#Men who encouraged women
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Anthropologist Zelia Nuttall transformed the way we think of ancient Mesoamerica

An illustration of the Aztec calendar stone surrounds a young portrait of anthropologist Zelia Nuttall. “Mrs. Nuttall’s investigations of the Mexican calendar appear to furnish for the first time a satisfactory key,��� wrote one leading scholar.Peabody Museum of Archaeology and Ethnology, Harvard University
By Merilee Grindle
Author, In the Shadow of Quetzalcoatl: Zelia Nuttall and the Search for Mexico’s Ancient Civilizations
On a bright day early in 1885, Zelia Nuttall was strolling around the ancient ruins of Teotihuacán, the enormous ceremonial site north of Mexico City. Not yet 30, Zelia had a deep interest in the history of Mexico, and now, with her marriage in ruins and her future uncertain, she was on a trip with her mother, Magdalena; her brother George; and her 3-year-old daughter, Nadine, to distract her from her worries.
The site, which covered eight square miles, had once been home to the predecessors of the Aztecs. It included about 2,000 dwellings along with temples, plazas and pyramids where they charted the stars and made offerings to the sun and moon. As Zelia admired the impressive buildings, some shrouded in dirt and vegetation, she reached down and collected a few pieces of pottery from the dusty soil. They were plentiful and easy to find with a few brushes of her hand.
The moment she picked up those artifacts would prove to be pivotal in the life and long career of this trailblazing anthropologist. Over the next 50 years, Zelia’s careful study of artifacts would challenge the way people thought of Mesoamerican history. She was the first to decode the Aztec calendar and identify the purposes of ancient adornments and weapons. She untangled the organization of commercial networks and transcribed ancient songs. She found clues about the ancient Americas all over the world: Once, deep in the stacks of the British Museum, she found an Indigenous pictorial history that predated the Spanish conquest; skilled at interpreting Aztec drawings and symbols, and having taught herself Nahuatl, the language of the Aztecs and their predecessors, she was the first to transcribe and translate this and other ancient manuscripts.
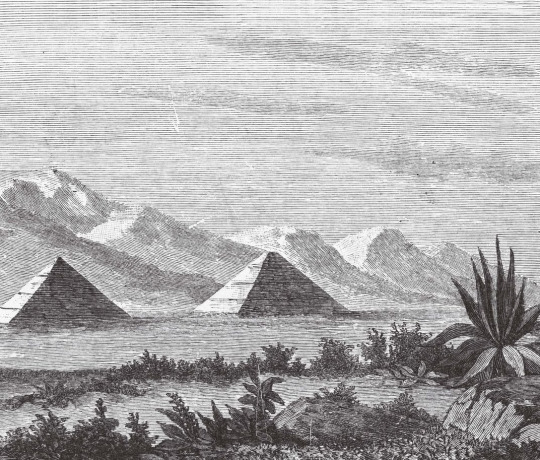

A 19th-century engraving of the pyramids of Teotihuacan. The Pyramid of the Sun was restored in 1910, on the centennial of the Mexican War of Independence. Bridgeman Images
She also served as a bridge between the United States and Mexico, living in both countries and working with leading national institutions in each. At a time when many scholars spun elaborate and unfounded theories based on 19th-century views of race, Zelia looked at the evidence and made concrete connections based on scientific observations. By the time she died, in 1933, she had published three books and more than 75 articles.
Yet during her lifetime, she was sometimes called an antiquarian, a folklorist or a “lady scientist.” When she died, scholarly journals and some newspapers ran notices and obituaries. After that, she largely passed from the public’s eye.
Today, anthropologists often have specialized expertise. But in the 19th century, anthropology was not yet a discipline with its own paradigms, methods and boundaries. Most of its practitioners were self-taught or served as apprentices to a handful of recognized experts. Many such “amateurs” made important contributions to the field. And many of them were women.
She was born in 1857 to a wealthy family in San Francisco, then a fast-growing city of about 50,000 people. Near the shore, ships mired in mud—many abandoned by crews eager to make their fortunes in the gold fields—served as hostels to a restless, sometimes violent and mostly male population. Other adventurers found uncertain homes in hastily built hotels and rooming houses. But the city was also an exciting international settlement. Ships arrived daily from across the Pacific, Panama and the east via Cape Horn.
Her well-appointed household stood apart from the city’s wilder quarters, but the people who lived there reflected San Francisco’s international character. Her mother, Magdalena Parrott Nuttall, herself the daughter of an American businessman and a Mexican woman, spoke Spanish, and her grandfather, who lived nearby, employed a French lady’s maid; a nursemaid from New York; a chambermaid, laundress, housekeeper, coachman and groom from Ireland; a steward from Switzerland; a cook and additional servants from France; and nine day laborers from China.
When Zelia was 8, her family left San Francisco for Europe. Along with her older brother, Juanito, and her younger siblings Carmelita and George, Zelia and her parents set off for Ireland, her father’s native land. Over the course of 11 years, the Nuttalls made their way to London, Paris, the South of France, Germany, Italy and Switzerland. Throughout that time, Zelia was educated largely by governesses and tutors, with some formal schooling in Dresden and London. But her time overseas shaped her interest in ancient history and expanded her language skills, as she added French, German and Italian to her fluent Spanish. All of this expansion thrilled her mind, but it also made her feel increasingly out of step with the expectations for young women of her age. “My ideas and opinions form themselves I don’t know how, and I sometimes am astonished at the determined ideas I have!” she wrote in a November 1875 letter.
