#Medication Delivery Systems Market
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Medication Delivery Systems Market Size, Share, Key Drivers, Trends, Challenges and Competitive Analysis
"Global Medication Delivery Systems Market – Industry Trends and Forecast to 2028
Global Medication Delivery Systems Market, By Type (Oral Drug Delivery System, Injection- Based Drug Delivery System, Inhalation/ Pulmonary Drug Delivery System, Transdermal Drug Delivery System, Trans Mucosal Drug Delivery System, Carrier- Based Drug Delivery System, Other Types), Technology (Prodrug, Implants and Intrauterine Devices, Targeted Drug Delivery, Polymeric Drug Delivery, Other Technologies), Carrier Type (Liposomes, Nanoparticles, Microspheres, Monoclonal Antibodies, Others), Application (Cardiovascular Diseases, Oncology, Urology, Diabetes, CNS, Ophthalmology, Inflammatory Diseases Infections, Other Applications), End-Users (Hospitals, Specialized Clinics, Clinical Research & Development Centers), Country (U.S., Canada, Mexico, Germany, Italy, U.K., France, Spain, Netherland, Belgium, Switzerland, Turkey, Russia, Rest of Europe, Japan, China, India, South Korea, Australia, Singapore, Malaysia, Thailand, Indonesia, Philippines, Rest of Asia-Pacific, Brazil, Argentina, Rest of South America, South Africa, Saudi Arabia, UAE, Egypt, Israel, Rest of Middle East and Africa) Industry Trends and Forecast to 2028
Access Full 350 Pages PDF Report @
The global Medication Delivery Systems Market is witnessing significant growth due to factors such as the increasing prevalence of chronic diseases, rising demand for self-administration devices, technological advancements in drug delivery systems, and the growing elderly population. The market is expected to showcase lucrative opportunities in the coming years, driven by the need for personalized and targeted drug delivery solutions, integration of digital health technologies, and the rising adoption of injectable biologics and biosimilars in healthcare practices. Moreover, the COVID-19 pandemic has further emphasized the importance of efficient medication delivery systems to ensure timely and accurate administration of therapies.
**Segments**
- By System Type: Prefilled syringes, autoinjectors, wearable injectors, injectable pens, infusion pumps, nasal sprays, nebulizers, and others. - By Application: Diabetes, oncology, autoimmune diseases, cardiovascular disorders, respiratory diseases, and others. - By End User: Hospitals & clinics, home care settings, ambulatory surgical centers, and others.
Considering the market players in the Medication Delivery Systems Market, several leading companies are actively participating in product innovation and strategic collaborations to strengthen their market position and cater to the evolving needs of healthcare providers and patients.
**Market Players**
- Becton, Dickinson and Company - Baxter International Inc. - Pfizer Inc. - Novartis AG - Gerresheimer AG - Johnson & Johnson Services, Inc. - GlaxoSmithKline plc - Novo Nordisk A/S - 3M - F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd
In conclusion, the Medication Delivery Systems Market is poised for substantial growth, fueled by the increasing demand for advanced drug delivery technologies, the rising burden of chronic diseases, and the shift towards patient-centric healthcare solutions. Market players are focusing on research and development initiatives to introduce innovative products and gain a competitive edge in the industry. With the integration of digital health solutions and emphasis on personalized medicine, the market is expectedThe Medication Delivery Systems market is experiencing remarkable growth, driven by various factors contributing to the expanding demand for efficient drug administration solutions. The surge in chronic diseases worldwide, coupled with the increasing elderly population, has necessitated the development of advanced medication delivery systems to ensure effective treatment outcomes. Moreover, the rising preference for self-administration devices and the advent of innovative technologies in drug delivery mechanisms have revolutionized the healthcare sector. The market is anticipated to witness significant opportunities in the foreseeable future, driven by the need for personalized drug delivery solutions and the integration of digital health technologies into medical practices.
Segmentation of the Medication Delivery Systems market based on system type includes prefilled syringes, autoinjectors, wearable injectors, injectable pens, infusion pumps, nasal sprays, nebulizers, among others. These diverse system types cater to a wide range of medical applications such as diabetes, oncology, autoimmune diseases, cardiovascular disorders, and respiratory conditions, among others. The market is also segmented by end-users, including hospitals & clinics, home care settings, and ambulatory surgical centers, reflecting the various settings where these medication delivery systems are utilized.
Key market players in the Medication Delivery Systems industry, such as Becton, Dickinson and Company, Pfizer Inc., Novartis AG, and Johnson & Johnson Services, Inc., are actively engaged in product innovations and strategic collaborations to enhance their market presence and meet the evolving needs of healthcare providers and patients. These companies are focusing on research and development efforts to introduce cutting-edge products that ensure efficient drug delivery and improve patient outcomes. The market landscape is characterized by intense competition, prompting companies to differentiate themselves through technological advancements and enhanced product offerings.
In conclusion, the Medication Delivery Systems market is set for substantial growth in the coming years, driven by the increasing demand for advanced drug delivery technologies and the escalating burden of chronic ailments globally. The industry's focus on patient-centric healthcare solutions, coupled with the integration of digital health solutions, is expected to propel market**Global Medication Delivery Systems Market**
- **Type:** Includes Oral Drug Delivery System, Injection-Based Drug Delivery System, Inhalation/Pulmonary Drug Delivery System, Transdermal Drug Delivery System, Transmucosal Drug Delivery System, Carrier-Based Drug Delivery System, and Other Types. - **Technology:** Encompasses Prodrug, Implants and Intrauterine Devices, Targeted Drug Delivery, Polymeric Drug Delivery, and Other Technologies. - **Carrier Type:** Comprises Liposomes, Nanoparticles, Microspheres, Monoclonal Antibodies, and Others. - **Application:** Targets Cardiovascular Diseases, Oncology, Urology, Diabetes, CNS, Ophthalmology, Inflammatory Diseases, Infections, and Other Applications. - **End-Users:** Includes Hospitals, Specialized Clinics, and Clinical Research & Development Centers.
The Global Medication Delivery Systems Market is witnessing robust growth and is poised for significant advancements in the forecast period. The proliferation of chronic diseases worldwide, coupled with the expanding elderly population, is fueling the demand for efficient drug delivery solutions. Technological innovations are revolutionizing the healthcare sector, with a focus on personalized and targeted drug delivery systems gaining traction. Integrating digital health technologies into medication delivery is a key trend shaping the market landscape, alongside the increasing adoption of injectable biologics and biosimilars in healthcare practices. The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic has underscored the critical need for precise and timely administration
Core Objective of Medication Delivery Systems Market:
Every firm in the Medication Delivery Systems Market has objectives but this market research report focus on the crucial objectives, so you can analysis about competition, future market, new products, and informative data that can raise your sales volume exponentially.
Size of the Medication Delivery Systems Market and growth rate factors.
Important changes in the future Medication Delivery Systems Market.
Top worldwide competitors of the Market.
Scope and product outlook of Medication Delivery Systems Market.
Developing regions with potential growth in the future.
Tough Challenges and risk faced in Market.
Global Medication Delivery Systems-top manufacturers profile and sales statistics.
Highlights of TOC:
Chapter 1: Market overview
Chapter 2: Global Medication Delivery Systems Market
Chapter 3: Regional analysis of the Global Medication Delivery Systems Market industry
Chapter 4: Medication Delivery Systems Market segmentation based on types and applications
Chapter 5: Revenue analysis based on types and applications
Chapter 6: Market share
Chapter 7: Competitive Landscape
Chapter 8: Drivers, Restraints, Challenges, and Opportunities
Chapter 9: Gross Margin and Price Analysis
How the Report Aids Your Business Discretion?
This section of this Market report highlights some of the most relevant factors and growth enablers that collectively ensure a high-end growth spurt
The report unravels details on pronounced share assessments across both country-wise as well as region-based segments
A leading synopsis of market share analysis of dynamic players inclusive of high-end industry veterans
New player entry analysis and their scope of new business models
The report includes strategic recommendations for new business veterans as well as established players seeking novel growth avenues
A detailed consultation services based on historical as well as current timelines to ensure feasible forecast predictions
A thorough evaluation and detailed study of various segments as well as sub-segments across regional and country-specific developments
Details on market estimations, market size, dimensions
A review of market competitors, their high-end product and service portfolios, dynamic trends, as well as technological advances that portray high end growth in this Market
Browse Trending Reports:
Asia Pacific Mainframe Market
Asia Pacific Menstrual Cramps Treatment Market
Europe Commercial Cleaning Equipment Market
Europe Mainframe Market
Europe Quantum Computing Market
Europe Tomatoes Market
Europe Utility Locator Market
India Blood Gas Analyzer Market
Middle East And Africa��Commercial Cleaning Equipment Market
Middle East And Africa Neurosurgery Market
Middle East And Africa Sports Medicine Market
Middle East And Africa Vaccines Market
Nigeria Cassava Starch Market
Nigeria Starch Processing Market
North America Menstrual Cramps Treatment Market
North America Neurosurgery Market
West Africa Baby Food Market
Antenna Market
Baby Apparel Market
Cassava Starch Market
Castor Oil Market
Cenospheres Market
Coconut Water Market
Collagen Casings Market
Facility Management Market
Functional Confectionery Market
Hemp Seed Market
Infrared Imaging Market
Instant Noodles Market
Laundry Detergents Market
Menstrual Cramps Treatment Market
Micro And Nano Plc Market
Motorcycle Market
Neurosurgery Market
Nickel Alloy Market
Over The Counter Probiotic Supplements Market
Polycystic Kidney Disease Adpkd Market
Private Label Food And Beverage Market
Recreational Cannabis Market
Tofu And Tempeh Market
Tomatoes Market
Vaccines Market
Varnish Makers Market
Wireless Medical Device Connectivity Market
About Data Bridge Market Research:
Data Bridge set forth itself as an unconventional and neoteric Market research and consulting firm with unparalleled level of resilience and integrated approaches. We are determined to unearth the best market opportunities and foster efficient information for your business to thrive in the market. Data Bridge endeavors to provide appropriate solutions to the complex business challenges and initiates an effortless decision-making process.
