#Missouri Legislature
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
It's not just in areas like abortion and restrictions on voting that makes Republicans want to turn back the clock 200 years.
In Missouri, a Republican legislator wants to bring back dueling. No, that isn't a typo.
A Missouri Republican’s proposal to reintroduce dueling to solve statehouse differences was branded “utter stupidity” by a leading historian of political violence. “Back in the day,” Joanne B Freeman of Yale tweeted, “they were smart enough to take dueling OUTSIDE. The draft that I saw suggests doing it in the chamber. This doesn’t show guts or bravery or manhood – if it’s supposed to. It shows utter stupidity.” Freeman is the author of The Field of Blood: Violence in Congress and the Road to Civil War. The state senator behind the proposal said he was making a point about the breakdown of regular order in Missouri politics. The draft rule change came to national notice when it was posted to social media by Democrats in the state senate. “The Missouri Republican civil war continues to escalate as a member of the Freedom Caucus faction has filed a proposed rule change to allow senators to challenge an ‘offending senator to a duel’,” they wrote.
Here's some of the language from the proposal...
The draft rule read: “If a senator’s honor is impugned by another senator to the point that it is beyond repair and in order for the offended senator to gain satisfaction, such senator may rectify the perceived insult to the senator’s honor by challenging the offending senator to a duel. “The trusted representative, known as the second, of the offended senator shall send a written challenge to the offending senator. The two senators shall agree to the terms of the duel, including choice of weapons, which shall be witnessed and enforced by their respective seconds. “The duel shall take place in the well of the senate at the hour of high noon on the date agreed to by the parties to the duel.” The author, Nick Schroer, represents District 2 in the Missouri senate.
I imagine that the Republican choice of weapons in such duels would be ketchup bottles with nitrogen gas.
Nick Schroer is rather typical of anti-democracy Republicans. He and another extremist held a stunt with flamethrowers last September which got international attention.
Republican candidate for Missouri governor vows to burn books after viral flamethrower video
Republicans like Schroer have more screws loose than a Boeing 737 Max 9. And people who vote for them are just as loony.
Nick Schroer is yet another reason we need to pay attention to state government – especially the state legislatures.
The first step is to find out just who represents you in your legislature.
Find Your Legislators Look your legislators up by address or use your current location.
If you have the misfortune of being represented by a MAGA Republican, contact your county or state Democratic Party and ask what you can do to turn your state blue.
#missouri#republicans#the far right#nick schroer#duels#dueling#flamethrowers#missouri legislature#missouri state senate#election 2024
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
A rare party switch in the Missouri House could be in the offing after one Republican on Wednesday wasn’t allowed to speak against a GOP plan to restrict gender-affirming care for minors.
Rep. Chris Sander, R-Lone Jack, one of two openly gay Republicans in the Legislature, said Wednesday that local, state and national Republicans needed to decide whether gay and transgender Republicans were welcome.
“If they want to tell all Republicans who are gay to get out and go to the Democrat Party, they just need to do that,” Sander, a 2001 graduate of Hazelwood West High School in St. Louis County, told the Post-Dispatch.
Sander was one of three Republicans to vote against the restrictions, which are headed to Gov. Mike Parson, a Republican, for his consideration.
House Majority Leader Jonathan Patterson, R-Lee’s Summit, and Rep. Gary Bonacker, R-House Springs, also broke with their party to vote with Democrats against the ban.
Sander, who said he is Republican committeeman for the Van Buren Township in Jackson County, said he planned to speak at the county party’s May 22 meeting.
Members of the county GOP have tried to censure Sander for filing a resolution that would overturn Missouri’s constitutional ban on same-sex marriage, which was nullified by a 2015 Supreme Court decision.
“I’m going to rail against them and I’m going to say how I think it should be, and if they don’t like it, they can just get rid of me, and if that happens then I’ll be an independent or a Democrat,” Sander said, adding he might also consider becoming a Libertarian if he left the GOP.
“If they kick me off that (Jackson County GOP) committee, I will not be a Republican,” Sander said.
If Sander were to quit the GOP, he would join a short list of other House members over the past decade to leave their political party.
In 2015, then-Rep. Keith English, a Florissant Democrat, said he was leaving the Democratic Party to become an independent.
“This is no longer the Democrat Party of Bill Clinton or John F Kennedy. I’m leaving the party because I love my state,” English said at the time.
English’s decision to ditch the Democrats followed another Democratic defection a day after the 2014 midterms.
Then-Rep. Linda Black, who had been a Democrat from Desloge, switched to the Republican Party a day after the election after she ran unopposed.
Her St. Francois County district had a long history of electing Democrats but voters there have bolted to the Republicans in recent election cycles.
Sander’s eastern Jackson County 33rd District is roughly 58% Republican and 39% Democrat, according to an analysis of the district’s partisan makeup.
“I can see myself winning an election as a Republican or a Democrat or an independent,” he said.
Republicans controlled 117 seats in the House in 2015 following Black’s switch.
The GOP now controls 111 seats despite continuing to hold a two-thirds majority.
Democrats hold 51 seats following Democratic Rep. Rasheen Aldridge’s resignation this year to join the St. Louis Board of Aldermen. Parson has not called a special election to replace him.
#us politics#news#2023#st. louis post dispatch#Missouri#republicans#conservatives#gop#Chris Sander#Democrats#independents#Missouri Legislature#Gov. Mike Parson#Jonathan Patterson#Gary Bonacker#Keith English#Linda Black#Rasheen Aldridge
15 notes
·
View notes
Text
Appealing to elected officials or moving doesn't hurt (I moved from Missouri to a friendlier state, I get it, but it's not an option for everyone under threat!) BUT there are far more avenues for taking action in opposition to this than I am seeing in the notes currently.
