#Grant and Subsidies
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
ARIA announces £143m in R&D funding to enhance global climate resilience
The Advanced Research + Invention Agency (ARIA) recently announced the launch of two new programmes: Forecasting Tipping Points, led by Programme Directors Gemma Bale and Sarah Bohndiek, and Synthetic Plants, led by Programme Director Angie Burnett. As with all ARIA programmes, Programme Directors have worked with the R&D community to identify areas which are under-explored, under-funded and hold…
#Agri Innovation#Agriculture#AgriFood Capital#AgriFood Science#AgTech#Artificial Intelligence in Agriculture#Climate Change#Climate Resilient#Crop Science#Food and Agribusiness#Grant and Subsidies#Research#Startups#Sustainable Agriculture
1 note
·
View note
Text
“Taxation is the price which civilized communities pay for the opportunity of remaining civilized.” - Albert Bushnell Hart:
The rightwing media would have us all bewailing the fate of the poor British farmer.
“New Tory leader Kemi Badenoch has vowed to reverse the Chancellor's hated inheritance tax raid on farmers." (Dailey Express: 15/11/24)
and
“Nigel Farage admits he is 'really worried' about family farmers facing inheritance tax raid." (GB News: 14/11/24)
Yet according to FarmingUK (21/11/23)
“Average business income by type of farm in England rose to £96,100 in 2022-2023 despite higher costs, according to the latest Defra figures.”
To be fair £96,100 is not a lot of money, with some farms doing better than others. Pig farmers for example had an average income of £135,000 for 2023/24 (Pigworld: 15/11/24) while some upland farmers only made £23,500 for the same time period. (GOV.UK: ‘Farm Business Income by type of farm in England 2023/24)
One thing the right wing media and commentators don’t tell you about are the deliberate reductions in farmers incomes introduced by the Tories, who began progressively cutting the amount of taxpayer subsidies they received through the Basic Payment Scheme. For the year 2022/23 farmers suffered a 19% cut in payments.
Neither do the right wing media ever admit the devastating cost of Brexit to British farmers.
“UK farmers face bankruptcies and closures as £1.8bn in EU cash stops with MPs warning ‘blind Brexit optimism’ may lead to higher food prices." (cityam.com:16/01/22)
I would of thought “bankruptcy and closure” are far worse than the yearly handful of farms having to pay inheritance tax.
This is not to deny that some farmers are really struggling financially to make a living. But in a free market neo-liberal economy the sad fact is the weak are MEANT to go to the wall. This, it is argued, increases efficiency and productivity with only the most productive businesses surviving in a competitive market. Given the majority of farmers have always supported the Tories, perhaps they should of paid more attention to what happens to turkeys when they vote for Christmas!
The Tories signed a trade deal with Australia that undercuts the price of British farm produce because under the deal Australian imported food stuffs do not have to be produced to the same safeguarding standards as is legally required of British farmers. In addition, Kemi Badenoch is calling for a similar deal with the USA which will not only see cheaper imports of food but food produced to lower standards, such as hormone-treated beef and chlorinated chicken.
Maybe protesting farmers should look to who the real enemy is? If cheaper, poorer quality foreign food is allowed to flood our markets then they wont have a farm to pass on to relatives because they will have gone bust.
It is not as though the inheritance tax rules will affect that many farmers. Treasury figures reveal that for 2021/22, 1730 farms were passed on to relatives of which 1264 were worth less than £1 million. This equates to around 500 farms a year being subject to the new 20% inheritance tax, hardly the great “tax raid” on farmers that the right-wing media would have us believe.
Farmers Weekly (17/01/23) informs us that according to research land ownership is dominated by the aristocracy, who hold almost one-third of land. Next come large corporations, which may have invested in land for its tax-saving opportunities, followed by tycoons.
Is this what all the protests are really about? The landed gentry, rich corporations, tycoons and oligarchs, trying to avoid paying tax on their assets?
Let me leave the last word to the Tory supporting Telegraph:
“Wealthy investors are hovering up agricultural land in order to avoid inheritance tax, pushing prices to record highs, and forcing out farmers." (18/06/23)
Maybe the new farmland inheritance tax will actually SAVE some farms. Now there's a thought!
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
जैविक खेती पर प्रति हेक्टेयर मिलेंगे 5-5 हजार रुपये, जानें पूरी योजना
भोपाल: देशभर में खाद संकट के चलते केंद्र और राज्य सरकारें किसानों को प्राकृतिक और जैविक खेती की ओर प्रोत्साहित करने के प्रयासों में जुटी हैं। इसी कड़ी में, मध्य प्रदेश सरकार ने एक महत्वपूर्ण कदम उठाया है। राज्य के मुख्यमंत्री मोहन यादव ने घोषणा की है कि प्रदेश में जैविक खेती को बढ़ावा देने के लिए किसानों को अनुदान प्रदान किया जाएगा। इसके तहत, किसानों को प्रति हेक्टेयर पांच-पांच हजार रुपये दिए…
#Benefits of Organic Farming#Government Support for Organic Farming#Madhya Pradesh Organic Farming Scheme#Organic Farming Grants for Farmers#Organic Farming in Madhya Pradesh#Organic Farming Subsidy#Organic Products Certification for Farmers
0 notes
Text
Government Policies for a Green Economy: Incentives and Regulations

