#Diabetes Complications Microvascular
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Diabetes Complications

Here learn about, Diabetes Complications. Know, 6 Unexpected Side Effects of Diabetes. Type 2 Diabetes Complications Timeline… Diabetes Tablets Side Effects… from Rajashree Gadgil… Top nutritionist in Thane & the founder of TruWellth Integrative Health Center… the best nutrition center in Thane.
#6 Unexpected Side Effects of Diabetes#What is the Most Common Complication of Diabetes?#What Are 5 Major Complications of Diabetes#Symptoms of Diabetes Complications#Complications of Diabetes Type 2#Uncontrolled Diabetes Complications#Type 2 Diabetes Complications Timeline#Diabetes Tablets Side Effects#Diabetes Complications Microvascular
0 notes
Text

Long term Complications of Diabetes Mellitus
Failure to control blood sugar will damage the body’s blood vessels, and this damage leads to complications of diabetes. These problems do not happen overnight, but their very insidious nature makes them all the more dangerous.
Read the full blog: https://www.freedomfromdiabetes.org/blog/post/long-term-complications-of-diabetes-mellitus/394
#Complications of Diabetes Mellitus#complications of diabetes#complications of diabetes mellitus#type2 diabetes complications#long term complications of diabetes#microvascular complication of diabetes#number one complication of diabetes#chronic complication of diabetes mellitus#what is complication of diabetes#short term complication of diabetes#most common complication of diabetes#the most complication of diabetes
0 notes
Note
I saw a comment on your blog that says 'the way you eat does not cause diabetes'...are you able to expand on that or provide a source I could read? I've been told by doctors that my pre-diabetes was due to weight gain because I get more hungry on my anti psychotics and I'd like to fact check what they've told me! Thank you so much!
Pre-diabetes was rejected as a diagnosis by the World Health Organization (although it is used by the US and UK) - the correct term for the condition is impaired glucose tolerance. Approximately 2% of people with "pre-diabetes" go on to develop diabetes per year. You heard that right - TWO PERCENT. Most diabetics actually skip the pre-diabetic phase.
There are currently no treatments for pre-diabetes besides intentional weight loss. (Hmm, that's convenient, right?) There has yet to be evidence that losing weight prevents progression from pre-diabetes to T2DM beyond a year. Interestingly, drug companies are trying to persuade the medical world to start treating patients earlier and earlier. They are using the term “pre-diabetes” to sell their drugs (including Wegovy, a weight-loss drug). Surgeons are using it to sell weight loss surgery. Everyone’s a winner, right? Not patients. Especially fat patients.
Check out these articles:
Prediabetes: The epidemic that never was, and shouldn’t be
The war on ‘prediabetes' could be a boon for pharma—but is it good medicine?
Also - I love what Dr. Asher Larmie @fatdoctorUK has to say about T2DM and insulin resistance, so here's one of their threads I pulled from Twitter:
1️⃣ You can't prevent insulin resistance. It's coded in your DNA. It may be impacted by your environment. Studies have shown it has nothing to do with your BMI.
2️⃣ The term "pre-diabetes" is a PR stunt. The correct term is impaired glucose tolerance (or impaired fasting glucose) which is sometimes referred to as intermittent hyperglycemia. It does not predict T2DM. It is best ignored and tested for every 3-5yrs.
3️⃣ there is no evidence that losing weight prevents diabetes. That's because you can't reverse insulin resistance. You can possibly postpone it by 2yrs? Furthermore there is evidence that those who are fat at the time of diagnosis fair much better than those who are thin.
4️⃣ Weight loss does not reverse diabetes in the VAST majority of people. Those that do reverse it are usually thinner with recent onset T2DM and a low A1c. Only a tiny minority can sustain that over 2yrs. Weight loss does not improve A1c levels beyond 2 yrs either.
5️⃣ Weight loss in T2DM does not improve macrovascular or microvascular health outcomes beyond 2 years. In fact, weight loss in diabetics is associated with increased mortality and morbidity (although it is not clear why). Weight cycling is known to impacts A1c levels.
6️⃣ Weight GAIN does NOT increase the risk of cardiovascular OR all causes mortality in diabetics. In fact, one might even go so far as to say that it's better to be fat and diabetic than to be thin and diabetic.
Dr. Larmie cites 18 peer reviewed journal articles (most from the last decade) that are included in their webinar on the subject, linked below.
