.
An unreliable narrator can present a distorted picture of events; a reliable one can render events with accuracy.
Example from Aesop's Ant and the Grasshopper:
"Cold and hungry, I watched the ant tugging over the snow a piece of corn he had stored up last summer. My feelers twitched, and I was conscious of a tic in my left hind leg. Finally I could bear it no longer. 'Please, friend ant,' I asked, 'may I have a bit of your corn?"
Readers only know the thoughts and feelings of the grasshopper. They know nothing about what the ant thinks or how the ant feels.
Determining Point of View
The attitudes and opinions of a narrator aren't necessarily those of the author.
Don't confuse a character with the author.
To determine point of view, ask who the narrator is and what pronoun the author attaches to the narrator.
Also ask yourself what role, if any, the narrator plays.
By using a particular point of view, an author determines how much the narrator reveals about the characters.
If these writing notes help with your poem/story, do tag me. Or send me a link. I'd love to read them!
More: Writing Notes & References ⚜ POV
#writing notes#pov#writeblr#writers on tumblr#writing prompt#literature#poetry#poets on tumblr#spilled ink#dark academia#light academia#studyblr#creative writing#writing tips#fiction#writing inspiration#writing reference#writing basics#writing refresher#writing resources
321 notes
·
View notes
Note
any tips for writing bingmei pov?
oh jeez, i'm not sure i'm actually all that qualified to answer this question 😅💦
bingmei is... very difficult for me to write personally, so please take all this advice with a grain of salt. a large grain of salt. perhaps keep the entire salt shaker handy while you consider this advice, in fact. that being said, these are some things that i personally try to keep in mind when considering his character:
even as a disciple, he's not actually a pure white lotus - he still spent some long, formative years experiencing misfortune and bullying. from sqq's pov this is less visible, but from bingmei's pov this reflects on his thought process a lot. he isn't going to be blindly trustful, and his predisposition to be a bit of a schemer/borderline manipulative is still there, even if his goals are different. it's just the difference between pre-abyss manipulating the disciple roster so that he's the one always available to help out sqq VS post-abyss manipulating huan hua into being his biggest supporter.
in the abyss and up until sqq's self destruction, lbh's motivations are very much along the lines of "i can fix this, so long as i have the chance to, everything can go back to how it was before." if he can just prove himself to be a righteous cultivator by making a name for himself with huan hua, then sqq will no longer have an issue with lbh's heritage. if he can just get sqq to sit still and have one solid conversation with him, then surely sqq will understand lbh the way he used to. the more things go wrong and prove that it isn't so easy to go back to the way things used to be, the more frustrated lbh is, and the more willing he is to take drastic measures (going from slowly building a reputation for himself at huan hua to allowing sqq to be locked up in a horrible prison, for example).
personally, i attribute a lot of lbh's willingness to hurt sqq to xin mo. he's willing to take more drastic measures on his own, and some things that sqq considers 'harmful' are things lbh doesn't necessarily think of as actually hurting him - for example, forcing sqq to consume his blood parasites - but lbh is truly taken off guard when something he does results in sqq being harmed in a meaningful way. that being said, because lbh does still act on those things, i think it means one of two things: either lbh interprets xin mo's influences as his own impulses, or xin mo erodes his own ability to understand consequences. either of these can make for interesting narratives, so i go with "whatever works for the specific au i'm working on," usually.
dfjgh that was a lot of rambling lmao. i wish i had more solid tips, but for as long i personally am unsure how best to write bingmei, all i can offer are the things i try to keep in mind when characterizing him 😅
also, a final tip that is purely selfish and maybe not a hundddreeeeddd percent canon driven and instead motivated by my desires to see more bingwife in the world: #1 tip is to wife that boy up / have him pursue being shizun's pretty little wife 😌😌😌
#ah dkfjgh i hope those tips help a bit !!! but otherwise. yeah i rly dont know what advice to give >.>;;#i'm gaining confidence in writing bingge's pov but bingmei is still a big challenge for me rip...#good luck with your own bingmei pov writing !!#nyoomerr ask#nyoomerr gives advice
41 notes
·
View notes
Text



I NEED A FLIP PHONE SO BAD, LIKE IMAGINE ARGUING ON THIS PHONE 😭😍😍😍
#female hysteria#girl core#lizzy grant#gaslight gatekeep girlblog#this is what makes us girls#girlblogging#girly memes#just girly things#2000s#y2k aesthetic#y2kcore#lana del ray aka lizzy grant#lana del rey#i must be ovulating#manifesting#obsessive daydreaming#obsessive love#lolita1997#bunny#sadgirl#ultraviolence#coquettecore#angelic#angelcore#back to school#study tips#hear me out#mental health#pov#femcel
36 notes
·
View notes
Note
What advice would you have with a story that doesn’t necessarily have one set main character, but rather a group of important characters that influence the world around them? Is one set main character necessary?