Green Economy A successful transition to a green economy requires a combination of public and private sector efforts, Green Economy with governments playing a crucial role in setting the framework for this transformation. Policies often target sectors such as energy, transportation, agriculture, waste management, and construction, which are significant contributors to environmental impacts. In this context, incentives and regulations serve as two sides of the policy coin, ensuring both the encouragement of sustainable practices and the enforcement of environmental protection.
One of the main goals of government policies for a green economy is to shift economic activity toward more sustainable practices. This involves reducing greenhouse gas emissions, promoting renewable energy, and ensuring that economic growth is decoupled from environmental degradation. To achieve these goals, governments employ a wide range of tools, including tax breaks, subsidies, grants, carbon pricing mechanisms, and strict environmental regulations.
A green economy also emphasizes social inclusiveness, Green Economy ensuring that the transition to sustainability benefits all members of society, particularly vulnerable groups who are most affected by environmental degradation. Green Economy Government policies often include provisions for job creation in green industries, education and training for new skills, and social protection measures to ensure that no one is left behind in the transition.
This section will delve into six key areas of government policies for a green economy: renewable energy incentives, carbon pricing mechanisms, green transportation policies, sustainable agriculture support, waste management and recycling regulations, and financial incentives for green innovation.
Renewable Energy Incentives Green Economy
One of the cornerstones of any green economy policy framework is the promotion of renewable energy sources. Governments have introduced a range of incentives to encourage the production and consumption of renewable energy, such as wind, solar, and hydropower. These incentives are critical for reducing reliance on fossil fuels, which are the primary source of greenhouse gas emissions.
Renewable energy incentives often take the form of subsidies and tax breaks. For instance, many governments offer production tax credits (PTCs) and investment tax credits (ITCs) to companies that generate renewable energy or invest in renewable energy infrastructure. These financial incentives lower the cost of renewable energy projects, making them more competitive with traditional fossil fuel-based energy sources.
Feed-in tariffs (FITs) are another common incentive mechanism. Green Economy Under a FIT program, renewable energy producers are guaranteed a fixed price for the electricity they generate, often over a long-term contract. This provides a stable revenue stream and reduces the financial risk associated with renewable energy investments. Net metering programs, which allow individuals and businesses to sell excess renewable energy back to the grid, are another way governments encourage the adoption of renewable technologies.
Governments also support renewable energy through research and development (R&D) funding. Green Economy By investing in the development of new technologies, governments can help bring down the cost of renewable energy and make it more accessible. Many governments also provide grants and low-interest loans for renewable energy projects, particularly for smaller-scale projects such as rooftop solar installations.
In addition to financial incentives, governments often mandate the use of renewable energy through renewable portfolio standards (RPS). An RPS requires utilities to obtain a certain percentage of their electricity from renewable sources, creating a guaranteed market for renewable energy. This not only supports the growth of the renewable energy industry but also helps reduce the overall carbon footprint of the energy sector.
Green Economy The combination of financial incentives and regulatory mandates has been instrumental in driving the rapid growth of renewable energy in many parts of the world. Countries such as Germany, Denmark, and China have become global leaders in renewable energy production, thanks in large part to strong government policies that promote green energy development.
Carbon Pricing Mechanisms
Carbon pricing is a critical tool in the fight against climate change and a key component of government policies for a green economy. By putting a price on carbon emissions, governments create an economic incentive for businesses and individuals to reduce their carbon footprint. There are two main types of carbon pricing mechanisms: carbon taxes and cap-and-trade systems.
A carbon tax directly sets a price on carbon by levying a tax on the carbon content of fossil fuels. This encourages businesses and consumers to reduce their use of carbon-intensive energy sources and shift toward cleaner alternatives. The revenue generated from carbon taxes is often used to fund green initiatives, such as renewable energy projects or energy efficiency programs, or to provide rebates to low-income households to offset higher energy costs.
Cap-and-trade systems, also known as emissions trading schemes (ETS), work by setting a limit (or cap) on the total amount of greenhouse gas emissions that can be emitted by covered entities, such as power plants or industrial facilities. Companies are issued emission allowances, which they can trade with one another. Companies that can reduce their emissions at a lower cost can sell their excess allowances to companies that face higher costs for reducing emissions. This creates a market for carbon allowances and incentivizes businesses to invest in cleaner technologies.
Both carbon taxes and cap-and-trade systems are designed to internalize the environmental cost of carbon emissions, making it more expensive to pollute and more profitable to invest in sustainable practices. These mechanisms can drive innovation, as businesses seek out new technologies and processes to reduce their carbon liabilities.
Several countries and regions have implemented carbon pricing policies with varying degrees of success. The European Union’s Emissions Trading System (EU ETS) is one of the largest and most established cap-and-trade programs in the world. Canada has implemented a nationwide carbon tax, with revenue returned to households through rebates. In the United States, some states, such as California, have implemented their own cap-and-trade programs in the absence of a national carbon pricing policy.
However, carbon pricing mechanisms face challenges, including political opposition and concerns about economic competitiveness. In some cases, businesses argue that carbon pricing increases costs and puts them at a disadvantage compared to competitors in countries without similar policies. To address these concerns, governments often include provisions to protect industries that are vulnerable to international competition, such as offering rebates or exemptions for certain sectors.
Green Transportation Policies
Transportation is a major source of greenhouse gas emissions, particularly in urban areas. To promote a green economy, governments are implementing a range of policies aimed at reducing emissions from the transportation sector. These policies focus on promoting the use of public transportation, encouraging the adoption of electric vehicles (EVs), and improving fuel efficiency standards.
One of the most effective ways to reduce transportation emissions is to encourage the use of public transportation. Governments invest in expanding and improving public transit systems, such as buses, trains, and subways, to make them more accessible and attractive to commuters. By providing reliable and affordable public transportation options, governments can reduce the number of cars on the road and lower overall emissions.
In addition to improving public transportation, governments are offering incentives for the purchase of electric vehicles (EVs). These incentives often take the form of tax credits or rebates for EV buyers, which help offset the higher upfront cost of electric vehicles compared to traditional gasoline-powered cars. Some governments also offer additional perks for EV owners, such as access to carpool lanes or free parking in city centers.
Governments are also investing in the infrastructure needed to support electric vehicles, such as building charging stations. A lack of charging infrastructure is often cited as a barrier to EV adoption, so governments play a critical role in addressing this challenge. By providing grants or partnering with private companies, governments can help build a network of charging stations that makes EVs a more convenient option for drivers.
Another important component of green transportation policies is improving fuel efficiency standards for cars and trucks. Governments set regulations that require automakers to produce vehicles that meet certain fuel efficiency targets, which helps reduce the amount of fuel consumed and the emissions produced by the transportation sector. Some governments also implement vehicle emissions standards, which limit the amount of pollutants that cars and trucks can emit.
In addition to these policies, governments are encouraging the use of alternative modes of transportation, such as biking and walking. Investments in bike lanes, pedestrian infrastructure, and bike-sharing programs make it easier for people to choose low-emission forms of transportation. These efforts not only reduce emissions but also improve public health by promoting physical activity.
Sustainable Agriculture Support
Agriculture is both a contributor to and a victim of environmental degradation. It is responsible for significant greenhouse gas emissions, deforestation, water use, and pollution from fertilizers and pesticides. At the same time, agriculture is highly vulnerable to the impacts of climate change, including more frequent droughts, floods, and changing weather patterns. As a result, governments are increasingly focusing on promoting sustainable agricultural practices as part of their green economy policies.