#diabetes#t2dm#type 2 diabetes#prediabetes#weight science#weight stigma#fat liberation#fat acceptance#inbox
30K notes
·
View notes
Note
Doing my uni course on macrovascular and microvascular complications in people with diabetes. Anyway, funniest thing ever to see “Erectile Dysfunction (Macro/Micro)
Get yourself a giant whose dick don’t work.
that’s fuckin awesome I love it
15 notes
·
View notes
Text
Diabetes
Introduction to Diabetes
Diabetes, a metabolic disorder characterized by chronic hyperglycemia, arises from abnormalities in insulin secretion, insulin action, or both. The condition’s prevalence has reached epidemic proportions globally, with significant health, economic, and social implications.
Types of Diabetes
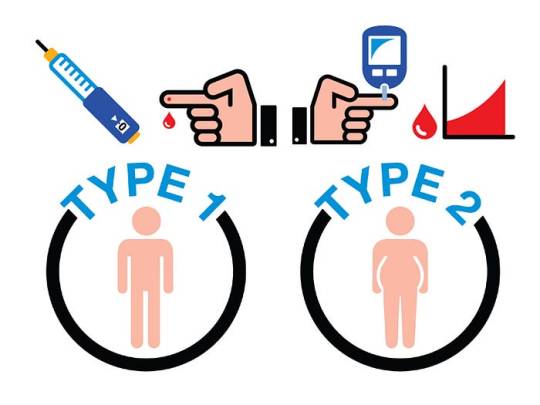
Type 1 Diabetes: This autoimmune disease results from the destruction of pancreatic beta cells, leading to absolute insulin deficiency. Genetics and environmental triggers play pivotal roles in its pathogenesis. Despite being less common than Type 2 diabetes, its onset during childhood or adolescence significantly impacts individuals’ lives.
Type 2 Diabetes: Predominantly a disorder of insulin resistance, Type 2 diabetes accounts for the majority of diabetes cases worldwide. Lifestyle factors, genetic predisposition, and obesity contribute to its development. Its insidious onset often leads to delayed diagnosis and increased risk of complications.
Gestational Diabetes: Occurring during pregnancy, gestational diabetes poses risks to both maternal and fetal health. Hormonal changes and insulin resistance characterize its pathophysiology. Effective screening and management are crucial to prevent adverse outcomes.
Other Types of Diabetes: Variants like MODY, LADA, and secondary diabetes present unique challenges in diagnosis and management, requiring tailored approaches to care.
Epidemiology and Prevalence
Diabetes prevalence varies across demographics, with disparities observed in age, gender, ethnicity, and socioeconomic status. The escalating burden of diabetes underscores the urgent need for targeted prevention and management strategies.
Symptoms and Causes
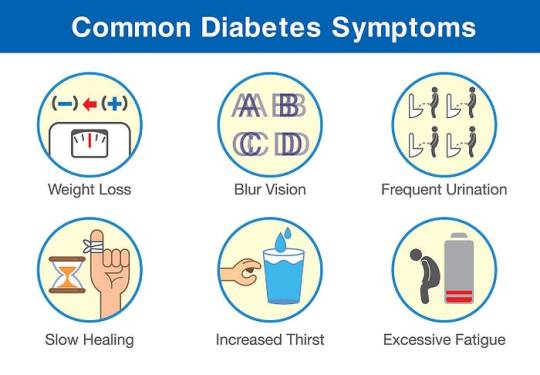
Hyperglycemia-induced symptoms like polyuria, polydipsia, and unexplained weight loss serve as clinical indicators for diabetes diagnosis. Understanding the complex interplay of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors elucidates the condition’s etiology.
Complications
Diabetes complications encompass a spectrum of microvascular and macrovascular disorders, significantly impacting quality of life and life expectancy. From diabetic retinopathy to cardiovascular disease, nephropathy, neuropathy, and diabetic foot complications, the ripple effects of uncontrolled diabetes are profound.
Diagnosis and Tests
Accurate diagnosis relies on comprehensive evaluation, including fasting glucose, oral glucose tolerance tests, and hemoglobin A1c measurements. Screening recommendations aim to identify at-risk individuals early, facilitating timely intervention and risk reduction.
Management and Treatment
Diabetes management strategies encompass pharmacotherapy, lifestyle modifications, patient education, and multidisciplinary care. Individualized treatment plans address glycemic control, blood pressure management, lipid optimization, and prevention of complications.
