#India’s second President
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Sarvepalli Radhakrishnan Quotes: 15 Lessons From India’s Greatest Teacher
Sarvepalli Radhakrishnan was a teacher, philosopher, statesman, and India’s second President. He came from a poor Brahmin family in Tamil Nadu and was born on September 5, 1888. As a scholar of Indian philosophy and religion, he taught at many universities in India and abroad. He contributed to the Indian independence movement and the Indian constitution. In 1954, he received the Bharat Ratna, India’s highest civilian honor. To know this great personality better, we will look at some Sarvepalli Radhakrishnan Quotes.

#India’s Greatest Teacher#India’s second President#Sarvepalli Radhakrishnan#Greatest teacher#Philosopher
0 notes
Text
#immigration#h-1b#green card#visa#perm#h-1b visa#uscis#india#usa#us#marriagecases#marriage green card usc#eb 5 us visa#usimmigrationlawyer#uscis certified translation services#bestimmigrationlawyer#best immigration consultants#policy immigration immigrationlawyer h1b greencard#education green card visa h 1b visa ewi#daca dream act green card immigration forum#immigration law news and updates: trump's 10 point u.s. immigration law plan new i 9 form december 2016 visa bulletin update eb 5 immigrant#president trump#h 1b professional visa#h 1b visa transfer#h 1visa#second round of h 1b lottery#http://www.visaserve.com#npz law group#npz lawyers david nachman michael phulwani phulwani zimovcak
0 notes
Text
India’s $13.9 billion aviation industry—projected to cater to over 300 million domestically by 2030—is a ticking time bomb.
This July, in the sweltering heat at the Delhi High Court, additional solicitor general Aishwarya Bhati announced that new rules on pilot duty and rest periods would not be implemented this year after all. Introduced by the Directorate General of Civil Aviation (DGCA) in January, the rules were designed specifically to combat pilot fatigue. They were set to take effect in June, but were abruptly retracted. The hearing addressed a writ petition filed by the Federation of Indian Pilots (FIP), seeking clarity on when the new norms would be enforced. The DGCA’s response followed its request to airline companies in April for a tentative implementation timeline.
Concerns over pilot fatigue had been mounting in the months leading up to the announcement of the new Flight Duty Period, Flight Time Limitations, and Prescribed Rest Periods by the DGCA. The urgency deepened in November 2023 when a 37-year-old Air India pilot, Captain Himanil Kumar, collapsed at Delhi Airport while training to fly the airline's Boeing 777 fleet, and later died at the hospital. Kumar was the second Indian pilot to die on duty within three months; in August, Captain Manoj Subramanyam, a 40-year-old IndiGo pilot, suffered a fatal cardiac arrest just minutes before his flight from Nagpur.
These back-to-back tragedies raised alarm in the industry. “Another young Indian pilot passed away today due to a suspected cardiac event,” reportedly tweeted Captain Shakti Lumba, a retired IndiGo VP who is now the president of the Professional Pilots Society in India (His tweet was since deleted.) “If this doesn’t convince the DGCA, civil aviation ministry, and airlines to urgently address the stress, fatigue, and anxiety among pilots, nothing will.”
The DGCA, India’s aviation watchdog, regulates the country’s Flight Duty Time Limitations (FDTL). At 13 hours of flight duty time, India’s FDTL is already demanding, but after the pandemic slowdown, increased route expansion and pilot shortages have forced many to fly beyond the recommended maximum of 60 hours a week, exacerbating crew exhaustion. The DGCA finally responded to the growing crisis by revising FDTL norms in January 2024.
The new guidelines increased weekly rest periods from 36 to 48 hours and introduced quarterly fatigue reports. Its scheduled implementation on June 1, 2024, was pushed back due to pressure from operators. An airline CEO, speaking anonymously to the Economic Times in January, claimed the proposed regulations would require a 20 percent increase in pilot numbers, which would escalate expenses and lead to huge numbers of flight cancellations. Still, the DGCA held firm on the FDTL implementation deadline till early March. By the end of the month, however, it appeared to have yielded to influence from the airline lobby. A notice on the regulator’s website announced the deadline had been deferred, without providing a reason or setting a new date.
The pilot fatigue problem isn’t unique to India. In January, two pilots for Indonesia-based Batik Air fell asleep for 28 minutes mid-flight, causing their plane to veer off course between Sulawesi and Jakarta. In April, unionized Virgin Atlantic pilots in the UK voted 96 percent in favor of pursuing an industrial action in response to rising fatigue. Earlier, the CEO of Wizz Air UK faced a backlash for urging crew members to push through their fatigue to avoid flight cancellations. In May, senior pilots at Virgin Australia raised safety concerns, claiming rostering systems were pushing them "to the limits.”
But in India, the belief that overwork and fatigue are not just acceptable but essential has become entrenched across industries. The aviation crisis is just the tip of the iceberg; it is the tech industry that is leading the charge. Last year, Infosys cofounder Narayana Murthy suggested that Indian youth should work 70 hours a week for the nation's development. Murthy’s advice came up at the Indian Parliament on the first day of its winter session and found support from a list of influential Indian tech leaders, including Bhavish Aggarwal, founder of India’s first AI unicorn, Ola Krutrim; Ayushmaan Kapoor, cofounder of the AI-powered customer platform Xeno; and even veterans like Sajjan Jindal, CEO and MD of JSW Group, and Vinod Khosla of Sun Microsystems. Almost all of them justified the extended work hours, which far exceed the maximum eight to nine hours per day stipulated by the International Labour Organisation and the Indian Labour Code, as necessary for strengthening India’s economy. “We have to make India an economic superpower that we can all be proud of,” Jindal wrote on X. He cited Indian prime minister Narendra Modi, “who works 14-16 hours everyday,”as a model. In July this year, the Karnataka State IT/ITeS Employee Union said the state government had plans to increase working hours in the sector from the current maximum of 10 hours (including overtime) to a staggering 14 hours a day. As the union planned massive campaigns to oppose the move, the labor minister stated that the push for the proposal had come from the companies.
The airline companies think they have a solution to the fatigue crisis: technology. IndiGo, India’s largest airline, announced it would be an “early adopter” of a wrist-worn fatigue-monitoring device it was developing with French defense and aerospace company Thales Group. The device can provide “detailed insights into demographic data, including routes, pairings, crew profiles, and more, going beyond traditional scheduling-focused biomathematical models,” the airline stated in a press release in September. The airline, which operates 2,000 flights daily and employs over 5,000 pilots, said the device would be rolled out after a proof-of-concept trial. No date for the rollout was announced.
Wearable activity trackers are not new to the aviation industry. IndiGo’s device sounds similar to Actiwatch, a now-discontinued line of research-grade actigraphs from Philips, used to monitor sleep patterns, study circadian rhythms, and track physical activity as part of an airline’s fatigue risk-management system. But they partly rely on performance tests and subjective measures, such as self-reporting, which often results in being targeted by the airlines, says Captain C. S. Randhawa, president of the Federation of Indian Pilots. Safety management systems on the whole tend to be neglected by operators and are viewed as an additional expense, says Captain Amit Singh of the NGO Safety Matters Foundation.
In May 2023, Air India launched safety management software called Coruson, as well as BAM (Boeing Alertness Model), a fatigue-mitigation tool integrated into its rostering system, which is used by airlines to create and manage pilot schedules. Coruson, developed by cloud software company Ideagen, centralizes, analyzes, and reports on safety-related data—such as incidents, hazards, and risk assessments. BAM, developed jointly by Boeing and the software company Jeppesen, predicts and manages pilot fatigue by analyzing flight schedules and performance data. These tools were designed to prevent the creation of fatiguing rosters and pairings, Air India CEO Campbell Wilson noted in an internal message to employees. The carrier also introduced two new digital tools for its crew—the Pilot Sector Report app, to help pilots easily submit information on flight performance, incidents, and observations post-flight; and DocuNet, a digital management system that facilitates the storage, retrieval, and sharing of documents (such as flight manuals, training records, and compliance documents).
Despite these measures, the airline was fined by the DGCA in March this year for violating FDTL limits and fatigue management rules. This May, Air India Express cabin staff called in sick en masse to protest against “mismanagement.” This followed a similar protest from the crew, mostly pilots, at Vistara airlines. Both Air India and Vistara are now owned by one of India’s largest conglomerates, the Tata Group, which took over the former from the Indian government in January 2022.
Twenty-five of those who called in sick at Air India Express were terminated. Others were reportedly served an ultimatum. Those sacked were later reinstated by the airline following an intervention by the chief labour commissioner. Nearly a week before, the regional labor commissioner of Delhi had allegedly written to the Tata group chairman pointing to “blatant violations of labour laws” and insisting the legitimate concerns of the cabin crew be looked into. According to CNBC, Vistara employees said the agitation at their end had to do with recent salary updates, which fixed pilot pay at 40 flight hours—down from 70. Protesting first officers claimed that the new salary structure would result in an almost 57 percent pay cut. Under the new terms they would also have to fly up to 76 hours to earn what they were previously earning at 70 hours.
To placate the pilots and get them back to work, management had assured them that salaries for the “extra working hours” would be credited once Vistara was integrated with Air India. At the time, two Air India pilots unions had written to the chairman of the company, saying that such issues were not isolated but systemic. Burnout was the other related issue, with many pilots complaining of inadequate rest and being pushed to their limits.
Captain Singh, a former senior manager at AirAsia, tells WIRED that such effects significantly increase the risk of accidents, but also adversely affect pilot health in the long run. Tail swaps—rushing between different types of aircraft to take off immediately after disembarking from another—have become more prevalent under the 13-hour rules, and can further contribute to exhaustion, as do hasty acclimatization and, most significantly, landing three, four, or more flights consecutively, which Captain Randhawa described as a “severe energy management challenge.”
In the 2024 “Safety Culture Survey” conducted by Singh’s Safety Matters Foundation in July, 81 percent of 530 respondents, primarily medium- to short-haul pilots, stated that bufferless rosters contribute to their fatigue. As many as 84 percent indicated concerns with the speed and direction of shift rotation. “That’s the problem with the new rostering softwares the operators are introducing,” a pilot from a private airline, who requested anonymity, says. “They’re optimizers designed to make pilots work every second of their 13-hour schedule, leaving no breathing room.” The buffer-deficient timetables push pilots to their limits, so any additional pressure—like unpredictable weather—can easily overwhelm them.
Solving this issue with wrist-worn fatigue-measuring devices is contentious. But that isn’t the only problem. A year since they were hyped up, the buzz around fatigue-management tech has all but fizzled out. There have been no updates from IndiGo about the wrist device. Neither IndiGo nor the Thales Group responded to requests to comment.
589 notes
·
View notes
Text
In the spring and summer of 2023, Senate Bill 403, which sought to add caste as a form of ancestry protected from discrimination, was making its progress through California’s legislative process. It was watched closely by the state’s 2 million people of South Asian descent, with Ambedkarite activists backing the effort and Hindutva groups opposing it. On 11 September 2023, SB 403 was sent to the governor’s office after receiving near-unanimous support in both the state assembly and senate. A few days later, the California governor, Gavin Newsom, went to Chicago to attend a meeting with donors to a political-action committee working on President Joe Biden’s re-election campaign. There, he met Ramesh Kapur, who runs a Massachusetts-based company manufacturing medical equipment as well as the US–India Security Council, a lobbying organisation. Kapur has been involved in fundraising for candidates of the Democratic Party since 1983, when he helped elect the future presidential nominee Michael Dukakis to a second term as Massachusetts governor. “If you want to be our next president, veto the bill,” Kapur told Newsom, according to Harper’s Magazine. Newsom did so on 7 October, sending Kapur an email hours before he issued the veto.
Every day I learn one new evil fact about gavin newsom
#the libs having to stop libbing out over every cartoon villain with a symmetrical smile#hindutva#indian politics#us politics
177 notes
·
View notes
Note
I’m wondering if you have thoughts on James Baldwin’s “open letter to the born again”? I’m struggling a bit with what his point is in that piece; it feels kinda dismissive on Jewish zionists agency in creation of Israel? But I may be missing parts or not getting things
The text in question.
And the segment I think anon is struggling with:
I know what I am talking about: my grandfather never got the promised “forty acres, and a mule,” the Indians who survived that holocaust are either on reservations or dying in the streets, and not a single treaty between the United States and the Indian was ever honored. That is quite a record.
Jews and Palestinians know of broken promises. From the time of the Balfour Declaration (during World War I) Palestine was under five British mandates, and England promised the land back and forth to the Arabs or the Jews, depending on which horse seemed to be in the lead. The Zionists—as distinguished from the people known as Jews—using, as someone put it, the “available political machinery,’’ i.e., colonialism, e.g., the British Empire—promised the British that, if the territory were given to them, the British Empire would be safe forever.
But absolutely no one cared about the Jews, and it is worth observing that non-Jewish Zionists are very frequently anti-Semitic. The white Americans responsible for sending black slaves to Liberia (where they are still slaving for the Firestone Rubber Plantation) did not do this to set them free. They despised them, and they wanted to get rid of them. Lincoln’s intention was not to “free” the slaves but to “destabilize” the Confederate Government by giving their slaves reason to “defect.” The Emancipation Proclamation freed, precisely, those slaves who were not under the authority of the President of what could not yet be insured as a Union.
It has always astounded me that no one appears to be able to make the connection between Franco’s Spain, for example, and the Spanish Inquisition; the role of the Christian church or—to be brutally precise, the Catholic Church—in the history of Europe, and the fate of the Jews; and the role of the Jews in Christendom and the discovery of America. For the discovery of America coincided with the Inquisition, and the expulsion of the Jews from Spain. Does no one see the connection between The Merchant of Venice and The Pawnbroker? In both of these works, as though no time had passed, the Jew is portrayed as doing the Christian’s usurious dirty work. The first white man I ever saw was the Jewish manager who arrived to collect the rent, and he collected the rent because he did not own the building. I never, in fact, saw any of the people who owned any of the buildings in which we scrubbed and suffered for so long, until I was a grown man and famous. None of them were Jews.
And I was not stupid: the grocer and the druggist were Jews, for example, and they were very very nice to me, and to us. The cops were white. The city was white. The threat was white, and God was white, Not for even a single split second in my life did the despicable, utterly cowardly accusation that “the Jews killed Christ’’ reverberate. I knew a murderer when I saw one, and the people who were trying to kilI me were not Jews.
But the state of Israel was not created for the salvation of the Jews; it was created for the salvation of the Western interests. This is what is becoming clear (I must say that it was always clear to me). The Palestinians have been paying for the British colonial policy of “divide and rule” and for Europe’s guilty Christian conscience for more than thirty years.
Finally: there is absolutely—repeat: absolutely—no hope of establishing peace in what Europe so arrogantly calls the Middle East (how in the world would Europe know? having so dismally failed to find a passage to India) without dealing with the Palestinians. The collapse of the Shah of Iran not only revealed the depth of the pious Carter’s concern for “human rights,” it also revealed who supplied oil to Israel, and to whom Israel supplied arms. It happened to be, to spell it out, white South Africa.
Well. The Jew, in America, is a white man. He has to be, since I am a black man, and, as he supposes, his only protection against the fate which drove him to America. But he is still doing the Christian’s dirty work, and black men know it.
My friend, Mr. Andrew Young, out of tremendous love and courage, and with a silent, irreproachable, indescribable nobility, has attempted to ward off a holocaust, and I proclaim him a hero, betrayed by cowards.
For context: Andrew Young, considered the right hand of MLK Jr, had a longstanding and occasionally fraught relationship with the Jewish community. He stepped down from Congress shortly after being forced to choose between voicing support for Palestine and continuing to work towards black-jewish interests by his constituents and fellow politicians, as he felt very strongly about supporting both. This was a fairly unpopular move. While I don't believe he ever called himself Jewish by the strictest sense, he was actively involved in Jewish communities and the known "white" ancestry within him is a Polish Jew in his great grandparents.
To be honest, I don't really see much a problem with this as I think it fairly closely matches up not only with my understanding of the history of this problem but also my own country's part in it as well as my personal feelings on it decades later. It pretty blatantly says that Zionism is utilizing a machination of white supremist colonism due to the extensive history of antisemitism and having had the ancestral land dangled in front of them like bait on a hook from the British Empire, which owned Palestine at the time. It also goes on to say that many Zionists aren't even Jewish and are antisemitic in nature, but are Christians happy to get rid of as many Jews as possible and how that tracks due to the Christian church's millennia-deep history of antisemitism.
I don't think it lets anyone off the hook. I think it pretty much flat out says this is a problem caused first and foremost by white Christians who hate Jews and Arabs alike and have a vested interest in getting the two populations to fight because it'll be easier to kill off just the one group instead of both of them, if one ends up eradicating the other. It even talks about the friction between the black community and the Jewish community, what caused it, what drives it, how that friction in itself is a tool of white supremacy to hurt us both.
235 notes
·
View notes
Text
Sylvia Browne was one of the most famous psychics of the turn of the millennium, and one of its most despicable. You may remember her from when she told the mother of Amanda Berry her daughter was deceased, which she believed, and she died believing that...but Barry was alive the whole time. Or from the dozens of other times she did something similar
Sylvia Browne released her predictions for the new year every year, like many psychics, but she was stupid enough to keep them online so people could judge them later. Her predictions for the year 2000 include Bill Bradley beating out the Reform Party for the Presidency (he lost the primary to Al Gore, and the Reform Party finished fourth, behind the Green Party with less than half a million votes), that David Letterman would retire (he stayed with the show for 15 more years), that small businesses would flourish in the 2000s, and that Donald Trump will not have a career in politics. Which did technically come true in that he didn't run in 2000, but uh
Also, from reading these at the time, she predicted the big one in California and the death of the Pope nearly every year. Only a keen psychic mind could predict that a man in his eighties could pass away from old age
There's one year she left out, though. She wiped her 2001 predictions from the internet...and her 9/12/2001 predictions. But thankfully, someone preserved them (they're not in the Wayback Machine bc its only 2001 save is in October. And apparently the thing below was a pop-up)