Learn how to source and distribute DIY HRT. Make friends in states where gender affirming surgeries are likely to remain legal so that you can better form housing & recovery networks for surgeries. Download and use signal. Connect with other trans people and form networks to collectively care for each other's transition/medical needs. Learn how to conceal what you're doing from the state. Connect with abortion funds and harm reduction groups - they've been doing work around criminalized medical needs for a long time, you can learn from their work and apply the lessons to your specific needs. Austin and DFW definitely already have trans and anarchist communities doing this work - find them before shit gets bad!
Texas’ HB 3399 bill will kill people if it passes. It will make hormone therapy illegal. For all ages. Period. This was never about women’s sports. It was never about bathrooms. It was never about “protecting the children”. They want us dead. If you’re a fellow trans person and you live in Texas, I strongly urge you to be ready to move somewhere safer.
#I don't have links rn but I was seeing flyers for an anarchist book fair in austin last month!#iirc there's longstanding bookstores in both metro areas that would be decent places to start#if you're by the border groups doing that work are good contacts as well#like I said. I moved. but queer activists in missouri and texas and florida are some of the hardest people I've met.#I learned from my time in MO that you really gotta hedge your bets against a red state legislature like#oppose the thing but prepare for what you'll do if it passes y'know?
34K notes
·
View notes
Text
Abortion Is On The Ballot
In ten states, there are ballot measures or questions which will be decided in the November election which will impact the future of abortion access in those states. Here’s what you need to know.
Arizona
Arizona Proposition 139 the Right to Abortion Initiative will amend the state constitution to provide for the fundamental right to abortion that the state of Arizona may not interfere with before the point of fetal viability unless justified by a compelling state interest.
To enshrine abortion rights protection in the state constitution Vote Yes
Colorado
Colorado Amendment 79, the Right to Abortion and Health Insurance Coverage Initiative will amend the state constitution to create the right to an abortion and authorize the use of public funds (Medicaid) to pay for abortion care.
To enshrine abortion rights protection in the state constitution Vote Yes
Florida
Florida Amendment 4, the Right to Abortion Initiative, will amend the state constitution to declare that "no law shall prohibit, penalize, delay, or restrict abortion before viability or when necessary to protect the patient’s health, as determined by the patient’s healthcare provider.” The current constitutional provision requiring parental consent for minors' abortions will not be affected.
To enshrine abortion rights protection in the state constitution and overturn the current six week abortion ban Vote Yes
Maryland
Maryland Question 1, the Right to Reproductive Freedom Amendment, will amend the state constitution to establish a right to reproductive freedom, defined to include "the ability to make and effectuate decisions to prevent, continue, or end one's own pregnancy."
To enshrine reproductive rights protection in the state constitution Vote Yes
Missouri
Missouri Amendment 3, the Right to Reproductive Freedom Initiative will amend the state constitution to provide the right for reproductive freedom, which is defined as "the right to make and carry out decisions about all matters relating to reproductive health care, including but not limited to prenatal care, childbirth, postpartum care, birth control, abortion care, miscarriage care, and respectful birthing conditions," and providing that the state legislature may enact laws that regulate abortion after fetal viability.
To enshrine broad reproductive rights protection including abortion in the state constitution and overturn the current complete abortion ban Vote Yes
Montana
Montana CI-128, the Right to Abortion Initiative will create a constitutional "right to make and carry out decisions about one’s own pregnancy, including the right to abortion," and allow the state to regulate abortion after fetal viability, except when "medically indicated to protect the life or health of the pregnant patient."
To enshrine broad reproductive rights protection including abortion in the state constitution Vote Yes
Nebraska
The Nebraska Prohibit Abortions After the First Trimester Amendment will amend the state constitution to elevate the current twelve week abortion ban law to a constitutional provision with limited exceptions for medical emergencies or in cases of rape.
To prevent the current legislative abortion ban from being enshrined in the state constitution Vote No
Nevada
Nevada Question 6, the Right to Abortion Initiative will amend the state constitution to create a constitutional right to an abortion, providing for the state to regulate abortion after fetal viability, except where medically indicated to "protect the life or health of the pregnant patient."
To enshrine abortion rights protection in the state constitution Vote Yes
New York
New York Proposal 1, the Equal Protection of Law Amendment will amend the state constitution to provide that people cannot be denied rights based on their "ethnicity, national origin, age, and disability" or "sex, including sexual orientation, gender identity, gender expression, pregnancy, pregnancy outcomes, and reproductive healthcare and autonomy."
To enshrine equal rights protection for pregnant people and abortion patients in the state constitution Vote Yes
South Dakota
The South Dakota Constitutional Amendment G, the Right to Abortion Initiative will amend the state constitution to protect the right to an abortion based on a trimester framework, with no restrictions permitted in the first trimester, only limited medical need restrictions permitted in the second trimester and allowing deeper restrictions in the third trimester except "when abortion is necessary, in the medical judgment of the woman's physician, to preserve the life and health of the pregnant woman."
To enshrine abortion rights protection in the state constitution and overturn the state's current full abortion ban Vote Yes
If you live in one of these ten states and abortion rights matter to you, get registered or double check your registration and make your voting plan today. Every single vote matters significantly in amendment questions.
#abortion is on the ballot#reproductive rights#abortion rights#us elections#us elections 2024#voter information
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
"For the first time in almost 60 years, a state has formally overturned a so-called “right to work” law, clearing the way for workers to organize new union locals, collectively bargain, and make their voices heard at election time.
