#Mark Seidenberg
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
For people who can read, there are no pure representations of the sounds of words in the brain because they’ve been contaminated by spelling. Language is a virus, as the musician-artist Laurie Anderson said, but orthography is the virus that infiltrates language, as observed by the noted British cognitive neuroscientist Uta Frith: “Learning an alphabetic code is like acquiring a virus [that] infects all speech processing, as now whole word sounds are automatically broken up into sound constituents. Language is never the same again.”
Mark Seidenberg, Language at the Speed of Sight: How We Read, Why So Many Can’t, and What Can Be Done About It (2017)
15 notes
·
View notes
Text

ME & MICKEY has been renewed for a third season, the vlog-style shorts is entitled “Happy Campers” and features Mickey speaking to preschoolers about various camping activities.
Premieres August 19 on Disney Junior, streaming September 13 on Disney+.
7 notes
·
View notes
Text





I'm just gonna have feelings about the 2011 team forever, I think
#boston bruins#tim thomas#patrice bergeron#mark recchi#andrew ference#adam mcquaid#johnny boychuk#dennis seidenberg#zdeno chara#shawn thornton#chris kelly#brad marchand#tuukka rask
13 notes
·
View notes
Text

contemporary views hold that it's appalling that an institution like the Teachers college at Columbia University would employ a pseudo-expert like Lucy Calkins, that reading educations specialists would be so undertrained as to be unable to do their jobs, and that everyone involved in the education of children is undereducated when it comes to research relevant to their work, but I still haven't read anything to suggest it should be otherwise. if anything, we're probably improving on 200 years of ignorance in the public school system in a slow battle against an issue that has two common sensical and uninformed camps taking up most of the discursive bandwidth
One of the most important things, if not the most important thing, I learned from studying the existing research on beginning reading is that it says nothing consistently. It says too much about some things, too little about others. And if you select judiciously and avoid interpretations, you can make research "prove" almost anything you want it to.
did you know research about reading fucking sucked up into the 60's? this comes after she drops the fact that none of the research on children learning to read goes past third grade.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
LITERACY QUOTE OF THE DAY

Thursday, April 25, 2024
“The gulf between science and education has been harmful. A look at the science reveals that the methods commonly used to teach children are inconsistent with basic facts about human cognition and development and so make learning to read more difficult than it should be. They inadvertently place many children at risk for reading failure. They discriminate against poorer children who could have become successful readers. Many children who do manage to learn to read under these conditions wind up disinterested in the activity. In short, what happens in classrooms isn’t adequate for many children, and this shows in the quality of this country’s literacy achievement. Reading is under pressure for other reasons, but educational theories and practices may accelerate its marginalization.” – Mark Seidenberg
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
The purpose of the Literacy Quote series is to shed light on the problem(s) of illiteracy. For more details, click here! Check out Kids Need to Read to help children discover the joy of reading and the power of a literate mind!
Enjoy what I do? Please consider supporting via Buy Me a Coffee! Like what you see and want to know when there’s more? Click here to subscribe for updates!
Watch MonriaTitans on��Twitch and YouTube! For more about MonriaTitans, click here! The image was made with the Quotes Creator App!
View On WordPress
#BecomeSmarterEveryday#Discrimination#Educational#EducationalPhilosophy#EducationalPost#EducationalPosts#FightIgnorance#FightStupidity#Illiteracy#JoyOfReading#KidsNeedToRead#LearnSomethingNewEveryday#Literacy#LiteracyQuote#LiteracyQuoteOfTheDay#LiteracyQuotes#LiterateMind#Marginalization#MarkSeidenberg#MarkSeidenbergQuote#MarkSeidenbergQuotes#MonriaTitans#MT#OaT#PromoteLiteracy#QuoteOfTheDay#QuotesAboutLiteracy#QuotesCreatorApp#Reading#Science
2 notes
·
View notes
Note
So what would you love to see for Disney TVA's 40th next year? asking this in terms of celebration from Disney themselves
I would love to see more greenlights for new shows many from BCG crew members, in terms of reboots i think there should be official PRs for the TaleSpin and Recess reboots but specially would love to see series greenlight order for C.H. Greenblatt - Disney Channel series, i think he really deserves to find sucess at Disney.