Contact Us:
Data Bridge Market Research
US: +1 614 591 3140
UK: +44 845 154 9652
APAC : +653 1251 975
Email: [email protected]"

0 notes
Text
Medical Polymer Market Outlook: Trends, Innovations, and Global Dynamics

The medical polymer market has become a pivotal sector, growing due to advancements in healthcare materials. Known for durability, flexibility, and biocompatibility, these polymers are essential across devices, surgical instruments, implants, packaging, and drug delivery systems. The rise in demand reflects industry trends, technological breakthroughs, and growing regulatory standards shaping this market.
The global medical polymer market is valued at USD 41.1 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 60.5 billion by 2029, growing at 8.0% cagr from 2024 to 2029.
Key Market Trends
Biocompatibility Innovations: Biocompatible materials are essential in medical applications where patient safety is paramount. To meet this need, polycarbonate, polypropylene, and polyethylene polymers are engineered to strict medical standards, creating materials that offer safe, effective performance within the body.
Surge in Disposable Devices: Single-use medical products like gloves, syringes, and catheters are gaining traction, especially post-pandemic. Disposable polymers allow manufacturers to produce cost-effective, hygienic products, addressing modern healthcare’s need for cleanliness and infection control.
3D Printing Advancements: Customization has transformed through 3D printing, as tailored prosthetics and surgical tools become accessible. Polymers like PEEK are favored here for strength and adaptability, enabling precise medical solutions suited to individual patient needs.
Sustainability Drives: With heightened environmental awareness, medical manufacturers are focusing on bio-based and recyclable materials. This shift aims to reduce the ecological impact of medical products, reflecting the global push towards sustainable solutions.
Enhanced Drug Delivery Applications: Drug delivery systems require polymers that ensure controlled, sustained release of medication. Bioresorbable polymers are particularly beneficial here, facilitating targeted treatment in chronic and long-term therapies without additional interventions.
Growth Drivers in the Medical Polymer Market
Demand for Minimally Invasive Devices: Polymers are ideal for minimally invasive surgery tools due to their flexibility and durability. As demand for less invasive procedures grows, so does the need for these high-performing materials, making them integral to medical advancements.
Aging Population and Chronic Disease: The global increase in chronic health conditions and an aging population drive demand for medical-grade polymers in implants, devices, and products for ongoing care. This market growth reflects the need for durable, biocompatible materials to improve patient care.
R&D and Technological Investments: Innovations in polymer chemistry and healthcare applications expand the versatility of these materials. Significant R&D investment is pushing the boundaries, enabling entry into new applications and meeting stringent regulatory demands across regions.
Regional Market Insights
The market for medical polymers is expanding globally, with strong growth in North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific. North America leads due to its advanced healthcare sector and robust R&D focus, while the Asia-Pacific region experiences rapid growth driven by healthcare expansion, population increases, and rising disposable incomes in emerging economies like China and India.
Emerging markets hold considerable growth potential, especially as they build their healthcare infrastructure and address increasing medical needs. Access to quality polymers helps these regions expand their healthcare capabilities, catering to larger populations with advancing healthcare needs.
Challenges and Future Prospects
The medical polymer market faces challenges, such as meeting rigorous regulatory requirements, managing high development costs, and addressing environmental concerns. Compliance with medical standards is necessary but can slow down product development and increase expenses. Additionally, the medical industry’s reliance on single-use polymers prompts a need for eco-friendly, recyclable solutions.
To know more Download PDF Brochure :
The future remains promising. The market’s growth, driven by healthcare demands and technological advances, opens new opportunities in medical material innovation. Companies prioritizing sustainability, compliance, and R&D will be well-positioned to capitalize on the evolving needs of this essential industry.
As materials science and healthcare continue to intersect, medical polymers are set to play a critical role in advancing medical technologies, improving patient outcomes, and meeting global healthcare needs.
#medical polymer market#biocompatible materials#disposable medical devices#3D printing in healthcare#sustainable polymers#biodegradable polymers#drug delivery systems#minimally invasive devices#chronic disease treatment#aging population healthcare#medical-grade polymers
0 notes
Text
Global Nasal drug Delivery Market, Forecast to 2030
Market Introduction
The parenteral route, commonly referred to as the nasal drug delivery system, is an alternate method of medication administration. Drugs that can only be administered intravenously have been administered orally as an alternate method to allow for systemic availability. The benefits of this technology include simple administration, patient compliance, minimal dosage requirements, bypassing first pass metabolism, great penetration, quick absorption, and favourable outcomes. To administer the pharmaceuticals to treat the majority of CNS illnesses, such as Parkinson's disease and Alzheimer's disease, several drug delivery systems for nasal administration of liquid, semisolid, and solid formulation are being researched.
Market Dynamics
The market for nasal drug delivery technology is predicted to expand throughout the course of the forecast period as a result of factors such as rising chronic illness incidence, advanced technology, and rising demand for nasal drug delivery systems. Additionally, it is anticipated that increasing self-administration practises will present more growth opportunities for companies involved in the nasal drug delivery technology market.
Click here for full report:
Market Scope
The "Global Nasal Drug Delivery Technology Market Analysis to 2030" is a specialized and in-depth study of the pharmaceutical industry with a special focus on the global market trend analysis. The report aims to provide an overview of nasal drug delivery technology market with detailed market segmentation by systems, containers, dosage form, therapeutic application, end user and geography. The global nasal drug delivery technology market is expected to witness high growth during the forecast period. The report provides key statistics on the market status of the leading nasal drug delivery technology market players and offers key trends and opportunities in the market.
Market Segmentation
The global nasal drug delivery technology market is segmented on the basis of systems, containers, dosage form, therapeutic application and end user. Based on systems, the market is segmented as, unit dose, bi-dose and multi dose. On the basis of containers, the market is segmented into, pressurized containers and non-pressurized containers. Based on the dosage form, the nasal drug delivery technology market is classified as, nasal powders, nasal gels, nasal drops & liquids and nasal spray. On the basis of application, the global nasal drug delivery technology market is categorized as, allergic & non-allergic rhinitis, nasal congestion, vaccinations and other applications. Based on the end user, the global nasal drug delivery technology market is segmented into hospitals and home health care.
Click here for full report:
Regional Analysis
The research provides an in-depth analysis of the market including both qualitative and numerical data. It provides analysis and forecast of the global Nasal Drug Delivery Technologies market based on several market categories. Additionally, it provides market size and forecast estimation for the five major regions of North America, Europe, Asia Pacific (APAC), Middle East and Africa (MEA) and South & Central America for the years 2023 to 2030. The Nasal Medication Delivery Technology Market is further divided into related nations and sectors for each region. The research includes a worldwide analysis and extrapolation for 18 nations as well as information on current trends and opportunities in this area.
The research examines factors influencing the market for nasal drug delivery technology from both the demand and supply sides. It also assesses market dynamics, such as drivers, constraints, opportunities, and future trends, that will have an impact on the market during the projected period. The study evaluates the political, economic, social, and technological aspects affecting the market for nasal drug delivery technology in each of the five regions, namely North America, Europe, APAC, MEA, and South & Central America. Following this evaluation, the report includes thorough PEST analyses for each of the five areas.
#Nasal Drug Delivery#Global Market#Innovations#Trends#Opportunities#Drug Delivery Systems#Pharmaceutical Industry#Medical Devices#Healthcare Solutions
0 notes
Text
[“To understand the shortage of beds, it helps to think of just-in-time delivery. Companies like to have just enough space for what they need, work with, and sell, not more and not less. For a hospital, the human body is the object that is to be delivered, altered, and shipped away just in time. There should never be too many bodies, or too few bodies. There should be just the right number of bodies on just the right number of beds.
Good doctors, good nurses, and good assistants resist this logic all the time, but they are pushing a boulder up a mountain. Maintaining beds costs money. No hospital, in American commercial medicine, is going to maintain a reserve of beds when other hospitals do not do so. Since financial logic dominates medical logic, the country must always be unprepared for epidemics. There can never be a reserve of beds, nor for that matter a reserve of protective equipment or ventilators. Managers counting on a quarterly profit cannot factor in pandemics, which arrive about once a decade. Each time a plague comes, the situation will be defined as exceptional, and the shortages will make the emergency even worse than it had to be. Then money will fly around: not to where the doctors might want, since they will not be asked, but to the sectors of the economy with the loudest voices. This just happened, and with commercial medicine it will keep happening.