This week, Michigan finalized the process of eliminating a decade-old “right to work” law, which began with the shift in control of the state legislature from anti-union Republicans to pro-union Democrats following the 2022 election. “This moment has been decades in the making,” declared Michigan AFL-CIO President Ron Bieber. “By standing up and taking their power back, at the ballot box and in the workplace, workers have made it clear Michigan is and always will be the beating heart of the modern American labor movement.”
[Note: The article doesn't actually explain it, so anyway, "right to work" laws are powerful and deceptively named pieces of anti-union legislation. What right to work laws do is ban "union shops," or companies where every worker that benefits from a union is required to pay dues to the union. Right-to-work laws really undermine the leverage and especially the funding of unions, by letting non-union members receive most of the benefits of a union without helping sustain them. Sources: x, x, x, x]
In addition to formally scrapping the anti-labor law on Tuesday [February 13, 2024], Michigan also restored prevailing-wage protections for construction workers, expanded collective bargaining rights for public school employees, and restored organizing rights for graduate student research assistants at the state’s public colleges and universities. But even amid all of these wins for labor, it was the overturning of the “right to work” law that caught the attention of unions nationwide...
Now, the tide has begun to turn—beginning in a state with a rich labor history. And that’s got the attention of union activists and working-class people nationwide...
At a time when the labor movement is showing renewed vigor—and notching a string of high-profile victories, including last year’s successful strike by the United Auto Workers union against the Big Three carmakers, the historic UPS contract victory by the Teamsters, the SAG-AFTRA strike win in a struggle over abuses of AI technology in particular and the future of work in general, and the explosion of grassroots union organizing at workplaces across the country—the overturning of Michigan’s “right to work” law and the implementation of a sweeping pro-union agenda provides tangible evidence of how much has changed in recent years for workers and their unions...
By the mid-2010s, 27 states had “right to work” laws on the books.
But then, as a new generation of workers embraced “Fight for 15” organizing to raise wages, and campaigns to sign up workers at Starbucks and Amazon began to take off, the corporate-sponsored crusade to enact “right to work” measures stalled. New Hampshire’s legislature blocked a proposed “right to work” law in 2017 (and again in 2021), despite the fact that the measure was promoted by Republican Governor Chris Sununu. And in 2018, Missouri voters rejected a “right to work” referendum by a 67-33 margin.
Preventing anti-union legislation from being enacted and implemented is one thing, however. Actually overturning an existing law is something else altogether.
But that’s what happened in Michigan after 2022 voting saw the reelection of Governor Gretchen Whitmer, a labor ally, and—thanks to the overturning of gerrymandered legislative district maps that had favored the GOP—the election of Democratic majorities in the state House and state Senate. For the first time in four decades, the Democrats controlled all the major levers of power in Michigan, and they used them to implement a sweeping pro-labor agenda. That was a significant shift for Michigan, to be sure. But it was also an indication of what could be done in other states across the Great Lakes region, and nationwide.
“Michigan Democrats took full control of the state government for the first time in 40 years. They used that power to repeal the state’s ‘right to work’ law,” explained a delighted former US secretary of labor Robert Reich, who added, “This is why we have to show up for our state and local elections.”"
-via The Nation, February 16, 2024
#michigan#united states#us politics#labor#labor rights#labor unions#capitalism#unions#unionize#gretchen whitmer#democrats#voting matters#right to work#pro union#workers#workers rights#good news#hope
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
Oklahoma and New Hampshire have used executive authority to create a state version of the DOGE commission. Texas, North Carolina and Missouri are introducing DOGE style reforms via their legislature.
DOGE like reforms are sweeping the country.
151 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Wyoming Republican Party is seeking to kill a bill working its way through the state Legislature proposing to raise the state's legal marriage age to 16, arguing that putting "arbitrary" limits on child marriage interferes with parental rights and religious liberty. The bill—which already passed the Republican-controlled Wyoming House of Representatives on a 36-25 vote late last month—proposes banning state residents from marrying anyone under the age of 16, while requiring anyone under the age of 18 seeking to get married to receive written consent from their parents under the eye of a competent witness.
Currently, Wyoming is one of just eight states in the country—including California, Michigan, Mississippi, New Mexico, Oklahoma, Washington and West Virginia—without a minimum age requirement for marriage, and it currently ranks among the top ten states in the country for child marriages, according to a 2021 study by advocacy group Unchained at Last.
Newsom had shared a clip on Twitter from a House Committee hearing in Missouri earlier this week where an opponent of Moon accused him of supporting minors as young as 12 getting married to adults. During a Senate debate on a bill to ban gender-affirming care for trans youth on Tuesday, Rep. Peter Merideth, a Democrat, confronted Moon about his previous vote opposing a bill that would have prevented children as young as 12 from getting married to adults.
"I've heard you talk about parents' rights to raise their kids how they want. In fact, I just double-checked, you voted no on making it illegal for kids to be married to adults at the age of 12 if their parents consented to it. You said actually that should be the law because it's the parents' rights and the kids' rights to decide what's best for them, to be raped by an adult," Merideth said. "That was the law, you voted no to change it."
Moon replied: "Do you know any kids who have been married at age 12? I do. And guess what? They're still married."
-
A Tennessee General Assembly bill to create a legal marriage pathway available only to straight couples will not advance this year following public outcry over the initial version of the legislation. The legislation sparked widespread condemnation after early versions failed to include an explicit minimum age requirement, which opponents argued could open minors up to abuse and underage marriages. The bill's sponsors, including Rep. Tom Leatherwood, R-Arlington, maintain that was never the intent of the bill, which was brought by opponents of same-sex marriage.
