#Gender Ethics
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
The Philosophy of Gender
The philosophy of gender examines the concepts, theories, and issues surrounding gender identity, roles, and equality. It delves into the nature of gender, its social and biological underpinnings, and its impact on individual lives and societal structures. This field of philosophy addresses fundamental questions about what gender is, how it is constructed, and what implications it has for justice and equality.
Key Themes in the Philosophy of Gender
Nature vs. Nurture:
One of the central debates in the philosophy of gender revolves around whether gender is primarily a biological phenomenon (nature) or a social construct (nurture).
Philosophers explore how biology and culture interact to shape gender identities and roles.
Gender Identity:
Gender identity refers to an individual's personal sense of their own gender, which may or may not align with their biological sex.
Philosophical inquiries into gender identity examine how it is formed, experienced, and expressed, and the implications for individuals who do not fit into traditional gender binaries.
Social Construction of Gender:
Many philosophers argue that gender is a socially constructed category, influenced by cultural norms, practices, and institutions.
This perspective highlights how gender roles and expectations vary across different societies and historical periods.
Feminist Philosophy:
Feminist philosophy is a major area within the philosophy of gender, focusing on issues of gender inequality, patriarchy, and women's rights.
Feminist theorists critique traditional philosophical ideas and advocate for greater gender equality and the dismantling of oppressive structures.
Intersectionality:
Intersectionality is a framework that examines how various forms of social stratification, such as race, class, and sexuality, intersect with gender.
This approach emphasizes that gender cannot be understood in isolation but must be considered within the broader context of other social identities and power dynamics.
Transgender and Non-Binary Perspectives:
The experiences and perspectives of transgender and non-binary individuals challenge traditional notions of gender.
Philosophers explore the ethical, social, and political implications of these identities and advocate for greater recognition and rights for trans and non-binary people.
Gender and Language:
Language plays a crucial role in shaping and reflecting gender norms.
Philosophers analyze how language can reinforce gender stereotypes and explore ways to make language more inclusive and representative of diverse gender identities.
Gender and Power:
The relationship between gender and power is a key focus, examining how gender roles and expectations contribute to power dynamics in society.
This includes analyzing how gender influences access to resources, decision-making power, and social status.
Gender and Ethics:
Ethical considerations surrounding gender include debates about gender justice, rights, and equality.
Philosophers explore issues such as reproductive rights, gender-based violence, and the ethics of gender reassignment.
Gender and Representation:
The representation of gender in media, literature, and art shapes societal perceptions and attitudes.
Philosophers critique stereotypical and limiting portrayals of gender and advocate for more diverse and nuanced representations.
The philosophy of gender provides a rich and complex framework for understanding one of the most fundamental aspects of human identity and social life. By exploring the nature, construction, and implications of gender, philosophers seek to uncover the underlying dynamics that shape our experiences and strive for a more just and equitable society.
#philosophy#epistemology#knowledge#learning#chatgpt#education#Gender Identity#Social Construction of Gender#Feminist Philosophy#Intersectionality#Transgender Perspectives#Gender and Language#Gender and Power#Gender Ethics#Gender Representation#Nature vs. Nurture in Gender#gender
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
"Shopping for clothes is already intimidating. There are so many options and styles to consider, as well as factors like sustainability and ethics.
But for people in fat, disabled, or queer and gender-nonconforming bodies, it’s even more arduous.
Nico Herzetty, Emma K. Clark, and Paul Herzetty wondered: What if there was a way people could shop — not necessarily by color or size — but by measurements, materials, and ethics?
So they set off to create their website: Phoria.
Here, shoppers can set up a free profile, add their body measurements (and “typical fit challenges”) and peruse over 270 brands. Once these data points are entered, users can personalize their pages with “saved,” “recommended,” or “hidden” brands.
Pages can be totally private, or shared with the community to connect over styles and brands.
Aside from fit, brands in the Phoria database (which claims to be “the largest database of plus-friendly brands”) can also be filtered as “gender-neutral,” “woman-run,” “small business,” or “natural fibers.” Users can also filter for price, preferred styles, and more.
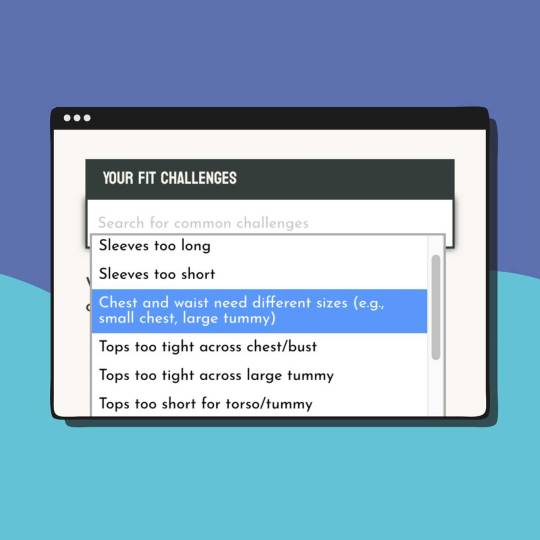
Pictured: A screenshot of the "Fit Challenges" feature on a Phoria user's profile.
Some brands include popular names like Athleta, Levi’s, and Patagonia. Others are small businesses, like Beefcake Swimwear, or Hey Peach.
“For so many people, it feels too damn hard to find and keep clothing that fits in all the ways that really matter. So we’re doing something about it,” the Phoria website reads.
“Unlike most online shopping experiences, we center the needs of plus-size women, nonbinary, and trans people, and prioritize supporting clothing brands focused on sustainability, ethics, and inclusion.” ...
That team — made up of Clark, and Nico and Paul Herzetty — calls themselves “fat, disabled, and very, very queer.”
“These are some of the main ways we identify, and they’re qualities that have directly impacted our ability to get dressed every day in a way that feels good,” the Phoria team introduces themselves on the website.
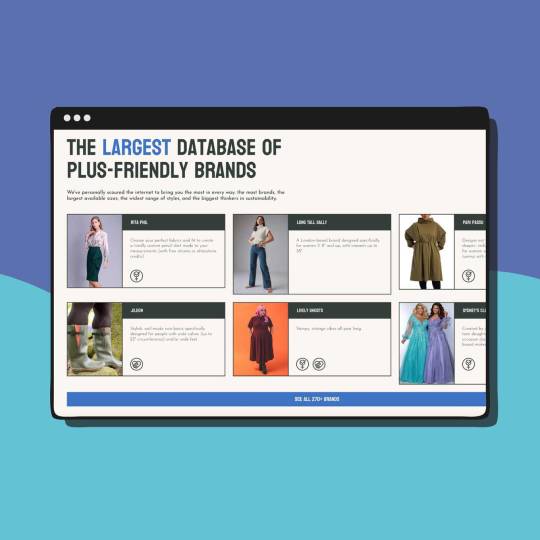
Pictured: A screenshot of Phoria's plus-size clothing brand database.
In addition to catering the user experience to women, non-binary, and trans people, Phoria is also a benefit corporation, or a B corp.
“We’ve legally required ourselves to consider the interests of all our stakeholders — customers, employees, the planet, and our shareholders,” the Phoria website explains.
“Our specific public benefit purpose is to reduce people’s dependence on buying mass-produced items made in unsustainable ways and to use human-centered business models to boldly challenge economic systems of inequity.”
Right now, in the early stages of the company’s business, it doesn’t make any money.
“We’re focused on building something that genuinely solves plus-size people’s challenges around clothes shopping and supports smaller and more sustainable brands,” Phoria’s website states.
So, spreading the word seems to be of utmost importance...
Additionally, TikTok creators @couplagoofs (a queer couple named Morgan and Phoebe), recently shared a video in which they discovered Phoria. They met the website’s creators at a fat liberation event in their city and were introduced to the tool.
Quickly, commenters responded with gratitude and excitement.
“It is so disappointing to sort through pages of plus size clothes that aren’t even plus size,” a TikTok user commented. “This is gonna be such a good tool!”
Some even shared emotional responses, speaking to the need at the heart of Phoria’s mission.
“I’m… gonna cry,” another commenter wrote. “I’ve needed this my whole life.”"
-via Goodgoodgood, November 20, 2023
#clothing#plus size#size inclusive fashion#body positive#fashion#slow fashion#style#gender affirming#trans inclusive#gender euphoria#disabled#lgbtq#gender nonconforming#small business#ethical fashion#ethical business#fatshion#fat positive#body positvity
2K notes
·
View notes
Note
How would the non-dateable characters react to an MC that spent their time in the surface world as a maid/butler and basically go out of their way to complete a task they’ve been asked?
Obey Me! Side characters with a Butler/Maid MC
Tags: Obey Me Side Characters x Reader, Butler/Maid!Reader, Platonic Relationships, Respect and Admiration, Hardworking MC, Humor and Teasing, Work Ethics, Supportive.

Diavolo
Diavolo would be absolutely captivated by your dedication. As the future Demon King, he holds a deep respect for responsibility and commitment, so seeing someone as committed as you would resonate strongly with him. In his mind, your unwavering determination to complete every task, no matter how small or seemingly insignificant, showcases qualities that are essential for leadership. It’s rare to find such commitment in the Devildom, where chaos often reigns, and your steadfast work ethic would be like a breath of fresh air to him.
