#Novel approaches in cancer study
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Recent Advances in the Therapeutic Approaches of Glioblastoma Multiforme_Crimson Publishers

Abstract
Glioblastoma Multiforme (GBM, WHO grade IV) is one of the most aggressive, invasive, and lethal intracranial neoplasms, with a low post-diagnosis survival rate. Standard-of-care treatment regimens involving maximal surgical resection, radiotherapy, and genetic anti-tumor compounds like Temozolomide have only been marginally effective in improving overall survival and quality of life. Cell fusion, autophagy, and other complex biological processes affecting GBM pathophysiology are being studied to improve GBM treatment. This paper therefore focuses on oncolytic virus therapy combined with surgical resection, photodynamic therapy, and novel gene therapy, demonstrating how GBM treatment for patients could result in immediate and authentic tumor cytotoxicity and removal, rather than treatment of recurrent GBM. Standard therapy for GBM, including surgery, radiotherapy, and chemotherapy, is called the Stupp regime with the inclusion of Temozolomide (TMZ). It is extremely difficult to design new and effective therapeutic approaches because of the numerous complex biological pathways involved in GBM pathogenesis. Even Stupp regime clinical outcomes have only shown modest benefits with less than 10% of overall 5-year survivorship. A major contributing factor in GBM development is also its interaction with the patient’s host immune system.
Read more about this article:
For more articles in Novel Approaches in Cancer Study
#cancer#breast cancer#crimson cancer#crimson publishers llc#novel approaches in cancer study#cancer open access journal#crimson nacs#open access journal
0 notes
Text
BBMCT: Set Up New Medical Research at AIIMS Hospital