Let's unpack this
She says bin Laden was behind it. An amazing prediction, except she posted this a few days after 9/11, when the media was already speculating he was responsible
She was "given information", which I guess is a way to phrase "watched CNN"
She just makes up a country. She says 9/11 was done by the "Palestinian Republic of Bundi". I can find forum threads from then wondering what the fuck she meant, and all these years later it's still baffling
Did she mean Burundi? A country in Southeastern Africa? There's villages named Bundi in Iran and India, but I can't even begin to imagine what she was even imagining, or why she didn't even begin to stop imagining it
"Triad of Jordan" also turns up nothing
The first name she mentioned just brings up Linkedin pages.
The second only turns up this post. Neither of those names seems to exist in any language
She tried to explain why she didn't predict 9/11, by saying she's not omniscient, and she warned of terrorism...in 1999. But that article I linked dug up her 1999 predictions, bc she left them online, and she said there'd be terrorism...in Florida and London
At the end of this, she takes care to note that 9/11 will NOT stop the Sylvia Browne cruise through Greece and Turkey!!
She saw 9/11, and rushed to make a statement trying to explain why the spirits didn't show her 9/11, and also make up a few countries to blame 9/11 on. Then she sold a cruise, deleted the page, and wrote a book claiming everyone who died on 9/11 was led there to die by their spirit guide to be martyrs to bring patriotism back. I'm glad we don't have celebrity TV psychics anymore but I almost miss them. Simply not justice in how she got off scot-free and our passive aggressive, intermittently-Jamaican queen Miss Cleo got nabbed
67 notes
·
View notes
Text
Excerpt from the Substack Distilled:
In the last few months, the Biden administration has quietly passed multiple federal policies that will transform the United States economy and wipe out billions of tons of future greenhouse gas emissions.
The new policies have received little attention outside of wonky climate circles. And that is a problem.
Earlier this year, I wrote that Biden has done more to mitigate climate change than any President before him. For decades, environmentalists tried and failed to convince lawmakers to pass even the most marginal climate policies. It wasn’t until Biden took office that the logjam broke and the climate policies flowed. And yet few American voters are hearing this story in an election year of huge consequence.
It’s been two and a half months since I wrote that article. In that short time, the Biden administration has passed a handful of climate policies that will collectively cut more than 10 billion tons of planet-warming pollution over the next three decades, more than the annual emissions of India, Russia, Japan, South Korea, Canada, Saudi Arabia, and the entire continent of Europe—combined.
One climate policy that flew under the radar recently was the administration's latest energy efficiency rule, unveiled at the beginning of May. The new rules will reduce the amount of energy that water heaters use by encouraging manufacturers to sell models with more efficient heat pump technology. The new regulation is expected to save more energy than any federal regulation in history.
Most people give little thought to how the water in their homes is heated, but water heaters are the second-largest consumer of energy in the average American home and one of the largest sources of climate pollution in the country.
A few days before the administration announced its water heater efficiency rules, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) announced another sweeping policy.
According to the new rules, existing coal power plants will need to either shut down or install carbon capture technology capable of removing 90% of their carbon pollution. The policy will also require any new natural gas power plants that provide baseload power—the ones that run throughout the day and night, as opposed to the peaker plants that only run for a small fraction of hours in the year—to install carbon capture technology.
The new power sector rules are effectively a death blow to coal power in America, which has slowly faded over the last two decades but still emits more carbon emissions than almost every country in the world.
The water heater rules and power plant regulations will help the country meet its goal of cutting emissions by 50% by 2030. But impactful as they will be, they weren’t the most important climate policy that the Biden administration passed in the last two months.
That honor goes to the EPA’s tailpipe rules, which are set to transform the auto industry over the next decade.
Today the transportation sector is the largest source of climate pollution in the United States. Within the sector, passenger cars and trucks are the biggest contributors to emissions. While electric vehicle adoption has grown in recent years, America lags behind many other countries in decarbonizing its vehicle stock.
The EPA’s new rules will force automakers to reduce the amount of pollution and carbon emissions that come from their vehicles. The federal policy doesn’t specifically mandate that automakers produce EVs or stop selling gas-powered cars but instead regulates the average carbon emissions per mile of a manufacturer's entire fleet over the next decade. That means automakers can still sell gas-guzzling, carbon-spewing trucks in 2035. They’ll just need to sell a lot more EVs or plug-in hybrids to bring their average fleet emissions down if they do.
Like the power plant rules, the EPA’s new auto regulations are designed to avoid being thrown out by a conservative and hostile Supreme Court.
128 notes
·
View notes
Text
Get Back Rewatch 55 Years On: Day 13
Ah it’s “coordinate with the carpet” day.
John could probably say “2+2=3” and Paul would be like “Oh you're sooo right, John.”
Literally the ADHD antics (jumping over a chair because it’s there and you can and it would be funner than going around) are so relatable.
Ringo putting Zac’s picture up? I don’t know much about him as a dad. Does anyone know? I mean I know part of the reason he and Mo left india was because they missed their kids, and in late 66 when John was making HIWTW and Paul was working on TFW and George was off learning filthy eastern ways, Ringo stayed home and ‘enjoyed the baby’. Was he a really good dad?
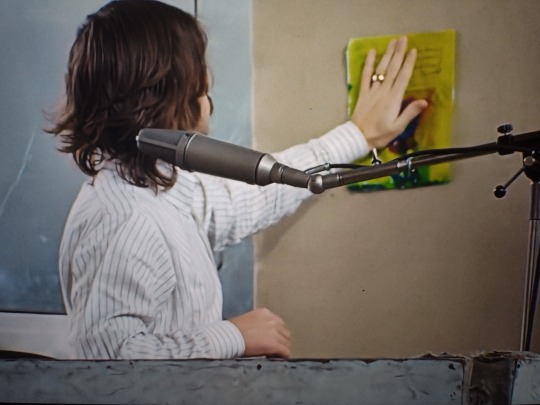

John: I really liked how that lead singer was singing so soft and nice. Paul: like this, John? Like this? John? John, look at me, do you like this?
Literally why are you even there, Yoko. Like, genuinely, not for the bands sake or anything, but for your own sake, go find somewhere else to be! Something, something, one of the few ways to find success as a woman was to attach yourself to a man and she was hustling with the best feminist tools available okay, okay. Ugh, I just don't know if I could stomach it.
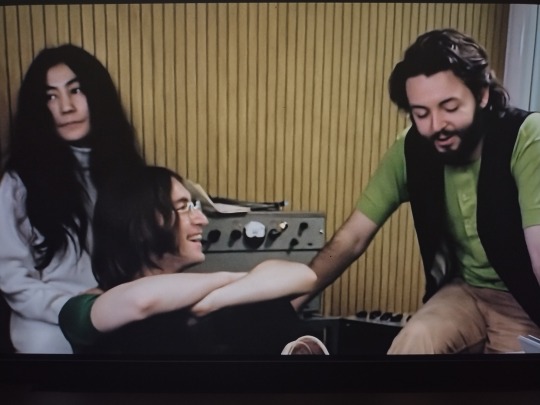

I heard John say “Rickie and the Red Streaks” and I was like, ummm, did you mean “Suzie and the Red Stripes”? But apparently it’s a real band. They were in the same Cavern show as the Beatles when they came back from Hamburg but never made it big. And Paul was purposely referencing them with Linda's pretend band because, as he said, he would have been happy to just have been them instead of the Beatles.
“John, can you take a little bit of bass off your guitar?” The faces. Paul told him to take some bass off a minute ago, didn't he? Or he just knows how much John hates to be told that. Anyway it's the silent communication for me.
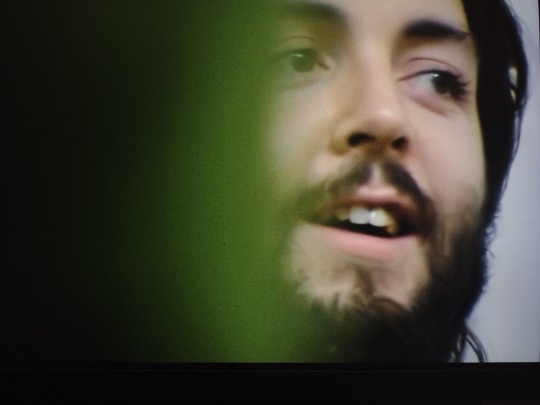
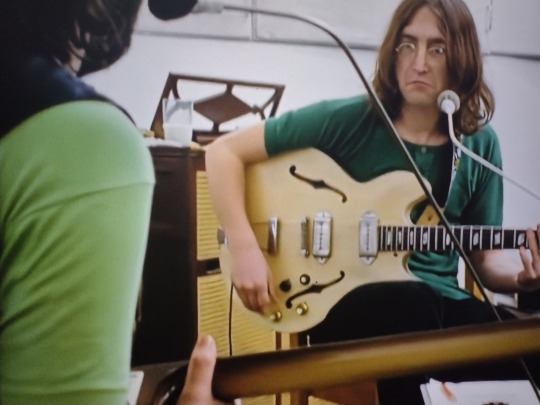



