#Gracchi brothers
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
It's the late Roman Republic...
Now put in the tags what you selected and who you THINK it's referring to... Because I sneakily had at least two people in mind when I made each option and when the poll is over I'll reveal who I had in mind for each option
#roman history#ancient rome#roman empire#how often do you think about the roman empire#ancient history#julius caesar#pompey#augustus#pompeius magnus#caesar#the roman empire is my roman empire#lucullus#crassus#Marius#gaius marius#marian reforms#sulla#pompey the great#mark antony#brutus#Hamilton#and peggy#lepidus#marcus agrippa#sextus pompey#octavian#the Gracchi#Gracchi brothers
173 notes
·
View notes
Text
what kinds of music i think each roman statesman would listen to: (as someone who listens to a wild range of genres)
caesar: 2000s pop, britney spears, rihanna, jason derulo etc. (not even gonna mention kesha, but you know the song) + chapel roan (rip julius caesar you would have loved “after midnight”)
pompey: taylor swift, his favourite eras are lover and red ❤️
crassus: idk like classical or smth
mark antony: specifically tumblr girls by g-easy, also anything by blackbear/keshi/dominic fike
cicero: soft pop girlies, beabadoobee, clairo, pinkpantheress. he listens to these bc tullia introduced him to them, and so he likes them bc she does
cato the younger: folk girlies, phoebe bridgers (i feel like he would like the punisher album), lucy dacus, adrianne lenker + hozier
brutus: carti, uzi, juice wrld. he’s always talking abt how much he misses cash carti and luv is rage 2 uzi from 2017 for nostalgia
octavian: like chase atlantic, but like in a derogatory way (not in the cute “falling” or “call me back” way) but like in the kind of cringe “swim” or “church” way. he also sometimes listens to agrippa’s lana songs but he likes romanticizing the evil ones abt toxic shit and shitty men
agrippa: forced to listen to octavian’s chase atlantic, but likes the cute songs like “falling” and “call me back” and “cassie” but as to his actual music taste he listens to lana del ray but in the sad way
gracchi brothers (they come as a set): rnb, they’re still waiting for frank ocean to drop another album and everyone’s telling them it’s not going to happen but they won’t believe it, they also like brent faiyaz and H.E.R.
sulla: i feel like he would listen to badass country girlies (i know nothing abt country music don’t ask me why i think this i just do)
clodius: charli xcx (loved brat summer), sabrina carpenter, tinashe (cue “is somebody gonna match my freak”). permanently in club hoe phase
#idk if this is something but i was thinking abt this and i had to share#roman empire#ancient rome#ancient civilizations#classics tag#the classics#julius caesar#agrippa#octavian#cicero#crassus#sulla#cato the younger#pompey#brutus#gracchi brothers#mark antony
13 notes
·
View notes
Text
someone at work made a joke about the “how often guys think about the Roman Empire” thing, and asked me what I think about that often. I don’t think she was expecting the answer to be: The Roman Empire.
#but seriously#a lot#though for me it is more likely to be either the roman republic or the far reaches of the empire#the second punic war occupies a lot of my mental attic#as do the gracchi brothers#and how much i hate cicero as a human being#and also roman occupied britain and how frustratingly little we actually know about it#and tacitus’ weirdness about the germans#…i just think about rome a lot is what i am saying
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
The coming ides of March may have instilled in me a spirit of thinking about monarchies
#like the people loved Caesar but the senate hated him because the republic had been rotten for years#Caesar was a dictator (Roman) but making the republic an empire was probably the best thing that could have happened#thing was falling apart from what I understand#Caesar didn’t doom the republic as much as the fuckers standing against the gracchi brothers did#i don’t know if that’s how you spell it but it’s fine#anyways I have feelings about rome and also about the demonisation of all forms of monarchy#feel like I’m gonna get hanged in public for that but like my interest in worldbuilding#has taken me into learning way too much about statecraft#sometimes it might be better to be able to behead a king rather than people blaming eachother for things oligarchs vote into being#anyways if a single person asks I’ll share a fun idea for a government that won’t ever happen#risks of this post getting deleted in future? moderate
5 notes
·
View notes
Text

On point commentary @toaarcan
Look, as much as I love celebrating Caesar’s death as the next Tumblrina, there’s an element to this that I think we need to address. About Caesar, about his assassination, about our reaction to it.
It didn’t work.
Killing Julius Caesar didn’t stop Rome from becoming an Empire. If anything it expedited the process. Because all the assassination did was turn Caesar into a martyr for his family and followers to turn into a standard to rally behind. The Republic fell, the Empire rose, and Caesar’s Assassination was the tipping point of it all.
In fact, there’s evidence Caesar had knowledge of the planned Assassination and went anyway, knowing what his death would turn him into. But why?
Fascists don’t get turned on by their followers when they die. They get turned on when they look weak.
By the time of his death, Caesar was sick. There’s evidence that he was incontinent and beginning to have mental problems. All in all, things that made him look weak.
I can’t say what would have happened in Brutus and the Senate had stayed their hand, but history would not have turned out the same way. Certainly, Caesar would not have been turned into a martyr with his assassination. If his followers had seen Caesar as he was, a shambling, dying, sick old man, would that have turned them on him? I can’t say.
The assassination of Julius Caesar isn’t a happy event, it’s a cautionary tale. I’m not saying this to ruin our Ides of March celebration, but I feel it needs to be said. Make Dictators look weak, and then stab them.
#another feather in my hats#I just read some books for classes last semester that said those exact things#some of them put the beginning of the end with the assassinations of the Gracchi brothers
6K notes
·
View notes
Text
if we ever get more information about Veritas Prime, it's probably going to lean more into the Roman Empire, but I foolishly cling to the hope it'll be Republic. I'll even take late Republic or early Augustan even if I'm so fucking tired of it
#Ryn plays Honkai Star Rail#I know I'm the odd one out for finding the Republic so interesting#like -- that is what I want to study as a historian#that or the Bronze Age#personally I think any of Scipios; the Gracchi brothers and Marius would make for good subjects of a tv series#if we wanna go back even further Horatius or Cincinnatus#probably not Coriolanus though...
0 notes
Text
Someday I will learn not to start essays on the day they are due.
#not an 11:58 essay this time#but it was at 11:11 which is a nice time#the gracchi brothers are so fun
0 notes
Text





























This is about brothers (and sisters): but this is about brothers who are trying to resurrect their brothers, this is about brothers who mourn, this is about brothers who drag the body of their dead brother around and plead, wait for me! don't go where I can't follow!
Antigone (Sophokles, trans. Frank Nisetich) || Elektra (Euripedes, trans. P Vellacott) || Joseph Gordon-Levitt (Interview with HuffPost) || Antigonick (Anne Carson) || detail from Antigone au chevet de Polynice (Benjamin-Constant) || Antigone (Sophokles, trans. Frank Nisetich) || Orestes (Euripedes, trans. Anne Carson) || Life of Cato Minor (Plutarch) || Oedipus at Colonus (Sophokles, trans. R Fagles) || Life of Lucullus (Plutarch) || detail from Cornelia, Mother of the Gracchi, Pointing to her Children as Her Treasures (Angelica Kauffmann) || Life of Lucullus (Plutarch) || Elektra (Sophokles, trans. Anne Carson) || Thebaid Book IX (Statius, trans. Jane Wilson Joyce) || detail from Orestes and Elektra || Oedipus at Colonus (Sophokles, trans. R Fagles) || Life of Crassus (Plutarch) || Orestes (Euripedes, trans. Anne Carson) || Magnus Pius: Sextus Pompeius and the transformation of the Roman Republic (Kathryn Welch) || The Phoenician Women (Euripides, trans. P Burian & B Swann) || Magnus Pius: Sextus Pompeius and the transformation of the Roman Republic (Kathryn Welch) || Antigone (Sophokles, trans. Frank Nisetich) || Nemean 10 (Pindar) || detail from Antigone Sentenced to Death by Creon (Giuseppe Diotti) || Nemean 10 (Pindar) || Cato the Younger: Life and Death at the End of the Roman Republic (F K Drogula) || App. BC 5.14.143 || Seven Against Thebes (Aeschylus, trans. A Hecht & H H Bacon) || Oresteia (Aeschylus, a new adaptation by R Icke)
195 notes
·
View notes
Text
So imagine that you're a little brother and your older brother is the biggest person in your life. You have a famous family with a famous grandfather and a famous mother and famous cousins and your brother is a soldier and a leader but actually what he is is a good man and imagine instead of following in the footsteps of your famous family you decide to be like your brother so you sign up to help him help people. He wants to give land to people who need it and food to people who are hungry. And imagine that this makes people so angry that they kill your brother, your brother, your BROTHER who just wanted to HELP PEOPLE.