British Biomedicine Clinical Trials (BBMCT) has become a pivotal player in advancing clinical research at prestigious medical institutions like the All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS) Hospital. As the medical field continues to evolve, collaboration with global leaders in clinical trials plays an essential role in driving progress. BBMCT, through its expert partnerships, has been instrumental in setting up new medical research at AIIMS Hospital, enriching patient care, accelerating innovation, and fostering collaborations that enhance the future of healthcare.
In this blog post, we will delve into the multiple ways in which BBMCT contributes to AIIMS Hospital’s research, its impact on patient care, and the broader medical community. The following subheadings will explore how BBMCT facilitates advancements in medical research at AIIMS and beyond.
## Enhances Patient Care and Outcomes
BBMCT plays a crucial role in improving patient care and outcomes by facilitating clinical trials that bring new treatments and therapies to the forefront. These trials not only help test the safety and efficacy of medical interventions but also give patients access to cutting-edge therapies that are not yet widely available. By setting up new clinical research initiatives at AIIMS Hospital, BBMCT ensures that patients receive the best possible care while contributing to the global understanding of disease management.
Furthermore, the data generated from clinical trials at AIIMS aids in creating tailored treatment plans for patients, improving long-term health outcomes. This personalized approach enhances the hospital’s capacity to treat complex conditions, such as cancer, cardiovascular diseases, and autoimmune disorders.
## Accelerates the Progress of Innovations
BBMCT has been instrumental in accelerating the progress of medical innovations at AIIMS Hospital. Through well-structured clinical trials, BBMCT supports the testing of novel drugs, medical devices, and treatment protocols. This fast-tracks the transition of groundbreaking innovations from laboratory research to real-world applications, benefiting patients and healthcare professionals alike.
Innovations in personalized medicine, gene therapy, and immunotherapy are among the key areas that BBMCT fosters at AIIMS. By supporting these cutting-edge studies, BBMCT plays a pivotal role in reshaping the future of healthcare by bringing innovative solutions to the clinical setting faster than traditional research timelines would allow.
## Establishes Partnerships with Leading Institutions
One of BBMCT’s core strengths is its ability to form strategic partnerships with leading medical institutions globally. This enables AIIMS Hospital to collaborate with renowned experts and access state-of-the-art research tools and resources. By creating these collaborative networks, BBMCT ensures that research conducted at AIIMS benefits from the latest global insights and methodologies.
These partnerships are essential in setting up new medical research projects, particularly in areas that require specialized expertise. Moreover, they help strengthen AIIMS’s position as a hub for advanced medical research in India, ensuring that the hospital remains at the forefront of global healthcare developments.
## Fills Significant Gaps in Knowledge
A major benefit of BBMCT’s involvement in clinical trials is its ability to fill critical gaps in medical knowledge. Despite significant advances in medicine, many diseases still lack effective treatments, and there are numerous unexplored areas in patient care. By facilitating clinical research at AIIMS Hospital, BBMCT provides a platform for addressing these gaps.
Research conducted through BBMCT often focuses on rare diseases, emerging health threats, and under-researched conditions, where traditional research may fall short. This focus allows AIIMS to contribute valuable insights into both common and niche medical conditions, benefiting not only Indian patients but the global population.
## Secures Funding for Research Projects
Conducting world-class clinical research requires substantial funding. BBMCT’s involvement at AIIMS Hospital significantly enhances the institution’s ability to secure grants and funding for critical medical research projects. The collaboration between BBMCT and AIIMS Hospital has attracted international funding from government agencies, private organizations, and philanthropic entities, ensuring that research can be carried out without financial constraints.
This funding also enables AIIMS to invest in state-of-the-art equipment, recruit top-tier researchers, and scale up promising research initiatives. The financial support secured by BBMCT ensures that AIIMS remains a leader in cutting-edge healthcare research in India.
## Improves the Institution’s Academic Reputation
AIIMS Hospital is renowned for its academic excellence, and BBMCT’s partnership further enhances its reputation as a leading institution in clinical research. By conducting high-quality clinical trials in collaboration with BBMCT, AIIMS attracts international attention, allowing it to recruit world-class researchers and practitioners to its team.
Furthermore, the findings from clinical trials conducted at AIIMS contribute to scientific literature, enhancing the institution’s academic standing. As a result, AIIMS becomes a sought-after partner for other research organizations and institutions looking to collaborate on innovative medical studies.
## Promotes Collaboration Among Research Teams
BBMCT’s involvement in clinical trials fosters a culture of collaboration among researchers, healthcare professionals, and experts from various fields. AIIMS Hospital, with its multidisciplinary approach to healthcare, greatly benefits from this collaboration. Researchers working on clinical trials, pharmaceutical companies, healthcare providers, and other stakeholders come together to achieve shared goals, ultimately advancing the field of medicine.
Collaboration also promotes knowledge exchange and the sharing of resources, making it easier to tackle complex medical problems. This networked approach accelerates the pace of discovery, ensuring that treatments and therapies are developed more efficiently.
## Supports Advancements Based on Evidence
BBMCT ensures that all clinical trials at AIIMS Hospital are rooted in evidence-based research. By relying on scientifically sound methodologies, the trials conducted through this collaboration lead to reliable and valid results that can be generalized to larger patient populations. This evidence-based approach is crucial in ensuring that any new treatment or therapy tested at AIIMS is not only safe but also effective.
Furthermore, this reliance on evidence supports informed decision-making in the medical field, providing healthcare providers with the information they need to offer the best care to their patients. It also plays a role in shaping public health policies based on proven data.
/media/fe48b75114c4a7ccf24b7775c9477286
— -
### FAQs About BBMCT and Its Role at AIIMS Hospital
**1. What is BBMCT’s role at AIIMS Hospital?**
BBMCT (British Biomedicine Clinical Trials) plays a crucial role in facilitating advanced clinical research at AIIMS Hospital by organizing and supporting clinical trials. These trials test new drugs, medical devices, and treatment protocols, enhancing patient care, improving health outcomes, and accelerating medical innovations. Through BBMCT’s partnership, AIIMS benefits from expertise, global collaborations, and increased funding for research.
**2. How does BBMCT improve patient outcomes?**
BBMCT improves patient outcomes by providing access to cutting-edge treatments that are still in clinical trial phases. Patients participating in these trials receive advanced medical care that might not be available through traditional treatment routes. The trials help test new therapies that can ultimately lead to better, more effective treatments for various diseases, improving long-term health outcomes.
**3. What innovations does BBMCT support at AIIMS?**
BBMCT supports a variety of innovative medical treatments at AIIMS, including advancements in gene therapy, immunotherapy, and personalized medicine. Through its clinical trials, BBMCT accelerates the development of new drugs, medical devices, and technologies, contributing to the advancement of healthcare solutions that address complex medical conditions such as cancer, cardiovascular diseases, and chronic illnesses.
**4. How does BBMCT help AIIMS secure research funding?**
BBMCT plays an essential role in helping AIIMS secure funding by attracting grants and sponsorships from government agencies, private foundations, and international research organizations. These funds are crucial for supporting the infrastructure and operations of clinical trials, ensuring that AIIMS remains equipped to conduct high-quality research that leads to breakthrough medical discoveries.
**5. How do BBMCT’s partnerships benefit AIIMS Hospital?**
BBMCT’s partnerships with leading medical institutions and research organizations enhance AIIMS’s ability to access cutting-edge research techniques, resources, and global expertise. These collaborations foster knowledge exchange, expand research opportunities, and improve the overall quality of research at AIIMS, helping the institution stay at the forefront of medical advancements.
— -
### Conclusion
British Biomedicine Clinical Trials (BBMCT) has been instrumental in advancing clinical research at AIIMS Hospital, contributing to improved patient care, faster medical innovations, and a stronger academic reputation for the institution. Through strategic partnerships, evidence-based research, and enhanced funding opportunities, BBMCT has positioned AIIMS as a leader in healthcare research. The collaborative spirit fostered by BBMCT ensures that AIIMS continues to make significant contributions to medical science, ultimately benefiting both Indian and global populations. With the continued support of BBMCT, AIIMS Hospital is poised to lead the way in groundbreaking medical research and patient care for years to come.
Subscribe to BBMCLINICALTRIALS YouTube channel for Research Insights
Be sure to subscribe to the **BBMCLINICALTRIALS YouTube channel** for exclusive access to the latest updates and in-depth insights into British Biomedicine Clinical Trials (BBMCT). Stay informed on cutting-edge research, clinical trial advancements, patient safety protocols, and breakthrough therapies being tested at AIIMS Hospital. Our channel provides expert discussions, industry trends, and detailed videos on the clinical trial process across various therapeutic areas. Whether you’re a healthcare professional, researcher, or simply interested in biomedical innovation, subscribing will keep you at the forefront of clinical research developments. Don’t miss out — join our community today!
#anya mouthwashing#artists on tumblr#agatha harkness#bucktommy#batman#cats of tumblr#captain curly#agatha all along#911 abc
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Inhibition of EIF4E Downregulates VEGFA and CCND1 Expression to Suppress Ovarian Cancer Tumor Progression by Jing Wang in Journal of Clinical Case Reports Medical Images and Health Sciences
Abstract
This study investigates the role of EIF4E in ovarian cancer and its influence on the expression of VEGFA and CCND1. Differential expression analysis of VEGFA, CCND1, and EIF4E was conducted using SKOV3 cells in ovarian cancer patients and controls. Correlations between EIF4E and VEGFA/CCND1 were assessed, and three-dimensional cell culture experiments were performed. Comparisons of EIF4E, VEGFA, and CCND1 mRNA and protein expression between the EIF4E inhibitor 4EGI-1-treated group and controls were carried out through RT-PCR and Western blot. Our findings demonstrate elevated expression of EIF4E, VEGFA, and CCND1 in ovarian cancer patients, with positive correlations. The inhibition of EIF4E by 4EGI-1 led to decreased SKOV3 cell clustering and reduced mRNA and protein levels of VEGFA and CCND1. These results suggest that EIF4E plays a crucial role in ovarian cancer and its inhibition may modulate VEGFA and CCND1 expression, underscoring EIF4E as a potential therapeutic target for ovarian cancer treatment.
Keywords: Ovarian cancer; Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E; Vascular endothelial growth factor A; Cyclin D1
Introduction
Ovarian cancer ranks high among gynecological malignancies in terms of mortality, necessitating innovative therapeutic strategies [1]. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) plays a pivotal role in angiogenesis, influencing endothelial cell proliferation, migration, vascular permeability, and apoptosis regulation [2, 3]. While anti-VEGF therapies are prominent in malignancy treatment [4], the significance of cyclin D1 (CCND1) amplification in cancers, including ovarian, cannot be overlooked, as it disrupts the cell cycle, fostering tumorigenesis [5, 6]. Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E (EIF4E), central to translation initiation, correlates with poor prognoses in various cancers due to its dysregulated expression and activation, particularly in driving translation of growth-promoting genes like VEGF [7, 8]. Remarkably, elevated EIF4E protein levels have been observed in ovarian cancer tissue, suggesting a potential role in enhancing CCND1 translation, thereby facilitating cell cycle progression and proliferation [9]. Hence, a novel conjecture emerges: by modulating EIF4E expression, a dual impact on VEGF and CCND1 expression might be achieved. This approach introduces an innovative perspective to impede the onset and progression of ovarian cancer, distinct from existing literature, and potentially offering a unique therapeutic avenue.
Materials and Methods
Cell Culture
Human ovarian serous carcinoma cell line SKOV3 (obtained from the Cell Resource Center, Shanghai Institutes for Biological Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences) was cultured in DMEM medium containing 10% fetal bovine serum. Cells were maintained at 37°C with 5% CO2 in a cell culture incubator and subcultured every 2-3 days.
Three-Dimensional Spheroid Culture
SKOV3 cells were prepared as single-cell suspensions and adjusted to a concentration of 5×10^5 cells/mL. A volume of 0.5 mL of single-cell suspension was added to Corning Ultra-Low Attachment 24-well microplates and cultured at 37°C with 5% CO2 for 24 hours. Subsequently, 0.5 mL of culture medium or 0.5 mL of EIF4E inhibitor 4EGI-1 (Selleck, 40 μM) was added. After 48 hours, images were captured randomly from five different fields—upper, lower, left, right, and center—using an inverted phase-contrast microscope. The experiment was repeated three times.
GEPIA Online Analysis
The GEPIA online analysis tool (http://gepia.cancer-pku.cn/index.html) was utilized to assess the expression of VEGFA, CCND1, and EIF4E in ovarian cancer tumor samples from TCGA and normal samples from GTEx. Additionally, Pearson correlation coefficient analysis was employed to determine the correlation between VEGF and CCND1 with EIF4E.
RT-PCR
RT-PCR was employed to assess the mRNA expression levels of EIF4E, VEGF, and CCND1 in treatment and control group samples. Total RNA was extracted using the RNA extraction kit from Vazyme, followed by reverse transcription to obtain cDNA using their reverse transcription kit. Amplification was carried out using SYBR qPCR Master Mix as per the recommended conditions from Vazyme. GAPDH was used as an internal reference, and the primer sequences for PCR are shown in Table 1.
Amplification was carried out under the following conditions: an initial denaturation step at 95°C for 60 seconds, followed by cycling conditions of denaturation at 95°C for 10 seconds, annealing at 60°C for 30 seconds, repeated for a total of 40 cycles. Melting curves were determined under the corresponding conditions. Each sample was subjected to triplicate experiments. The reference gene GAPDH was used for normalization. The relative expression levels of the target genes were calculated using the 2-ΔΔCt method.
Western Blot
Western Blot technique was employed to assess the protein expression levels of EIF4E, VEGF, and CCND1 in the treatment and control groups. Initially, cell samples collected using RIPA lysis buffer were lysed, and the total protein concentration was determined using the BCA assay kit (Shanghai Biyuntian Biotechnology, Product No.: P0012S). Based on the detected concentration, 20 μg of total protein was loaded per well. Electrophoresis was carried out using 5% stacking gel and 10% separating gel. Subsequently, the following primary antibodies were used for immune reactions: rabbit anti-human polyclonal antibody against phospho-EIF4E (Beijing Boao Sen Biotechnology, Product No.: bs-2446R, dilution 1:1000), mouse anti-human monoclonal antibody against EIF4E (Wuhan Sanying Biotechnology, Product No.: 66655-1-Ig, dilution 1:5000), mouse anti-human monoclonal antibody against VEGFA (Wuhan Sanying Biotechnology, Product No.: 66828-1-Ig, dilution 1:1000), mouse anti-human monoclonal antibody against CCND1 (Wuhan Sanying Biotechnology, Product No.: 60186-1-Ig, dilution 1:5000), and mouse anti-human monoclonal antibody against GAPDH (Shanghai Biyuntian Biotechnology, Product No.: AF0006, dilution 1:1000). Subsequently, secondary antibodies conjugated with horseradish peroxidase (Shanghai Biyuntian Biotechnology, Product No.: A0216, dilution 1:1000) were used for immune reactions. Finally, super-sensitive ECL chemiluminescence reagent (Shanghai Biyuntian Biotechnology, Product No.: P0018S) was employed for visualization, and the ChemiDocTM Imaging System (Bio-Rad Laboratories, USA) was used for image analysis.
Statistical Analysis
GraphPad software was used for statistical analysis. Data were presented as (x ± s) and analyzed using the t-test for quantitative data. Pearson correlation analysis was performed for assessing correlations. A significance level of P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
3D Cell Culture of SKOV3 Cells and Inhibitory Effect of 4EGI-1 on Aggregation
In this experiment, SKOV3 cells were subjected to 3D cell culture, and the impact of the EIF4E inhibitor 4EGI-1 on ovarian cancer cell aggregation was investigated. As depicted in Figure 1, compared to the control group (Figure 1A), the diameter of the SKOV3 cell spheres significantly decreased in the treatment group (Figure 1B) when exposed to 4EGI-1 under identical culture conditions. This observation indicates that inhibiting EIF4E expression effectively suppresses tumor aggregation.
Expression and Correlation Analysis of VEGFA, CCND1, and EIF4E in Ovarian Cancer Samples
To investigate the expression of VEGFA, CCND1, and EIF4E in ovarian cancer, we utilized the GEPIA online analysis tool and employed the Pearson correlation analysis method to compare expression differences between tumor and normal groups. As depicted in Figures 2A-C, the results indicate significantly elevated expression levels of VEGFA, CCND1, and EIF4E in the tumor group compared to the normal control group. Notably, the expression differences of VEGFA and CCND1 were statistically significant (p < 0.05). Furthermore, the correlation analysis revealed a positive correlation between VEGFA and CCND1 with EIF4E (Figures 2D-E), and this correlation exhibited significant statistical differences (p < 0.001). These findings suggest a potential pivotal role of VEGFA, CCND1, and EIF4E in the initiation and progression of ovarian cancer, indicating the presence of intricate interrelationships among them.
EIF4E, VEGFA, and CCND1 mRNA Expression in SKOV3 Cells
To investigate the function of EIF4E in SKOV3 cells, we conducted RT-PCR experiments comparing EIF4E inhibition group with the control group. As illustrated in Figure 3, treatment with 4EGI-1 significantly reduced EIF4E expression (0.58±0.09 vs. control, p < 0.01). Concurrently, mRNA expression of VEGFA (0.76±0.15 vs. control, p < 0.05) and CCND1 (0.81±0.11 vs. control, p < 0.05) also displayed a substantial decrease. These findings underscore the significant impact of EIF4E inhibition on the expression of VEGFA and CCND1, indicating statistically significant differences.
Protein Expression Profiles in SKOV3 Cells with EIF4E Inhibition and Control Group
Protein expression of EIF4E, VEGFA, and CCND1 was assessed using Western Blot in the 4EGI-1 treatment group and the control group. As presented in Figure 4, the expression of p-EIF4E was significantly lower in the 4EGI-1 treatment group compared to the control group (0.33±0.14 vs. control, p < 0.001). Simultaneously, the expression of VEGFA (0.53±0.18 vs. control, p < 0.01) and CCND1 (0.44±0.16 vs. control, p < 0.001) in the 4EGI-1 treatment group exhibited a marked reduction compared to the control group.
Discussion
EIF4E is a post-transcriptional modification factor that plays a pivotal role in protein synthesis. Recent studies have underscored its critical involvement in various cancers [10]. In the context of ovarian cancer research, elevated EIF4E expression has been observed in late-stage ovarian cancer tissues, with low EIF4E expression correlating to higher survival rates [9]. Suppression of EIF4E expression or function has been shown to inhibit ovarian cancer cell proliferation, invasion, and promote apoptosis. Various compounds and drugs that inhibit EIF4E have been identified, rendering them potential candidates for ovarian cancer treatment [11]. Based on the progressing understanding of EIF4E's role in ovarian cancer, inhibiting EIF4E has emerged as a novel therapeutic avenue for the disease. 4EGI-1, a cap-dependent translation small molecule inhibitor, has been suggested to disrupt the formation of the eIF4E complex [12]. In this study, our analysis of public databases revealed elevated EIF4E expression in ovarian cancer patients compared to normal controls. Furthermore, through treatment with 4EGI-1 in the SKOV3 ovarian cancer cell line, we observed a capacity for 4EGI-1 to inhibit SKOV3 cell spheroid formation. Concurrently, results from PCR and Western Blot analyses demonstrated effective EIF4E inhibition by 4EGI-1. Collectively, 4EGI-1 effectively suppresses EIF4E expression and may exert its effects on ovarian cancer therapy by modulating EIF4E.
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) is a protein that stimulates angiogenesis and increases vascular permeability, playing a crucial role in tumor growth and metastasis [13]. In ovarian cancer, excessive release of VEGF by tumor cells leads to increased angiogenesis, forming a new vascular network to provide nutrients and oxygen to tumor cells. The formation of new blood vessels enables tumor growth, proliferation, and facilitates tumor cell dissemination into the bloodstream, contributing to distant metastasis [14]. As a significant member of the VEGF family, VEGFA has been extensively studied, and it has been reported that VEGFA expression is notably higher in ovarian cancer tumors [15], consistent with our public database analysis. Furthermore, elevated EIF4E levels have been associated with increased malignant tumor VEGF mRNA translation [16]. Through the use of the EIF4E inhibitor 4EGI-1 in ovarian cancer cell lines, we observed a downregulation in both mRNA and protein expression levels of VEGFA. This suggests that EIF4E inhibition might affect ovarian cancer cell angiogenesis capability through downregulation of VEGF expression.
Cyclin D1 (CCND1) is a cell cycle regulatory protein that participates in controlling cell entry into the S phase and the cell division process. In ovarian cancer, overexpression of CCND1 is associated with increased tumor proliferation activity and poor prognosis [17]. Elevated CCND1 levels promote cell cycle progression, leading to uncontrolled cell proliferation [18]. Additionally, CCND1 can activate cell cycle-related signaling pathways, promoting cancer cell growth and invasion capabilities [19]. Studies have shown that CCND1 gene expression is significantly higher in ovarian cancer tissues compared to normal ovarian tissues [20], potentially promoting proliferation and cell cycle progression through enhanced cyclin D1 translation [9]. Our public database analysis results confirm these observations. Furthermore, treatment with the EIF4E inhibitor 4EGI-1 in ovarian cancer cell lines resulted in varying degrees of downregulation in CCND1 mRNA and protein levels. This indicates that EIF4E inhibition might affect ovarian cancer cell proliferation and cell cycle progression through regulation of CCND1 expression.
In conclusion, overexpression of EIF4E appears to be closely associated with the clinical and pathological characteristics of ovarian cancer patients. In various tumors, EIF4E is significantly correlated with VEGF and cyclin D1, suggesting its role in the regulation of protein translation related to angiogenesis and growth [9, 21]. The correlation analysis results in our study further confirmed the positive correlation among EIF4E, VEGFA, and CCND1 in ovarian cancer. Simultaneous inhibition of EIF4E also led to downregulation of VEGFA and CCND1 expression, validating their interconnectedness. Thus, targeted therapy against EIF4E may prove to be an effective strategy for treating ovarian cancer. However, further research and clinical trials are necessary to assess the safety and efficacy of targeted EIF4E therapy, offering more effective treatment options for ovarian cancer patients.
Acknowledgments:
Funding: This study was supported by the Joint Project of Southwest Medical University and the Affiliated Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital of Southwest Medical University (Grant No. 2020XYLH-043).
Conflict of Interest: The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
#Ovarian cancer#Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E#Vascular endothelial growth factor A#Cyclin D1#Review Article in Journal of Clinical Case Reports Medical Images and Health Sciences .#jcrmhs
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Innovative Chemotherapy Approach Shows Promise Against Lung Cancer - Technology Org
New Post has been published on https://thedigitalinsider.com/innovative-chemotherapy-approach-shows-promise-against-lung-cancer-technology-org/
Innovative Chemotherapy Approach Shows Promise Against Lung Cancer - Technology Org
Lung cancer is not the most common form of cancer, but it is by far the deadliest.
Kytai T. Nguyen, the Alfred R. and Janet H. Potvin Distinguished Professor in Bioengineering at UTA. Image credit: UTA
Despite treatments such as surgery, radiation therapy and chemotherapy, only about a quarter of all people with the disease will live more than five years after diagnosis, and lung cancer kills more than 1.8 million people worldwide each year, according to the World Health Organization.
To improve the odds for patients with lung cancer, researchers from The University of Texas at Arlington and UT Southwestern Medical Center have pioneered a novel approach to deliver cancer-killing drugs directly into cancer cells.
“Our method uses the patient’s own cellular material as a trojan horse to transport a targeted drug payload directly to the lung cancer cells,” said Kytai T. Nguyen, lead author of a new study on the technique in the peer-reviewed Bioactive Materials and the Alfred R. and Janet H. Potvin Distinguished Professor in Bioengineering at UTA. “The process involves isolating T-cells (a type of immune cell) from the cancer patient and modifying them to express a specific receptor that targets the cancer cells.”
The crucial step in this new technique involves isolating the cell membrane from these modified T-cells, loading the membranes with chemotherapy medications, and then coating them onto tiny drug-delivery granules. These nanoparticles are roughly 1/100 the size of a strand of hair.
Jon Weidanz, associate vice president for research and innovation and professor of kinesiology and bioengineering. Image credit: UTA
When these membrane-coated nanoparticles are injected back into the patient, the cell membrane acts as a guide, directing the nanoparticles to the tumor cells with precision. This approach is designed to deceive the patient’s immune system, as the coated nanoparticles mimic the properties of immune cells, avoiding detection and clearance by the body.
“The key advantage of this method lies in its highly targeted nature, which allows it to overcome the limitations of conventional chemotherapy that often lead to detrimental side effects and reduced quality of life for patients,” said co-author Jon Weidanz, associate vice president for research and innovation and a researcher in kinesiology and bioengineering.
“By delivering chemotherapy directly to the tumor cells, the system aims to minimize collateral damage to healthy tissues,” continued Weidanz, who also is a member of UTA’s Multi-Interprofessional Center for Health Informatics.
In the study, researchers loaded the nanoparticles with the anti-cancer drug Cisplatin. The membrane-coated nanoparticles accumulated in parts of the body with the tumors rather than in other parts of the body. As a result, this targeted delivery system reduced the size of the tumors in the control group, demonstrating its efficacy.
“This personalized approach could pave the way for a new era of medicine tailored to each patient’s unique characteristics and the specific nature of their tumor,” Nguyen said. “The potential for reduced side effects and improved effectiveness makes our technique a noteworthy advancement in the field of cancer treatment.”
Source: University of Texas at Arlington
You can offer your link to a page which is relevant to the topic of this post.
#approach#bioengineering#Biotechnology news#Cancer#cancer cells#cancer treatment#cell#Cells#chemotherapy#detection#directing#Disease#drug#drugs#effects#express#form#Genetic engineering news#Health#Health & medicine news#immune cells#immune system#Innovation#it#life#Link#lung cancer#material#materials#medical
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Exploring the Potential of a Glutamine Transporter Inhibitor
Introduction
Cancer cells exhibit distinct metabolic characteristics, and targeting specific metabolic pathways has become an area of intense research in cancer therapeutics. JPH203, a glutamine transporter inhibitor, has emerged as a promising drug candidate for disrupting the metabolic processes crucial to cancer cell survival and proliferation. This article aims to explore factual evidence regarding the efficacy and potential applications of JPH203.
Understanding JPH203
JPH203 is a selective inhibitor of the glutamine transporter ASCT2 (alanine, serine, cysteine-preferring transporter 2). ASCT2 plays a critical role in transporting glutamine, an amino acid essential for cancer cell growth and survival[¹^]. By targeting ASCT2, JPH203 aims to disrupt glutamine uptake and subsequently alter cancer cell metabolism.
The Mechanism of Action
Inhibition of Glutamine Uptake: JPH203 binds to ASCT2, preventing the transport of extracellular glutamine into cancer cells. This disruption hampers the availability of glutamine, an essential nutrient for cancer cell metabolism, thereby impairing their growth and survival[²^].
Factual Evidence Supporting JPH203
Preclinical Studies: Initial preclinical studies have demonstrated the efficacy of JPH203 in inhibiting cancer cell growth across various types of cancers, including lung, breast, pancreatic, and colorectal cancers[³^][⁴^]. These studies have shown that JPH203 treatment led to reduced glutamine uptake, impaired cell proliferation, and increased cell death.
Combination Therapy: JPH203 has been investigated in combination with other anticancer agents, such as chemotherapeutic drugs and targeted therapies. Preclinical studies have suggested synergistic effects when JPH203 is used in combination with other treatments, leading to enhanced anticancer activity[⁵^][⁶^]. These findings highlight the potential of JPH203 as an adjunct therapy to improve treatment outcomes.
Metabolic Reprogramming: Glutamine is a crucial nutrient for cancer cells, serving as a building block for macromolecules and as a source of energy. By inhibiting glutamine uptake, JPH203 disrupts cancer cell metabolism. This metabolic reprogramming can render cancer cells more susceptible to other therapies and potentially overcome drug resistance[⁷^].
Clinical Development
JPH203 is currently undergoing clinical trials to evaluate its safety, tolerability, and efficacy in patients with advanced solid tumors. These studies aim to determine the optimal dosage, treatment duration, and potential side effects to further establish the therapeutic potential of JPH203 in clinical settings[⁸^].
Conclusion
JPH203, a selective inhibitor of the glutamine transporter ASCT2, shows promise as a targeted approach to disrupt cancer cell metabolism. Preclinical studies have demonstrated its ability to inhibit glutamine uptake, impair cancer cell growth, and enhance cell death. The ongoing clinical trials will provide valuable insights into the safety and efficacy of JPH203 in human patients and its potential as part of combination therapies.
While JPH203 holds significant potential as a novel anticancer agent, further research is needed to fully understand its mechanisms of action, optimize treatment strategies, and identify the patient populations that may benefit most from its use. The development of JPH203 represents an exciting advancement in the quest for more effective and targeted cancer therapeutics.please visit MedChemExpress
(Note: This article is for informational purposes only and should not replace professional medical advice. Always consult your healthcare provider for personalized treatment recommendations.)
3 notes
·
View notes
Note
HIIII I see that u hv a match up goin on and Id like to try! Would u mind doing one for me with Obey Me?
Pronouns : She/they
Sexuality: Im not sure exactly??... still discovering but I know that I like both sexes
Infp 4w5 / Cancer sun Taurus moon n Scorpio rising (I saw some doing not just the sun sign so i think it would be fun if i include all 3 lol)
Appearance: Im South East Asian. Around 5'2. I hv shoulder length black hair, black eyes and olive toned skin. My hairstyle is akin to the jellyfish hair. I rarely wear makeup and would just hv my bare face out due to its sensitivity to breakouts. And my clothing, its mostly modest/covering for academic places or just comfy and quick with any cool baggy tees i hv. Its my current closet, since i dont hv much occasions to go grand and i just wanna blend in with everyone around me lookin like an npc. But id love to wear more self expressing stuff in the future, to my desire. More accessories, colorful makeups and fashions like dark couquette/gyaru or so!
Personality: My personality, id say its two sided. I guess hv an open mind and easy going (to some degree ofc). A dream chaser and a listener. Sometimes (just sometimes), i can get my mind through a problem and stay grounded. Im also empathic? I like consoling with people and I appreciate the smallest details. I feel for people's struggle and I hold hopes in them. However, i can get moody, its so unexpected and intense that even im scared of it. I can be very quiet then, and dissociative. Id just want to be alone by that time to figure out my situation. Ive been said to appear gloomy or hard to approach too :cry: If im pissed, im venomous. And im actually an anxious person, of all sorts of things. Self deprecating too, i almost forgot abt that. But if i feel suitable, i get funky and enjoy myself hehe.
Likes/Dislikes : I like visual novels, rhythm games and those with good storytelling; a variety of music genres that focus on melody, instrument, composing; local asian food; sleeping with plushies; arts n crafts; esoteric things; philosophy study; my friends; solitude and continuation; aesthetic or hidden values and uhhh nice, mannered intriguing people.
I dont like smelly people doe. People who are narrow minded icks me oops. Pls dont tryna barge in on me when im busy unless it helps. I hate the sun... And not getting myself tented after a long day. I dislike my parents as well, yikes. Worst of all, being opressed.
Hobbies : doll, bracelet making; drawing, online shopping, rhythm game arcade, reading philosophy works, uhh getting invested in random medias...
Anyways, thats my submission! If u do reply, tysm for the matchup!!!
Hi Anon! Thank you for the request! I hope you like your matchup!
In Obey Me, I match you with...