One of the key ways governments support sustainable agriculture is through financial incentives for farmers who adopt environmentally friendly practices. These incentives can take the form of subsidies, grants, or low-interest loans for practices such as organic farming, agroforestry, and conservation tillage. By providing financial support, governments encourage farmers to invest in sustainable practices that might otherwise be cost-prohibitive.
Governments also provide technical assistance and education to help farmers transition to more sustainable practices. This can include training programs on topics such as water conservation, soil health, and pest management, as well as access to research and technology that supports sustainable farming. Extension services, which provide hands-on assistance to farmers, are another important tool for promoting sustainable agriculture.
In addition to financial and technical support, governments implement regulations to reduce the environmental impact of agriculture. These regulations can include restrictions on the use of certain pesticides and fertilizers, requirements for buffer zones to protect water sources from agricultural runoff, and mandates for the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions from livestock and manure management.
Governments are also working to promote more sustainable food systems by encouraging the consumption of locally produced and organic foods. Public procurement policies, which require government institutions such as schools and hospitals to purchase a certain percentage of their food from sustainable sources, are one way governments support the development of local, sustainable food systems.
Another important aspect of sustainable agriculture policies is protecting biodiversity and promoting ecosystem services. Governments often provide incentives for farmers to preserve natural habitats on their land, such as wetlands, forests, and grasslands, which provide important ecosystem services such as carbon sequestration, water filtration, and pollination. By promoting biodiversity and ecosystem health, governments help ensure that agricultural systems are more resilient to environmental changes.
Waste Management and Recycling Regulations
Effective waste management is a critical component of a green economy. Governments play a key role in regulating waste disposal, promoting recycling, and encouraging the reduction of waste generation. These efforts are aimed at reducing the environmental impact of waste, including greenhouse gas emissions from landfills, pollution from improper disposal, and the depletion of natural resources through excessive consumption.
One of the main ways governments regulate waste is by setting standards for waste disposal. This includes regulating landfills, incinerators, and hazardous waste facilities to ensure that they operate in an environmentally responsible manner. Governments also implement bans or restrictions on certain types of waste, such as single-use plastics, to reduce the amount of waste that ends up in landfills or the environment.
In addition to regulating waste disposal, governments are increasingly focusing on promoting recycling and waste reduction. Many governments have implemented extended producer responsibility (EPR) programs, which require manufacturers to take responsibility for the disposal of the products they produce. This can include requirements for companies to fund recycling programs or take back products at the end of their life cycle.
Governments also implement policies to encourage households and businesses to recycle more. This can include providing curbside recycling services, setting recycling targets, and offering incentives for recycling, such as deposit return schemes for beverage containers. Public awareness campaigns and education programs are also important tools for promoting recycling and waste reduction.
In some cases, governments use economic instruments to promote waste reduction, such as charging fees for waste disposal or providing financial incentives for businesses that reduce waste. Pay-as-you-throw programs, which charge households based on the amount of waste they generate, are one example of how governments use pricing mechanisms to encourage waste reduction.
Another important component of waste management policies is promoting the circular economy, which focuses on keeping materials in use for as long as possible through recycling, reusing, and remanufacturing. Governments support the circular economy by providing incentives for businesses that adopt circular practices, such as designing products for durability and recyclability, and by setting targets for reducing waste and increasing recycling rates.
Source :
Government Policies for a Green Economy: Incentives and Regulations
#Carbon Pricing Mechanisms#Circular Economy Policies#Clean Energy Subsidies#Climate Change Mitigation Strategies#Climate Resilience Planning#Community Sustainability Programs#Eco-Friendly Transportation Initiatives#Eco-Tourism Development Strategies#Energy Efficiency Standards#Environmental Policy Frameworks#Environmental Protection Regulations#Government Grants For Green Projects#Government Policies For A Green Economy#Green Building Regulations#Green Job Creation Initiatives#Green Tax Incentives#Incentives For Energy Audits#Incentives For Sustainable Development#Investment In Green Technologies#Low-Emission Vehicle Incentives#Pollution Control Policies#Public Transport Expansion Regulations#Regulations Promoting Renewable Energy#Renewable Energy Certificates#Smart City Regulations#Sustainable Agriculture Policies#Sustainable Forestry Practices#Sustainable Urban Development Policies#Waste Management Policies#Water Conservation Regulations
1 note
·
View note
Text
USA please listen to me: the price of “teaching them a lesson” is too high. take it from New Zealand, who voted our Labour government out in the last election because they weren’t doing exactly what we wanted and got facism instead.
Trans rights are being attacked, public transport has been defunded, tax cuts issued for the wealthy, they've mass-defunded public services, cut and attacked the disability funding model, cut benefits, diverted transport funding to roads, cut all recent public transport subsidies, cancelled massive important infrastructure projects like damns and ferries (we are three ISLANDS), fast tracked mining, oil, and other massive environmentally detrimental projects and gave the power the to approve these projects singularly to three ministers who have been wined and dined by lobbyists of the companies that have put the bids in to approve them while one of the main minister infers he will not prioritise the protection of endangered species like the archeys frog over mining projects that do massive environmental harm. They have attacked indigenous rights in an attempt to negate the Treaty of Waitangi by “redefining it”; as a backup, they are also trying to remove all mentions of the treaty from legislation starting with our Child Protection laws no longer requiring social workers to consider the importance of Maori children’s culture when placing those children; when the Waitangi Tribunal who oversees indigenous matters sought to enquire about this, the Minister for Children blocked their enquiry in a breach of comity that was condemned in a ruling — too late to do anything — by our Supreme Court. They have repealed labour protections around pay and 90 day trials, reversed our smoking ban, cancelled our EV subsidy, cancelled our water infrastructure scheme that would have given Maori iwi a say in water asset management, cancelled our biggest city’s fuel tax, made our treasury and inland revenue departments less accountable, dispensed of our Productivity Commission, begun work on charter schools and military boot camps in an obvious push towards privatisation, cancelled grants for first home buyers, reduced access to emergency housing, allowed no cause evictions, cancelled our Maori health system that would have given Maori control over their own public medical care and funding, cut funding of services like budgeting advice and food banks, cancelled the consumer advocacy council, cancelled our medicine regulations, repealed free prescriptions, deferred multiple hospital builds, failed to deliver on pre-election medical promises, reversed a gun ban created in response to the mosque shootings, brought back three strikes = life sentence policy, increased minimum wage by half the recommended amount, cancelled fair pay for disabled workers, reduced wheelchair services, reversed our oil and gas exploration ban, cancelled our climate emergency fund, cut science research funding including climate research, removed limits on killing sea lions, cut funding for the climate change commission, weakened our methane targets, cancelled Significant National Areas protections, have begun reversing our ban on live exports. Much of this was passed under urgency.
It’s been six months.
18K notes
·
View notes
Text
Big Changes to Singapore’s Welfare System: What Every Family Needs to Know!
The Singapore government has rolled out several key welfare initiatives aimed at improving support for the elderly, expanding housing grants for low-income families, and strengthening family welfare programs. These changes will provide increased financial aid in areas like healthcare, housing, and childcare, ensuring that vulnerable groups in society have better access to essential…
#childcare subsidies#elderly support Singapore#family welfare programs#government grants Singapore#healthcare assistance Singapore#housing grants#low-income families#Singapore welfare 2024#social safety net#welfare policy changes.
0 notes
Text

