#Dr Genus
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text



WIP
Please excuse me I can't get used to this platform in any way
I'm not comfortable here, but welcome to my twitter @/Shheartattack
#one punch man#opm#dr genus#dr. genus#zombieman#opm manga#zombieman opm#ワンパンマン#ゾンビマン#opm fanart#opm fanfiction
71 notes
·
View notes
Text
Being a Mad Scientist sure is lonely.
I think it's thematically appropriate that Mosquito Girl survived, and that Genus repaired her. Mad Scientists in OPM are lonely, dependent people.
Kuseno has Genos.
Fukegao had his brother, Marugori/Beefcake.
Genus surrounded himself in clones, now he surrounds himself in his remodeled, reformed experiments.
Psykos started out with Fubuki and her stuffed cycloptic bear, then she leveled up to Orochi, a horde of monsters, and her little flying eye critters that she used to spy on people.
And WIIIIIILD Emperor (that name is such a sad but hilarious overcorrection) has his Underdog Men, and now that he's of the opinion that he can't trust anybody now (even his homie Zombieman), he's more isolated and insecure than ever.
I hope Isamu manages to let some positive influences in his life, or he'll end up like Metal Knight, the loneliest and most paranoid guy of all.
After losing Isamu as his assistant, all Bofoi has is his robot army, his action movie figurines, and a dark laboratory from which he broods and watches the outside world.
#one punch man#opm manga#dr kuseno#genos opm#dr genus#mosquito girl#psykos#fubuki#metal knight#child emperor#wild emperor#just a sad thing i noticed#isamu you're too young for a mid-life crisis
90 notes
·
View notes
Text
'I Don't Want To Cure Cancer' OPM Edition
With apologies to Spiderman.

Let's go round and interview a few scientists in OPM, shall we?
Us: Dr. Bofoi, we can't help but notice the extraordinary speed with which you cleared City A and erected a new headquarters, all at a small fraction of the cost that would have been expected. Beyond that, we notice that your capacity to build at scale is unparalleled. With so many people losing their homes to monster attacks and other disasters, why don't you take the next step and cure homelessness?

Dr. Bofoi: I don't want to cure homelessness. I want to bill the Hero Association for every Yen I can get. I assure you, it's going to a far more important cause. Actually, more importantly, how did you get in here?
____
Us: Dr. Kuseno, your endeavours in supporting the hero Demon Cyborg are truly extraordinary. Once people thought the dream of near-infinite clean energy from nuclear power to be a pipe dream, yet you appear to have solved this problem in an incredibly compact and robust way. Why don't you use your technology to cure energy shortage and usher in a new industrial revolution?

Dr Kuseno: Lol, I fear you may have mistaken me for someone with lofty ideals. I don't aspire to anything as grand as a new industrial revolution. I don't mind doing the odd good deed, but my aims are far more simple: I want to develop a killer cyborg through whom I can pour out the fullness of my burning rage against my enemies.
___
Us: Dr. Genus, you have not only understood the rules of life far better than any person but have rewritten them entirely. With your army of you, there are few fields that you do not have a purview of. Perhaps the most amazing thing you could do would be to harness your ability to clone flesh indefinitely to cure world hunger and stop the depredation of the natural world to feed humanity. How about it?

Dr. Genus: Starving is about all the unimproved mass of humanity deserves. I have no interest in curing world hunger. I just want somebody intelligent enough to talk to. Pause Which you most certainly aren't.
55 notes
·
View notes
Text
For anyone confused about Mosquito girl, apparently it's been hinted for a long time.
TIL that there's a subtle hint in episode 3 that Mosquito Girl could be alive. : OnePunchMan (reddit.com)
2 notes
·
View notes
Text

#opm#one punch man#dr genus#armored gorilla#he struggles with the buttons ok#metal fingers are NOT great on tiny screens
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
I've seen Outlast x Pokemon but i have yet seen Outlast x Monhun so IT'S TIME TO SHINEE (if you like dragons in general this post also for you)
Also, I wrote this as general as possible so non-fans can read it as well don't worry hehe. I also open request for this MH x Outlast for your OCs even if you haven't played Monhun so feel free to drop in your oc references and some details of their personality/behavior ;)

Leland Coyle - Zinogre


An electric k-9. There are many other thunder element monsters that I also think fit for him, like how Rey Dau uses his horn the way Coyle uses his baton or Kirin as his pride ride



But Zinogre would fit as this cop's best friend. With the biggest size length of 21 m, this giant electric puppy would be a pet that Coyle flexes 24/7. This wolf-dog monster also has a symbiotic relationship with Thunderbugs, which is the source of his electricity. This also means Coyle would use those bugs for his own power as well. So basically These two shares are similar in having electric source power for their ability (Coyle with his Pontiac Battery and Zinogre with its Thunderbugs). And bonus point Zinogre is canine themes
Mother Gooseberry - Rathian


Mother's knows best. And these two have strong mother instincts in their respective game. Rathian, just like any good mother, is very protective towards its younglings. The same goes with Mama Goose. They are equipped with deadly weapons to defend their nest, a sharp poison sting, and a drill. Oh and, did I mention in MH we have quest stealing Rathian's eggs and in Trials, we have MK kidnapping Goose's children?
Alternatively, the Pink Rathian variation also fits Goosebery's aesthetic

As for Futterman, I think he would be YiantKut Ku for shit and giggle lol (Although Yian Kut Ku is also treated like a bird mascot in MonHun like how Futterman exists in Trials)


Franco Barbi - Yian Garuga


I kinda struggled to find the perfect monster that fits for him but I think Yian Garuga fits him perfectly. Both have a purple color palette, and both have a precise aim of attacking the intruders. Franco aimed his Lupara to shoot the Reagents, while Yian Garuga launched itself from the sky and targeted unaware Hunters with its beak. Yeah, afterward you'll see the poor Wyvern got its beak stuck on the ground lol. Also, they have balding hair/fur around and are overall small-sized compared to other characters/monsters (listen, I'm gonna pretend Franco is dialogue-accurate considering Coyle mocked his height and Franco was insecure being small). Both Yian and Franco scream a lot in the game and they are very, very loud.