“I see so much of myself in you,” Diavolo says with a warm, almost nostalgic smile. “When I was younger, I felt the same drive to ensure every detail was perfect, no matter how minor it seemed. It’s inspiring to witness that same dedication in you.” He chuckles, adding, “I’d wager that the Devildom could use more people with your sense of duty.”
He might even seek your insight on royal duties or discuss his plans for the future with you, curious about how you’d approach certain situations. Diavolo’s admiration goes beyond just respect—he values hard work, and he might even hint that someone with your skill and diligence could play an important role in shaping the Devildom’s future.
Barbatos

Barbatos would be one of the few who truly understands the depth of your dedication and what it takes to work behind the scenes. As Diavolo’s ever-loyal butler, Barbatos has devoted centuries to perfecting his craft and upholding an unmatched standard of service. He’d recognize the subtle signs of a fellow professional immediately—the precision, the thoughtfulness, the unwavering sense of responsibility. To Barbatos, every detail matters, and seeing you approach your tasks with the same level of care would spark a deep respect.
“MC, I must say, your approach to your duties is remarkable. You understand the importance of even the smallest task, something that many overlook,” he’d remark, his tone steady and approving. “It’s rare to find someone who appreciates the significance of every detail.”
However, Barbatos would also be watchful of your well-being. He knows firsthand how easy it can be to prioritize work over oneself. Occasionally, he might offer gentle guidance, or even a word of caution to ensure you don’t push yourself too hard. If he saw you struggling, he wouldn’t hesitate to subtly offer assistance, perhaps suggesting ways to streamline your work. In his own reserved way, he’d likely take pride in seeing your growth and would be one of your staunchest supporters.
Solomon

Solomon would take an amused interest in your sense of duty. As a powerful sorcerer, he’s grown accustomed to delegating and isn’t one to fuss over the finer points of daily life. So, encountering someone who insists on carrying out every task with thoroughness would be both intriguing and slightly endearing to him. Your dedication might even remind him of his younger days, though he’d be more likely to show his appreciation through playful teasing.
“Now, now, aren’t you the diligent one?” he’d say with a smirk, watching as you focused intently on some task. “I must admit, I can’t remember the last time I put that much care into… well, anything.”
In his lighthearted way, Solomon might offer to teach you magical shortcuts or charms to make your work easier, though he’d secretly admire that you’d likely still do things the hard way, for the sake of thoroughness. He might jokingly call you his “favorite overachiever,” but he’d always keep an eye on you, making sure you didn’t overwork yourself. Despite his teasing, his respect for your dedication would be genuine, and he’d find your work ethic refreshing in a world that’s often focused on power over responsibility.
Simeon

Simeon would be touched by your dedication and strong sense of responsibility, qualities that would resonate deeply with him as an angel. Your commitment to every task, no matter how small, would be something he not only respects but also cherishes. To Simeon, it would be a sign of your compassionate nature—your desire to give your best for the people around you, simply because you care.
“You’re truly remarkable, MC,” he’d say with a gentle smile, his eyes full of warmth. “It’s not everyone who approaches their work with such kindness and devotion. I can see that you care deeply for those you serve.”
Simeon would often check in on you, making sure you were balancing work with self-care. If he noticed you were pushing yourself too hard, he’d gently encourage you to take a step back. Perhaps he’d suggest spending time together outside of your duties—walking through the gardens, sharing stories, or simply relaxing. Simeon would genuinely value you for who you are, not just for what you can do, and he’d encourage you to find joy and fulfillment outside of work.
Luke

Luke would be thrilled by your dedication, finding your sense of duty truly admirable. As a young angel-in-training, he takes his responsibilities very seriously, though his youthful energy often leads him to be overly eager. Seeing you work with such focus would inspire him, but it would also make him a bit protective, especially if he thought you were overworking yourself.
“Wah, MC, you’re amazing! I wish I could be as amazing as you,” he’d say, his eyes wide with admiration. “But, you um don’t need to do everything by yourself, you know! I could help too!”
Luke would likely offer to assist you with smaller tasks or encourage you to take a break to play or have some snacks with him. He’d try his best to make sure you didn’t take on more than you could handle, insisting on being your little “assistant.” Despite his young age, Luke would look out for you in his own way, making sure you took time to rest and have some fun, believing that even the most dedicated workers deserve a break.
Thirteen

Thirteen would have a mix of amusement and genuine respect for your work ethic. As someone who’s used to being a bit chaotic and doing things her own way, she might initially find your dedication a bit too serious for her tastes. However, as she watched you work, she’d come to admire your commitment, even if she’d never admit it outright. Deep down, she might even feel a bit jealous of your dedication, though she’d cover it with teasing remarks.
“Look at you, all serious and diligent,” she’d say with a smirk. “I didn’t know anyone could take their job so… intensely. Are you sure you’re not a demon in disguise? Because even I don’t have that kind of energy.”
She’d tease you relentlessly, calling you “the Devildom’s best maid/butler,” but there’d be a hint of genuine respect in her tone. At times, she might even playfully sabotage your tasks to see if you could keep up, though she’d secretly lend a hand when you needed it most. She might even challenge you to relax or try out her chaotic methods, just to see if you’d let loose a little. But ultimately, she’d appreciate your commitment and offer her support in her own mischievous way.
Raphael

Raphael would be one of the few who completely understands your sense of duty. As a disciplined and morally driven angel (Seraphim), he believes that diligence and devotion are marks of true character. Seeing someone with such a strong work ethic would earn his immediate respect, though he’d also be quietly concerned if he noticed you sacrificing too much of yourself for your duties.
“MC, your devotion is commendable,” Raphael would say with a thoughtful nod. “I admire how you approach your tasks with such earnestness. Few people possess such a pure sense of responsibility.”
He’d encourage you to maintain a balance between work and personal well-being, often checking in to make sure you were not pushing yourself to the point of exhaustion. Raphael might even offer advice on meditation or relaxation techniques, subtly guiding you toward a healthier work-life balance. To him, dedication is a virtue, but he’d remind you that it’s just as important to preserve your own strength to continue serving others.
Mephistopheles

Mephistopheles would be intrigued by your dedication, though he’d probably find it a bit amusing as well. As someone with a sharp mind and a tendency to look down on others, he’d quickly recognize the value in having someone like you around. Your willingness to go above and beyond would be an asset he’d appreciate, though he might never openly say it. Instead, he’d express his admiration in his usual sarcastic, somewhat aloof manner.
“Diligent, aren’t we?” he’d comment with a raised eyebrow and a smirk. “I suppose it’s good to have someone who knows how to get things done. Just don’t let it go to your head. You’re only useful as long as you don’t burn out.”
Mephistopheles would likely test your limits, occasionally giving you more than you could handle to see if you’d falter. He respects hard work, but he’d also enjoy pushing you to see how far your dedication could take you. Behind his somewhat cold (more like self centred) exterior, there’d be a grudging respect, though he’d rarely express it openly.

#x reader#obey me x gender neutral reader#obey me x y/n#obey me x you#obey me x mc#obey me x reader#obey me diavolo#obey me barbatos#obey me solomon#obey me simeon#obey me luke#obey me thirteen#obey me raphael#obey me mephistopheles#obey me side characters#butler/maid!reader#platonic relationships#respect and admiration#hardworking#humor#teasing#work ethics#supportive#obey me diavolo x reader#obey me barbatos x reader#obey me solomon x reader#obey me simeon x reader#obey me thirteen x reader#obey me raphael x reader#obey me mephisto x reader
173 notes
·
View notes
Text
This is not asking whether it's okay to hit anyone. This is also not asking whether it's sexist for someone to be fixated on being "allowed" to hit women.
–
We ask your questions anonymously so you don’t have to! Submissions are open on the 1st and 15th of the month.
#polls#incognito polls#anonymous#tumblr polls#tumblr users#questions#polls about ethics#submitted jan 1#sexism#gender#violence
145 notes
·
View notes
Text
New publication with my best title yet! Using CRISPR gene editing as an anchor, I offer reflections on high-tech conversion practices, high-tech medical transition, and the ethics of hype.
Link to the paper here.
Link to an audio version here.

#lgbtq#queer#transgender#lgbtqia#trans#lesbian#lgbt#gay#gene editing#gender affirming care#gender affirming healthcare#medical transition#hrt#crispr#conversion practices#transphobia#science#bioethics#medical ethics
395 notes
·
View notes
Text
The forest floor was soft. The morning air and dew cool against your knees, the palms of your hands were laid flat on the ground. The scrolls you’d brought per Master Halsin’s instructions were discarded elsewhere, as was the bottom half of your Druid attire.
Master Halsin had always been so generous, even now as he was barely held together, resisting the urge to push your head to the ground and fuck you until Sylvanuus could hear it. Such moments were reserved for study periods, when you needed to learn focus.
You’re brought back to the present as your hands slip along the grass and your head falls, Master Halsin chuckles softly, keeping a hold of your hips. He slows his thrusts, cock still nestled comfortably inside you, “Are you alright, sprout?” He chuckles.