Hi, thank you for the question!
Managing Multiple Main Characters
One main character is definitely not necessary. However, it depends how you define a main character. Are main characters just characters that have their own POV and arc? Or are they the point of the story telling? How significant does their impact on the world need to be?
Typically, even stories with multiple main characters (characters with POV and their own major arc), still has one main arc to follow that the others work with.
To make this point clearer, imagine a story with two main characters--one is a ballerina trying to land the main role of the show. The other is an astrophysicist discovering new things about our universe. At the end of the story, the ballerina lands the role, and the astrophysicist lands their promotion. One might wonder why these stories couldn't have each been their own novel, right?
So imagine instead, a ballerina is trying to land their dream role, and an astrophysicist is discovering new things about the universe. The theme for the upcoming ballet is space, so the ballerina goes to the astrophysicist for inspiration--leading to a blending of discovery, dance and science that leads the ballerina to landing the role and the physicist to opening their perspective on the universe.
Two main characters, but one 'story' that draws them together.
This is the most important part about writing multiple MCs. Readers typically expect--at some point--for the arcs of the MCs to intersect and work together. That's to say, if you have two characters who are both going through their own individual arcs completely separate from each other (such as the ballerina and physicist), at some point, they will have to interact or impact each other, and typically finish the story together, strengthened by their connection.
In cases of more than two main characters, it gets a bit more difficult. The more arcs and MCs your story has, the longer and more complicated it becomes.
To help with this, you can do a few things:
1. Have several arcs work together
Just like with two MCs, you can combine several of your MCs to going through arcs together. They may have the same objective (maybe for different reasons/motivations/goals, but the same 'end-game'), or otherwise they have to help each other or bounce off each other to get to their goal.
Romantic subplots are a really easy example of this. Two characters have an arc that both contribute to the same thing: the relationship.
2. Make some arcs 'weigh' more than others
The project I'm working on right now has five major characters who all have arcs and POV chapters. Character A and B are the protagonists, but character A is the 'more main' character out of the two of them. Then characters C, D, and E still have arcs, but theirs are much smaller than A and B. They still take the entirety of the story to fulfill their arc, but require less chapters and scenes to do it.
Thus, the breakdown in amount of time spent with characters is easy:
A - 40%, B - 30%, C - 15%, D - 10%, E - 5%
It's a bit less common to find a story with a lot of main characters that are all equal in their main character-ness. They may all impact the world and the story, but they aren't necessarily equal in doing so.
3. If all your characters are equal, they probably all have the same objective
Now, characters all having the same objective doesn't mean they're all going through the same arc. Objective may just be 'save the world from evil', but character A wants to save it for their family, character B wants to save it to have some control over it, character C wants to save it to promote their podcast, etc. etc. Their goals (or what they want out of achieving the objective) will be different, but they can band together to accomplish the same objective.
This keeps your astrophysicist and your ballerina together. Your characters' stories have meaning to each other, and a point to being put in the same novel.
Good luck!
#writing#writers#writing tips#writing advice#writing inspiration#creative writing#writing community#books#film#filmmaking#screenwriting#novel writing#fanfiction#writeblr#managing multiple main characters#multiple POVs
505 notes
·
View notes
Text

At first Minato thinks the sound he hears is his eardrums popping, but a moment later he realizes that it came from a distance– a distance they’re closing as they sprint onward, in fact.
In front of him, Sanada stops short. “What–?” Minato can barely hear him. “Dammit… Both of you, hang on!” He takes off again, not even short of breath.
Minato is almost jealous. Despite all of his time spent with the track team, he feels dizzy and ready to collapse by the time the alleyway behind Port Island Station comes into view. Every breath might as well be filling his lungs with tar instead of air.
The shadows in the alley sharpen and focus into human shapes– not two, but three of them: one sprawled on the ground; one standing as tall as it can; the third looming over them both, arm extended towards the smallest figure, taking aim–
“Takaya!” Minato’s voice sounds foreign in his own ears. He wouldn’t have guessed he’d be able to speak at all, much less shout.
Everything happens all at once after that.
Takaya’s whole body jerks towards Minato’s voice.
The shape on the ground lunges up and forward, taking the smaller figure crashing back down with it.