And then imagine ten years later you get elected to the same office your brother held and you still want to be like him even though he's dead now. Imagine you're getting ready to give a speech proposing another law that will make the senate angry (last time they got angry they killed your brother) and imagine that instead of facing toward them you decide to face toward the people your brother wanted to help. The first time anyone had ever faced away from then in almost 500 years of history.
And the law you're proposing really will help people. It will make the justice system more fair and it will feed people (really really hungry people) and it will be a continuation of your brother's work (the work they killed him for) and imagine you do it anyways. And it passes.
And they kill you for it.
And you're dead (as dead as your brother) but your name (your brother's name) is written on stones all across your country. Those stones redistributed land. That land fed people. That land helped people. And those stones with your (brother's) name are going to sit there for a thousand years, two thousand years, and you'll still be dead but the stones will be there.
If I think too much about Gaius Gracchus I will cry
#you must occasionally sentimentalize history#not all the time#and not to the point you forget that all of these people were killers#but some killers are also little brothers#and you can't forget that either#classics#tagamemnon#gracchi
1 note
·
View note
Note
Were Danton and Camille really as close as almost every biography/novel/movie, etc. makes them out to be? For a long time I believed they were best friends, but I realize that I don't know much about what really happened (only that Camille mentioned him as a friend several times in his letters).
Sorry if a similar question has already been asked, and thank you for all your wonderful posts. I read each one with great interest.

Thank you! I’m throwing in their wives too for good measure.
As popular as the idea of Danton and Desmoulins being friends already before the revolution is among novelists (A Place of Greater Safety (1992) by Hilary Mantel, The Gods Are Thirsty (1996) by Tanith Lee) and even biographers (Danton (2012) by David Lawday, Georges-Jacques Danton (1987) by Frank Dwyer) I have not been able to discover any evidence indicating this to actually have been the case. The very first connection I’ve found between the two dates to December 12 1789, when Desmoulins for the very first time mentions Danton’s name in his recently founded journal Révolutions de France et de Brabant:
As I do not have the advantage of being from the illustrious Cordeliers District, I am addressing this motion [to make it forbidden to use the term Queen of the French in public acts] to it through this journal. I beg its worthy President M. d'Anton to propose it to the honorable members, to discuss it in their wisdom and address it to the fifty-nine others; I leave my motion on their desks, and I sign it... A Frenchman.
The second time Camille mentions Danton’s name in Révolutions de France et de Brabant is eleven numbers later (March 1 1790). In the number, Camille describes how he on February 24 for the very first time enters the Cordeliers district and enrolls himself as a member. The very same session, he, alongside Danton, Fabre d’Eglantine, Paré and Dufourny de Villiers are named commissioners for the editing of a report by the club requesting the construction of a building ”worthy the National Assembly” on the place of the destroyed Bastille. This is the earliest confirmed meeting between Danton and Desmoulins that I’ve been able to find.
By the end of the same month, in number 17 (March 20) and number 18 (March 29) of Révolutions de France et de Brabant, Camille loudly protests against the fact Danton (”this lustrous president of the Cordeliers district”) has been decreed under arrest by le Châtelet de Paris, accused of having threatened to ring the tocsin in order to mobilize the Faubourg Saint−Antoine for the defense of his district when the National Guard came by:
If you put on trial a citizen who has put forward an extravagant opinion in his district, you will therefore also have to put on trial, with much more reason, the judge who, in his company, has opined in an extravagant manner; it will therefore be necessary to hang the judge who will have sentenced to death an accused whom the majority will have absolved, since this judge will have approved the death of an innocent person, which is much worse than making an extravagant motion in a district.
Desmoulins brings up Danton in Révolutions de France et de Brabant a few more times throughout the rest of 1790, calling him both ”the lustrous Danton” (number 31, June 28, number 35, July 26) as well as the more bombastic ”the most robust athlete of the patriots, the only tribune of the people who could have been heard in the Champ-de-Mars, and with his voice rally the patriots around the tribune, the only man whose veto the aristocracy had to fear, and in whom it could have found both the Gracchi brothers and a Marius.” (number 44, September 27). When Danton in the fall is appointed judge at Saint-Germain, Camille celebrates (number 47, October 18):
The Philoctetes of Hercules, d’Anton, is also appointed judge at Saint-Germain. He is well worthy of sitting next to M. Le Grand de Laleu. Honor to the city of Saint-Germain! Based on these two choices we can only augur well for the others. I would be tempted to believe that our patriarch Robe did so many readings of his poem on the revolution there, that he inflamed all the voters with a patriotism which dictated to them these excellent choices. The Parisians, ungrateful, forgot in the elections Danton, and Abbé Fauchet, and Brissot, and Carra, and Manuel; but it seems that the surrounding districts were responsible for the recognition.
On December 27 1790 Danton, alongside twelve other well known ”patriots,” signed the Desmoulins couple’s wedding contract. He was however not present for the actual wedding ceremony two days later, something which I suppose could be read as implying he and Desmoulins were not that close yet. On the other hand, the way Desmoulins does describe his wedding witnesses in a letter to his father written five days later (”Péthion [sic] and Robespierre, the elite of the National Assembly, M. de Sillery who wanted to be there, and my two colleagues Brissot de Warville and Mercier, the elite among the journalists”), it almost sounds like he’s chosen them less out of friendship and more out of prestige, so maybe this doesn’t have to mean that much either… After the wedding, Camille and Lucile moved to Rue du Théâtre 1 (today Rue de l’Odeon 28) roughly a ten minute walk from the Dantons’ apartment on 20 cour du Commerce-Saint-André (today destroyed). The ease with which they would come and go between these two apartments will be seen through Lucile’s diary 1792-1793.
In number 63 (February 7 1791) of Révolutions de France et de Brabant, Camille celebrates the fact that ”the excellent patriot Danton” has become a member of the department of Paris — ”If there is only one patriot of this caliber in the 83 departments, all the projects of our enemies from within and without will fail against his firmness, his ascendancy, his vigilance and his incorruptibility.” In a letter to La Marck dated March 10 1791, Mirabeau claimed to ”have evidence Danton was behind (a fait faire) the latest number of Camille-Desmoulins,” which, regardless of whether the charge was true, suggests a certain closeness between the two at this point. In number 72 (April 11) Camille exclaims: ”how the true jacobin Danton made blush the adulators that his excellency had already found.” Two numbers after that (April 25), he celebrates Danton’s actions the 18th the same month, the day the royal family tried to leave for Saint-Cloud but was stopped by a mob. In the number, Camille writes that Danton told him how he on the day in question had found himself at the Department when Bailly and La Fayette came there to demand permission to proclaim martial law and order the National Guards to fire on the crowd surrounding the royal family if necessary. Danton had successfully intervened and reduced them to silence. Camille praises this move in the number:
Courage, dear Danton! how much the patriotic writers must congratulate themselves today, who fought with obstinacy to praise you, and constantly nominated you for the votes of the people. By the parallel of your tribunitian eloquence, of your incorruptibility, of your masculine courage, with the academic and lachrymatory sentences of the courtier Bailly and his telescope which would have made us fall into the well with the astronomer in a scarf, continue to cover with shame all the citizens who gave him votes due to your patriotism.