Speaking of D23 Expo, would love to see Disney Legends Awards giving awards to Tad Stones, Bob Schooley, Mark McCorkle, Rob LaDuca, Bob Roth , Bill Motz, Paul Germain, Joe Ansolabehere, Dan Povenmire, Jeff Swampy Marsh, Jose Zelaya, Bobs Gannaway, Craig Gerber,Mark Seidenberg, Paul Rudish and Noah Z. Jones for their contributions on the studio over it's 40 years.

Would love to see something akin to Once Upon a Studio, my perfect idea would be Mickey and the entire characters of the studio getting ready to welcome to StuGo, Sam Witch, North Woods, Dog & Frog, Fantasy Sports, Neon Galaxy, InterCats, Rhona, Witchverse, Dusty Dupree, Cookies & Milk, North Woods, Tiny Trailblazers casts on a big party for the 100 series and next 100 shows.
Finally would love to see Very Important House getting revived this time for Disney Channel as next year is also the 10th anniversary of the pilot getting picked up for Disney XD
Finally something like Wish did with it's end credits with each show created at Disney TVA on the credits of The School Of Sensitive Souls.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Royal Mail to Stop Using Freight Trains After Almost 200 Years

Royal Mail is to stop running its freight trains by 10 October and switch to road haulage after almost 200 years. The move is part of a larger plan to drag the business into the modern age as it fights off a £3.6bn takeover bid. This development impacts not just tradition but also environmental objectives. Royal Mail will axe almost 200 years of using its own trains to move the mail. It will retire its last freight trains by 10 October and instead use more road transport. The move comes as International Distributions Services, its parent company, battles a £3.6 billion takeover bid from Czech billionaire Daniel Křetínský.The Royal Mail introduced trains into its arsenal of letter and parcel delivery in 1830. Prior to World War II, there were upwards of over 130 trains in use; today, they operate only six, nearly 30 years old, and difficult to service. A Royal Mail spokesperson said, "It is hard to get parts for those old trains." Having considered new trains, Royal Mail has decided to instead rent space on commercial rail services and increase road deliveries."To improve resiliency, drive cost efficiency, and remain consistent with our environmental ambitions, we've decided, over the next couple of months, to not use our own trains any longer," the spokesperson said. "But we will still use a mix of rail, road, and air to deliver mail across the UK." Yet DB Cargo, which runs Royal Mail's train services, does not agree with that decision. This decision has gone against Royal Mail's commitment outlined earlier to increase rail freight use in order to achieve net zero emissions by 2040. Last year, Royal Mail said it would treble the number of mail volumes moved by rail and cut the number taken by road. Andrea Rossi, chief executive of DB Cargo UK, described himself as "profoundly disappointed" by the change, fearing it could add 10,000 more HGVs to already busy roads.The reality currently is that only some 3% of Royal Mail's mail is moved by rail. The move to road will involve the creation of more than 30 full-time driving roles. This company has 5,000 electric vans and many HGVs running on biodiesel. This follows the recent reduction in the number of chartered flights per day for mail down to 18. It is part of IDS CEO Martin Seidenberg's plans for the largest changes to Royal Mail's network in 20 years.Royal Mail intends to forge ahead with these changes despite Křetínský's ongoing takeover bid through his company EP Group. There are also commitments within the takeover offer to continue delivering first-class post six days a week. Royal Mail trains have been intrinsic to British culture. They have inspired a famous WH Auden poem, 1936's "Night Mail" and also the documentary film that followed a train's journey from London to Aberdeen. In 1963 came the Great Train Robbery when thieves got away with more than £2.6 million—at today's value, it's the then equivalent of £69 million—from a Royal Mail train.This will mark the end of an era for Royal Mail Rail, with the intention to update and enhance the delivery system to meet today's needs and the "green" agenda. Read the full article
0 notes
Note
There is a book called Language at the Speed of Sight by Mark Seidenberg. We love him, hes a very kind man who gets very grumpy because all of the research in the world is pointing to how we learn to read and also governments are slow and this change is not worth it for them apparently.
He has quite a bit to say about language and how we can be the best we can be, but he narrows it down int he first chapter to this:
Read. A lot. Mostly new stuff.
You can't get better at dancing without moving. You can't get better at reading without reading. You need to do it a lot to stay fresh, and you need to have new experiences and gather new insight/information from a variety of sources to continue developing.