The gun goes off with a sound like–
Like a gunshot.
It isn't a clap of thunder. It's not at all like the crack of a whip.
There is no metaphor that can soften the truth.
The noise that tears open the silence of the Dark Hour is a gun being fired: a spark igniting powder propelling a bullet at shattering speeds towards the soft, vulnerable bodies of his friends.
Speckles of something dark and reflective fan through the air, glittering obscenely where they catch the light of the moon. Takaya almost seems to glow under that sickly light; pale skin and hair and eyes and shining silver gun gleaming ghost-bright in the murk of the alley, in stark contrast to the dark shapes huddled on the ground.
He meets Minato's eyes briefly. His expression is openly astonished for less than a moment before it shifts to fury, then is immediately papered over with a mask of calm indifference. He says something, but Minato is still too far away to hear. The Dark Hour swallows him up faster than Minato would have assumed possible.
He isn't terribly preoccupied with Takaya's Houdini act at the moment though, because–
"Shinji–!"
Aragaki lies prone on the pavement with Amada pinned underneath, whose breath is coming in shallow, panicked gasps, his face pale under dark splotches of blood. The bullet intended for Amada has shredded Aragaki’s right shoulder into a confusion of gore and torn wool and glimpses of pinkish-white that Minato tries not to think too hard about.
“Hang in there, Shinji!” Sanada hauls him off of Amada and onto his back, revealing another wound in his gut, a black well of blood. More of it dribbles sluggishly from the corner of his mouth. Aragaki doesn’t cry out in pain as Sanada and Mitsuru rearrange him in their hold, lifting him off of the cold concrete and supporting his head. He hardly makes any noise at all.
Minato feels like his ears have been jammed full of cotton. He can tell people are talking, but he can no longer pick out any voices or words. His vision tunnels, phantom colors chewing at the edges.
He stands there and watches as Yukari frantically tears out of her jacket and hands it off to Mitsuru, who packs it hard against Aragaki’s ruined shoulder.
He stands there and watches as Junpei unties his own jacket from around his waist and uses it to dab gingerly at the side of Amada’s face– it’s only now that Minato realizes that not all of the blood that Amada is wearing is Aragaki’s. The shape of Amada’s left ear is all wrong, like some of it is just missing, but Minato only catches a brief glimpse before Junpei presses the jacket over the injury and holds it there, hiding it from sight.
Yukari tries to summon her persona. Io flickers above her like a mirage for less than a second before vanishing. She pulls the trigger again, but the result is the same. She pulls the trigger again and again and again, face contorted and body heaving with sobs that Minato can’t hear. Io stops appearing at all. He stands there and watches.
It’s no use. They’re too far from Tartarus or any powerful shadow that could be harboring a piece of its influence. They’re too close to the end of the Dark Hour. Minato has two personas that can cast Recarm, but they wouldn’t be of any use even if he could draw his evoker, if he could move at all.
He stands there. And he watches.
Aragaki is saying something to Amada, and Amada answers through his sobs. Their mouths are moving, but Minato still can't hear. Why can’t he hear anything? Why does it feel like his mind is clouded over in static?
Something jabs hard into his side and suddenly Minato’s ears work again, like a loose wire has been jarred back into place.
“--ato! Minato! Hey, are you listening?!” He blinks, dumbfounded, and turns to the source of the voice. Junpei is staring at him. Minato has no idea what he’d call the expression Junpei is making at him, but it’s not one he’s ever seen him wear before. “Give Sanada-san your coat, man! We need to stop the bleeding!”
Even though he can hear again, it still takes him far too long to actually comprehend what’s being said. Junpei starts to repeat himself before it finally clicks and Minato shucks his jacket and hands it over. Junpei passes it off to Sanada, and Sanada presses it against the hole in Aragaki’s stomach. Aragaki doesn’t even flinch, just looks over at Koromaru gently nudging his hand. He pets him weakly. It’s probably the most movement he can manage.
“Just a few minutes–” Fuuka says, nearly hysterical. “The Dark Hour ends in a few minutes. As soon as it does, I-I’ll call an ambulance!”
“Did you hear that, Shinji?” With the hand that isn’t leaning on the makeshift bandage, Sanada grabs Aragaki’s, gripping tight. Aragaki grips back, much weaker. “Just hold on for a bit longer!”
“Aki…” Aragaki’s voice is quiet and thready, but everyone falls silent at the sound of it. “Take care of him…” He slowly inclines his head towards Amada.
“Don’t talk like you won’t be around!” Sanada says through gritted teeth.
“Pr…promise me, Aki.”