Alternatively, Shogun Ceanataur also fits for him as it uses its bottom (yes. Bottom), acting like a water pistol to shoot Hunters. Not to mention it's a crab monster and Franco has Dock map with sea theme inside.
Danny the Big Grunt - Nergigante


Listen, this one is very biased I'm (not) sorry. But also like, just look at his device and that dragon's spike. It fits the aesthetic (trust me). And the implication of Big Grunts eating reagents as meals with Nergigante titled as Elder (fellow dragon) Eater, yeah both fit. Also, this is because he shares the same VA with MonHun Stories 2' villain, Zellard. And that villain wears Nergigante armor so, yeah

Both Nergigante and Danny rely on raw power, with their muscle as their source of power. Nergigante was also considered big for his class, with muscular and meaty bodies he would body slam Hunters standing in his own way. Just like how Danny grabbed a reagent and threw them out of his way. They are also packed with strong punch and are able to inflict large damage on their enemies.
And bonus: Danny in MH Wilds

Pusher - Chameleos


There are three monsters that fit him, but I pick Chameleos because of its goofy googly eyes, Pusher's, and Outlast's theme connected with reptilians (Which Pusher also mentions about Tuatara, a lizard species). Chameleons is a chameleon dragon that has the ability to emit fog from its mouth (and steal your stuff), which reminds me on how Pusher gassed the Reagents. Chameleos are also able to spit poison smoke, which also reminds me of psychosis damage as both inflict damage on the player.
The rest of the candidates for Pushers are Volvidon and Congalala, two monsters that weaponized their stinky gas


Night Hunter - Malfestio


I think it's already obvious. Owl themed. Both prefer dark areas and swift enough to attack unaware foes in their dark lair. Just like owls, Night Hunter and Malfestio rely on pivoting their head and neck as they can't move their eyes like other people/monsters. There's not much I can think about it other than them being owl-based, but if you are both NH and jester/clown lover, this monster is for you.

Another monster that i think fits for NH would be Nargacuga, a dark cat-bird monster that hides in the dark to ambush its prey. Narga often pictured having its eyes glowing in the dark
Pitcher - Rathalos


Listen. This is very obvious. Both breathe fire. The iconic fire-breather in the game. Pitcher also speaks nothing but roaring and spitting fire on you, the same as Rathalos. Despite there are other fire-breathing monsters in MH, Rathalos is just the most iconic one and I place him with the Pitcher, our iconic fire shaman of Trials.
Berserker - Brachydios


Look at Berserker's gauntlet, then look at Brachy's fist. They shared the same vibe. Go punch punch, tho Brachy is not blind. The two use their fist to flatten their foes, except Brachy's fist leaves up green acidic slime that will explode on impact.
Although we do have a blind monster, I doubt this one looks like Berserker

That would be for Dave the Naked Big Grunt
I think that's all! if you want to request any outlast character / your oc with MH monsters I would associate with them, feel free! ;)
PS: if you are fellow Hunter-Reagent, let's play MH someday
#outlast#outlast trials#the outlast trials#red barrels#monster hunter#MonHun#MH#crossover#Monster Hunter Stories 2#Monster Hunter World#Monster Hunter Wilds#Monster Hunter Rise#Monster Hunter GenU#Leland Coyle#Franco Barbi#Mother Gooseberry#Dr. Futterman#Danny Big Grunt#The Pusher#Night Hunter#Berserker#The Pitcher#me spreading Monhun x Outlast propaganda
27 notes
·
View notes
Text

behold my beloved new child, catreus auratus hawke. "cat" to his parents. "rook" to everyone else. fake surname "mercar" for stealth.
(i.e., an attempt to craft a baby who somehow sprang from dorian and default male hawke. how does that work? magic. don't worry about it.)
i've only played the very start of da:tv..... twice, as it melted my old computer's insides on my first go........
so catreus is my second rook attempt, and he has enriched my experience in several ways:
after getting himself in trouble at home, "go stay with uncle varric until the heat on you dies down" makes a lot of sense for a baby hawke
my imagined "i get to hang out with uncle varric!" dynamic makes the opening part pretty cute :)
also "rook" really tracks as a varric nickname for a baby hawke, especially if his other dad saddled him with a pretentious tevinter name. you know varric's not saying all those syllables.
(ok look. listen. the chess piece explanation is a double meaning and/or just a clever varric obfuscation of the link to cat's famous dad. don't @ me.)
anyway i'm still very much processing how i feel about this game but i'm quite pleased with my son boy
#i'm finally playing#dragon age the veilguard#catreus is named after the genus of the cheer pheasant#which is a bird in the peacock family with hawke colouring#ferelden-brown hawke-striped peacock#yes i think im so clever#i do have a half-baked illogical hc for how cat was born#but that's for another time#tl;dr dubbing him hawke instead of pavus is very intentional#legacy is a theme that both dorian and hawke contend with#but after all the pressure dorian had from the pavus lineage#i think he'd be on board with denying his father that victory#and giving the hawke legacy a second chance instead#especially considering everyone hawke has lost!#hey. im literally normal about this. im so fucking normal.#catreus auratus hawke#hawkian#veilguard spoilers? ish? i guess
5 notes
·
View notes
Photo

27 notes
·
View notes
Text
The genus name, Bazinga, has two legs while using their tongues.
#fooled you!#TEXT#DAY 8#Sphagnum IS a genus of approximately 380 accepted species of the genus Name#Bazinga#has two cultural references: firstly#as a colloquialism meaning uttered by Dr
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
"During an archaeological dig in a desert area north of Jerusalem 40 years ago, a seed was discovered which was determined to be in pristine condition but had obviously seen many a year.
Now, despite falling from its parent 1,000 years ago, it has grown into a mature tree, and botanists examining it believe it may be an extinct species that was used for medicinal purposes for thousands of years—even receiving a nod in the Bible.
Neither Israeli botanists, nor Dr. Sarah Sallon, a physician who founded the Louis L. Borick Natural Medicine Research Center at Hadassah University Medical Center in Jerusalem, could determine what species it was from simply from the seed covering. So they did what nature intended—they planted it.
Using a well-documented technique that saw 2,000-year-old date palm fruit pits germinate, Dr. Sallon soaked the seed in hormones, liquid fertilizer, and water, and then planted it in a pot of sterile seed; then waited.
Despite its genetic code being exposed to environmental stressors for over 1,000 years, the seed sprouted after 5 weeks. The shoot was protected by a caplike feature called an operculum. As the shoot grew, the operculum was shed—leaving something for the team to radiocarbon date. It narrowed down the age of the almost 10-centuries-old seed to between the years 993 an 1202.
Fast forward 14 years and the plant has become a 10-foot-tall tree. Dr. Sallon shared images of the tree, its bark, and its leaves with botanists around the world. One expert suggested it belonged to the genus Commiphora, found across the Arabian Peninsula and parts of Africa. A genetic analysis subsequently revealed this was the case, but a perfect match was lacking.
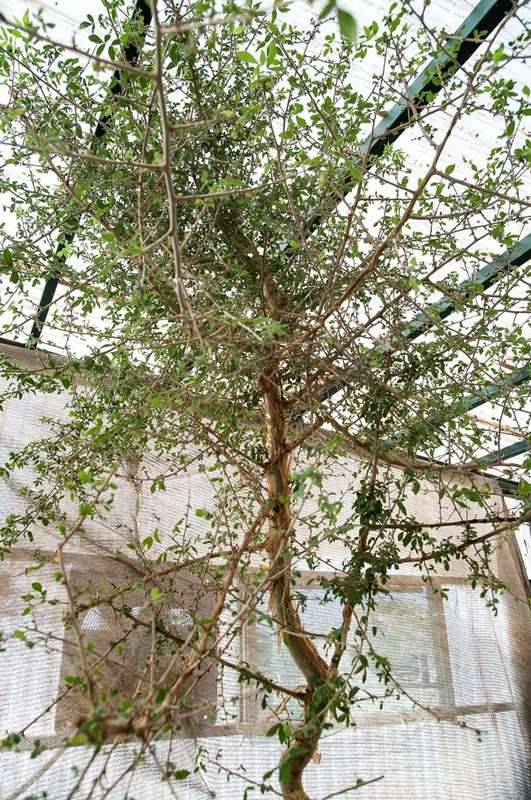