In the same number, Camille also attributed to Danton and Kersaint an address placing the blame on what had happened on the 18th not on the people, but on the king: ”The same day the department of Paris presented the king with an address, the first, perhaps, which was written in the style of a free people. Also, it had been written by Danton and Kersaint: [transcription of the address].” According to Danton (1978) by Normann Hampson, Camille is however mistaken here, as the address had actually been written by Talleyrand and Pastoret…
In the next number (May 2 1791) Camille writes the following, which I’m not sure how to interpret, but which Hervé Leuwers reads as assassins having been after both Camille, Danton and Fréron when the three were walking home a week earlier: ”I have learned that four assassins waited for me Tuesday evening (April 26), until midnight. Me, D’anton [sic] and the Orator of the People (Fréron).” In number 81 (June 18 1791) he lifts Danton, Garran de Coulon and Manuel as ”the candidates whom I would most strongly recommend to the 83 departments, for the next legislature.”
In number 82 (June 27 1791), Camille writes that, eleven o’clock in the evening of June 20, ”I was walking home from the Jacobins together with Danton and other patriots. We only saw but one patrol the whole way. Paris seemed so abandoned to me that night that I could not help but remark on it. One of us (Fréron according to Leuwers) who had in his pocket a letter which I will speak about, which warned him that the King had to leave that night, wanted to observe the castle, he saw M. Lafayette enter it at 11 o'clock.” The next morning, Paris woke up to the discovery that the royal family had indeed left the capital during the night. The very same day, Camille goes to the Jacobin club and arrives in the middle of Robespierre holding a speech about the current situation which moves him deeply. After him, Danton mounts the rostrum, and about the same time Lafayette enters the club. Danton delivers a speech blaming him for the king’s flight and asking he explains himself that Camille records in the journal. At the end of the speech, Alexandre Lameth rises to support Lafayette, recalling that he has always thought Lafayette would fall at the head of the patriots in case of a counter-revolution.
Danton came back to sit down next to me. Is it possible? I said to him. Yes, [he answered], and rising up, he confirmed that M. Alexandre Lameth had always said this to him about M. La Fayette. My blood boiled. I was tempted to cry out to Alexandre Lameth: you used very different language with me; and I declare that almost everything I wrote at La Fayette, I wrote, if not under your dictation, at least under your guarantee. But Danton held me back.
While all of this was going down, Lucile Desmoulins and Gabrielle Danton was staying at the apartment of the latter, something which we know through a letter Lucile wrote her mother on either June 24 or June 25, when the royal family had been captured and was on their way back to Paris. Unfortunately I have not been able to transcribe it in its entirety, but these are all the places mentioning Gabrielle that I could find:
…Ever since papa came with [warnings?] to us madame Danton and I have not left each other. I would have [gone crazy?] had I remained alone. These three days we have left [her place?] only at 9 o’clock [in the evening?] Sometimes people came to tell us that we were lost, and when we were told good news, madame Danton, her eyes filled with tears, threw herself around my neck. I’ve supped at her place during this time and [with?] all the patriots. […] Oh God o God, I’m going to send your beautiful [p..?] to madame Danton.
On July 15 the Jacobins entrusted Brissot with writing a petition asking for the abdication of Louis XVI. The session was closed at midnight. Afterwards, Camille, Danton, Brune and La Poype all went over to Danton’s house to further discuss the petition (this was revealed by Brune in an interrogation held August 12 1791, published in number 34 (August 26) of the journal Gazette des nouveaux tribunaux). Two days later, the two were there once again, this time together with Fréron, Fabre, Santerre, Brune, Duplain, Momoro and Sergent-Marceau, and discussing the lynching of two men at the Champ-de-Mars the same morning, when, at nine o’clock, Legendre arrived and told the group that two men had come home to him and said: We are charged with warning you to get out of Paris, bring Danton, Camille and Fréron, let them not be seen in the city all day, it is Alexandre Lameth who engages this. Camille, Danton and Fréron follow this advice and leave, and were therefore most likely not present for the demonstration and shootings on Champ-de-Mars the very same day (this information was given more than forty years after the fact by Sergent-Marceau in volume 5 of the journal Revue rétrospective, ou Bibliothèque historique : contenant des mémoires et documens authentiques, inédits et originaux, pour servir à l'histoire proprement dite, à la biographie, à l'histoire de la littérature et des arts (1834)).
In the aftermath of the massacre on Champ de Mars, arrest warrants were issued against people deemed guilty for them. On July 22, the Moniteur reports that the journalists Suleau and Verrières have been arrested, and that the authorities have also fruitlessly gone looking for Fréron, Legendre, Desmoulins and Danton, the latter three, the journal assures, having already left Paris. Camille hid out at Lucile’s parents’ country house in Bourg-la-Reine together with Fréron, while Danton went to Arcis-sur-Aube, where he was sheltered by his friend Courtois, and then to Troyes (it’s also commonly stated he went to England during this period, but Hampson expresses some doubt over it). If Camille’s fellow journalist Louis Marie Prudhomme’s Histoire générale et impartiale des erreurs, des fautes et des crimes commis pendant la Révolution (1797) is to be believed, on August 14, Danton told Camille and Fabre d’Églantine: the ”b.... won't have me; rather they will all be exterminated first.”
The rather flimsy charges against Danton and Camille — Danton was accused of having cheered on a crowd demanding Lafayette’s head on June 21, Camille of having made incendiary remarks at Café Procope café, saying that it was necessary to shoot the national guards — were however dropped after about six weeks, and in September 1791 they were both back in Paris to stand for election to the Legislative Assembly. Neither did however get in. Camille had also had to resign as journalist in the aftermath of the massacre on Champ-de-Mars.
In Histoire des Montagnards (1847) Alphonse Esquiros writes that Albertine Marat had told him that her brother, Danton and Desmoulins ”liked to come together, from time to time, to rest their souls in the sweet serenity of nature”:
In this contrast of the noise of revolutions with the silence, with the serious serenity of a sunset, under the trees, at the water's edge, a league from Paris, the three friends then had before their eyes the two faces eternal aspects of the world, history and nature, God in movement and God at rest. Danton, this eloquent thunderbolt, this large head of a genius on which smallpox had left big marks, Danton ordered dinner. Whatever efforts one agreed to make during the frugal meal, to keep irritating subjects out of the conversation, one was obliged to go there at dessert; because the company was too preoccupied with the dangers of the State not to mix public affairs with their most personal conversations.
When the question of war in December 1791 became the main topic of discussion, both Danton and Desmoulins joined the minority that cautioned against it. Already on December 16, right after Brissot had held his very first speech in favour of the idea, Danton, while praising the speaker as an excellent patriot, objected to the thought of a war right at the moment — ”I want us to have war; it is essential. We must have war. But above all, we have to exhaust the means that could save us from it.” Ten days later, December 26, Desmoulins did him too deliver a speech against war. Four days after that, after Brissot had just finished his second speech on the subject, Danton and Robespierre both demanded a change be made to a passage when it got printed. Following this moment, it would however appear Danton abandons the question. Camille on the other hand released the pamphlet Jean Pierre Brissot démasqué in February 1792, mocking Brissot and painting him as a fool. Danton’s name got mentioned three times throughout, Camille calling him and Robespierre ”the best citizens.” Danton also got mentioned a total of eight times in the journal La Tribune des Patriots Camille and Fréron published from April to June the very same year, but not in any way that could give us more insight into their relationship.
In her memoirs, Manon Roland claims that Danton and Fabre d’Églantine in the summer of 1792 often came home to her. At one point Fabre told her that “We have a newspaper project which we will call Compte rendu au Peuple souverain, and which will present the picture of the last revolution. Camille Desmoulins, Robert, etc, work on it.” Manon suggested they bring it to her husband for him to subsidise it, something which the two apparently never did, and there was no more talk of the journal again.