All reading education stems from this thank god its intuitive.
Kind of related to your literacy post
Do you know of any resources to help improve literacy as an adult?
I like reading, and I read a lot, and I'm fine with basic comprehension, I understand the story being told. But I struggle with the more in-depth stuff. Themes and symbolism, that kind of thing.
I understand what they are, and in school, I usually understood how a certain theme or symbol was relevant to a story after it was explained, but I've never understood how to find those things for myself.
Okay so this is not my field of expertise, so anyone feel to correct me. I did notice kind of the same thing with myself after undergrad where I wasn’t reading as much, and I realized I actually had to work at it to stay at the level I was. Based on that here’s my best shot at advice:
The number one thing that helps me keep those skills sharp is just like regular and consistent practice. I am super busy and not always great at this, but i still try really hard to pick a book to read for fun and read a few times a week. Great before bed i sleep so much better.
I also think consistently writing about what you read can be SO helpful. I love to annotate! Just like questions, comments, lines I think are cool, motifs I keep noticing, whatever I see that I want to remember and think about more. Sometimes I’ll also do a quick paragraph in a notebook or on here or on my notes app that’s just like “I noticed X thing a lot and I think it’s really interesting. Why is it important or interesting to me?”
Talking about what you’re reading can also be super fun, book clubs are cool. Local libraries are awesome for building communities like that.
Shaking up what kinds of things you read can also be really fun! If you’re having some trouble picking out all the things in analyzing what’s happening in a novel, try a movie, or a play, or a short story, or something nonfiction, or something at a YA/HS level. Practice is practice!
Analysis isn’t a scavenger hunt. There’s not like one secret correct answer about what the theme is or what the symbols are and do hidden in the text for you to find. You have to give yourself grace and avoid feeling embarrassed if it’s hard. It feels like making stuff up a lot. That doesn’t mean you’re bad at it. A lot of the time, starting out looks like asking yourself “What did I notice happening? What seemed important? What might this be about?” And then you make up answers to the questions using the text as a guide.
Really prioritize having fun with it and being willing to try stuff out and write stuff down even if it never sees the light of day.
160 notes
·
View notes
Text
Where every player played during the 2004-05 NHL lockout: Philadelphia
Czech Extraliga: Branko Radivojevič (Vsetínská Hokejová) EBEL: Eric Chouinard (E.C. Red Bull Salzburg) Liiga: Sami Kapanen (Kalevan Pallo) LNAH: Donald Brashear (Quebec Radio X) NL: Kimo Johnsson (C.D.H. Ambrì-Piotta) SEL: Branko Radivojevič (Luleå Hockeyförening) Slovak Extraliga: Michal Handzuš (H.K.M. Zvolen) Vysshaya Liga: Danny Markov (K.K. Vityaz Moscow) & Alex Zhamnov (K.K. Vityaz Moscow) AHL: Todd Fedoruk (Philadelphia Phantoms), Randy Jones (Philadelphia Phantoms), Boyd Kane (Philadelphia Phantoms), Freddy Meyer IV (Philadelphia Phantoms), Antero Niittymäki (Philadelphia Phantoms), Joni Pitkänen (Philadelphia Phantoms), Dennis Seidenberg (Philadelphia Phantoms) & Patrick Sharp (Philadelphia Phantoms) Didn't play: Tony Amonte, Sean Burke, Jean Desjardins, Robert Esche, Simon Gagné, John LeClair, Vladimir Malakhov, Keith Primeau, Mark Recchi & Jeremy Roenick
#Sports#Hockey#Hockey Goalies#NHL#Philadelphia Flyers#Czech Republic#Austria#Finland#Canada#Quebec#Switzerland#Sweden#Slovakia#Russia#AHL#Lehigh Valley Phantoms#Pennsylvania
0 notes
Photo

#The Flintstones I Yabba Dabba Do!#The Flintstones#I Yabba-Dabba Do!#William Hanna#Rich Fogel#Mark Seidenberg#VHS#90s
159 notes
·
View notes
Photo

HOT DOG! MICKEY MOUSE MIXED-UP ADVENTURES, A NEW CHAPTER OF DISNEY JUNIOR’S HIT SERIES MICKEY AND THE ROADSTER RACERS, DEBUTS MONDAY, OCT. 14 Season to Spotlight Updated Version of the Popular “Hot Dog!” Song and New Hot Diggity-Dog Tales Short-Form Series Disney Junior’s Mickey and the Roadster Racers featuring Disney’s #1 star, Mickey Mouse, and…
Mickey Mouse Mixed-Up Adventures Premieres on October 14, 2019 was originally published on Anime Superhero News
