#Empress Irene
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text


some friends and I have a fancast of Greta Garbo in a 1930s historical epic about the byzantine Empress Irene so ofc I drew it
2K notes
·
View notes
Text

Empress Irene (750/756-803) by Herbert Norris.
#herbert norris#empress irene#irene of athens#augusta#empress of the romans#byzantine empire#empress consort#Ειρήνη η Αθηναία#full length portrait#Byzantine regent#Σαρανταπήχαινα#Sarantapechos#Σαραντάπηχος#full-length portrait#Isaurian dynasty#Βασιλεία Ῥωμαίων#Byzantine Iconoclasm#royalty
27 notes
·
View notes
Text

Day 4: Queen - Irene Sarantapechaina
#jenstober23#irene sarantapechaina#irene of athens#empress irene#byzantium#byzantine empire#byzantine emperor#history art#traditional art#8th century#9th century#inktober#inktober 2023#drawtober#drawtober 2023#artober#artober 2023#witchtober#witchtober 2023#day 4#greek tag#roman tag
32 notes
·
View notes
Text
@caesarsaladinn finally getting their due gracing the most hilariously non-sequitor book cover I've ever seen:


70 notes
·
View notes
Text

"During the reign of her husband the primary function of an Augusta was the orchestration of ceremonial at the imperial court, a highly stylised and intricate affair given the ceremonial nature of imperial life, which was based primarily around the Great Palace, a huge complex extending from the hippodrome to the sea walls, with its own gardens, sporting grounds, barracks, audience halls and private apartments; the Great Palace was the official residence of the emperor until 1204, though under Alexios Komnenos the imperial family usually occupied the Blachernai Palace in the north-west of the city, while there were other residential palaces in and outside of the capital. Empresses’ public life remained largely separate from that of their husbands, especially prior to the eleventh century, and involved a parallel court revolving around ceremonies involving the wives of court officials. For this reason an empress at court was considered to be essential: Michael II was encouraged to marry by his magnates because an emperor needed a wife and their wives an empress.
The patriarch Nicholas permitted the third marriage of Leo VI because of the need for an empress in the palace: ‘since there must be a Lady in the Palace to manage ceremonies affecting the wives of your nobles, there is condonation of the third marriage…’ While the empress primarily presided over her own ceremonial sphere, with her own duties and functions, she could be also present at court banquets, audiences and the reception of envoys, as well as taking part in processions and in services in St Sophia and elsewhere in the city; one of her main duties was the reception of the wives of foreign rulers and heads of state. Nor were empresses restricted to the capital: both Martina and Irene Doukaina accompanied their husbands on campaign.
The empress was also in charge of the gynaikonitis, the women’s quarters in the palace, where she had her own staff, primarily though not entirely composed of eunuchs, under the supervision of her own chamberlain; when empresses like Irene, Theodora wife of Theophilos, and Zoe Karbounopsina came to power they often relied on this staff of eunuchs as their chief ministers and even their generals. Theodora the Macedonian was unusual in not appointing a eunuch as her chief minister, perhaps because her age made such gender considerations unnecessary. The ladies of the court were the wives of patricians and other dignitaries: a few ladies, the zostai, were especially appointed and held rank in their own right. The zoste patrikia was at the head of these ladies (she was usually a relative of the empress),and dined with the imperial family."
Byzantine Empresses: Women and Power in Byzantium AD 527-1204, Lynda Garland
#history#women in history#women's history#byzantine empresses#byzantine empire#byzantine history#eastern roman empire#queens#historyedit#historyblr#medieval history#irene of athens
94 notes
·
View notes
Text