Adding this word to my list of Words That Actually Mean Money For Artists.
Grant
Commission
Subsidy
Fellowship
Residency
Honorarium
Development
Support
Collaboration
Sometimes these words are used because they have a specific meaning, like Residency = a free place for an artist to live for a while without paying money for rent.
Other times it seems like these words are used by people who are afraid to talk about money directly. If you are an artist, when you see any of these words, just replace them with the word money in your mind, so it is easier to understand clearly.
#words that actually mean money for artists#grant#commission#subsidy#residency#honorarium#development#support#collaboration
1 note
·
View note
Text
Barrie CDAP Assistance

Transform your Barrie business with Barrie CDAP Assistance's CDAP digital strategies.
Contact us:
Barrie, Ontario
(705)413-3751
#CDAP#Canada Digital Adoption Program#Small Business Loan#Small Business Grant#$15k Business Grant#$100k Business Loan#SME Grant Canada#SME Loan Canada#Government Business Loans#Canadian Government Loan#BDC Canada Loan#BDC Canada Grant#Canada Digital Advisor#Canadian Business Funding#Government Business Grant#$15000 CDAP Business Grant#$100 000 CDAP Business Loan#$7 300 Wage Subsidy Canada#Interest Free Business Loan#Technology Business Grant#Technology Business Loan#Barrie Business $100 000 Loan#Barrie Business $15 000 Grant
1 note
·
View note
Link
The Startup SG Founder, Startup SG Tech and Start Digital are some of the government grants and subsidies to apply for when starting a business in Singapore
0 notes
Text
"Cody Two Bears, a member of the Sioux tribe in North Dakota, founded Indigenized Energy, a native-led energy company with a unique mission — installing solar farms for tribal nations in the United States.
This initiative arises from the historical reliance of Native Americans on the U.S. government for power, a paradigm that is gradually shifting.
The spark for Two Bears' vision ignited during the Standing Rock protests in 2016, where he witnessed the arrest of a fellow protester during efforts to prevent the construction of the Dakota Access Pipeline on sacred tribal land.
Disturbed by the status quo, Two Bears decided to channel his activism into action and create tangible change.
His company, Indigenized Energy, addresses a critical issue faced by many reservations: poverty and lack of access to basic power.
Reservations are among the poorest communities in the country, and in some, like the Navajo Nation, many homes lack electricity.
Even in regions where the land has been exploited for coal and uranium, residents face obstacles to accessing power.
Renewable energy, specifically solar power, is a beacon of hope for tribes seeking to overcome these challenges.
Not only does it present an environmentally sustainable option, but it has become the most cost-effective form of energy globally, thanks in part to incentives like the Inflation Reduction Act of 2022.
Tribal nations can receive tax subsidies of up to 30% for solar and wind farms, along with grants for electrification, climate resiliency, and energy generation.
And Indigenized Energy is not focused solely on installing solar farms — it also emphasizes community empowerment through education and skill development.
In collaboration with organizations like Red Cloud Renewable, efforts are underway to train Indigenous tribal members for jobs in the renewable energy sector.
The program provides free training to individuals, with a focus on solar installation skills.
Graduates, ranging from late teens to late 50s, receive pre-apprenticeship certification, and the organization is planning to launch additional programs to support graduates with career services such as resume building and interview coaching...
The adoption of solar power by Native communities signifies progress toward sustainable development, cultural preservation, and economic self-determination, contributing to a more equitable and environmentally conscious future.
These initiatives are part of a broader movement toward "energy sovereignty," wherein tribes strive to have control over their own power sources.
This movement represents not only an economic opportunity and a source of jobs for these communities but also a means of reclaiming control over their land and resources, signifying a departure from historical exploitation and an embrace of sustainable practices deeply rooted in Indigenous cultures."
-via Good Good Good, December 10, 2023
#indigenous#native americans#first nations#indigenous rights#tribal sovereignty#solar energy#solar power#solar panels#renewable energy#green energy#sioux#sioux nation#sustainability#climate hope#electrification#united states#hope#good news
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
Corruption in liberal democracies is one of those things that don't materially affect the working class unless it's a really, really massive corruption case, but what usually defines corruption (usage of public/state funds for private/non-state interests) is actually very inherent to the normal functions of a liberal democracy. What sets corruption apart is the benefit of an individual person, either a politician or a politician's family or friends. But the act itself of allocating state funds for "corporate" interests is very legal and publicized all the time. It's the investment in private research, the granting of public works projects such as infrastructure to companies, the uncountable number of grants for every kind of small business endeavor under the sun. This is little more than the class character of the bourgeois state in its normal role of protecting, legitimizing and upholding the capitalist infrastructure. The only difference between this and "corruption" is the benefit being driven towards an individual instead of the capitalist class itself. And in comparison to individual cases of corruption, the amounts of money transferred to the pockets of the capitalist class, even if unimaginably large for you and I, for workers, always shrink in comparison to the hundreds of millions liberal democracies allocate in their budget towards grants, subsidies, investments, semi-atate enterprises, etc.
252 notes
·
View notes
Text
Major grant for British bio-input company will boost African agriculture
Providing sub-Saharan smallholders with a cost-effective alternative to expensive artificial nitrogen fertiliser has come a step closer for British agri-biotech company Legume Technology, following the award of a grant from The Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation and the UK’s Foreign, Commonwealth & Development Office (FCDO). The Nottinghamshire company, which has been working on microbial…
#Agri Innovation#Agriculture#AgriFood Capital#AgriFood Science#AgTech#Biofertilizers#Biologicals#Fertilisers for Farming#Food and Agribusiness#Grant and Subsidies#Startups#Sustainable Agriculture
1 note
·
View note
Text
Dandelion News - January 22-28
Like these weekly compilations? Tip me at $kaybarr1735 or check out my Dandelion Doodles!
1. Sunfish that got sick after aquarium closed has recovered — thanks to human cutouts