#Ana Gasteyer#disney channel#disney junior#Disney Television Animation#DisneyNOW#Jay Leno#Kate Micucci#Madison Pettis#Mark Seidenberg#maulik pancholy#McKenna Grace#Mickey and the Roadster Racers#Mickey Mouse Mixed-Up Adventures#Nazneen Contractor#Patton Oswalt#Rob LaDuca#Thomas Hart
1 note
·
View note
Text
Speech is great and powerful, but it has some terrible design features. Utterances can only be produced as a series of words rather than in big chunks. Speakers have to plan what to say next while they finish saying the current bit. Formulating and generating a mostly grammatical utterance that more or less expresses an intended message with a modicum of fluency is hard. We can hear the difficulty in everyday speech: the mispronunciations, grammatical errors, and pauses; how often we start a sentence and change direction in midstream; how much we rely on gestures and facial expressions to help. These phenomena reflect the intrinsic challenges of speech production rather than personal deficiencies. As listeners we are stuck with what gets served. An utterance unfolds. Words appear sequentially, lasting only as long as it took someone to say them, and then disappear to make room for the next part. Listening would be just like Lucy wrapping chocolates as they came down the conveyor belt if the device stopped, backtracked, and changed speeds at unpredictable intervals. Listeners have to wrap spoken words as they pass by, with no option to stuff a few in their mouth or pocket if they fall behind. For a capacity that is so deeply ingrained in our species, our abilities to produce and comprehend speech are remarkably mismatched. We can comprehend speech at faster rates than we can fluently produce it. The reading chair is a lot more comfortable. Behold a text, ready for consumption, nicely plated, the effort that went into preparing it tactfully hidden in the kitchen. We, not the person who produced it, control the pace at which it is ingested. And [...] text does not disappear as it is read. Language may have originated in the spoken channel, but reading is version 2.0.
Mark Seidenberg, Language at the Speed of Sight: How We Read, Why So Many Can't, and What Can Be Done About It (2017)
3 notes
·
View notes
Text

Disney Publishing Worldwide & Disney Deluxe Re-Publishing Adventures Of The Gummi Bears Comics As Next Entry On Disney Afternoon Adventures Re-Issue Series
Bouncing here and there and everywhere, high adventure that's beyond compare until Seth Rogen, Evan Golberg and Point Grey Pictures get their hands to reboot them, They are the Gummi Bears! 🎶
Start to celebrate Disney Television Animation's 40th Anniversary year and 100th series debut year with one of the ones who started it all, since 2022 Disney Press & Disney Deluxe have re-published the Disney Afternoon Adventures Comics in different collections with "Darkwing Duck" on 2022 and TaleSpin & Chip 'n Dale Rescue Rangers.
The next issue slated for February 6,2024 is a republish of the Adventures of The Gummi Bears comics from the Disney Adventures magazine.
📚 Adventures of the Gummi Bears: A New Beginning
By Bobbi JG Weiss, Doug Gray, Lee Nordling
208 Pages
Disney Deluxe
Disney Press
Disney Publishing Worldwide
Bounce into epic quests and comedy in the kingdom of Dunwyn: Disney’s original Gummi Bears lead a classic Disney Afternoon comics collection which also includes Darkwing Duck, DuckTales and more!From Disney Adventures and its Gen-X sister magazines come tales of epic thrills and chills! In “A New Beginning,” find out how the Gummi Bears first forged an uneasy alliance with humans to defend the land of Dunwyn from evil Duke Igthorn, his stinky ogres, and his devastating giant catapult! In “The Legend of Silverhorn,” Chip ’n Dale and the Rescue Rangers follow a shipwrecked sailor into a world of high-seas piracy. Then, in DuckTales’ “The Arcadian Urn,” Scrooge McDuck and the gang find a lost world of ancient Greeks… and Donald Duck and Launchpad face off with a city-stomping kaiju! Plus Darkwing Duck, TaleSpin and more! Full-color illustrations throughout
#Adventures Of The Gummi Bears#The Adventures Of The Gummi Bears#Michael Eisner#Mark Seidenberg#Tad Stones#Alan Zaslove#The Disney Afternoon#Disney Afternoon#Disney Comics#Disney Books#Disney Publishing Worldwide#Disney Deluxe#Disney Press
22 notes
·
View notes
Note
Ditching phonics makes no sense! I learnt to read full novels in 4 months and read Lord of the Rings when others were struggling with early learner books. Why do schools allow ideologues render so many children illiterate?