Grand Duke Louis IV of Hesse with his surviving children: Princess Victoria of Battenberg, Marchioness of Milford-Haven, Grand Duchess Elizabeth Feodorovna of Russia, Princess Irene of Prussia, Empress Alexandra Feodorovna of Russia and Grand Duke Ernest Louis of Hesse, 1884.
#Grand Duke Louis IV of Hesse#grand duke ludwig iv of hesse#Princess Victoria of Battenberg#princess victoria marchioness of milford haven#Grand Duchess Elizabeth Feodorovna of Russia#Grand Duchess Elizabeth Feodorovna#Grand Duchess elizabeth of russia#empress alexandra feodorovna of russia#empress alexandra feodorovna#empress alexandra of russia#Princess Irene of Prussia#princess henry of prussia#Grand Duke Ernest Louis of Hesse#princess alix of hesse#princess victoria of hesse#princess irene of hesse#princess elizabeth of hesse#1880s#1884#imperial russia#imperial family#russian imperial family#romanovs#victorian#colored photography#british royal family#german royalty#1880s fashion#history colored
83 notes
·
View notes
Text
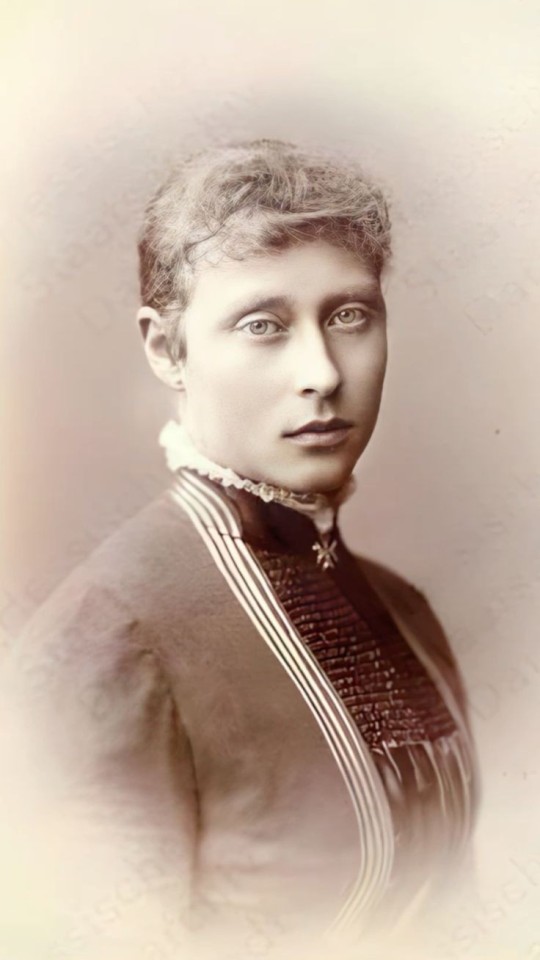
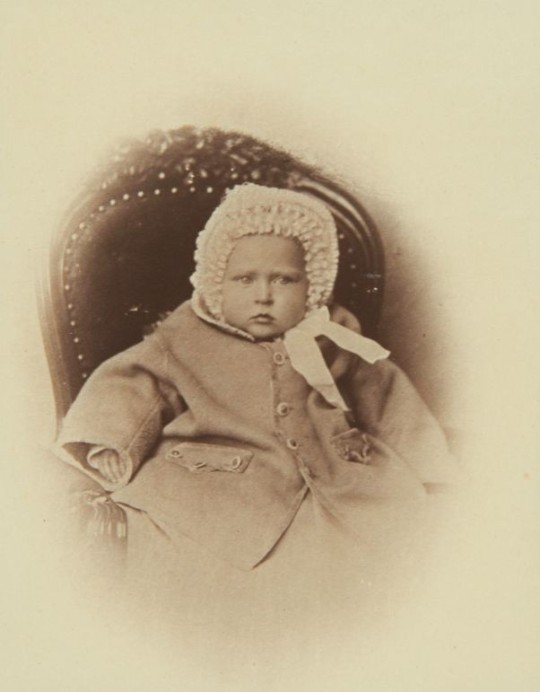
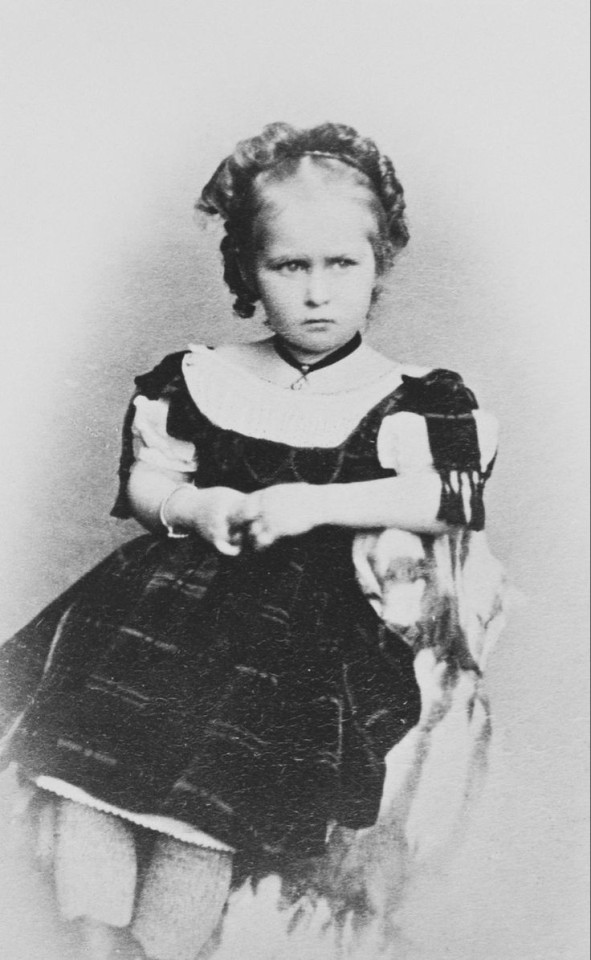
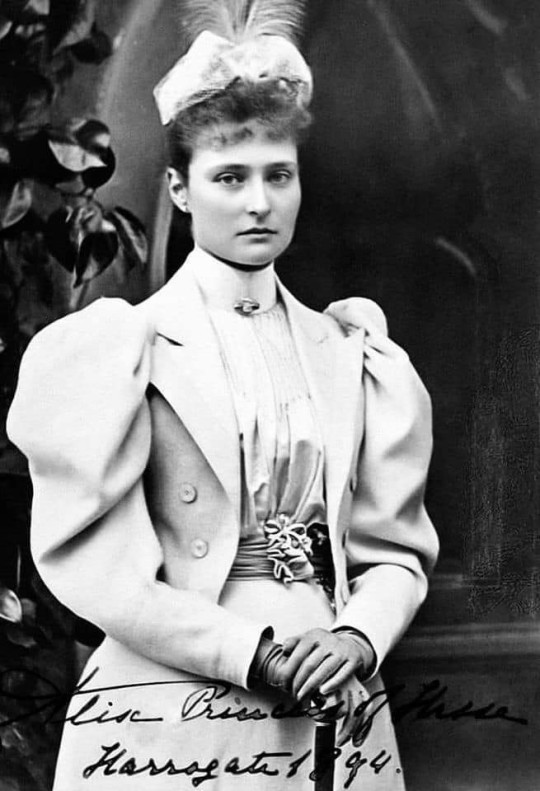