Prevention
Prevention initiatives target modifiable risk factors through health promotion, public health interventions, and community engagement. Emphasizing the role of nutrition, physical activity, and behavioral changes empowers individuals to mitigate their diabetes risk.
Outlook and Prognosis
Prognostic factors such as glycemic control, adherence to therapy, comorbidity burden, and psychosocial support influence long-term outcomes. Enhanced collaboration among healthcare providers, policymakers, and stakeholders is essential to improve diabetes prognosis globally.
Living With Diabetes

Coping with diabetes requires resilience, self-management skills, and social support networks. Empowering individuals through education, self-monitoring tools, and peer support enhances their capacity to navigate the challenges of daily diabetes management.
Impact on Individuals and Society
Diabetes exerts a profound socioeconomic burden, encompassing healthcare costs, productivity losses, and reduced quality of life. Addressing the psychosocial dimensions of diabetes care is integral to fostering holistic well-being and societal resilience.
Future Directions and Research

Advancements in diabetes research, including precision medicine, digital health technologies, and novel therapeutics, offer promising avenues for disease management and prevention. Collaborative research endeavors aim to translate scientific discoveries into tangible clinical benefits.
Conclusion
In conclusion, diabetes represents public health challenge necessitating a comprehensive, patient-centered approach. By fostering awareness, promoting early detection, and advancing evidence-based interventions, we can mitigate the impact of diabetes on individuals, families, and communities worldwide.
Medical students encounter significant academic challenges during their studies, balancing coursework, clinical rotations, research, and personal commitments. Expert Academic Assignment Help offers tailored assistance to meet their needs, providing study materials, tutoring, assignment help, and exam preparation. Beyond academics, it fosters a supportive environment for mentorship and guidance. In essence, Expert Academic Assignment Help is a valuable resource for medical students, empowering them to excel academically and develop into competent healthcare professionals. Contact at [email protected] for assistance.
#assignment help#healthcare#medical students#nursing student#nursing school#medical school#medical student#medicine#health tips#health and wellness#health#health & fitness#diabetes#diabetic#medical help#medical assistance#pharmacy student#pharmacy technician#homework help#academic assignments#expert assignment writers
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Microvascular Angina: The Overlooked Heart Condition
When we think about heart problems, most of us immediately picture blocked arteries or heart attacks. However, there’s another heart condition that often gets overlooked: microvascular angina. This condition can be just as serious as more well-known heart diseases, yet many people, including doctors, may not be aware of it or how to diagnose it properly. So, let’s take a closer look at microvascular angina, how it affects the body, and why it’s important to recognize it.
What is Microvascular Angina?
Microvascular angina, also known as cardiac syndrome X, occurs when the small blood vessels in the heart (microvessels) are not functioning properly. Unlike the typical form of angina, which is caused by blockages in the large coronary arteries, microvascular angina happens when the tiny vessels that supply blood to the heart muscle constrict or have abnormal blood flow. This leads to chest pain or discomfort, often with no visible blockages on standard heart tests like an angiogram.
Symptoms of Microvascular Angina
The symptoms of microvascular angina can often mimic those of more common heart conditions. Chest pain is the most frequent symptom, and it can range from mild to severe. Many people report that the pain feels like pressure or tightness in the chest, and it may radiate to the shoulders, arms, neck, or jaw.
Interestingly, microvascular angina often occurs during physical activity, stress, or cold weather, though it can sometimes appear without any obvious trigger. Some individuals may also experience shortness of breath or fatigue, making it harder to distinguish this condition from other types of heart problems.
Why is Microvascular Angina Often Overlooked?
Microvascular angina is difficult to diagnose because standard heart tests, like angiograms, often don’t show any blockages in the larger coronary arteries. Since the problem lies in the smaller vessels, it doesn’t show up on traditional diagnostic imaging. Because of this, it’s easy for doctors to overlook or misdiagnose the condition.
Another reason this condition is often missed is that many people with microvascular angina may not fit the typical profile of a person at risk for heart disease. For example, women, especially those under 50, are more likely to develop microvascular angina. Many doctors may not immediately suspect the condition in women, as heart disease is often thought to affect older men more frequently.