Paul: *stops his little wordless moan-singing for two seconds*. John: Everybody had a wet drea–SING, Paul! Paul: Ooohh yeah! He’s sooo happy I’m melting. Paul McCartney wants one thing in this life, and it’s for John Lennon to tell him to sing.
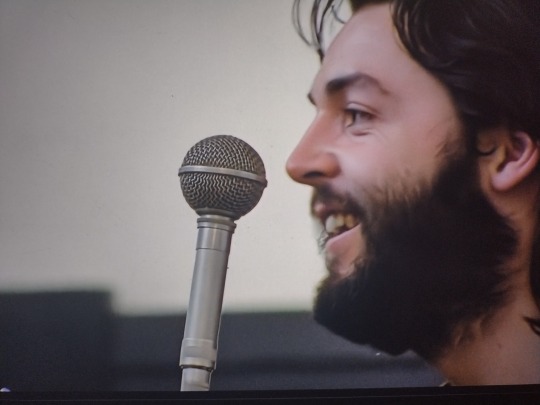
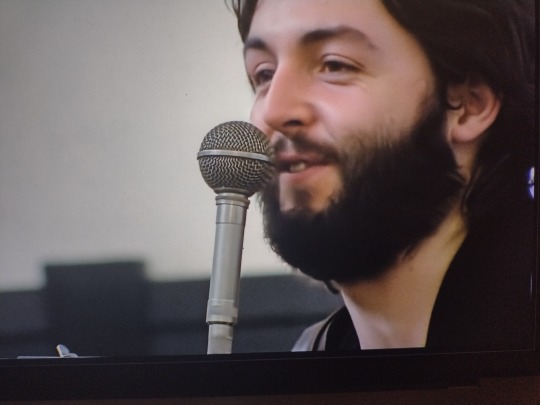
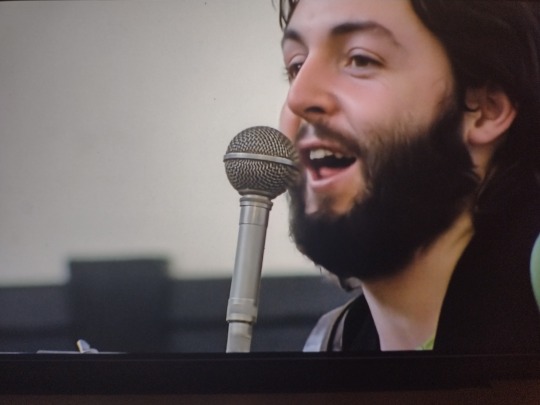
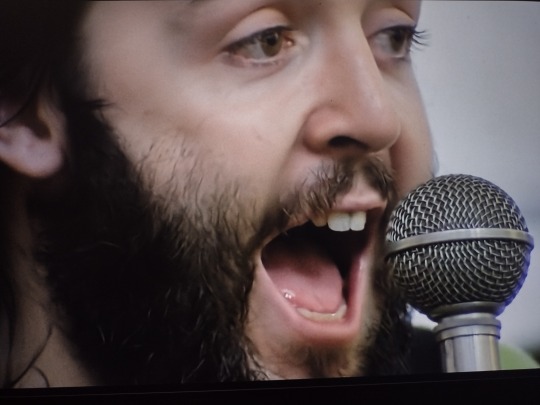




“He would’ve been president, you know.” John, bless your naive, lovely heart.
Paul: shrieking. John: moves the microphone the way a mom takes the sharpie out of her toddler’s hand.
“If you can get ‘em off Mimi’s wall.” I have a hard time with Mimi. Sometimes she’s adorable. Sometimes she’s horrible. I really can’t get a read. And maybe that was the problem. Maybe John couldn’t either.
This moment. My little ND baby. Someone just hit your g spot, didn’t they? But to be fair, it is incredibly impressive. Billy has never heard the song before, and he just jumps in with the perfect fill? I love Billy. So talented, such a cutie, so cool, so kind. And look at him. Having such a good time.
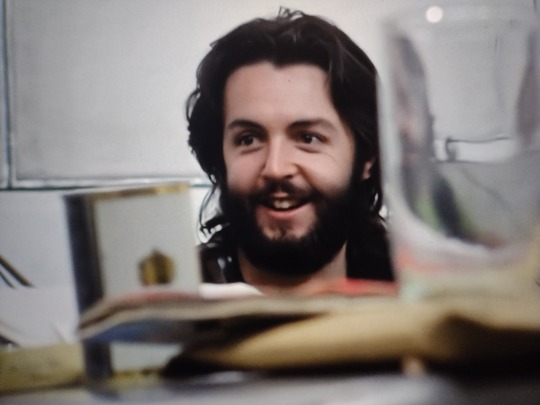
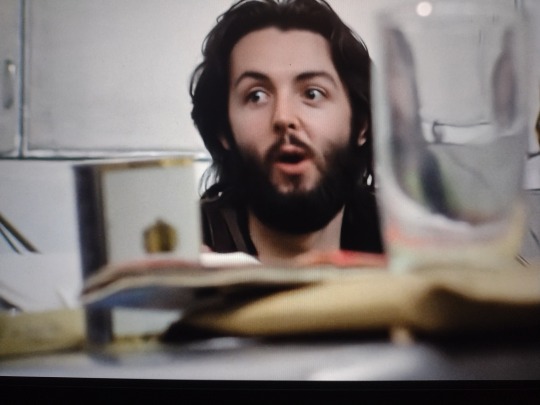
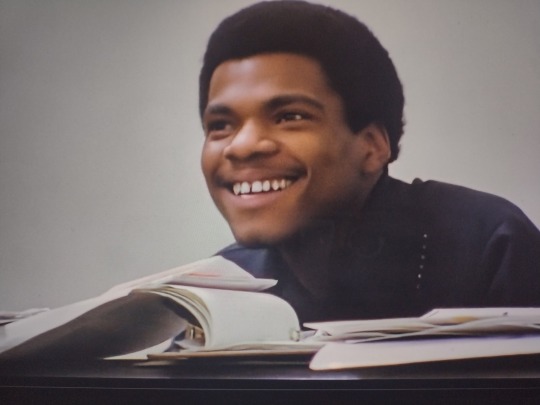



The silent communication again here. “Are you hearing this?” “Yeah, baby, I’m hearing this.” Then, John vocalizes the decision. How many Beatles decisions were made like this? Thinking specifically of Brian's account of their decision for him to manage, but probably this happened constantly.
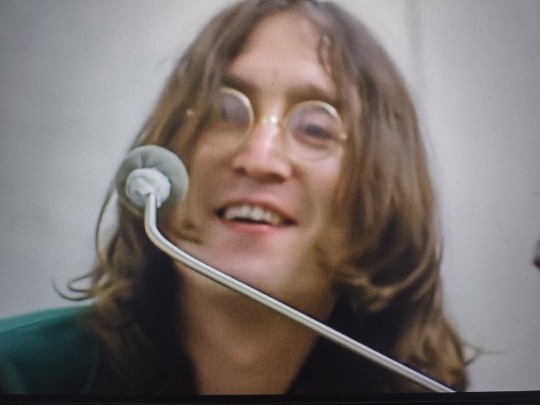

Yoko reading “The Beatles Complete History”. I love that she’s like, “Everything John tells me is ‘Paul this, Paul that, wah, wah, wah’. I need to get some cold hard facts.”
Billy’s piano actually is insanely sexy though.
John: *complains about his rock and roll finger* Paul, turning up the scouse: Come on, son, now try your hardest. John continues, soft, needy' Lookie, look at him. *holding up his finger* Paul, genuine: Ah, I know. I just love the different ways they take care of each other.
Poor George, dissociating himself into another dimension as John’s crooning about Paul’s eating habits. Look. At. How. He’s. Looking. At. Him. You’d think Paul was in that moment creating the heavens and the earth. Nope. Just rocking back and forth like a catatonic, probably getting crumbs all in his greasy beard.
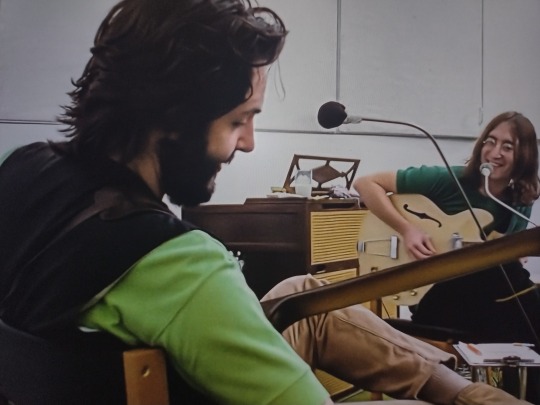

But seriously HOW is everyone in this room watching these two men, taking in to account all of their behaviors, scream "All I want is you!" at each other and not forcing them immediately into either fucking or therapy or both?!
Ringo’s holey pocket, my beloved.