She took refuge in singing and tried to be pleased with the few social events she attended. Photos from the time show Zelia as an attractive young woman with large, dark eyes, arched eyebrows and stylishly arranged hair. Nevertheless, she was unhappy. “I was infinitely disgusted with some of the idiotic specimens of mankind I danced with,” she wrote in an 1876 letter after a party.
The Nuttalls returned to San Francisco in 1876, when she was nearly 20. Two years later, she met a young French anthropologist, Alphonse Pinart, already celebrated in his mid-20s as an explorer and linguist. He had been to Alaska, Arizona, Canada, Maine, Russia and the South Sea Islands. Pinart may have led the family to understand that he was wealthy. In fact, he was almost penniless, having already spent his significant inheritance.
They were married at the Nuttall home on May 10, 1880. During the next year and a half, the couple traveled to Paris, Madrid, Barcelona, Puerto Rico, Cuba, the Dominican Republic and Mexico. Pinart introduced Zelia to a burgeoning academic literature in ethnology and archaeology, and she began to understand the theories of linguistics. She found 16th-century Spanish hardly a challenge as she consulted annotated codices—pictorial documents that traced pre-Columbian genealogies and conquests in Mesoamerica. While Pinart dashed from project to project and roamed widely among countries, tribes and languages, Zelia began to demonstrate an intellectual style that was more focused and precise.
Despite the excitement of discovery, something began to go wrong in the marriage. Hints of Zelia’s distress can be found in her effusive letters home. There was, for example, the shipboard admission that her husband was less attentive than she had anticipated. She noted that he was “so quiet and undemonstrative” that it was hard to imagine they were newly married. Some fellow passengers thought they were brother and sister—an odd assumption to make, even in Victorian times, about newlyweds.
By contrast, Zelia is nowhere to be found in Pinart’s surviving correspondence. On April 6, 1881, she gave birth to a daughter, Roberta, who lived only 11 days. To add to this melancholy time, her beloved father died in May, leaving her doubly devastated. A letter Pinart wrote to a friend just a few months later from Cuba appeared on stationery with a black border, signifying mourning, but he made no reference to his wife, her father or their child.
Zelia found solace in learning about her heritage when she and Pinart traveled to Mexico in 1881. She was eager to see her mother’s homeland and to hone her understanding of its pre-Columbian cultures. While Pinart carried out his own research, she began to learn Nahuatl, and she toured villages where dialects of the language were still spoken and ruins where the marks of the past could still be found.
The couple returned to San Francisco on December 6, 1881. By then, Zelia was pregnant again. In late January, Pinart set out to spend several months in Guatemala, Nicaragua and Panama, while Zelia awaited the birth of her second child, Nadine, at her mother’s house.
What finally drove Zelia to sue for divorce, on the grounds of cruelty and neglect, remains elusive. She may have felt that Pinart had married her for access to her family’s fortune. Many years later, she angrily informed Nadine that Pinart had spent the $9,000 she had inherited from her father as well as her marriage settlement. When the money was gone, and when her family was firm that he shouldn’t expect any more, he abandoned his wife and child. Once Zelia demanded a separation, he did not contest it, though obtaining the divorce was a long process that started soon after the couple’s return from their travels and didn’t conclude until 1888.
In later life, Nadine Nuttall Pinart would reflect on how much it had cost her to grow up without a father. “From the time before I can remember, he was taboo to me,” she wrote in a 1961 letter to Ross Parmenter, a New York Times editor who wrote numerous books about Mexico and developed a fascination with Zelia Nuttall. “I was frightened by the violent scoldings I got for mentioning his name. Later, I compromised with myself and when asked about him quietly said, ‘I never knew him!’ I realized that people thought he was dead and were sorry for me and said no more. In those days it was a disgrace to have a divorced mother.”
If the period between 1881 and 1888, when Zelia finalized her divorce, was fraught with tension and heartache, this was also when she set about redefining herself as a woman with a vocation. She spent five months in Mexico with her mother, her daughter and her brother between December 1884 and April 1885, visiting Cuernavaca, Mexico City and Toluca, and exploring archaeological ruins. It was during this time that Zelia made her fateful winter visit to Teotihuacan and acquired her first artifacts.
The pieces of pottery she picked up that day were small terra-cotta heads. They were abundant in the area among the pyramids. At the time, the site was still being used as farmland, and the artifacts came to the surface during ploughing. The heads themselves were an inch or two long, with flat backs and a neck attached. Scholars before Zelia—Americans, Europeans and Mexicans—had mused creatively about such relics, describing differences in their facial features and the variety of headdresses they had sported. Drawing on 19th-century fascination with the topic of race, the French archaeologist Désiré Charnay became convinced that he could see in them African, Chinese and Greek facial features. Charnay mused: Had their creators migrated from Africa, Asia or Europe? And if racial identity was a marker of human development, as many believed at the time, what might this curious mixture of features reveal about civilizations in the Americas?
This kind of thinking was typical. Mistaken ideas about Darwinism led many Western scholars to believe that civilizations evolved along a linear, hierarchical path, from primitive villages to ancient kingdoms to modern industrial and urban societies. Not surprisingly, they used this to legitimize beliefs about the superiority of the white race.

Zelia Nuttall divided her collection of terra-cotta heads into three classes. The first included rudimentary efforts to represent a human face (as seen above, far left). The second class (including the bald second head from the left above) had holes for attaching earrings and other ornaments. The third category included the rest of the heads pictured here, sporting what Zelia called “a confusing variety of peculiar and not ungraceful headdresses.” Public Domain
Zelia generally accepted her era’s assumptions about race and class, and she was comfortable with her elite status and its privileges. Yet in her research, she did not categorize civilizations as primitive, savage or barbaric, as other scholars did, nor did she indulge in racial theories of cultural development. Instead, she sought to sweep aside this kind of speculation and replace it with observation and reason.
