#FastAPI
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

Python Full Stack Trending Topics
Upgrade your skills with the most in-demand technologies:
✅ AI + ML with Django
✅ Serverless App Development
✅ Superfast APIs using FastAPI
✅ Scalable apps with Microservices
🎯 Perfect for beginners and professionals!
Start your Full Stack journey with us today
📞 Call: +91 9704944488
🌐 Visit: www.pythonfullstackmasters.in
📍 Location: Hyderabad, Telangana
#PythonFullStack#LearnPython#DjangoDeveloper#FastAPI#MicroservicesArchitecture#AIwithPython#FullStackDevelopment#PythonCourse#WebDevelopment#CareerInTech#PinterestLearning#OnlineCourseIndia#UpSkillToday
0 notes
Text
🚀 Free Python & Full Stack Python Training – Join Our Live Demo!
Looking to start a career in Python development? 🚀 Join our Free Demo Session and explore the world of Python, Django, Flask, and FastAPI with hands-on learning!
📅 New Batch: 3rd April | 🕓 4:00 PM IST 📌 Register Here: https://tr.ee/2YzYUA
🔥 What You’ll Learn: ✅ Python Fundamentals & Advanced Topics ✅ Full Stack Development with Django, Flask, FastAPI ✅ Real-world Projects & Career Guidance
📌 For More Details & Upcoming Batches: 🌐 https://linktr.ee/NIT_Training
📩 Join Our Communities: 📌 Telegram: https://t.me/NIT_Training 📌 WhatsApp: https://chat.whatsapp.com/NIT_Training

🚀 Start your coding journey today!
0 notes
Text
Mastering Event-Driven Programming in Python
Me learn Python magic! Make fire with asyncio, make big noise with Tkinter, talk fast with WebSockets, and hunt big data with FastAPI. Me test, me debug, me become Python master! Join now, make code dance!
Yo, fam! 🔥 Get ready to SLAY event-driven programming in Python! 🚀- **asyncio** - Code like a boss without blocking! - **GUI** - Whip up some dope apps with Tkinter! - **WebSockets** - Keep it LIT with real-time updates! - **FastAPI** - Build some next-level microservices! - **Debugging** - Fix your code like a PRO! Grab this book, dive in, and LEVEL UP your Python game! 💪
Book -> Free

0 notes
Text
Python Web Frameworks in 2025: Which One Will Dominate?
The future of Python web development is here! Check out the top frameworks of 2025 and choose the right one to supercharge your web app projects.
0 notes
Text
Flask vs FastAPI: Choosing the Right Framework for Your Project Discover the key differences between Flask and FastAPI with this in-depth guide by IB Arts Pvt Ltd. Whether you're building a lightweight web application or a high-performance API, understanding the strengths of each framework can help you make the right choice for your development needs. Explore factors like speed, ease of use, community support, and scalability to decide which one suits your project better.
Key Insights Include:
Performance comparison between Flask and FastAPI
Usability and flexibility for developers
Ideal use cases for each framework
Ready to make an informed decision? Read the full guide here and take your development skills to the next level!
0 notes
Text
Asynchronous LLM API Calls in Python: A Comprehensive Guide
New Post has been published on https://thedigitalinsider.com/asynchronous-llm-api-calls-in-python-a-comprehensive-guide/
Asynchronous LLM API Calls in Python: A Comprehensive Guide
As developers and dta scientists, we often find ourselves needing to interact with these powerful models through APIs. However, as our applications grow in complexity and scale, the need for efficient and performant API interactions becomes crucial. This is where asynchronous programming shines, allowing us to maximize throughput and minimize latency when working with LLM APIs.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the world of asynchronous LLM API calls in Python. We’ll cover everything from the basics of asynchronous programming to advanced techniques for handling complex workflows. By the end of this article, you’ll have a solid understanding of how to leverage asynchronous programming to supercharge your LLM-powered applications.
Before we dive into the specifics of async LLM API calls, let’s establish a solid foundation in asynchronous programming concepts.