Sponsors of the legislation added amendments specifying a man and woman seeking the contract must have "attained the age of majority," which is 18 in Tennessee. Though the bill garnered condemnation over child marriage concerns, the legislation was initially filed as an anti-gay marriage measure. Supporters of the legislation, including former state Sen. David Fowler, say they can't conscientiously sign Tennessee marriage licenses because LGBTQ couples are now afforded the right to marry.
Conservative Republicans are obsessed with the sex lives and bodies of young girls [and boys].
#Wyoming#Tennessee#Florida#Ohio#Missouri#2020s#2023#marriage in America#child marriage#teen marriage#marriage laws#Unchained at Last#Mike Moon#parent's rights#American politics#misuse of the word grooming#state legislature#republican fearmongering#american sex and gender issues#child sex abuse
4K notes
·
View notes
Text
Cheers to Olivia Rodrigo! 🍻👍🏼
Pop singer Olivia Rodrigo teamed up with the Missouri Abortion Fund to give out free emergency birth control pills and condoms to concertgoers at her St. Louis show. Rodrigo visited St. Louis on Tuesday evening as part of her GUTS world tour. X user @cowboylikekin posted a viral photo of the condoms and Julie contraceptive pills that were distributed at the concert. The image has been liked more than 30,000 times. Volunteers with the Missouri Abortion Fund handed out the pills, condoms and stickers at Tuesday’s concert. The nonprofit aims to provide assistance to Missouri residents who cannot afford the cost of abortion care.
Missouri has been taken over by far right MAGA extremists. Fortunately there is a ballot measure being proposed to restore reproductive freedom in the state.
Abortion rights advocates with Missourians for Constitutional Freedom are pushing for a ballot measure through Missouri’s initiative petition process, looking to amend Missouri’s constitution with a law that would make abortion legal until viability. To place the issue on this November’s ballot, the campaign must collect around 180,000 signatures in support of the petition and turn the signatures in to the Missouri Secretary of State’s Office by May 5.
If you're in Missouri, consider lending a hand with the ballot measure.
Missourians for Constitutional Freedom
And whichever state you live in, get more involved in state politics and particularly the state legislature. Most of the far right anti-freedom badness originates in legislatures in red states. Start by discovering who represents your legislative district(s).
Find Your Legislators Look your legislators up by address or use your current location.
Only one party is dedicated to restoring reproductive freedom nationally.

#olivia rodrigo#guts world tour#abortion#a woman's right to choose#reprodective freedom#emergency birth control pills#missouri#st. louis#missouri abortion fund#fund 4 good#text right by you#roe v. wade#restore roe#the sanctity of reproductive freedom#state government#state legislatures#election 2024#vote blue no matter who
26 notes
·
View notes
Text
Article by Fortesa Latifi:
"Being the child of an influencer, Vanessa tells me, was the equivalent of having a full-time job—and then some. She remembers late nights in which the family recorded and rerecorded videos until her mother considered them perfect and days when creating content for the blog stretched into her homeschooling time. If she expressed her unease, she was told the family needed her. “It was like after this next campaign, maybe we could have more time to relax. And then it would never happen,” she says. She was around 10 years old when she realized her life was different from that of other children. When she went to other kids’ houses, she was surprised by how they lived. “I felt strange that they didn’t have to work on social media or blog posts, or constantly pose for pictures or videos,” she says. “I realized they didn’t have to worry about their family's financial situation or contribute to it.”
Vanessa, who requested anonymity to speak freely about her family dynamics, says she helped create content for huge companies like Huggies and Hasbro when her mom landed endorsement deals. When she reached puberty and began menstruating, her mother had her do sponsored posts for sanitary pads. “It was so mortifying,” she says. “I just felt like I wanted to crawl into a hole and never come out.”
Being part of an influencer family changed everything about her life, Vanessa says. “Sometimes I didn’t know where the separation was between what was real and what was curated for social media.” And her mother’s online presence indelibly warped their relationship. “Being an influencer kid turned my relationship with my mom into more of an employer-employee relationship than a parent-child one,” she says. “Once you cross the line from being family to being coworkers, you can’t really go back.”
...
Khanbalinov has had zero new offers since he took his kids offline. “When we were showing our kids, brands were rolling in left and right—clothing companies, apps, paper towel companies, food brands. They all wanted us to work with them,” he says. “Once we stopped, we reached out to the brands we had lined up and 99 percent of them dropped out because they wanted kids to showcase their products. And I fought back, like, you guys are a paper towel company—why do you need a kid selling your stuff?”
The law has woefully lagged behind the culture here, but there’s signs that policymakers might finally be catching up. In 2023, in addition to Illinois, three other states—New York, Washington State, and New Jersey—proposed bills to protect influencer kids. Contrast that with the flurry of legislative activity in just the first two months of 2024. Seven more states—Maryland, Georgia, Ohio, Missouri, California, Arizona, Minnesota—have introduced similar legislation. Some of the bills are going one step further to protect the privacy of the kids featured in this content. In some states, proposed legislation would include a clause that borrows from a European legal doctrine known as the “right to be forgotten”—it would allow someone who was featured in content when they were a child to request that platforms permanently delete those posts. None of the current legislation introduced, however, would outright bar the practice of featuring minors in monetized content.
...
The movement on this issue was glacial for years, but it finally feels like the ice has thawed. Much of that progress is thanks to activists like Cam Barrett (she/they), a 25-year-old creator (@softscorpio) who uses TikTok to talk about her experience of being overshared in their childhood and adolescence. Barrett doesn’t go by her legal name anymore because of the online history it’s tied to. “I love my legal name,” Barrett tells me. “I just don’t love the digital footprint attached to it.” Last year, Barrett testified in front of the Washington State legislature as a proponent of a bill to protect influencer kids. This year, they testified again—this time, in front of the Maryland legislature.