On June 23 1792 Lucile starts keeping a diary. The first time any of the Dantons show up in it is already on Wednesday June 27 — ”Madame D(anton) came, we played music.” A few days later Lucile gives this rather odd account: ”My head is spinning. I was madame D(anton) after dinner.” The day after that, July 6, she gives birth to her first child, and a week later, Camille writes to tell his father that said child ”was immediately sent to a wetnurse in Isle-Adam, with the little Danton” (François-Georges, born February 2 1792). If Camille and Lucile made a conscious choice of sending their son to the same wetnurse as Georges and Gabrielle’s (perhaps on the suggestion of their friends) one can only speculate in.
A week after Camille wrote his letter, Lucile traveled to her parents’ country house in Bourg-la-Reine. On July 25 Camille writes to tell her that ”I was brought to Chaville this morning by Panis, together with Danton, Fréron, Brune, at Santerre’s” (letter cited within Camille et Lucile Desmoulins: un rêve de république). Lucile returned to Paris on August 8. In a diary entry written four months later she reveals that she, in the afternoon of August 9, together with others went over to the Dantons. ”Her mother was crying, she was sad, her father looked dazed. D(anton) was resolute. As for me, I was laughing like a madwoman! They feared that the affair [the insurrection of August 10] would not take place; although I was not at all sure, I told them, as if I knew it well, that it would take place. “But can we laugh too?” mde D(anton) said to me. ”Alas, I said to her, that presages to me that I will perhaps shed a lot of tears this evening!” At the end of the day, Lucile, Gabrielle (and others?) go home to Gabrielle’s mother to go for a walk and eventually sit down next to a cafe with her. When groups of sans-culottes and troops on horseback pass by, Lucile gets scared and tells Gabrielle that they should go. ”She laughed at my fear, but by dint of telling her, she too became scared and we left. I say to her mother: ”Farewell! You will soon hear the toscin sound!” The two go back to Gabrielle’s apartment, where a scared Lucile eventually admits to Camille she doesn’t want him to get involved in the dangerous insurrection — ”He reassured me by telling me that he would not leave D(anton).” Lucile and Gabrielle are soon left alone in the apartment with Louise de Kéralio-Robert, but after only a little while Danton returns home and goes to bed. This eventually upsets Louise who tells Lucile that if her husband dies in the insurrection she will stick a knife in Danton. ”From that moment on I never left her. What did I know what could happen? To know what she was capable of…” Some additional time later Camille returns to the apartment and falls asleep on Lucile’s shoulder. Louise tells her that “I can’t stay here any longer! Madame D(anton) is unbearable to me, she seems to be calm, her husband does not want to expose himself!” Lucile therefore suggests she come with her and Camille to their apartment to get some rest. When they around noon go back to the Dantons’ place again ”Madame D(anton) ran up to us to see how we were, she was soon informed when she saw the silence of one and the tears of the other. We waited long enough without knowing anything. Finally they came to tell us that we were victorious.” In a letter to her mother penned down the very same day, Lucile, similarly to how she described them during the Flight to Varennes, writes: ”Mme Danton and I do not leave each other, when I would have liked to flee it would have been impossible, the women are kept from going out.” The following night Camille and Lucile sleep over at the Roberts. When Lucile returns home on the 12th she learns that Danton has been appointed minister of justice. ”These news gave me great pleasure, especially when C(amille) came to tell me that he was secretary.” One day later Camille writes a letter revealing the very same news to his father:
My friend Danton has become minister thanks to the canon. This bloody day could only end, for the two of us especially, in being raised or hoisted together. He said to the national assembly: If I had been defeated, I would have been a criminal. The cause of liberty has triumphed, and Danton has associated me to his triumph.
According to Prudhomme’s Histoire générale et impartiale… (1797), it was Camille and Fabre themselves who three o’clock in the morning announced to Danton that he had been named minister of justice, after which they demanded he make them his secretaries:
”But, are you sure that I am appointed minister?” [said Danton]. “Yes,” replied the two midshipmen; and we will not leave you until we have your word for these two places.” ”Right on time,” said Danton. And everything was arranged according to the wishes of the two revolutionary patriots; but all this does not praise their disinterestedness.
After Camille and Danton had gotten their new occupations, both families briefly went to live at Hôtel de Bourvallais. Lucile writes:
I really liked it there, but only one thing bothered me, it was Fréron. Every day I saw new progress and didn’t know what to do about it. I consulted Maman, she approved of my plan to banter and joke about it, and that was the wisest thing to do. Because what to do? Forbid him to come? He and C(amille) dealt with each other every day, we would meet. To tell him to be more circumspect was to confess that I knew everything and that I did not disapprove of him; an explanation would have been needed. I therefore thought myself very prudent to receive him with friendship and reserve as usual, and I see now that I have done well. Soon he left to go on a mission. I was very happy with it, I thought it would change him. But many other cares to be taken… I realized that D(anton)… Oh, of that one, I was suspicious! I had to fear the eyes of his wife with whom I did not want to be hurt. I did so well that one did not know that I had noticed it, and the other that it might be. We spent three months like this quite cheerfully. At the end of this time C(amille) was appointed deputy and we returned to our first home.
Somewhere during Camille and Danton’s time in the ministry we find the following undated letter ”from the minister of justice to citizen Desmoulins, national commissioner in Vervins” (Camille’s father). Charles Vellay, who published the letter in 1792, did however find it more likely for the author of the letter, unlike what the header leads you to believe, was Camille, seeing as it is in a secretary’s handwriting and the letter was found among his and not Danton’s papers:
I am pleased to learn, Citizen, that yielding to the wishes of your compatriots, you have accepted the position of Natal Commissioner at the Vervins District Tribunal. You could undoubtedly desire some rest after the long fatigues you have had and the feeling which invited you to retire was very legitimate; but it was worthy of your good citizenship to still make the sacrifice for your country, and I am convinced that it was not in the midst of the agitations which precede the most beautiful of centuries that you would have left without regret a career where you you still have services to render to public affairs for a long time to come. It is not fair, however, to forget that the more you redouble your efforts, the more it is in your fellow citizens' interest to prescribe reasonable limits for yourself, and it is also your duty to moderate your zeal and not to forbid you these considerations which can be reconciled with public service and the care of your health. Your colleagues will themselves urge you to give nature the moments of relaxation it needs; a few temporary absences can be infinitely useful to you, and certainly they will not harm the interests of business if some attention is given to the circumstances and replacement measures. I will approve the first of wise precautions which I feel the necessity of and sure of my attachment to your duties I will rely with confidence on your respect for this moral responsibility as sacred as the will of the laws to true republicans.
Danton would however not remain minister of justice for a long time, already on August 26 Camille reported to his father that:
It seems that several departments will nominate me and especially Danton [to the National Convention], and he will not hesitate for a moment to leave the ministry to be representative of the people. You can imagine that I would follow an example that I would have given him, if I were in his place. Danton is from Paris no more than I am, and it is a remarkable thing that among all the principal authors of the revolution and among all of our friends, we perhaps do not know a single one who was born in Paris.