Asynchronous programming allows multiple operations to be executed concurrently without blocking the main thread of execution. In Python, this is primarily achieved through the asyncio module, which provides a framework for writing concurrent code using coroutines, event loops, and futures.
Key concepts:
Coroutines: Functions defined with async def that can be paused and resumed.
Event Loop: The central execution mechanism that manages and runs asynchronous tasks.
Awaitables: Objects that can be used with the await keyword (coroutines, tasks, futures).
Here’s a simple example to illustrate these concepts:
import asyncio async def greet(name): await asyncio.sleep(1) # Simulate an I/O operation print(f"Hello, name!") async def main(): await asyncio.gather( greet("Alice"), greet("Bob"), greet("Charlie") ) asyncio.run(main())
In this example, we define an asynchronous function greet that simulates an I/O operation with asyncio.sleep(). The main function uses asyncio.gather() to run multiple greetings concurrently. Despite the sleep delay, all three greetings will be printed after approximately 1 second, demonstrating the power of asynchronous execution.
The Need for Async in LLM API Calls
When working with LLM APIs, we often encounter scenarios where we need to make multiple API calls, either in sequence or parallel. Traditional synchronous code can lead to significant performance bottlenecks, especially when dealing with high-latency operations like network requests to LLM services.
Consider a scenario where we need to generate summaries for 100 different articles using an LLM API. With a synchronous approach, each API call would block until it receives a response, potentially taking several minutes to complete all requests. An asynchronous approach, on the other hand, allows us to initiate multiple API calls concurrently, dramatically reducing the overall execution time.
Setting Up Your Environment
To get started with async LLM API calls, you’ll need to set up your Python environment with the necessary libraries. Here’s what you’ll need:
Python 3.7 or higher (for native asyncio support)
aiohttp: An asynchronous HTTP client library
openai: The official OpenAI Python client (if you’re using OpenAI’s GPT models)
langchain: A framework for building applications with LLMs (optional, but recommended for complex workflows)
You can install these dependencies using pip:
pip install aiohttp openai langchain <div class="relative flex flex-col rounded-lg">
Basic Async LLM API Calls with asyncio and aiohttp
Let’s start by making a simple asynchronous call to an LLM API using aiohttp. We’ll use OpenAI’s GPT-3.5 API as an example, but the concepts apply to other LLM APIs as well.
import asyncio import aiohttp from openai import AsyncOpenAI async def generate_text(prompt, client): response = await client.chat.completions.create( model="gpt-3.5-turbo", messages=["role": "user", "content": prompt] ) return response.choices[0].message.content async def main(): prompts = [ "Explain quantum computing in simple terms.", "Write a haiku about artificial intelligence.", "Describe the process of photosynthesis." ] async with AsyncOpenAI() as client: tasks = [generate_text(prompt, client) for prompt in prompts] results = await asyncio.gather(*tasks) for prompt, result in zip(prompts, results): print(f"Prompt: promptnResponse: resultn") asyncio.run(main())
In this example, we define an asynchronous function generate_text that makes a call to the OpenAI API using the AsyncOpenAI client. The main function creates multiple tasks for different prompts and uses asyncio.gather() to run them concurrently.
This approach allows us to send multiple requests to the LLM API simultaneously, significantly reducing the total time required to process all prompts.
Advanced Techniques: Batching and Concurrency Control
While the previous example demonstrates the basics of async LLM API calls, real-world applications often require more sophisticated approaches. Let’s explore two important techniques: batching requests and controlling concurrency.
Batching Requests: When dealing with a large number of prompts, it’s often more efficient to batch them into groups rather than sending individual requests for each prompt. This reduces the overhead of multiple API calls and can lead to better performance.
import asyncio from openai import AsyncOpenAI async def process_batch(batch, client): responses = await asyncio.gather(*[ client.chat.completions.create( model="gpt-3.5-turbo", messages=["role": "user", "content": prompt] ) for prompt in batch ]) return [response.choices[0].message.content for response in responses] async def main(): prompts = [f"Tell me a fact about number i" for i in range(100)] batch_size = 10 async with AsyncOpenAI() as client: results = [] for i in range(0, len(prompts), batch_size): batch = prompts[i:i+batch_size] batch_results = await process_batch(batch, client) results.extend(batch_results) for prompt, result in zip(prompts, results): print(f"Prompt: promptnResponse: resultn") asyncio.run(main())
Concurrency Control: While asynchronous programming allows for concurrent execution, it’s important to control the level of concurrency to avoid overwhelming the API server or exceeding rate limits. We can use asyncio.Semaphore for this purpose.