The guy with the RP accent and the suit coming up to John like the bad guy in every American children’s movie. “I’ve spoken to Mr. Klein.” Dun, dun, dun.
160 notes
·
View notes
Text

Abu Mohammed, 40, is the spokesperson of al-Aqsa Martyrs Brigade, a militia affiliated with Fatah: "I was supposed to be dead many years ago.". Abu Mohammed was working in the security team of president Yasser Arafat and he is now a police officer for the Palestinian Authority as well as a commander of al-Aqsa Martyrs' Brigades. After training in Yemen, Algeria and India, he started fighting during the second Intifada. He escaped several targeted killings attempts and he is still a hunted man. His first daughter was born 14 years after he got married, but his constant hiding made any encounter with his wife dangerous: "I hope when she grows up she can live in peace and be a doctor… or a fighter. I will leave only two things to my daughter: this rifle and this handgun." Gaza, April 2015. Photo Credit: Lorenzo Tugnoli.
106 notes
·
View notes
Text
Captain Nemo, Freedom Fighter

There's a lot of historical and cultural significance in Twenty Thousand Leagues Under the Sea which is not widely known by modern audiences. Here some some facts I find very interesting:
-> In Verne’s original character notes, he was going to be a POLISH noble whose family was killed by Russians.
Verne’s publisher argued with him about that for a long time because of his large Russian fanbase. Verne reluctantly gave in, but eventually changed Nemo’s backstory to that of an Indian Prince whose family was killed by the British.
With that in mind, that makes the Soviet miniseries more interesting: A Polish revolutionary is actually mentioned by Captain Nemo in the second episode. Vladislav Dvorzhetsky, the actor portraying Nemo, was actually half-Polish himself!
-> Captain Nemo was written as a foil to Confederate Navy Captain Raphael Semmes.
Captain Raphael Semmes had portraits of General Robert E. Lee and the Confederate President Jefferson Davis on the cabin wall of the CSS Alabama, while Captain Nemo has portraits of Abraham Lincoln and the radical abolitionist John Brown in the cabin walls of the Nautilus.
Semmes was a supporter of slavery while Captain Nemo was an abolitionist.
Raphael Semmes stated that India should never be free from British rule, while Captain Nemo was an Indian who fought to be free from British rule.
A list of more comparisons between Jules Verne's "Twenty Thousand Leagues Under the Sea" and Raphael Semmes' "Memoirs of Service Afloat During the War Between the States" can be found on Wikipedia.
Thus, in Twenty Thousand Leagues Under the Sea, Jules Verne was trying to point fingers at the cruelty of the British towards India, the Russians towards the Polish, AND Americans towards people of color.
There are many fascinating rabbit trails to explore in regards to Jules Verne's literary masterpiece. Here are some sources:
#jules verne#20000 leagues under the sea#captain nemo#classic literature#twenty thousand leagues under the sea#tkluts#steampunk#french literature#history#literary history#Капитан Немо#Vladislav Dvorzhetsky#20kleaguesunderthefeed#20kluts#20k leagues#civil war#civil rights#european history
94 notes
·
View notes
Note
Could you tell me more about your take/takes on human Elita?
And do you have any ideas for Human Optimus? I'd like to hear that too 😁
ofc!! I have stuff for tfone, aligned/prime and earthspark but as of rn only aligned is the most developed followed by earthspark lol, but I'm gonna include all of them so there's gonna be quite a bit
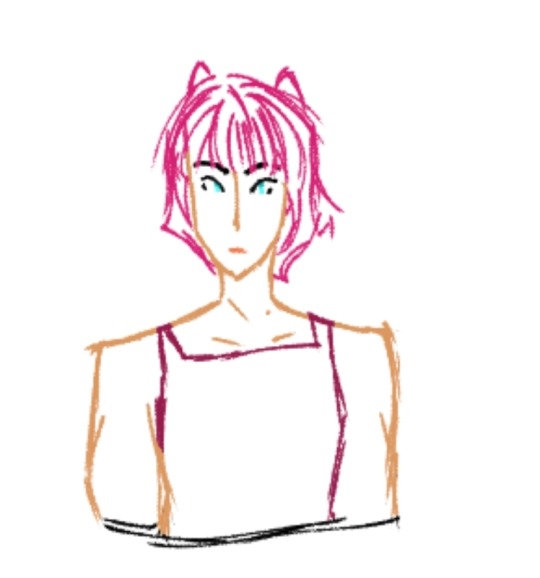
My tfp Elita is Argentine with major face claim inspo from Anya-Taylor Joy!! (who I think would be an AMAZING elita if they do another celeb cast for her) with her name being Ariel Caballero (meaning knight/horseman)
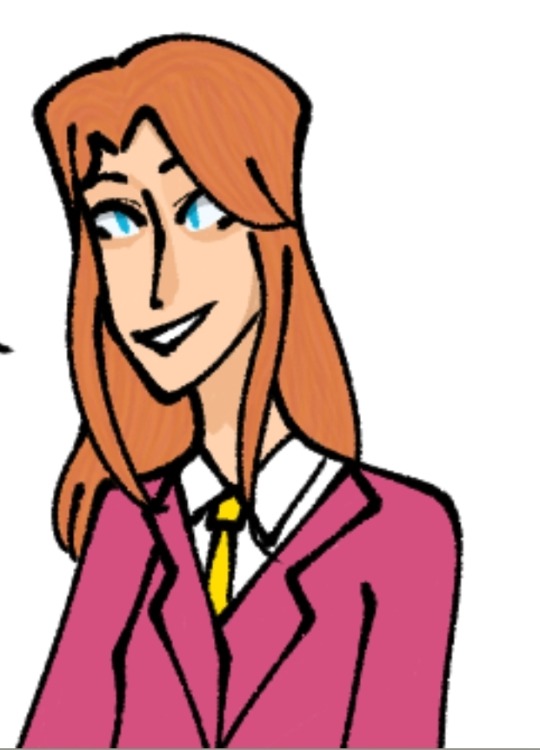
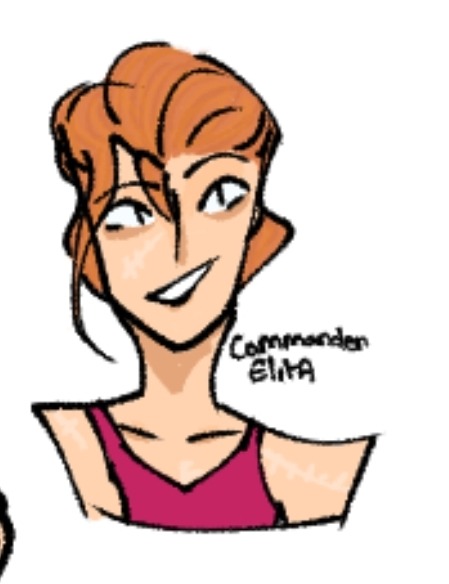




(this art is like almost 2 years old lmao 😭) she had strawberry blonde hair and a plethora of pink suits (like 2 years ago I had a humanformers boarding school au so a lot came from that) and she's sisters with chromia and moonracer! She'd be first lady (with op being prime minister ?? president ?) and military commander, and the niece of alpha trion! her not being in tfp gave me a lot of free reign omg 😭
I do have a human OP design!!! only tfp rn tho 😭 i'm thinking of ones for tf one and genuinely earthspark reminds me of a basic ass european descent grandpa so that's basically it for es 😭
He's Greek-Persian! (tho, general Achaemenid empire descent), I can't remember the name I actually gave him but I do remember Orion was his first name (he either had pax, a greek surname or a persian one 😭)
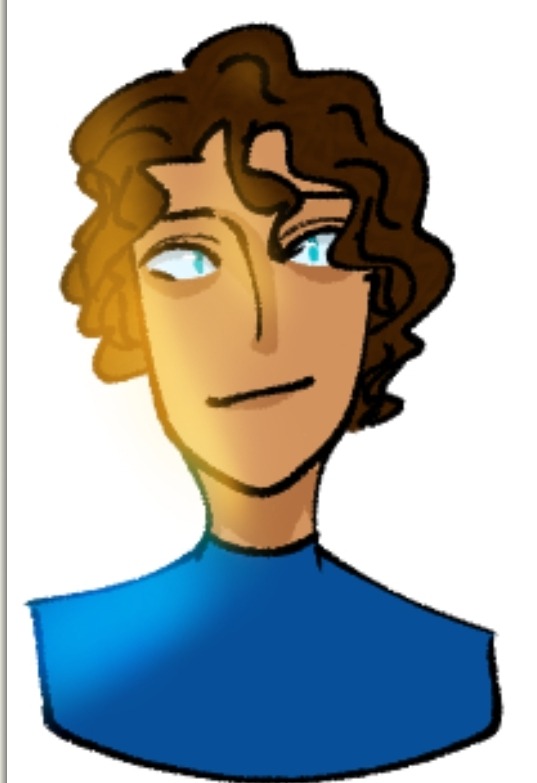