In the hospital, sad to say, a body is a widget. Kindly assistants, competent nurses, and decent physicians try to humanize the widget, but they are constrained by a system. A body creates revenue if the body is the right kind of sick for the right length of time. Certain kinds of illnesses, especially ones treatable (or reputed to be treatable) with surgery and drugs, make money. No one has an economic incentive to keep you healthy, to get you well, or for that matter to keep you alive. Health and life are human values, not financial ones; an unregulated market in the treatment of our bodies generates profitable sickness rather than human thriving.”]
timothy snyder, from our malady: lessons in liberty from a hospital diary, 2020
428 notes
·
View notes
Note
I guess I should call you Mr. Curly then! Or Miss, Mrs..? Correct me if I'm wrong! What happens if you go bald or, worse, get a buzzcut haha
Your frustration with FibroFree... I get it. I don't have FMS myself, but my sister-in-law does. I remember how much she suffered while fighting for the right to affordable healthcare. That's the kind of thing I expect when TRPC-R finally hits the market. The system is broken. Don't tell me if it's too personal - do you have FMS?
I wasn't part of the team developing TRPC-R though I was here when the incident occured. I got the second-hand account from my late mentor in the immediate aftermath and, oh boy... she's deceased, so sharing won't put her in legal trouble, although I must be vague for the details aren't public.
Let's just say... you know how TRPC channel activation increases cardiac growth, right? And TRPC-R regulates the activation of these channels in low gravity to counteract hypotrophy in astronauts. No problems there. HOWEVER. Say one of the test subjects got their hand on sweetener from a 'small-horse delivery' company (not naming names) and, say, the sweetener happens to be cut with a stimulant that causes exponential growth in combination with TRPC-R... now, I'm not a medical professional like you, but I'm sure you'll agree that a human heart should remain INSIDE the body, and it certainly shouldn't explode out of their chest.
The examination room was on lockdown for a week. I can't fathom how the poor nurse doing the medical check felt, but they left on the next shuttle to Earth and we haven't heard from them since.
By the way - you probably know already - there's a super galactic storm heading in your direction. It might miss you. If it doesn't, please, please, PLEASE message me as soon as you can.
- xoxo, Pheobe
P.S. I'm SO glad you asked about anoxygenic photosynthesis! Here are the facts: one, AP is photosynthesis in the abscence of oxygen. Two: two domains are capable of AP - archae and bacteria. Three: all known extant Martian organisms are believed to belong to these domains. These three facts are foundational to Martian/Terran Divergent Theory. You may be thinking "Pheobe, what about subterranean Martians; how do they photosynthesize in the abscence of light?" - an excellent question! This is the crux of the matter, and a heated source of debate. You see... [read more]
Attachment: 'Review of ATP and NADH Synthesis in Sub-Terranian Martians and the Evidence for Divergence', pdf, 1.7 Tb
Please, 'Mr Curly' was my father, I assure you that 'Curly' is perfectly fine. :-) I fear to imagine the day I go bald, I guess I'll just have to change my ID.
I don't have FMS, no, but with the amount of people that was funnelled through the hospital I worked at I got to see many cases, and it's incredibly frustrating to have the treatment readily available yet to be completely barred from accessing it. I'm thinking of going rogue sometimes, but you never heard it and I never said it. I'm sorry to hear about your sister-in-law.
...Okay, I did not actually know about the stimulant in sweetener, and I studied the packaging. This is...concerning. Even if the chances of someone being on TRPC-R are already low, and even lower of them ingesting a certain brand of sweetener, even one case is one too many -- and makes me wonder what else I'm not aware of that I should be. You've given me a lot to investigate, thank you! Albeit at the cost of...erm... a cor extrathoracicum event. Yeesh. I've seen many a harrowing case, but I don't think a spontaneous heart evacuation like that was amongst them.
Wow, that is a hefty file, I'm setting it to download immediately. Many thanks! Please know that you are saving me from frankly lethal levels of boredom with so much to read.
Right, forgot to add -- thank you for the heads up on the storm too! I'm sure we'll be fine, the ship is in very capable hands. :-) See you on the other side.
--Curly
#n.n.#ask box temporarily closing soon!#ask blog#mouthwashing#curly mouthwashing#nurlysays#also anon i love you
8 notes
·
View notes
Text


Author: Kevin Carson Topics: health care, left-libertarianism
Mutualist, at the livejournal blog of the same name, writes on “Building Consensus with Egalitarian Liberals in Healthcare Reform.”
His argument is that libertarians and egalitarian liberals are likely to disagree on demand-side issues like single-payer insurance vs. medical savings accounts, because they’re so closely tied up with differences in purchasing power. But liberals are more likely to be sympathetic to proposals to open up the supply of healthcare to competition. Breaking the power of the license cartels and the patent system, and eliminating barriers to a fully functioning market (i.e., permitting price competition through advertising) would drastically reduce the price of healthcare and greatly empower the consumer.
And, I’d add, if we did that, discussion of demand-side reforms might be a lot more politically feasible.
Liberal welfare-statism is a pretty natural--if misguided--reaction to a society in which the state, through privilege, creates great disparities in income. Privilege creates massive distortions, made cumulative through the process of feedback, that must be dealt with somehow. One way of dealing with the consequences is through a Rube Goldberg device like redistributive welfare policy, another layer of policy to counteract the first layer, to prevent underconsumption from becoming too destabilizing and the underclass from becoming too radicalized. The other way is to eliminate the privilege itself--a lot simpler.
But make no mistake. If the privilege remains, statist “corrective” action will be the inevitable result. That’s why I don’t get too bent out of shape about the statism of the minimum wage or overtime laws--in my list of statist evils, the guys who are breaking legs rank considerably higher than the ones handing out government crutches. All too many libertarians could care less about the statism that causes the problems of income disparity, but go ballistic over the statism intended to alleviate it. It’s another example of the general rule that statism that helps the rich is kinda sorta bad, maybe, I guess, but statism that helps the poor is flaming red ruin on wheels.
Libertarians need to stop admiring the emperor’s clothes and pretending that disparities in income reflect the triumph of industrious ants over lazy grasshoppers. Liberals might be a lot easier to talk to then. That Galt’s Gulch bullshit can be kind of hard to listen to sometimes.
I’ve argued elsewhere myself, by the way, that we need to go beyond cooperative solutions to healthcare finance, and get into cooperatively organizing delivery of service, as well.
#libertarian#leftism#healthcare#health care#libertarianism#politics#medicine#science#kevin carson#anarchism#anarchy#anarchist society#practical anarchy#practical anarchism#resistance#autonomy#revolution#communism#anti capitalist#anti capitalism#late stage capitalism#daily posts#libraries#social issues#anarchy works#anarchist library#survival#freedom
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
Earlier this week, The New Yorker published a piece about a young woman killed by Texas’ abortion ban. Yeniifer Alvarez-Estrada Glick, the first reported post-Dobbs death, had diabetes, hypertension, and a history of pulmonary edema; she went to the emergency room with breathing problems just seven weeks into her pregnancy, and multiple times thereafter with ever-increasing issues. Yet even as Yeni got sicker and sicker, at no point did a doctor advise an abortion. No one even mentioned the possibility.
A big part of what makes abortion bans dangerous is the fear they instill in doctors and other medical professionals—it’s not just illegal to perform an abortion in Texas, but to ‘aid and abet’ one. As NPR reported last year, the law has doctors in the state “talking in code” about ending pregnancies. And one of the vital points made by New Yorker reporter Stephania Taladrid, is the way that bans impact “informed consent,” the principle that “doctors are ethically bound to give the patient enough information to grasp the possible costs and benefits of her choices.”
Yeni wasn’t given informed consent because of the abortion ban in Texas, but also because the hospital treating her was part of a Catholic health system—and religiously-affiliated hospitals don’t believe in abortion.
As I read the New Yorker investigation into Yeni’s death, I took note of the hospital system that failed her: Ascension. The name sounded familiar.
The very same day that Yeni’s story was shared with the world, National Nurses United (NNU) released a report showing how Ascension is fueling the U.S. maternal mortality crisis. In fact, NNU called Ascension, which has 140 hospitals in 19 states, “one of the nation’s worst offenders for closing obstetrics units.” From their report:
“Over the past decade, our analysis found that Ascension has eliminated obstetrics services at 16 hospitals, slashing approximately 26 percent of its labor and delivery departments it previously provided in 2012. Since 2022 alone, Ascension has shuttered five maternity wards, all in moderately-to-highly concentrated health care markets. …These cuts, predominantly in low-income neighborhoods that are disproportionately Black and Latine, are forcing pregnant patients to travel farther and endure longer wait times to receive care.”
Ascension, which claims to have a mission that pays “special attention to those who are poor and vulnerable,” reported a net income of over $5.7 billion in 2021, with a CEO who made more than $13 million that same year. They’re the second-largest and wealthiest Catholic health system in America.
In a moment when reproductive and maternal health care deserts are spreading, and maternal deaths are on the rise—especially among women of color, Black women, in particular—the report is incredibly damning. It tracks how Ascension has created maternal health deserts in multiple states, and how the health system’s bottom line trumps patient care.
Remember, right now nearly 2 million American women live in a “double desert”—a county without abortion access or maternal health care. And a report last year from the March of Dimes shows that nearly 6 million women live in counties with limited or no access to maternity care services. Those are deadly numbers.
The NNU’s study, for example, found that after Ascension closed an obstetrics unit in one of their Florida hospitals in 2019, the maternal death rate in the county more than doubled by 2021.