import asyncio from openai import AsyncOpenAI async def generate_text(prompt, client, semaphore): async with semaphore: response = await client.chat.completions.create( model="gpt-3.5-turbo", messages=["role": "user", "content": prompt] ) return response.choices[0].message.content async def main(): prompts = [f"Tell me a fact about number i" for i in range(100)] max_concurrent_requests = 5 semaphore = asyncio.Semaphore(max_concurrent_requests) async with AsyncOpenAI() as client: tasks = [generate_text(prompt, client, semaphore) for prompt in prompts] results = await asyncio.gather(*tasks) for prompt, result in zip(prompts, results): print(f"Prompt: promptnResponse: resultn") asyncio.run(main())
In this example, we use a semaphore to limit the number of concurrent requests to 5, ensuring we don’t overwhelm the API server.
Error Handling and Retries in Async LLM Calls
When working with external APIs, it’s crucial to implement robust error handling and retry mechanisms. Let’s enhance our code to handle common errors and implement exponential backoff for retries.
import asyncio import random from openai import AsyncOpenAI from tenacity import retry, stop_after_attempt, wait_exponential class APIError(Exception): pass @retry(stop=stop_after_attempt(3), wait=wait_exponential(multiplier=1, min=4, max=10)) async def generate_text_with_retry(prompt, client): try: response = await client.chat.completions.create( model="gpt-3.5-turbo", messages=["role": "user", "content": prompt] ) return response.choices[0].message.content except Exception as e: print(f"Error occurred: e") raise APIError("Failed to generate text") async def process_prompt(prompt, client, semaphore): async with semaphore: try: result = await generate_text_with_retry(prompt, client) return prompt, result except APIError: return prompt, "Failed to generate response after multiple attempts." async def main(): prompts = [f"Tell me a fact about number i" for i in range(20)] max_concurrent_requests = 5 semaphore = asyncio.Semaphore(max_concurrent_requests) async with AsyncOpenAI() as client: tasks = [process_prompt(prompt, client, semaphore) for prompt in prompts] results = await asyncio.gather(*tasks) for prompt, result in results: print(f"Prompt: promptnResponse: resultn") asyncio.run(main())
This enhanced version includes:
A custom APIError exception for API-related errors.
A generate_text_with_retry function decorated with @retry from the tenacity library, implementing exponential backoff.
Error handling in the process_prompt function to catch and report failures.
Optimizing Performance: Streaming Responses
For long-form content generation, streaming responses can significantly improve the perceived performance of your application. Instead of waiting for the entire response, you can process and display chunks of text as they become available.
import asyncio from openai import AsyncOpenAI async def stream_text(prompt, client): stream = await client.chat.completions.create( model="gpt-3.5-turbo", messages=["role": "user", "content": prompt], stream=True ) full_response = "" async for chunk in stream: if chunk.choices[0].delta.content is not None: content = chunk.choices[0].delta.content full_response += content print(content, end='', flush=True) print("n") return full_response async def main(): prompt = "Write a short story about a time-traveling scientist." async with AsyncOpenAI() as client: result = await stream_text(prompt, client) print(f"Full response:nresult") asyncio.run(main())
This example demonstrates how to stream the response from the API, printing each chunk as it arrives. This approach is particularly useful for chat applications or any scenario where you want to provide real-time feedback to the user.