Asmo is the best person to hype you up about wearing more self-expressing things. He’s great at putting outfits together and will give you honest and genuine feedback.
Doesn’t mind your personality changes. He knows what mood swings are like so he’s very understanding.
Please go online shopping with him! But set a budget because you’re both liable to get caught up in the energy and spend too much. But online shopping with Asmo would be so much fun.
Not great at giving you alone time but if you say you need some space, he’ll respect your wishes. While you’re enjoying your alone time, he’ll do a spa day or hang out with some of his friends.
Asmo loves your plushies. He thinks they’re really cute and, if you’re okay with it, would love to borrow some of them to sleep with as well. He’ll take good care of them and swaps them out occasionally so you’ve got a constantly rotating roster of plushies in your room.
#writing#fanfic#matchup#matchup request#request#obey me#obey me shall we date#obey me nightbringer#asmodeus
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
JANINE AND EGON'S WEDDING QUESTIONS (MOVIE, NOVELIZATION AND COMICS VERSE)
@spengnitzed @bixiebeet @professorlehnsherr-almashy @angelixgutz
Imagine what music they'd have? What food? Would it be outside? What kind of theme, if any, would they have?
Jazz and jewish folk music. The ceremony would be outside in the garden, while the dinner reception, with Ashkenazi jewish food from Poland, Russia and Ukraine and the dancing party would be inside the house of their friend, Ray. The theme would be woodlands and mycology.
Who would they invite?
Ray (who is Egon's best man and provider of the house where the wedding is celebrated), Winston, Peter, Dana, Egon's mother, brother, sister-in-law and baby nephew, Janine's parents, sister, grandmother and maternal uncles and cousins.
What season is it? Day or night? What colors do people wear?
Autumn, evening till night, starting at 15:00 pm. While the decoration is green and brown, the guests are left free to choose the colors of their clothes.
Is it traditional or do they do something wild?
The ceremony follows traditional jewish marriage rituals, along with including a justice of peace to assist the civil legalization and documentation of the wedding.
Did they write their own vows? Who is the priest/priestess/minister marrying you? Or is it a family member or other platonic F/O?
They do write their own vows, taking some inspiration from literature. Janine's family rabbi and a paid justice of peace marries her and Egon.
Are they wearing suits? Dresses? Something else entirely?
Janine wears a tea-length dress with a lace top and puffy skirt.