“As a former content kid myself, I know what it’s like to grow up with a digital footprint I never asked for,” Barrett told the Maryland House of Delegates Economic Matters Committee in February. “As my mom posted to the world my first-ever menstrual cycle, as she posted to the world the intimate details about me being adopted, her platform grew and I had no say in what was posted.” And yet, Cam says her activism has been healing.
For Cam and other influencer children, getting a paycheck won’t give them back what they lost—a normal childhood unobstructed by the cameras pushed into their faces. But it could be the beginning of some version of restitution. “My friends say I’m fighting for little Cam,” she tells me. “It feels very healing because I didn’t have anyone to fight for me as a kid.”"
Read the full article here: https://www.cosmopolitan.com/lifestyle/a60125272/sharenting-parenting-influencer-cost-children/
423 notes
·
View notes
Text
If you are getting sick of the two-party system and elections running candidates you hate, or incumbents you can't rebuke without electing someone so much worse, or partisan primaries repeatedly giving you the wing of your too-large-tent party that sucks... You need to look into making voting reform a big part of your political priorities.
Ranked Choice Voting (RCV) can be a big part of that!
And in 2024, RCV (also sometimes called IRV for "instant-runoff voting") is going to be on a lot of ballots, so check your state and get informed! Here's a list that I'm not sure is comprehensive, but I did research it for you to have somewhere to start:
First off, here's a post with some resources for you to do your ballot research with! I used Ballotpedia to look up this list, for example, after most of the RCV news only mentioned the 4 states with the most straightforward "vote yes for RCV" measures.
In Alaska... the state approved a RCV system in 2020 that has been a model success, but now the people with narrower support who lost their elections to broadly popular moderates introduced the Repeal Top-Four Ranked-Choice Voting Initiative to repeal it. This will be on the Nov 5 ballot as an Initiative, and people need to Vote No.
In Arizona... it's possible that optional RCV and a workaround RCV ban will both be on the ballot. The ban from the Legislature doesn't stop RCV but prevents the primary system often used with it - the goal is to make RCV harder to implement. It will be on the Nov 5 ballot as Proposition 133, and people need to Vote No. The Eliminate Partisan Primaries Amendment has RCV options and has turned in its signatures, so it may be on the Nov 5 ballot - Keep Watch and Vote Yes if it appears.
In Colorado... a Top-Four Ranked-Choice Voting Initiative modeled on Alaska's could bring RCV to state executive, state legislative, and congressional office elections. This may be on the Nov 5 ballot - Keep Watch and Vote Yes if it appears.
In Idaho... a Top-Four Ranked-Choice Voting Initiative modeled on Alaska's will bring RCV to Congressional office, state legislature, elective state office, and county elective office elections. This will be on the Nov 5 ballot as an Initiative (1), and people need to Vote Yes.
In Missouri... the Missouri GOP has been shoehorning in deceptive Constitutional Amendments to reduce voter influence for the past several elections. This year it's a ban on RCV hidden under a useless ban on non-citizen voting (which is already illegal and the state Constitution already says "citizens" when saying who can vote). This will be on the Nov 5 ballot as the Require Citizenship to Vote and Prohibit Ranked-Choice Voting Amendment, and people need to Vote No.
In Montana... signatures have been submitted for two separate constitutional amendments, one establishing Top-Four primaries and another requiring a majority-vote system to be implemented (which would likely be a run-off or RCV system). These may be on the Nov 5 ballot - Keep Watch and Vote Yes if they appear.
In Nevada... In 2022 the first round of a Top-Five Ranked-Choice Voting Initiative was approved by 52.94%. It has to be approved again in 2024 in order to be implemented. It will bring RCV to Congressional office, statewide executive, and state legislature elections. This will be on the Nov 5 ballot as Question 3, and people need to Vote Yes.
In Oregon... a Ranked-Choice Voting for Federal and State Elections Measure will bring RCV to Presidential, Congressional office, governor, Secretary of state, attorney general, state treasurer, and commissioner of labor and industries elections. This will be on the Nov 5 ballot as a Measure, and people need to Vote Yes.
And a bonus in South Dakota... it's not RCV, but the Top-Two Primary Elections Initiative (Amendment H) would be a significant voting reform, and it will be on the Nov 5 ballot. Do some research if you live there and decide if this would help or hinder elections.
#politics#voting#2024 presidential election#ranked choice voting#2024 elections#resources#us politics#ladyluscinia
162 notes
·
View notes
Text

Mass deportation update: 🚨Missouri has officially proposed bounty system to report illegal aliens in their state.
This bill would give residents a $1,000 payout for reporting migrants who entered our country illegally, which is also one of seven bills introduced in the state’s legislature to focus on their immigration issues.
Senate Bill 72 would also develop a “Missouri Illegal Alien Certified Bounty Hunter Program,” which would certify people to be bounty hunters to track down these tips.
Updates coming soon.