Sanada’s breath hitches and he bites his lip against it. “…Alright. Alright, I– I will. I promise I will.”
Aragaki smiles and Minato’s heart lurches. It’s sad. It’s final.
It’s relieved.
Aragaki is smiling like a weight has finally been lifted from his shoulders. He looks so content that Minato almost envies him. “This is…how it should be…” he sighs.
He slumps in Mitsuru and Sanada’s arms. Minato’s ears ring. There is a chorus of strangled cries from his teammates.
Amada chokes like he’s been stabbed. “No–! H-he can’t–!”
“Is he–?” Junpei’s voice shakes.
“He’s alive,” Sanada gasps, still clutching Aragaki’s hand. “He’s still breathing–”
“I can feel his pulse,” Mitsuru affirms, pressing two fingers gently to Aragaki’s neck. “It’s weak, but it’s there. He’s only passed out, but unless he gets medical attention soon…” She can’t even finish her sentence, but she doesn’t need to. The implication is heavy enough.
“Still breathing,” Sanada murmurs to himself. “He’s still breathing–” He says it again and again, as though he can force the words to remain true through sheer repetition.
Without fanfare, the green glow of the Dark Hour vanishes. The murky clouds that had blotted out the stars disappear and the moon returns to its normal size.
“Yamagishi!” Mitsuru exclaims.
“R-right!” Fuuka is already dialing. Her voice is strained and thin but steady as she relays the necessary details, and the person on the other end of the line thankfully seems to understand. It isn’t until she closes her phone that Fuuka allows a choked sob to escape. “Th…they’re on the way,” she says, her voice breaking.
All they can do now is wait. Nobody speaks. Most of the team crowds around Aragaki, if nothing else to assure themselves that he’s still alive. Only Amada stays off to the side, until Junpei breaks away to crouch next to him and speak quietly.
And Minato. He’s frozen in place, staring at the battered body of a man he’s come to greatly respect as the life slowly leaves him. His eyes burn, but it doesn’t feel like the sting of tears. They don’t feel wet at all. Has he been blinking?
A hand rests on his shoulder. “Minato-san,” Aigis says, her vocals strangely gentle. How does she feel about all of this, Minato briefly wonders. “Are you alright?”
“...No,” he answers, voice barely audible even to himself. Minato hasn’t felt like this since… not since Back Then. Not since the bridge, and the car.
Aigis’ face remains as impassive as always, but somehow she still looks sadder than she ever has. Sadder than Minato thought she was capable of. “I am here if you need me.” The compassion in her voice feels like a brick thrown against his chest.
It’s only a few minutes until they hear sirens, but it’s the most agonizing few minutes of their lives. Even in Tartarus, where a minute can stretch like taffy, time has never seemed to creep by so slowly.
A group of punks has started to gather, trying to gawk at the sprawled figure hidden within the protective ring formed by his teammates. They scatter as soon as the ambulance pulls up, stopping right next to the huddle. Four paramedics pour out and swarm around the injured parties as fast as they can. Two police cars arrive moments later. Officer Kurosawa steps out of one of them.
The alley is filled with disorienting pulses of red and blue light. Minato almost misses the sickly haze of the Dark Hour.
There’s a whirlwind of voices– explanations and questions and medical jargon– but Minato absorbs none of it. He just watches (again– again, he just watches, and does nothing) as three of the first responders transfer Aragaki onto a stretcher and load him into the ambulance. The fourth gently guides Amada inside as well.
Everyone wants to go with them, but there’s only enough spare room for one more person. Minato isn’t surprised when Sanada insists it be him. Nobody argues, and the ambulance takes off the moment Sanada is inside.
The last train has already left the station, so the rest of them will have to find another way to the hospital. And they will. They have to.
None of them can bear the idea of doing anything less.
#Persona 3#P3#Persona 3 Reload#P3R#Shinjiro Aragaki#Akihiko Sanada#Ken Amada#Minato Arisato#Junpei Iori#Yukari Takeba#Fuuka Yamagishi#Aigis#Still Breathing AU#SBAU Main Plot#SBAU Canon#SBAU October#SBAU October 4#fic#violence cw#gun violence cw#major injury cw#moderate description of injuries#(minato's weird bond with takaya made him call out)#(thereby disrupting the angle of his shot and making it not *as* lethal as it is in canon)#(the worst part is that minato will never know that actually saved this life)#(there is no way for him to know that that action is what tipped the scale from 'Shinji dies' to 'Shinji lives')#(also including a little bit of our headcanon regarding why just using healing magic wasn't an option)#(god do you know how hyped we are about posting this part)#(this is where things REALLY kick off we are so excitedddd)#minato pov
34 notes
·
View notes
Text
it’s always crazy to me when i meet somebody who has only watched the heaven official’s blessing donghua, and sometimes they don’t even know there’s a novel. im just like, do you know?? how much you’re missing out on?? do you know?? let me help you. here’s a 2000-page pdf of the entire story. or would you rather an epub? what’s your email?