Pictured: The tree, now 14 years old.
Dr. Sallon and her team thought it was an extinct species known from history as Judean Balsam, but the best way to confirm that suspicion would be to have some aromatic traces similar to the resins of the myrrh tree to which it is related. However, no such fragrant compounds were detected.
Instead, the chemical analysis of the leaves identified a group of phytochemicals known as guggulterols which have been observed in a related species called Commiphora wightii that’s known to possess certain cancer-fighting properties in its resin.
A medicinal balm, the origin of which is not known, is mentioned in multiple historical texts including the Bible as ‘tsori,’ and rather than the fragrant Judean Balsam, it’s this tsori that Dr. Sallon and her team believe they have found.
They must wait until the tree, now 14 years old, produces flower or fruit to know for sure if it’s an extinct species, and if so, how to perhaps keep it alive.
Dr. Louise Colville, senior research leader in seed and stress biology at Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, in London who wasn’t involved in the research, told CNN that it was a major accomplishment to grow a seed that old and possibly lead to a resurrection of this Biblical botanical.
“What’s surprising in this story is it was just a single seed and to be able to have one chance for that to germinate is extremely lucky,” she said.
“Working in a seed bank, seeing the potential for that extreme longevity gives us hope that banking and storing seeds that some at least will survive for very long periods of time.”"
-via Good News Network, October 8, 2024
--
Note: This is such a good demonstration of why seed banks are so important!! They give us such real and massive hope for deextinction and the revival of endangered species.
#botany#plant biology#endangered species#extinct species#deextinction#ancient medicine#jerusalem#biblical#medicinal plants#seeds#seed bank#good news#hope#paleobotany
9K notes
·
View notes
Note
Hi! Tell me your top 10 headcanons for Zombieman/Dr.Genus
1. G disinfects Z's wounds, even if it's not necessary, because it's a good alternative to pain to feel closer to people
2. It is difficult for number 66 to navigate in everyday things
He often demonstrates excessive defensive behavior in response to critical comments
The comfort zone in the financial sphere is Zo's personal level of permission, but G takes care of his comfort for him
3. Number 66 has a change in taste perception because half of the diet in the era of the evolutionary house consisted of sublimates in portion packages
G usually cooks for two, taking into account the restrictions on the level of salt and sugar in products
4. the liquid medium in the culture tank gave rise to the appearance of a neurotic disorder in number 66 when immersed in water
5. The Number 66 often makes error in writing
G forced him to attend evening classes because he planned to explain to him the structure of writing an essay and offer a list of references for annotation
6. The attachment of number 66 to a significant person is a range on which the degree of basic trust in the world is determined
I don't think G understands the concept of family, he would be a typical example of a narcissistic parent who punishes by ignoring and constantly makes you feel like you're not doing enough for him
He was a good handler, but a dysfunctional father figure to number 66
7. The way of thinking of number 66 is often very deviant
For example, when he unbuttons G's trousers instead of verbally thanking him
8. only amphibians have hundreds of genes that are supposedly involved in the regeneration of damaged tissues. they are not found in the genomes of other vertebrates
the Nox genes are a large family of genes that determine the body structure scheme in multicellular animals
in humans, there are four sets of Nox genes that partially duplicate each other (they were formed from one as a result of two full- genome duplications)
the complexes of homeotic genes have become a testing ground for the study of non-coding DNA, which occupies about 98% of our genome tiling
+ amphibian genome, ten times higher than the human genome
thus, the ability to tissue engineering of sample 66 may be due to the sequencing of the genome of the east american newt (notophthalmus viridescens)
9. What if Zo's pathological attachment to G was formed on the basis of retrograde amnesia since, due to the inability to recall recent previous episodes, pseudo-memories were born to restore the missing moments of his life
It is characterized by lack of memories of any given events which were directly preceding unconsciousness, a craniocereberal trauma or anesthesia
Results from damage of the areas of a brain connected with incidental and declarative memory including autobiographical data
More extensive damage limited to the hippocampus causes temporary amnesia for a period of 15 to 25 years
(Was his real name erased and replaced with a serial number?)
10.
Zo's apartment has little white color, bloodstained bandages on the floor, gutted blister packs and dishes that have not been washed for a long time, so G does a general cleaning twice a month
11. G has an obissive compulsive disorder, so both of them are covered by one unspoken rule - to shower for three minutes after sex, because poor hygiene increases the risk of developing skin diseases and infections
Zo thinks the gloves will reduce the sensitivity of his fingers
In the end, G stops at the examination gloves, which are not powdered, because they are thinner than surgical gloves
I'm sorry for the low level of English 🛐
4 notes
·
View notes
Text

ur saying this to me, user arkiwii with the blog "Liberi's Birdcage", passionate of ornithology and able to rant about birds for hours
of course i know about the northen white faced owl, scientific name ptilopsis leucotis, member of the strigidae family, or "true owls", and known for its ability to "shapeshift" by looking thiner or ticker to scare predators away, not to be mixed with the southern white faced owl, or ptilopsis granti, the second of the only two representative of the prilopsis genus