It's really wierd. "Whole word"/"whole language"/"three-cueing" functions as a kind of ideology and worldview. It's not based on anything demonstrably true about how people learn to read, and adherents cling to it with resolute faith.
It seems to comprise part of a larger philosophy that teachers actually teaching, and students actually learning, useful skills like the alphabet, how to read, how to add and multiply, is oppressive, limiting and "rote learning." And we should instead open up the world to kids to just let them absorb all this stuff and figure it out for themselves. Just show them how fulfilling, how great reading is, and they'll pick it up on their own. It feels nice to these people. Which, of course, is the most important thing. Not working with kids through the hard process of building a life skill that could make or break their future.
Two thirds of American Ed School professors teach the homeopathy of "Whole Word," aka "Three-Cueing" to their classes of future teachers. And I say "homeopathy" deliberately, in that "whole word" crusaders believe kids magically absorb reading in the same way homeopaths believe water magically absorbs the properties of other chemicals.
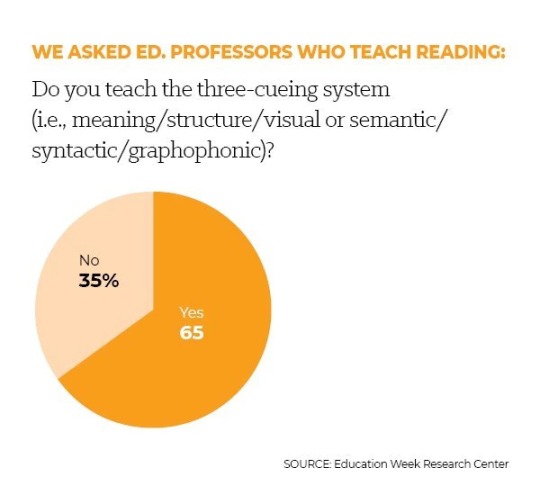
This is like two thirds of geography teachers teaching that the Earth is flat, or two thirds of chemistry teachers teaching about how you should stay away from "chemicals."
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Reading#Whole_language
In his 2009 book, Reading in the Brain, cognitive neuroscientist, Stanislas Dehaene, said "cognitive psychology directly refutes any notion of teaching via a 'global' or 'whole language' method". He goes on to talk about "the myth of whole-word reading", saying it has been refuted by recent experiments. "We do not recognize a printed word through a holistic grasping of its contours, because our brain breaks it down into letters and graphemes". In addition, cognitive neuroscientist Mark Seidenberg, in his 2017 book Language at the Speed of Sight, refers to whole language as a "theoretical zombie" because it persists in spite of a lack of supporting evidence.
This is from the US government's Nation's Report Card website.

[ Note: This is part of a larger infographic; I trimmed it down to include just reading and writing. You can see the whole thing at the original website. ]
It's minority and underprivileged kids who suffer from this reading woo because they may not have as many books at home, may not have as stable a home life, might not have family members who can take the time to spend on the alphabet or reading practice if, for example, it's a single-parent household with a parent holding down two jobs to make ends meet. Or didn't learn to read properly themselves. These are kinds of considerations that grifters like Kendi and DiAngelo never factor into their sweeping narratives of systemic this and that. And cast you as a bigot for even suggesting.
How about, before implementing the toxic poison of the tenets of Critical Race Theory, you actually teach the kids to read? How about before implementing divisive oppressor-vs-oppressed programs of unsubstantiated postmodern philosophy in Kindergarten, you teach the alphabet and then see what sort of life success your students get.
As Roland Fryer remarked:
"I've been in fifth grade classrooms in which they're still learning the clock, and how to tell time, in fifth grade. I told the principal, if they can't tell time, at this point, they'll have no place to be on time for."