#my polls#princess victoria of hesse#victoria mountbatten#grand duchess elisabeth feodorovna#elisabeth of hesse#princess irene of hesse#princess henry of prussia#empress alexandra feodorovna#alix of hesse#hessian sisters
51 notes
·
View notes
Text

Famous byzantine empresses drawn by Sato Futaba, author of the historical mangas "Utae, Erinna!" and "Anna Komnene":
Aelia Eudocia (401-460 AD) was the wife of emperor Theodosius II and a great poetess whose works are great examples of how her Christian faith and Greek heritage and upbringing were intertwined, exemplifying a legacy that the Roman empire left behind on the Christian world.
Theodora (c. 490/500-548 AD) was the wife of emperor Justinian I the Great. She was of humble origins and one of her husband's chief advisers.
Martina (date of birth unknwon- died after 641 AD) was the wife and niece of emperor Heraclius.
Irene of Athens (750/756-803 AD) was the wife of emperor Leo IV from 775 to 780, regent for her son Constantine VI from 780 until 790, co-ruler from 792 until 797, and finally sole ruler of the Eastern Roman empire from 797 to 802.
#byzantine#byzantine empire#byzantine history#historical art#historical people#Aelia Eudocia#Theodora#Martina#Irene of Athens#manga#Sato Futaba#women in history#women’s history#women at work#empress
14 notes
·
View notes
Text
░ ✧ IRENE DELLA CASA in DIE KAISERIN (2022)
MINI GIF PACK • By clicking the source link, you'll find a page containing 30 gifs of italian actress/director Irene Della Casa, in the show Die Kaiserin (2022), from season 1. They were made by me, and can be used (creditless) for roleplays & similar personal uses, and (credited) in posted works such as edits/video edits. I don't care what themes you're using them for or if they're "problematic" so long as you're not hurting anyone.If you use this gifpack, please like and/or reblog this post, thank you!