You groan softly, clutching the grass beneath you, “Y—yes Master Halsin,” you replied.
Master Halsin leans closer, his body over yours, he places a hand over one of yours and squeezes it gently, “Good, wouldn’t want you to lose focus during your reward.”
#halsin x male reader#halsin x reader#you gotta commune with nature sometimes 🌚#archdruid halsin who has a favorite student druid he dotes on and is super invested in a totally normal way#halsin x gender neutral reader#somewhere out there a book of ethics is being written to smack me on the head with however Halsin is a snack and I am starving 🤤
185 notes
·
View notes
Text
“Kill them with kindness”
WRONG. TRANSGENDER BEAM!!!! 🏳️⚧️🏳️⚧️⚧️🏳️🌈💥💥⚧️🏳️🌈🏳️⚧️💥⚧️💥⚧️🏳️⚧️🏳️🌈🏳️⚧️🏳️🌈⚧️💥🏳️⚧️🏳️🌈🏳️🌈🏳️⚧️🏳️⚧️💥🏳️⚧️🏳️⚧️🏳️🌈🏳️⚧️💥🏳️⚧️🏳️🌈🏳️🌈🏳️⚧️🏳️🌈🏳️⚧️💥🏳️⚧️🏳️⚧️

#a hat in time#ahit badge seller#badge seller#Ahit#the badge seller#The Badge sellers va turning me into a boy with his gorgeous fucking voice:#Fuck you Mick lauer you turned me into a man#Fellas is it ethical to hate on Mick lauer BC his voice is so pretty it transed my gender?#Was tempted to do this with the projectile badge instead but yk#I love how the badge abilities range from magnet to no fall damage to BAZOOKA
159 notes
·
View notes
Text
the phrase "girls girl" is sexism evolved and created in fear of being labeled as misandry and/or the south's fear of being labeled of a leftist, liberal, or feminist.
I am all for being a girls girl, but men aren’t required to like all men. Women now are required to like all women and everything about them. We must like someone’s music just because a woman made it. They can’t be competitive and trash talk like men because that’s not being inclusive for all women. We can’t talk about how we dislike a certain style, god forbid we hate a certain style; god forbid we say we hate something a woman is a part of.
women can take the same amount of criticism a man gets. BUT. Women shouldn’t be criticized just for being a woman. They shouldn’t be harmed, discriminated, hated just for BEING a woman.
I hate this new “girls girl” culture. I hate how people criticize Taylor Swift (womp womp) for being competitive on the charts and calling her “not a girls girl” simply for doing what a man would do with other men.
men don’t have to be a “boys boy” or whatever. Why?
Even in “feminist culture” we see harmful things.
don’t just say you’re a girls girl to gentrify and make yourself less scary to men. Say you’re a feminist. Criticize women. Advocate on your own life that every woman, even the ones you criticize are safe and treated as equal.
We are now held to the same standard we were in 1950 to always be pleasant and never to hate anyone. But it's been re-branded to being a girls girl.
But it's so entertaining when we are, isn't it? That's something we may never escape no matter what we do.
Be someone who fights for women. Be someone who believes all women are equal and all deserve to live life as freely as men. But you do not have to like every woman, just as you come prepared in mind that you may not be liked.
All that is truly important is that we don't put down other women to intentionally HURT them. There is a line between simply not liking a woman and putting them down intentionally.
AND WHILE I'M ON THE SUBJECT, I am also tired of this "pick-me" shit that's been going around. Blatant sexism that comes stems from the expectation of how women should act. You have no cause to call a woman a pick me just for mentioning that she likes video games, or may just get along better with boys- it depends on how she treats about women. That is all that matters!
And yes- you get to not like her. Because? We're human too.
Writing this very essay has made me feel inhuman. We need a guide on how to be morally right because we keep having to put up with how society wants us to be. We should be girls girls, but we also need to entertain by getting pulled into rivalries intentionally for the sake of.
If you skipped everything I said, this is the only thing you need to worry about. TREAT EVERYONE AS EQUAL AND HAVING SUCH EQUALITY TO EXERCISE AN INHERENT LIKE TO OUR OWN FUCKING FEELINGS TOWARD PEOPLE. TREAT EVERYONE AS EQUAL; AS YOU WOULD NOT CARE FOR ONE TO DISLIKE YOU, BUT WOULD CARE VERY MUCH IF THEY ALLOWED YOU TO BE HARMED, EMOTIONALLY OR PHYSICALLY. BUT- HATING OR DISLIKING SOMEONE FOR A QUALITY THEY WERE BORN WITH CANNOT BE JUSTIFIED BY ANY FORM; UNLESS SAID QUALITY HARMS OTHERS.
THAT IS FEMINISM. LIBERATE YOURSELF FROM THE NARRATIVE AND GO FREELY.
#writers on tumblr#female writers#writing#my writing#writeblr#on writing#feminism#liberal feminism#sexism#fuck the patriarchy#girl's girl#smash the patriarchy#fuck trump#personal essay#essay#in this essay i will#food for thought#gender roles#democratic party#leftists#leftism#liberals#morality#ethics#philosophy#ideology#morals#women#womanhood#girls supporting girls
21 notes
·
View notes
Text
Out: Puritan and Quaker America
In: America lived with the Shakers because they saw him as just another sad little abandoned orphan and with their interpretation of God leaning more mystical they weren't freaked out by him not aging normally
#but honestly the Shakers are (where) a super interesting group of people#progressive in terms of gender and racial equality+ had a work ethic that was like yeah you had to work but you should also make art#and invent things to make your like and the life of others easier#and other religious groups HATED them for that like it was viewed as being super whacky and unchristian#from a academic perspective I have to wonder how many Shakers were gay/lesbian/asexual+ and they just didnt have a term for not wanting#heterosexual marriage in early 1700s England so they just sorta did their best to create their own community in the environment#they already had available to them#I also really like this for Nyo America due to how I think it would have impacted her mentality about being a leader#hws america#aph america#nyo america#hetalia america#hetalia#historical hetalia#alfred f jones#amelia jones
75 notes
·
View notes
Text
Nothing is wrong with you.
Nothing is wrong with me.
Nothing is wrong with us.
#love#reassurance#reminder#lgbt#lgbtqia#nonbinary#trans#mixed race#human#human things#gay#pansexual#polyamorous#nonmonogamy#ethical non monogamy#lesbian#sapphic#gender fluid#multigender#adhd#autism#neurodivergent#actually autistic#actually adhd
127 notes
·
View notes
Text
Transcript Episode 93: How nonbinary and binary people talk - Interview with Jacq Jones
This is a transcript for Lingthusiasm episode 'How nonbinary and binary people talk - Interview with Jacq Jones'. It’s been lightly edited for readability. Listen to the episode here or wherever you get your podcasts. Links to studies mentioned and further reading can be found on the episode show notes page.
[Music]
Gretchen: Welcome to Lingthusiasm, a podcast that’s enthusiastic about linguistics! I’m Gretchen McCulloch. Today, we’re getting enthusiastic about nonbinary speech with Dr. Jacq Jones. They’re a lecturer at Te Kunenga ki Pūrehuroa / Massey University in Auckland, New Zealand. But first, our most recent bonus episode was about various kinds of fun mishearings and missayings and misparsings that people make in songs, in phrases, in idioms – all sorts of, like, you know when you hear “an acorn,” and you think it might actually be “an egg-corn” because it’s like the egg of the tree? Well, we talk about what strange things that you mishear, or misparse, can tell us about how language works. Go to patreon.com/lingthusiasm to listen to this bonus episode, many more bonus episodes, and help us keep the show running.
[Music]
Gretchen: Hello Jacq!
Jacq: Hi Gretchen!
Gretchen: Thanks for coming on the podcast.
Jacq: Thanks for inviting me. It’s awesome.
Gretchen: Before we get into all of the cool research that you’ve done about how nonbinary people talk that you’re working on, let’s talk a little bit about your origin story. How did you get into linguistics?
Jacq: Okay, well, I mean, how far back do you wanna go, I guess? I was a high school dropout. I was in my teens. I was going around North America, in Canada and the United States, working and this and that. I decided I wanted to go back to school. I did get into an adult education programme and finished up my high school. It was in a really small town in rural Alberta. It had a community college, and they didn’t have that many classes. I went into geography.
Gretchen: That’s super related to linguistics.
Jacq: You’d be surprised.
Gretchen: Great.
Jacq: Yeah, because I had spent time in the southern United States and in Alberta and in Ontario and things, and so I liked seeing all the different places. I went into geography. For people who don’t know, geography has these two big branches. There’s physical geography and human geography. Physical geography is rocks and trees and mountains and weather, and human geography is how people affect the world and how the world affects people.
Gretchen: So, like cities and stuff.
Jacq: Yeah, right. So, I was sitting in a class, and we were talking about how goods move across borders and how a lot of human influences – including language and political borders – can affect the movement of goods and, alternatively, how languages can be stopped by things like mountains.
Gretchen: Oh! Okay.
Jacq: You’ll have dialects that won’t go over the top of a mountain because you have this physical barrier. I was like, “That’s amazing.” Somehow, something about this interaction between this natural world and something like language, which is very, sort of, in your heads – but of course, you’re not gonna walk up a mountain to go talk to the person on the other side.