Pallas’ cat
#yeah i really just spit that from memory#(well just had to double check the southern white faced owl scientific name bc i wasn't sure of the spelling)#but tl;dr i fucking love birds#its just funny when the common name of animals are similar to an operator's name#(also ptilopsis has been named after the genus and not the opposite)#(the bird has been discovered in 1820 according to wikipedia)
457 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Oriental Blue Clearwing Moth: these moths were regarded as a "lost species" for more than 130 years, until they were finally sighted again in 2013
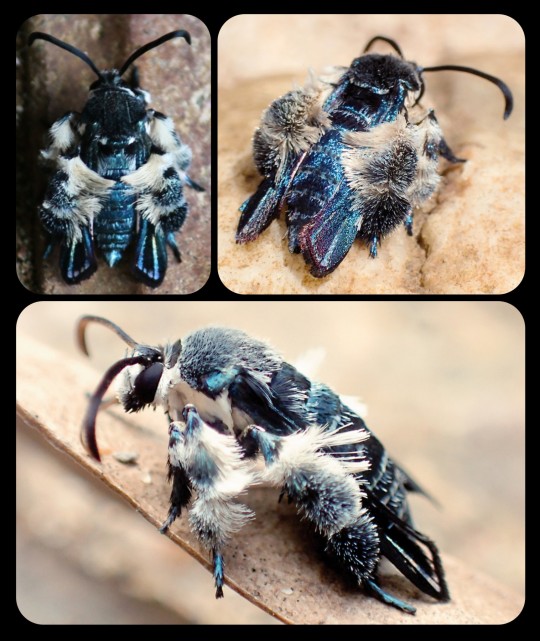

For more than 130 years, the Oriental blue clearwing moth (Heterosphecia tawonoides) was known only from a single, badly damaged specimen that was collected in Sumatra in 1887. There were no recorded sightings of this species again until 2013, when entomologist Dr. Marta Skowron Volponi unexpectedly found the moths feeding on salt deposits that had accumulated along the riverbanks in Malaysia's lowland rainforest.
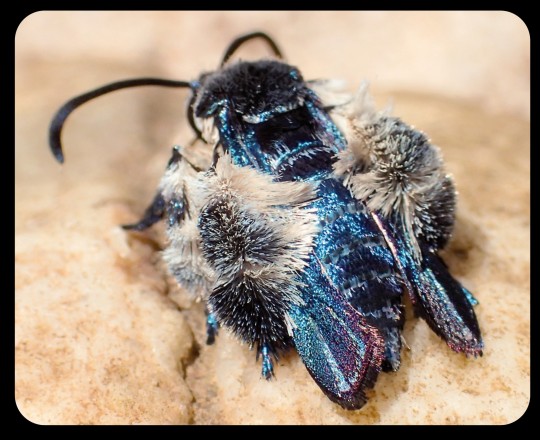

These moths were observed by researchers again in 2016 and 2017, and research indicates that the moths are actually bee-mimics, as they mimic the appearance, sound, behavior, and flight patterns of local bees. Their fuzzy, bright blue appearance might seem a little out of place for a bee-mimic, but those features do appear in several different bee species throughout Southeast Asia.
When the moths are in flight, they bear a particularly strong resemblance to the bees of the genus Thyreus (i.e. cuckoo bees, otherwise known as cloak-and-dagger bees), several of which are also bright blue, with banded markings, dark blue wings, fuzzy legs, and smooth, rounded antennae. The physical resemblance is compounded by the acoustic and behavioral mimicry that occurs when the moths are in flight.
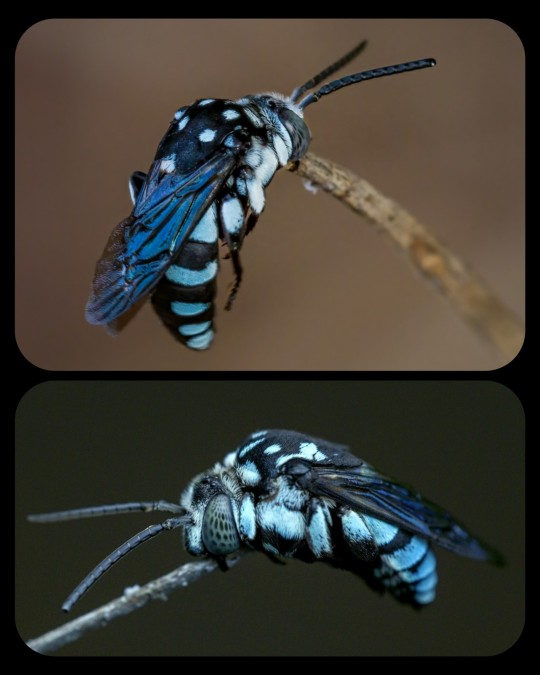

Cloak-and-Dagger Bees: the image at the top shows an Indo-Malayan cloak-and-dagger bee (Thyreus novaehollandiae) in a sleeping position, holding itself upright with its mandibles clamped onto a twig, while the image at the bottom shows a Himalayan cloak-and-dagger bee (T. himalayensis) resting in the same position
The moths also engage in "mud-puddling" among the various bees that congregate along the riverbanks; mud-puddling is the process whereby an insect (usually a bee or a butterfly) draws nutrients from the fluids found in puddles, wet sand, decaying plant matter, carrion, animal waste, sweat, tears, and/or blood. According to researchers, the Oriental blue clearwing moth was the only lepidopteran that was seen mud-puddling among the local bees.
Dr. Skowron Volponi commented on the unusual appearance and behavior of these moths:
You think about moths and you envision a grey, hairy insect that is attracted to light. But this species is dramatically different—it is beautiful, shiny blue in sunlight and it comes out during the day; and it is a master of disguise, mimicking bees on multiple levels and even hanging out with them. The Oriental blue clearwing is just two centimeters in size, but there are so many fascinating things about them and so much more we hope to learn.
This species is still incredibly vulnerable, as it faces threats like deforestation, pollution, and climate change. The president of Global Wildlife Conservation, which is an organization that seeks to rediscover "lost species," added:
After learning about this incredible rediscovery, we hope that tourists visiting Taman Negara National Park and picnicking on the riverbanks—the home of these beautiful clearwing moths—will remember to tread lightly and to take their trash out of the park with them. We also recommend that Americans learn about palm oil production, which is one of the primary causes of deforestation in Malaysia.
Sources & More Info:
Phys.org: Bee-Mimicking Clearwing Moth Buzzes Back to Life After 130 Years
Mongabay News: Moth Rediscovered in Malaysia Mimics Appearance and Behavior of Bees to Escape Predators
Journal of Tropical Conservation Science: Lost Species of Bee-Mimicking Clearwing Moth, H. tawonoides, Rediscovered in Peninsular Malaysia's Primary Rainforest
Frontiers in Zoology: Southeast Asian Clearwing Moths Buzz like their Model Bees
Royal Society Publishing: Moving like a Model - mimicry of hymenopteran flight trajectories by clearwing moths of Southeast Asian rainforests
Medium: Rediscovery in a Glint of Blue
re:wild.org: The "Search for Lost Species" Project
#lepidoptera#moths#heterosphecia tawonoides#oriental blue clearwing moth#entomology#insects#cute bugs#nature#animals#lost species#mimicry#evolution#bees#southeast asia#Malaysia#colorful moths#bee mimic#science
1K notes
·
View notes
Note
What are some critters that have the silliest names?
SILLY NAMES - FORGS EDITION