Egon wears a black suit and bowtie.

What is their cake like if they have one?
Is a cake decorated with candy mushrooms and sugar leafs, topped with two snails representing the couple.
Do they throw the bouquet for someone to catch or do they pass out one flower to everyone so they let everyone know they are worthy of love?
Janine appears like she will throw one bouquet to one person, then surprises everyone when the flowers are untied and everybody catches a flower.
Do they have a party afterwards? What music?
A dancing party with the music of Cleo Laine, Harry Belafonte, Ofra Haza and The Parvarim.
What is their honeymoon like? Is it a stay at home one? Do they go somewhere exciting? How long is their trip?
A three week vacation to San Diego, California.
How many kids do they have? What are their names?
Three kids: Noemi, Tobin and Batya.

NICKNAME(S): Baby Smurf, Sugar Plum.
FACECLAIM: Violet Ramis (child), Jenny Slate (adult).
BIRTH: August 25th 1984.
ZODIAC SIGN: Virgo.
SEXUALITY: Bissexual.
GENDER: Female.
ORIGIN: Forest Hills, Queens, New York City.
NATIONALITY: US American.
CHARACTERISTICS:
+ Curious, inquisitive, creative, extroverted, with a fascination for gallows humor;
+ Loves colorful clothes, cartoons and comic books;
+ Has a strong temper and rarely disguises when she has either contempt or desire to kill someone she perceives as an enemy;
WEAPON OF CHOICE:
+ P.K.E Meter
+ Proton Pack
+ Ghost Trap
OTHER PERSONAL INFO:
+ While she inherited the academic talent of her father, she has the more outgoing and bold approach to social interactions of her mother;
+ Considers the other Ghostbusters her uncles, with Ray and Winston being her favorites;
+ Is a huge fan of the Smurfs and Asterix comics and cartoons and a cosplayer;
+ Before deciding to pursue a career in STEM and Parapsychology, for a while she considered taking religious studies to become a rabbi. While she didn't went through with that, she still became and expert in Jewish Mythology and Folklore;
+ Besides being a Ghostbuster, Noemi also teaches about the paranormal at Columbia University.