Gretchen: I live in Montreal, which doesn’t even really have a mountain by proper mountain-people standards, and I don’t wanna walk up that mountain just to talk to someone at the top. I totally understand that prehistoric people also did not wanna do this.
Jacq: Exactly. People, you know, live along rivers, so you have languages and language change and language contact all along these natural systems. That was the bug.
Gretchen: That’s fascinating. That’s so cool.
Jacq: And then I went from this community college – this adult education programme – to university, took a linguistics class, and as they say, that was it. Fell in love with phonetics and acoustics and all the meaty bits inside of you that create language. And here we are.
Gretchen: You do sounds – phonetics, how people talk – and specifically, I first encountered your research when I was in New Zealand last year at the New Zealand Linguistic Society Annual Meeting in Dunedin. You were giving a talk about your dissertation on how nonbinary people talk. How did you get into that topic?
Jacq: Sure. I think for most linguists, if you can press them, for most people in academia, what you’re into – there’s always something personal in it. There’s always something in what you’re doing. As a nonbinary person, navigating the 2010s – the late 2010s – trying to navigate what “gender” means, I kept catching myself really interrogating, really thinking about how I interact with people around me and what assumptions they’re going to put on me, what assumptions I’m putting on myself. You know, I’m getting on the bus, how low do I wanna talk to the bus driver? Just really silly stuff like that.
Gretchen: Like, are they gonna “sir” or “ma’am” me to show how they’re parsing my gender?
Jacq: Exactly. And do I want either of those options? Not really.
Gretchen: Which are both wrong.
Jacq: But if I can barely figure out what being nonbinary means to me as a nonbinary person, how can I expect the, you know, 60-year-old parent that I’m talking to, or a random person at the coffee shop I’m talking to, to understand all these backflips that I’m trying to do in presenting my gender? I mean, I’m into phonetics. I’m into acoustics. I’ve always been interested, linguistically, in this space between “This is how people talk because they are from Canada,” “This is how people talk because they’re a woman” – or because they’re a certain socio-economic class, or this – versus “This is how a jock or a burnout talks,” “This is how somebody asserts their identity.” When you’re looking at gender, that’s really this difference between a lot of stuff that we’re taught growing up and a lot of stuff that people might argue is inherent – a lot of stuff that is constrained by physiology, in some ways, by your existence in a meat suit – but you still always have control over it. That’s where this is. Part of it is being nonbinary and wanting that legitimacy of examining the numbers and proving that I exist, and nonbinary people exist, which are not represented historically. That’s changing now. And so, wanting that studying me and people like me to show “Hey, we exist. This is a thing that we can measure. This is a thing that we can look at,” and studying why, and yeah.
Gretchen: If you study all the other nonbinary speakers, then they’ll just tell how you need to talk now. So, that’ll be really handy.
Jacq: I mean, that’s part of it, too, right, is something that’s really exciting about studying nonbinary people during my dissertation – and I think that this is very much changing for the better, and I’m so happy that there are so many more options for young people in terms of gender and for old people in terms of gender and for anybody in terms of gender, but at the time, it really felt like all the templates that were out there were very binary – all the methodologies for studying speech, all of variation studies, everything, was, “This is how men talk,” “This is how women talk,” “This is how you’re supposed to talk if you’re a man or a woman,” or you want to present yourself – it was all binary.
Gretchen: I remember even when I was just being trained at grad school, everything was very binary. People weren’t even really questioning that. Even 10 years later, it seems like there’s been a lot more people thinking that through.
Jacq: Exactly. That is so amazing. From the point of view – putting on the researcher hat – studying it at the point where the speakers are making these first decisions without any templates – without a YouTube person to look at to model this kind of language on – felt really exciting.
Gretchen: And then somebody else who’s doing this study in another 10 years or 20 years or something when possibly nonbinary identity may have coalesced a bit more, then they have this to compare to as a baseline to see – it’s not often we get to watch a new gender evolve in real time. I mean, that’s not quite true because non-cis people have always existed, but the coherent, legible, nonbinary category, we get to watch it evolve in real time.
Jacq: Exactly. Traditionally, in these linguistic studies of dialect formation, that’s the 10-dollar word. You’re looking at something that’s very geographically bound. You have a group of people from one dialect that are moving to another place for another dialect. You have this contact, and you can study things coming out of that. But for nonbinary gender, even now, I can say, “Aw, there’s so many more nonbinary people out there.” I mean, realistically, if we think about our own networks, we do not have – I mean, I guess I can’t say this about everybody – but most of us don’t have a huge amount of nonbinary people in it compared to how many other LGBT people or how many other men or women – there just aren’t that many nonbinary people. We do tend to find each other, but we don’t have these big communities.
Gretchen: There’s a certain clustering, but it’s also not absolute, and there’s lots of other stuff. Do you feel like the internet has an influence on how nonbinary people talk?
Jacq: I think it does in the sense that the internet – and in particular, that kind of American sphere of the internet – influences everything that everybody does all of the time in some ways. But I also think that gender – sex and gender, in particular – these core identity things interact so strongly with where we are and our immediate context that it’s not quite as – in terms of speech, I don’t think it’s quite as strong. I did have one participant – if I can talk about my dissertation a little bit.
Gretchen: Oh, yeah, please, no, tell us about how the nonbinary people talk.
Jacq: One of my participants, Istus, is nonbinary and very femme. One of the things I talked about at that conference talk that you saw me – the slides are on my website, if you wanna take a look.
Gretchen: Excellent, we can link to those.
Jacq: Sweet. Istus is nonbinary and also very femme. This is something that really challenges the stereotypes that we have. Even me as a researcher coming into this had this idea of you have these men and women, and then you have these nonbinary people that are challenging these stereotypes, but “nonbinary” is not necessarily “non-femme.” So, Istus’s femininity was very nonbinary. When she talked about trying to construct her voice, this femininity that she wanted to get across, she would talk about putting on, basically, a Californian accent. She would say, “I can talk like this, and I sound very feminine, but I also sound like I’m smiling all the time, and I’m not that nice a person.”
Gretchen: Is Istus a New Zealander? Because you’re doing your PhD in New Zealand.
Jacq: All of my participants were from Christchurch (Ōtautahi), New Zealand. They were mostly between the ages of 18 and 22 – so this really specific first year of university cohort where you’re learning your identity and really stretching out from under your parents’ wings for the first time. I also had a couple of participants that were over 40. That’s interesting because it also challenges our stereotypes of gender as this static thing that you’re a man or a woman. When we look at how language can change over time, we don’t always think about how the people that are speaking can change over time.
Gretchen: A lot of the most visible nonbinary people are younger, but there’re also older people who are saying, “Oh, these young people have described a word for this thing that I’ve felt my whole life, and actually, I’m also this identity, and now there’s a word for it.”
Jacq: Absolutely. I mean, being a 45-year-old nonbinary person, you don’t necessarily want to speak like a 20-year-old nonbinary person, right.
Gretchen: Totally.
Jacq: If 20-year-old nonbinary people are trying to navigate what sex and gender is, if you’re 40, there’s that much more history of trying to figure all of this out.
Gretchen: Absolutely. Going back to Istus, who is the subject of the talk that you gave at the New Zealand Linguistic Society, one of the things that struck me about this talk when you were doing it is that you had participants take selfies of what they wearing at the same points as they were doing recordings. They did a bunch of recordings with different people in different environments, so you could see how they changed how they talked in relation to both what they’re wearing and also who they’re talking to.
Jacq: Absolutely. Because I think all of us have this experience of thinking about how we’re perceived by somebody else. That perception, for many of us, isn’t limited to just our voices. We don’t exist as a voice that wanders around in the ether.
Gretchen: We are not disembodied voices. We are meat suits wearing clothing suits.
Jacq: Yes. Which is super frustrating for many people, too. I call these recordings “in the wild” because I had this idea of David Attenborough following – “And here, he encounters the cis person.” But yeah, knowing that how we choose to present ourselves in that way is gonna change the way that we talk. This is pretty established. Also, the person that we’re talking to is gonna change the way that we talk. If you’re talking to your parent, you’re gonna talk to them differently than if you’re talking to your boss. We know this. But I was particularly interested in the way that these gendered relationships are navigated for nonbinary people.
Gretchen: Do you have an example of how some of your participants talked differently with different people?
Jacq: One example is Istus would play with makeup in really interesting ways. When I had the participants come, they would show me their selfies of these recordings, and I’d say, “Describe this outfit to me,” so I could see what they found really important because what you choose to wear has a lot more different – like, you know what is significant to what you’re wearing versus you don’t know if I’m wearing my lucky socks. That kind of thing.
Gretchen: Yeah, I dunno if your socks are lucky. I dunno if this is, like, the same shirt I’ve been wearing for three days which gives it a different valance to me compared to “Oh, yeah, this is my favourite shirt that I never wear, and I only wear on special occasions.”
Jacq: Istus didn’t have this in a picture, but she described her “stealth outfit,” which was every aspect of the outfit presented very masculine – sort of a suit jacket and loafers and this kind of thing. But every minute aspect of the clothing was actually feminine. The buttons were on – I can’t remember what side buttons are supposed to be on – but the buttons were on –
Gretchen: Neither can I.