Building Async Workflows with LangChain
For more complex LLM-powered applications, the LangChain framework provides a high-level abstraction that simplifies the process of chaining multiple LLM calls and integrating other tools. Let’s look at an example of using LangChain with async capabilities:
This example shows how LangChain can be used to create more complex workflows with streaming and asynchronous execution. The AsyncCallbackManager and StreamingStdOutCallbackHandler enable real-time streaming of the generated content.
import asyncio from langchain.llms import OpenAI from langchain.prompts import PromptTemplate from langchain.chains import LLMChain from langchain.callbacks.manager import AsyncCallbackManager from langchain.callbacks.streaming_stdout import StreamingStdOutCallbackHandler async def generate_story(topic): llm = OpenAI(temperature=0.7, streaming=True, callback_manager=AsyncCallbackManager([StreamingStdOutCallbackHandler()])) prompt = PromptTemplate( input_variables=["topic"], template="Write a short story about topic." ) chain = LLMChain(llm=llm, prompt=prompt) return await chain.arun(topic=topic) async def main(): topics = ["a magical forest", "a futuristic city", "an underwater civilization"] tasks = [generate_story(topic) for topic in topics] stories = await asyncio.gather(*tasks) for topic, story in zip(topics, stories): print(f"nTopic: topicnStory: storyn'='*50n") asyncio.run(main())
Serving Async LLM Applications with FastAPI
To make your async LLM application available as a web service, FastAPI is an great choice due to its native support for asynchronous operations. Here’s an example of how to create a simple API endpoint for text generation:
from fastapi import FastAPI, BackgroundTasks from pydantic import BaseModel from openai import AsyncOpenAI app = FastAPI() client = AsyncOpenAI() class GenerationRequest(BaseModel): prompt: str class GenerationResponse(BaseModel): generated_text: str @app.post("/generate", response_model=GenerationResponse) async def generate_text(request: GenerationRequest, background_tasks: BackgroundTasks): response = await client.chat.completions.create( model="gpt-3.5-turbo", messages=["role": "user", "content": request.prompt] ) generated_text = response.choices[0].message.content # Simulate some post-processing in the background background_tasks.add_task(log_generation, request.prompt, generated_text) return GenerationResponse(generated_text=generated_text) async def log_generation(prompt: str, generated_text: str): # Simulate logging or additional processing await asyncio.sleep(2) print(f"Logged: Prompt 'prompt' generated text of length len(generated_text)") if __name__ == "__main__": import uvicorn uvicorn.run(app, host="0.0.0.0", port=8000)
This FastAPI application creates an endpoint /generate that accepts a prompt and returns generated text. It also demonstrates how to use background tasks for additional processing without blocking the response.
Best Practices and Common Pitfalls
As you work with async LLM APIs, keep these best practices in mind:
Use connection pooling: When making multiple requests, reuse connections to reduce overhead.
Implement proper error handling: Always account for network issues, API errors, and unexpected responses.
Respect rate limits: Use semaphores or other concurrency control mechanisms to avoid overwhelming the API.
Monitor and log: Implement comprehensive logging to track performance and identify issues.
Use streaming for long-form content: It improves user experience and allows for early processing of partial results.
#API#APIs#app#applications#approach#Article#Articles#artificial#Artificial Intelligence#asynchronous programming#asyncio#background#Building#code#col#complexity#comprehensive#computing#Concurrency#concurrency control#content#Delay#developers#display#endpoint#Environment#error handling#event#FastAPI#forest
0 notes
Text
FastAPI Authentication Security with Token: A Comprehensive Guide
Benefit from the collective wisdom of the FastAPI community. August Infotech shares community insights, tips, and tricks to enhance your understanding of FastAPI and stay abreast of the latest developments in the ecosystem.
FastAPI is a powerful tool, and with the right knowledge, you can harness its potential to build secure and efficient APIs. August Infotech's comprehensive guide is your go-to resource for mastering FastAPI authentication and security. Elevate your development skills, fortify your applications, and stay ahead of the curve with this must-read guide.
Ready to embark on a journey towards secure and performant FastAPI applications? Read the full guide here: https://bit.ly/48yyyk1
#WebDevelopment #APIs #TokenAuthentication #Python #TechBlog
0 notes
Text
Learn Ruby on Rails with The Pragmatic Programmers Book Bundle!