Their research also showed that Ascension closes down labor and delivery units in areas where the hospital system has market dominance—that means the company can cut staff and care without worrying about their revenue. Again, this is in spite of the fact that Ascension is a multi-billion dollar business.
This massive religious hospital system isn’t just putting people in danger through their obstetric services cuts—but cuts across the board. In 2022, The New York Times reported that “the heart of Ascension’s business strategy [is] cutting costs,” often at the expense of patient safety:
“At one point, executives boasted to their peers about how they had slashed $500 million from the chain’s labor costs. In the years before the pandemic, they routinely refused requests to hire more medical workers or fill open jobs, according to current and former hospital administrators and employees.”
The NYT investigation described patients at Ascension hospitals waiting for hours on gurneys despite needing urgent care, overworked staff, and nurses raising the alarm again and again only to be ignored. In one formal complaint, a nurse wrote, “Someone is going to die if this continues, and there is no indication that anyone is concerned.”
Someone did die: Yeniifer Alvarez-Estrada Glick. And like this nurse, I’m shocked at the lack of care in response to her story.
In the New Yorker, Taladrid reports that the hospital where Yeni sought care, Ascension Seton Edgar B. Davis, had shut down their labor and delivery unit years earlier. But with the closest OB ward thirty miles away, patients with urgent needs had nowhere else to go. Hospital staff told Taladrid that they were seeing more and more women giving birth, and that it felt like “uncontrolled chaos.”
This chaos, combined with a mandate from the hospital and the state to refuse to talk about abortion, is deadly. In a statement, NNU President Jean Ross slammed Ascension for ignoring their mission, saying, “Ascension’s creation of obstetric health care deserts increases the risk of dangerous complications and reduces opportunities for timely, lifesaving care for expecting parents and babies.”
I’ll be writing more about Ascension in the coming days, but I want to repeat something I’ve said often this week: We have to be loud and clear about what is causing post-Dobbs deaths. Stories around pregnancy and healthcare can be complicated, and still have a fundamental truth—that abortion bans kill.
The reality is that companies like Ascension are inextricably linked to abortion bans. They’re both part of the same system that prioritizes extremist religious ideology over women’s lives.
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
A novel radiation treatment for cancer with a 100-percent success rate in its pilot trial is now in Phase 3 pivotal trials ahead of receiving Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval.
Jerusalem-based startup Alpha TAU is expanding its trials of the treatment for skin and other cancer, after its first trial of 10 patients succeeded beyond the company’s expectations.

“Those patients got 100 percent CR [complete response],” Sofer says.
The pilot trial, conducted at multiple locations in the US last year, examined whether Alpha TAU’s DaRT (Diffusing Alpha-emitters Radiation Therapy) technology could successfully deliver targeted radiation therapy to patients with malignant skin and superficial soft tissue tumors that had returned or could not be removed surgically.
Alpha TAU had hoped that the treatment would be successful in at least seven of the 10 trial participants, but instead registered successful delivery to all 10. CT scans showed a 100 percent complete response rate at 12 weeks after the treatment and again at 24 weeks, with no evidence of the disease recurring in any of the subjects.

The results showed only mild or moderate side effects related to the device, and no systemic toxicity from it.
Radiation therapy for cancer normally uses beta and gamma particles. Alpha particles, while proving deadly for cancer cells in a tumor, are not traditionally used as they cannot travel far in solid masses.
Alpha DaRT, however, delivers the alpha particles directly into the tumor via a narrow device, inserted under local anesthetic, for a period of two to three weeks. The device is then removed and the patient monitored.
The findings of the pilot trial were published this month in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA), months after submitting the results to the FDA.
The treatment is now undergoing its pivotal trial – the final one before the American agency gives it approval.
“We submitted the results that you see now to the FDA, and the FDA told us that we can submit the protocol for the last phase, the pivotal,” says Sofer.
A pivotal trial is required by the US and European Union drug agencies in order to receive approval to market a new form of medication; studies can involve thousands of subjects and test the efficacy and impact of a drug.
Sofer says that the successful findings of the trial has led to medical institutes around the world clamoring to work with Alpha TAU, but for now research is limited to just a handful of locations for the pivotal trial.
“Many, many, many centers all around the world want to participate,” he says. “We are working with 20 centers in the US, two or three centers in Canada and another four in Israel that are going to participate in this trial.”
youtube
Sofer says Alpha TAU will be ready to submit the findings of the pivotal trial in around a year and a half from now.
“We will have six months of follow up, then we will analyze the results and send it to the FDA,” he says of the current trial. “The submission to the FDA can be in about 18 months from now.”
The revolutionary treatment is also being tried on other cancers, according to Sofer, who clarifies that, “right now it’s only for solid tumors.”
“We’re working on pancreas and lung and breast [cancer],” he says, explaining that the company is currently at various stages of testing for these other forms of malignant tumors.

The device itself is easy to use and does not require specialized and often costly equipment in order to treat patients.
“When it is approved, it will be for any hospital, medical cancer center, all over the world,” Sofer explains.
“You don’t need any special equipment, and you don’t need the shielding,” he says, referring to the protective gear used in other forms of radiation therapy but are not needed for alpha particles.
“It will be very simple to implement. You don’t need special equipment or investment in capital expenditure or something like that, [just] regular tools.”
70 notes
·
View notes
Text
Investment Surge in GLP-1 Drugs Market: Trends and Future Prospects
Market Growth and Investment Trends
The GLP-1 drugs market has seen substantial investment from pharmaceutical companies and venture capitalists. This is driven by the increasing prevalence of type 2 diabetes and obesity, coupled with the efficacy of GLP-1 drugs in managing these conditions. Key trends include:
Rising Prevalence of Diabetes and Obesity: The global rise in lifestyle-related health issues is fueling demand for effective treatments.
Innovative Drug Development: Companies are investing heavily in R&D to develop next-generation GLP-1 drugs with improved efficacy and fewer side effects.
Strategic Collaborations and Partnerships: Collaborations between pharmaceutical giants and biotech firms are accelerating innovation and market entry of new drugs.
Recent Developments
Several notable developments have occurred in the GLP-1 drugs market:
New Drug Approvals: Regulatory bodies like the FDA and EMA have recently approved several new GLP-1 receptor agonists, expanding treatment options.
Clinical Trials and Research: Ongoing clinical trials are investigating the broader therapeutic potential of GLP-1 drugs, including their effects on cardiovascular health and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
Technological Advancements: Innovations in drug delivery systems, such as oral formulations and long-acting injectables, are enhancing patient compliance and convenience.
Browse Press Release
Future Opportunities
The future of the GLP-1 drugs market holds numerous opportunities for growth and innovation:
Expansion into New Therapeutic Areas: Research suggests potential applications of GLP-1 drugs in conditions beyond diabetes and obesity, such as neurodegenerative diseases and inflammation.
Personalized Medicine: Advances in genomics and biomarkers may enable personalized GLP-1 therapies tailored to individual patient profiles, improving outcomes.
Emerging Markets: Increasing healthcare access and rising diabetes prevalence in emerging markets present significant growth opportunities for GLP-1 drugs.
Conclusion
The GLP-1 drugs market is poised for remarkable growth, driven by robust investment, innovative developments, and expanding therapeutic applications. As research progresses and new technologies emerge, GLP-1 receptor agonists will play a crucial role in addressing the global burden of diabetes, obesity, and potentially other diseases, offering improved health outcomes for millions.
About iDataAcumen
iDataAcumen is a global business intelligence and management consulting firm providing data driven solutions to a wide array of business challenges. Our clients are present across major geographies globally and belong to industries ranging mainly from healthcare, pharmaceuticals, life science, biotechnology, medical devices, food industry, chemicals, among others. We have catered to more than 500 clients across these industries.
We aspire to help our clients build a sustainable business by providing them robust business insights that are derived from sound data driven analysis. In today’s ever changing business environment, its become important to look objectively at your own business just as it is important to look at the competition. Technological advancement including but not limited to big data, artificial intelligence, and machine learning are helping industries worldwide to make informed business decisions. Our research process also makes use of some of these advanced tools to uncover valuable insights from vast amount of data to arrive at logical conclusions.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Friday, May 10, 2024
Biden Says the U.S. Will Not Supply Israel With Weapons to Attack Rafah (NYT) President Biden acknowledged on Wednesday that American bombs have been used to kill Palestinian civilians as he warned that the United States would withhold certain weapons if Israel launches a long-threatened assault in southern Gaza. In some of his strongest language to date on the seven-month war, Mr. Biden said the United States would still ensure Israel’s security, including the Iron Dome missile defense system and Israel’s “ability to respond to attacks” like the one Iran launched in April. But he said he would block the delivery of weapons that could be fired into densely populated areas of Rafah, where more than a million Palestinians are sheltering. The president had already halted the shipment of 3,500 bombs last week out of concern that they might be used in a major assault on Rafah—the first time since Hamas attacked Israel on Oct. 7 that Mr. Biden has leveraged U.S. arms to try to influence how the war is waged. On Wednesday, he said that he would also block the delivery of artillery shells.
