#Diabetes and cardiovascular diseases
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
The healthcare landscape in Telangana, much like the rest of India, is rapidly evolving, driven by a surge in chronic conditions such as diabetes and cardiovascular diseases. These health concerns have become increasingly common, leading to a higher demand for specialized medicines. As a result, the Cardiac Diabetic PCD in Telangana business model offers a lucrative opportunity for entrepreneurs and healthcare professionals to enter the pharmaceutical sector. By partnering with established pharmaceutical companies, you can distribute high-demand medications and contribute significantly to healthcare in the state.
PCD (Propaganda Cum Distribution) is an effective business model where pharmaceutical companies allow franchise partners to market and distribute their products. In the specific niche of cardiac and diabetic care, the PCD model is particularly valuable due to the increasing prevalence of these health conditions across Telangana. Franchisees benefit from the strong brand and product support of the parent company while operating independently in their assigned territory.
#Cardiac Diabetic PCD In Telangana#diabetes and cardiovascular diseases#best cardiac pcd pharma franchise in telangana#top diabetic pcd pharma company in telangana
0 notes
Text
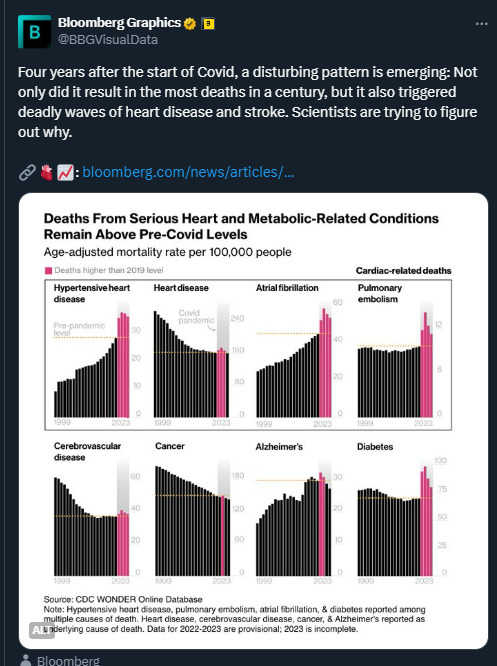
Statistics don't lie It just blows my mind that people can't see or understand that COVID is a dangerous virus that can damage your body. Getting infected multiple times will have serious consequences for many.
#covid#sars cov 2#long covid#heart issues#heart damage#diabetes#cancer#alzheimers#pulmonary embolism#atrial fibrillation#cardiovascular disease#hypertensive heart disease
253 notes
·
View notes
Text

Sugar and Sprouts
Love sugar? Too much can damage your blood vessels, increasing your risk of diabetes and cardiovascular disease. Love artificial sweeteners? Unfortunately, they too may increase your risk of cardiovascular disease. Researchers investigated in zebrafish embryos. Fluorescence microscopy revealed exposing embryos to lots of sugar or artificial sweeteners caused excessive blood vessel sprouting (angiogenesis) along the length of the body (pictured) – a process linked to diabetic complications in humans, including cardiovascular disease. Looking closer at embryos exposed to artificial sweeteners, they found cells lining their blood vessels (endothelial cells) developed into cells that promote sprouting. Analysing the RNA of these cells revealed changes in gene activity, notably reduction of one, Foxo1a (highlighted in red in the vessels along the fish embryo), was underlying the increase in sprouting when the embryos were exposed to sugar. Further experiments confirmed activity of this gene played the same role in embryos exposed to artificial sweeteners, uncovering how these sugar alternatives can negatively affect blood vessels.
Written by Lux Fatimathas
Image from work by Xiaoning Wang, Jinxiang Zhao and Jiehuan Xu, and colleagues
Affiliated Hospital of Nantong University, Nantong Laboratory of Development and Diseases, School of Life Science; Co-innovation Center of Neuroregeneration, Nantong University, Nantong, China
Image contributed by the authors under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) licence
Published in eLife, October 2024
You can also follow BPoD on Instagram, Twitter , Facebook and Bluesky
#science#biomedicine#immunofluorescence#biology#blood vessels#cardiovascular diseases#diabetes#sugar#sugar substitutes#zebrafish#angiogenesis
12 notes
·
View notes
Text
Like 10,000 to 20,000 people died of the flu every year before covid?
Sure, that’s not a lot compared to the 100,000+ we expect to die of covid this winter, but also still not great.
we eliminated an entire strain of flu by masking in 2020. It’s just gone.
imagine if we invested in clean air and just generally masked in higher risk settings.
weirdest side effect of the pandemic is how many people i know who get sick and say 'but my covid tests are negative so i should be fine' like you know other illnesses. exist. right.