Buy me a ☕?
#viscardi gifpacks#irene della casa#die kaiserin#the empress#the empress netflix#italian fc#face claim#gif#gif pack#gif hunt#gif set#rp help#rp resources#rph#rph resources#indie rph#costume drama#period drama#historical drama
10 notes
·
View notes
Text


Lesbians if they were apart of the foundation in some way. By the way.
(LOVELY LADY ON THE LEFT BELONGS TO @revier3 FOLLOW. NOW.)
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
love that i've just done such a good job keeping the whole rings of power fiasco out of my life that i only just saw someone experiencing agony from the show making gandalf derive from "grand elf." I was like huh so is gandalf in the show then. Lmao.
#fellow silmarilliondiseased are experiencing 20 stages of grief meanwhile i've deactivated my tolkien fungus and am chilling. 😎#thinkin about dinosaurs. and empress irene mainly
12 notes
·
View notes
Text
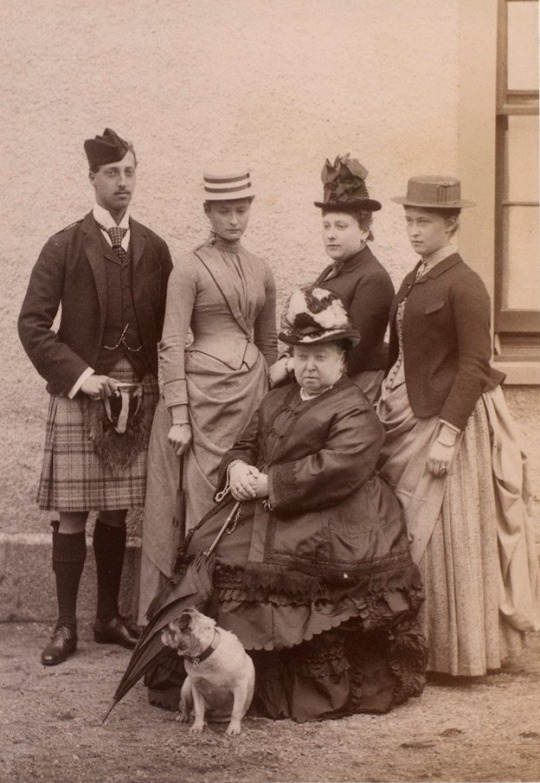



Group photographs of Princesses Alix and Irene, with their maternal cousin and aunt, Prince Albert Victor of Wales and Princess Henry of Battenberg, along with Queen Victoria and Basco the pug, Balmoral, September 1887.
#irene of hesse#irene of hesse and by rhine#alix of hesse#alix of hesse and by rhine#alexandra feodorovna#princess alice#princess alice of the united kingdom#queen victoria#victoria#prince albert#albert#victorian#victorian era#germany#hesse#rhine#prussia#russia#princess#empress#tsarina#czarina#tsaritsa#royal#royalty#history#portrait#photo#albert victor of wales#princess beatrice
77 notes
·
View notes
Text

“It's an understatement to say that Alice of Hesse's daughters had a profound influence on the 20th century. Victoria, the grandmother of Philip, Duke of Edinburgh, who was the husband of the late Queen Elizabeth II. Elisabeth, who is venerated as a saint and was canonized by the Russian, Greek, and Eastern Orthodox Churches. Irene, who identified Anastasia/Anna Anderson as a fraud. Alix, the Empress of the Russian Empire, exerted significant influence on Russia's domestic and international policies, albeit often for the worse, later canonized as a Saint and a holy martyr. And poor little Marie, whose untimely death at an early age played a pivotal role in shaping Alix's shy and sorrowful personality.” - Submitted by Anonymous
#Princess Victoria of Hesse and by Rhine#Grand Duchess Elizabeth Feodorovna#Princess Irene of Hesse and by Rhine#empress alexandra feodorovna
39 notes
·
View notes
Text
Everyone is too harsh on Irene of Athens. I mean, if you weren't her son or an iconoclast, she was a pretty pleasant person to hang out with.
#Irene of Athens#byzantine empire#byzantine#byzantium#eastern roman empire#Byzantine empress#Empress
25 notes
·
View notes
Text