Learn Ruby on Rails with The Pragmatic Programmers Book Bundle! #sale #ruby #rubyonrails #rails #microservices #book #education #learning #coding #programming #software #ebook
Check out the three book bundle options at this link. Want to write powerful, easy-to-maintain code with the Ruby programming language? Looking to create great web apps quickly with Rails? This bundle of books from the experts at Pragmatic Programmers will get you on track! Explore topics like metaprogramming, optimization, testing, sustainable development, and much more, and help support Active…

View On WordPress
#book#books#coding#ebook#ebooks#education#fastapi#humble bundle#microservices#programmer#programming#python#ruby#ruby on rails#sale#software#swift
0 notes
Text
ใช้ FastAPI ให้เร็วขึ้นถึงเกือบเท่า Go Gin
จากบทความก่อนหน้านี้ Python ก็เร็วเท่า GoLang ได้ จริงไหม? เรามาทำให้ FastAPI ของเราให้เร็วขึ้นถึงเกือบเท่า Go Gin ในบทความนี้ จะทำการใช้ Docker เข้ามาช่วยในการทดสอบความเร็วในการประมวลผล ระหว่าง Python3.11 pypy3.10 และ Go1.20.6 นะครับ โดย Docker จะถึงตั้งค่าไว้แบบเดี่ยวกัน และใช้ โค๊ต การทำงานแบบเดียวกัน โค๊ตที่ใช้ในการทดสอบด้วย FastAPI import timeit import platform from fastapi import…

View On WordPress
1 note
·
View note
Text

🚀 Trending Niches for Python Full Stack Devs in 2025 💻
Want to level up your career as a Python developer? Here are the top niches to tap into this year:
✨ AI-Powered SaaS Tools ⚡ Serverless Full Stack Apps 💡 Micro SaaS for Freelancers 🛠️ HTMX + Django (No heavy JS!) 📊 Custom Dashboards & Internal Tools
Whether you're building your portfolio or launching your first SaaS, these are the trends that matter. Stay ahead. Stay relevant.
📚 ENROLL NOW at Python Full Stack Masters and start building real-world projects that make an impact!
🔗 www.pythonfullstackmasters.in 📞 +91 9704944488
#PythonDeveloper#FullStackDev#SaaS#MicroSaaS#Django#FastAPI#WebDevelopment#TechTrends#LearnToCode#HTMX#Streamlit#BuildInPublic#WebDev2025
0 notes
Text
FASTAPI: A Simple Guide with Installation Steps
FASTAPI is a modern, fast (high-performance), web framework for building APIs with Python. It is known for its simplicity, scalability, and speed. In this article, we will walk you through the installation process and provide a basic understanding of how to get started with FASTAPI. Installation Steps To begin with FASTAPI, you need to have Python installed on your system. Make sure you have…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Link
This week's issue contains some of the most interesting articles and news, selected from all the content published in the previous week on the Developers News website. In this issue you will read about, Container Face-Off, React 18 with Redux, Continuous Testing, Kubernetes vs OpenStack, Tech Books, Go Pointer, FastAPI, Helm, SQL JOIN, and more
#devs_news_weekly#devs_news#react#javascript#kubernetes#OpenStack#go#FastAPI#Helm#book#sql#container#microservices#redux
0 notes
Text
Man why is working with web apps so obnoxious. "422 unprocessable entity teehee. Good luck figuring out which entity it is, much less why I refuse to process it"
#i almost went apeshit when fastapi refused to take a numpy int because it WOULDN'T TELL ME WHICH VARIABLE WAS THE PROBLEM#luckily i realized i could put a breakpoint right into my python code before i went entirely off the deep end#programming
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
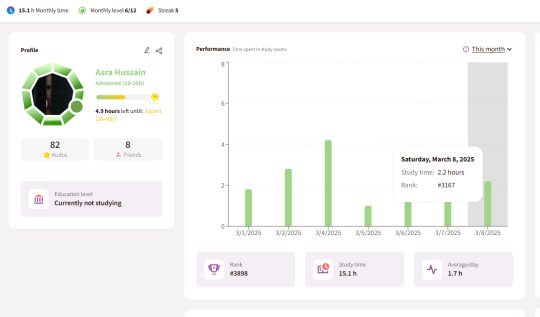
today im feeling a lot better
i will create a fastapi + frontend for a movie rec site (i am doing this to understand fastapi and docker) maybe even deploy something idk.
and also today for 2 hours i will solve aws quiz.
i will read chapter 6,7 of the kubernetes book.
and i will reach the yellow gem (expert) on this site!!!