The more Zelia examined her terra-cotta heads, the more she realized she needed guidance from someone who had more experience in the study of antiquity than she had. At the time, there were no departments of anthropology in colleges or universities, no degrees to be earned, no clear routes to building a career. To pursue her burgeoning interest in the ancient civilizations of Mexico, and to decipher the meaning of an assortment of terra-cotta heads, she contacted Frederic Ward Putnam, the curator of Harvard’s Peabody Museum of Archaeology & Ethnology and a leading expert on Mesoamerica. He agreed to meet her in the fall of 1885. The meeting was all she hoped for: Putnam warmed to her work and encouraged her to follow her intuitive grasp of how to observe and interpret evidence.
Putnam’s regard for women’s intellectual capacities was clear. He was one of a small number of Harvard researchers who gave lectures at “the Annex,” an institution established for women who had passed the college’s admissions test but were not allowed to attend classes or earn a degree. (The Harvard Annex eventually became Radcliffe College.) He hired a resourceful administrative staff of women and encouraged them to play a role in managing the museum. He also had a “correspondence school,” which he conducted through a widespread exchange of letters. As he once wrote, “Several of my best students are women, who have become widely known by their thorough and important works and publications; and this I consider as high an honor as could be accorded to me.”
Within months of their first encounter, in late 1885, Putnam asked Zelia to become a special assistant in Mexican archaeology for the Peabody. Less than a year later, in the annual report of the Peabody Museum, he wrote about her appointment in glowing terms: “Familiar with the Nahuatl language … and with an exceptional talent for linguistics and archaeology, as well as being thoroughly informed in all the early native and Spanish writings relating to Mexico and its people, Mrs. Nuttall enters the study with a preparation as remarkable as it is exceptional.”
With guidance from Putnam, Zelia wrote an investigation of the terra-cotta heads, her first published scientific report, which appeared in the spring 1886 issue of the American Journal of Archaeology. “At the first glance,” she wrote, “the multitude and variety of these heads are confusing; but after prolonged observation, they seem to naturally distribute themselves into three large and well-defined Classes.”
Each class, she theorized, had been created at a different time and represented a different stage in the culture. The first class contained “primary and crude attempts at the representation of a human face.” The second class included the first efforts at artistry. Her inspection revealed “holes, notches and lines,” suggesting ways in which tiny headdresses, feathers or beads could have been attached to the heads, and noted traces of several colors of paint and different kinds of clay.
The third class was the most important, Zelia argued, because of the quality of the molding and carving. This class had “modifications of feature sufficient to give every specimen an individuality of its own,” she wrote. “The faces are invariably in repose, in some the eyes are closed … faces young and smooth, others very elongated, some with sunken cheeks, others with wrinkles.”
By comparing these terra-cotta heads with ancient pictographs and writings, she showed that some of the heads represented children while others depicted young men, warriors or elders. Others showed the distinct hairstyles described in the writings of Bernardino de Sahagún, a 16th-century Franciscan friar who spent 50 years studying the Aztec culture, language and history. “The noblewomen used to wear their hair hanging to the waist, or to the shoulders only. Others wore it long over the temples and ears only,” Sahagún had written. “Others entwined their hair with black cotton-thread and wore these twists about the head, forming two little horns above the forehead. Others have longer hair and cut its ends equally, as an embellishment, so that, when it is twisted and tied up, it looked as though it were all of the same length; and other women have their whole heads shorn or clipped.”
These concrete observations allowed Zelia to challenge popular ideas about the supposed African, Asian, European or Egyptian origins of the “races” in the Americas. For example, by studying the ornamentation the heads displayed, she was able to identify the person or god each artifact represented and interpret its ritual or symbolic purpose. One clearly corresponded with Tlaloc, the pan-Mesoamerican god of rain, who had been shown in the pictographs with a curved band above the mouth and circles around the eyes. Another head, molded with a turban-like cap, corresponded with the goddess Centeotl; Zelia speculated that the clay turbans once had real feathers attached. She also noted the significance of various poses. “In the picture-writings, closed eyes invariably convey the idea of death,” she wrote.
The article revealed how Zelia intended to be seen as a scholar. First, she made it clear that she had read what others had written. Then she revealed that she would go beyond existing speculation to answer questions that had puzzled others; hers was to be original and important work.
In 1892, Zelia presented a paper in Spain about the Aztec calendar stone. Buried during the destruction of the Aztec Empire, the calendar stone had been unearthed in December 1790, when repairs were being made to the Zócalo, Mexico City’s central plaza. The sculpted stone, some 12 feet in diameter and weighing 25 tons, became a popular attraction exhibited in the Mexico City Cathedral, steps from where it had been found. Antonio de León y Gama, a Mexican astronomer, mathematician and archaeologist, had written about its discovery and praised the intelligence of the Aztecs who had created it. Alexander von Humboldt, who saw the stone when he visited Mexico in 1803-1804, included a drawing in his Views of the Cordilleras and Monuments of the Indigenous Peoples of the Americas, published in 1810, and encouraged Mexican intellectuals to study the meaning of its concentric circles and numerous glyphs. Many others took on its puzzles in the years that followed.
At the time of Zelia’s presentation, the Mexican upper classes were carefully crafting a new national image—a story that would allow Mexico to take its place among the modern nations of the world. The Aztecs, Maya, Olmecs, Toltecs, Zapotecs and other cultures had left their imprints throughout the country in magnificent temples, enigmatic statues, gold jewelry, jade figurines and painted murals. This history was reclaimed as a national heritage every bit as glorious as those of Greece and Rome. A statue of Cuauhtémoc, the Aztec king who resisted Cortés, took its place on Mexico City’s elegant Paseo de la Reforma in 1887. The calendar stone had been installed in a place of honor in the National Museum in 1885. But little was known about the actual customs and beliefs of those ancient people.