The Link Between Microvascular Angina and Other Health Conditions
Microvascular angina is often linked to other health issues such as high blood pressure, diabetes, and high cholesterol. These conditions can cause damage to the small blood vessels over time, leading to the development of microvascular angina. Moreover, stress, lack of exercise, and smoking can all contribute to the worsening of this condition.
Interestingly, microvascular angina has also been linked to a higher risk of developing more severe heart diseases later on. Individuals with this condition may have an increased risk of heart attacks, heart failure, and other cardiovascular complications. Therefore, recognizing and managing microvascular angina early is key to preventing more serious heart issues down the line.
How is Microvascular Angina Diagnosed?
Diagnosing microvascular angina can be a challenge since it doesn’t show up on routine heart tests. Doctors may need to perform additional tests to evaluate the small blood vessels in the heart. This can include a test called a coronary function test, which measures the ability of the coronary arteries to dilate and relax. In some cases, doctors may also recommend an MRI or a positron emission tomography (PET) scan to get a better view of the blood flow in the smaller vessels.
If you experience unexplained chest pain, it’s important to speak with a healthcare provider who can help identify the cause. If microvascular angina is suspected, a heart specialist in Bhubaneswar or a cardiologist can help guide you through the diagnostic process and determine the best course of treatment.
Treatment for Microvascular Angina
While there is no one-size-fits-all treatment for microvascular angina, there are several strategies that can help manage the symptoms and improve quality of life. Medications, such as nitrates, beta-blockers, and calcium channel blockers, are commonly used to relax the blood vessels and reduce chest pain. These medications help improve blood flow to the heart and can alleviate discomfort.
In some cases, doctors may recommend lifestyle changes, such as regular exercise, a heart-healthy diet, and stress management techniques. These changes can help reduce the strain on the heart and improve overall cardiovascular health. If other underlying conditions, such as high blood pressure or diabetes, are present, managing these factors is critical for preventing further damage to the small blood vessels in the heart.
The Importance of Early Detection
Since microvascular angina can lead to serious complications if left untreated, early detection and management are crucial. If you’re experiencing chest pain, shortness of breath, or other related symptoms, don’t hesitate to see a heart specialist Bhubaneswar. With the right diagnosis and treatment, it’s possible to manage microvascular angina and prevent the progression of heart disease.
Conclusion
Microvascular angina is a heart condition that often goes undiagnosed because it doesn’t show up on standard heart tests. It affects the small blood vessels in the heart, causing chest pain and discomfort. If you have symptoms of heart disease but normal test results, it’s important to discuss the possibility of microvascular angina with your doctor. Early recognition and treatment can help manage symptoms and reduce the risk of more severe heart problems in the future.If you’re experiencing chest pain or other symptoms, reach out to a heart specialist in Bhubaneswar as Dr Gyana Ranjan Nayak for a comprehensive evaluation and to discuss your options for treatment. With the right care, you can take steps to protect your heart and improve your overall health.
#best cardiologist bhubaneswar#best cardiologist doctor in bhubaneswar#heart specialist bhubaneswar#best cardiologist in india#top 10 cardiologist in bhubaneswar#health & fitness#healthyheart#healthylifestyle#health
0 notes
Text
I have a diabetic pt who is on OCP. My preceptor and I discussed whether she should continue being on them given her risk of ASCVD.
Google says:
According to the Mayo Clinic, oral contraceptives may be a good choice for women with diabetes, but they may need to be tested more often. According to the University of Colorado OB-GYN, studies suggest that diabetic women who take birth control pills for more than two years may have an increased risk of complications like diabetic nephropathy, diabetic retinopathy, and diabetic neuropathy. The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends against combined oral contraceptives for women with diabetic nephropathy, neuropathy, or retinopathy. The WHO also recommends against combined oral contraceptives for women who have had diabetes for more than 20 years, as microvascular damage is likely to be present.