75 notes
·
View notes
Text
The number of commercial-scale Bitcoin mining operations in the U.S. has increased sharply over the last few years; there are now at least 137. Similar medical complaints have been registered near facilities in Arkansas and North Dakota. And the Bitcoin mining industry is urgently trying to push bills through state legislatures, including in Indiana and Missouri, which would exempt Bitcoin mines from local zoning or noise ordinances. In May, Oklahoma governor Kevin Stitt signed a “Bitcoin Rights” bill to protect miners and prevent any future attempts to ban the industry. Much of the American Bitcoin mining industry can now be found in Texas, home to giant power plants, lax regulation, and crypto-friendly politicians. In October 2021, Governor Greg Abbott hosted the lobbying group Texas Blockchain Council at the governor’s mansion. The group insisted that their industry would help the state’s overtaxed energy grid; that during energy crises, miners would be one of the few energy customers able to shut off upon request, provided that they were paid in exchange. After meeting with the lobbyists, Abbott tweeted that Texas would soon be the “#1 [state] for blockchain & cryptocurrency.” Technically there is federal mandate to regulate noise, which stems from the 1972 Noise Control Act—but it was essentially de-funded during the Reagan administration. This leaves noise regulation up to states, cities, and counties. New York City, for instance, has a noise code which officially caps restaurant music and air conditioning at 42 decibels (as measured within a nearby residence). Texas’s 85 decibels, in contrast, is by far the loudest state limit in the nation, says Les Blomberg, the executive director of the nonprofit Noise Pollution Clearinghouse. “It is a level that protects noise polluters, not the noise polluted,” he says. The residents of Granbury feel they’ve been lied to. In 2023, the site’s previous operators, US Bitcoin Corp, constructed a wall around the mine almost 2,000 feet long and claimed that they had “solved the concern.” But Shirley says that the complaints from the community about the sound actually increased when the wall was nearing completion last fall. Since Marathon bought the facility outright in December, its hash rate, or computational power expended, has doubled. Any statewide legislation is sure to hit significant headwinds, because the very idea of regulation runs contrary to many Texans’ political beliefs. “As constitutional conservatives, they have taken our core values and used that against us,” says Demetra Conrad, a city council member in the nearby town of Glen Rose. In the week before this article’s publication, two more Granbury residents suffered from acute health crises. The first was Tom Weeks. “This whole thing is an eye opener for me into profit over people,” Weeks says in a phone call from the ICU. The second person affected was the five-year-old Indigo Rosenkranz. Her mother, Sarah, was terrified and now feels she has no choice but to get a second mortgage to move away from the mine. “A second one would really be a lot,” she says. “God will provide, though. He always sees us through.”
shocking! texans suffer from deregulation and ineffective walls
93 notes
·
View notes
Text
Eleven abortion referendums will be in front of voters in 10 states this Election Day — the largest number of pro-choice amendments the country has ever seen during a single election cycle.
From red states like Missouri and South Dakota to blue states like New York, the abortion rights ballot measures could have a monumental impact on access throughout the country. Over 20 states have enacted abortion bans since the Supreme Court repealed federal abortion protections in 2022. Citizen-led initiatives, like most of this year’s abortion rights measures, have become the response to many of the near-total abortion bans passed by Republican-controlled state legislatures.
“This is a public health crisis that we have right now,” said Chris Melody Fields Figueredo, executive director at the Ballot Initiative Strategy Center, who has worked with campaigns in all 10 states where an abortion rights amendment is in play. “The citizens, in the absence of their local elected officials, are addressing it. They’re taking power into their own hands.”
In 2022, there were six ballot measures addressing abortion, which at the time was the most in a single year. Voters protected abortion care in every state it was on the ballot during that election cycle, including in deeply Republican states like Kentucky. Ohio, a state with a long and extreme anti-abortion history, also voted to codify abortion rights into its state constitution just last year.
This year’s ballot measures range in their approaches to and levels of abortion protections. Nebraska will have two competing abortion measures, one to restrict access and one to expand. Maryland, New York and Colorado are all seeking to codify abortion protections throughout pregnancy — exceptions to the rest of the measures, which would primarily enshrine access until viability or around 24 weeks. Colorado’s Amendment 79 would also allow the use of public funds for abortion care. Missouri’s Amendment 3 would restore abortion access until viability and protect women from being prosecuted for pregnancy outcomes like miscarriage and stillbirth — a particularly progressive measure in a notoriously anti-abortion state.
If passed, most amendments would generally go into effect shortly after Election Day or at the start of 2025. Measures in Montana and South Dakota would tentatively go into effect in July 2025, while Nevada’s may not until 2026. There will be litigation in any state that passes a pro-choice measure; this is likely the time when states will bring legal challenges against successful ballot initiatives and fight to keep other abortion regulations like waiting periods and other long-standing targeted restrictions on abortion providers.
The historic number of abortion rights measures is emblematic of just how politically prominent abortion care has become. And despite conservatives who claim to want to “leave abortion to the states” since Roe fell, many did everything in their power to stop voters from weighing in on abortion rights measures.
“This is not just a reproductive freedom issue, it’s also a democracy issue,” Fields Figueredo said. “It’s about who has power and who has the determination to control what happens to their body.”
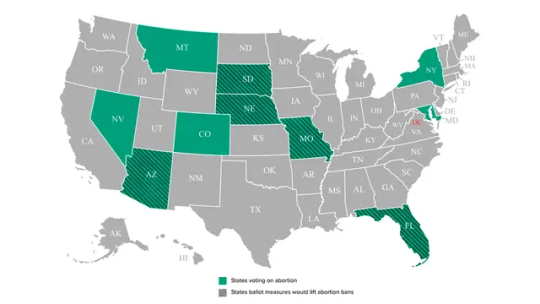
Arizona
Arizona’s Proposition 139 seeks to enshrine access to abortion up until fetal viability, or around 24 weeks, into the state constitution. If passed, the state of Arizona will not be able to limit access to abortion before viability unless the government “has a compelling reason and does so in the least restrictive way possible,” according to the measure. Under the amendment, also known as the Right to Abortion Initiative, abortions would be allowed after fetal viability only when the health or life of the pregnant person is at risk. The measure also bars future laws from punishing anyone who assists someone getting an abortion.