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
How Python Powers Scalable and Cost-Effective Cloud Solutions

Explore the role of Python in developing scalable and cost-effective cloud solutions. This guide covers Python's advantages in cloud computing, addresses potential challenges, and highlights real-world applications, providing insights into leveraging Python for efficient cloud development.
Introduction
In today's rapidly evolving digital landscape, businesses are increasingly leveraging cloud computing to enhance scalability, optimize costs, and drive innovation. Among the myriad of programming languages available, Python has emerged as a preferred choice for developing robust cloud solutions. Its simplicity, versatility, and extensive library support make it an ideal candidate for cloud-based applications.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into how Python empowers scalable and cost-effective cloud solutions, explore its advantages, address potential challenges, and highlight real-world applications.
Why Python is the Preferred Choice for Cloud Computing?
Python's popularity in cloud computing is driven by several factors, making it the preferred language for developing and managing cloud solutions. Here are some key reasons why Python stands out:
Simplicity and Readability: Python's clean and straightforward syntax allows developers to write and maintain code efficiently, reducing development time and costs.
Extensive Library Support: Python offers a rich set of libraries and frameworks like Django, Flask, and FastAPI for building cloud applications.
Seamless Integration with Cloud Services: Python is well-supported across major cloud platforms like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud.
Automation and DevOps Friendly: Python supports infrastructure automation with tools like Ansible, Terraform, and Boto3.
Strong Community and Enterprise Adoption: Python has a massive global community that continuously improves and innovates cloud-related solutions.
How Python Enables Scalable Cloud Solutions?
Scalability is a critical factor in cloud computing, and Python provides multiple ways to achieve it:
1. Automation of Cloud Infrastructure
Python's compatibility with cloud service provider SDKs, such as AWS Boto3, Azure SDK for Python, and Google Cloud Client Library, enables developers to automate the provisioning and management of cloud resources efficiently.
2. Containerization and Orchestration
Python integrates seamlessly with Docker and Kubernetes, enabling businesses to deploy scalable containerized applications efficiently.
3. Cloud-Native Development
Frameworks like Flask, Django, and FastAPI support microservices architecture, allowing businesses to develop lightweight, scalable cloud applications.
4. Serverless Computing
Python's support for serverless platforms, including AWS Lambda, Azure Functions, and Google Cloud Functions, allows developers to build applications that automatically scale in response to demand, optimizing resource utilization and cost.
5. AI and Big Data Scalability
Python’s dominance in AI and data science makes it an ideal choice for cloud-based AI/ML services like AWS SageMaker, Google AI, and Azure Machine Learning.
Looking for expert Python developers to build scalable cloud solutions? Hire Python Developers now!
Advantages of Using Python for Cloud Computing
Cost Efficiency: Python’s compatibility with serverless computing and auto-scaling strategies minimizes cloud costs.
Faster Development: Python’s simplicity accelerates cloud application development, reducing time-to-market.
Cross-Platform Compatibility: Python runs seamlessly across different cloud platforms.
Security and Reliability: Python-based security tools help in encryption, authentication, and cloud monitoring.
Strong Community Support: Python developers worldwide contribute to continuous improvements, making it future-proof.
Challenges and Considerations
While Python offers many benefits, there are some challenges to consider:
Performance Limitations: Python is an interpreted language, which may not be as fast as compiled languages like Java or C++.
Memory Consumption: Python applications might require optimization to handle large-scale cloud workloads efficiently.
Learning Curve for Beginners: Though Python is simple, mastering cloud-specific frameworks requires time and expertise.
Python Libraries and Tools for Cloud Computing
Python’s ecosystem includes powerful libraries and tools tailored for cloud computing, such as:
Boto3: AWS SDK for Python, used for cloud automation.