The Aztec calendar stone, a central focus of Zelia’s research, has been on display at Mexico City’s National Museum of Anthropology since 1885. Alamy
With her extraordinary knowledge of surviving codices, Zelia offered a novel “reading” of the giant calendar stone that had stumped others and provided new insights into the annual and seasonal cycles of daily life in ancient Mexico, illuminating the cosmology, agriculture and trade patterns of the Aztecs. She presented another version of the paper at the World’s Columbian Exposition in Chicago in 1893.
Zelia returned to Mexico City in February 1902, and after a personal audience with Mexican President José de la Cruz Porfirio Díaz, arranged by the U.S. ambassador, she embarked on a spree of travel to archaeological sites she had long wanted to visit. In May, she and 20-year-old Nadine joined friends at the Oaxacan ruins at Mitla, a religious center, where the “place of the dead” harbored both Mixtec and Zapotec art and architecture. On this dry, high plain ringed by mountains, Zelia strolled across vast stone patios, inspected the elaborate geometric friezes that lined and decorated them, explored temples and imagined a sophisticated society of kings, priests, nobles, artisans and farmers.
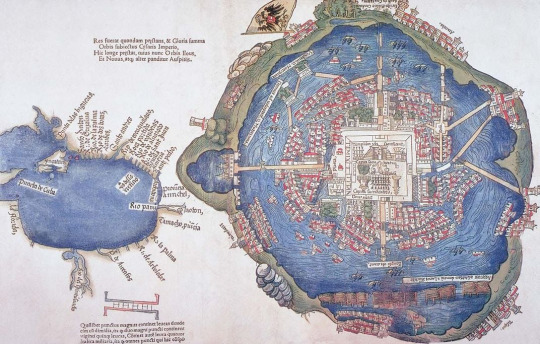
When the Spaniards arrived in Mexico in the 16th century, the Aztec Empire dominated the area. This map of its largest city, Tenochtitlan (now the historic center of Mexico City), was printed in 1524 in Nuremberg, Germany, likely based on a drawing by one of Hernán Cortés’ men. It shows the city’s elaborate network of roads, bridges and canals, complete with aqueducts and bathhouses. The Spaniards executed the last Aztec ruler, Moctezuma II Xocoyotzin, and forced his people to convert to Catholicism. Alamy
Zelia was welcomed into the international community of anthropologists in Mexico. She and Nadine traveled in the Yucatán with the young American anthropologist Alfred Tozzer, where they were beset by frequent rain and terrible roads. Arriving tired and wet in a small town, Tozzer, who would one day chair Harvard’s department of anthropology, was impressed by the women’s resilience. “Imagine the picture,” he wrote to his family on April 8, 1902. “Mrs. Nuttall, never accustomed to roughing it, a woman entertained by the crowned heads of Europe, sitting at a bench with the top part of my pajamas on drinking chocolate and her daughter with a flannel shirt of mine on doing the same.”
After a few months, Zelia and her daughter returned to Mexico City and purchased a mansion they called Casa Alvarado, in the upscale suburb of Coyoacán. The grand house never failed to impress. Frederick Starr, an anthropologist from the University of Chicago, was one of many who found the palace beautiful and restful: “We rode out to Coyoacán where we found Mrs. Nuttall and her daughter really charmingly situated. The color decoration is simple and strong. Nasturtiums are handsomely used in the patio and balcony effects. … While Mrs. Nuttall dressed, Miss Nuttall showed us through the garden, where a real transformation has been effected.”
Living in Mexico energized Zelia. In addition to her affiliation with Harvard, she had funding to travel and collect artifacts for the Department of Anthropology at the University of California. “With me here, in touch with the government and people, I think that American institutions can but profit and that I can do some good in advancing Science in this country,” she confided to Putnam.
Impressed by her knowledge of the country’s past, public officials and foreign visitors came to see her and listened carefully as she led them around her home and garden, explaining the collection she was busy assembling. Her garden, patio and verandas were home to an increasingly large number of stone artifacts, a beautiful carving of the serpent god Quetzalcóatl, revered for his wisdom, among them. She took up “digging” near Casa Alvarado, an activity one guest later recalled fondly. “Every morning after breakfast Mrs. Nuttall would give me a trowel and a bucket. She herself was equipped with a sort of short-handled spade, and we would go out into the surrounding country and ‘dig.’ We mostly found broken pieces of pottery, but she seemed to think some of them were significant, if not valuable. … She was a very handsome woman and very charming. She lived in great style, with many Mexican servants.”

The Codex Borgia, an accordion-folded document of Aztec life, was brought to Europe during the Spanish colonial period. Made of animal skins and stretching 36 feet when unfolded, the codex catalogs different units of time and the deities associated with them. It also includes astrological predictions once used for arranging marriages. Zelia drew on the codex to help her decode the Aztec calendar. Courtesy Ziereis Facsimiles

A section from the Codex Borgia
Zelia continued to travel throughout the country. She found a 14-page codex painted on deerskin, with commentary in Nahuatl, that she believed so valuable that she bought it with her own money, selling some of her possessions to afford it. “Owing to my residence here I must keep it a profound secret that I possess and sent out of the country this Codex,” she wrote to Putnam.
While she was not above smuggling treasures out of Mexico, Zelia also worked in the National Museum, contributing to its displays and archives, and she became an honorary professor of the institution.