The Husbands of the Four Graces
Some time ago, I read a very interesting book about Queen Victoria's Hessian Granddaughters (Victoria, Elizabeth, Irene, and Alix.) The title was "The Four Graces," and ever since I read it, that is the way I think about the daughters of Grand Duke of Louis IV of Hesse and by Rhine and the beautiful princess Alice of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha, second daughter of Queen Victoria.
These young women were among the most marriageable princesses of their generation. They were beautiful, accomplished and Queen Victoria's granddaughters. There was no need to look for husbands for them. Among their suitors could be found future Kaisers, Tsars and Kings of England even though it was well known that any or all of the princesses could be carriers of hemophilia (inherited from their august grandmother Victoria.) Their sons might be bleeders. One of their brother's had been, therefore Princess Alice, their mother, had been a carrier.
The four men they married appear in the first photograph above; one marquess, one prince, one grand duke, and one Emperor (all of them very handsome):
👑Louis Mountbatten, first Marques of Milford Heaven (the man all the way to the left on the picture) married Princess Victoria Alberta Elisabeth Mathilde Marie of Hesse and By Rhine. Victoria and Louis had two sons and neither one of them had hemophillia.
👑The Hohenzollern Prince and brother of the German Keiser, Prince Heinrich of Prussia (the man to the right of Mountbatten in the photograph) married Princess Irene Luise Marie Anne of Hesse and By Rhine. They were first cousins since Heinrich was the son of Queen Victoria's eldest daughter, the Princess Royal, who was the older sister of Princess Alice. They had three sons. Two out of the three had hemophilia. One died in childhood of causes related to that disease.
👑 Grand Duke Sergei Alexandrovich of Russia (the man to the right of Prince Heinrich) married Princess Elizabeth Alexandra Louise Alice of Hesse and by Rhine. Sergei and Elizabeth had no children.
👑The soon-to-be Tsar Nicholas II of Russia married Alix Viktoria Helene Luise Beatrix. Alix had one son, and he had hemophilia. (gcl)
#russian history#imperial russia#empress alexandra feodorovna#princess alix of hesse#princess Irene of Hesse#Princess Victoria of Hesse#Princess Elizabeth of Hesse#Tsar Nicholas II#Prince Heinrich of Prussia#Louis Mountbatten#Hessian princesses#hemophilia#gcl
23 notes
·
View notes
Text