(ref by kibbitzer for the one on the right!!!!) Also old art lmao, he wasn't developed as far as elita was but i don't think that'd be a shocker based on my account 😭 He actually has freckles now but at the time of drawing those he didn't :')
back to the regular elita programming nowjdks
My earthspark Elita is Japanese!
Bushida Aeri is her name :) Bushida meaning warrior and Aeri being from ariel. I don't have many drawings for her but there's thesee



the first one is an old design for her but I still think it fits, the second being a younger Elita so like ig when she'd be Ariel in earthspark time line and the bottom is my most recent sketch of her!! I don't have a face claim inspo for her but Elita in general (not just earthspark) has always reminded me of Irene of Red Velvet! both leaders in pink lmao
For tfone there's like nothing new at all except this art
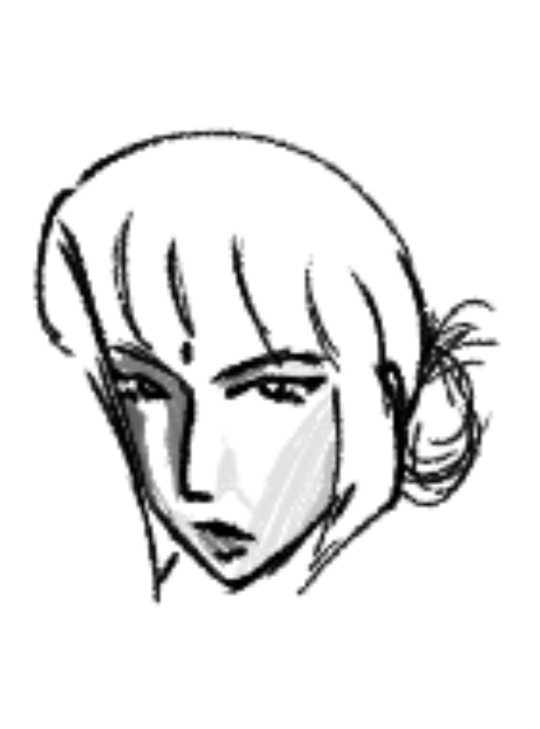