What's further difficult to stomach is that this has been known for over 60 years.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Why_Johnny_Can%27t_Read
Why Johnny Can't Read—And What You Can Do About It is a 1955 book-length exposé on American reading education by Rudolf Flesch. It was an immediate bestseller for 37 weeks and became an educational cause célèbre. In this book, the author concluded that the whole-word (look-say) method was ineffective because it lacked phonics training. In addition, Flesch was critical of the simple stories and limited text and vocabulary in the Dick and Jane style readers that taught students to read through word memorization. Flesch also believed that the look-say method did not properly prepare students to read more complex materials in the upper grade levels.
Just think about that. For over sixty years, many kids have been taught to read using known substandard, ineffective methods, and any success they had was in spite of that teaching, not because of it.
Think of how many kids dropped out of school or did poorly because they were frustrated by not being able to fully participate, or concluded that school wasn't for them because they couldn't "get it." Who watched more advantaged kids streak ahead of them, thinking that there was something wrong with them. And if you can't read, how well can you possibly write?
Think of how many underprivileged kids perpetuated a cycle of dropping out of school, possibly early or single parenthood, low income prospects or even crime, and eventually unable to help their own kids learn to read properly, because the school will not. On the basis of an unevidenced ideology that asserts that "learning to read English comes naturally to humans, especially young children, in the same way that learning to speak develops naturally."
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Whole_language#State_of_the_debate
One neuroscientist, Mark Seidenberg, says "[Whole-language quack Ken] Goodman's guessing game theory was grievously wrong" and "the impact was enormous and continues to be felt". When it come to evidence supporting the whole-language theory, he emphatically states "There wasn't any".
Dr. Lyell Asher goes into this in a segment of his larger series. Part 12 is specifically about "The Reading Debacle," but Part 11, "The Knowledge Gap," gives some important background that explains the criticality of literacy.
youtube
youtube
Other people like Emily Hanford and Belinda Luscombe have been writing about this as well.
It's amazing that something so fundamental could become yet another ideological warzone, with kids caught in the crossfire.
#ask#science of reading#phonics#reading#literacy#basic literacy#sound it out#whole word method#whole language method#corruption of education#education#pseudoscience
65 notes
·
View notes
Text
Title: The New Annotated Hobbit
Author: George Lakoff, Mark Johnson, and Mark Seidenberg
Rating: 5/5 stars
If you like your fantasy in a serious and sober, almost austere manner, then George Lakoff, Mark Johnson, and Mark Seidenberg's forthcoming edition of The Hobbit might well be for you. And it has all the right cultural prestige behind it: its authors are three of the most prominent cognitive linguisticians around, and the New Annotated Hobbit is its highly anticipated companion volume to Lakoff and Johnson's The Metaphors We Live By.
I can't promise you this book will change your mind about Tolkien (indeed, there's a lot you may not like there!), but I know from my conversations with people who have read Tolkien that there are more readers out there who might be persuaded by their message than one might otherwise think.
First and foremost, though, this book is very, very impressive. The Hobbit and The Lord of the Rings are full of the most vivid and colorful worldbuilding, and what's more, it takes place on a world that really is distinct, with its own language and social rules and mores. Tolkien created such a world, in part, by taking the old oral tradition and then filling it with all kinds of elaborate metaphor and metonymic shorthand. And it's not just verbal: even the maps have meaning, and the maps are maps of maps, like the one I described back there. But to keep up with those worldbuilding details, you'd need to do a lot of close reading, and there are all kinds of mistakes and idiosyncrasies in the text. It's easy to miss things, and if you try to do so, you'll miss out on a lot of the worldbuilding.
(Tolkien is also very... deliberate in the way he creates his worldbuilding. For every detail he invented -- the language, the customs, the maps -- he often did a great deal of research in order to make sure he got it right. This is not necessarily a good trait in a fantasy writer, because it can lead to dry, pedantic worldbuilding, especially if the details are presented very explicitly and clearly. Tolkien gets off easy here because his world is so large that his footnotes are often longer than the books themselves, but this is not a characteristic that many fantasy writers can boast.)
This book solves the problem of Tolkien's elaborate worldbuilding by presenting us with a new work of fantasy that is its own thing, with its own complex and unique system of rules -- only to make it clear, very early on, that these rules are actually rules.