“A solitary sunfish […] appeared unwell days after the facility closed last month for renovations. As a last-ditch measure to save the popular fish, its keepers hung their uniforms and set up human cutouts outside the tank. The next morning, the sunfish ate for the first time in about a week and has been steadily recovering[….]”
2. Costco stands by DEI policies, accuses conservative lobbyists of 'broader agenda'

“[Each of the board of directors and 98% of shareholders voted to reject a measure against DEI.] Costco's board wrote that “our commitment to an enterprise rooted in respect and inclusion is appropriate and necessary[….]””
3. Nearly $37 Million Will Support Habitat Restoration in Coastal Louisiana

“The project will restore nearly 380 acres of marsh and construct more than 7,000 feet of terraces in St. Bernard Parish. […] Coastal wetlands help protect communities [… from] wind, waves, and flooding[… and] support a statewide seafood industry valued at nearly $1 billion per year.”
4. Cooling green roofs seemed like an impossible dream for Brazil's favelas. Not true!

“[… A Brazilian nonprofit] teaches favela residents how to build their own green roofs as a way to beat the heat without overloading electrical grids[…,] dampen noise pollution, improve building energy efficiency, prevent flooding by reducing storm water runoff and ease anxiety.”
5. Bacteria found to eat forever chemicals -- and even some of their toxic byproducts
“"Many previous studies have only reported the degradation of PFAS, but not the formation of metabolites. We not only accounted for PFAS byproducts but found some of them continued to be further degraded by the bacteria," says the study's first author[….]”
6. A father and daughter’s to turn oil data into life-saving water

“The aquifer [discovered through oil-owned seismic data], it turned out, was vast enough to provide water for 2 million people for more than a century.”
7. Trump’s funding pause won’t impact federal student loans, Pell Grants
“[… T]he temporary pause will not impact “assistance received directly by individuals,” including federal direct student loans and Pell Grants, which are government subsidies that help low-income students pay for college.”
8. In Uganda, a women-led reforestation initiative fights flooding, erosion

“[… T]he Kasese municipality has established nurseries to provide free tree seedlings, particularly to women, to support reforestation efforts. [… They] plant Ficus trees near their homesteads to provide shade and help control erosion, and Dracaena trees on their fields to retain soil moisture.”
9. [A Texas school board] votes yes to provide low-cost housing to staff at no cost to the district

“The program will include 300 homes[…] only a short commute to campuses. […] Rent will be determined on a sliding scale based on their salaries, with those making less receiving a larger discount. The proposed community would include amenities, like childcare facilities[….]”
10. Heat pumps keep widening their lead on gas furnaces

“Americans bought 37% more air-source heat pumps than the next-most-popular heating appliance, gas furnaces, during the first 11 months of the year. That smashes 2023’s record-setting lead of 21%.”
January 15-21 news here | (all credit for images and written material can be found at the source linked; I don’t claim credit for anything but curating.)
#hopepunk#good news#fish#sunfish#mola mola#aquarium#us politics#costco#dei#diversity equity and inclusion#louisiana#habitat restoration#green infrastructure#brazil#global warming#science#forever chemicals#recycling#water#water scarcity#big oil#student loans#federal aid#reforestation#gardening#low income#affordable housing#housing#school#heat pump installation
124 notes
·
View notes
Text
If you or anyone you care about is relying on:
Food stamps/SNAP/EBT
SSI/SSDI/social security
a tax refund not yet received as of May 2023
a government employee salary
Medicaid
Medicare
Pell grants that have not yet been disbursed
Or anything else paid out by the US federal government—
You need to be aware of what's happening with the debt ceiling!
Because any or all of the items listed above might not be funded right away in June 2023.
The US government is increasingly looking like it will run out of money on or around June 1st, and no one has yet made the rules about which bills WILL get paid when that happens.
The usual way the gov stops this from happening is being blocked by Republicans who insist they won't let the problem be fixed until programs keeping people alive are cut. (They won't cut corporate subsidies though.)
You and people you care about could be impacted by this.
Please save back any money you can, fill your prescriptions now, and look up news about the debt ceiling.
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
Henry and Simon’s dynamic over the three seasons
For YR Faves Fest 2024 organised by @youngroyals-events Prompts: 2. Favourite teen side character (+ 7. Favourite not-quite friendship)
In one of my replies to the recent side character ask game, I briefly mentioned being partial to the dynamic between these two. So for this Faves Fest, I decided to elaborate with an analysis post (featuring screenshots of variable quality)!
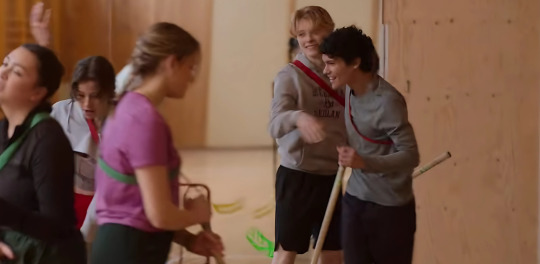
I want to preface this with a brief acknowledgment of Henry’s privilege and classism. It is not my intention to diminish them. I do, however, feel that it’s a bit apples-to-oranges to compare them to Simon’s views (citrus pun intended). 🍊 is politically active and has put in the effort to form his own beliefs, while 🍏 shows us time and again that he is ignorant of the world outside the elite bubble and not inclined towards deep reflection. He is largely a product of his upbringing and the (liberal conservative) values imparted by his parents.
While Henry doesn’t grow enough to change his core views and values in the canon timeline, he does change his views on Simon. This isn’t enough progress for them to become actual friends before we leave off (I doubt Simon could be friends with someone who only exempts him), but I would still argue that they end the show on amicable terms.
And yes, I mean that in a mutual sense, even if Simon doesn’t soften towards Henry quite as much as Henry softens towards him!
So, let’s dive in!
Dialogue taken from the English CC and [abbreviated or corrected].
1.01: the tax debate
Henry: “Take my dad’s estate, for example. They’re struggling to make ends meet because of the high taxes.” [Simon chuckles and explains his views] Simon: “Like your dad. [Do you know how much he gets in EU subsidies every year]”? Henry: “And what the fuck does your dad do?”