The state currently has a 15-week abortion ban in effect with no exceptions for rape or incest. Earlier this year, the Arizona state Supreme Court greenlit a near-total abortion ban that the Republican-controlled legislature voted to repeal.
The measure needs a simple majority to pass.
Colorado
Colorado’s pro-choice amendment would create a constitutional right to abortion care throughout pregnancy and mandate that Medicaid and private insurance companies cover abortion care. Amendment 79, also known as the Right to Abortion and Health Insurance Coverage Initiative, would repeal a 1984 addition in the Colorado constitution which barred the use of public funds for abortion care.
The measure is distinct for two reasons. Nearly every other state where abortion is on the ballot is trying to enshrine access until fetal viability, not throughout pregnancy. Additionally, requiring that abortion care be a covered service under all health insurance plans is a step pro-choice groups have been pushing for for decades.
The state does not currently restrict abortion at any point in pregnancy, making it a refuge for those who need abortion care later in pregnancy. The measure needs at least 55% of the vote to pass.
Florida
Amendment 4 would restore abortion access until viability by adding language to the Florida constitution that states “no law shall prohibit, penalize, delay, or restrict abortion before viability or when necessary to protect the patient’s health, as determined by the patient’s healthcare provider.” The ballot measure, also titled Amendment to Limit Government Interference with Abortion, does not change the state’s current law that requires parental consent for a minor to obtain an abortion.
Since the Supreme Court repealed Roe v. Wade in 2022, the state passed a 15-week abortion ban with no exceptions for rape or incest and then a six-week ban with exceptions for rape or incest. Under the leadership of Gov. Ron DeSantis (R), Florida has become one of the most extreme anti-abortion states in the country. If voters restore abortion access until viability, it would reestablish Florida as a critical safe haven in the Southeast, where most states have near-total abortion bans.
Florida has a supermajority requirement for citizen-led ballot initiatives, meaning the amendment needs to get at least 60% of the vote to pass.
Maryland
Maryland’s Question 1 guarantees the right to reproductive freedom, defined in the measure as “the ability to make and effectuate decisions to prevent, continue, or end one’s own pregnancy.” The amendment specifies that the government cannot “directly or indirectly, deny, burden, or abridge the right unless justified by a compelling State interest achieved by the least restrictive means.”
The Right to Reproductive Freedom Amendment would codify Maryland’s current law, which allows access to abortion care at any point in pregnancy and has made the state a safe haven for abortion access. It’s an exception to most other pro-choice measures on the ballot this year because it enshrines abortion access throughout pregnancy without limits. Colorado and New York are the only two other states where pro-choice groups are hoping to codify abortion access throughout pregnancy.
The amendment would pass with a simple majority.
Missouri
Amendment 3 would codify the right to reproductive freedom, including abortion access until fetal viability, into the Missouri constitution. The measure would protect the right to make decisions about other reproductive health issues including birth control, prenatal care, childbirth, postpartum care, miscarriage care and “respectful birthing conditions.” The Right to Reproductive Freedom initiative states plainly that, if passed, Missourians cannot be prosecuted for their pregnancy outcomes including miscarriage, stillbirth and abortion.
The initiative is extremely progressive for a deep-red state that has such a long anti-abortion history. The state only had three abortion clinics in 2017, and the last clinic closed shortly after Roe fell. Missouri currently has a near-total abortion ban with an exception to save the life of a pregnant person.
If the amendment passes, it would be a huge win for reproductive rights groups, and Missouri could become one of the few Midwest states with abortion access. But the state would still have a lot of work to do since many of the prior abortion regulations, such as Missouri’s 72-hour waiting period and ban on telemedicine, would need to be challenged in court.
The measure needs a simple majority to pass.
Montana
Montana’s Right to Abortion Initiative would enshrine the “right to make and carry out decisions about one’s own pregnancy, including the right to abortion” until fetal viability. The government could regulate abortion after viability except in cases where abortion care is needed to protect the life or health of the pregnant person. The measure also protects Montanans from being prosecuted for “actual, potential, perceived or alleged pregnancy outcomes,” as well as protecting anyone who helps someone seeking abortion care.
The amendment would codify the state’s current abortion law, which restricts abortion care after 24 weeks. Montana voters need a simple majority to pass the amendment.
Nebraska
Nebraska will have two ballot measures addressing abortion, one in favor of abortion rights and one against. It’s the first time competing abortion measures will be on a state ballot since the Supreme Court repealed Roe.
The pro-choice amendment, also known as the Right to Abortion Initiative, would enshrine abortion access until fetal viability into the state constitution. The measure opposed to abortion rights seeks to codify the state’s current 12-week abortion ban, or a ban on abortion after the first trimester. The anti-choice initiative does have exceptions for rape, incest and in cases of a medical emergency.
Both amendments need a simple majority to pass.
Nevada
Nevada’s Question 6 would enshrine the right to abortion access until viability and when necessary to protect the health or life of the pregnant person throughout pregnancy. The amendment states that the right to abortion until viability “shall not be denied, burdened, or infringed upon unless justified by a compelling state interest that is achieved by the least restrictive means.”
The measure, which needs a simple majority to pass, would enshrine Nevada’s current abortion law into the state constitution.
New York
Proposal 1 would amend New York’s Equal Rights Amendment to include protections for “pregnancy, pregnancy outcomes, and reproductive healthcare and autonomy” which would codify abortion protections throughout pregnancy. While it does not explicitly state abortion protections, including protections for pregnancy outcomes and reproductive decisions in the state constitution would safeguard abortion access in the state.
The state’s Equal Rights Amendment currently criminalizes the denial of rights to people based on “race, color, creed or religion.” Proposal 1 would add ethnicity, national origin, age, disability, sexual orientation, gender identity and gender expression, as well as reproductive health outcomes.