That seems to me a really smart move, and it comes from the fact that, as I've argued elsewhere, one of the hardest things about reading stories like Tolkien's is deciding what is meant by the author when he uses words like "mountain" and "valley." There are all these beautiful metaphors and echoes of older stories, and you're still left with the very basic question of what the text is saying about the world it is describing. Which is exactly what the authors of this book -- and, more importantly, the authors of the Hobbit, in particular -- have solved with their new system of worldbuilding, by which they create a whole new set of rules, many of which are meant to be understood in a way that is analogous to the way, say, the world of Tolkien is understood.
They start by describing this world in "realistic" terms: the new world is not unlike the real world, and we can understand what it is saying about the real world if we just pay attention to the details of the worldbuilding. We start with the map, and see that it has a river running along the middle. Then we see that the map is made from one of many sections of a large world map, with the rivers connecting these sections. When we look at the rivers, we see that they have some of the same features as the rivers we see on the real map, but some of them have very different features, and we can see that our world has two mountains in the east and two rivers in the west and a mountain in the middle. And so on.
Once we've seen these basic "realistic" building blocks, and we've gotten a feel for the basic pattern of the world as a whole, the authors take us to the most "metaphorical" parts of their new world. They introduce a kind of language of metaphor. For each element of the real world they introduce a corresponding element in their metaphorical language, which means you can "translate" from one to the other: the mountains have heights, the rivers run with water, the valleys have depths, and so on. In this way, the authors create a set of rules for their world, the rules of their metaphorical language, whose rules aren't necessarily like any rules that govern the real world. So you have for example the rule "the river flows into the deep valley, then it flows out of the deep valley and into the shallow river." These rules don't have to be consistent with real, physical processes. If we were to see a map of a real world and then look at this metaphorical language, we'd notice that its rules don't always follow the rules of the map.
Once you have this metaphorical language, the authors have a bunch of other tools for the worldbuilding. They say a character has "blue eyes" even though he's not actually blue (but because of some things they've put in his story, such as the magic rings that turn him blue in part to avoid his enemies' noticing him). And they say a person's hair grows long even though it doesn't really grow at all. Or maybe it actually does grow but in a very different way: Tolkien's dwarves, for example, don't really have hair but they have big ears and long snouts so that is roughly equivalent. And as the readers notice these things, the authors notice the same things, in that all of these small things are part of one big, coherent whole, one world made of things that all fit together in a coherent system.
That's what the book does, in a way that's very different from what Tolkien did, and I'm glad that some of the best people in the world are doing it.
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
April 2024 Wrap-Up

Artist Shout-Outs Shared
Current AI ‘art’ is created on the backs of hundreds of thousands of artists and photographers who made billions of images and spend time, love and dedication to have their work soullessly stolen and used by selfish people for profit without the slightest concept of ethics. – Alexander Nanitchkov
April’s Artist Shout-Outs
Apr. 1st: Quentin Papleux
Apr. 6th: InstaMAT
Apr. 7th: Gwendolyn Grey
Apr. 8th: Charles Joseph Cabrera
Apr. 13th: Cameron Suter
Apr. 14th: Furkan Akin
Apr. 15th: Phạm Ngọc Khuyến
Apr. 20th: Harley Howl
Apr. 21st: Clara Martín
Apr. 22nd: Helen Jarosz
Apr. 27th: Munchbud Ink
Apr. 28th: stellarbagle
Apr. 29th: Yerim Lee
April’s Opinions
Blog Posts
Apr. 3rd: Why I Say I’m ADtistic Instead of an AuDHDer
Apr. 17th: The Love Languages: Including the Autistic Ones
April’s Streams and Videos
Blog Posts
Apr. 5th: Let’s Read Some $#!7 by Peter S. Beagle, Melissa Sweeney, & Ann Liang
Apr. 7th: Let‘s Discuss Some $#!7 — Behind the Scenes
Apr. 12th: Let’s Play Some Demos! — Part 3
Apr. 14th: Let’s Play Some $#!7! — Hades
Apr. 28th: Let’s Play Some $#!7! — Boyfriend Dungeon!
Apr. 29th: Let’s Read Some $#!7 by Howard Zinn, The Brothers Grimm, & 3dtotalPublishing
Poems Written
I Am Autism
“Try Harder”
“You’re Doing It On Purpose”
NSFW
Don’t Lay Down!