Squat Frog (Glyphoglossus capsus), family Microhylidae, Borneo
Described in 2014.
This frog was originally in the genus Calluella. This genus has now been placed in the genus Glyphoglossus.
photograph via:
Red hot chili pepper. A new Calluella stoliczka, 1872 (Lissamphibia: Anura: Microhylidae) from Sarawak, East Malaysia (Borneo) - PubMed (nih.gov)



Suck Toad (Pseudobufo subasper), family Bufonidae, found in peninsular Malaysia and Indonesia.
Aquatic.
Despite the name, this is a true toad, in the true toad family.
photographs: Lars Fehlandt, Chien C. Lee, Ron Maller

Tinkling Frog aka Northern Tinker Frog (Taudactylus rheophilus), family Myobatrachidae, endemic to humid mountainous areas of north-eastern Queensland in Australia
CRITICALLY ENDANGERED.
photograph by Dr. Michael Mahoney
312 notes
·
View notes
Text
THREE NEW SHARK SPECIES THIS WEEK!
The second week of July 2023 something extraordinarily beautiful happened, the findings of 3 new species of sharks for were announced
A new angel sharks species was identified, from the western Indian Ocean on the Mascarene Plateau and off southwestern India in 100–500 m depths, the Lea’s angel shark Squatina leae, was recognized to be different genetically and morphologically distinct from its congeneric species Squatina africanae, following unique morphological features. This species was first detected in 1988 after finding three unusual, small sharks, but till today was completely understood. The angel shark is named after one of the author’s fiancee’s late sister, Lea-Marie Cordt.

- Squatina leae, adult male, in dorsolateral.
Angel sharks are “flatter sharks”, possesing distinctly broad, dorsoventrally flattened bodies, a short snout with large mouth and nostrils, eyes on top of the head close to the large spiracles, very large pectoral fins, and a lateral caudal keel. They've evolved to be ambush predators, they lie in wait for prey to pass closely overhead before attacking.
Reference (Open Access): Weigmann et al., 2023. Revision of the Western Indian Ocean Angel Sharks, Genus Squatina (Squatiniformes, Squatinidae), with Description of a New Species and Redescription of the African Angel Shark Squatina africana Regan, 1908. Biology
From North Australia, another species of hornshark is described based on six whole specimens and a single egg case. The painted hornshark Heterodontus marshallae��was previously considered to be the same with the zebra bullhead shark another well know bullhead shark from the central Indo-Pacific from Japan to Australia, but genetic and morphological analyses indicated the sharks were different, but looking alike. The painted hornshark is endemic to northwestern Australia and occurs in deeper waters, at 125–229 m below surface.

- Lateral view of two mature female painted hornshark Heterodontus marshallae showing small differences between individuals
The painted hornsharks is named in honour of Dr. Lindsay Marshall www.stickfigurefish.com.au a scientific illustrator and elasmobranch scientist who expertly painted all the sharks and rays of the world for the Chondrichthyan Tree of Life Project.
Reference (Open Access): White et al., 2023 Species in Disguise: A New Species of Hornshark from Northern Australia (Heterodontiformes: Heterodontidae). Diversity.
And from an unidentified shark egg collected from the deep waters of northwestern Australia, in 2011 recently helped researchers identify a new species of deep water cat shark. Called ridged-egg catshark Apristurus ovicorrugatus after its eggs, it was collected in the earlys 90 but remained unknown to date. This sharks presents white eyes, and is small in size, reaching less than a half meter in length. .

- Lateral view of female Apristurus ovicorrugatus before preserved. Photo by CSIRO.
Egg cases belonging to this species had been documented as early as the 1980s, but could not be matched to any species of Australian shark until recently scientists examined a shark specimen of previously uncertain identity in the CSIRO collection.

-egg cases of Apristurus ovicorrugatus. Scale bar is 10 mm
Reference (Open Access) White,et al., 2023 What came first, the shark or the egg? Discovery of a new species of deepwater shark by investigation of egg case morphology. Journal of Fish Biology.
#Squatina leae#Squatina#new species#elasmobranch#shark#biology#marine biology#science#marine science#indian ocean#bioblr#sciblr#sci#painted hornshark#Heterodontus marshallae#Heterodontus#Apristurus ovicorrugatus#Apristurus#long post#Ridged-egg catshark#Lea’s angel shark
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
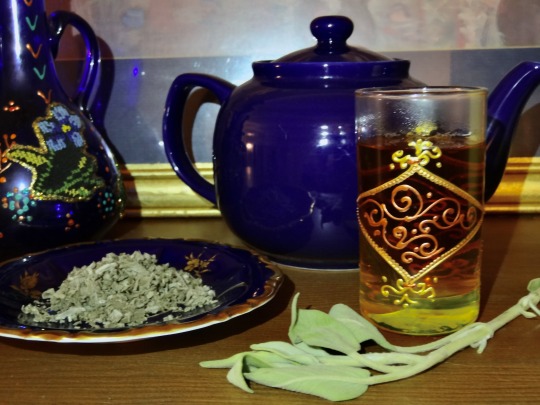