Zelia had never owned a home until she bought Casa Alvarado in 1902. In a letter, she described the property as “a beautiful old place with extensive gardens.” Smithsonian Archives
Her Sunday teas at Casa Alvarado were a study in salon orchestration. “She would have 30 or 40 people and she would change the groups she invited,” one visitor recalled. “Sometimes they were all people who knew each other. Or else she would bring people together she wanted to introduce to each other. They weren’t like old-style Mexican parties, with all the women on one side and men on the other. The men and women were mixed together.”
According to an oft-repeated legend, at one of her soirées, she advanced to welcome an eminent guest just as her voluminous Victorian drawers came loose and dropped to her ankles. She calmly stepped out of them and proceeded as if nothing had happened. Zelia was, above all, self-confident.
Zelia Nuttall left Mexico during the early months of 1910 and did not return to her beloved Casa Alvarado for seven years. Throughout that time, Mexico was in the midst of a violent revolution. As many as two million people lost their lives in the ten-year conflict, and the country’s infrastructure was reduced to tatters. Even after the end of the most extensive violence, turmoil erupted sporadically until the late 1920s.
By then, visitors to Casa Alvarado agreed that Zelia was rooted in a bygone era. She was a middle-aged woman with thick glasses who favored shawls, laces and jet beads. Her palace was still filled with stuff only a Victorian could accumulate, but Mexico was telling new stories about itself.

The writer D.H. Lawrence used Zelia as a model for a fictional character—“an elderly woman, rather like a Conquistador herself in her black silk dress and her little black shoulder-shawl.” Antropo Wiki
The elites of the previous generation had asserted that descendants of the Aztec, Maya and other civilizations deteriorated into poverty and abandon. Young artists and intellectuals now rejected this belief. In Diego Rivera’s vast public murals, he showed the people of Mexico being ground into poverty and submission by Spanish conquistadors, a rapacious church, foreign capitalism, the army and cruel politicians. Quetzalcóatl replaced Santa Claus at the National Stadium; Chapultepec Park hosted Mexico Night.
Zelia did not like the revolution and she did not approve of what came after it. She did not celebrate the masses; she believed in hierarchy and a natural order of classes and races. Yet she was determined to be relevant to a new era in Mexico. Casa Alvarado became a meeting place for politicians, journalists, writers and social scientists from Mexico and abroad, many of whom came to witness the possibilities of change in the aftermath of a people’s revolution.
Nevertheless, the stubborn elegance of Casa Alvarado in the 1920s was clear testimony that Zelia was not willing to give up her lifestyle. When the French American painter Jean Charlot was a guest at one of Zelia’s teas, he was aghast at the Mexican servants in white gloves.
When Zelia Nuttall died in 1933, the U.S. consul in Mexico City wrote to Nadine—by then a 51-year-old widow living in Cambridge, England—assuring her that they’d given her mother a tasteful funeral. “Your Mother was very highly thought of here, as evidenced by the floral offerings and the number of her friends who came to the funeral service at the cemetery, it being estimated that about one hundred persons were present.”
By that time, the field of anthropology was dramatically changing, becoming more systematic and organized. Those who entered the field in the 1920s and 1930s built expertise in the classroom and under supervision in the field, passing a variety of tests and milestones determined by academic experts and acquiring a credential as proof of the right to pursue these inquiries. With these rigorous new standards, they asserted their superiority as scholars over those of Zelia’s generation.
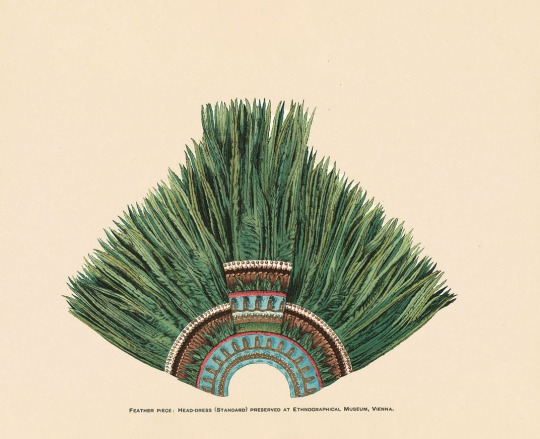
Researchers thought this item at Vienna’s Museum of Ethnology was a “Moorish hat” before Zelia identified it as a Mesoamerican headdress. Alamy
Yet Alfred Tozzer, in his memorial in the journal American Anthropologist, reflected that Zelia “was a remarkable example of 19th-century versatility.” She was wrong in some of her overarching theories. For instance, she fallaciously argued that ancient Phoenician travelers had carried their culture to Mesoamerica. But she was right about many other things. Through her letters, articles and books, we can trace what she got right and what she got wrong as a scholar, and we can follow her as she moved from one research obsession to the next.
Her private life is harder to grasp. Among all the artifacts, there is little about the quips and gossip she exchanged with friends, the piano music she liked to play and sing. We cannot know what was in the boxes of papers in the cellar of Casa Alvarado that were burned in the housecleaning undertaken by its new tenants. We cannot retrieve personal and public documents lost in the San Francisco earthquake in 1906.
What we do know is that she had to make sacrifices, often very personal ones. We can feel her vulnerability, uncertainty, anger and embarrassment in the letters she wrote, as well as her self-assuredness. It required unusual self-discipline to learn so many languages and to gain a mastery of ancient pictographs. Her almost constant travels imperiled her health even while they advanced her vast network of friends, colleagues and patrons. But she continued to work, and that work helped establish the foundation on which many others now build.
A single mother pursuing a career while looking after a family in a man’s world: In some ways, Zelia Nuttall was a very modern woman.