Esita Won, she's of Indian and Chinese descent, but mostly Indian, she probably speaks Punjabi or Tamil (ik completely different areas of India 😭), she reminds me of that one desi older sister who takes no crap and is not afraid to beat your ass and also makes the best curry idk
I noticed a lot of Elita's helm designs lean into traditional east Asian hair styles and clothing so I really wanted to represent those parts of her designs and the franchise's Japanese heritage :))
(omg i didn't realise how long this would end up being 😭😭)
#some times a girl has to self project her ethnicity onto her comfort characfer#I actually have a bunch of tfp human designs including arcee bee and ko moonracer lmao but they're all old#I repeated a lot I told you before sorry😭#transformers#elita one#elita 1#tf one#tf one elita#earthspark elita one#tfp elita one#Elita-1#Elita-One#humanformers#Orion Pax#optimus prime#fan art#transformers art#maccadam#maccadams
25 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Quasi-War
The Quasi-War (1798-1800) or 'Half War' was a limited, undeclared naval conflict fought between the United States and the First French Republic. Hostilities arose when French privateers began attacking neutral American shipping, resulting in several minor naval skirmishes before the conflict was de-escalated in September 1800. The war led to the strengthening of the US Navy.
In 1793, the United States asserted its neutrality in the ongoing French Revolutionary Wars (1792-1802) and decided to suspend repayment of French loans. The following year, it signed the Jay Treaty, which fostered stronger political and commercial ties between the US and Great Britain. Revolutionary France viewed these actions as violations of the 1778 Treaty of Alliance, whereby the two nations had allied against Britain during the American Revolution; in retaliation for this perceived betrayal, France authorized privateers to begin attacking American shipping in the West Indies in late 1796. Within a year, nearly 300 American merchant ships had been captured.
In October 1797, US President John Adams sent a delegation to Paris to negotiate a new treaty and diffuse tensions. This resulted in the XYZ Affair, in which the French refused to negotiate unless the US agreed to pay a large bribe. Outraged, the US began preparing for war. The US Department of the Navy was established, and multiple frigates were commissioned and put to sea, tasked with protecting American merchant ships and hunting French privateers. This resulted in several naval engagements, with the most notable including the USS Constellation capture of the French frigate L'Insurgente in February 1799. Still hoping to avoid a full-scale war, President Adams sent a second delegation to Paris in October 1799. These commissioners had more luck dealing with the new French government, under Napoleon Bonaparte, leading to the Commission of 1800, which ended the war and restored Franco-American relations.
Background
In 1778, the Kingdom of France signed treaties of alliance and commerce with the fledgling United States and entered the American Revolutionary War (1775-1783). France was eager to humiliate and weaken its rival, Great Britain, and duly provided the American rebels with arms, ammunition, uniforms, troops, and ships. French intervention expanded the war into a global conflict, forcing Britain to divert its military resources from North America in order to defend its more valuable colonies in the Caribbean and India. Furthermore, French soldiers and ships proved critical to the decisive American victory at the Siege of Yorktown. When the Treaty of Paris of 1783 ended the war and recognized the independence of the United States, it could be said that French aid had been a key factor in the American victory. Both nations considered the 1778 treaties of alliance to still be in effect.
Signing of the Treaties of Alliance between the US and France, 1778
Charles Elliott Mills (Public Domain)
Then, in 1789, France became embroiled in its own revolution. After the Storming of the Bastille, the revolutionaries gradually eroded the authority of the Ancien Régime until 21 September 1792, when the monarchy was finally overthrown and replaced by the First French Republic. Initially, the French Revolution enjoyed widespread support in the United States, where it was viewed as a continuation of the Americans' own struggle against tyranny. American supporters took to wearing tricolor cockades in solidarity with their French brothers-in-arms, while political clubs called Democratic-Republican societies popped up across the country to praise the Jacobin ideals of 'liberty, equality, and fraternity'. But it was not long before the French Revolution took a radical turn: the deposed King Louis XVI of France was guillotined on 21 January 1793, shortly before the Jacobin government began arresting and executing anyone suspected of counter-revolutionary activity. As it bathed in blood, the French Republic grew bolder and soon sought to spread its revolution beyond its borders; by March 1793, Revolutionary France was at war with most of the great powers of Europe including Austria, Prussia, Spain, the Dutch Republic, and Great Britain. This began a series of total wars that would devastate Europe for much of the next quarter century.
As the French Revolution continued to escalate in Europe, the French revolutionaries looked to the United States for support. They considered the 1778 Treaty of Alliance to still be in effect, as did a large subset of Americans who still supported the Jacobins despite the bloodshed of the Reign of Terror. Thomas Jefferson, leader of the burgeoning Democratic-Republican Party, still referred to the French Republic as 'our little sister' and brushed off the violence, having once said that "the tree of liberty must be refreshed from time to time with the blood of patriots and tyrants”. Jefferson and his supporters (also known as Jeffersonian Democrats) still viewed Britain as an enemy and wanted to support France in its war against the British. In early 1793, France itself sought to whip up support in the United States. Its ambassador, Charles-Edmond Genêt – better known as Citizen Genêt – traversed the country and spoke at Democratic-Republican societies, hoping to rekindle anti-British fervor amongst the American populace. Genêt even went so far as to recruit American privateers to attack British vessels.
Although some Americans supported the French, many others did not. The nationalist Federalist Party was horrified by the chaotic radicalism of the French revolutionaries and feared that similar bloodshed could come to American shores. President George Washington agreed with the Federalists on this point and believed that the United States could not withstand another war with Britain. For these reasons, Washington sought to distance US policy from France. He condemned the actions of Citizen Genêt as incendiary and refused to meet with him, and on 22 April 1793, he issued a Proclamation of Neutrality, wherein he promised to keep the United States out of the French Revolutionary Wars. Around the same time, Congress decided to suspend the repayments of French loans that had been borrowed during the American Revolution; the loans, Congress argued, had been borrowed from the French monarchy which no longer existed and need not be paid to the republic that had taken its place.
Naturally, this was perceived as an insult by the French Republic, but tensions would only worsen the following year. In addition to being anti-French, the American Federalists were generally pro-British; they believed that Britain was the natural ally of the US and sought stronger political and commercial ties between the two nations. This goal was achieved with the controversial Jay Treaty, ratified by Congress in 1795, which resolved some of the issues left over from the American Revolution and fostered trade between the US and Britain. The French were incensed by the Jay Treaty, which they interpreted as a British-American alliance and a betrayal of the 1778 treaties of alliance. In retaliation, France authorized privateers to begin attacking neutral American shipping in late 1796, proclaiming that any American merchant ship carrying British cargo was a valid prize of war. Within a year, nearly 300 American ships had been captured, and their crews were often subjected to maltreatment.
Continue reading...
32 notes
·
View notes
Text
Unseen Pillars: The Indispensable Role of Immigrant Healthcare Workers in the U.S.
Introduction:
Highlight the often-overlooked significance of immigrant workers in maintaining the U.S. healthcare system's efficiency and reach.
Present a question or statistic to draw readers in, emphasizing the breadth of roles filled by immigrants beyond just physicians and nurses.
The Backbone of Healthcare:
Provide statistics on the percentage of immigrant healthcare workers in various roles, from doctors and nurses to support staff.
Include anecdotal evidence or quotes from healthcare administrators about the critical gaps these workers fill, especially in underserved areas.
Beyond Numbers: Personal Stories of Dedication and Sacrifice:
Share narratives of individual immigrant healthcare workers who have made significant impacts in their communities.
Discuss the personal and professional challenges they face, from cultural adaptation to navigating the immigration system.
Challenges in the Immigration Landscape:
Outline the specific visa and immigration challenges that affect healthcare workers, such as long waits for green cards and limited visa options.
Explain how these challenges hinder not only the individuals but also the healthcare institutions that rely on their services.
The Call for Reform:
Argue for specific changes in immigration policy that could benefit the healthcare sector, like expanding visa quotas or creating fast-track options for medical professionals.
Discuss the potential benefits of such reforms, including improved healthcare access and quality in rural and underserved regions.
Conclusion:
Reiterate the essential role of immigrants in the healthcare system and the urgent need for policy changes.
End with a compelling call to action for policymakers, healthcare leaders, and the general public to acknowledge and support these vital workers.
Contact Information
If you or your family members have any questions about how immigration and nationality laws in the United States may affect you, or if you want to access additional information about immigration and nationality laws in the United States or Canada, please do not hesitate to contact the immigration and nationality lawyers at NPZ Law Group. You can reach us by emailing [email protected] or by calling us at 201-670-0006 extension 104. We also invite you to visit our website at www.visaserve.com for more information.
#immigration#visa#h-1b#green card#perm#h-1b visa#uscis#india#us#usa#h 1b professional visa#nationality lawyer#lawyer naturalizatin#nationality citizenship n 400 citizens#naturalization#new company#video updates about immigration and nationality law in the u.s. from the nachman phulwani zimovcak (npz) law group p.c. visaserve. this we#npz lawyers david nachman michael phulwani phulwani zimovcak#h 1visa#h 1b visa transfer#h 1b nafta visa immigration cbp cis ice#second round of h 1b lottery#immigration law news and updates: trump's 10 point u.s. immigration law plan new i 9 form december 2016 visa bulletin update eb 5 immigrant#president trump#tn canada#canadavisa#canadianvisa#canadaimmigration#canadianimmigration#canada visa
0 notes
Text
In Ukraine’s prolonged struggle against Russia, the election of Donald Trump as the next U.S. president was a black swan event.
Among other positions, Trump ran on the promise of extricating the United States from the conflict in Ukraine. His closest allies have openly disparaged Kyiv and made overtures to Russian President Vladimir Putin. Thus, with this transition of power begins a new chapter of the war in which Western support for Ukraine could fall by the wayside.
Outgoing U.S. President Joe Biden’s belated decision to allow Ukraine to use U.S. missiles to strike targets deep within Russian territory, a critical condition of Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky’s “victory plan,” is hardly a godsend. These missiles cannot singlehandedly change the course of the war, and they put Zelensky in an awkward position. Striking Russian targets will trigger not only the wrath of Putin, but also that of Trump, who will undoubtedly view any escalation as a shot against his own prospects for dealmaking.
With Trump making threats to pull out of NATO and cut a deal with Putin, Europe is also having second thoughts on backing Ukraine. German Chancellor Olaf Scholz spoke with Putin on Nov. 15 about bringing an end to the war, while Czech President Petr Pavel announced plans in October to send a new ambassador to the Czech Embassy in Moscow in early 2025.
Meanwhile, United Nations Secretary-General António Guterres recently attended the annual summit of the BRICS countries—Brazil, Russia, India, China, South Africa, and several recently added members—hosted in Kazan, Russia. The U.N.’s involvement in an event hosted by a country engaged in a war of aggression, whose president is wanted under an International Criminal Court warrant, sends a disheartening message.
Almost three years into Russia’s full-scale invasion, the West is tired. It no longer has the political will to help Ukraine win by military means and is seeking a settlement with the aggressor instead.
The U.S. shift toward isolationism may hasten the inevitable: Ukraine and the West will soon find themselves negotiating with Russia to define the terms of a settlement—and, by extension, shaping a new world order. This emerging order will not be the rules-based system established after World War II, but one driven by idiosyncratic dealmaking among strongmen.