Like most viewers, I find it a lot easier to relate to Simon’s views than Henry’s here – but I do think Henry often gets judged quite harshly for insulting Simon at the end. His comment does not come out of nowhere (cf. Stella’s unprompted dirty look at Simon and Sara when she talks about welfare scamming).
Henry only knows that his father has said their estate is struggling, so of course he won’t take kindly to Simon suggesting that they are actually getting undeserved subsidies instead. It’s also important to note that this estate isn’t just any old farm. It was granted to one of his ancestors as a reward for their services to the Crown, which makes it a core part of his family history. As we learn in 1.04, Henry is a Society boy and very proud of his noble ancestry, and Simon’s comment likely feels like an insult to his entire family. So although his retort is unquestionably rude, it is understandable that he lashes out.
Also, Henry has no way of knowing that Micke is a deadbeat. He is just applying a common stereotype (and potentially making assumptions based on the views Simon just expressed on welfare).
1.02: parallel but separate experiences

Early in this episode, we see Simon side-eye Henry and Walter for the paid tutoring. He decides to follow their example, but as we know he can’t actually afford it, we can already guess it won’t go as well for him as it did for them.
Next, we see Henry in the group as the rowing team ignores Simon at morning training. The camera also pans to him and Walter when August gives that bizarre speech about Simon’s class journey.
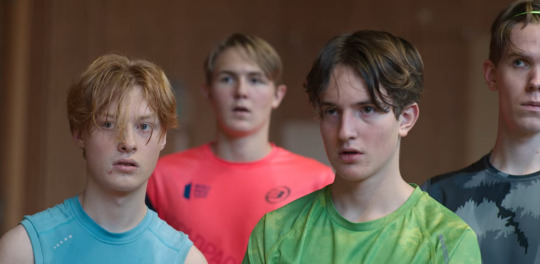
These moments highlight how different life at Hillerska (and beyond) looks for Henry and Simon. They are technically coexisting and even doing the same things, but their experiences are nothing alike.
However, there is also some potential for development here. August’s words about rowing bringing people together (and also about the class journey) should absolutely be taken with a heap of salt, but as we no longer see any open animosity between Henry and Simon, we can still wonder if rowing played a part.
Being on the same sports team is an entirely new frame of reference for these guys. They are no longer just the sosse and aristocrat who have been going to school together since pre-canon and clashing over their views; they are crewmates. They may be able to ignore each other for most of the time, but they may also have to do some team activities or even cooperate on occasion. At the very least, they will be around each other several extra times a week from late September/early October to Christmas break. This could definitely help to put them on more neutral ground.
1.05: Henry pays attention to Wilmon
In this episode, Henry learns more about Wilmon than the average Hillerska student knows. He is present when August tells the Society that Wille and Simon “hang out”, and also when Wille changes the plan from Simon to Alexander.
What’s more, he actually looks fairly thoughtful leaving that last meeting. We don’t know if it’s just shock over Wille’s ruthlessness, if he’s thinking about the plan to set up Alexander, or if there’s something else on his mind.

Now, this may veer into overinterpretation, but for the sake of thoroughness, let’s also include the blink and you’ll miss it moment before the Lucia procession where Henry notices Wilmon texting each other. In this cropped screenshot, you can see him looking at Simon, who has just put his phone down and is looking over at Wille.

1.06: Henry shows restraint
As we know, Henry is the only classmate who tries to treat Wille normally after the video, asking if he “saw the match yesterday” (he absolutely knows Wille didn’t). What is perhaps less noticeable is that he also shows more restraint than most of his schoolmates when the rumour mill gets going.

In this scene, Henry is pretty dispassionate reminding Walter that Wilmon sat next to each other at movie night and the two of them talked about it. There is a stark contrast to Walter, who absolutely pounces on that bit of gossip.
This one quick scene could just be a coincidence, but the same thing happens again when Wilmon return to school. Instead of engaging with the others who are all eagerly talking and whispering, Henry is already sitting at his desk minding his own business when Wille arrives. His only reaction to Simon showing up is this quick look, which is immediately followed by his show of kindness to Wille:

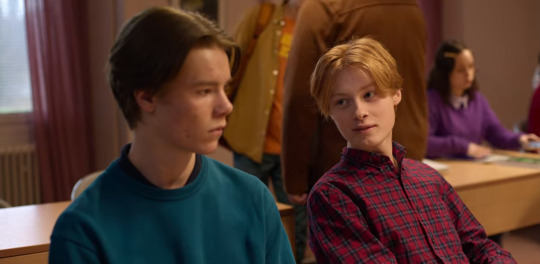
So the restraint does look very intentional.
As an aristocrat, monarchist and Society boy, Henry is loyal to Wille, who he now knows has been carrying on with Simon for a while already. He also knows how far Wille went to protect Simon, despite the fact that Simon had actually supplied the drugs, so he is going to side with Wille.
What’s more, Henry’s behaviour in these scenes also confirms that he isn’t hostile to Simon. We can surmise he probably doesn’t think Simon is the most appropriate choice of partner for the crown prince, but he is willing to take his cues from Wille. We never see him sneer, joke, or say anything nasty about Wilmon as a couple (cf. Stella and Fredrika joking about surrogacy).
We are also shown his reaction to Wille hugging Simon before we move on to season two.