#illness#why do people not care about getting sick?#like these things cause auto-immune diseases too#there’s evidence covid may cause dementia and parkinson’s in addition to the increased cardiovascular and diabetes risks
156K notes
·
View notes
Text
rybelsus 3 mg price
If you're considering diabetes management options, the Rybelsus 3 mg price is an essential factor to explore. Rybelsus, an oral medication for type 2 diabetes, offers effective blood sugar control, but pricing can vary significantly. Factors such as pharmacy pricing, insurance coverage, and available discounts play a crucial role in determining the cost. By shopping around and taking advantage of savings programs, patients can find affordable options for purchasing Rybelsus online. Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure you are making the best decision for your health.
#Rybelsus#Semaglutide#Type 2 diabetes#Oral medication#Blood sugar control#GLP-1 receptor agonist#Weight management#Diabetes treatment#Once-daily dosing#Non-insulin option#HbA1c reduction#Appetite suppression#Weight loss#Metabolic health#Cardiovascular benefits#Prescription medication#Diabetes management#Glycemic control#Self-management#Healthy lifestyle#Insulin sensitivity#Diabetes support#Chronic disease management#Patient education#Dosage instructions#Side effects#Drug interactions#Rybelsus benefits#Rybelsus risks#Diabetes care
0 notes
Text
0 notes
Text
Cardiovascular benefits of SGLT2 and GLP-1 drugs in diabetic patients
Metabolism in diseases: the revolution In recent years, sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors and glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists have revolutionized the treatment of type 2 diabetes, offering not only improved glycemic control but also important cardiovascular benefits. Large clinical trials have shown that these drugs reduce the risk of major adverse cardiovascular…
#cardiovascular disease#cardiovascular risk#cardiovasculopathy#chonic kidney disease#chronic heart failure#GLP-1#insulin secretion#SGLT2 inhibitors#type 2 diabetes
0 notes
Text
Finding the Top Treatments for Type 2 Diabetes
Read full article on-line: #Type2Diabetes #DiabetesManagement #Metformin #SGLT2Inhibitors #GLP1Agonists #DiabetesMedications #HealthTips #BloodSugarControl #Wellness #ChronicConditions #DiabetesAwareness #HealthyLiving #WeightManagement #HeartHealth
When considering non-insulin medications for managing type 2 diabetes, patients have a diverse array of options. This article explores these medications and the key factors to help determine which treatment may be the most suitable for you. Non-Insulin Medications for Type 2 Diabetes A variety of medication classes are prescribed for effectively treating type 2 diabetes: Metformin Metformin…
#blood sugar control#cardiovascular health#chronic kidney disease#diabetes management#DPP-4 inhibitors#GLP-1 receptor agonists#healthcare#insulin sensitizers#Metformin#Non-insulin medications#SGLT-2 inhibitors#Sulfonylureas#type 2 diabetes#weight management
0 notes
Text
As healthcare needs continue to rise across India, states like Kerala are facing an increasing demand for specialized medications, particularly for chronic conditions like diabetes and cardiovascular diseases. With a significant portion of Kerala's population suffering from these lifestyle-related ailments, the need for high-quality medications is critical. For those looking to tap into this booming market, the Cardiac Diabetic PCD in Kerala model offers a lucrative opportunity. Entrepreneurs and healthcare professionals can partner with established pharmaceutical companies to distribute life-saving medications, making a positive impact on public health while building a profitable business.