"The most notable players in Palaiologue politics were the empresses Yolanda-Irene of Montferrat and Anna of Savoy, and on the whole their record is woeful: Yolanda-Irene of Montferrat, second wife of Andronikos II, was unable to comprehend the succession rights of her eldest stepson, Michael IX, and since her husband remained obstinately unmoved by her representations she flounced off with her three sons to Thessalonika where she kept a separate court for many years from 1303 to her death in 1317. From her own domain she issued her own decrees, conducted her own foreign policy and plotted against her husband with the Serbs and Catalans: in mitigation, she had seen her five-year-old daughter married off to the middle-aged Serbian lecher Milutin, and considered that her eldest son John had been married beneath him to a Byzantine aristocrat, Irene Choumnaina. She died embittered and extremely wealthy.
When Yolanda’s grandson Andronikos III died early, leaving a nine-year old son John V and no arrangements for a regent, the empress Anna of Savoy assumed the regency. In so doing she provoked a civil war with her husband’s best friend John Kantakouzenos, and devastated the empire financially, bringing it to bankruptcy and pawning the crown jewels to Venice, as well as employing Turkish mercenaries and, it appears, offering to have her son convert to the church of Rome. Gregoras specifically blames her for the civil war, though he admits that she should not be criticised too heavily since she was a woman and a foreigner. Her mismanagement was not compensated for by her later negotiations in 1351 between John VI Kantakouzenos and her son in Thessalonika, who was planning a rebellion with the help of Stephen Dushan of Serbia. In 1351 Anna too settled in Thessalonika and reigned over it as her own portion of the empire until her death in c. 1365, even minting her own coinage.
These women were powerful and domineering ladies par excellence, but with the proviso that their political influence was virtually minimal. Despite their outspokenness and love of dominion they were not successful politicians: Anna of Savoy, the only one in whose hands government was placed, was compared to a weaver’s shuttle that ripped the purple cloth of empire. But there were of course exceptions. Civil wars ensured that not all empresses were foreigners and more than one woman of Byzantine descent reached the throne and was given quasi-imperial functions by her husband.
Theodora Doukaina Komnene Palaiologina, wife of Michael VIII, herself had imperial connections as the great-niece of John III Vatatzes, and issued acts concerning disputes over monastic properties during her husband’s reign, even addressing the emperor’s officials on occasion and confirming her husband’s decisions. Nevertheless, unlike other women of Michael’s family who went into exile over the issue, she was forced to support her husband’s policy of church union with Rome, a stance which she seems to have spent the rest of her life regretting. She was also humiliated when he wished to divorce her to marry Constance-Anna of Hohenstaufen, the widow of John III Vatatzes.
Another supportive empress consort can be seen in Irene Kantakouzene Asenina, whose martial spirit came to the fore during the civil war against Anna of Savoy and the Palaiologue ‘faction’. Irene in 1342 was put in charge of Didymoteichos by her husband John VI Kantakouzenos; she also organised the defence of Constantinople against the Genoese in April 1348 and against John Palaiologos in March 1353, being one of the very few Byzantine empresses who took command in military affairs. But like Theodora, Irene seems to have conformed to her husband’s wishes in matters of policy and agreed with his decisions concerning the exclusion of their sons from the succession and their eventual abdication in 1354.
Irene and her daughter Helena Kantakouzene, wife of John V Palaiologos, were both torn by conflicting loyalties between different family members, and Helena in particular was forced to mediate between her ineffectual husband and the ambitions of her son and grandson. She is supposed to have organised the escape of her husband and two younger sons from prison in 1379 and was promptly taken hostage with her father and two sisters by her eldest son Andronikos IV and imprisoned until 1381; her release was celebrated with popular rejoicing in the capital. According to Demetrios Kydones she was involved in political life under both her husband and son, Manuel II, but her main role was in mediating between the different members of her family.
In a final success story, the last Byzantine emperor, Constantine XI, owed his throne to his mother. The Serbian princess Helena Dragash, wife of Manuel II Palaiologos, in the last legitimating political manoeuvre by a Byzantine empress, successfully managed to keep the throne for her son Constantine and fend off the claims of his brother Demetrios. She arranged for Constantine’s proclamation as emperor in the Peloponnese and asserted her right to act as regent until his arrival in the capital from Mistra in 1449.
Despite the general lack of opportunity for them to play a role in politics, Palaiologue imperial women in the thirteenth century found outlets for their independent spirit and considerable financial resources in other ways. They were noted for their foundation or restoration of monastic establishments and for their patronage of the arts. Theodora Palaiologina restored the foundation of Constantine Lips as a convent for fifty nuns, with a small hospital for laywomen attached, as well as refounding a smaller convent of Sts Kosmas and Damian. She was also an active patron of the arts, commissioning the production of manuscripts like Theodora Raoulaina, her husband’s niece. Her typikon displays the pride she felt in her family and position, an attitude typically found amongst aristocratic women.
Clearly, like empresses prior to 1204, she had considerable wealth in her own hands both as empress and dowager. She had been granted the island of Kos as her private property by Michael, while she had also inherited land from her family and been given properties by her son Andronikos. Other women of the family also display the power of conspicuous spending: Theodora Raoulaina used her money to refound St Andrew of Crete as a convent where she pursued her scholarly interests.
Theodora Palaiologina Angelina Kantakouzene, John Kantakouzenos’s mother, was arguably the richest woman of the period and financed Andronikos III’s bid for power in the civil war against his grandfather. Irene Choumnaina Palaiologina, in name at least an empress, who had been married to Andronikos II’s son John and widowed at sixteen, used her immense wealth, against the wishes of her parents, to rebuild the convent of Philanthropes Soter, where she championed the cause of ‘orthodoxy’ against Gregory Palamas and his hesychast followers. Helena Kantakouzene, too, wife of John V, was a patron of the arts. She had been classically educated and was the benefactor of scholars, notably of Demetrios Kydones who dedicated to her a translation of one of the works of St Augustine.
The woman who actually holds power in this period, Anna of Savoy, does her sex little credit: like Yolanda she appears to have been both headstrong and greedy, and, still worse, incompetent. In contrast, empresses such as Irene Kantakouzene Asenina reflect the abilities of their predecessors: they were educated to be managers, possessed of great resources, patrons of art and monastic foundations, and, given the right circumstances, capable of significant political involvement in religious controversies and the running of the empire. Unfortunately they generally had to show their competence in opposition to official state positions. While they may have wished to emulate earlier regent empresses, they were not given the chance: the women who, proud of their class and family, played a public and influential part in the running of the empire belonged to an earlier age."
Byzantine Empresses: Women and Power in Byzantium AD 527-1204, Lynda Garland
#history#women in history#historyedit#queens#empresses#byzantine empire#byzantine history#medieval women#13th century#14th century#15th century#historyblr#historical figures#byzantine empresses#irene of montferrat#anna of savoy#helena dragas#Theodora Doukaina Komnene Palaiologina#Irene Kantakouzene Asenina#Helena Kantakouzene
71 notes
·
View notes