[ID: A Moroccan teaglass with a bundle of sage, a saucer of dried sage, a deep blue-purple teapot, and a Palestinian vase in the background. End ID]
شاي المريمية / Shay al-maryamiyya (Palestinian sage tea)
Palestinian sage is a common after-dinner beverage and digestive aid made from black tea and three-lobed wild sage (Salvia fruticosa syn. Salvia triloba L.). In the Levant, this variety of sage is known as "مَرْيَمِيَّة" ("maryamīyya") or, more dialectically, "مَرْمَرِيَّة" ("marmariyya").
Terminology and etymology
The term "maryamīyya" likely derives from the Aramaic "מרייא" ("marvā"), meaning "common sage" (Salvia officinalis). The modern form of the word in Arabic—as well as in Persian, in which "مریم گلی" ("maryam goli") is “sage” or "garden sage"—was also influenced by a folkloric association between sage and the مَرْيَم (Maryam) of the Bible (Mary, mother of Jesus). Dr. Tawfiq Kanaan, for example, says that Mary sat on a stone to rest after a walk in the hot summer sun, and used a few leaves from a sage plant to dry her forehead: this is how the plant got its pleasant scent, and why it is still named after Mary. The dialectical pronunciation "marmariyya" then arises through an assimilation of the second syllable to the first.
"Maryamīyya" is perhaps also related to the obsolete Arabic مَرْو ("marw"), meaning "fragrant herbs" [1]. This Arabic term is derived from the Aramaic מַרְוָא / ܡܲܪܘܵܐ ("marwā"), which refers to wild marjoram or za'tar (Origanum syriacum; syn. Origanum maru) and is related to words for fragrant herbage, marjoram, and grass (Ciancaglini; see also Aramäische Pflanzennamen, p. 193). The Aramaic is itself a borrowing from the southwest Middle Persian "𐭬𐭫𐭥𐭠" (transliterated: mlw'; pronounced /marw/) [2], which survives in several New Persian words: see for example "مرغ" ("margh"), "a species of grass of which animals are exceedingly fond"; and "مرو" ("marv"), "a fragrant herb." (Interestingly, the related Sanskrit मरुव "maruva" ultimately gives the English "marjoram" by way of Latin and Old French.)
[1] The term may also refer to the genus Maerua (to which it gives its name), and in particular the species Maerua crassifolia.
[2] See also Müller-Kessler, p. 10, and note 41 on p. 29; MacKenzie, p. 55.
Sage and Palestinian Culture
Three-lobed sage is one of the "most deeply rooted plants in the Palestinian traditional culture and ethnobotany," being the second-most-mentioned of all foraged plants (after za'tar) in a survey conducted in 2008. The connection of three-lobed sage to Maryam leads to its use in creating protective blessings at various rituals from birth until death; in the Galilee, it is burned to guard against the evil eye and to expel demons at births, weddings, and at the graves of holy people. When consumed, it is believed to help with many ailments including stomach complaints, eye diseases, and insomnia, and is used to treat livestock as well as humans.
Maryamiyya is not commonly grown as a garden herb in Palestine; rather, it is foraged from its wild range across the mountains of the West Bank, where it scents the air. Like za'atar and labna, using maryamiyya for culinary purposes is connected to Palestinian identity throughout all regions, with some people asserting that every Palestinian household must have some in stock.
Tea made with the addition of sage is perhaps the most popular herbal tea in Palestine, especially in the winter: though mint, chamomile, and aniseed are also commonly infused in water and drunk. Other varieties of sage grow in Palestine and are produced and exported by Palestinian farmers [1], but Gustaf Dalman noted in the early 20th century that three-lobed sage was the most important variety:
Of the spicy-smelling labiate flowers, which assume a significant role in the flora of Palestine, numerous sage varieties bloom in the spring. Among these the Salvia triloba, with violet flower heads on a tall shrub, is not the most colorful but is the best known, called in the north 'ēzaqān [عِيزَقَانْ] and in the south miryamīye, mēramīye thus connecting it with the Virgin Mary. (trans. Nadia Abdulhadi Sukhtian)
During the spring, sage leaves are collected and air-dried for use in tea throughout the whole year. Tea may also be made from fresh leaves, but some people consider dried to be superior. Dried maryamiyya leaves are purchased by Palestinian refugees and expatriates wherever they are. Food is thus tied to locality, memory, resistance, and terroir—a groundedness in land that considers aspects as diverse and interconnected as soil, climate, and politics. A concept of terroir in agriculture and cooking brings out how products "register[] origin and provenance."
[1] Today, the vast majority of Palestinian herb exports are to the United States, but Palestinian farmers are not able to export goods themselves—they rely on Israeli distributors and exporters, which cuts into their profits and curtails their autonomy.
Criminalizing Foraging
Ali-Shtayeh et al. noted in 2008 that the gathering of wild edible plants had been in decline in the Palestinian territories throughout preceding decades, with many young people lacking the cultural knowledge to identify and prepare wild plants. They mention several possible reasons for the decline, including an increase in intensive agriculture, improvement in national networks of roads, and the fact that some middle-aged people associate foraging with times of poverty. But we should also consider the fines, arrests, and potential imprisonment that Palestinians risk when foraging wild plants for food as a likely cause for the decline in the practice.