NICKNAME(S): Bean Bunny.
FACECLAIM: Anton Yelchin (child and adult).
BIRTH: June 23th 1989.
ZODIAC SIGN: Cancer.
SEXUALITY: Asexual.
GENDER: Male.
ORIGIN: Forest Hills, Queens, New York City.
NATIONALITY: US American.
CHARACTERISTICS:
+ Calm, caring, empathetic, studious, who enjoys safety and tranquility;
+ Loves cooking, gardening and drawing;
+ Is anxious and gets stuck in a place when frightened;
WEAPON OF CHOICE:
+ P.K.E Meter
+ Ghost Trap
OTHER PERSONAL INFO:
+ Has the more quiet temperament of his father, and the belief in intuition from his mother, wich is formative of his view of science mainly as an instrument of nurturing;
+ Collects mold, spores and fungus, and also enjoys botanics, specially harvesting the mushrooms, fruits and vegetables to use in dishes he cooks for his friends and family;
+ Loves the Pogo comic strips, Fraggle Rock and the Dave the Gnome cartoon;
+ Studies to become a Landscape Architect, Environmental Engineer and Manager;
+ When reluctantly involved in Ghostbusting by his older sister, he only uses the P.K.E Meter and the Ghost Trap, seeing these instruments as something to try to communicate with the ghosts and help them get shelter and defend humans from harm, but he doesn’t handle the Proton Pack because is heavy and because he sees it as a intimidating gun.

NICKNAME(S): Ladybug.
FACECLAIM: Flora Guiet (child), Alexandra Socha (adult).
BIRTH: September 29th 1991.
ZODIAC SIGN: Libra.
SEXUALITY: Biromantic and demisexual.
GENDER: Female.
ORIGIN: Forest Hills, Queens, New York City.
NATIONALITY: US American.
CHARACTERISTICS:
+ Likes to keep things well organized to facilitate the work and everyday life of other people;
+ Physically agile;
+ In a conversation, can see connections between topics that the other person listening her would never imagine being related;
WEAPON OF CHOICE:
+Walkie-talkie
+Proton Pack
+Ghost Trap
+ Ecto Goggles
OTHER PERSONAL INFO:
+ Inherited her mother’s taste for racquetball, and also plays tennis;
+ Loves RPG, be they tabletop or video games, eventually getting a Masters Degree in Game Theory and Game Design;
+ Is fascinated with prehistoric animals, studying History, Biology, Zoology, Archeology and Paleontology, the area where she intends to become a Doctor;
+ Also enjoys photography;
+ Is a mix between a Explorer Historian, whose greatest pleasure is delving into the new world that they are exploring in search of knowledge as the greatest reward, and a Socializer Strategist, happy to collaborate in order to achieve bigger and better things than she could on her own, while having no problems assuming leadership if it means keeping the group safe and sound when the situation becomes especially dangerous.
Where do they live?
In an old two storey boarding house in Forest Hills, Queens, chosen because it looked similar to a drawing that Janine made in her childhood of her dream house, which should be old and covered with vines like the house that served as Madeline's boarding school.

#tumblr mutuals#fandom musings#ghostbusters 1984#egon spengler#janine melnitz#harold ramis#annie potts#janegon#spengnitz#egonine
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
📅 Aug 2023 📰 New mRNA-based malaria vaccine shows promise in preclinical trials 🗞 News-Medical.net
The focus of the collaborative research investigating a novel target for malaria was originally on peptide-based vaccines. However, in 2018, the team shifted their approach and started investigating RNA-based vaccines – a decision that, so far, seems to have paid off with the recent success of RNA technology in vaccine development.
"While our successful peptide-based vaccines targeting malaria only contain small protein fragments of a malaria protein, mRNA vaccines encode an entire malaria protein," says the University of Melbourne's Dr Lauren Holz, Research Officer at the Doherty Institute and co-author of the paper.
To pack an extra protective punch, the mRNA vaccine has been combined with an adjuvant – originally developed at the Malaghan and Ferrier Institutes for cancer immunotherapies – which targets and stimulates liver-specific immune cells. This additional ingredient helps localise the RNA vaccine response to the liver, a key site in preventing the parasite from developing and maturing in the body.

"When the parasite first enters the bloodstream, it travels to the liver where it develops and matures before going on to infect blood cells, which is when disease symptoms occur," says Dr Mitch Ganley, Postdoctoral Research Fellow at the Ferrier Research Institute, and co-author of the study.
"Unlike the COVID-19 vaccine that works by neutralizing antibodies, our unique approach relies on T-cells which play a critical role in immunity. Specifically, a type of T-cell called a tissue-resident memory T-cell, that halts malaria infection in the liver to completely stop the spread of infection."
Dr Holz says the key advantage of this vaccine is that it isn't affected by previous exposure to malaria.
"A lot of malaria vaccines undergoing trials have worked really well in animal models or when they're given to people who haven't had malaria before, but they don't work well when given to people living in malaria-endemic regions. In contrast, our vaccine is still capable of generating protective liver-specific immune cells and providing protection even when the animal models have been pre-exposed to the disease," says Dr Holz.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
AACR Conference Coverage 2025: Insights by DelveInsight

The AACR Annual Meeting 2025 is recognized as one of the most significant events in oncology, drawing together leading researchers, clinicians, pharmaceutical executives, and patient advocates from around the world. As a trusted authority in market intelligence and healthcare consulting, DelveInsight offers comprehensive AACR Conference Coverage 2025, delivering deep insights into emerging trends, groundbreaking research, and transformative developments in cancer care.
Key Highlights of AACR Annual Meeting Coverage 2025
Revolutionary Advances in Cancer Research: At AACR 2025, pioneering studies will challenge conventional thinking and redefine our understanding of cancer. Researchers will unveil novel insights into tumor biology, genetic mutations, and the molecular mechanisms that drive cancer progression. Sessions will emphasize targeted therapies, precision medicine, and immuno-oncology—innovations that are setting the stage for the future of cancer treatment.
Breakthroughs in Immunotherapy and Targeted Therapies: Immunotherapy remains at the forefront of modern cancer treatment. AACR 2025 will feature cutting-edge research on immune checkpoint inhibitors, CAR-T cell therapy, and cancer vaccines. With a focus on overcoming resistance and enhancing patient responses, the conference will spotlight innovative therapeutic combinations. DelveInsight’s coverage will detail these advancements and their potential impact on future drug development and clinical practice.
Precision Medicine: The Era of Personalized Oncology: Personalized treatment is transforming cancer care by tailoring therapies to an individual’s genetic profile. Discussions will cover biomarker-driven strategies, companion diagnostics, and the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) in optimizing treatment protocols. DelveInsight’s AACR Conference Coverage 2025 will provide exclusive insights into how genomic data is being leveraged to develop highly targeted therapies.
Advancements in Early Detection and Cancer Prevention: Early detection is a cornerstone of effective cancer management. AACR 2025 will showcase innovative screening technologies—such as liquid biopsies and next-generation imaging techniques—that enhance early diagnosis. Experts will also explore the role of AI in detecting cancer sooner, potentially improving treatment outcomes and reducing mortality rates. DelveInsight will assess the clinical impact of these breakthroughs.
The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Oncology: AI is revolutionizing cancer research by streamlining drug discovery, diagnostics, and treatment optimization. At AACR 2025, sessions will focus on AI-driven predictive analytics, machine learning applications, and AI-assisted radiology. DelveInsight will explore how these advancements facilitate clinical decision-making and accelerate the development of next-generation cancer therapies.
Clinical Trials and Drug Development Insights: Clinical trials are pivotal for advancing cancer treatments. The AACR Annual Meeting 2025 will provide updates on ongoing studies, late-stage drug candidates, and promising investigational therapies. DelveInsight will offer in-depth analysis of key clinical trial data, regulatory updates, and potential approvals that could reshape the oncology landscape.
Patient-Centered Approaches and Survivorship: Patient advocacy and quality of life are central themes at AACR 2025. Sessions will address survivorship programs, the psychosocial impact of cancer, and strategies to enhance outcomes beyond treatment. DelveInsight will highlight initiatives aimed at improving patient support, broadening access to innovative therapies, and ensuring long-term cancer management.
Oncology Market Trends and Industry Collaborations: AACR Annual Meeting 2025 is also a critical platform for the pharmaceutical and biotechnology sectors. Industry leaders will announce strategic partnerships, licensing deals, and new drug development initiatives. DelveInsight will provide exclusive market analysis, identifying key players, emerging trends, and investment opportunities in the oncology sector.
DelveInsight’s Comprehensive AACR Conference Coverage 2025
As a leading market research and consulting firm, DelveInsight ensures that stakeholders remain informed on the latest developments in cancer research and treatment through:
Detailed reports on breakthrough therapies, emerging trends, and pipeline developments.
Expert analysis of clinical trial data, regulatory updates, and market impact.
Exclusive interviews with key opinion leaders, researchers, and industry executives.
Live updates and post-conference insights to keep industry professionals informed.
Conclusion
The AACR Annual Meeting 2025 promises to be a transformative event that brings together the brightest minds in oncology to advance cancer research and treatment. DelveInsight is committed to delivering unparalleled AACR Conference Coverage 2025, ensuring that healthcare professionals, industry leaders, and investors remain at the cutting edge of the rapidly evolving oncology landscape. Stay tuned for our expert insights and analysis on the innovations that will shape the future of cancer care.
List of top Selling Reports
Congenital Heart Defect Market
CXCR Inhibitors Market
Endoscopic Ultrasound Market
Joint Reconstruction Devices Market
Percutaneous Arterial Closure Device Market
Perennial Allergic Rhinitis Market
Peripheral Nerve Injuries Market
Radiation Dermatitis Market
Rhinosinusitis Market
Schistosomiasis Market
Somatotropin Deficiency Market
Surgical Stapling Devices Market
Temporomandibular Disorders Market
Type 1 Diabetes Market
Vaginal Rejuvenation Systems Market
Ventral Hernia Market
Cardiogenic Shock Market
Coronary Angioplasty Market
Persistent Depressive Disorder Market
Psoriasis Vulgaris Market
Respiratory Syncytial Virus Market
Short Bowel Syndrome Market
Ulcerative Colitis Market
Vital Sign Monitors Devices Market
Vulvar Cancer Market
About DelveInsight
DelveInsight is a leading market research and consulting firm, offering in-depth insights into the life sciences and healthcare sectors.
Contact:Kanishk | Email: [email protected]
0 notes
Text
Unstipulated and InexactIndeterminate Dendritic Cell Tumour_Crimson Publishers