However, before the opening of the National Convention, the so called September Massacres took place. In l’Histoire générale et impartiale des erreurs… (1797) Prudhomme attributed big responsibility for the prison killings to both Danton and Desmoulins, portraying them as aware of what was going to happen already on September 2, the day before they began:
September 2, at midday, I go, hearing the noise of the tocsin and the cannon of alarm, to my section de l'Unité. People came to announce that the barriers had been closed. A general consternation was painted on all faces. At the news of the arrival of the Prussians in Paris, as well as of a conspiracy of the prisoners against the patriots (a vague rumor had been circulating about it for fifteen days), a number of citizens questioned me on this subject. ”Your profession as a journalist should enable you to know something,” one said to me. ”I know nothing,” I responded, ”but I’m going to visit someone who could tell me.” As I knew Camille Desmoulins since a long time back, I thought it a good idea to go to his house. I didn’t find him anywhere, one assured me that he was at Danton’s, minister of justice. It was about half past two in the afternoon, I went home to the minister, and told him: ”I have come, in the quality of pure patriotism and in my own name, to ask you what this canon of alarm, this toscin and the arrival of the Prussians to Paris.” ”Calm down, old friend of liberty,” Danton responded, ”it’s the toscin of victory.” ”But,” I told him, ”people talk about slitting throats.” ”Yes,” he told me, ”we were all about to have our throats cut this night, starting with the most patriotic. All those arisocrat rascals, who are in the prisons, had been provided with firearms and daggers. At a specified time next night, the gates were to be opened to them; they would have spread in different quarters to cut the throats of the wives and children of the patriots who will leave to march against the Prussians. We addressed ourselves principally, above all, to those who had demonstrated the principles of freedom.” ”All this comes off as a bit made up to me,” I responded, ”but what means are to be employed to prevent the execution of such a plot?” ”What means?” he said. ”The People, irritated and instructed in time, want to do justice themselves to all the bad subjects inside the prisons.” At these words I was seized with horror; I told him that such a measure appeared to me unworthy of a people who claimed to be free. At this moment, Camille Desmoulins entered. ”Hello there!” Danton said to him. ”Prudhomme just asked me what is to be done. ”Yes,” I said, ”and I am heartbroken after what I have just heard. ”So you (tu) didn’t tell him that one won’t mix up the innocent with the guilty? Camille said to Danton. ”All those who will be claimed by their sections will be returned.” ”Seems to me that we could take a less violent measure,” I responded. ”Spilling blood is an abominable act of which those who govern are responsible. The people will one day make those who make them commit this crime pay dearly. Let Paris march en masse against the Prussians. Send the wives and children of those who are to march at the enemy out of Paris to avoid them getting massacred by the prisoners, let us lock them up in fortified castles.” ”Any kind of moderate measure is useless,” Danton said. ”The anger of the people is at its height, there would even be danger in stopping it.” His first anger assuaged, one could make him listen to reason. ”But,” I say, ”if the Legislative body and the constituted authorities spread themselves through Paris, and harangued the people?” ”No, no,” replied Camille, ”that would be too dangerous; for the people, in their first wrath, might make victims in the person of their dearest friends.” I withdrew filled with pain.
Exiting Danton’s house, Prudhomme adds:
As I passed through the dining room, I saw the wives of Camille, Danton, Robert, etc, Fabre-d'Eglantine, and other guests. I did not know what to think of the tranquility that reigned at the house of the Minister of Justice; everything led me to believe that it was indeed impossible to stop the resentment of the People, at the news of a conspiracy hatched by the nobles and priests.
The next day, Prudhomme also claims that Théophile Mandar went over to Danton’s place, where he saw ”all ministers, with the exception of Roland, Lacroix, president [of the Assembly], Pétion, mayor of Paris, Robespierre, Camille-Desmoulins, Fabre d’Églantine, Manuel and several members of the so-called Commune of August 10. The presidents and commanders from each of the 48 sections had come as well.” Half past seven in the evening everyone sat down in Danton’s salon to discuss the means to save Paris, Danton staying firm in his conviction of what had just happened and was still happening as necessary.
On September 8, two days after the end of the massacres, the time had come for Camille to be elected to the National Convention. He did at first come under question for his friendship with the royalist journalist François Suleau, killed in the Insurrection of August 10. The journal Gazette nationale de France does however report that Camille after this ”was defended with a lot of energy and eloquence by M. Danton and his election was almost unanimous.” With that, Desmoulins became the sixth elected deputy representing Paris (Danton was the second).
In December 1792, Lucile returns to keeping a diary. On the 22nd she writes: ”I went to supper with little Brune at mde D(anton’s). How detestable she is!” It’s hard to tell if it’s Gabrielle or madame Brune she designates as detestable, and even harder to know what she had done in order to get called that… Two days later, December 24, Lucile documents the following:
We had dinner at mde D(anton's), mde R(obert), B(rune) and B(oyer) were there. After dinner the men asked themselves if they should go to the Jacobins. They said yes. We were asked if we would go. We say no. Madame D(anton) said to me: ”do you (vous) want to spend the evening with me?,” I said yes, but soon I did not know what to do. Brune suggested I go to the theater! It was very embarrassing. Madame Brune said aloud: “I have never been to the Jacobins, I would be very happy to go there.” "Well, I'm going with you," I tell her. Finally, here we are, all ready to leave, when I see Mme Brune and Boyer whispering in each other’s ears. I, like a fool, go to ask them what they’re saying to each other. Mde R(obert) told me that she was very embarrassed, that she would like to go with us to the Jacobins. I was very kind, I said a few words to her that meant nothing, then I went into the antechamber. She came there soon and told me to wait for her, that she was going to follow me, she came back near madame D(anton). Brune came and told me “let’s go”. I followed her saying: ”but mde R(obert) who wants to come?” Finally, we are hardly in the middle of the staircase when we hear someone who says “here they are, here they are!”, then we descend with astonishing speed, and when we are in the street we run even harder. We took a fairly long detour. God knows how we laughed! Nothing, too, was more comical.
Throughout the first two halves of January, Lucile goes to the Convention to follow the trial of Louis XVI every single day. If Gabrielle went with her to these sessions is not confirmed, but not disproven either. Danton was absent on a mission in Belgium for most of the trial, but on January 14 he returned to Paris and two days later he voted for death, just like Camille. One day after the execution of the king, January 22 1793, Lucile writes: ”I went to Robert’s. Danton came there. His jokes are as boorish as he is. Despite this, he is a good devil. Madame Ro(bert) seemed jealous of how he teased me…” Two days later she witnesses the funeral procession of the recently assassinated Michel Peletier from the window of Jeanne-Justine Boyer, an event which moves her deeply. Once all her guests have left for the evening ”I felt that I could not be alone and bear the horrible thoughts that were going to besiege me. I ran to D(anton’s). He was moved to see me still pale and defeated. We drank tea, I supped there.” A week later, January 29, Lucile reports that ”we had dinner at D(anton's), where I just laughed, because I was preventing Brune from eating by saying "poa, poa, poa". D(anton) too couldn't keep himself from laughing.” Four days after that, February 3, Lucile writes ”I went to see madame Danton. Sick.” Three days later, she goes back to see her friend — ”I went to see madame Danton… She is very ill.” Yet another three days later Lucile writes ”Madame Danton is ill. She has given birth to a girl.” and at last, the day after that: ”I had dinner with Maman. Madame Danton is dead.” Two days after the death of her friend, Lucile goes to visit Gabrielle’s mother together with madame Brune and Robert. Shortly after that, she and Camille do however leave for Essonne, the latter having been apointed to a mission there, while Georges returned to Paris after another mission in Belgium to receive the sad news. Lucile did however not forget about him, in a letter to her mother Annette dated February 16 she asks her to ”give us news regarding Danton.” Apropos of Annette eventually joining them in Essonne Lucile adds: ”I forgot to mention a facility that could be of use for you, it’s Danton’s carriage. No doubt he could still have it.”
On March 26 1793, Desmoulins and Danton were both elected for the so called Commission of Public Safety, alongside 23 others. The commission, which consisted of both fervent montagnards and fervent girondins, was however off to a rocky start, and already on April 6 it was put to death and replaced by the Committee of Public Safety. A little more than a month later, May 17, Desmoulins announced the release of his new pamphlet l’Histoire des Brissotins to the Jacobins. Danton’s name gets mentioned eleven times in it, but only one can be used to really say something about their relationship, and it’s when Camille on page 54 writes: ”Jérôme Pétion told Danton in confidence that ”what makes poor Roland saddest is the fact people will discover his domestic sorrows and how bitter being a cuckold is to the old man, troubling the serenity of that great soul.” This implies Danton went and shared Roland’s secret with Camille after Pétion had confided it to him. Two weeks later, on June 7, a ”member” is recorded to have voiced suspicion on Danton’s current sentiments — ”This deputy isn’t as revolutionary as he used to. He doesn’t come to the Jacobins anymore. He left me the other day to approach a general.” In response, Camille is recorded to have ”advocated Danton’s good citizenship.” In Lettre de Camille Desmoulins, député de Paris à la Convention, au général Dillon en prison aux Madelonettes released a few months later, Camille calls Robert Lindet, Robespierre and Danton ”the best citizens of the Convention.”