Article to read: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3626808/
1 note
·
View note
Text
Uncontrolled Glycemia in Diabetes Affects Oral Health-Related Quality of Life

Diabetes Mellitus (DM) is considered as one of the main public health problems worldwide and increases the rate of hospitalizations, disabilities, and mortality. The World Health Organization estimates that, in 2014, 422 million adults in the world (8.5% of the population) had diabetes, and since 1980, this number has quadrupled. This increase is related to the risk factors such as being overweight, sedentary lifestyle, and alimentation. DM is characterized by prolonged increased levels of glucose in the blood which leads to the development of microvascular complications (retinopathy, neuropathy, nephropathy, amputation, and periodontitis) and macrovascular complications (cardiovascular and stroke) [1-6]. Glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) is the gold standard for monitoring glycemic control and higher levels of HbA1c (>6.5%) has been associated to increase the risk to develop diabetes complications. There is strong evidence that periodontitis is associated with DM and both diseases have a bidirectional relationship. Therefore, an uncontrolled glycemia in DM patients triggers immunological repercussion, physiological, psychological, and social problems. Oral Health-Related Quality of Life (OHRQL) can be assessed using the Spanish version of the Oral Health Impact Profile-14 (OHIP-14sp), which is an instrument validated in the Spanish speaking population and measures physical, social, and psychological aspect in individual’s life that adversely affects oral health. Some studies have demonstrated that quality of life is affected among patients that present loss of epithelial attachment, loss of teeth, and cavities among others.
Read More About This Article: https://crimsonpublishers.com/iod/fulltext/IOD.000610.php
Read More About Crimson Publishers: https://crimsonpublishers.com/
#peer review journals#open access journals#crimsonpublishers llc#crimsonpublishers#diabetes mellitus
0 notes
Text
Best Diabetic Foot Surgery in Basavanagudi Bangalore — Himas Hospital
When it comes to diabetic foot surgery in Basavanagudi, Bangalore, Himas Hospital stands out as a premier institution offering top-notch care and treatment. In this article, we’ll explore why Himas Hospital is renowned for its diabetic foot surgeries and what sets it apart from others in the field.
Why Choose Himas Hospital?
Reputation for Excellence
Himas Hospital has established a reputation for excellence in diabetic foot surgery, backed by years of experience and a dedicated team of specialists.
Experienced Surgeons
The hospital boasts a team of highly experienced surgeons who are experts in diabetic foot care and surgical interventions. Their expertise ensures that patients receive the best possible care and outcomes.
State-of-the-art Facilities
Himas Hospital is equipped with state-of-the-art facilities and cutting-edge technology to perform advanced diabetic foot surgeries with precision and accuracy.
Comprehensive Services Offered
Assessment and Diagnosis
Before proceeding with surgery, patients undergo a thorough assessment and diagnosis to determine the most suitable treatment plan.
Surgical Procedures
Himas Hospital offers a wide range of surgical procedures for diabetic foot conditions, including wound debridement, nerve decompression, and amputation when necessary.
Post-operative Care and Rehabilitation
The hospital provides comprehensive post-operative care and rehabilitation services to ensure patients recover fully and regain mobility as soon as possible.
Advanced Surgical Techniques
Minimally Invasive Surgery
Himas Hospital specializes in minimally invasive surgical techniques, which offer numerous benefits such as smaller incisions, reduced pain, and faster recovery times.
Microvascular Surgery
For complex cases requiring precise microsurgical techniques, Himas Hospital has the expertise and technology to perform microvascular surgery with excellent outcomes.
Tissue Reconstruction
In cases where tissue loss or damage is significant, Himas Hospital offers advanced tissue reconstruction procedures to restore function and appearance.
Importance of Diabetic Foot Surgery
Prevention of Complications
Diabetic foot surgery plays a crucial role in preventing complications such as infections, ulcers, and amputations, thereby improving the quality of life for patients.
Preservation of Limb Function
By addressing underlying issues and restoring proper foot function, diabetic foot surgery helps preserve limb function and mobility, allowing patients to lead active and independent lives.
Improved Quality of Life
For individuals living with diabetic foot conditions, surgery can significantly improve quality of life by relieving pain, enhancing mobility, and reducing the risk of further complications.
Patient-Centric Approach
Individualized Treatment Plans
At Himas Hospital, each patient receives personalized care and treatment tailored to their unique needs and circumstances.
Emphasis on Patient Education
The hospital places a strong emphasis on patient education, empowering individuals with the knowledge and tools they need to manage their condition effectively.
Supportive Environment
Patients at Himas Hospital benefit from a supportive and compassionate environment, where their physical and emotional well-being are prioritized throughout the treatment process.
Success Stories and Testimonials
Patient Testimonials
Many patients have shared their success stories and positive experiences at Himas Hospital, highlighting the excellent care they received and the life-changing results achieved through surgery.