The initiative is noteworthy because, if passed, it will be the first equal rights amendment to include protections for pregnant people and pregnancy outcomes. Abortion is currently legal in New York until viability. Expanding the equal rights amendment to include pregnant people would codify the current law.
South Dakota
South Dakota’s Amendment G breaks down abortion protections by trimesters, similar to the 1973 Roe v. Wade decision. The initiative would codify abortion protections until 13 weeks or through the first trimester, and then allow the government to regulate abortion in the second trimester “only in ways that are reasonably related to the physical health of the pregnant woman.” In the third trimester, the state could regulate or ban abortions except in instances when the health or life of the pregnant person is at risk.
If the measure passes it would be a huge win for abortion rights groups because the state currently has a near-total abortion ban with no exceptions other than to save the life of a pregnant person. Pro-choice groups would still have a long way to go in restoring abortion access in the state, however. Even before Roe fell, South Dakota only had one abortion clinic left and zero in-state providers, and some regulations — like the state’s 72-hour waiting period before being able to access care — would likely need to be challenged in court.
The initiative needs a simple majority to pass.
63 notes
·
View notes
Text

Rejection of the Proposed Child Labor Constitutional Amendment by the State Legislature of Missouri
Record Group 46: Records of the U.S. SenateSeries: Committee Papers of the Committee on the JudiciaryFile Unit: Petitions and Memorials, Resolutions of State Legislatures, and Related Documents, which were Referred to the Committee on the Judiciary from the 68th Congress
HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES
53RD GENERAL ASSEMBLY
Jefferson City, Missouri
January 13, 1925
Hon. Seldon P. Spencer,
House of Representatives,
Washington, D.C.
Dear Sir:
I am instructed by the House of Representatives of
the State of Missouri that the following resolutions
have been adopted:
WHEREAS: The Congress of the United States has sub-
mitted to the several States for ratification and
amendment to the Constitution of the United States,
giving Congress the power to regulate the labor of
all persons under eighteen years of age, and
WHEREAS: This House, though opposed to the commer-
cialization of childhood, believes that this should
be prevented without undue infringment[sic] on the rights
of the State or the individual rights of the people,
and,
WHEREAS: The regulation of child labor by Congress
under proposed amendment would mean an additional army
of bureaucrats, acting as snooping agents, invading
our homes, therefore be it
RESOLVED: That it is the sense of this House that
this amendment should be rejected; that the Congress
of the United States should offer an amendment that
will give the Congress of the United States the un-
questioned rights to forbid the entry of any product
into the interstate or foreign commerce that has been
produced through or by the commercialization of child
labor, and be it further
RESOLVED: That a copy of this resolution be forwarded
to the Senators and Representatives in Congress from
Missouri.
Chief Clerk WM Funbette
Per Assistant
36 notes
·
View notes
Text
Unfortunately one way to try to drive up voter turnout and make people pay more attention to politics that would probably work is fully legalizing betting on elections. And not just the presidential election, downballot elections, school board elections, you name it. People could bet on the over-under on turnout in the New Mexico gubernatorial election. Do you really believe the Vegas line that the Democrat is 20-to-1 odds to win that Missouri state legislature seat? Put your money where your ballot is! And best of all, if you sign up on FanDuel right now you can use the promo code IVOTED to get $150 in bonus bets! Please gamble responsibly
35 notes
·
View notes
Text
Alex Bollinger at LGBTQ Nation:
Nine states are now seeing Republican efforts to overturn Obergefell v. Hodges, the 2015 Supreme Court decision that legalized marriage equality in all 50 states. This is a new trend; state Republican lawmakers have been focused on rolling back trans rights since 2020.
In five of the states — Idaho, Michigan, Montana, North Dakota, and South Dakota — Republican lawmakers have introduced resolutions calling for the Supreme Court to overturn Obergefell. Those measures have been passed by at least one chamber of the state legislature in Idaho and North Dakota. In the four other states – Missouri, Oklahoma, Tennessee, and Texas – Republican legislators have introduced bills to privilege heterosexual marriages, with some of the states referring to a new institution called “covenant marriage,” which would be limited to heterosexual couples. The point there, according to the sponsor of one such bill in Oklahoma, is to create inequality in marriage rights between opposite- and same-sex couples and invite a legal challenge that could be taken to the Supreme Court to overturn Obergefell.
Two justices on the Supreme Court have openly stated that they want to overturn Obergefell, and the Court has moved to the right since 2015. Justices Ruth Bader Ginsburg, Anthony Kennedy, and Stephen Breyer were all in the Obergefell majority but have either retired or passed away in the last ten years. Only one was replaced by a Democratic president. It is not clear if there are the five votes needed to protect marriage equality on the Court if it were to take up a test case. Thirty-five states have amendments or statutes banning same-sex marriage, and most would likely go into effect if the Supreme Court were to overturn Obergefell. Because of the 2022 federal Respect for Marriage Act, though, state and federal governments would have to recognize same-sex marriages performed in other states.
Nearly 3 years after Dobbs v. Jackson Women’s Health Organization (a case that largely focused on abortion), GOP-run states are pushing measures to end marriage equality, such as resolutions calling for the overturning of Obergefell v. Hodges and pass “covenant marriage” measures with the intent to harm LGBTQ+ rights.
#LGBTQ+#Anti LGBTQ+ Extremism#Marriage Equality#LGBTQ+ Rights#Obergefell v. Hodges#Covenant Marriage#Respect For Marriage Act#Dobbs v. Jackson Women's Health Organization
26 notes
·
View notes