The problem is that any deal will amount to Ukraine’s—and the West’s—capitulation to Russia.
A bad peace is better than a good quarrel, according to a Russian proverb. If the West is set on securing this “bad peace,” then it must have a negotiating strategy along four critical parameters: territories, security guarantees for Ukraine, reparations, and sanctions.
Even before Trump’s election, some of Ukraine’s staunchest allies began expressing the view that Ukraine would have to accept some loss of land. The most obvious settlement strategy, then, would likely involve buying Ukrainian and European security with territory—possibly including Donetsk; large chunks of the Luhansk, Zaporizhzhia, and Kherson regions; and the peninsula of Crimea, which Russia first seized in 2014.
This outcome is a far cry from the Western leaders’ earlier commitments to Ukraine’s territorial integrity and hopes for regime change in Russia, but realpolitik leaves little room for moral considerations.
Should Zelensky agree to this loss of territory, the only realistic security guarantee for Ukraine would be membership in NATO. Yet this runs counter to what U.S. Vice President-elect J.D. Vance has lobbied for: a demilitarized zone along the current front lines and an enduring commitment to Ukraine’s neutrality.
The next White House does not seem to have a plan for what happens to Europe in a few years, when it would face a revanchist Russia with a subdued Ukraine at its Western borders. Such an outcome is not in Trump’s best interest. Another option, therefore, may have Trump concede to Ukraine’s membership in a new NATO—one without the United States, perhaps—leaving Europeans to be the masters of their own security.
Battered and curtailed but still sovereign, Ukraine would gain a nuclear umbrella against future Russian aggression, and Europe would fund the postwar reconstruction. There would be no international tribunal and no reparations. (Putin won’t be negotiating his own sentence.) Sanctions against Russia would remain for the time being. Europe would accept the occupation de facto, but it wouldn’t de jure recognize the territory as Russian land.
It will be difficult to come up with a deal that satisfies all parties. But in any negotiation, reaching a mutually satisfactory outcome depends on the motivation and constraints of those involved. The West is motivated to settle in Ukraine because it is tired of war, and because Trump is uninterested in leading the existential fight for democracy. Ukraine, understanding that it cannot win on its own, can be motivated to settle in order to stop the now-pointless bloodshed.
Putin’s motivations are murkier. In fact, a closer look would reveal that Putin has no need for lasting peace.
Putin’s megalomaniacal intransigence is now reinforced by his perception that he is winning, even if it is taking longer than he hoped. Piecemeal shipments of Western military aid have made Russian advances slow and painful—but they have been advances nevertheless. While Ukraine’s ability to affect Russian military logistics was until recently severely hampered by Western restrictions, the Russian army has faced no such limitations, regularly bombing civilian infrastructure and military targets alike.
In wars of attrition, the side with more resources is poised to win, and Russia still mobilizes resources with frightening force. Russia has activated the economic and cultural mechanisms necessary for around-the-clock military production—bread-making factories churning out drones, schoolchildren making camouflage nets, and old Soviet tanks hauled out of Siberian forests and shipped to Ukrainian front lines.
Now that the economy has been switched on to military footing, there is no shortage of munitions. Meanwhile, government payouts ensure an ample supply of volunteers to enlist in the military, meaning Russia does not have a manpower crisis like Ukraine does.
No human toll is too high for Russia. During World War II, Russia lost more than 27 million people—the largest number of fatalities of all involved. Peter the Great’s 18th-century Great Northern War, which established Russia’s power in the Baltics, lasted 21 years and incurred enormous casualties, as did the 25-year-long Livonian War fought by Ivan the Terrible in the 16th century.
Russia has already suffered upward of 700,000 people dead or wounded during the Ukraine war, according to estimates from the National Interest. But with families of dead soldiers mollified by the “coffin money” they receive, society writ large has not budged in its support for the war. It will likely stay that way short of another mobilization.
It certainly helps that the brunt of the war is borne by recruited volunteers, who sign up to fight to improve their and their family’s economic standings, and by convicts—both groups making up a significant number of those killed and wounded in Ukraine. Another large constituency fighting Russia’s war is national minorities, often from depressed economic areas and the lowest strata of society. And now, those minorities are joined by North Korean soldiers and potentially by citizens of the other dictatorships that Putin courts.
Contrast this low visibility of Russia’s war toll, further obscured by Kremlin propaganda, to its loudly celebrated nativist successes. In the last two years, not only did Russia fail to fold under the weight of Western sanctions, but it also managed to build parallel economic, financial, and cultural structures that are independent of the West.
Economically, Russia has reoriented itself toward the East, increasing trade with China, India, and other countries in Asia and the Middle East. It has shifted its energy exports away from Europe and developed domestic production capabilities. Despite sanctions, oil money—the main source of Russia’s war financing—keeps flowing, albeit from a different direction than before. Cross-border payments are now handled through SPFS, a homegrown alternative to the SWIFT global financial system, and the Mir payment system that replaced Visa and MasterCard. Russia touts these systems to its BRICS partners as alternatives to “Western financial hegemony.”
If anything, the war in Ukraine has given Putin more money to play with than before. Assets belonging to Western companies exiting Russia have been nationalized or bought for cheap and redistributed to businesses with ties to the Kremlin—one of the largest property transfers in Russia’s history. Cut off from Western banks, Russian oligarchs must invest their money domestically. Sanctions evasion schemes protect Russians’ access to Western consumer goods, creating enormous enrichment opportunities for Russian and Western business agents alike. Tankers shuttle Russian oil with payments cleared through offshore shell companies. Putin’s personal wealth, estimated at somewhere between $70 billion and $200 billion, remains safe. Though he is a product of a socialist state, the Russian leader is a master of capitalism.
Cultural shifts in Russia increase Putin’s confidence in victory. What little dissent remained before the war has largely been rooted out, with Russians closing ranks around their leader. According to a recent poll conducted by the Levada Center in September and October, more than two-thirds of Russians who said they want the war to end are against returning Russian-occupied territories to Ukraine.
On the global stage, Russia has managed to upgrade its status from a regional power to a leader of the anti-Western coalition. These coalition members have their own stakes in Ukraine. A Russian victory would embarrass the United States, weakening its influence in Asia and helping China. North Korea has found exports—bad shells and soldiers—that it can exchange for food, money, and energy. And Iran is happy to keep the United States distracted from the Middle East.
Even if Putin wanted to end the war, it would entail serious risk for his regime. Drones, shells, and missile production would have to be scaled down, ending the economic boom. The sudden drop in government spending would create real prospects of an economic collapse. Around 1.5 million veterans would have to be pulled out of Ukraine to find new roles in a corrupt Russian society. The manufactured sense of national unity would give way to envy that beyond the border, on Russia’s “ancestral lands,” Ukrainians are thriving under European Union and NATO banners.
Taken together, in a country reacclimatized to grand-scale violence, the prospect of revolt becomes clear and present. To find an outlet for that aggression, Putin would have to start a new war not long after agreeing to settle for peace.
Ultimately, the status quo—an ongoing border squabble with conventional weapons—suits all but Ukraine and Europe, for which security deteriorates in direct proportion to Putin’s success.
The Putin that the West would face at the negotiating table is a former underdog—a man on a mission to free the world from what he has characterized as Western “hegemony,” his economy thriving, his new and old friends paying court, and his people unified behind him.
He is not, however, as invincible as he seems. The BRICS countries are not rushing to replace SWIFT with the Russian alternative. By putting all his economic eggs into the military basket, Putin has siphoned off resources from everywhere else, an unsustainable move. Inflation is real, and the ruble is weakening. Even the overheated military sector can’t keep up with demands. Moreover, as a student of Russian history, Putin knows that the support and adoration of the Russian masses can turn on its head overnight.
But Putin also knows how to keep a poker face. Having staked his survival on this war, Putin would be negotiating from the position of strength and with obligations to his domestic and international stakeholders in mind.
He has already shot an opening volley at the U.S. president-elect: After a call during which Trump told the Russian leader not to escalate in Ukraine, Russian state television released a special on Melania Trump’s modeling career, including nude photos of the once and future first lady.
The West, meanwhile, will be negotiating from a position of inherent weakness. After tiptoeing around the Kremlin’s red lines throughout the war, Western leaders have signaled their readiness to consider cessation of a large chunk of Ukrainian territory, wishing away what little leverage they had.
There is nothing stopping Putin from believing that he can’t get more. Unless Russia is decisively defeated on the battlefield or Putin is given precisely what he wants, he will not stop.
Of the options put forward for a negotiated solution, the only one that Putin would agree to is the one that gives him Ukraine’s capitulation on a platter. He will never agree to a thriving, independent, armed, and Western-aligned Ukraine on his border, because he would lose too much face. Putin will therefore demand an unviable Ukraine—without an army and without NATO membership—and, in effect, a Western surrender.
The issue of European security cannot be solved by a settlement with Moscow because appeasement only increases the aggressor’s appetite. Only the containment of Putin’s expansionism by military means will remove the existential threat to his neighbors. So long as there is an aggressive, revanchist Russia in the picture, lasting peace is an illusion.
32 notes
·
View notes
Text
All The Women’s News You Missed This Week:
9/30/24-10/7/24
want this sent to your email? Subscribe here
Transgender and Gender Critical News:
Major cases before the Supreme Court deal with transgender rights, guns, nuclear waste and vapes
Death threats assail Brazil’s trailblazing trans candidates as they campaign
Reproductive Rights:
US Supreme Court rebuffs Biden administration on emergency abortions in Texas
Women in War, Israel/Occupied Palestine:
A picture of her grief gripped the world. A year on, Gaza woman haunted by memories
Far from Gaza, a Thai mother grieves for her missing son
Policewoman killed and 10 injured in shooting in Israel
Girl who lost eye in Israeli raid that killed father carries ‘pain mountains can't bear’
UK-Israeli hostage has been forgotten, says mum
Women in the news:
Harris talks abortion and more on ‘Call Her Daddy’ podcast as Democratic ticket steps up interviews
Supermodel Naomi Campbell admits failures at charity, denies misconduct, media reports say
San Francisco’s first Black female mayor is in a pricey battle for a second term
Mexico’s new president promises to resume fight against climate change
For migrant women who land in Colorado looking for jobs, a common answer emerges: No
In their 80s, these South Korean women learned reading and rap
Pope Francis urges unity as advocates for women’s ordination press cause at Vatican gathering
Male Violence:
Judge denies Wisconsin attorney general’s request to review Milwaukee archdiocese records
Gang rapists sentenced to life in Tanzania prison
Abbington has 'no regrets' about Strictly complaints
India government says criminalising marital rape 'excessively harsh'
Arts and Culture:
Movie Review: ‘The Substance’ is brilliantly disgusting and deranged
Movie Review: Helen Mirren tells a story of evil and hope during WWII in ‘White Bird’
Movie Review: A transcendent Saoirse Ronan illuminates true-life addiction drama ‘The Outrun’
As always, this is global and domestic news from a US perspective covering feminist issues and women in the news more generally. As of right now, I do not cover Women’s Sports. Published each Monday afternoon.
#radblr#radical feminism#radical feminist#char on char#radical feminists do touch#radical feminist theory#radfem safe#radfems#All The Women’s News You Missed This Week
26 notes
·
View notes
Text