Opinion
Indeterminate dendritic cell tumour emerges as an extremely exceptional tumefaction composed of proliferation of dendritic cells or cells of histiocytic lineage. Additionally designated as indeterminate cell histiocytosis, indeterminate cell tumour or indeterminate dendritic cell tumour, true cutaneous dendritic cell tumour may depict solitary or multifocal lesions. Generally, tumefaction is confined to diverse cutaneous surfaces wherein deep seated visceral or regional lymph node involvement is exceptional. Tumour forming indeterminate cells simulate Langerhans cells vis-à-vis morphological and antigenic features. However, indeterminate cells appear devoid of Birbeck granules and lack immune reactivity to langerin (CD207). Median age of disease emergence is 45 years although no age of disease occurrence is exempt. An almost equivalent gender predilection is encountered. Indeterminate dendritic cell tumour predominantly(~88%) implicates diverse cutaneous surfaces. Infrequently, regional lymph nodes (9%) or spleen (2.3%) may be involved [1,2]. Of obscure a etiology, neoplasm expounds varied concurrence between indeterminate cells and Langerhans cells as ~indeterminate cells manifest as Langerhans cells devoid of Birbeck granules ~indeterminate cells represent as immature Langerhans cells. A subset of neoplasms express dendritic cell marker ZBTB46, thereby indicating the emergence of neoplasms directly from bone marrow progenitors, in contrast to embryonic precursors which undergo localized cutaneous regeneration [1,2].
Read more about this article:
For more articles in Novel Approaches in Cancer Study
#cancer#breast cancer#crimson cancer#crimson publishers#novel approaches in cancer study#open access journal#crimson nacs
1 note
·
View note
Text
Checkpoint Inhibitor Refractory Cancer Treatment Market Forecast, Size, Share by 2024-2032 | Reports and Insights

The Reports and Insights, a leading market research company, has recently releases report titled “Checkpoint Inhibitor Refractory Cancer Treatment Market: Global Industry Trends, Share, Size, Growth, Opportunity and Forecast 2024-2032.” The study provides a detailed analysis of the industry, including the global Checkpoint Inhibitor Refractory Cancer Treatment Market share, size, trends, and growth forecasts. The report also includes competitor and regional analysis and highlights the latest advancements in the market.
Report Highlights:
How big is the Checkpoint Inhibitor Refractory Cancer Treatment Market?
The global checkpoint inhibitor refractory cancer treatment market size reached US$ 35.6 billion in 2023. Looking forward, Reports and Insights expects the market to reach US$ 89.6 billion in 2032, exhibiting a growth rate (CAGR) of 10.8% during 2024-2032.
What are Checkpoint Inhibitor Refractory Cancer Treatment?
Checkpoint inhibitor refractory cancer treatment refers to therapeutic strategies designed for patients whose cancers do not respond to or progress despite treatment with immune checkpoint inhibitors, such as PD-1, PD-L1, or CTLA-4 inhibitors. These treatments focus on overcoming resistance mechanisms by employing alternative immunotherapies, such as bispecific antibodies, cancer vaccines, CAR-T cell therapies, or combination approaches with chemotherapy, targeted therapies, or radiation. Emerging strategies also include leveraging novel immune modulators, epigenetic therapies, and personalized medicine approaches to enhance immune response. This area of treatment addresses a critical unmet need, aiming to improve outcomes for patients with resistant or relapsed cancers.
Request for a sample copy with detail analysis: https://www.reportsandinsights.com/sample-request/2225
What are the growth prospects and trends in the Checkpoint Inhibitor Refractory Cancer Treatment industry?
The checkpoint inhibitor refractory cancer treatment market growth is driven by various factors and trends. The checkpoint inhibitor refractory cancer treatment market is gaining momentum due to the increasing prevalence of cancers resistant to immune checkpoint inhibitors like PD-1, PD-L1, and CTLA-4 inhibitors. Key drivers include growing research into novel immunotherapies, such as bispecific antibodies, CAR-T cell therapies, and personalized cancer vaccines, aimed at overcoming treatment resistance. Advancements in combination therapies that integrate checkpoint inhibitors with chemotherapy, radiation, or targeted drugs are also fueling market growth. Rising investments in oncology R&D, the expansion of clinical trials, and the increasing adoption of precision medicine approaches further propel the market. This segment addresses a critical unmet need, offering hope for improved outcomes in refractory and relapsed cancers. Hence, all these factors contribute to checkpoint inhibitor refractory cancer treatment market growth.
What is included in market segmentation?
The report has segmented the market into the following categories:
By Application
Hodgkin Lymphoma
Kidney Cancer
Melanoma
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
Others
By Distribution Channel
Hospital Pharmacies
Retail Pharmacies
Online Pharmacies
North America
United States
Canada
Europe
Germany
United Kingdom
France
Italy
Spain
Russia
Poland
Benelux
Nordic
Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
China
Japan
India
South Korea
ASEAN
Australia New Zealand
Rest of Asia Pacific
Latin America
Brazil
Mexico
Argentina
Middle East Africa
Saudi Arabia
South Africa
United Arab Emirates
Israel
Rest of MEA
Who are the key players operating in the industry?
The report covers the major market players including:
AstraZeneca
Merck
Genentech/Hoffmann-La Roche
Regeneron Pharmaceuticals
Merck KGaA and Pfizer
Bristol-Myers Squibb
Janssen Research and Development, LLC
4D pharma plc.
4SC AG
OncoSec Medical
Mirati Therapeutics
View Full Report: https://www.reportsandinsights.com/report/Checkpoint Inhibitor Refractory Cancer Treatment-market
If you require any specific information that is not covered currently within the scope of the report, we will provide the same as a part of the customization.
About Us:
Reports and Insights consistently mееt international benchmarks in the market research industry and maintain a kееn focus on providing only the highest quality of reports and analysis outlooks across markets, industries, domains, sectors, and verticals. We have bееn catering to varying market nееds and do not compromise on quality and research efforts in our objective to deliver only the very best to our clients globally.
Our offerings include comprehensive market intelligence in the form of research reports, production cost reports, feasibility studies, and consulting services. Our team, which includes experienced researchers and analysts from various industries, is dedicated to providing high-quality data and insights to our clientele, ranging from small and medium businesses to Fortune 1000 corporations.
Contact Us:
Reports and Insights Business Research Pvt. Ltd. 1820 Avenue M, Brooklyn, NY, 11230, United States Contact No: +1-(347)-748-1518 Email: [email protected] Website: https://www.reportsandinsights.com/ Follow us on LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/report-and-insights/ Follow us on twitter: https://twitter.com/ReportsandInsi1
#Checkpoint Inhibitor Refractory Cancer Treatment Market share#Checkpoint Inhibitor Refractory Cancer Treatment Market size#Checkpoint Inhibitor Refractory Cancer Treatment Market trends
0 notes
Text
Engineers develop a vibrating, ingestible capsule that might help treat obesity
New Post has been published on https://thedigitalinsider.com/engineers-develop-a-vibrating-ingestible-capsule-that-might-help-treat-obesity/
Engineers develop a vibrating, ingestible capsule that might help treat obesity