Success Rates and Outcomes
Himas Hospital boasts impressive success rates and outcomes for diabetic foot surgery, with the majority of patients experiencing significant improvements in their condition and overall quality of life.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Himas Hospital in Basavanagudi, Bangalore, is the go-to destination for diabetic foot surgery. With its unparalleled expertise, state-of-the-art facilities, and patient-centric approach, it continues to set the standard for excellence in diabetic foot care.
0 notes
Text
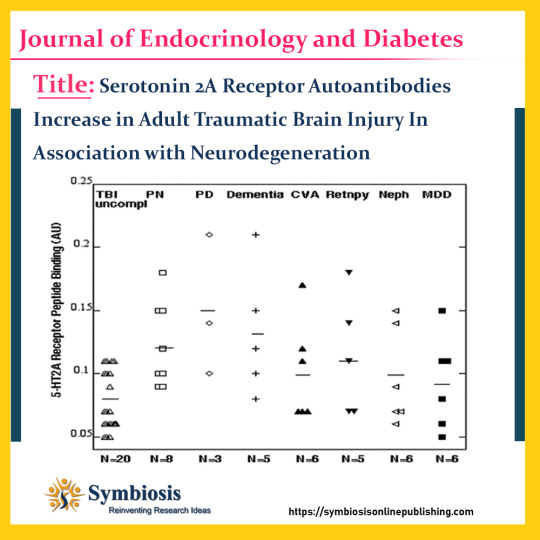
#traumaticbraininjury (TBI) is associated with an increased risk of late #neurodegenerative complications via unknown mechanisms. Circulating neurotoxic 5-hydroxytryptamine 2A receptor (5-HT2AR) autoantibodies were reported to increase in subsets of obese #type2 diabetes having microvascular complications. We tested whether 5-HT2AR autoantibodies increase in adults following #traumaticbraininjury in association with neurodegenerative complications.
View more visit @ https://symbiosisonlinepublishing.com/endocrinology-diabetes/endocrinology-diabetes142.php
#symbiosisonlinepublishing#endocrinologia#endocrinology#endocrinologist#diabetes#diabetesawareness#diabetes2#diabetescare#TBIRecovery#tbiawareness#tbisurvivor#endocrinesystem#endocrine#plasma#antibody#hydroxytryptamine#journals#journal#pubmed#peerreview#openaccess#openaccessjournal
0 notes
Text
HYPERTENSION RISK IN DIABETIC PATIENTS
Blood pressure is determined by both the amount of blood pumped by your heart and the resistance to blood flow in your arteries. The higher your blood pressure, the more blood your heart pumps and the narrower your arteries. Get the best outcomes at the Diabetes Treatment in Kukatpally, Hyderabad at AED hospitals, Hyderabad, and reverse your diabetes with our specialists.
Asymptomatic hypertension is possible. Even when there are no symptoms, damage to the blood vessels and heart can be detected. The most common co-morbid condition associated with diabetes is hypertension. It is a major risk factor for both microvascular and macrovascular diabetes complications.

Diabetes and Hypertension Relationship
Hypertension is a significant predictor of metabolic syndrome. Diabetes increases the risk of developing hypertension and other cardiovascular problems because diabetes damages the arteries, predisposing them to atherosclerosis (narrowing of the arteries). Concurrent hypertension raises the chances of developing left ventricular hypertrophy, cardiac failure, stroke, peripheral vascular disease, renal dysfunction, and retinopathy. Hypertension Types
Hypertension that is essential. This is the most common type of hypertension, with no symptoms and occasional headaches, tiredness, dizziness, or nose bleeds. Although the exact cause is unknown, studies have shown that obesity, smoking, alcohol, a high-calorie diet, and heredity all play a role in essential hypertension.
Secondary hypertension. Secondary hypertension is a type of high blood pressure that appears suddenly and causes higher blood pressure than primary hypertension. Secondary hypertension can be caused by a variety of conditions and medications; among the risks of hypertension are:
Kidney issues
Tumors of the adrenal gland
Thyroid issues
Certain birth defects in blood vessels (congenital)
Birth control pills, cold remedies, decongestants, over-the-counter pain relievers, and some prescription drugs are examples of medications.
Cocaine and amphetamines are examples of illegal drugs.