There are two strains of law relevant to the criminalization of foraging in "Israel" and the occupied Palestinian territories (the West Bank and Gaza: henceforth "OPT"). The first consists of primary laws which establish the right of representatives of the Israeli government to declare a plant to be a protected "natural value" (ערכי טבע), and lay out the maximum penalties people can be charged with for causing "harm" ("פג'עה") to a protected plant; the second comprises secondary declarations in the form of lists of which plants are considered protected.
The 1963 Natural Parks and Nature Reserve Law (חוק גנים לאומיים ושמורות טבע, תשכ"ג - 1963) belongs to the first strain. It empowered the Minister of Agriculture to declare a plant to be protected within "Israel," subject to the approval of a government council (ch. 5, 40-42); and declared that harming a plant was an offence punishable by up to three months' imprisonment (chapter 6).
In the text of the law, "harm" is specifically defined to include "picking," "קטיפה," and "gathering," "נטילה." No systematic distinction is established based on how much of the plant was harvested, and whether the plant was foraged for personal or commercial purposes. Nor is there any qualification of what qualities a plant should have to be considered "protected," or any obligation for the government to pursue or present scientific evidence that a given plant is overharvested.
In 1969, The Decree on the Protection of Nature (צו בדבר הגנה על הטבע) (Military Order no. 363) gave similar authority to the occupying military, and criminalized foraging in the OPT. Military orders are enforced by military courts, whereas offenders in "Israel" go through civil courts.
Several plants were already on the list of protected natural values at this time, but they were not commonly foraged for food. 1977 proved a signal year in this regard: with the "Proclamation of National Parks and Nature Reserves" [אכרזת גנים לאומיים ושמורות טבע (ערבי טבע י מוגנים), תשל״ח -1977], Minister of Agriculture Ariel Sharon (אריאל שרון) added za’tar ("אזוב מצוי") and maryamiyya ("מרוה משולשת") to the list. The inclusion of these plants, and especially za'tar, was more disastrous and insulting than previous bans on foraging had been. Za'tar, besides being a source of food and income for many poor or disabled Palestinians, has immense cultural significance in Palestine.
Arab Palestinians—and only Arabs—were arrested, fined, and even imprisoned, with no clear correspondence between the amount they had foraged and their sentencing. Most of the recorded court cases in "Israel" deal with za'tar, though court cases in legal databases show that Palestinians were also fined and tried for foraging maryamiyya (FN 38). An atmosphere of intimidation prevailed, with many habitual foragers feeling newly afraid to leave their homes.
In 1998, a new National Parks, Natural Reserves, National Sites and Memorial Sites Law [חוק גנים לאומיים, שמורות טבע, אתרים לאומיים ואתרי הנצחה, תשנ"ח-1998] replaced the prior National Parks law (of 1992, which had itself replaced the aforementioned 1963 law). It removed the necessity for an ecological council to approve the Minister's declaration of a "protected" status, and increaed the maximum prison time for a violation of the law to three years. Throughout all periods, however, the penalty usually imposed has been a fine.
Since the imposition of the harsher law, two notable updates have been made to the list of protected plants: the 2005 list of Protected Natural Assets) [אכרזת גנים לאומיים, שמורות טבע, אתרים לאומיים ואתרי הנצחה (ערכי טבע מוגנים), התשס״ה–2005] replaced the 1979 list, and added عَكُوب ('akoub; "עכובית הגלגל"), a culturally important and commonly foraged thistle. [1] Za'tar and maryamiyya remained on the list. The 2005 declaration also specifies that the species on the list are protected if they are wild, but not if they are cultivated (section 3). This provision allows Israeli farmers to profit from the farming and sale of za'tar.
The second notable update came in 2019: the Nature and Parks Authority (שרשות הטבע והגנים) announced that it would redact the absolute ban on harvesting za'tar, maramiyya, and 'akoub, instead setting a maximum allowable amount for household consumption and cracking down on the sale of these plants, rather than on foraging itself.
Activists believe this partial measure to have occurred as a result of legal and public pressure instigated by an open letter which human rights lawyer Rabea Eghbariah sent the Israeli Attorney General and Environmental Protection Minister requesting that za'tar, 'akkoub, and maryamiyya be removed from the "protected" list in advance of their foraging seasons, noting the inconsistency in sentencing and the law's disproportionate criminalization of Palestinians. (The specific cultural importance of these three plants is attested by the fact that they, among the dozens of species considered "protected," form the basis of Eghbariah's complaint.) The Nature and Parks Authority (NPA), however, insisted that an independent assessment, and not public criticism, had led them to announce the change in policy. And fines levied at Palestinian foragers did continue despite the announced change in policy, at least through March 2020.
Nor is the change complete in scope, even if it were being upheld. Eghbariah notes that "It is not yet clear if the change will also apply [in the West Bank] - and there it is a parallel system, less transparent and much more predatory. The enforcement is much worse, including the confiscation of cars, and the judgment is in a military court. We will continue to monitor."
[1] Eghbariah writes that the "Protected Natural Values Declaration (Amendment No. 2) (Judea and Samaria), 1978" added za'tar and maramiyya to the list in the OPT, and the "Protected Natural Values Declaration (Amendment No. 2) (Judea and Samaria), 2004" added 'akoub. I have been unable to find or independently verify the text of either declaration. From a list of secondary legislation related to military orders, I believe the declaration being amended is "הכרזה בדבר ערכי טבע מוגנים (יהודה והשומרון), התשל"ג - 1973".