Google Cloud Client Library: Helps interact with Google Cloud services.
Azure SDK for Python: Enables seamless integration with Microsoft Azure.
Apache Libcloud: Provides a unified interface for multiple cloud providers.
PyCaret: Simplifies machine learning deployment in cloud environments.
Real-World Applications of Python in Cloud Computing
1. Netflix - Scalable Streaming with Python
Netflix extensively uses Python for automation, data analysis, and managing cloud infrastructure, enabling seamless content delivery to millions of users.
2. Spotify - Cloud-Based Music Streaming
Spotify leverages Python for big data processing, recommendation algorithms, and cloud automation, ensuring high availability and scalability.
3. Reddit - Handling Massive Traffic
Reddit uses Python and AWS cloud solutions to manage heavy traffic while optimizing server costs efficiently.
Future of Python in Cloud Computing
The future of Python in cloud computing looks promising with emerging trends such as:
AI-Driven Cloud Automation: Python-powered AI and machine learning will drive intelligent cloud automation.
Edge Computing: Python will play a crucial role in processing data at the edge for IoT and real-time applications.
Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Strategies: Python’s flexibility will enable seamless integration across multiple cloud platforms.
Increased Adoption of Serverless Computing: More enterprises will adopt Python for cost-effective serverless applications.
Conclusion
Python's simplicity, versatility, and robust ecosystem make it a powerful tool for developing scalable and cost-effective cloud solutions. By leveraging Python's capabilities, businesses can enhance their cloud applications' performance, flexibility, and efficiency.
Ready to harness the power of Python for your cloud solutions? Explore our Python Development Services to discover how we can assist you in building scalable and efficient cloud applications.
FAQs
1. Why is Python used in cloud computing?
Python is widely used in cloud computing due to its simplicity, extensive libraries, and seamless integration with cloud platforms like AWS, Google Cloud, and Azure.
2. Is Python good for serverless computing?
Yes! Python works efficiently in serverless environments like AWS Lambda, Azure Functions, and Google Cloud Functions, making it an ideal choice for cost-effective, auto-scaling applications.
3. Which companies use Python for cloud solutions?
Major companies like Netflix, Spotify, Dropbox, and Reddit use Python for cloud automation, AI, and scalable infrastructure management.
4. How does Python help with cloud security?
Python offers robust security libraries like PyCryptodome and OpenSSL, enabling encryption, authentication, and cloud monitoring for secure cloud applications.
5. Can Python handle big data in the cloud?
Yes! Python supports big data processing with tools like Apache Spark, Pandas, and NumPy, making it suitable for data-driven cloud applications.
#Python development company#Python in Cloud Computing#Hire Python Developers#Python for Multi-Cloud Environments
2 notes
·
View notes
Quote
AI アプリケーションの構築に大金を費やす必要はありません。最高の AI 開発ツールはオープンソースであり、AI を誰もが利用できる優れたエコシステムが進化しています。 このオープンソース AI スタックの主要コンポーネントは次のとおりです。 1.フロントエンド 美しい AI UI を構築するには、NextJS や Streamlit などのフレームワークが非常に役立ちます。また、Vercel はデプロイメントに役立ちます。 2.埋め込みと RAG ライブラリ Nomic、JinaAI、Cognito、LLMAware などの埋め込みモデルと RAG ライブラリは、開発者が正確な検索機能と RAG 機能を構築するのに役立ちます。 3.バックエンドとモデル アクセス バックエンド開発の場合、開発者は FastAPI、Langchain、Netflix Metaflow などのフレームワークを利用できます。モデル アクセスには、Ollama や Huggingface などのオプションが利用できます。 4.データと取得 データの保存と取得には、Postgres、Milvus、Weaviate、PGVector、FAISS などのいくつかのオプションが利用できます。 5.大規模言語モデル パフォーマンス ベンチマークに基づく、Llama、Mistral、Qwen、Phi、Gemma などのオープン ソース モデルは、GPT や Claude などの独自の LLM の優れた代替手段です。
EP146: オープンソース AI スタック - ByteByteGo ニュースレター
2 notes
·
View notes