#Cardiac Diabetic PCD In Kerala#healthcare#diabetes and cardiovascular diseases#pharmaceutical industry#best cardiac pcd pharma franchise in kerala#leading pcd pharma franchise in kerala#top diabetic pcd company in kerala
0 notes
Text
Navigating Diabetes Prevention Globally
Navigating Diabetes Prevention Globally @neosciencehub #Diabetes #WorldHealthOrganization #NationalDiabetesPreventionProgram #CentersforDiseaseControlandPrevention #NationalProgramme forPreventionandControlofDiabetesCardiovascularDiseasesandstroke
Diabetes has emerged as a significant global health challenge, with millions affected worldwide and its prevalence continuing to rise. The World Health Organization (WHO) has recognized the urgent need for effective diabetes prevention strategies, leading to the establishment of various national diabetes programs across different countries. This article provides an overview of global efforts in…
#and Stroke (NPCDCS)#Cardiovascular Diseases#Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)#Diabetes#featured#National Diabetes Prevention Program (NDPP)#National Programme for Prevention and Control of Diabetes#NHS Diabetes Prevention Programme (NHS DPP)#sciencenews#World Health Organization (WHO)
0 notes
Text
#Heart disease symptoms#Types of heart disease#Coronary artery disease#Heart disease risk factors#Heart disease prevention#Signs of heart disease#Heart disease treatment#Heart attack vs heart disease#Heart disease in women#Congenital heart disease#Heart disease and lifestyle#Hypertension and heart disease#Cardiovascular disease#Cholesterol and heart disease#Heart disease and diabetes#Heart disease genetics#Heart failure#Heart disease complications#Coronary artery bypass surgery#Heart disease medications#Statins and heart disease#Preventing heart disease naturally#Atherosclerosis#Heart disease risk assessment#Cardiomyopathy#Arrhythmia and heart disease#Heart disease diet#Heart disease stress#Exercise and heart disease#Heart disease in older adults
1 note
·
View note
Text
The Connection Between Oral Health and Systemic Diseases: How Your Mouth Reflects Your Body's Health
When it comes to understanding our health, we often overlook a crucial indicator: our mouth. Oral health is more than just a beautiful smile; it serves as a window to the body’s overall health. Research consistently shows that conditions like cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and even respiratory issues can manifest first in the mouth, offering critical early warning signs (Sanz et al., 2020).…
#cardiovascular disease and oral health#connection between oral health and body health#dental-care#dental-health#dental-hygiene#diabetes and oral health#diet#health#inflammation and oral bacteria#mouth and body health#oral health#oral-health#oral-hygiene#periodontal disease#respiratory health and oral hygiene#rheumatoid arthritis and gum disease#systemic diseases
0 notes
Text
Prioritize Your Heart Health: Recognizing Early Symptoms and Scheduling Check-Ups

Maintaining heart health is essential for overall well-being. Learn to identify early warning signs of heart issues to ensure timely intervention. This guide emphasizes the importance of staying informed about heart health and scheduling regular check-ups with your healthcare provider. Consider exploring a Heart Health Package to get a comprehensive evaluation and personalized care plan tailored to your needs.
#best pathology lab in Mumbai#pathology labs in thane#pathology lab in borivali#Diabetes complications#Kidney and heart failure prevention#Best pathology lab in Mumbai#Cardiovascular Wellness#Heart Disease Prevention#Cholesterol Management#Hypertension Control#Heart Health Check-up#hearthealth#cardiovascularhealth#hearthealthylifestyle
0 notes
Text

10 Complications of Diabetes Mellitus
Diabetes is a metabolic disorder, caused by the body’s inability to use the insulin produced by its own pancreas or insufficient insulin production. As glucose begins to accumulate in the bloodstream, it begins to damage the blood vessels in organs large and small across the body.
Read more how to Reduce Complication of Diabetes: https://www.freedomfromdiabetes.org/blog/post/10-complications-of-diabetes-mellitus/2713
#10 Complications of Diabetes Mellitus#Diabetes and Alzheimer's Disease#Diabetic Nephropathy#Diabetes and Cardiovascular Disease#Diabetic Retinopathy#Diabetic Neuropathy#Diabetes and Oral Health#Diabetes in Pregnancy#Diabetes and infertility#Diabetes and Hypertension#Obesity and Diabetes#complications of diabetes mellitus#chronic complications of diabetes mellitus#long term complications of diabetes
0 notes
Text
Organic and metal pollutants doing their job: aromatics eliciting diabetes, metals harding coronaries
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is a critical public health issue, with its prevalence expected to rise sharply worldwide. Recent evidence points to environmental pollution, specifically exposure to hazardous chemicals like styrene (STY) and ethylbenzene (ETB), as a contributing factor. Found in plastics, synthetic rubbers, and resins, these pollutants are pervasive in the environment and pose…
#air pollution#cardiovascular risk#environment#environmental pollution#heart disease#heavy metals#polluttants#risk factor#type 2 diabetes
0 notes
Text
Statins and Diabetes Risk: Evidence and Recommendations
Statins and Diabetes Risk: Evidence and Recommendations,"Explore the benefits of statins in lowering cholesterol and preventing cardiovascular events, while also understanding the potential risk of developing diabetes. Backed by scientific studies,
Understanding the link between statins and diabetes risk is crucial for those managing cholesterol levels and overall health. In this blog post “Statins and Diabetes Risk: Evidence and Recommendations,” we delve into the latest research and expert advice on this important topic. Statins are widely prescribed to lower cholesterol, but emerging studies suggest a potential increase in diabetes risk.…
#Cardiovascular health#Cardiovascular research#Cholesterol#Cholesterol Management#Diabetes Prevention#Diabetes Risk#Health and wellness#heart disease prevention#LDL Cholesterol#Medical Studies#Patient Care#Statin Benefits#Statin Side Effects#Statin Therapy#Statins
0 notes