Jacq: – the buttons were on –
Gretchen: The feminine side.
Jacq: Yeah, and the shoes were from the women’s section. There was this whole stealth coding that Istus was doing for herself – not for other people unless they’re cued in.
Gretchen: If she needs to go about as someone who doesn’t want her gender remarked on that particular day.
Jacq: Yeah, then she can choose where that gets presented. She would also wear different kinds of makeup. She would describe it as “enough eyeshadow so you can’t see the bags under my eyes” was one of her quotes.
Gretchen: Love it.
Jacq: The other quote was “makeup for the sake of wearing makeup” versus makeup that you would wear sort of a more natural face. You’ll forgive me if I get any of this wrong. I am not a makeup person. It was interesting because the – in her voice – the feminine cues that she used would change based on how overt her makeup was.
Gretchen: This is something that stood out to me about your talk, the makeup thing, because I’m very femme, I’m very cis. To me, I want all of my gender vectors or all of my gender points in the femme tally. But what Istus did in this thing was, if she was wearing makeup, she would do less femme gender vocal cues, like she’s counterbalancing the gender points, and as long as you have enough in the femme category and enough in the masc category, then it balanced in her head for whatever her personal definition of “balanced” is, which isn’t how I approach gender but is a really interesting thing that I learned from your talk.
Jacq: Aw, thank you. I’m glad that you found it interesting. Yes, Istus – and this is a theme throughout all of the participants. I should say that I also interviewed binary participants – men and women – and there were certain themes there, too. I don’t want to leave them all the way out.
Gretchen: Totally. You gotta have a control group.
Jacq: Yeah. But for the nonbinary participants, there was this – in my dissertation, I called it “incongruence” – but this idea that if you want to create some kind of mixed signal or if you wanna create something that isn’t quite in the two boxes that the people who are listening to you maybe have, then you can either take cues from both, or you can try to find some kind of middle ground. Those are two quite different things. Something very overtly feminine in your physical presentation combined with something a little bit less feminine or more masculine in maybe your vocal presentation, that can still get to something that isn’t binary in a way different than being very neutral-sort-of-middle-ground is.
Gretchen: The neutral-middle-ground is like, “I’m just gonna wear a hoodie and jeans because every gender can wear a hoodie and jeans, and then nobody will be able to perceive me as any gender at all,” whereas in a clothing way, doing something that has mixed signals would be like, “Okay, I’m gonna have a beard and also this super sparkly eyeshadow” or something like that.
Jacq: Yeah, yeah, absolutely. And that wasn’t quite where any of my particular participants went. But the idea that if you only have these two options, and you need to create a third option, there isn’t only one way to do a third option. There isn’t only one way to be nonbinary. A lot of how you do that, I found in my dissertation, is based on your own personality, which is like, “Oh, surprise, people have agency in how they talk,” and some people don’t like wearing super sparkly eyeshadow.
Gretchen: Totally. But also, sometimes you need to do the academic version of establishing that baseline because you could say, “Well, based on my friends, a lot of them which are nonbinary, people seem to do these strategies,” but having written it down in this academically legible place and gone through and done it with some statistics or something lets you say, “Okay, here’s what we have in terms of what we know now and maybe this would change in another decade if there becomes a more socially legible category of nonbinary-ness.”
Jacq: And I think, also, part of including binary participants in this work is to bring nonbinary people into both an academic conversation that’s already happening, which is, again, that sort of talk of legitimacy and saying, “Here’s an established body of work,” and bringing a “new population” – I’m making finger quotes; they’re not actually new – but bringing a different population – an “understudied” population, let’s say – into the fold, at the same time, that allows you to interrogate what’s already there. We have this whole body of literature that ignores that nonbinary people exist –
Gretchen: But that also doesn’t ask cis people or people that we’re presuming are cis, “How did you know that you’re cis? How do you know your gender? What are you doing to signal your gender with your voice? And how much of that are you doing deliberately?”
Jacq: I think that that’s really valuable, too, the idea that – I mean, there’s nothing that says a cis person isn’t allowed to think about masculinity, or how they present masculinity, or how they present femininity, or what that means. I mean, personally, I think it would be really useful if more cis people did that. If more people just thought about gender in ways that weren’t binary, talking to the binary men and women in my study, I was a little bit surprised, but it was amazing to see – I mean, some people never thought about it. There’s questions about “How do you feel about being a woman?” or being a man, and people said, “I dunno. I never thought about it. It just felt right.” But not everybody. Some of the participants that I spoke to did deeply interrogate their gender at some point in their lives. One of my cis male participants talked about thinking that maybe they were trans for a while and then realising they weren’t. I think the fact that we, as people – and also, we as linguists doing these studies on language – can interrogate even binary gender from these perspectives is really valuable.
Gretchen: This was something that came up in a recent episode that we did about the vowel space and how gender affects the vowel space, which we can link to. One of things that I find neat about that research is that even kids who haven’t gone through puberty yet who still have all identical vowel spaces or vowel spaces with as much variation as they have in heights but nothing specifically affected by the physical changes of puberty are still doing social genders and actually have different vowels based on the genders in their heads even though their bodies aren’t affecting what sounds they can produce yet.
Jacq: That works the other direction, too. We often think of puberty as this thing where a bunch of stuff happens to you, and then you pop out the other end like, talking and looking like –
Gretchen: A gender, now.
Jacq: A gender. You are this. But that’s not – I mean, the variation that almost any given human can produce is so much wider than the constraints of physiology. I’m not the only person to look at this. I know that Viktoria Papp has done really excellent work with transmasc people. Lal Zimman also works with transmasc populations a lot, too. You can take testosterone, and it can thicken your vocal folds, and it can create a drop in pitch, but that’s not what it means to talk like a man if you’re transmasc. That’s not the end of it. At the risk of summing up someone else’s research in two sentences, what you tend to see, I think, in Vietze’s work is a drop, an initial drop, from testosterone, and then it kind of pops back up again with the idea that, as people become more comfortable in their bodies and in their lives and in their situations, there’s less pressure to perform some stereotypical masculinity and more to just be the person they are, the transmasc person they are, or the nonbinary person they are.
Gretchen: That sounds neat. We can link to that study so that if people want to hear more than the two-sentence summary version, they can follow up on that.
Jacq: And Lal Zimman’s work is amazing. Every single thing that Lal has written is fantastic, too.
Gretchen: Yes. Everyone’s in the Lal Zimman fan club. So, you have a corpus, which is delightfully called, I think, “The RAINBO Corpus.”
Jacq: Yeah, “Recorded Audio-visual Interviews with nonbinary and Binary Orators. It’s “RAINBO” without a W.
Gretchen: Oh, and it spells “RAINBO” – that’s so good!
Jacq: For the sake of the acronym.
Gretchen: That’s such a beautiful acronym. You have six nonbinary participants in there, and six binary participants, and they held this speech that you looked at the pitch of it, and you’ve looked at how they do their vowels and things. You also have a talk and a paper, I think, you’re working on that’s co-authored with one of those research participants who then de-anonymised themself from the previous anonymous corpus work that they were in.
Jacq: Yeah.
Gretchen: I find this really interesting because there’s this interesting balancing act in academic between, “Oh, I’ve got a research participant. They’ve got sensitive data. I’m going to preserve their anonymity,” and also, sometimes when people are telling us really interesting things about their lives or their language choices or their identities, giving them credit for that intellectual contribution to the work which names them – yeah, can you talk about this balancing act about participant and researcher collaboration?
Jacq: Absolutely. I would love to. I’ve been thinking about it a lot. I don’t want to portray myself as an expert. There is a whole other body of work where your collaborators, your language consultants, work very closely with the researcher, but that’s not always the same methodology as the bigger picture, what we call “variationist,” studies where we’re trying to look at large groups of people and how they speak. Kaspar is the name of the person that I worked with. And I got their permission before this episode – I asked them how they wanted to be referred, and they said, “Okay.” We’ll call them Kaspar, which is great because that’s their name, so it’s super easy for me to remember.
Gretchen: But they also had a pseudonym in the study originally.
Jacq: Yeah. In the study, if you read my dissertation – which you don’t have to, but if you do – in the study, they were called “Alex.”
Gretchen: Dissertations are notably very long and, often, in the years after a dissertation comes out, people will write some shorter papers that summarise small bits of the dissertation. Keep an eye on Jacq and their website. Maybe there’ll be shorter versions. But if you really wanna read the whole dissertation or skim through it and pick out the bits that look interesting to you, we will link to it.
Jacq: I had set up, for my dissertation, you know, as a – I think there’s something else. Dissertations are a long work, and you’re learning as you go. That’s the point. When you’re planning these ethics and all of the things in planning this dissertation, you go through the process that has already been established. I did that. It’s fine. Kaspar came and was recorded. It ended up, as it happens, after I had done my data collection, Christchurch is not a huge place. Kaspar and I were in the same social circles, and we became friends after the data collection. Every once in a while, we would talk about the work that I was doing and stuff I was studying because they were super interested. They have a background in mathematics, and they’re familiar with linguistics, so it’s not like they knew nothing about linguistics.