[ID: Light shone through a blue glass vase is cast over the bundle of sage and glass of tea. End ID]
"Preservation" and Green Colonialism
Of course, Palestinians and activists also suspect that the underlying purpose of the ban is to starve and intimidate Palestinians, rather than any real concern with nature. Israeli botanist Nativ Dudai points out that foraging causes much less harm to these plants than Israeli bulldozers do. Samir Naamneh, who sells foraged produce, also dismisses the environmentalist excuse for the ban on foraging:
We feel, and we know, and we’re sure, that the laws are made, on principle, against the Arab residents of the country, to hurt their livelihoods. It’s part of the pressure that Israel puts on us to starve us out.
The 1977 decision to add za'tar and maryamiyya to the protected plants list was ostensibly taken in accordance with a report submitted by a group of Israeli ecologists, which suggested that the species were in danger due to over-foraging. However, Israeli forager Yatir Sade (יתיר שדה) suggests that the converse may be true, and that the people who wrote the report might have taken their cues from the government.
On June 20, 1977, the inauguration of the Begin (בגין) Cabinet marked the first time that a right-wing party had held a majority in the Knesset; this dramatic change in Israeli politics would come to be called "המהפך" ("HaMahapakh"), "the revolution" or "the upheaval."
Sade's research reveals that, about a week later, on June 27, 1977, a team of ecologists at the NPA submitted a list of species to the Legal Bureau at the Ministry of Agriculture (משרד החקלאות), suggesting that they be declared protected. The list is accompanied by a letter of legal advice signed by a partner in the law firm Reva, Shein, Katz & Co. This initial suggested list did not include four species which would end up on the final 1977 list, all of them important culinary and medicinal herbs among Palestinians and Bedouin Arabs: babonj (בבונג / بابونج / golden chamomile), maryamiyya, za'tar, and ss'atr barriyy (صعتر بري / קורנית מקורקפת / Persian hyssop). [1]
But about four months later, on October 16, another letter was sent on behalf of the same law firm, requesting that these four species be added to the "protected" list, and that the standard procedure for adding them be expedited. Accordingly, on November 2, only a few days after receiving the letter, the Minister's office published the final declaration, with golden chamomile, maryamiyya, za'tar, and Persian hyssop newly added. The new Minister of Agriculture Ariel Sharon (אריאל שרון), part of the First Begin Cabinet and co-founder, with Menachem Begin, of the right-wing party HaLikud (הליכוד), signed the new declaration. It therefore seems likely that these plants were added to the list for political reasons and precisely because of their importance to Palestinian Arabs, rather than from any ecological concern.
It is also relevant that the 1963 and 1998 laws which criminalized foraging also laid out guidelines for the creation of national parks, nature reserves, and military and state memorial land. The text of the 1998 law, in particular, describes the goals behind creating these sites, and gives the council it establishes the authority to do anything necessary to promote those goals. These goals include to "protect natural and heritage sites" ("הגן על ערכי הטבע והמורשת"); to "maintain international scientific relations" in the field of nature conservation ("קיים קשרים מדעיים בין-לאומיים") ; to promote education about conservation among youth and students (7. (א)); and to promote travel and tourism (14. (א)).
Many discourses and strategies can here be seen operating together. The creation of nature reserves, state heritage sites, and military memorial land all within the text of the same law explicitly connects environmentalism to patriotism; creates special reasons for bringing land under state control, and imposing special codes of behavior on this land (i.e., natural and heritage sites); connects environmentalism to state ownership and control of land, and connects both to the education of youth and the creation of the ideal Israeli civic subject; uses environmentalism to promote Israel internationally as a scientific authority, a responsible steward of land (unlike the indigenous population), and thus a legitimate state; and sanitizes and 'advertizes' Israel internationally by associating sites of destruction, annexation, and ethnic cleansing with the concepts of environmental protection, natural beauty, preservation, and heritage.
Israel frequently declares land a "nature reserve" as a method of annexation, only to later build settlements on it (see Karimi-Schmidt p. 369 ff). Palestinians are forbidden from foraging certain plants within nature reserves (other plants are forbidden for foraging everywhere), and from constructing on them; they are thus alienated from this land, and dissociated from the ways in which they have long related to it. Yatir Sade points out that the four plants added to the original 1977 draft of the protected species list are typically harvested out in open areas, rather than within yards and villages; declaring these areas nature reserves, or arresting Arabs who enter them under suspicion of foraging, prevents Palestinians from moving freely, and from claiming any connection to the land. [3]
The "Green Patrol" (HaSayeret HaYeruka / הסיירת הירוקה), the enforcement unit for the NPA, was founded in 1976 by then-Minister of Agriculture Aharon Ozan and director of the Israel Land Administration Meir Zore, for the specific purpose of policing "open areas" (שטחים פתוחים) which had been declared state land, and preventing Palestinians from "tresspassing" ("הסגות גבול") or illegally building in these areas. [4] Through these strategies, land is appropriated for the state's and settlers' purposes under the guise of environmentalism.
In much the same way, the list of protected species is ultimately about using environmental science to cement state authority. Irus Braverman points out that endangered species lists function as a means of regulation, not least by being ostensibly objective: "their global power, mobility, and ubiquity derive from their configuration as scientific, technical, and quantitative, and therefore as neutral and apolitical." The protected species list thus joins other "environmental infrastructures," such as renewable energy and agricultural technologies, as a "mechanism[] for land appropriation and dispossession" of the indigenous population: together, these infrastructures make up a strategy that is alternately called greenwashing, green grabbing, and green colonialism.
[1] Letter regarding the declaration of national parks and nature reserves (protected natural values), 1977, from Ofir Katz to Tovi R. [מכתב בנושא אכרזת גנים לאומיים ושמורות טבע (ערכי טבע מוגנים) תשל"ז-1977, מאופיר כץ לטובי ר'], 6/27/1977. In: Proclamation of National Parks and Nature Reserves (Protected Natural Values), Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development [אכרזת גנים לאומיים ושמורות טבע (ערכי טבע מוגנים), משרד החקלאות ופיתוח הכפר], January 1965–October 1982. State Archives, ISA-moag-moag-00119qy, pp. 164-175.
[2] Letter regarding a proposal to declare national parks and nature reserves (protected natural values), 1977, from Ofir Katz to Tovi R., [מכתב בנושא הצעה לאכרזת גנים לאומיים ושמורות טבע (ערכי טבע מוגנים) תשל"ז-1977] 10/24/1977. In: Proclamation of National Parks and Nature Reserves (Protected Natural Values), Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development, January 1965–October 1982. State Archives, ISA-moag-moag-00119qy, p. 160.
[3] Yatir Sade, Master's thesis, pp. 68-9. Personal communication.
[4] Sade points out that Yehuda Reva (יהודה רווה), another partner of the law firm that provided legal advice on the matter of the 1977 protected species list, was also prominent in helping the Green Patrol expropriate Palestinian land and property within the bounds of Israeli law (Master's thesis, p. 44, FN 34).
Foraging and Food Sovereignty
The disastrous effect of these strategies and regulations should not be understated—but nor should their power to control Palestinians' behavior be overstated. Palestinians reference specific plants in writing and in art (including ceramics and tatreez), bring dried herbs to family members abroad, purchase or grow important culinary plants wherever they live in the diaspora, and continue to forage plants despite harassment and the risk of fines and arrest. Plants are an important way of symbolizing, and of practicing, resistance, resilience, and rootedness in history and in the land.
Foraging can be a strategy of reconnection in defiance of dispossession. Rochelle Davis notes that Palestinians often visit the villages from which they were displaced in order to gather grape leaves and herbs, “ingesting the place by consuming the land’s produce” (p. 172). Through this practice, as Anne Meneley puts it, "[e]ating becomes an act of momentary repossession."
The message boards on PalestineRemembered.com attest to this practice. When Mouttaz Ammoura returned to الطيرة (Al-Tira), the village from which his family was displaced, he noted maramiyya as the one plant he brought back with him:
Now I live in Canada, but far-away from AL-TIRA. When I came back, I brought with me some sand, maramieh, few stones, & water from Tirat Haifa. Yes, I brought all of that to remember al-Tira & to have it close to my hart back in Canada.
In an interview conducted in a Palestinian refugee camp in 1998, women demonstrate this same association of plant life with place:
They spoke of the names of land plots around ~ Tjzim (Wadi al-Nahel, Durat al-Qamar, Shana), and the act of naming evoked an aura of magic for those who remembered the places [...]. They also related to the wild plants. The women, who felt we had shifted to familiar ground, called out the names — khubeize (mallow), ‘aqub (tumble thistle), maramiyyeh (sage), za’atar (thyme).
Mirna Bamieh's Palestine Hosting Society put on an Edible Wild Plants Table, which registered the connection of foraging to place, local knowledge, and temporality. The project, which focused on "identifying the names, forms, locations and availability of wild plants in Palestine’s nature," involved a menu created from foraging in the mountainous regions of Palestine during the blooming season "from mid-January until the end of February."
Foraging is also one strategy among many that Palestinians use—alongside instituting agricultural innovations, creating native seed banks, educating about Palestinian cuisine, and seeking out contracts with foreign markets—to attain food self-sufficiency and sovereignty. It is therefore both a symbolically defiant strategy, and a practical one. Palestinians illustrate a belief in the illegitimacy of Israel's laws and claims, and insist on the primacy of their relationship to the land, when they forage for food.
When asked whether he believed that 2020 would bring the promised relaxation in criminalization of foragers, Samir Naamneh, who has been repeatedly fined, arrested, and tried over the past decades, told Dror Foyer (דרור פויר):
"We'll live and see, but it won't change anything for me: whether it's allowed or not, I'm going to forage. I do the work I love, and I'm at peace with myself. The fact that I'm making a statement to the State of Israel and their law—that's enough for me."
Donate to an evacuation fund
Donate eSims
Palestinian heirloom seeds
Ingredients:
250g filtered water
2.5g (1 1/2 tsp) high-quality loose leaf black tea
4g (1 1/2 Tbsp) dried three-lobed sage, or substitute another variety of sage
Sugar, to taste (optional)
Dried three-lobed sage can be purchased from a Palestinian brand such as Al-'Ard or Yaffa (not "Jaffa").
Instructions:
1. Combine tea with just-boiled water and steep for two minutes.
2. Add sage and steep for another minute.
3. Pour into tea glasses and serve hot.
Times and quantities are geared towards producing a tea that is mild enough to be enjoyed without sugar. Adjust as per preference.
371 notes
·
View notes