With inflation soaring, Argentina will start printing 10,000 peso notes (AP) Prices in Argentina have surged so dramatically in recent months that the government has multiplied the size of its biggest bank note in circulation by five—to 10,000 pesos, worth about $10. The central bank announcement Tuesday promised to lighten the load for many Argentines who must carry around giant bags—occasionally, suitcases—stuffed with cash for simple transactions. Argentina’s annual inflation rate reached 287% in March, among the highest in the world. The new denomination note—five times the value of the previous biggest bill—is expected to hit the streets next month in a bid to “facilitate transactions between users,” the central bank said. The 10,000 peso note is worth $11 at the country’s official exchange rate and $9 at the black market exchange rate.
A grand Olympic plan. But first, the tent camps have to go. (Washington Post) He’d been living in the tent for nine days when the police arrived. “Bonjour, monsieur!” an officer shouted. “Reveille!” Ba Dak crawled out of his sleeping bag, unzipped the tent flap and stepped into the frigid February air. The camp, tucked beneath the Charles de Gaulle Bridge on the northern bank of the Seine River, bustled with movement in the windy pre-dawn darkness. Police officers in neon green vests marched between rows of tents, whose inhabitants rose from slumber to pack their belongings. The government was seeking to remove unhoused people from its streets before the Olympic Games shines a global spotlight on Paris this summer. Officials billed it as an innovative effort to ease Paris’s housing crisis, by relocating people to newly constructed facilities around the country rather than hotels in the city’s emergency shelter system. But advocates for refugees claim the government had more specific motives: to clear Paris of its tent villages, free up thousands of hotel rooms before the Games and identify people who aren’t eligible to legally remain in the country.
The mothers and wives of missing Russian servicemen have become some of the war effort’s biggest critics. (WSJ) Tens of thousands of relatives and friends use social media to swap information in the hopes of learning their loved ones’ fates. Under Russian law, soldiers aren’t declared dead without a recovered body, a death certificate from a medical examiner or a court ruling. In Ukraine, many troops are unaccounted for including deserters and prisoners of war. The Kremlin hasn’t released the number of MIAs. Russian antiwar commentators accuse the military of abandoning dead fighters to avoid compensating their families. President Vladimir Putin ordered them to get the equivalent of $54,600, plus the previously set compensation of around $26,000. Russian officials didn’t respond to a request for comment.
Ukrainians are using the cover of war to escape taxes (Economist) Since Russia invaded in 2022, Ukraine’s economy has shrunk by a quarter. But the ravages of war are not the only reason for the government’s reduced tax take. Businesses are also making use of the chaos to dodge paying their fair share. This is particularly true in agriculture, which before the war was responsible for 40% or so of Ukraine’s exports by income. The sector has been transformed by a scramble to find export routes safe from Russian attack. As Taras Kachka, Ukraine’s deputy minister for agriculture, notes, this disturbance has provided plenty of opportunity for farmers to “optimise taxes”. Around 6.5m Ukrainians—or 15% of the country’s pre-war population—have left the country, shrinking the domestic food market. At the same time, Russia is targeting transport infrastructure, grain silos and other agricultural equipment, which has driven up costs. Many workers have been recruited by the armed forces, and are at the front. Farmers therefore not only have new opportunities to dodge taxes, they are also increasingly desperate. The result is that two of every five tonnes of grain harvests now avoid contributing to state coffers, according to Mr Kachka’s estimates.
Myanmar: A hidden war (NYT) A people take to arms and fight for democracy. A military terrorizes civilians with airstrikes and land mines. Tens of thousands are killed. Millions are displaced. Yet it is all happening almost completely out of view in the Southeast Asian nation of Myanmar. Now, for the first time, the rebels claim control of more than half of Myanmar’s territory. In recent weeks they have overrun dozens of towns and Myanmar military bases. Even without foreign intervention, or much Western aid at all, the Myanmar resistance has pushed back the junta. Rebels are now within 150 miles of the capital, Naypyidaw. But that may have been the easy part. The resistance is—perhaps hopelessly—splintered. More than a dozen major armed ethnic groups are vying for control over land and valuable natural resources. Much of Myanmar is fractured between different groups, all heavily armed. Crime is flourishing. The country is now the world’s biggest producer of opium. Jungle factories churn out meth and other synthetic drugs that have found their way to Australia. Myanmar’s civil war may be overshadowed by other global conflicts. But to the Burmese who live with uncertainty and chaos, the war has never been more urgent or real.
In rapidly ageing China, millions of migrant workers can’t afford to retire (Reuters) After three decades selling homemade buns on the streets of the Chinese city of Xian, 67-year-old Hu Dexi would have liked to slow down. Instead, Hu and his older wife have moved to the edge of Beijing, where they wake at 4 a.m. every day to cook their packed lunch, then commute for more than an hour to a downtown shopping mall, where they each earn 4,000 yuan ($552) monthly, working 13-hour shifts as cleaners. The alternative for them and many of the 100 million rural migrants reaching retirement age in China over the next 10 years is to return to their village and live off a small farm and monthly pensions of 123 yuan ($17). The generation that flocked to China’s cities at the end of last century, building the infrastructure and manning the factories that made the country the world’s biggest exporter, now risks a sharp late-life drop in living standards.
Rafah and humanitarian aid (Washington Post) By Tuesday, Israeli forces had seized the pivotal Rafah border crossing that links Gaza to Egypt’s Sinai peninsula. Israel intensified bombardments on parts of the city, hitting houses and residential towers, and prompted more than 100,000 people into a panicked evacuation. The Rafah border crossing was closed, though Israeli authorities said another crossing at Kerem Shalom remained open to funnel critical supplies into Gaza—a claim questioned by aid groups. “The crossing area has ongoing military operations and is an active war zone,” Louise Wateridge, a spokeswoman for UNRWA, the U.N.’s agency for Palestinians, currently in Rafah, said Wednesday. “We are hearing continued bombardments in this area throughout the day. No fuel or aid has entered into the Gaza Strip, and this is disastrous for the humanitarian response.” “All the fuel that entered Gaza went through Rafah crossing,” said Jeremy Konyndyk, president of Refugees International, at a joint news briefing Wednesday of prominent humanitarian organizations. “The whole aid operation runs on fuel, so if the fuel is cut off, the humanitarian operation collapses. Water can’t be pumped. Lights cannot be kept on in hospitals. Vehicles cannot distribute aid.”
“Annihilation Prevention”—Why Some Gaza Families Choose To Split Up (Zumadaraj/English edition) Umm Raja Barbakh, a Gazan woman in her 60s, had a particular request to her children and grandchildren amid Israel’s relentless bombing campaign: when we flee, let’s choose different destinations. The reason is as simple as it is grim: She doesn’t want all her progeny in the same place for fear that the whole family could be annihilated. “The decision to disperse my children and grandchildren is a way to limit the chance that the whole family is gone in case of a bombing on a single place,” she explained. “Their presence in more than one place will reduce the risk of the family disappearing completely.” Indeed, that’s what happened with her sister, who was killed in an Israeli bombing along with her children and grandchildren. Barbakh’s family has instead scattered in different locations in the cities of Khan Younis and Rafah in southern Gaza. The oldest of her four children has sheltered in a tent in the Mawasi area in Rafah along with his seven children. A second son and daughter were living with their children in different locations in Rafah. The fourth lives with his five children in Khan Younis.
Smile! (Les Echos/France) It’s amazing to think that this slight movement of the lips and facial muscles, which sometimes lights up an entire face, can resonate so deeply within us and awaken a whole range of emotions—even if it comes from a complete stranger. Neuroscience has established that smiling feels good, and it starts very early. Fetal ultrasound scans have shown that, from the 26th week, babies smile to express a form of satisfaction, particularly after their mother has eaten a certain type of food. We now know that smiling stimulates the areas of the brain associated with reward circuits. And that it lowers levels of cortisol, the stress hormone. It slows the heart rate and lowers blood pressure. Two recent studies have even shown that this beneficial effect holds true even when we smile mechanically, though more modestly—it’s as if the simple act of mobilizing one of the 15 muscles involved in smiling sends a positive signal to the brain. Another older study from Wayne State University suggests that smiling increases life expectancy. It was based on photographs of 230 American baseball league players taken in 1952. The sportsmen who did not smile in the photographs died at an average age of 72.9. Those who had big smiles lived to 79.9. Smiles also open doors. Traveler Charly Guérin has had many opportunities to verify this. He met a Bolivian grandmother in Sucre on her front doorstep who, simply on the strength of an impromptu smile, invited him into her home, where he ended up spending the afternoon chatting. “If you take the time to meet someone, a smile is a real open sesame,” the globetrotter says. On his blog, he also tells the story of Sarah, a French woman who set off around the world on a shoestring budget and who, when she wanted to attend a concert or sporting event, didn’t hesitate to stand in front of the entrance to the venue with a sign: “Exchange a free ticket for a smile.” And incredible as it may seem, it worked on many occasions.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Healthcare IT Integration Market Size Expected to Reach USD 11.16 Billion by 2030
The global Healthcare IT Integration market size, which was valued at USD 4.38 billion in 2022, is anticipated to witness remarkable growth, reaching USD 11.16 billion by 2030. This projection reflects a robust Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 12.4% over the forecast period spanning from 2023 to 2030.
The increasing demand for efficient healthcare delivery systems, coupled with the rising adoption of electronic health records (EHRs) and other digital solutions, is driving the growth of the Healthcare IT Integration market. Healthcare organizations worldwide are realizing the significance of integrating disparate systems and applications to streamline workflows, improve patient care, and enhance operational efficiency.