2.02: the floorball hug and walk-by
The first interaction between Henry and Simon in S2 is them celebrating a floorball goal with a spontaneous hug, as seen at the top of this post. What a difference a term makes!
Now, I don’t think this moment is meant to signify that they are friends all of a sudden, and I do feel it comes slightly out of the blue. I suspect it was included as a nod to those who already liked Henry after S1, but I for one would’ve preferred to actually see their reconciliation.
But then again, if their initial antagonism was always class conflict rather than personal beef, maybe there was no need for apologies…? Maybe each of them just accepted that the other was going to be around and decided to try and get along (potentially aided by their shared rowing team history)? Henry is following Wille’s lead as we already saw – and as for Simon, I doubt he would be hugging Henry even in the heat of a game if he held a grudge. Whether we saw it or not, they have moved on.
In the same episode, we also have the locker room scene.

Contrary to popular opinion, I don’t believe Henry actually overhears the entire conversation, but he may have still heard something about them having to wait two years (as Simon did raise his voice for that). It’s also possible he comes out of this scene assuming that Wilmon still “hang out” in secret. In any case, he probably assumes that Wille wants to keep the whole thing quiet, as per the usual “policy” on queer relationships among the upper classes. In addition to his monarchist ways, he also seems to be casually friendly with Wille in S2 (keeps inviting him to do stuff, from coffee to pranking Sprucewood). So it makes a lot of sense for him to keep whatever he overhears or suspects to himself.
2.03, 2.05 and 2.06: book report scenes
While Henry must be a nightmare to have in the group, he and Simon are nice to each other in all the book report scenes. This is further proof that they are in a place where they can talk civilly and even work together.
They start the project before the rowing race and only present it the day before the gun range scene, which means they had these group sessions for at least a few weeks (the timeline is a bit wonky here).

2.04: Henry snitches on Wille and Felice
The lunch scene at the start of the episode starts with this bit of vicarious interaction, as Henry and Simon (and Wille too) are amused by the nonsense Walter is spouting about girls:

Also, Walter's monologue feels more comphet every time rewatch it, but I digress.
As this post is focused on Henry and Simon, I’m not going to dig too deep into Henry’s role in spreading the story about Wille and Felice. Suffice it to say that he did tell his canonically gossipy bestie Walter, and it was recently pointed out to me that he seems to have let something slip to someone else as well. In the common room, Walter goes “det var du som sa till…” [you were the one who said to…] just as the focus shifts to Wille and Nils, which suggests that Henry either purposely told someone or misspoke without realising it. The latter would explain why he seems genuinely appalled when Wille confronts him, but it’s not a hill I’d be willing to die on!
If Henry did spread the story on purpose, I assume it was because getting with Felice was considered a credit to Wille and also “fair game” to tell, unlike the relationship with Simon that Wille wanted to keep hidden.
Still, Henry and Simon are definitely on better terms in S2. Even though Henry inadvertently causes pain to Simon with his part in the Wille and Felice thing, they still keep working together on the book report without any animosity.
Insofar as Henry’s lacklustre effort can be called working. Simon is a bigger person than I am for not blowing up at him when he announces minutes before the presentation that he won’t be taking any questions.
3.01: background Henry
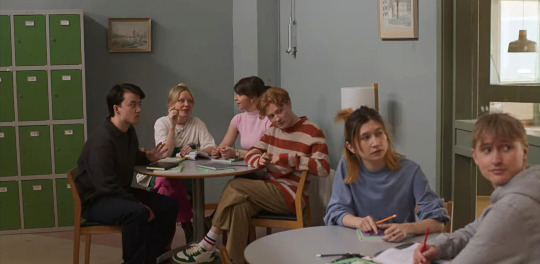
We start S3 off with this one-sided interaction where Henry reacts to Wilmon kissing with a mild smirk. No more waiting or secrets to keep.
3.02: double standards on the camping trip

It’s not entirely clear what Henry is thinking when he says the infamous line about gay couples being allowed to share but not straight ones. I think some people read it as him deliberately putting Wilmon on the spot, but personally, I doubt he even realises it’s going to make them uncomfortable. He’s just noticing the double standard and pointing it out to mess with the teacher.
While Simon is very clearly not pleased with Henry for the comment (glares at him while saying to Wille that people are going to think they plan to have sex), he does not seem to hold that against him. Because what we do see them doing soon?
Sitting next to each other by the fire, even though Henry could’ve easily sat with Walter and Simon with Wille:

Also, it seems Henry isn't new to camping, as he tells Wille that part of the fire is too hot to grill a sausage in.
The part where things get interesting is when Henry acts classist towards the Marieberg students.
Henry seems to be down with meeting Rosh and Ayub, who are there as Wille and Simon’s friends. But after Fredrika brings up New York, he agrees that the situation turned “stiff as fuck.” That stiffness was entirely Fredrika’s fault (I think she is at least semi-consciously trying to mark herself as the most compatible partner for Stella there), but Henry seems to feel it was more about Rosh and Ayub not fitting in.
He also sneers and makes nasty comments when the other Marieberg students get into an altercation with Malin, which elicits a frown from Simon.