On October 30, 22 girondins were sentenced to death. In Les mysterès de la mère de Dieu dévoilès (1794) Joachim Vilate described a dramatic reaction from Camille’s part upon hearing the final verdict: ”hearing the juror's declaration, he suddenly threw himself into my arms, agitated, tormenting himself:”ah my god, my god, it's me who kills them: my Brissot dévoilé [sic], ah my god, it’s that which kills them.” If Dominique-Joseph Garat’s Memoirs of the revolution; or, an apology for my conduct, in the public employments which I have held (1795) are to be believed, Danton too was deeply moved by the fate of the girondins, to the extent it motivated him to, on October 12, ask for a leave of absence to go to Arcis-sur-Aube in order to recruit his health:
I could not convince myself that among all those who, since May 31, had retained great popularity, there was not one who did not still retain a little humanity, and I went to Danton. He was ill, it only took me two minutes to see that his illness was above all a deep pain and a great dismay at everything that was coming. ”I won't be able to save them (the girondins)”, were the first words out of his mouth, and, as he uttered them, all the strength of this man, who has been compared to an athlete, was defeated, big tears strolled down his face, whose shapes could have been used to represent that of Tartarus. […] When the fate reserved for the twenty-two [girondins] seemed inevitable, Danton already heard, so to speak, his death sentence in theirs. All the strength of this triumphant athlete of democracy succumbed under the feeling of the crimes of democracy and its disorders. He could only talk about the countryside, he was suffocating, he needed to escape from men in order to be able to breathe.
Danton’s absence did not go unnoticed. In a letter from Toulon written October 18, Fréron tells Lucile that ”I have been really worried about Danton. The public papers announce that he is ill. Let me know if he has recovered. Give him 1000 friendships from my part.” Through the next letter Fréron writes Lucile, dated December 11, we learn that Danton had a nickname within this inner circle of friends — ”I would like to have news of Patagon (Brune), Saturne (Duplain) and Marius (Danton).” It can be observed that Camille, as seen above, had likened Danton to Marius in Révolutions de France et de Brabant already in 1790.
Danton was however back in Paris again on November 22, when he is recorded to have spoken of ”the relief to be granted to abdicated priests” at the Convention. Two weeks later, December 3, he was accused of ”moderatism” by Coupé d’Oise for having opposed the suggestion of sending a group with a portable guillotine to Seine-Inférieure in order to deal with rebels fleeing the Vendée. Robespierre did however rise to defend Danton, saying that he had always seen him serve his homeland with zeal and ending by asking that everyone says what he sincerely thinks about Danton. Aside from Merlin de Thionville, who hailed Danton as the saviour of the republic, no one said anything, and Momoro therefore concluded this meant no one had anything to accuse Danton of. The discussion therefore ended with Danton embracing the president of the club amidst loud applause. Just two days later, the first number of Camille’s new journal, the Vieux Cordelier, was released. In the number, Desmoulins designates the session at the Jacobins on the 5th as the event that caused him to return to the journalistic pen:
Victory is with us because, amid the ruins of so many colossal civic reputations, Robespierre’s in unassailed; because he lent a hand to his competitor in patriotism, our perpetual President of the “Old Cordeliers,” our Horatius Cocles, who alone held the bridge against Lafayette and his four thousand Parisians besieging Marat, who now seemed overwhelmed by the foreign party. Already having gained stronger ground during the illness and absence of Danton, this party, domineering insolent in society, in the midst of the most sensitive places, the most compelling justification, in the tribunes, jeering, and in the middle of the meeting, shaking its head and smiling with pity, as in the speech of a man condemned by every vote. We have won, however, because after the crushing speeches of Robespierre, in which it seems that talent grows in pace with the dangers of the Republic, and the profound impression he has left in souls, it was impossible to venture to raise a voice against Danton without giving, so to speak, a public quittance of guineas of Pitt. […] I learned some things yesterday. I saw how many enemies we have. Their multitude tears me from the Hotel des Invalides and returns me to combat. I must write.
If Danton had a bigger role in the Vieux Cordelier than simply being part of the event that caused Camille to start writing it is debated. When Robespierre a little more than three months later was working out the dantonists’ indictment, he claimed that Danton had been the ”president” of the Vieux Cordelier, whose prints he had corrected and made changes to, and that Camille had been his and Fabre’s ”dupe.” In Memoirs of the revolution; or, an apology for my conduct… (1795) Garat claimed that Danton during his stay in Arcis-sur-Aube had been cooking up a ”conspiracy” with a goal to ”restore for the benefit of all the reign of justice and of the laws, and to extend clemency to his enemies,” and to which ”all of his friends,” including Desmoulins, entered into. In Histoire générale et impartiale des erreurs… (1797) Prudhomme claimed that Danton, Lacroix, Camille-Desmoulins and Fabre-d'Églantine made up a secret party wishing to overthrow the Committee of Public Safety, and that Camille, as part of this plan, got charged with a ”moral attack,” leading to the creation of the Vieux Cordelier. Danton’s friend Edme-Bonaventure Courtois wrote in Notes et souvenirs de Courtois de l’Aube, député à la Convention nationale (cited in La Révolution française: revue d’histoire moderne et contemporaine (1887), that ”it was in these painful moments that [Desmoulins] put to paper (in his Vieux Cordelier) the reflections that his indignation could no longer contain, and whose acrimony Danton, through his advice, softened in many places.” Finally, in his Camille Desmoulins And His Wife: Passages From The History Of The Dantonists (1876), Jules Claretie included the following passage:
I know, through information given to me by M. Labat the elder, that one evening in that mournful summer of 1793, Danton and Camille Desmoulins had walked to the Cour du Commerce, along the Seine, by the quay des Lunettes, and, thinking of that 31st of May, which was to end in the events of the 31st of October, Danton pointed out to Camille the great river in which the rays of the sun, setting behind the hill of Passy, were reflected so vividly that the river looked like blood. ”Look,” said Danton — and, like Garat, Camille saw the tribune's eyes fill with tears — ”see, how much blood! The Seine runs blood! Ah! too much blood has been spilt! Come, pick up your pen again; write and demand clemency, I will support you!”
However, considering Robespierre’s notes had an interest in wanting to paint the ”dantonists” as a unified grupp (and perhaps also to absolve Desmoulins of some responsibility), while all the other testimonies were reported after the fact, its hard to be sure of anything.
Danton went unmentioned in the rest of number 1, as well as number 2 (released December 10) of the Vieux Cordelier. When Camille on December 14 passed through the Jacobins ongoing scrutiny test, he regrettingly admitted that ”a well marked fatality willed that, among the sixty [sic] people who signed my wedding contract, I only have two friends left — Danton and Robespierre. All the others have emigrated or been guillotined.” In the Vieux Cordelier’s third number (released December 18), he wrote the following about Danton, apropos of underlining he was not asking for moderation:
In this duel between liberty and servitude, and in the cruel alternative of a defeat a thousand times more bloody than our victory, overruling the revolution therefore had less danger and was even better than remaining behind it, as Danton said, and it is necessary, above all, for the republic to secure the battlefield. […] Despite so many guineas (guinées) said Danton, name for me a single man strongly pronounced in the revolution, and in favor of the republic, who has been condemned to death by the revolutionary tribunal?
Danton went unmentioned again in number 4 (December 21), but in number 5 Camille brings him up seven times, writing that ”I said with Danton, that to outrage the revolution was less dangerous and even better than to remain within it; that, on the course taken by the vessel, it was better to approach the rock of exaggeration, than the sandbar of moderation,” insisting he has never ceased to ”conspire against the tyrants with Danton and Robespierre,” denouncing Hébert for having attacked him, Danton and nine other deputies and claiming to have heard Danton say that ”[Hébert’s] pipe resembles the trumpet of Jericho, when he has smoked three times around a reputation, it must fall of itself.” At one point he also accuses Barère of having discussed the arrest of Danton on June 2.