Gretchen: So, when you were showing them some pretty graphs, they were like, “Oh, cool, graphs. I like those.”
Jacq: Yeah. And then I can’t remember if I asked them or they offered to do some proofreading before I had submitted it, and I sent them a draft. I got it back, and there were smiley faces and frowny faces on a lot of stuff. Then because we’re friends, we went and hung out and talked about it, and there’s something different. You’re participating in research. You’re getting recorded. And then research comes out. You know that you’re maybe nonbinary. You’re this population. And then you see yourself on a graph that plots your pitch somewhere, and you know what the stereotypes about feminine pitch and masculine pitch are. I mean, I did a bad thing in that sense. I hurt somebody, right, in not earth-shattering ways, I don’t think – or at least Kaspar didn’t tell me it was earth-shattering.
Gretchen: But in frowny face ways, yeah.
Jacq: And we share this perspective of the importance of examining new populations using established methodology and these traditional ways of doing things to grant – whatever you wanna call it – some kind of legitimacy from the academy – or however we wanna navigate this – but then this is still real people that are given little dots or little diamonds and plopped on a graph. I can say in 300 words how this isn’t meant to tell people how gendered they are; this is meant to examine nonbinary people and compare them on equal footing with binary populations, but of course, nonbinary people don’t come to the table with no baggage, with nothing behind them. You come, and you come with a gendered upbringing, a gendered – you exist in a world, right. You can’t just not.
Gretchen: Totally.
Jacq: That was really hard. We had a lot of conversations about that through the course of proofreading a dissertation and submitting it and trying to get to a point. And I didn’t have – because of the way that the ethics works – I couldn’t contact every other participant afterward and get the same insights and things. But it’s not all bad. Kaspar expressed to me how interesting it was and how amazing it was to see their plots there and the joy of seeing themself not in the ASAB cohort that they expected versus the sadness when they came a little bit too close or that kind of thing. We gave a talk about this and, hopefully, a paper that examines that a little bit more. The other benefit is that, now I have a collaborator and a co-author, it means that we can do a lot more really interesting stuff with data.
Gretchen: Well, and if they know all this math, you can do such cool math.
Jacq: And we can track them over time, and we can do new recordings and even stuff about how these interviews with people, or these recordings, are still a snapshot in time. Things aren’t static. People change, and people’s interpretations of themselves are reinvented constantly. I’m really excited. Watch for that paper.
Gretchen: That sounds really cool and really exciting. We will look forward to the Jacq-Kaspar collaboration, Kaspar-Jacq collaboration. You can keep swapping your names for who goes first if you do a whole bunch of different co-authorships like people do.
Jacq: It made me glad that I wasn’t recording myself.
Gretchen: Were you sometimes interviewing or the interlocutor?
Jacq: Yeah. We did these “in the wild” recordings, and then we had the traditional sociolinguistic interview with all of these questions. We recorded me at first thinking there might be accommodation stuff, but then it’s also just like, I can’t transcribe, like, 400 million hours of –
Gretchen: So, “linguistic accommodation” is the thing where, when you’re talking with someone, especially if you like them or you’re trying to get along with them, you talk more like the person you’re talking to, which happens to lots of people lots of the time. I certainly do it. And you were thinking, well, maybe if people are talking more like you when they’re talking with you, then that might shift things, but also, you end up with a lot of data.
Jacq: Yeah, that’s true. It ended up doing a little bit of spot checking. It didn’t seem quite there because of these outsider-insider relationships of I am Canadian sitting in New Zealand interviewing people. There was enough of a gulf that it didn’t seem –
Gretchen: They didn’t all start sounding Canadian when you were interviewing them. I’m shocked.
Jacq: They weren’t like, [stereotypical Canadian accent] “Oh, hey, thanks for interviewing me.”
Gretchen: Maybe this is a good segue actually because you’re a fellow Canadian, hello, “Welcome to the podcast, eh” – [laughter] – who’s been living in New Zealand for nine years now.
Jacq: Yeah, almost a decade.
Gretchen: Amazing. We’ve had a previous interview with Ake Nicholas talking about Cook Islands Māori if people want to hear someone with a more New Zealand accent.
Jacq: Actual New Zealand accent.
Gretchen: An actual New Zealand accent. But this is presumably a linguistic experience for you. Do you wanna say anything about what it’s been like? Do you talk differently to people other than me who don’t have a similar Canadian accent?
Jacq: It’s kind of hard to know. I think there’re a few things. I noticed about four or five years in that I was losing my Canadian raising. We had gone somewhere, and I said, “Aw, look at those three houses.” I was like, “Ah! What did I just do?” Instead of saying /haʊsəz/, I said /haʊzəz/. I was like, “Ugh.” Which is funny because when I lived in Canada, I never noticed Canadian raising. It was one of those things that was so –
Gretchen: So, Canadian raising, which we actually haven’t talked about on Lingthusiasm yet – so maybe someday in the future –
Jacq: What!
Gretchen: – is the thing that is responsible for the differences between how I say the vowel in “house” [noun] versus “house” [verb] or in “height” versus “high” – “height,” “high,” “house,” “house.” I will say, I don’t Canadian raise that much, so it’s a difference in terms of how you say the vowel between /t/ and /d/ or /s/ and /z/. There’re some people who say something like, “about,” more like /əboʊt/. There’s a stereotype that Canadians say /əbʊt/, and that’s not true. I want to correct that right now. People in lots of other English-speaking environments don’t do this Canadian raising, and you noticed that you were stopping doing it. Anecdotally, I also notice people that move to Canada do start doing more Canadian raising, so this seems to be one of the ones that’s flexible in people’s speech.
Jacq: Yeah, I think that’s true. It’s funny because it’s so stereotyped in Canada. I don’t think it’s as strong as the stereotype, but it’s definitely sticky in a weird way. I did lose it. But probably, in this interview, it’s back.
Gretchen: It clicks back in.
Jacq: Yeah.
Gretchen: Any other things that you’ve noticed?
Jacq: I remember when I first landed in New Zealand – so New Zealand is non-rhotic. There’s no R. Words that are spelt E-A-R, like “ear,” and words that are spelt A-I-R, like “air,” have merged, so they’re pronounced the same. I was sitting on the airplane waiting to disembark, and the announcer came on, and they said, “Could everyone exit via the /ɹiəɹ stiəɹz/?”
Gretchen: Oh. [Laughs]
Jacq: I had this moment of, like, cows stacked up at the back of a plane. Like, and it’s sat with me, and I think it’s because the context wasn’t quite enough for me to get – but I was like, “Rear steers? Rear steers. What?”
Gretchen: Well, it’s what you exit the “ear-plane” by, obviously.
Jacq: “When you exit the ear-plane by the rear steers, or alternatively, exit the airplane by the rare stairs,” which are the stairs that they don’t bring out that often.
Gretchen: We have to save the rare stairs and the fine china for guests.
Jacq: Exactly.
Gretchen: That’s exactly the kind of thing that, especially, when you’re hitting something out of context, and they seem to be more fond of using that, so if you weren’t used to that particular phrase, either, it would catch.
Jacq: Yeah, and I mean, you’re also in a new place and all of this, and you’re trying to pay attention because you have to do what the airplane people tell you because that’s the rules. I have one more anecdote that is very deeply only Canadian and New Zealand overlap.
Gretchen: Please, I wanna hear it.
Jacq: Maybe this is only western Canada. We’ll see. So, Gretchen, what do you call the front row of seats in the classroom?
Gretchen: Oh, that’s where the “keeners” sit.
Jacq: That’s where the “keeners” sit, right, that’s the “keener” seats, right?
Gretchen: I dunno if I have “keener seats” specifically as a phrase, but like, absolutely, totally understand you when you say this.
Jacq: So, if somebody’s a “keener,” that’s the person at the front of the class, yeah.
Gretchen: Absolutely, yeah. I have told people about this Canadianism myself.
Jacq: Amazing! I’m glad it’s a super salient Canadianism.
Gretchen: I’ve introduced Lauren to it, in fact.
Jacq: So, it’s not a thing in New Zealand. They don’t have keeners, but New Zealanders say “keen” all the time.
Gretchen: Oh, but for something different.
Jacq: You’ll say – and apologies to any New Zealanders if I get these pragmatically a little bit wrong – but you’ll say, “Ah, I’m going for coffee. Is anyone keen?” Or you might say, “Ah, the movie’s coming out next week,” and someone else might say, “Keen,” like they’re keen to go.
Gretchen: Oh, okay, yeah, I think I could say, “I’m keen to go,” but not “keen” by itself in a phrase like that.
Jacq: No, and I think that my impression – my 8-year-old, 9-year-old Canadian impression – is that you don’t really use “keen” – because it has a little bit of that odd, negative – I mean, it’s a “keener” thing, so unless you’re really claiming –
Gretchen: That you’re a big fan of Star Wars, and you’re a Star Wars keener, and you definitely have to go see the new one.
Jacq: If you’re keen to go to Star Wars, you wanna be in the front row.