Key Market Segments:
The Healthcare IT Integration market is segmented by Products & Services type, End User, and Regions:
Products & Services Type:
Products: Interface Engines, Media Integration Software, Medical Device Integration Software, Other Integration Tools
Services: Support and Maintenance Services, Implementation and Integration Services (Training and Education Services, Consulting Services)
End User:
Hospitals
Clinics
Diagnostic Imaging Centers
Laboratories
Other End Users
Regions: The global market forecast covers various regions across the globe.
Market Outlook:
The increasing adoption of electronic health records (EHRs) and healthcare information exchange (HIE) solutions is propelling the demand for Healthcare IT Integration products and services. Interface engines and integration software play a pivotal role in connecting disparate systems within healthcare organizations, enabling seamless data exchange and interoperability.
Moreover, the emergence of advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and blockchain in healthcare is further driving the need for robust IT integration solutions. These technologies require seamless integration with existing healthcare IT infrastructure to harness their full potential in improving patient outcomes and optimizing healthcare processes.
As healthcare providers continue to prioritize interoperability and data exchange to support value-based care initiatives and enhance patient engagement, the demand for Healthcare IT Integration solutions is expected to witness significant growth in the coming years.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Data Science Unveiled: A Journey Across Industries
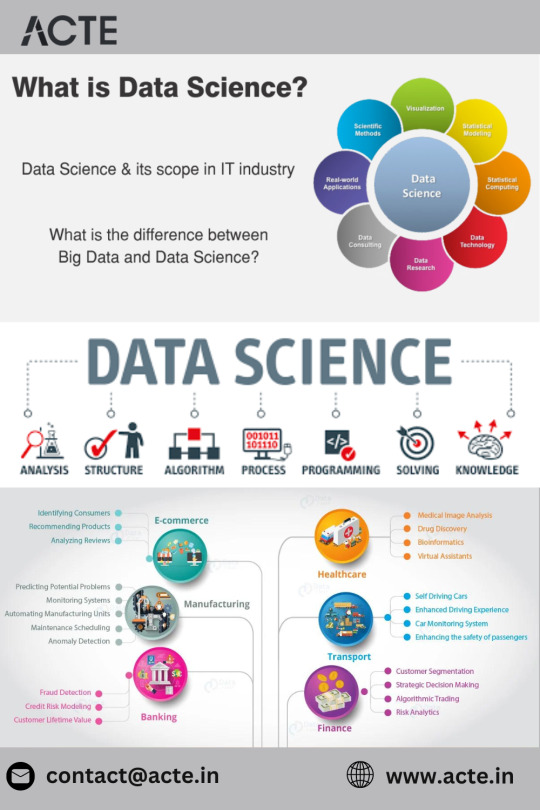
In the intricate tapestry of modern industries, data science stands as the master weaver, threading insights, predictions, and optimizations. From healthcare to finance, e-commerce to education, the applications of data science are as diverse as the sectors it transforms. Choosing the Top Data Science Institute can further accelerate your journey into this thriving industry. In this exploration, we'll embark on a journey to unravel the pervasive influence of data science across various domains, witnessing its transformative power and impact on decision-making in the digital age.
Healthcare: Pioneering Precision Medicine
In the healthcare sector, data science acts as a beacon of innovation. It plays a pivotal role in patient diagnosis, treatment optimization, and personalized medicine. By analyzing vast datasets, healthcare professionals can identify patterns, predict disease outcomes, and tailor treatments to individual patients. This not only enhances the efficiency of healthcare delivery but also contributes to groundbreaking advancements in medical research.
Finance: Navigating Risk and Detecting Fraud
The financial landscape is ripe for data science applications, particularly in risk management, fraud detection, and algorithmic trading. Data-driven models analyze market trends, assess risk exposure, and identify fraudulent activities in real-time. This not only safeguards financial institutions but also empowers them to make informed investment decisions, optimizing portfolios for better returns.
E-commerce: Crafting Personalized Experiences
In the bustling world of e-commerce, data science is the engine driving personalized experiences. Recommendation systems powered by data analysis understand user behavior, preferences, and purchase history. This results in tailored product suggestions, optimized pricing strategies, and a seamless shopping journey that boosts sales and enhances customer satisfaction.
Telecommunications: Enhancing Connectivity and Predicting Maintenance
Telecommunications companies leverage data science for network optimization, predictive maintenance, and customer churn analysis. By analyzing vast datasets, they can optimize network performance, predict potential issues, and proactively address concerns. This not only enhances the reliability of communication networks but also improves the overall customer experience.
Marketing: Precision in Targeting and Campaign Optimization
Marketers rely on data science for precision in targeting and campaign optimization. Customer segmentation, behavior analysis, and predictive modeling help marketers tailor their strategies for maximum impact. This ensures that marketing efforts are not only more effective but also cost-efficient, yielding higher returns on investment.
Education: Tailoring Learning Experiences
In the realm of education, data science is reshaping how students learn. Personalized learning experiences, performance analytics, and resource optimization are made possible through data analysis. By understanding student behavior and learning patterns, educators can tailor educational strategies to individual needs, fostering a more adaptive and effective learning environment.
Manufacturing: Predictive Maintenance and Quality Control
Manufacturing enterprises harness data science for predictive maintenance, quality control, and supply chain optimization. Analyzing data from sensors and production lines allows for predictive maintenance, minimizing downtime and reducing defects. This not only enhances operational efficiency but also contributes to cost savings. Choosing the best Data Science Courses in Chennai is a crucial step in acquiring the necessary expertise for a successful career in the evolving landscape of data science.
Energy: Sustainability and Operational Efficiency
Data science is a driving force in the energy sector, contributing to sustainability and operational efficiency. Predictive maintenance of equipment, analysis of energy consumption patterns, and optimization of energy production are facilitated through data-driven insights. This not only ensures reliable energy supply but also contributes to the global push for sustainable practices.
Transportation and Logistics: Optimizing Routes and Operations
In transportation and logistics, data science is instrumental in optimizing routes, predicting demand, and managing fleets efficiently. By analyzing data on traffic patterns, delivery times, and inventory levels, companies can optimize logistics operations, reduce costs, and improve overall service delivery.
Human Resources: Talent Acquisition and Workforce Planning
Human Resources (HR) departments utilize data science for talent acquisition, employee engagement analysis, and workforce planning. Analyzing data on employee performance, satisfaction, and recruitment processes enables HR professionals to make informed decisions, attract top talent, and optimize organizational performance.
Social Media: Enhancing User Engagement and Content Recommendation
Social media platforms leverage data science for enhancing user engagement and content recommendation. Algorithms analyze user interactions, preferences, and behaviors to recommend personalized content and improve overall user experience. This not only keeps users engaged but also enhances the platform's ability to deliver relevant content.
Government and Public Policy: Informed Decision-Making
In the realm of government and public policy, data science aids in informed decision-making. Analyzing data on various facets, including crime rates, resource allocation, and citizen services, enables governments to optimize policies for the welfare of the public. This data-driven approach enhances governance and contributes to more effective public services.
As we traverse the vast landscape of industries, it becomes evident that data science is not merely a tool but a transformative force that connects and elevates diverse sectors. Its ability to extract insights, predict outcomes, and optimize processes is reshaping the way businesses and institutions operate. In an era defined by data, data science stands as a thread weaving through the fabric of innovation, connecting industries and shaping the future of decision-making. As we continue to explore the frontiers of technology, the influence of data science is set to expand, leaving an indelible mark on the evolution of industries across the globe.
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
#Nasal Drug Delivery#Global Market#Innovations#Trends#Opportunities#Drug Delivery Systems#Pharmaceutical Industry#Medical Devices#Healthcare Solutions
0 notes
Text
Why Human Factors Engineering is Crucial in Medical Device Design
The medical device industry is constantly evolving, and at the forefront of this innovation is Voler Systems. As a trusted medical device development company, we specialize in providing full-service research and development (R&D) consulting. With more than four decades of experience, our team has successfully supported the development of cutting-edge medical devices, from the initial concept and design through to production. Since 1979, Voler Systems has been the go-to partner for companies looking to create groundbreaking wearable medical devices, sensors, and measurement electronics that meet the highest standards of safety, quality, and efficacy.
Expert Medical Device Design Consulting
At Voler Systems, we understand that the process of designing and developing medical devices requires expertise, precision, and attention to regulatory requirements. Our team consists of seasoned engineers, designers, and consultants who specialize in creating devices for human use. Whether you are creating a personalized healthcare solution, a wearable sensor, or an advanced diagnostic tool, we offer comprehensive medical device design consulting to guide your project from idea to reality.

We recognize the complexities of the regulatory process involved in medical device development. Our team is well-versed in navigating the various certifications, including FDA approvals, ISO standards, and CE marking. This deep knowledge ensures that the products we help create not only meet the necessary requirements but also stand out in the competitive medical device market.
Personalized Healthcare Development with Wearable Sensors
One area where Voler Systems excels is in the development of wearable healthcare devices. These devices are revolutionizing patient care by enabling continuous monitoring, real-time feedback, and personalized treatment. Whether it’s a sensor for chronic disease management, an activity tracker for health monitoring, or a medical-grade device that provides crucial patient data, we help companies bring these products to life with precision engineering and user-centric design.
By integrating sensors and advanced measurement electronics, Voler’s medical devices are designed to improve patient outcomes, enhance quality of life, and streamline healthcare delivery. We leverage our extensive experience to deliver wearable devices that are not only functional and reliable but also comfortable, intuitive, and safe for users to wear and interact with on a daily basis.