Adapted from In the Shadow of Quetzalcoatl: Zelia Nuttall and the Search for Mexico’s Ancient Civilizations by Merilee Grindle, published by The Belknap Press of Harvard University Press. Copyright © 2023 by Merilee Grindle. Used by permission. All rights reserved.
#Women in history#Women in Anthropology#Zelia Nuttall#The Aztecs#Merilee Grindle#In the Shadow of Quetzalcoatl: Zelia Nuttall and the Search for Mexico's Ancient Civilizations#Books by women#Books about women#teotihuacan#mesoamerica#Nahuatl#Published women#Many of the first anthropologists were women#Alphonse Pinart was just another man who blew through his money#Women's careers flourishing after dumping a parasitic man#Frederic Ward Putnam#Men who encouraged women#The Annex#Lady scientist
45 notes
·
View notes
Text
we need more feminist horror
#there is so much potential there#rambling#the beauty industry… anti ageing… dieting….#female gender roles as a demon haunting you…#the prison of femininity…#menstruation pregnancy abortion as body horror#subversing horror tropes of female exploitation and male violence…#men as monsters… the patriarchy as a haunted house… competition between women as curse…#or just female slashers and serial killers who are not sexy for the female gaze#liberal feminism encouraging ‚sex work‘ as a cult#as some sort of commentary#WITCHES… the last girl becoming ‚evil‘ but what really is evil…#intergenerational female trauma…#male religion > occult horror#zombie as symbolism of trauma…#MOTHER DAUGHTER RELATIONSHIPS
111 notes
·
View notes
Text
questioning sexuality is so exhausting
#(edit: sorry for the rant in the tags and i just. i want someone to talk to me)#i keep on doing it for no apparent reason#someone was talking about lust yesterday and i realised today that.#even tho id thought i don't experience it. i possibly do. but exclusively towards women.#i hate it here!#for a multitude of reasons i will never have a relationship with a woman but! i may be incapable of having a relationship with a man!#at some point in the last few months i have abruptly pivoted from definitely wanting marriage and kids to being ambivalent on marriage#and not wanting kids. that's such an outlier in my life that it might just be a mental health thing tho idk#but at the same time i. want to be loved.#i don't know what i want anymore and im tired of questioning myself#i definitely overthink it but idk how to stop it#and i hate hate hate how the moral obsessions have bee lately#this isn't entirely related but it kind of is#like Am i a terrible morally bankrupt person for having certain thoughts or is it just religious ocd go brrrr?? am i overthinking it?#i don't know. i don't know!#for a while labelling myself as arospec ace kinda calmed that down but. i don't know#i do't want to be attracted to women. i don't want to have to look away so often. i don't want any of that.#but i don't know how to stop it.#i don't even know if i'm attracted to men at all.#this is a cry for help and encouragement and prayers no matter what your views on these matters are#queer stuff tag#i nearly fessed up to my friend yesterday about same sex attraction and i might've except that it would have probably outed me as#the person who anonymously sent in a question several months ago about the side b movement to a church thing#ive only told one person at church about any of that sort of stuff and it was very vaguely worded#also see: this friend is the mother of the boy i?? i don't even know how i feel about him#i increasingly think it wasn't romantic at all. but i don't know#i would love any encouragement you got. anything at all.#i don't know how much this stuff is affected by the fact that i consider myself unloveable and think it highly unlikely any boy will ever#care for me#now im rambling. sorry
42 notes
·
View notes
Text
no actual news source that i can find for it but pcs is showing six stages for the 2025 tour de l'avenir femmes, the most in any edition of the race so far
#that's very encouraging - and only two less than the men who will have 8. women's race the week before the men.#interestingly pcs also has visma on the start list which is kinda weird bc historically it's been a national team race#there's been discussion of changing that to trade teams (also for the men's race) but afaik there's been no actual news on that
14 notes
·
View notes
Text
i'm stressed for the day the govt decides to make pronouns illegal, by which the law will actually be implemented as "if someone decides you don't look like the gender THEY think you are, you will be charged with a crime"
and how in some workplaces like mine, where people show their preferred pronouns in work emails, that'll result in many people with digital email trails that could get them arrested (which of course means trans people in the workplace get charged, people who look cis and use he/him and she/her in their emails to be supportive probably will just be told to stop putting it in their emails)
and like. i know i probably can't do anything, except maybe stay in the closet. i know the workplace is not guaranteed to fucking warn their employees to maybe remove the digital proof of their pronouns if there's a law at risk of existing soon. and i know people's gender identity is really personal and important to a lot of people, including cis people. But i kind of wish there was a widespread trend in these workplace situations of EVERY (or at least a majority) of cis people putting "they/them/their" in their email signatures. The cis people (particularly those who look very gender conforming) will be the ones in the least danger of being charged with a crime. They are at very low risk of being charged with a crime, so they're the perfect people to break the law by saying their preferred pronouns are "they/them" and then taking the law to court if such a law restricting preferred pronouns passes. And if a trans employee is charged with a crime, the cis employees all using they/them can say their trans coworker is only doing EXACTLY THE SAME THING ALL THESE CIS PEOPLE ARE (using a pronoun someone thinks doesn't align with the gender they're assumed to be), and then saying either ALL employees need to be charged with a crime (which can then go to court) or none of them should be. Yeah that would require solidarity... I know I can't convince a bunch of cis people to start putting "they" as a pronoun in their emails (or some other pronoun that would result in them breaking the same 'preferred pronoun' type of law like "ze/zim"). But god, I wish I could.