Chronic alcohol use or alcohol abuse It can be difficult to stick to lifestyle changes, especially when there are no symptoms of high blood pressure. Motivate yourself by recalling the dangers of uncontrolled high blood pressure. Enlisting the help of family and friends would also be beneficial. Diabetes can lead to heart disease, stroke, and other severe complications. Luckily, you can take action and reduce your risk of diabetes, stroke, and heart disease with minimal care and continuous follow-up at the Best Diabetes Specialist Doctors in Kukatpally, KPHB with AED Hospitals. Book your appointment with us to know more.
#Diabetes Center in Kukatpally#Hyderabad#Diabetes Treatment in Kukatpally#Best Diabetes Specialist Doctors in Kukatpally#KPHB
0 notes
Text

Long term Complications of Diabetes
Consistently high or low blood sugar, as we all know is an indicator of diabetes. And this high blood sugar if left unchecked will inevitably result in a number of long-term medical conditions that can seriously compromise health. Failure to control blood sugar will damage the body’s blood vessels, and this damage leads to complications of diabetes. These problems do not happen overnight, but their very insidious nature makes them all the more dangerous.
Read more to know facts: https://www.freedomfromdiabetes.org/blog/post/long-term-complications-of-diabetes-mellitus/394
#Complications of Diabetes Mellitus#complications of diabetes#complications of diabetes mellitus#type2 diabetes complications#long term complications of diabetes#microvascular complication of diabetes#number one complication of diabetes#chronic complication of diabetes mellitus#what is complication of diabetes#short term complication of diabetes#most common complication of diabetes#the most complication of diabetes
0 notes
Text
The primary factors contributing to organ failure include the following:
1. Infections and Sepsis: Severe infections, notably sepsis, can induce organ failure by triggering dysregulated body responses, causing inflammation and damage to multiple organs.
2. Cardiovascular Factors: Conditions like heart attacks and congestive heart failure can diminish blood supply to organs, leading to oxygen and nutrient deprivation, ultimately resulting in organ dysfunction.
3. Trauma and Injury: Physical trauma from accidents can directly damage organs or set off events leading to gradual organ dysfunction.
4. Chronic Diseases: Conditions like diabetes and chronic kidney disease can progressively undermine organ health, resulting in eventual failure.
5. Autoimmune Disorders: Immune system attacks on the body's tissues, as seen in rheumatoid arthritis, contribute to inflammation and organ damage, fostering organ failure.
6. Drug and Medication-Induced: Some medications, especially when misused, can be toxic to organs, leading to failure over time.
7. Genetic Factors: Inherited disorders can predispose individuals to organ failure by affecting specific organ structures or functions.
8. Ischemia and Hypoxia: Insufficient blood supply or low oxygen levels can lead to organ failure, often caused by conditions like blood vessel blockages.
9. Metabolic Disturbances: Imbalances in electrolytes or severe acid-base disturbances can profoundly affect organ function, arising from conditions like diabetic ketoacidosis.
10. Inflammatory Responses and Cytokine Storms: Exaggerated immune responses, like cytokine storms, can cause widespread tissue damage, contributing to organ failure in conditions like severe viral infections.
11. Microvascular Dysfunction: Abnormalities in tiny blood vessels can significantly impact organ health, as seen in diseases like systemic sclerosis.
12. Environmental Exposures: Long-term exposure to environmental toxins, such as air pollution, has been linked to cardiovascular and respiratory issues, leading to organ dysfunction.
13. Age-Related Factors: Advancing age increases susceptibility to organ failure due to gradual declines in organ function.
14. Nutritional Deficiencies: Inadequate nutrition, including specific nutrient deficiencies, can compromise the body's ability to maintain optimal organ function.
15. Endocrine Disorders: Disruptions in the endocrine system can lead to hormonal imbalances affecting organs like the liver, kidneys, and heart.
16. Surgical Complications: Postoperative complications, such as infection or excessive bleeding, can contribute to organ failure, especially in complex surgeries.
17. Psychosocial Factors: Chronic stress, depression, and anxiety can influence physiological changes that may contribute to organ dysfunction over time.
18. Immunodeficiency States: Compromised immune systems increase the risk of organ failure, especially in the presence of infections.
Doctors suggest undergoing regular full body health checkups to detect and manage risk factors for organ failure before the condition becomes fatal.