Your Trusted Partner in Medical Device Development
At Voler Systems, we’re more than just a medical device development company – we are your strategic partner in turning innovative ideas into tangible products. Our holistic approach means we’re there every step of the way, offering guidance and expertise throughout the entire design, development, and production process. We prioritize collaboration, working closely with our clients to understand their vision, goals, and challenges, ensuring the final product aligns perfectly with their expectations.
We’re committed to delivering products on time and within budget, using our in-depth knowledge and advanced engineering techniques to meet even the most demanding project timelines. Our clients know they can trust us to provide reliable, high-quality products that will stand the test of time.
Let's Discuss Your Next Project
Whether you’re ready to embark on your next medical device project or need expert guidance to move forward, Voler Systems is here to help. With our decades of experience, multidisciplinary team, and proven track record, we’re ready to assist you in designing and developing innovative medical devices that have a meaningful impact on healthcare.
Don’t hesitate to reach out to Voler Systems today and let us help you take the first step toward bringing your medical device to life. We are here to transform your ideas into reality, with precision, creativity, and expertise.
Contact Voler Systems to discuss your next design project and explore the possibilities of innovation in medical device development!
#engineering design#electronics design#design#electronics#product devlopment#Medical Device Design Consultant#Medical Device Product Development#Wearable Medical Device#Electronic Product Design#Electronics Design Company#Product Design Electronics
0 notes
Text


Topics: health care, monopoly
In a recent article for Tikkun, Dr. Arnold Relman argued that the versions of health care reform currently proposed by “progressives” all primarily involve financing health care and expanding coverage to the uninsured rather than addressing the way current models of service delivery make it so expensive. Editing out all the pro forma tut-tutting of “private markets,” the substance that’s left is considerable:
What are those inflationary forces? . . . [M]ost important among them are the incentives in the payment and organization of medical care that cause physicians, hospitals and other medical care facilities to focus at least as much on income and profit as on meeting the needs of patients. . . . The incentives in such a system reward and stimulate the delivery of more services. That is why medical expenditures in the U.S. are so much higher than in any other country, and are rising more rapidly. . . . Physicians, who supply the services, control most of the decisions to use medical resources. . . . The economic incentives in the medical market are attracting the great majority of physicians into specialty practice, and these incentives, combined with the continued introduction of new and more expensive technology, are a major factor in causing inflation of medical expenditures. Physicians and ambulatory care and diagnostic facilities are largely paid on a piecework basis for each item of service provided.
As a health care worker, I have personally witnessed this kind of mutual log-rolling between specialists and the never-ending addition of tests to the bill without any explanation to the patient. The patient simply lies in bed and watches an endless parade of unknown doctors poking their heads in the door for a microsecond, along with an endless series of lab techs drawing body fluids for one test after another that’s “been ordered,” with no further explanation. The post-discharge avalanche of bills includes duns from two or three dozen doctors, most of whom the patient couldn’t pick out of a police lineup. It’s the same kind of quid pro quo that takes place in academia, with professors assigning each other’s (extremely expensive and copyrighted) texts and systematically citing each other’s works in order to game their stats in the Social Sciences Citation Index. (I was also a grad assistant once.) You might also consider Dilbert creator Scott Adams’s account of what happens when you pay programmers for the number of bugs they fix.
One solution to this particular problem is to have a one-to-one relationship between the patient and a general practitioner on retainer. That’s how the old “lodge practice” worked. (See David Beito’s “Lodge Doctors and the Poor,” The Freeman, May 1994).
But that’s illegal, you know. In New York City, John Muney recently introduced an updated version of lodge practice: the AMG Medical Group, which for a monthly premium of $79 and a flat office fee of $10 per visit provides a wide range of services (limited to what its own practitioners can perform in-house). But because AMG is a fixed-rate plan and doesn’t charge more for “unplanned procedures,” the New York Department of Insurance considers it an unlicensed insurance policy. Muney may agree, unwillingly, to a settlement arranged by his lawyer in which he charges more for unplanned procedures like treatment for a sudden ear infection. So the State is forcing a modern-day lodge practitioner to charge more, thereby keeping the medical and insurance cartels happy—all in the name of “protecting the public.” How’s that for irony?
Regarding expensive machinery, I wonder how much of the cost is embedded rent on patents or regulatorily mandated overhead. I’ll bet if you removed all the legal barriers that prevent a bunch of open-source hardware hackers from reverse-engineering a homebrew version of it, you could get an MRI machine with a twentyfold reduction in cost. I know that’s the case in an area I’m more familiar with: micromanufacturing technology. For example, the RepRap—a homebrew, open-source 3-D printer—costs roughly $500 in materials to make, compared to tens of thousands for proprietary commercial versions.
More generally, the system is racked by artificial scarcity, as editor Sheldon Richman observed in an interview a few months back. For example, licensing systems limit the number of practitioners and arbitrarily impose levels of educational overhead beyond the requirements of the procedures actually being performed.
Libertarians sometimes—and rightly—use “grocery insurance” as an analogy to explain medical price inflation: If there were such a thing as grocery insurance, with low deductibles, to provide third-party payments at the checkout register, people would be buying a lot more rib-eye and porterhouse steaks and a lot less hamburger.
The problem is we’ve got a regulatory system that outlaws hamburger and compels you to buy porterhouse if you’re going to buy anything at all. It’s a multiple-tier finance system with one tier of service. Dental hygienists can’t set up independent teeth-cleaning practices in most states, and nurse-practitioners are required to operate under a physician’s “supervision” (when he’s out golfing). No matter how simple and straightforward the procedure, you can’t hire someone who’s adequately trained just to perform the service you need; you’ve got to pay amortization on a full med school education and residency.
Drug patents have the same effect, increasing the cost per pill by up to 2,000 percent. They also have a perverse effect on drug development, diverting R&D money primarily into developing “me, too” drugs that tweak the formulas of drugs whose patents are about to expire just enough to allow repatenting. Drug-company propaganda about high R&D costs, as a justification for patents to recoup capital outlays, is highly misleading. A major part of the basic research for identifying therapeutic pathways is done in small biotech startups, or at taxpayer expense in university laboratories, and then bought up by big drug companies. The main expense of the drug companies is the FDA-imposed testing regimen—and most of that is not to test the version actually marketed, but to secure patent lockdown on other possible variants of the marketed version. In other words, gaming the patent system grossly inflates R&D spending.
The prescription medicine system, along with state licensing of pharmacists and Drug Enforcement Administration licensing of pharmacies, is another severe restraint on competition. At the local natural-foods cooperative I can buy foods in bulk, at a generic commodity price; even organic flour, sugar, and other items are usually cheaper than the name-brand conventional equivalent at the supermarket. Such food cooperatives have their origins in the food-buying clubs of the 1970s, which applied the principle of bulk purchasing. The pharmaceutical licensing system obviously prohibits such bulk purchasing (unless you can get a licensed pharmacist to cooperate).
I work with a nurse from a farming background who frequently buys veterinary-grade drugs to treat her family for common illnesses without paying either Big Pharma’s markup or the price of an office visit. Veterinary supply catalogs are also quite popular in the homesteading and survivalist movements, as I understand. Two years ago I had a bad case of poison ivy and made an expensive office visit to get a prescription for prednisone. The next year the poison ivy came back; I’d been weeding the same area on the edge of my garden and had exactly the same symptoms as before. But the doctor’s office refused to give me a new prescription without my first coming in for an office visit, at full price—for my own safety, of course. So I ordered prednisone from a foreign online pharmacy and got enough of the drug for half a dozen bouts of poison ivy—all for less money than that office visit would have cost me.
Of course people who resort to these kinds of measures are putting themselves at serious risk of harassment from law enforcement. But until 1914, as Sheldon Richman pointed out (“The Right to Self-Treatment,” Freedom Daily, January 1995), “adult citizens could enter a pharmacy and buy any drug they wished, from headache powders to opium.”
The main impetus to creating the licensing systems on which artificial scarcity depends came from the medical profession early in the twentieth century. As described by Richman:
Accreditation of medical schools regulated how many doctors would graduate each year. Licensing similarly metered the number of practitioners and prohibited competitors, such as nurses and paramedics, from performing services they were perfectly capable of performing. Finally, prescription laws guaranteed that people would have to see a doctor to obtain medicines they had previously been able to get on their own.
The medical licensing cartels were also the primary force behind the move to shut down lodge practice, mentioned above.
In the case of all these forms of artificial scarcity, the government creates a “honey pot” by making some forms of practice artificially lucrative. It’s only natural, under those circumstances, that health care business models gravitate to where the money is.
Health care is a classic example of what Ivan Illich, in Tools for Conviviality, called a “radical monopoly.” State-sponsored crowding out makes other, cheaper (but often more appropriate) forms of treatment less usable, and renders cheaper (but adequate) treatments artificially scarce. Artificially centralized, high-tech, and skill-intensive ways of doing things make it harder for ordinary people to translate their skills and knowledge into use-value. The State’s regulations put an artificial floor beneath overhead cost, so that there’s a markup of several hundred percent to do anything; decent, comfortable poverty becomes impossible.