On January 7, Camille and Robespierre got into a fight at the Jacobin club after the latter had denounced the fifth number of Vieux Cordelier as counter-revolutionary, but insisting that its author had been ”led astray by bad company,” and therefore proposing that the Society forgive him and ”just” burn the latest numbers of the Vieux Cordelier. When Camille refused that ultimatum, exclaiming that ”burning isn’t answering,” the fight worsened until Danton stepped in to act as meditator between the two:
Danton: Camille mustn’t be frightened by the rather severe lessons Robespierre’s friendship has just given him. Citizens, let justice and cold-headedness always preside over our decisions. In judging Camille, be careful to not strike a deadly blow against the liberty of the press.
In a letter to Fréron dated January 13, Lucile regretfully reports that ”Marius is not listened to anymore, he loses courage and vigour.” Around the same time, her father was arrested and locked up in the Carmes prison due to a few objects decorated with fleurs-de-lys having been found in his home. On January 24 Camille protested against his arrest at the Jacobins, gaining the support of Bourdon d’Oise who asked that the Committee of General Security make a report about the case in three days. Danton did however object to this, but did make the more vague suggestion that ”the Convention consider ways to do justice to all the victims of arbitrary measures and arrests, without harming the action of the revolutionary government”:
I oppose the kind of distinction of privilege which would seem to be granted to Desmoulins' father-in-law. I want the Convention to deal only with general affairs. If we want a report for this citizen, we also need one for all the others. […] My colleague's complaint is fair in itself, but it would give rise to a decree unworthy of us. If we were to give priority, it would belong to citizens who do not find in their fortune and in their acquaintance with members of the Convention hopes and resources in the midst of their misfortune: it must be to the unfortunate, to the needy, that you should first hold out your hands. I ask that the Convention consider ways to do justice to all the victims of arbitrary measures and arrests, without harming the action of the revolutionary government. I would be careful not to prescribe the means here. I request the referral of this question to the consideration of the Committee of General Safety, which will consult with the Committee of Public Safety; that a report be made to the Convention, and that it be followed by a broad and in-depth discussion; because all the discussions of the Convention have resulted in the triumph of reason and liberty.
When Robespierre about two months later was preparing the dantonists’ indictment, he wrote that ”during this last visit [to my place], [Danton] spoke of Desmoulins with contempt. He attributed his deviances to a vice that is private and shameful, but absolutely foreign to the crimes of the conspirators to the Revolution. Laignelot was witness.” Robespierre used this as evidence Danton had ”an ungrateful and dark soul,” as he previously had ”highly recommended the last productions of Desmoulins.”
Both Danton and Camille were arrested in the night between March 30 and March 31. They were taken to the Luxembourg prison and placed in solitary confinement. On April 1, in his very last written letter, Camille regrettingly tells Lucile:
How to believe that a few jokes in my writings, against colleagues that had provoked me, have erased the memory of my services! I do not disguise the fact that I die as a victim of these jokes and my friendship with Danton. I thank my assassins for letting me die with him and Philippeaux. And since my colleagues have been cowardly enough to abandon us and listen to calumnies that I don’t know, but must be the most vulgar, I can say that we die as victims of our courage to denounce traitors, and of our love for the truth. We can well carry this testimony with us, that we die as the last republicans.
It would however appear Lucile wanted to do something about the situation. We have the following anecdote published in Histoire de la Révolution française (1850) by Nicolas Villiaumé, which, as far as I’m aware, is the only known connection we have between the Desmoulins couple and Danton’s second wife Louise-Sébastienne Gély (married June 14 1793):
[After the arrest of Danton and Desmoulins] Lucile ran to Madame Danton to suggest that she come with her to go find Robespierre, ask him for an explanation, and recall the feelings of friendship which had attached him to their husbands. Madame Danton refused, saying that she wanted nothing from a man who had showed himself to be the enemy of her husband. (I obtained this particularity from Madame Danton herself, who was then pregnant. She gave birth fifteen days after Danton's death, but her child did not live.)
On April 2, Danton, Desmoulins and seven other deputies were brought from the Luxembourg to the Conciergerie prison. If Mémoires d’un detenu pour servir à l’histoire de la tyrannie de Robespierre(1795) by Honoré Riouffe are to be believed, the accused were kept in seperate cells here as well. He writes:
Danton, placed in a cell next to Westermann, didn’t stop talking, less to be heard by Westermann than by us. […] Here are some phrases I retained: […] ”What proves Robespierre is a Nero, is that he never spoke as kindly to Desmoulins as on the day before his arrest.”
Their trial began the very same day. For three days, the accused defended themselves (or at least tried to) against the charges of ”complicity with d'Orléans and Dumourier, with Fabre d'Eglantine and the enemies of the Republic, of having been involved in the conspiracy tending to re-establish the monarchy, to destroy the national representation and the republican government” side by side. It did however not go that well, and on April 5, Danton, Desmoulins and thirteen others were sentenced to death. The execution took place the very same afternoon. Contrary to the myth of Danton and Camille sitting next to each other in the same tumbril as they were driven to Place de la Révolution, number 561(April 6 1794) of Suite du Journal de Perlet reports that ”they were in three tumbrils: in the first was Danton, next to Delacroix; Fabre near the executioner; Hérault opposite Chabot. In the second, Phelippeaux [sic], Westermann, Camille Desmoulins, Basire and Launai d’Angers [sic]. […] Danton […]seemed to pay little attention to the crowd around him: he was chatting with Lacroix and Fabre. […]Desmoulins spoke almost continually to the people; the courage he affected seemed like a painful effort, he was an actor who was studying to play his last part well.”
After the death of Camille and, eight days later, Lucile, their son Horace was taken in by his maternal grandparents and aunt, who then permanently retired to their country house in Bourg-la-Reine. Danton’s sons Antoine and François-Georges were they too adopted by their maternal grandfather and uncles. In 1805, the two moved from Paris to Arcis-sur-Aube where they instead got looked after by their paternal grandmother. I have not been able to find anything indicating the families stayed in touch to process the grief or let the children come together, something which we on the other hand know Lucile’s mother did with Philippeaux’s widow.
#danton#desmoulins#georges danton#camille desmoulins#frev friendships#lucile desmoulins#gabrielle danton#frev#ask#interesting how it’s to lucile (and albertine) we owe the best information for her husband’s friendship with danton…
65 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Gracchi Brothers
Tiberius Sempronius Gracchus (c. 163-133 BCE) and his younger brother Gaius (c. 154-121 BCE) were tribunes of the plebs in the Roman Republic. Serving in 133 BCE, Tiberius introduced a land reform but was beaten to death after his term. Eleven years later in 122-121 BCE, Gaius reaffirmed his brother's land reform and attempted to curb corruption. He met the same fate as his brother.
Continue reading...
169 notes
·
View notes
Text
#roman history#ancient rome#roman empire#how often do you think about the roman empire#ancient history#augustus#pompey#julius caesar#roman republic#romans#tbe roman empire is my Roman empire#brothers gracchi#the gracchi#tiberius gracchus#gaius gracchus#sulla#gaius marius#marius#marian reforms#pompeius magnus#gaius julius caesar#Caesar#Cicero#cinna
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
Cornelia:

Mother of the Gracchi brothers! Highly intelligent and influential woman who educated her sons and helped shape their political careers. OG Roman MILF
Clodia

Catullus' "Lesbia" Wealthy and highly educated woman who had a talent for poetry (none survives :( ) Cicero hated her and called her "the Medea of the Palatine" (huge W for Clodia) Known for taking many lovers and accused of incest with her own brother (Catullus did not take the breakup well)
Fulvia

The first (real) woman to appear on Roman coinage. Married to Marc Antony (her third husband) and very involved in politics. Cassius Dio wrote "the following year Publius Servilius and Lucius Antonius nominally became consuls, but in reality it was Antonius and Fulvia. She, the mother-in‑law of Octavian and wife of Antony, had no respect for Lepidus because of his slothfulness, and managed affairs herself, so that neither the senate nor the people transacted any business contrary to her pleasure." Plutarch wrote "Fulvia wished to rule a ruler and command a commander and she schooled Antony to obey women." (marc antony is into femdom he's just like me fr fr) Acted as both a political and military leader.