And yet, Simon does not condemn Henry as strongly as he might have done in the past.
Importantly, Simon tells Wille “it wasn’t the right time for everyone to meet.” This indicates that he could’ve imagined them all getting along at a better time, and it’s pretty clear that also includes Henry. Furthermore, “you [meaning Wille and the others] don’t realise how privileged you are sometimes” is actually a pretty neutral way of putting it. Simon would have been entirely justified if he had said the others were classist pricks, but he blames their privilege and lack of understanding instead of their character.
All of this forms a backdrop for my interpretation of the scenes in the next episodes.
3.03: First of May
Simon: “You do know that you’re not off so you can party the day before, right?” Henry: “Uhh…what?” Simon: “It’s the First of May.” […] “The day of the labour movement?” Henry: “Okay, so what’s their style? How do they celebrate?” Simon, scoffing: “You don’t celebrate. You demonstrate.” [Henry and Walter share a chuckle]
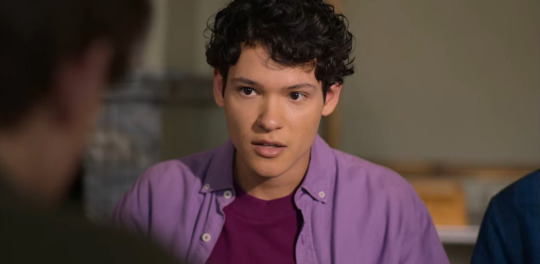


This may be a controversial take, but I don’t think Henry is being particularly nasty to Simon here.
He actually looks and sounds quite sincere asking how the labour movement celebrates. When he and Walter laugh, it reads more as “there he goes again, our very own sosse, saying wacky things!” than the kind of disdain he expressed towards the Marieberg students in the last episode.
Simon also doesn’t take the laughter as an insult; he’s just stupefied by their ignorance. Also, note that he already scoffed at Henry’s question, marking the question as silly.
This exchange is immediately followed by Vincent attacking Simon for his beliefs, which feels like an intentional trick to create contrast between his and Walty’s treatment of Simon.
3.04: the lollipop


In this scene, Henry starts out asking quite nicely and seriously if Simon has another lollipop, as if they had that kind of rapport. Simon makes a face, but then he just shakes his head and nicely says no. It’s only then that Henry switches to offering money for the already half-eaten lollipop, to which Simon reacts with disbelief.
He does not, however, get snarky with Henry. He settles for exchanging a look with Wille as Walty go on to complain about the hunger strike. Only when Henry isn’t present anymore does he point out to Wille how ridiculous Henry was being.
In a sort of parallel to the lunch scene, Simon and Wille now share a chuckle at the wacky thing Henry said:

Feel free to disagree, but I actually wonder if this could be a common pattern between Simon and Henry. They have accepted that they aren’t going to see eye to eye on many things, but instead of getting into conflict, they just roll their eyes/laugh at how the other can seriously believe/say such things. Then they let the conversation move on to something else.
Which is a perfectly valid dynamic. They can acknowledge that their outlooks on life are wildly different without hating each other for it.
3:06: Henry includes Simon
Look, I dislike the library scene as much as the next person. The talk that Henry interrupts between Wilmon was so much more important than anything he could possibly say. It was just a moment of comic relief that didn’t add anything to the story.
Except… Now that we are tracing Henry and Simon’s “not-quite friendship” arc, this scene does give us a conclusion.
Henry: “Hi! Uh, what are you wearing tonight?” [He rambles on about clothes] Wille: “I don’t know if… If I’m coming.” Henry: “Okay…?” Simon: “I don’t know if I can come either.” Henry: “Oh come on, you two have to come!” [He rambles on about how much fun it will be] Simon: “Yeah, we’ll see. I have to go now.” Henry: “The point is that we have to be together! This is the only night we have together, maybe ever. [I mean, we are brothers!]”

In Swedish, Henry goes “vi är ju bröder” just as the music starts. This has been translated to “we are like brothers” in the English CC, which is already quite something, but the little word ju makes the original even stronger. It means that something is true, so instead of just saying they are like brothers, Henry is saying that is what they are.
(In the dub, there is an audible pause after like, so Henry is actually using it as a filler word. They should have put a comma in the CC to denote that.)
Given that Henry prefaces this ramble with “you two have to come” and barely stops to acknowledge Simon’s exit, there’s every reason to assume he is still talking about all of them. He is saying he considers himself, Wille, and also Simon part of the brotherhood that will be disbanded indefinitely come morning and wants them all to have one last night of fun together.
Simon never hears the brothers part and is of course frustrated with Henry for interrupting, but he still takes his leave on a casually friendly note. He gets that Henry wants him to come and have fun (Henry is unaware that Simon doesn’t drink when he tries to persuade them both by talking about the alcohol). Thus, Simon politely says “we will see” even though he has zero intention of going.
We do not see them interact at the party when Simon goes after all, but we do hear Henry being ushered away when Simon comes to talk to Wille. We don’t see it’s Henry, but someone insists that he wants to stay just as we see Walter and Alexander leave, and all three of them were there moments before:
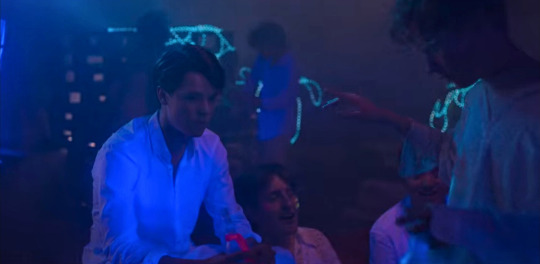
I’m tempted to end this with a parallel to Wille’s initiation party.
Way back in 1.01, Henry and Simon were explicitly shown discussing the first party with their friends. They never talked about it with each other or interacted there – Henry attended as part of the in-crowd, and Simon only got to go because he supplied the alcohol. But for this last party, Henry was the one to get the alcohol, and he specifically invites Simon to come. They still don’t hang out as they are both there with their respective friends, i.e. in their own bubbles, but those bubbles do bump into/brush past one another without clashing.
Kind of like Henry and Simon’s lives.
Thank you for reading this marathon post! I hope my take on these two brings something to your next rewatch, whether you agree with me or not!
#young royals#henry young royals#simon eriksson#young royals analysis#henry and simon#yr faves fest#yr events#YRFavesFest2024#long post#with pictures!#wish i had the energy to write something new about these two#scheduled post#young royals meta
115 notes
·
View notes
Text


Israeli officials also claim Rwanda and Congo have agreed to accept thousands of displaced Palestinians
We will see if both countries refute this claim as well
#yemen#jerusalem#tel aviv#current events#palestine#free palestine#gaza#free gaza#news on gaza#palestine news#news update#war news#war on gaza#republic of chad#rwanda#congo
289 notes
·
View notes