Books Read
The Last Unicorn
Sensory: Life on the Spectrum
Cause of the Month: Different Brains

Autism Acceptance Month Quotes of 2024
QUOTE 1: Pete Wharmby
QUOTE 2: Orion Kelly — That Autistic Guy
QUOTE 3: Temple Grandin
QUOTE 4: Tito Rajarshi Mukhopadhyay
QUOTE 5: Patrick Jasper Lee
QUOTE 6: Jeannie Davide-Rivera
QUOTE 7: Karina Poirier
QUOTE 8: Michael Braccia
QUOTE 9: Lyric Rivera
QUOTE 10: Ember Green
QUOTE 11: Allie
QUOTE 12: Samantha Stein
QUOTE 13: Yulika Forman, PhD, LMHC
QUOTE 14: @Neurodivergent_Lou
QUOTE 15: @AuDHD_Therapist
Check out Different Brains, who “strives to encourage understanding & acceptance of individuals who have variations in brain function and social behaviors known as neurodiversity”.
April’s Neverending Reading List Shares
Apr. 11th: The Neverending Reading List: Book LIII — The Adventures of Sherlock Holmes
Apr. 23rd: The Neverending Reading List: Book LIV — They Say / I Say
Apr. 25th: The Neverending Reading List: Book LV — Fahrenheit 451
Apr. 30th: The Neverending Reading List: Book LVI — 100 Plants That Heal
April’s Artbook Collection Items Shared
Apr. 2nd: The Art of Dragon Age: Inquisition
Apr. 4th: Faeries of the Faultlines
Apr. 16th: Guweiz: The Art of Gu Zheng Wei
Apr. 18th: The World of Guweiz
April’s Video Game Quotes Shared
QUOTE 1: “Darkest Dungeon”
QUOTE 2: “Fallout 4”
QUOTE 3: Thaliak, FFXIV
QUOTE 4: Llymlaen, FFXIV
QUOTE 5: Eulogia, FFXIV
QUOTE 6: Azeyma, FFXIV
QUOTE 7: Oschon, FFXIV
QUOTE 8: “The Legend of Zelda: Ocarina of Time”
QUOTE 9: “The Legend of Zelda: Spirit Tracks”
April’s Literacy Quotes Shared
QUOTE 1: Story Shares
QUOTE 2: Isaac Asimov
QUOTE 3: Robert S. McNamara
QUOTE 4: Joshua Hammer
QUOTE 5: Robert Popple
QUOTE 6: Donalyn Miller
QUOTE 7: Sally Armstrong
QUOTE 8: Mark Seidenberg
QUOTE 9: E.A. MacKay
April’s Stupidity Quotes Shared
QUOTE 16: Torron-Lee Dewar
QUOTE 17: Dietrich Bonhoeffer
QUOTE 18: Sukant Ratnakar
Kickstarter Items Received
Kickstarter Item Arrived: Weird Wastelands by Web DM!
To expand the Opinions & Truth (O&T) blog, MonriaTitans started The Weekend Game Show ( WGS) to educate on and discuss different aspects of game development, and to show why video games can take years to make, to prevent another Cyberpunk 2077 launch scenario. Watch MonriaTitans on Twitch and YouTube!
In addition, she shares educational quotes to promote literacy, the legitimacy of video games as an artistic medium, and regarding a Cause of the Month to raise awareness, while giving Artist Shout-Outs to human artists to combat AI art theft. Want to learn more about the Artist Shout-Outs? Click here! #createdontscrape
The Artists Shout-Out posts can be seen here, on Instagram, Facebook, Discord, and more!
She is also an artist under the handle TitansMonriArt.
-
Like what you see and want to know when there’s more? Click here to subscribe for updates and/or hit the Follow button! Enjoy what I do? Please consider supporting via Buy Me a Coffee! Lastly, posts may contain affiliate links.
View On WordPress
#BecomEmpowered#BecomeSmarterEveryday#BEmpowering#Educational#EducationalPost#EducationalPosts#LearnSomethingNewEveryday#MonriaTitans#MonriaTitansWGS#MonthlyWrapUp#MT#OaT#QuotesCreatorApp#TitansMonriArt#TMA#TriggerWarning#WGS#WrapUp
1 note
·
View note