On 10 February 1973, Princess Anne visited Asmara War Cemetery, Eritrea, during a two-week tour of what was then Ethiopia and The Sudan.

In 2004, Princess Anne visited Malta to celebrate the 40th anniversary of the island’s independence. During her trip, she visited the CWGC’s Malta Memorial, Floriana, where she laid a wreath and paid tribute to the nearly 2,300 airmen who lost their lives during the Second World War.

The Princess Royal was the guest of honour as they opened The CWGC Visitor Centre in France. The princess took a tour of their new site, seeing the hard work of their teams and meeting some of the key staff involved in bringing the visitors centre to life, in 2019.

Princess Anne visited Etaples Military Cemetery in celebration of the 100-year anniversary of King George V’s ‘King’s Pilgrimage’, in 2022.

Madra's War Cemetery, India, 1985.

Khartoum War Cemetery, Sudan, 1985.

Fajara War Cemetery, Gambia, 1990.

Sai Wan War Cemetery, 1997.

Port Moresby (Bomana) War Cemetery and Memorial, Papua New Guinea, 2005.

Kranji War Cemetery, Singapore, 2005.

Simon's town (Dido Valley) Cemetery, South Africa, 2012.

Jawatte Cemetery, Colombo, Sri Lanka, 2024.

The Commission’s Headquarters, Berkshire, 2024.
Princess Anne, President of the Commonwealth War Graves Commission ✨
70 notes
·
View notes