#organ failure#sepsis#infections#ischemia#hypoxia#trauma#injury#endocrine disorders#full body health checkup package#full body checkups#regular health checkups
0 notes
Text
Mastering the Complex Maze: Navigating Type 2 Diabetes with Medvantage's Advanced Certification
Introduction:
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM) stands as a formidable challenge in the realm of healthcare, marked by its intricate pathophysiology and the far-reaching implications it holds for affected individuals. The Advanced Certificate in Diabetes Mellitus, offered by Medvantage, serves as a beacon of knowledge, equipping healthcare professionals with in-depth insights into T2DM. This article explores the program's focus on pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, diagnostic criteria, and evidence-based management strategies.
Pathophysiology of T2DM in Advanced Certificate in Diabetes Mellitus
1.Insulin Resistance: The foundation of T2DM lies in peripheral insulin resistance, where vital tissues—skeletal muscle, adipose tissue, and the liver—show diminished responsiveness to insulin. This disruption hampers glucose uptake and utilization, forming a key focus in the program's curriculum.
2.Beta-Cell Dysfunction: A progressive decline in pancreatic beta-cell function exacerbates hyperglycemia. Genetic factors, chronic inflammation, and metabolic stress contribute to the deterioration of insulin-secreting beta cells.
3.Adipose Tissue Dysregulation: Obesity-induced dysfunction in adipose tissue triggers an inflammatory milieu, releasing adipokines and free fatty acids. These factors intricately contribute to insulin resistance and disrupted glucose homeostasis, an aspect thoroughly explored in the advanced curriculum.
Clinical Manifestations:
1.Polyuria, Polydipsia, Polyphagia: The classical symptoms of T2DM find their roots in hyperglycemia-induced osmotic diuresis. It delves into the intricacies of fluid loss, increased thirst, and excessive hunger as cardinal signs demanding clinical attention.
2.Fatigue and Malaise: The program underscores the link between inefficient glucose utilization and persistent fatigue, recognizing the clinical relevance of energy metabolism in T2DM.
3. Microvascular and Macrovascular Complications: The comprehensive care required for individuals with T2DM, shedding light on the microvascular complications (retinopathy, nephropathy, neuropathy) and macrovascular complications (cardiovascular disease) resulting from chronic hyperglycemia.
Diagnostic Criteria:
1.Fasting Plasma Glucose and Oral Glucose Tolerance Test: The Course emphasizes the importance of precise diagnostic criteria, including elevated fasting plasma glucose levels and abnormal oral glucose tolerance tests.
2.Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c): With a focus on long-term glycemic control, the program recognizes HbA1c levels as pivotal diagnostic and monitoring tools in T2DM.
Management in Advanced Certificate in Diabetes Mellitus:
1.Lifestyle Modification: The role of lifestyle interventions—regular physical activity, weight management, and a balanced diet—as fundamental pillars in T2DM management, addressing both insulin resistance and beta-cell dysfunction.
2.Oral Antidiabetic Medications: The curriculum covers a spectrum of pharmacotherapy options, including metformin, sulfonylureas, thiazolidinediones, and dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors, each targeting specific aspects of T2DM pathophysiology.
3.Injectable Therapies: In advanced cases, the program explores the necessity of insulin therapy or glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists to optimize glycemic control.
4.Patient Education and Continuous Monitoring: Medvantage underscores the pivotal role of patient empowerment through education on self-monitoring, medication adherence, and lifestyle management for long-term success.
Conclusion:
The Advanced Certificate in Diabetes Mellitus provided by Medvantage represents a milestone in advancing expertise in T2DM. Through a multifocal approach and a deep understanding of pathophysiology, the program lays the foundation for evidence-based clinical practice. As research progresses, the personalized care plans and tailored therapeutic strategies fostered by the course provides hope for improved outcomes and an enhanced quality of life for individuals navigating the complexities of T2DM.
#fellowship in diabetes mellitus#medvantage#diabetes mellitus#Advanced Certificate in Diabetes Mellitus#Advanced Certificate Course in Diabetes Mellitu#Certificate in Diabetes Mellitus
0 notes
Text
#Diabetes#Heart Health#Vascular Disease#Hypertension#healthy#healthcare#kauvery hospital#healthcare news#newsletters
0 notes
Text

Things that reduce mortality in diabetics: should be on a statin, metformin, BP needs to be controlled at less than 130/80, A1c goal should be less than 7% (unless they're old, in which case higher A1c is acceptable to prevent hypoglycemia and it's complications in elderly people); they also need to stop smoking if they smoke. The other stuff (ophthalmology visit, urine microalbumin, checking feet) are for preventing microvascular complications.
1 note
·
View note