I think about this because in the last few years, my state tried to make a law against using preferred pronouns in schools and government jobs (you know... which likely won't charge any cis person using the pronouns that match their gender even though that's a preferred pronoun too). And now that my state govt is a majority republican, they'll probably try to pass it again. I worry about all my coworkers with massive email trails, because they were TOLD to tell people their preferred pronouns, because the workplace said it would respect them, but I doubt the workplace will Protect them if it's no longer legal. My workplace had the shittiest answer when I raised my concerns, they said "don't worry about it until it happens"... once it happens, a bunch of trans people will be breaking the law by existing, and they will not have had the chance to protect themselves in advance (and their workplace will have done nothing in advance to protect them - such as warn them not to leave proof of their preferred identity after X date, and promising the workplace won't consider any pronouns said before X date to be breaking the law as far as reporting goes).
#rant#us politics#..............................................................................................................................#i worry about all the people online too that share their preferred pronouns (here. twitter. bluesky. instagram) because again its a digital#trail. but i don't think the government can have as easy of a time making a law that effects what people say online#because people can claim 'oh i was lying/joking/didn't mean to write it' if its online#whereas laws affecting govt and public school employees are much easier for the govt to pass#and much easier for the govt to argue ARE preferred pronouns because there's many#formal documents of the employees gender labelled and the employee self identifying their gender and pronouns.#and the govt probably can eventually make laws effecting private workplaces. so that would probably be their next plan to attack#i am just so pissed my workplace said oh we're supportive! then fucking doesnt plan to protect any employees#or plan for any situations where suddenly employees are at risk for something they were encouraged to do their whole time at the job#i just think if straight cis people EN MASS used not-expected preferred pronouns then any such law would be much easier to be challenged#and it'd be at least slightly easier to protect trans people (who could point to cis people also breaking law and unpunished#and who could potentially lie and say they're just doing the same as all cis people - making a point in protest and thats not Genuinely t#their preferred pronoun)#also i say they/them just because then maybe cis people wont feel they have to misgender themselve s or be as uncomfortable as if#i was asking cis men to go by her/she and cis women to go by he/him#just because MOST people are called they when someone doesn't know them or their gender yet#but cis people who DID protest by going with more contrasting preferred pronouns#would likely be very effective as a protest move
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Okay but what if SSA women aren't men and being SSA isn't some kind of proof we have male tendencies and what if women can appreciate women who are vulnerable losers without being directly attracted to exploiting that vulnerability because, again, we're not men and don't think like men??
#like the concept of the 'bimbo' is cultivated and encouraged by men#specifically for the purpose of exploitation#'loser' women exist on their own for lots of reasons#**one of which being that women who don't try at femininity and pleasing men are just called losers**#SSA women making posts to appreciate or encourage this overly shamed demo of women#are NOT doing the same thing men are when they reward women for being exploitable
40 notes
·
View notes
Text
if we're going to (rightfully) complain about the 4B movement and other forms of women's protest, could we at least provide better alternatives?
in the meantime, yes, I absolutely am cutting off interacting with most men unless it's absolutely necessary. if they want to make a world where the only man I talk to is my husband, they can have that.
#there's a lot of context there with the obvious topic here of intersectionality and having some male friends#but at the same time I've had to grow up watching my classmates go missing -#women the generation before me being married off at 12#and I've gotten to see women constantly loaded with pregnancies so that they cannot leave :)#my response is going to be extreme because it needs to be extreme#and while I don't encourage any particular movement#a very strongly encourage women to look carefully at the people they have in their lives and reevaluate who should be in their space#because it's not just men this time - there's a ton of these white women supporting them
3 notes
·
View notes
Text

I love being in school for film I enjoy it so much and I'm so grateful for the privilege but I hate hate hate the pretentious film guys who are in charge of teaching us and writing our text books and grading our assignments who all talk and act like this.
#“that's just a guess of course” what if you died#not to mention my professor who assigned this book having the same narrow minded ideas of the pieces of scripts that “work” or “don't work”#YOU'RE SUPPOSED TO TEACH US HOW TO MAKE IT WORK NOT TELL US THAT WE WILL INHERENTLY FAIL#fuck film bros#and then all my women professors are so excited to be here!!! They're so excited to teach the facets of their craft and encourage us to#create things outside of boundaries and rules and they have all been so kind and uplifting#and then the male professors are all so fucking pretentious and pessimistic and cynical and arrogant#and if you don't do things their way then you're doing it wrong and you'll fail#idk I'm just tired of men in the arts#film
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
I think female character enthusiasts would like bliss lai of i was born for this fame
#she radiates an aura that attracts bisexual women to become her friends and makes straight men uncomfortable#lowkey including her bf#she encourages said bisexual women to engage in heroics on her behalf#she doesnt know who famous people are. She goes to a fandom meetup for her bfs band as essentially an anthropologist#she has 7 twitter followers#she needs a hat ‘bi women want me straight men fear me’
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
“in order to create loving males we need to love males” means teach boys that they can be themselves without being less of a man. it means being encouraging and nurturing of their emotions so they don’t become cold and hateful. it means showing boys, early in their lives, that they have value outside of what our society deems proper masculinity. what it doesn’t mean is that it’s our job to handhold men who see women as walking sex toys through the concept of empathy, and maybe if we’re really really nice to them and don’t say things that hurt their feelings they’ll stop killing us for saying no
28K notes
·
View notes
Text
Sometimes I want to make posts wondering about comphet in hockey and their relationships but I know it would get taken in a tin hat-ty way instead of me just ruminating on sexuality and conformity
#chatter#like rpf is fun but i do sometimes think about like#how much the guys are encouraged to settle#and to settle down and have kids like#and how i often wonder how happy some of these men are lmao#not in an 'oh such and such player never smiles in photos with his wife'#bc i find that a bit parasocial and i try not to speculate tooooo hard#but in the opposite way (which admittedly is still parasocial)#its interesting to think about the players that do seem to love their wives openly#or just seem to have fun with them?#stromers wife teasing him on insta or marns turning into a Wife Guy or even tbear and his heart eyes in his wedding photo#(like full on landy stallion interview heart eyes)#or even just drat and his fiance having videos of them dancing and having fun at a party that isnt staged wedding photos lmao#and ofc everyone knows those interviews where guys talk about how the things they love most about their wives is that#they are mothers and they do things for them#this was also brought on tho by the sheer amount of womens players who date and marry other womens players like... makes you think!#also ofc the couples ive mentioned earlier are just players i know and idk them maybe their relationships arent happy whatever
1 note
·
View note
Text
raised as a girl? raised as a boy?