Gretchen: Of course! Yeah, okay, yeah, I sort of get that. It’s not as neutral. It’s like you’re really actively excited. You’re not just like, “Oh, yeah, I’d be good to go” or like “I’d be down to go.” “I’d be keen to go” is like, “I’d be so keen to go! That would be great!” not just like, “It’d be fine.”
Jacq: Yeah, but if you’re keen, you’re like, “Yeah, I could” – if you wanted to be extra, you could double up the New Zealandisms and you could be “keen as.”
Gretchen: Oh, yeah, I’ve heard the “as.”
Jacq: You could be “keen as,” but I don’t know – that’s where my knowledge of New Zealand lexical items stops is at “as.”
Gretchen: I love “keener” as a Canadianism because my prof friends will be like, “Oh, one of my keeners came to my office hours today,” and they’ll mean that student who’s always asking really good questions and is really excited to be there and stuff like that. It’s very positive when my prof friends who were all themselves keeners back in the day use it. Maybe some people use it negatively, but I sure don’t know any of them.
Jacq: If you are a keener, then “keener” is quite positive, but maybe less so if you're not.
Gretchen: Maybe less so. So, you finished your PhD, and you’re teaching now. I have been told that you make students stab themselves with toothpicks for science. Can you tell us about that?
Jacq: I would love to tell you about that, with a caveat: I tell students to very carefully try not to stab themselves with toothpicks, but it doesn’t quite translate. I teach phonetics, which involves learning about all of the sounds and how we make them. If you’re a speaker of English, you might be familiar with this little sound called “R.”
Gretchen: R is a sound, yes, that I’m familiar with.
Jacq: The alveolar approximate, the /ɹ/ noise. The R sound, the /ɹ/, can be made about 16 million different ways. There’s something like eight or nine different things that you can do with your mouth that will get you close enough to /ɹ/ for people to understand you.
Gretchen: Oh, wow. When I was learning phonetics, they told us there were two different ways, and there’s actually six or eight of them.
Jacq: There’s two different tongue positions, and that’s where the toothpick comes in. But you can also do – there’s different stuff with the back of your mouth. Some people have lip rounding, and some people don’t. Some people raise this and that – yeah, there’s different ways to do it. But you were right when you were learning phonetics.
Gretchen: But because it all produces approximately the same sound, kids just hear adults making the sound, and they experiment with their mouths to produce The Sound, and because the meat suit part of our throats is kind of squishy, you can manipulate it in different ways and end up with the same thing that comes out.
Jacq: You get close enough. In English, we don’t have a lot of other stuff in that area, too. When you think about it, if you’re a kid, if you think about something like a /p/, if you’re a baby looking at a caregiver going /p/, you can really see that, right, but a /ɹ/, you get a face, and you don’t really know what’s going on.
Gretchen: You just get a blank face. You can’t see what they’re doing. With something like a /k/, you can’t necessarily see what they’re doing, but the sound is very distinct that they’re making. /ɹ/ is this approximate sound, which is why it’s called an “approximant” in the International Phonetic Alphabet because it’s just sort of like, “Eh, I dunno.”
Jacq: Close enough, yeah. What you get is you have this sound where there’s a bunch of different ways to make it, and also a bunch of speakers that don’t really know how they make it. When you say something like a /k/, you make that sound, and you’re like, “Oh, my tongue goes here.” But when you’re making a /ɹ/, it changes – depending on where it is in the word – all this stuff. As you learned in your phonetic class, there are two ways that your tongue can be shaped when you’re making a /ɹ/ sound. This may blow some people’s minds because they never thought about it before and didn’t realise that the other way is possible. The two big ways are – they have a million different names because of course they do – but one is called the “bunched R,” usually.
Gretchen: This is when your R, like the back part of your tongue sort of crunches up or gloms up into a bit of a shape at the back that doesn’t actually touch the roof of your mouth.
Jacq: The back of your tongue is all crunched up, and the front of it is down at the bottom of your mouth. The other way to do it is often called the “retroflex R,” or the “curly R,” so you have bunch-y R and curly R. The curly R – the retroflex R – the front of your tongue is curled up and back a little bit.
Gretchen: It’s almost like the tip of the bottom of your tongue is touching, or almost touching, the roof of your mouth.
Jacq: Yes. Which one do you make? It’s hard to –
Gretchen: I know which one I make!
Jacq: Awesome! One of the important points of science is confirmatory analysis. You should replicate this finding and see if it still holds true. If you wanna know which R you make, there’s a way that you can do this with just a toothpick. It’s really easy. All you do is you take a toothpick, a clean one – and make sure you wash your hands – and then you take your toothpick, and you make an R sound – /ɹ/ – or you can pretend you’re a dog and go [imitates dog growl], something like that, just make your /ɹ/ noise. Then you take your toothpick, and you rest it on your bottom teeth or however you wanna – kind of have it centrally into your mouth – and as you go /ɹ/, slowly and carefully, and not stab-ily, put the toothpick into your mouth, and then go, “bleh,” stick your tongue out. The toothpick will either be touching the top of your tongue or the bottom of your tongue.
Gretchen: Whoa! And this tells you which R you have?
Jacq: Yes. And if it’s touching the bottom of your tongue, you’re making a retroflex – you’re making a curly R. And if it’s touching the top of your tongue, you’re making a bunched R.
Gretchen: So, you’re either a curler or a buncher, and you can tell this based on which side you are. I actually went looking for toothpicks so that I could try this and ended up finding a cotton swab, like a Q-Tip, before I saw my toothpicks, and so I tried this with a cotton swab and did not stab myself. This is the safety conscious version you can do if you like because it also works.
Jacq: As long as it’s clean and your hands are clean, that’s a good, safe way to do it.
Gretchen: I’m a buncher, which I thought I was, and I have just confirmed that.
Jacq: Anecdotally, in Canada, it was usually about 50/50 when we go through classes, or we try it. This is in Alberta.
Gretchen: And in New Zealand is it also 50/50, or is it different?
Jacq: In New Zealand, there are a lot more bunchers. I think this might have to do with New Zealand being non-rhotic. I don’t have a paper on this. I don’t know anything. But there’s also a lot less lip rounding. In Canada, lip rounding is almost universal, like it’s on Rs a lot.
Gretchen: Yeah, I lip round.
Jacq: But in New Zealand, that’s not the case. Most people don’t round their lips.
Gretchen: Jacq, thank you so much for joining us on the podcast. As we ask at the end of every interview, “If you could leave people knowing one thing about linguistics, what would it be?”
Jacq: It would be that you’re the boss of your language. How you communicate with people – it’s all on you. People can tell you how they think you should talk. Even linguists can say, “Well, this is how people talk.” But if you’re not feeling it, do something different. You can change it. You can do whatever you want, communicate however you wanna communicate. Don’t let anyone tell you what to do.
[Music]
Gretchen: For more Lingthusiasm and links to all the things mentioned in this episode, go to lingthusiasm.com. You can listen to us on all of the podcast platforms or at lingthusiasm.com. You can get transcripts of every episode on lingthusiasm.com/transcripts. You can follow @lingthusiasm on all the social media sites. You can get scarves with lots of linguistics patterns on them including the IPA, branching tree diagrams, bouba and kiki, and our favourite esoteric Unicode symbols, plus other Lingthusiasm merch – like our “Etymology isn’t Destiny” t-shirts and aesthetic IPA posters – at lingthusiasm.com/merch. You can find our co-host, Lauren Gawne, on social media, and her blog is Superlinguo. Links to my social media can be found at gretchenmcculloch.com. My blog is AllThingsLinguistic.com. My book about internet language is called Because Internet. You can find our guest, Jacq Jones, on their website at jacq.land – that’s J-A-C-Q-dot-L-A-N-D. Lingthusiasm is able to keep existing thanks to the support of our patrons. If you wanna get an extra Lingthusiasm episode to listen to every month, our entire archive of bonus episodes to listen to right now, or if you just wanna help keep the show running ad-free, go to patreon.com/lingthusiasm or follow the links from our website. Patrons can also get access to our Discord chatroom to talk with other linguistics fans and be the first to find out about new merch and other announcements. Recent bonus episodes include spoonerisms, mondegreens, and eggcorns; secret codes and the joys of cryptic word puzzles; and inner voice, mental pictures, and other shapes for our thoughts. Can’t afford to pledge? That’s okay, too. We also really appreciate it if you can recommend Lingthusiasm to anyone in your life who’s curious about language. Lingthusiasm is created and produced by Gretchen McCulloch and Lauren Gawne. Our Senior Producer is Claire Gawne, our Editorial Producer is Sarah Dopierala, our Production Assistant is Martha Tsutsui-Billins, and our Editorial Assistant is Jon Kruk. Our music is “Ancient City” by The Triangles.
Jacq: Stay lingthusiastic!
[Music]
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
#linguistics#lingthusiasm#language#podcast#episodes#transcripts#podcasts#Jacq Jones#phonetics#phonology#gender and speech#nonbinary speech#binary speech#linguistic research#research ethics#interview#geology#geology as a gateway to linguistics
28 notes
·
View notes
Text
jaime is so gender in a way that makes sense. like he is a dude who is totally comfortable with being a dude. he could be the younger more beautiful queen if he wanted to but even then he would be doing it in a very man way. he crossdressed his way through childhood but he doesnt really care. despite all of his problems and his flaws, he knows how his gender works and nothing's really a threat to it.