A good analogy is subsidies to freeways and urban sprawl, which make our feet less usable and raise living expenses by enforcing artificial dependence on cars. Local building codes primarily reflect the influence of building contractors, so competition from low-cost unconventional techniques (T-slot and other modular designs, vernacular materials like bales and papercrete, and so on) is artificially locked out of the market. Charles Johnson described the way governments erect barriers to people meeting their own needs and make comfortable subsistence artificially costly, in the specific case of homelessness, in “Scratching By: How the Government Creates Poverty as We Know It” (The Freeman, December 2007).
The major proposals for health care “reform” that went before Congress would do little or nothing to address the institutional sources of high cost. As Jesse Walker argued at Reason.com, a 100 percent single-payer system, far from being a “radical” solution,
would still accept the institutional premises of the present medical system. Consider the typical American health care transaction. On one side of the exchange you’ll have one of an artificially limited number of providers, many of them concentrated in those enormous, faceless institutions called hospitals. On the other side, making the purchase, is not a patient but one of those enormous, faceless institutions called insurers. The insurers, some of which are actual arms of the government and some of which merely owe their customers to the government’s tax incentives and shape their coverage to fit the government’s mandates, are expected to pay all or a share of even routine medical expenses. The result is higher costs, less competition, less transparency, and, in general, a system where the consumer gets about as much autonomy and respect as the stethoscope. Radical reform would restore power to the patient. Instead, the issue on the table is whether the behemoths we answer to will be purely public or public-private partnerships. [“Obama is No Radical,” September 30, 2009]
I’m a strong advocate of cooperative models of health care finance, like the Ithaca Health Alliance (created by the same people, including Paul Glover, who created the Ithaca Hours local currency system), or the friendly societies and mutuals of the nineteenth century described by writers like Pyotr Kropotkin and E. P. Thompson. But far more important than reforming finance is reforming the way delivery of service is organized.
Consider the libertarian alternatives that might exist. A neighborhood cooperative clinic might keep a doctor of family medicine or a nurse practitioner on retainer, along the lines of the lodge-practice system. The doctor might have his med school debt and his malpractice premiums assumed by the clinic in return for accepting a reasonable upper middle-class salary.
As an alternative to arbitrarily inflated educational mandates, on the other hand, there might be many competing tiers of professional training depending on the patient’s needs and ability to pay. There might be a free-market equivalent of the Chinese “barefoot doctors.” Such practitioners might attend school for a year and learn enough to identify and treat common infectious diseases, simple traumas, and so on. For example, the “barefoot doctor” at the neighborhood cooperative clinic might listen to your chest, do a sputum culture, and give you a round of Zithro for your pneumonia; he might stitch up a laceration or set a simple fracture. His training would include recognizing cases that were clearly beyond his competence and calling in a doctor for backup when necessary. He might provide most services at the cooperative clinic, with several clinics keeping a common M.D. on retainer for more serious cases. He would be certified by a professional association or guild of his choice, chosen from among competing guilds based on its market reputation for enforcing high standards. (That’s how competing kosher certification bodies work today, without any government-defined standards). Such voluntary licensing bodies, unlike state licensing boards, would face competition—and hence, unlike state boards, would have a strong market incentive to police their memberships in order to maintain a reputation for quality.
The clinic would use generic medicines (of course, since that’s all that would exist in a free market). Since local juries or arbitration bodies would likely take a much more common-sense view of the standards for reasonable care, there would be far less pressure for expensive CYA testing and far lower malpractice premiums.
Basic care could be financed by monthly membership dues, with additional catastrophic-care insurance (cheap and with a high deductible) available to those who wanted it. The monthly dues might be as cheap as or even cheaper than Dr. Muney’s. It would be a no-frills, bare-bones system, true enough—but to the 40 million or so people who are currently uninsured, it would be a pretty damned good deal.
#health care#monopoly#us healthcare#us politics#healthcare#medicine#science#kevin karson#anarchism#anarchy#anarchist society#practical anarchy#practical anarchism#resistance#autonomy#revolution#communism#anti capitalist#anti capitalism#late stage capitalism#daily posts#libraries#leftism#social issues#anarchy works#anarchist library#survival#freedom
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Global Nuclear Medicine Market 2030: Trends, Drivers, and Projected 12% CAGR Growth Shaping Healthcare
The nuclear medicine market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 12% during the forecast period.Key drivers include the rising prevalence of cancer and cardiovascular diseases, increasing adoption of hybrid imaging systems, advancements in radiopharmaceuticals, and government investments in nuclear medicine research. However, restraints such as high costs of equipment and radiopharmaceuticals, regulatory hurdles, and limited availability of radioisotopes may hinder market growth.
The nuclear medicine market involves advanced diagnostic and therapeutic methods utilizing radioactive substances to evaluate and treat a wide range of diseases. Central to these methods are radiopharmaceuticals and molecular imaging technologies, which provide precise insights into physiological processes and enable targeted treatment delivery. Predominantly applied in fields such as oncology, cardiology, and neurology, nuclear medicine offers non-invasive solutions for early disease detection and effective therapies.
Download a free sample report for in-depth market insights
Rising Prevalence of Cancer and Cardiovascular Diseases
The increasing global burden of cancer and cardiovascular diseases significantly drives the demand for nuclear medicine. These conditions require precise diagnostic tools and effective treatment strategies, which nuclear medicine offers through its capability to visualize cellular-level changes and deliver targeted radiation therapy. According to WHO, cardiovascular diseases are the leading cause of death globally, claiming an estimated 17.9 million lives annually as of 2019. Similarly, the International Agency for Research on Cancer reported nearly 20 million new cases of cancer in 2022, along with 9.7 million cancer-related deaths. Nuclear imaging modalities, such as PET and SPECT, are vital in the early detection, staging, and monitoring of these conditions. Radiopharmaceutical therapies, such as theranostics, provide tailored treatment options that improve outcomes. As awareness grows among healthcare professionals and patients, nuclear medicine adoption continues to rise, ensuring timely interventions and better prognosis for life-threatening diseases.
Next-Generation Radiopharmaceuticals: Enhancing Diagnostics and Therapy
The introduction of innovative radiopharmaceuticals is reshaping the nuclear medicine market by expanding its scope in diagnostics and therapeutics. Novel isotopes, such as Lutetium-177 and Actinium-225, are being developed for targeted radioligand therapy, offering precise cancer treatment with minimal damage to healthy tissues. On the diagnostic side, fluorine-based tracers and other innovative molecules enhance imaging capabilities for conditions like Alzheimer’s disease and neuroendocrine tumours. Significant investments in research and collaborations between pharmaceutical companies and academic institutions drive these advancements. By addressing limitations in existing isotopes and expanding therapeutic applications, these novel radiopharmaceuticals are making nuclear medicine more effective and accessible. This progress is fostering the adoption of personalized treatment approaches, improving patient outcomes, and fueling market growth.
Competitive Landscape Analysis
The global nuclear medicine market is marked by the presence of established and emerging market players such as GE Healthcare; Jubilant Life Sciences Ltd; Nordion, Inc.; Bracco Imaging S.P.A; The Institute for Radioelements (IRE); NTP Radioisotopes SOC Ltd.; The Australian Nuclear Science and Technology Organization; Eczacıbaşı-Monrol; Lantheus Medical Imaging, Inc; Eckert & Ziegler; Mallinckrodt; and Cardinal Health among others. Some of the key strategies adopted by market players include new product development, strategic partnerships and collaborations, and geographic expansion.
Unlock key data with a sample report for competitive analysis: https://meditechinsights.com/global-nuclear-medicine-market/request-sample/
Market Segmentation
This report by Medi-Tech Insights provides the size of the nuclear medicine market at the regional- and country-level from 2023 to 2030. The report further segments the market based on product, application and end-user.
Market Size & Forecast (2023-2030), By Product, USD Million
Diagnostics
SPECT
TC-99m
TL-201
GA-67
I-123
Others
PET
F-18
SR-82/RB-82
PYLARIFY (piflufolastat F 18)
Illuccix (gallium Ga 68 gozetotide)
Others
Therapeutics
Alpha Emitters
RA-223
Others
Beta Emitters
I-131
Y-90
SM-153
Re-186
Lu-177
Others
Brachytherapy
Cesium-131
Iodine-125
Palladium-103
Iridium-192
Others
Market Size & Forecast (2023-2030), By Application, USD Million
Cardiology
Neurology
Oncology
Thyroid
Lymphoma
Bone Metastasis
Endocrine Tumor
Pulmonary Scans
Urology
Other
Market Size & Forecast (2023-2030), By End-user, USD Million
Hospitals
Diagnostic Centers
Others
Market Size & Forecast (2023-2030), By Region, USD Million
North America
US
Canada
Europe
UK
Germany
Italy
Spain
Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
China
India
Japan
Rest of Asia Pacific
Latin America
Middle East & Africa
About Medi-Tech Insights
Medi-Tech Insights is a healthcare-focused business research & insights firm. Our clients include Fortune 500 companies, blue-chip investors & hyper-growth start-ups. We have completed 100+ projects in Digital Health, Healthcare IT, Medical Technology, Medical Devices & Pharma Services in the areas of market assessments, due diligence, competitive intelligence, market sizing and forecasting, pricing analysis & go-to-market strategy. Our methodology includes rigorous secondary research combined with deep-dive interviews with industry-leading CXO, VPs, and key demand/supply side decision-makers.
Contact:
Ruta Halde Associate, Medi-Tech Insights +32 498 86 80 79 [email protected]
0 notes