#Cloud Computing & Storage
Text
i have so little control over what the technology i paid hundreds of dollars for does. every pertinent setting is hidden behind thirteen different menus and permissions and accounts and logins, if it's available at all. i shouldn't need constant internet access to use any and every piece of technology, i don't need or want my actions to be watched at all times. not to sound too tin foil hat-esque but corporations have invaded the privacy of our personal home machines and it seems nigh impossible to wrest control back to the hands of the user
#fuck cloud storage and fuck needing to have an account with a login just to own a fucking computer or a phone#right now i am most angry at onedrive but this could be about anything if im being honest#im in the mire of attempting to store my files locally. HARDER THAN I THOUGHT
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
attempting to claw my brain out of The Rottening by allowing myself to spend money on things that will improve my household life even though I've been reluctant to commit to them
#a drill for projects around the house because I've either been borrowing a friend's or just not doing those projects#a large external drive for the desktop computer because eventually i do want to upgrade that computer and i need backups#also i have just been solving problems by dumping stuff into cloud storage and that's really not sustainable#and a wireless keyboard + mouse because my computer is set up as the living room TV and having the controls tethered is uh inconvenient#it's not even stuff that's hard for me to afford!#i just get weird about dipping outside my weekly budget#and none of these things can be easily purchased within that budget#anyway. very excited to go home and try out this drill#i also bought a new shade for the bathroom#because i don't like having vinyl blinds that have broken slats as a privacy shield#like. my neighbor's house is Right There#and it's not a very big broken area but i am constantly aware of it#so it would be nice to just. fix it.
19 notes
·
View notes
Text

sneak peek at my next post (it’s nark, duh)
this part on its own looks v suggestive 👀 lmao BUT I SWEAR IT ISNT LOOK SPARROW SAID THEY JUST CAME BACK FROM A JOG LOL
#dungeons and daddies#dndads#dndaddies#lark oak garcia#lark oak#dndads s2#dndaddies s2#nark#nark nation#it’s just a dumb lil comic i made bc i wanted to draw lark and i was like#what if i turn it into nark lmao#it’s a goofy lil comic but this one part LOOKS LKE SOMETHJNG ELSE IS HAPPENFIFN BUT INDIDNT MENA TO#also my wifi is down and i haven’t saved it so i can’t upload it yet even tho it’s done and i can’t save it to my computer bc i don’t have#any room and i like having it in the cloud rather than my drive bc of storage reasons#also did anyone ever make a nark nation discord bc i haven’t checked the tag or anything in a while#pls no one judge me over making a lark thirst trap lmao#wip#my art
74 notes
·
View notes
Text
youtube
Open Source & Private File Sync Made Simple
Syncthing Tutorial
#education#free education#technology#Syncthing Tutorial#open source#cloud storage#educate yourselves#educate yourself#cloudcomputing#Private File Sync#file management#computer tips#youtube#Syncthing#Youtube
3 notes
·
View notes
Note
i mean yeah the first thing i did was look for vermillioncrown or rabittotouka but i already figured you used a different username
1) you didn't find it? the perma url was stuck on vermillioncrown for a long time
2) list failed approaches, too--helpful for documentation and being methodical
(unless that's cached from my own browsing history...)
anyways. i think I'm gonna nuke my ff.net account soon, no point if i don't use it anymore
#inquiry#anonymous#which means the fic will be going away#my philosophy on unfinished fics + deleting works is#you can hope an author keeps things up but there's no imperative for them to do so#and as someone who read much more than she has written...#if you have the type of emotional dependency on anything such that you'll fall to pieces if it ever disappears#find more things you value in your life. things come and go. we will all pass on one day#^(learned from accidentally nuking many computers/digital storage pre-cloud)
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
Just deleted a bunch of big chonky files and programs I don't actually need, want, or use and freed up like 16.5GB on my harddrive. Which is great, because I literally had just over 100 megabytes left on my C drive this morning, lol.
#I feel so free#do really I need to get more external storage though because jesus fucking christ#your boy really does just keep enormous MP4 files on his drive Forever for No Reason#to say nothing of all that fucking software I haven't used for years???#I don't even have an InDesign subscription anymore!#what were InDesign and the Adobe Creative Cloud app doing on my fucking computer???#this is why I make like one vid every three years#because I could make my shitty 4 GB RAM laptop play ball if I had more than a teaspoon of space on my SSD at any given time#but yeah there is like... no reason for me to be storing media files on my fucking computer#that is what secondary storage is for!#I could literally buy almost a TB of storage on fucking USB sticks for about thirty quid right now!