#the donghua is great and beautiful in its own way#but it’s so lacking in the whimsy and humor that you get from xie lian’s pov#also at this rate when is it ever going to be finished#it’s just so interesting that that’s some people’s entire conception of tgcf bc to me#those arcs are just the very beginning lol#the very tip of the iceberg#tgcf#lily posts#Heaven official’s blessing#tian guan ci fu#mxtx#danmei#donghua#cnovel
23 notes
·
View notes
Note
This is more of a writing question as I really admire your work and I’m trying to write my own IF but am kind of stuck. I’ve done a lot of the character drafting and plot drafting, but when it comes down to actually sitting down and WRITING the story (even just a small portion) I just get stuck.
So I guess my question is, is how did you start writing the actual story of Infamous? How do you get about moving the story along?
Thank you and OK! This is going to be long because I'll share my beat sheet for the first act of Infamous!
So I've talked about this very briefly, but I will never stop championing beat sheets. I get so many questions every day asking me how I write so much and so quickly, and it's because I already have a layout planned that's basically just holding my hand. I'm not a magical wizard with a writing wand (though I wish...)
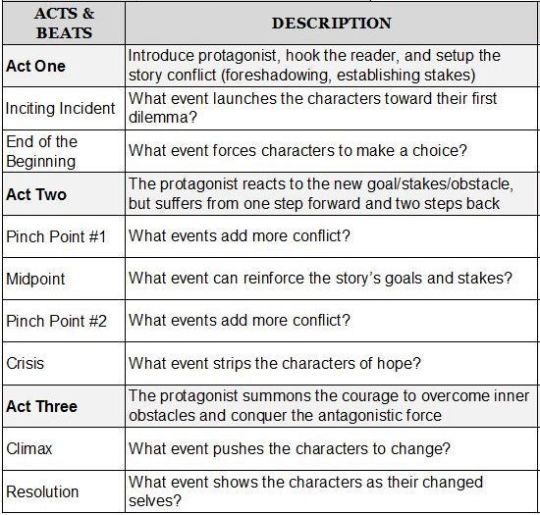
This is a traditional novel system and my only background is writing traditional novels. Infamous is my first IF, and I did have to tweak how I approach writing because they're just not the same. IFs are different because they're essentially multiple novels in one. One route can look completely different to another route, but the basics at least helps you with narrative plotting.
Once you recognize the building blocks of a story, it'll become easier to write it. For example, here's the beat sheet for Hunger Games. It is known that Hunger Games follows a beat sheet beat by beat and does it very well.
I will give you my beat sheet for Infamous

MC has a dream of the final goal of the band. It's meant to mirror what the end goal of the story is supposed to be. Ruining it by wakening up is meant to hook the reader by making them realize it's not true yet. Set up the story conflict: the tour. I introduce the characters and their dynamics (orion getting angry at MC for sleeping, Rowan joking around with Orion, Iris and Devyn etc.) I foreshadow a few things and I set up the stakes of the tour and how much the band needs this. (They talk about their gigs and how they want to do more.)

The inciting incident for INFAMOUS is winning the audition and finally getting on tour. That's what incites the story! The first dilemma is getting into a fight at the party due to cheating allegations. Now the reader is aware that this isn't all sunshine and daisies. We're all just fucked, basically. j/

Well. This is pretty obvious. Having to make a choice on the bus. It helps that the tour hasn't started yet and both options deal with characters that have conflict with MC and the band (Seven and UWB) so now it's like: this decision will impact the rest of the tour, and makes it much bigger than just choosing to ride with a band every other week.

obviously this is all spoilery but your goal is basically: how do i make my MC suffer as much as i can? conflict is fun to read, it's what drives people to continue watching/reading/ investing. For IFs it goes beyond that, because people like making decisions on how to fix conflict or make it worse!
I love talking technical writing on my personal @amyreads I don't talk about it much here because it can get boring. But yeah! If you have more questions you can swing by there :)
That's all! I hope it helps a bit! <3
#inbox#writing advice#i really said i'd take a break#I WILL!#once im done with orion pov heh#writing tips#writing chat
231 notes
·
View notes