honestly, "raised as the youngest" contains much more useful information about the childhood I had and the person I became as a result
#like apart from rejecting the gender essentialist concepts of ''soclialized male/female''...#...and the idea of a Universal Girlhood that all trans men have access to and all trans women are excluded from#it honestly depends on how much gender nonconforming behavior your adult caretakers tolerated!#and by that metric I'd argue on the whole (i know outliers exist) trans WOMEN's childhoods are much more oppressed by structural misogyny!#like i grew up in the ''grrl power'' white US suburban 90s#where most ppl were ok with their ''daughters'' wearing shorts and playing sports#but ''boys'' were not encouraged to like ''girly'' things#even parents who didn't recoil in disgust still encouraged their ''sons'' to hide or suppress anything ''effeminate''#in an attempt to protect their child from ''becoming'' an object of systemic oppression violence and hate#(paternalism)#what's more patriarchal than trying to control someone's life right down to their clothes and haircut ''for their own good''?
1 note
·
View note
Text
What the fuck it cut off my tags, whatever
I do deserve a treat :( Thank you <3
sorry for ranting, also sorry half the rant was cut off

this is the single worst way i've ever read to describe an erection, frank herbert
#Well see he wrote dune and some young men are super into his work because of it but then they do something stupid like make me read#soul catcher and then complain when I didn't like it right before bitching I couldn't get through helstrom's hive#and like I never want to disparage something that someone I love is super into but oh my god are they dismissive of anything I like or very#superficially lip service encouraging with no actual engagement and then get super pissy that I don't think frank herbert is a genius#But they'll act like I can't have that opinion until I have read whichever books of his that they personally think are good examples#but like no... He's a bad author#sorry#you ever read someone's work and get the sense you would fundamentally disagree as people?#like you would just find them viscerally off putting and they'd have an automatically low opinion of you for no good reason?#and also get the nagging sense that they'd be bad at sex or in a relationship?#Anyway Frank Herbert DNI#Like read the books -I- like before forming your opinions ffs play myst games and then tell me what you actually think of them#stop demanding that I live up to your expectations or wants or engage with you in a one sided way I break up with people for doing that#also when I tell a partner about something I am writing or working on and their first words to me is "oh you should check out _______'s wor#as if to say this person is already doing that and probably doing it better instead of engaging with me over my _own_ ideas as a way to#shut the conversation down and stop having it#makes me want to scream#like if they were just making recommendations based on what I like I wouldn't take it that way#but they do this thing where the more I keep trying to engage over what I am working on the more they just keep repeating#“You should REALLY check out _________” [it's often something by Neil Gaiman or something similar in tone] as a way to shut down#having to continue the interaction that's when it reads like they are telling me to see what the greats have done with the idea#before I bother trying to do something that seems similar to them or try to bother them with it#I feel like that's a pet peeve about young nerdy menTM that only comes up when you are an afab writer#the inherent assumption and attitude that your every idea and project is derivative and not worth engaging with earnestly#and worse they seem to learn from each other that this is HOW you SHOULD respond to your partner sharing their writing ideas with you#to start listing off the talents that have already done something that seems similar... *screaming* I'm sure trans women get it to actually#just anyone socially interpreted as a woman who creates in nerd spaces#well I'm a man now and I don't date so whatever#but a guy doing this to me became a massive red flag because the underlying attitude was always a base level of contempt for me#and inability to see me as a fully intelligent and rational peer
34K notes
·
View notes
Text
there's this well-meaning but I think quite misguided Thing where someone transmasuline whose transition has left them looking, for lack a better term, very conventionally masc - bearded, muscular, liable to be assumed cisgender - will be held up in an argument that essentially goes "lmao you dumbass terfs really want THIS GUY to use the women's bathroom???" as if it's inherently absurd that someone who looks that way would use the women's bathroom. and these tend to get passed around quite a lot to cackle at the stupid terfs who want huge hairy men in women's bathrooms.
and like, let's get one thing straight: no, of course they don't want that guy to use the women's bathroom. they want him to die or detransition; that's their actual goal. they want him to not exist as a trans person. let's just be clear on that.
but the thing that actually bothers me is that this rather steamrolls over the fact that for every transmasuline person who looks like that, there are also transfeminine, nonbinary, and intersex people who look like that and want access to women's bathrooms, and setting up their presence as some kind of absurdity really isn't doing them any favors. nor is it helping the less "passing" trans people who want to use men's bathrooms! this is in fact reinforcing the idea that public bathrooms are a space to be policed based on appearance, that you only gain access to if you can look a certain way.
which is absurd for many reasons, including that it's a fucking bathroom. people are there to piss. ideally anybody should be able to piss next to anybody and we could stop bothering with gender separated bathrooms at all, but in the meantime let's at least not take part in actively encouraging people to decide at a glance who's allowed to piss where.
18K notes
·
View notes