Agrippina the Younger:

One of the most powerful of the Julio-Claudian women and a big influence on behind the scenes politics. Mother of Nero by her first husband. Was exiled for a conspiracy to assassinate her brother Caligula, but later returned. May have poisoned her second husband in order to marry the Emperor Claudius. She was the one to convince Claudius to name Nero heir, instead of Claudius' own son. May have poisoned Claudius in order to make Nero emperor. Ruthless, ambitious, and domineering #girlboss. Fave moment was when Nero engineered a boat designed to sink specifically to assassinate her. She swam to shore, realized her shitty son had tried to kill her (again), and wrote a letter to him letting him know that she had survived a terrible accident by divine fortune.
Messelina

Third wife of Claudius and hugely influential, directly responsible for the execution of several people and tried to get young Nero assassinated so that her own son would have the throne. Hated Agrippina for obvious reasons. Executed for a conspiracy to assassinate Claudius. Pliny wrote a famous (and certainly fake) story of her challenging a famous prostitute to see who could sleep with the most men in one night. (Messalina won at 25)
Julia the Elder:

Augustus once famously remarked that he had two difficult daughters: Rome and Julia. Married off by her father several times, all for political reasons. Clashed with her controlling father on many occasions about her spending, behavior, etc. Augustus passed laws making adultery a crime and then had to exile her for adultery (after killing and exiling her lovers) She was popular with the Roman people, who petitioned for her recall from exile, and was known for her kindness, intelligence, and wit. She never returned to Rome, and died in exile.
Livia:
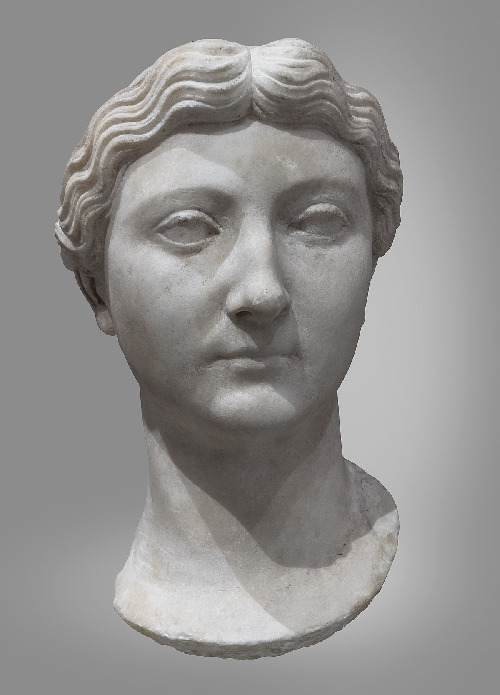

Wife of Augustus and first Roman empress. One of, if not the, the most powerful and influential women in the early Roman Empire. iirc she was the first woman to be deified. Cassius Dio wrote "Livia was destined to hold in her lap even Caesar's power and to dominate him in everything."
Hortensia
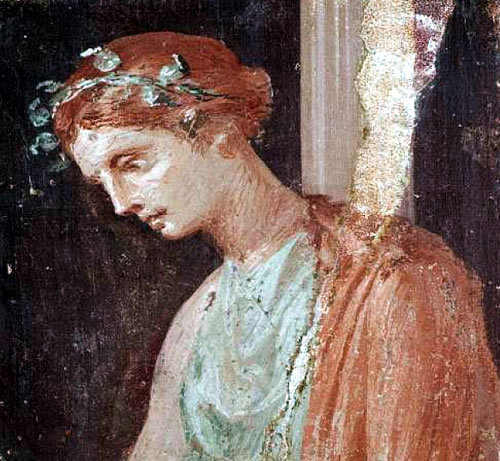

A skilled orator, best known for her public speech given in the forum in protest of a tax put on women to fund the civil war after the assassination of Caesar. She was successful, reducing the number of women taxed down to 400, with new taxes on men being levied to make up the difference. (Using this image of a fresco from Pompeii because there's, surprisingly, no art I can find of her from a google search)
Empress Theodora

Byzantine empress. She was the daughter of a bear trainer and an actress, and worked as an actress and prostitute in her youth. Married the Emperor Justinian and became his advisor, preforming jobs that were usually only done by the emperor (receiving envoys and corresponding with foreign rulers) and helped pass laws for women's rights.
#i wanted to include terentia and servilia but you can only have a max of ten#so suggestions for 'other' i guess#also wanted to keep it like. completely factual women that we know existed#but shout out to rhea silvia lucretia cloelia tarpeia etc#also wanted an honorable mention to eumachia but again#max ten options
385 notes
·
View notes
Note
Hi, I have a question about Volantis.
The only people who can became Triarchs are the citzens of Volantis with unbroken Valyrian descent, the so called Old Blood, which leads me to believe that both Tiger Triarchs and Elephant Triarchs are form the Old Blood. However, the Tigers defend military conquest, while the Elephants defend a comercial conquest, and it is said that "The Old Blood favored the sword, while the merchants and moneylenders advocated trade."
So, for all of that to make sense, The Elephant party has to be composed of merchants and moneylenders (as well as any other freeborn property owner citzen who agrees with their policy) as well as some of the Old Blood, with the Old Blood members being the only ones allowed to run for office.
If so, do you think that, in the begining, the Elephants were composed only by the merchants and moneylenders, with some of the Old Blood jumping in when they realised the war was lost, or do you think that, for the Elephants to exist as a party in the first place, they needed to have someone from the Old Blood with them from the begining, since this is the only way for them to compete in the election for Triarch?
Sorry for the long question.
Sorry for the delay in answering your excellent question!
I think the elephants always had a leadership drawn from the more forward thinking minority among the Old Blood, similarly to how the Populari faction in the Roman Republic was mostly led by men with populist beliefs who were themselves nobiles (like the Gracchi brothers or Marcus Livius Drusus) more often than they were led by "novus homo" like Gaius Marius.
Keep in mind, the "Old Blood" just means that you can trace your ancestry back to Valyria - and Valyria was not composed entirely of noblemen; it had its merchants and craftsmen and the like. Given that Volantis spent most of its history as a trading outpost of the Valyrian Empire, I imagine that quite a few of the "Old Blood" came from the middling classes of Valyria - especially since it doesn't seem like Volantis had any native dragonlords - rather than the aristocracy.
40 notes
·
View notes
Text

Some more Extra History bean person fanart for the soul. This time we have the Brothers Gracchi, Gaius and Tiberius respectively. Enjoy! :D
#extra history#extrahistory#eh#extra credits#extracredits#ec#art#digital art#artwork#fanart#i made this#illustration#history#animated history#live laugh love extra history#make this go viral#make this blow up#artists on tumblr
14 notes
·
View notes
Note
you know one of those fun things with dont look back is the convince Anakin that Democracy is good actually but like, the jedi are not a democracy 12 people voting on stuff. Leia did not grow up remotely near a Democracy in sight, even the rebellion is a military. so only one that has any leg to stand on is Padme who was a democratic QUEEN with all the power and autho. convincing Anakin that Palps be a terrible Tyrant there are better ones, we will GET you a Caesur, or Gracchi Brothers.
The good news is that Leia has 0 interest in convincing Anakin democracy is good. She just doesn't want him to become a Sith Emperor's lapdog. Padmé is much more invested in Anakin having good political opinions, and while she was queen and is senator, she's got a much better grasp of how democracy can actually work and why it would be good.
And luckily for all of us, Anakin doesn't need to be convinced that democracy is good in order for this to be a fix it. Vader set the bar pretty damn low in that respect.
33 notes
·
View notes