When you eat a large meal, your stomach sends signals to your brain that create a feeling of fullness, which helps you realize it’s time to stop eating. A stomach full of liquid can also send these messages, which is why dieters are often advised to drink a glass of water before eating.
MIT engineers have now come up with a new way to take advantage of that phenomenon, using an ingestible capsule that vibrates within the stomach. These vibrations activate the same stretch receptors that sense when the stomach is distended, creating an illusory sense of fullness.
In animals who were given this pill 20 minutes before eating, the researchers found that this treatment not only stimulated the release of hormones that signal satiety, but also reduced the animals’ food intake by about 40 percent. Scientists have much more to learn about the mechanisms that influence human body weight, but if further research suggests this technology could be safely used in humans, such a pill might offer a minimally invasive way to treat obesity, the researchers say.
“For somebody who wants to lose weight or control their appetite, it could be taken before each meal,” says Shriya Srinivasan PhD ’20, a former MIT graduate student and postdoc who is now an assistant professor of bioengineering at Harvard University. “This could be really interesting in that it would provide an option that could minimize the side effects that we see with the other pharmacological treatments out there.”
Srinivasan is the lead author of the new study, which appears today in Science Advances. Giovanni Traverso, an associate professor of mechanical engineering at MIT and a gastroenterologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, is the senior author of the paper.
A sense of fullness
When the stomach becomes distended, specialized cells called mechanoreceptors sense that stretching and send signals to the brain via the vagus nerve. As a result, the brain stimulates production of insulin, as well as hormones such as C-peptide, Pyy, and GLP-1. All of these hormones work together to help people digest their food, feel full, and stop eating. At the same time, levels of ghrelin, a hunger-promoting hormone, go down.
While a graduate student at MIT, Srinivasan became interested in the idea of controlling this process by artificially stretching the mechanoreceptors that line the stomach, through vibration. Previous research had shown that vibration applied to a muscle can induce a sense that the muscle has stretched farther than it actually has.
“I wondered if we could activate stretch receptors in the stomach by vibrating them and having them perceive that the entire stomach has been expanded, to create an illusory sense of distension that could modulate hormones and eating patterns,” Srinivasan says.
As a postdoc in MIT’s Koch Institute for Integrative Cancer Research, Srinivasan worked closely with Traverso’s lab, which has developed many novel approaches to oral delivery of drugs and electronic devices. For this study, Srinivasan, Traverso, and a team of researchers designed a capsule about the size of a multivitamin, that includes a vibrating element. When the pill, which is powered by a small silver oxide battery, reaches the stomach, acidic gastric fluids dissolve a gelatinous membrane that covers the capsule, completing the electronic circuit that activates the vibrating motor.
In a study in animals, the researchers showed that once the pill begins vibrating, it activates mechanoreceptors, which send signals to the brain through stimulation of the vagus nerve. The researchers tracked hormone levels during the periods when the device was vibrating and found that they mirrored the hormone release patterns seen following a meal, even when the animals had fasted.
The researchers then tested the effects of this stimulation on the animals’ appetite. They found that when the pill was activated for about 20 minutes, before the animals were offered food, they consumed 40 percent less, on average, than they did when the pill was not activated. The animals also gained weight more slowly during periods when they were treated with the vibrating pill.
“The behavioral change is profound, and that’s using the endogenous system rather than any exogenous therapeutic. We have the potential to overcome some of the challenges and costs associated with delivery of biologic drugs by modulating the enteric nervous system,” Traverso says.
The current version of the pill is designed to vibrate for about 30 minutes after arriving in the stomach, but the researchers plan to explore the possibility of adapting it to remain in the stomach for longer periods of time, where it could be turned on and off wirelessly as needed. In the animal studies, the pills passed through the digestive tract within four or five days.
The study also found that the animals did not show any signs of obstruction, perforation, or other negative impacts while the pill was in their digestive tract.
An alternative approach
This type of pill could offer an alternative to the current approaches to treating obesity, the researchers say. Nonmedical interventions such as diet exercise don’t always work, and many of the existing medical interventions are fairly invasive. These include gastric bypass surgery, as well as gastric balloons, which are no longer used widely in the United States due to safety concerns.
Drugs such as GLP-1 agonists can also aid weight loss, but most of them have to be injected, and they are unaffordable for many people. According to Srinivasan, the MIT capsules could be manufactured at a cost that would make them available to people who don’t have access to more expensive treatment options.
“For a lot of populations, some of the more effective therapies for obesity are very costly. At scale, our device could be manufactured at a pretty cost-effective price point,” she says. “I’d love to see how this would transform care and therapy for people in global health settings who may not have access to some of the more sophisticated or expensive options that are available today.”
The researchers now plan to explore ways to scale up the manufacturing of the capsules, which could enable clinical trials in humans. Such studies would be important to learn more about the devices’ safety, as well as determine the best time to swallow the capsule before to a meal and how often it would need to be administered.
Other authors of the paper include Amro Alshareef, Alexandria Hwang, Ceara Byrne, Johannes Kuosmann, Keiko Ishida, Joshua Jenkins, Sabrina Liu, Wiam Abdalla Mohammed Madani, Alison Hayward, and Niora Fabian.
The research was funded by the National Institutes of Health, Novo Nordisk, the Department of Mechanical Engineering at MIT, a Schmidt Science Fellowship, and the National Science Foundation.
#Animals#approach#battery#bioengineering#body weight#Brain#Cancer#capsules#Cells#change#devices#diet#drugs#effects#electronic#electronic devices#Electronics#engineering#engineers#Exercise#fluids#Food#Foundation#Full#Global#Health#hormone#hormones#how#human
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Immunohistochemistry Business Growth, Development Factors, Current and Future Trends till 2034.