CERSEI, meanwhile, is so gender in a way that is so deeply confusing i get a headache every time i think about it.
#tyrion isnt really gender. hes kinda like that ethics teacher at my school who called me a nobody underclassmen last week.#spiritual successor to the brienne gender meta#jaime is extremely comfortable in his masculinity. dont have a fucking clue what cersei's on though.#cersei lannister#jaime lannister#asoiaf#house lannister#a song of ice and fire#my posts#tyrion lannister
189 notes
·
View notes
Text
Parker Molloy for The Objective:
When Donald Trump signed an executive order on Tuesday attempting to end gender-affirming care for anyone under the age of 19, encourage the prosecution of doctors who provide this care, and strip insurance coverage from trans people, neither the New York Times nor the Washington Post thought this development warranted a push notification to their readers. This is a clear illustration of how leadership at these outlets’ view of attacks on trans rights: they’re standard political developments rather than acts of state-sponsored discrimination targeting a vulnerable minority. The lack of push notifications might seem like a small thing, but it speaks to these newsrooms’ failure to recognize the gravity of this moment — one that stems directly from these outlets’ inability to see their own role in making it possible. The Times‘ coverage, in particular, demonstrates the paper’s refusal to take accountability for its role in seeding anti-trans sentiment.
For years, the newsroom has published article after article casting doubt on gender-affirming care, portraying trans healthcare as “controversial” despite overwhelming medical consensus supporting it, and giving ample space to anti-trans activists while rarely quoting trans people themselves. All the while, anti-trans opinion columnists at the paper, such as Pamela Paul, have churned out piece after piece delegitimizing and demeaning trans existence. Tuesday’s coverage continued this pattern — in reporting on an executive order directly impacting trans Americans, the Times didn’t quote a single trans person.
This isn’t an accident or oversight. It’s part of a consistent pattern at the paper that reflects an editorial choice — with material harm given the Times’ role as the U.S. paper of record. As documented in The Flaw’s 2024 investigation of media coverage, the Times‘ reporting has repeatedly been cited by lawmakers and used in legal briefs to justify anti-trans legislation across the country. The paper’s consistent framing of gender-affirming care as “controversial” and “dangerous,” rather than as standard medical care supported by every major medical association, provides intellectual cover for the sweeping restrictions Trump is now attempting to implement nationwide. Even now, with Trump explicitly calling trans healthcare “chemical and surgical mutilation” in official government documents, the Times maintains its stance of faux-neutrality, similar to how its leadership ignored queer Americans during the inception of the AIDS crisis while giving cover to the poor government response. The paper amplifying mainstream anti-trans talking points now acts as though it’s merely documenting the inevitable, rather than watching the seeds it planted bloom into full-blown institutional discrimination.
The Washington Post‘s coverage, while marginally better in including some trans voices, still treats this as just another policy story rather than what it is: an unprecedented attack on the healthcare rights of both trans youth and adults that will put lives at risk. Both papers frame this primarily as follow-up coverage on Trump’s campaign promises rather than a human rights story about state-sponsored discrimination. This is what happens when newsrooms fail to adequately include trans voices, both in coverage and in editorial decision-making.
Parker Molloy wrote for The Objective how mainstream media outlets such as The New York Times normalized anti-trans sentiments and downplayed Trump’s cruel anti-trans policies.
#Parker Molloy#Media Ethics#Media Bias#The New York Times#The Objective#Transgender#Anti Trans Extremism#Gender Affirming Healthcare#LGBTQ+
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
some of it i think is that everyone got so fed up of the spats on dogblr that people either quit, mutually blocked each other, or matured, but i am fascinated by the drama that is shared by dogblr and dogbook, vs the drama that i get just on dogbook and not on dogblr
#this brought to you by this week's ccpdt meltdown#which i have not seen a whiff of on tumblr and that's fine#i do think its Inchresting the gender dynamics at play and how nobody is talking about those#anyway#ethics in dog training
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
To imagine a sexuality that doesn't conform to law or nature is not what disturbs people. But that individuals are beginning to love one another - there's the problem.
Michel Foucault, Ethics: Subjectivity and Truth
165 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Social Consequences of Marketing
Marketing, while essential for businesses and economies, has also been criticized for causing harm to society in various ways. Here are some significant ways in which marketing has negatively impacted society:
1. Promotion of Consumerism
Excessive consumption: Marketing often encourages the idea that happiness and success are linked to material goods, promoting a culture of consumerism. This has led to excessive consumption, debt, and environmental damage, as people are driven to buy more than they need.
Planned obsolescence: Companies sometimes design products with limited lifespans, encouraging consumers to buy new versions frequently. This practice contributes to waste, depletion of resources, and increased consumer spending.
2. Exploitation of Insecurities
Body image and self-esteem: Advertising in industries like fashion, beauty, and fitness often exploits people's insecurities by promoting unrealistic beauty standards. This can lead to mental health issues such as low self-esteem, anxiety, body dysmorphia, and even eating disorders.
Fear-based marketing: Some marketing strategies use fear to sell products, such as insurance, security systems, or health products, by making consumers feel unsafe or inadequate without them.
3. Targeting Vulnerable Populations
Children: Marketing often targets children, who are particularly susceptible to persuasive messages. This leads to the commercialization of childhood, with kids exposed to unhealthy food, consumerist values, and a materialistic mindset from an early age.
Low-income groups: Companies sometimes market harmful products, such as payday loans or unhealthy foods, more aggressively to low-income populations, exacerbating financial hardship or health problems.
4. Perpetuation of Stereotypes and Social Divides
Gender roles: Marketing often reinforces gender stereotypes, portraying women as caregivers or men as breadwinners, thereby perpetuating outdated norms that limit gender equality and diversity.
Cultural appropriation and tokenism: Some brands use cultural symbols or minority groups in marketing campaigns without understanding their significance, which can lead to cultural appropriation and tokenism, alienating and misrepresenting marginalized communities.
5. Environmental Damage
Overemphasis on fast fashion and disposable goods: Marketing has contributed to the rise of fast fashion and a throwaway culture, promoting short-term use of cheap, disposable products. This has serious environmental consequences, including pollution, resource depletion, and the generation of vast amounts of waste.
Greenwashing: Some companies falsely market products as "environmentally friendly" or "sustainable" in an attempt to capitalize on consumers' eco-consciousness, misleading the public and delaying genuine action on environmental issues.
6. Manipulation and Misinformation
False advertising: Companies sometimes make exaggerated or false claims about their products, misleading consumers and creating false expectations. This can be particularly harmful when it comes to health products, pharmaceuticals, or weight-loss treatments.
Addictive design: Marketing techniques are increasingly used to promote addictive behaviors, particularly in the context of social media, video games, or gambling. Companies manipulate users through behavioral nudges and psychological triggers that keep them hooked.
7. Invasion of Privacy
Data mining and surveillance: With the rise of digital marketing, companies have gained unprecedented access to consumers’ personal data. Many firms engage in data mining and targeted advertising based on individuals' online behavior, often without full transparency or consent, leading to concerns about privacy and data security.
Personalization and manipulation: Highly personalized marketing can lead to manipulation, as companies can target individuals with ads tailored to their specific vulnerabilities, making it harder for consumers to make objective decisions.
8. Promotion of Unhealthy Lifestyles
Junk food advertising: Aggressive marketing of unhealthy foods, particularly to children, has been linked to rising rates of obesity, diabetes, and other diet-related diseases.
Alcohol and tobacco marketing: Despite restrictions in some countries, marketing of alcohol, tobacco, and vaping products continues to glamorize these potentially harmful substances, leading to addiction and public health crises.
9. Contributing to Financial Instability
Credit and debt marketing: Marketing of credit cards, loans, and other financial products often promotes spending beyond one's means, contributing to personal debt and financial instability. Predatory lending practices, such as payday loans, are frequently marketed to those already in financial difficulty.
10. Reduction of Authenticity and Creativity
Commercialization of art and culture: Marketing can sometimes reduce art, culture, and creativity to mere products to be sold, stripping them of their authenticity. This can lead to the commodification of creative expression and a focus on profit over substance.
Trend exploitation: By constantly pushing new trends, marketing fosters a culture of superficiality and short-term thinking, where value is placed on what is fashionable or trending rather than what is meaningful or lasting.
While marketing plays a critical role in the economy by connecting consumers with products, it also has significant social, psychological, and environmental consequences. From promoting overconsumption and exploiting insecurities to targeting vulnerable groups and contributing to environmental degradation, marketing practices have often prioritized profit over societal well-being. Reforming marketing to be more ethical and socially responsible is essential for creating a healthier, more sustainable society.
#philosophy#epistemology#knowledge#learning#education#chatgpt#ethics#economics#society#politics#Consumerism and Materialism#False Advertising#Gender Stereotypes in Media#Data Privacy and Surveillance#Environmental Impact of Marketing#Exploitation of Insecurities#Ethical Marketing Practices#Targeting Vulnerable Populations#consumerism#marketing#advertising#capitalism
9 notes
·
View notes