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
A Complete Guide to Mastering Microsoft Azure for Tech Enthusiasts
With this rapid advancement, businesses around the world are shifting towards cloud computing to enhance their operations and stay ahead of the competition. Microsoft Azure, a powerful cloud computing platform, offers a wide range of services and solutions for various industries. This comprehensive guide aims to provide tech enthusiasts with an in-depth understanding of Microsoft Azure, its features, and how to leverage its capabilities to drive innovation and success.
Understanding Microsoft Azure
A platform for cloud computing and service offered through Microsoft is called Azure. It provides reliable and scalable solutions for businesses to build, deploy, and manage applications and services through Microsoft-managed data centers. Azure offers a vast array of services, including virtual machines, storage, databases, networking, and more, enabling businesses to optimize their IT infrastructure and accelerate their digital transformation.

Cloud Computing and its Significance
Cloud computing has revolutionized the IT industry by providing on-demand access to a shared pool of computing resources over the internet. It eliminates the need for businesses to maintain physical hardware and infrastructure, reducing costs and improving scalability. Microsoft Azure embraces cloud computing principles to enable businesses to focus on innovation rather than infrastructure management.
Key Features and Benefits of Microsoft Azure
Scalability: Azure provides the flexibility to scale resources up or down based on workload demands, ensuring optimal performance and cost efficiency.
Vertical Scaling: Increase or decrease the size of resources (e.g., virtual machines) within Azure.
Horizontal Scaling: Expand or reduce the number of instances across Azure services to meet changing workload requirements.
Reliability and Availability: Microsoft Azure ensures high availability through its globally distributed data centers, redundant infrastructure, and automatic failover capabilities.
Service Level Agreements (SLAs): Guarantees high availability, with SLAs covering different services.
Availability Zones: Distributes resources across multiple data centers within a region to ensure fault tolerance.
Security and Compliance: Azure incorporates robust security measures, including encryption, identity and access management, threat detection, and regulatory compliance adherence.
Azure Security Center: Provides centralized security monitoring, threat detection, and compliance management.
Compliance Certifications: Azure complies with various industry-specific security standards and regulations.
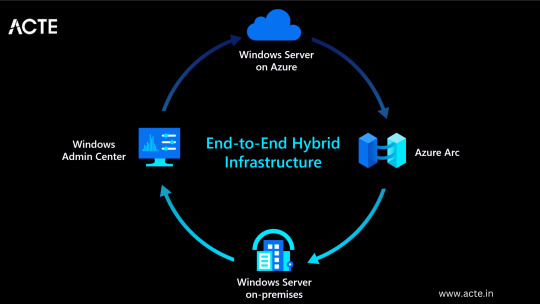
Hybrid Capability: Azure seamlessly integrates with on-premises infrastructure, allowing businesses to extend their existing investments and create hybrid cloud environments.
Azure Stack: Enables organizations to build and run Azure services on their premises.
Virtual Network Connectivity: Establish secure connections between on-premises infrastructure and Azure services.
Cost Optimization: Azure provides cost-effective solutions, offering pricing models based on consumption, reserved instances, and cost management tools.
Azure Cost Management: Helps businesses track and optimize their cloud spending, providing insights and recommendations.
Azure Reserved Instances: Allows for significant cost savings by committing to long-term usage of specific Azure services.
Extensive Service Catalog: Azure offers a wide range of services and tools, including app services, AI and machine learning, Internet of Things (IoT), analytics, and more, empowering businesses to innovate and transform digitally.
Learning Path for Microsoft Azure
To master Microsoft Azure, tech enthusiasts can follow a structured learning path that covers the fundamental concepts, hands-on experience, and specialized skills required to work with Azure effectively. I advise looking at the ACTE Institute, which offers a comprehensive Microsoft Azure Course.

Foundational Knowledge
Familiarize yourself with cloud computing concepts, including Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS).
Understand the core components of Azure, such as Azure Resource Manager, Azure Virtual Machines, Azure Storage, and Azure Networking.
Explore Azure architecture and the various deployment models available.
Hands-on Experience
Create a free Azure account to access the Azure portal and start experimenting with the platform.