The Global Immunohistochemistry Market is expected to reach USD 7.95 billion in 2034, based on an average growth pattern, and the report projects that the market will grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.5% from 2024 to 2034. Revenue from the global immunohistochemistry market is projected to reach USD 3.68 billion by 2024.
Immunohistochemistry (IHC) is a pivotal technique in histology and immunology that involves the detection of antigens in biological tissues. Using labeled antibodies, IHC provides invaluable insights for diagnostic, therapeutic, and research purposes. Over the years, this field has witnessed robust advancements, making it a cornerstone in personalized medicine and translational research.
Get a Sample Copy of Report, Click Here@ https://wemarketresearch.com/reports/request-free-sample-pdf/immunohistochemistry-market/1595
Immunohistochemistry Market Drivers
Increasing Cancer Prevalence:
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), cancer is one of the leading causes of mortality worldwide, with an estimated 10 million deaths in 2020.
IHC is instrumental in identifying cancer biomarkers like HER2, ER/PR, and Ki-67, which guide treatment decisions.
Emergence of Targeted Therapy:
The shift towards precision medicine has fueled demand for IHC in identifying predictive and prognostic markers for diseases.
Companion diagnostics, especially for immunotherapies and targeted drugs, heavily rely on IHC.
Advancements in Automation:
The development of automated IHC platforms such as Ventana (Roche) and Benchmark Ultra has revolutionized workflows, reducing human error and increasing reproducibility.
Applications in Neuroscience and Infectious Diseases:
Beyond oncology, IHC is being used to study neurodegenerative disorders (e.g., Alzheimer's, Parkinson's) and infectious diseases, including HIV and COVID-19-related complication
Emerging Trends in the Market
Multiplex IHC:
Multiplexing enables the simultaneous detection of multiple biomarkers within a single tissue sample, enhancing diagnostic accuracy in complex diseases.
This approach is becoming increasingly popular in research settings, especially for immuno-oncology studies.
Integration with Digital Pathology and AI:
AI-powered tools are being integrated with digital pathology systems to assist pathologists in interpreting IHC slides with greater precision.
AI algorithms can quantify marker expression and identify patterns missed by the human eye.
Advent of Novel Biomarkers:
Research is driving the discovery of new biomarkers for diseases like lung cancer, autoimmune disorders, and cardiovascular diseases.
These biomarkers are increasing the demand for specific IHC reagents and kits.
Immunohistochemistry Market Challenges
High Cost of Instruments and Reagents:
Automated systems and high-quality reagents remain expensive, limiting their adoption in low-income regions.
Lack of Skilled Professionals:
Accurate interpretation of IHC results requires extensive training, which is a barrier in under-resourced settings.
Regulatory Constraints:
Diagnostic products, especially those used in companion diagnostics, face stringent regulations, delaying their approval and market entry.
Immunohistochemistry Market Opportunities for Growth
Expansion in Emerging Markets: Governments in countries like India and China are investing in healthcare infrastructure, opening new opportunities for IHC companies.
Customizable IHC Solutions: Demand for tailor-made antibodies and reagents is growing as research expands into niche areas.
Partnerships and Collaborations: Companies are forming strategic alliances to accelerate research and development, ensuring quicker market penetration.
Immunohistochemistry Market Segments
By Product
Antibodies
Kits
REAGENTS
By End-User
Hospitals
Academic
Diagnostic Labs
By Application
Forensic
Diagnostic
Research
Immunohistochemistry Key Market Players
The Immunohistochemistry Market is dominated by a few large companies, such as
F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd
Agilent Technologies, Inc.
Danaher Corporation (Leica Biosystems)
Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.
Merck KGaA (MilliporeSigma)
Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc.
Abcam plc
Biocare Medical, LLC
Cell Signaling Technology, Inc. (CST)
PerkinElmer Inc.
Sakura Finetek Japan Co., Ltd.
Becton, Dickinson and Company (BD)
Immunohistochemistry Industry: Regional Analysis
North American market's forecast
North America is the world's largest market, with more than 38% of the worldwide market in 2023. Among the factors contributing to the region's dominance include a stable healthcare system, the presence of significant market participants, an emphasis on cancer research and individualized treatment, and the widespread application of state-of-the-art diagnostic techniques. The United States and Canada are the two countries that contribute the most to this industry.
Asia-Pacific Market Forecasts
Growing demand for individualized treatment, increased knowledge of early cancer detection, and increased spending in healthcare infrastructure are the main drivers of growth in this area. Leading contributors to the regional market include South Korea, Japan, China, and India. There are many potential for the market to grow in this area due to the growing number of pharmaceutical and biotechnology businesses as well as the availability of a big patient pool.
Market Statistics for Europe
The market is expanding in this region due to a number of factors, including the growing incidence of chronic illnesses, rising healthcare costs, and a strong focus on research and development in nations like Germany, France, and the UK. The growth of the IHC market in Europe is further supported by the existence of advantageous reimbursement and regulatory frameworks.
FAQs on the Immunohistochemistry (IHC) Market
1.What is Immunohistochemistry (IHC)?
2. What factors are driving the growth of the IHC market?
3. Which regions are leading the IHC market?
4.What are the major market segments in IHC?
0 notes
Text
"Global Elotuzumab Market Report: Trends, Forecast & Insights (2024-2034)"
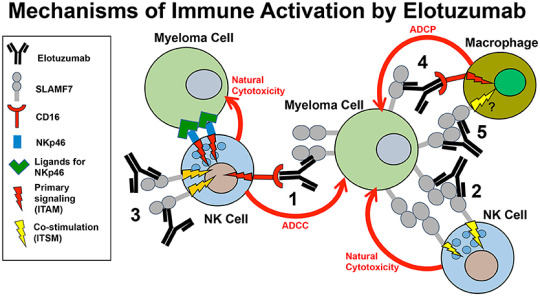
The Elotuzumab Market: Trends, Challenges, and Future Prospects
Introduction
In the evolving landscape of oncology, targeted therapies are transforming the way we approach cancer treatment. Elotuzumab, an innovative monoclonal antibody, is making waves in the treatment of multiple myeloma, a malignancy of plasma cells. Known under the brand name Empliciti, Elotuzumab has shown significant promise in clinical settings, particularly when combined with other therapies. This blog will delve into the current state of the Elotuzumab market, exploring its growth drivers, challenges, and future outlook.
Request Sample PDF Copy:
https://wemarketresearch.com/reports/request-free-sample-pdf/elotuzumab-market/1494
What is Elotuzumab?
Elotuzumab is a monoclonal antibody designed to target and stimulate the immune system against cancer cells. Specifically, it binds to a protein called SLAMF7 (Signaling Lymphocytic Activation Molecule Family member 7) found on multiple myeloma cells and natural killer (NK) cells. By enhancing the immune system's ability to attack cancer cells, Elotuzumab helps improve outcomes in patients with multiple myeloma, particularly when used in combination with other drugs such as lenalidomide and dexamethasone.
Current Market Landscape
Elotuzumab Market Growth Drivers
Increasing Incidence of Multiple Myeloma: The rising prevalence of multiple myeloma, driven by an aging population and improved diagnostic techniques, is a major factor propelling the Elotuzumab market. With the global incidence of multiple myeloma on the rise, the demand for effective therapies like Elotuzumab continues to grow.
Advancements in Combination Therapies: Elotuzumab's efficacy is significantly enhanced when used in combination with other drugs, leading to better patient outcomes. This synergistic effect has made Elotuzumab a valuable component of combination regimens, contributing to its growing market adoption.
Improved Patient Outcomes: Clinical studies have demonstrated that Elotuzumab, in combination with standard treatments, can lead to prolonged progression-free survival and improved overall survival rates in multiple myeloma patients. These positive outcomes are driving its acceptance and usage in clinical practice.
Ongoing Research and Development: Research into expanding Elotuzumab's indications beyond multiple myeloma, including its potential use in other cancers and earlier stages of the disease, could open new market opportunities and broaden its therapeutic reach.
Elotuzumab Market Challenges
High Cost of Therapy: Elotuzumab is a high-cost medication, and its price can be a barrier to access for some patients. The high cost of treatment may impact market growth, particularly in regions with limited healthcare budgets.
Competition from Other Therapies: The multiple myeloma treatment landscape is highly competitive, with several other therapies and new entrants vying for market share. Elotuzumab faces competition from other monoclonal antibodies, proteasome inhibitors, and novel agents, which can affect its market positioning.
Side Effects and Safety Concerns: While generally well-tolerated, Elotuzumab can cause side effects such as infections and infusion-related reactions. Managing these side effects is crucial for patient adherence and overall treatment success, and any safety concerns can impact market acceptance.
Elotuzumab market Opportunities
Expansion into New Indications: Exploring new therapeutic indications and combinations could significantly expand the market for Elotuzumab. Ongoing research into its use in other hematological malignancies or solid tumors could provide new opportunities for growth.
Emerging Markets: As healthcare infrastructure improves in developing regions, there is potential for growth in these markets. Strategic partnerships and pricing strategies could enhance Elotuzumab’s reach and accessibility in these areas.
Innovative Combination Therapies: Developing and optimizing new combination therapies involving Elotuzumab could lead to better patient outcomes and increased market demand. Collaboration with other pharmaceutical companies and research institutions could drive innovation in this space.
Future Outlook
The Elotuzumab market is poised for continued growth, driven by increasing disease prevalence, advancements in combination therapies, and ongoing research and development. However, challenges such as high treatment costs and competition from other therapies will require strategic planning and adaptation.
Looking ahead, the future of Elotuzumab will likely involve efforts to expand its therapeutic indications, improve patient access, and navigate the competitive landscape. Continued innovation and research will be crucial in realizing the full potential of this promising therapy.
Conclusion
Elotuzumab Market has established itself as a significant player in the treatment of multiple myeloma, offering hope for improved patient outcomes through its unique mechanism of action. As the market evolves, addressing challenges and seizing emerging opportunities will be key to maximizing its impact. Stay tuned to our blog for the latest updates on the Elotuzumab market and other developments in the pharmaceutical industry.
#ElotuzumabMarket#Elotuzumab#MultipleMyelomaTreatment#MarketForecast#GlobalMarketAnalysis#HealthcareTrends
0 notes
Text
Radiation Oncology Market Trends: Key Drivers, Challenges, and Opportunities Ahead
The global radiation oncology market is expected to reach USD 21.14 billion by 2030, registering a CAGR of 12.3% from 2024 to 2030, according to a new report by Grand View Research. The growth of the market is attributed to the global rise in cancer burden, the growing geriatric population, and supportive reimbursement programs undertaken by the government and private organizations. Furthermore, the increasing technological innovation and advancement in radiotherapy offer lucrative opportunities for market growth.
The world is witnessing an increasing prevalence of cancer cases which is the key factor driving the radiation oncology market growth. For instance, according to Globocan, in 2020, more than 20.0 million people were diagnosed with cancer, and 10.0 million died of cancer. Moreover, the aging population is at high risk of cancer due to a weak immune system and comorbid conditions; thereby, the rising geriatric population further fuels market growth. For instance, in 2020, according to WHO estimates, the global geriatric population was approximately 1.0 billion and is expected to reach 2.1 billion by 2050.
Extensive research activities for the development of novel radiotherapy techniques and multidisciplinary therapeutic approaches are expected to lead to an increased survival rate and a more favorable prognosis of cancer. For instance, in December 2022, Elekta Unity demonstrated MR-Linac use for pancreatic tumors, where the first-ever patient was treated with new advanced radiotherapy motion management.
Similarly, in June 2020, Isoray signed a research agreement with the University of Cincinnati Physicians Company to study neck and head cancer treatment. The companies will evaluate the efficacy of Keytruda along with Cesium-131 post-surgical resection. Using such medical isotopes for cancer treatment may boost the research in developing a new target-specific radiation therapy system by understanding disease complexity & patients' need, thereby widening the opportunity in the market.
Furthermore, supportive reimbursement and regulatory policies for radiation therapy are also expected to drive the radiation oncology market growth. For instance, in July 2021, the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) developed a new Radiation Oncology Payment Model (RO-APM) for the diagnosis of cancer and radiotherapy services. It enhances the quality of care of the patients and reduces the annual Medicare expenditure.
Radiation Oncology Market Report Highlights
By type, the external beam radiation therapy (EBRT) segment accounted for a 64.53% share of the radiation oncology market in 2022 due to the rapid technological advancement, and increased adoption in the treatment of various types of cancers
Based on technology, in 2022 intensity-modulated radiotherapy (IMRT) segment dominated the market due to the increased availability of technologically advanced IMRT's in countries with unmet treatment needs. However, brachytherapy is estimated to be the fastest-growing segment during the forecast period
In 2022, EBRT segment held the highest market share in the application space. Moreover, EBRT segment is also anticipated to maintain its dominance during the forecast period
North America dominated the global market in 2022 owing to the factors such as the increase in new cancer cases, high awareness among healthcare professionals about advanced radiotherapy, and better healthcare access in the region
Radiation Oncology Market Segmentation
Grand View Research has segmented the global radiation oncology market based on the type, technology, application, and regions:
Radiation Oncology Type Outlook (Revenue, USD Million, 2018 - 2030)
External Beam Radiation Therapy
Linear Accelerators (Linac)
Compact advanced radiotherapy systems
Cyberknife
Gamma Knife
Tomotherapy
Proton Therapy
Cyclotron
Synchrotron
Internal Beam Radiation Therapy
Brachytherapy
Seeds
Applicators and After loaders
Electronic Brachytherapy
Systemic Beam Radiation Therapy
Others
Radiation Oncology Technology Outlook (Revenue, USD Million, 2018 - 2030)
External Beam Radiation Therapy
Image-Guided Radiotherapy (IGRT)
Intensity Modulated Radiotherapy (IMRT)
Stereotactic Technology
Proton Beam Therapy
3D Conformal Radiotherapy (3D CRT)
Volumetric Modulated Arc Therapy (VMAT)
Brachytherapy
Low-Dose Rate Brachytherapy
High-Dose Rate Brachytherapy
Radiation Oncology Application Outlook (Revenue, USD Million, 2018 - 2030)
External Beam Radiation Therapy
Prostate Cancer
Breast Cancer
Lung Cancer
Head and Neck Cancer
Colorectal Cancer
Others
Internal Beam Radiation Therapy
Prostate Cancer
Gynecological Cancer
Cervical Cancer
Breast Cancer
Penile Cancer
Others
Radiation Oncology Regional Outlook (Revenue, USD Million; 2018 - 2030)
North America
US
Canada
Europe
Germany
UK
France
Italy
Spain
Denmark
Sweden
Norway
Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
China
India
Japan
Australia
South Korea
Thailand
Rest of APAC
Latin America
Brazil
Mexico
Argentina
Rest of LATAM
Middle East & Africa
South Africa
Saudi Arabia
UAE
Kuwait
Rest of MEA
List of Key Players
Varian Medical Systems, Inc.
Elekta AB
Accuray Incorporated
IBA Radiopharma Solutions
BD (Becton, Dickinson and Company)
Isoray Inc.
Mevion Medical Systems
Nordion, Inc.
NTP Radioisotopes SOC Ltd.
Curium
View Ray Technologies, Inc.
Order a free sample PDF of the Radiation Oncology Market Intelligence Study, published by Grand View Research.
0 notes