Practice creating and managing virtual machines, storage accounts, and networking resources within the Azure portal.
Deploy sample applications and services using Azure App Services, Azure Functions, and Azure Containers.
Certification and Specializations
Pursue Azure certifications to validate your expertise in Azure technologies. Microsoft offers role-based certifications, including Azure Administrator, Azure Developer, and Azure Solutions Architect.
Gain specialization in specific Azure services or domains, such as Azure AI Engineer, Azure Data Engineer, or Azure Security Engineer. These specializations demonstrate a deeper understanding of specific technologies and scenarios.
Best Practices for Azure Deployment and Management
Deploying and managing resources effectively in Microsoft Azure requires adherence to best practices to ensure optimal performance, security, and cost efficiency. Consider the following guidelines:
Resource Group and Azure Subscription Organization
Organize resources within logical resource groups to manage and govern them efficiently.
Leverage Azure Management Groups to establish hierarchical structures for managing multiple subscriptions.
Security and Compliance Considerations
Implement robust identity and access management mechanisms, such as Azure Active Directory.
Enable encryption at rest and in transit to protect data stored in Azure services.
Regularly monitor and audit Azure resources for security vulnerabilities.
Ensure compliance with industry-specific standards, such as ISO 27001, HIPAA, or GDPR.
Scalability and Performance Optimization
Design applications to take advantage of Azure’s scalability features, such as autoscaling and load balancing.
Leverage Azure CDN (Content Delivery Network) for efficient content delivery and improved performance worldwide.
Optimize resource configurations based on workload patterns and requirements.
Monitoring and Alerting
Utilize Azure Monitor and Azure Log Analytics to gain insights into the performance and health of Azure resources.
Configure alert rules to notify you about critical events or performance thresholds.
Backup and Disaster Recovery
Implement appropriate backup strategies and disaster recovery plans for essential data and applications.
Leverage Azure Site Recovery to replicate and recover workloads in case of outages.
Mastering Microsoft Azure empowers tech enthusiasts to harness the full potential of cloud computing and revolutionize their organizations. By understanding the core concepts, leveraging hands-on practice, and adopting best practices for deployment and management, individuals become equipped to drive innovation, enhance security, and optimize costs in a rapidly evolving digital landscape. Microsoft Azure’s comprehensive service catalog ensures businesses have the tools they need to stay ahead and thrive in the digital era. So, embrace the power of Azure and embark on a journey toward success in the ever-expanding world of information technology.
#microsoft azure#cloud computing#cloud services#data storage#tech#information technology#information security
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
Most in-demand Azure cloud skills that IT professionals should have
In today’s competitive job market, having the right skillset is key to success. Azure cloud skills are becoming increasingly important for IT professionals and developers. With the help of Azure cloud services, organizations can build secure and reliable applications that can scale up or down as needed. Azure cloud skills can be used to develop applications that run on the cloud, manage data, automate processes and deploy solutions quickly and efficiently. It also allows developers to create hybrid solutions by combining on-premise resources with public cloud offerings. Having the right Azure cloud skills can open up new opportunities for IT professionals in terms of career growth and salary potential. It is essential for IT professionals to stay up-to-date with the latest developments in this field in order to remain competitive in this ever-evolving job market. The following are some of the most in-demand Azure cloud skills that IT professionals should have:
1. Azure cloud services: This includes developing applications that run on Microsoft Azure and managing data, automating processes and deploying solutions quickly and efficiently.
2. Azure IaaS: Determines how an organization can build secure, reliable applications by using public cloud resources in combination with on-premise resources to create hybrid solutions for maximum efficiency.
3. Windows Server: In order to develop solutions for either public or private clouds, developers need familiarity with this server operating system which includes Microsoft Azure hybrid solutions.
4. Windows: Determines how an organization can harness the power of the cloud by leveraging the powerful development toolset for this platform and its wide range of applications.
#Azure#Cloud#Cloud computing#Microsoft Azure#Azure Active Directory#Azure Virtual Machines#Azure Storage#Azure Networking#Azure DevOps#Azure Kubernetes Service#Azure SQL#Azure Machine Learning#Azure Automation#Azure Security#Azure IoT#Azure Functions#Azure Logic Apps#Azure App Service#Azure ExpressRoute#Azure Monitor#Azure Cost Management#Azure Backup#Azure Site Recovery#Azure AD B2C#Azure AD B2B
2 notes
·
View notes
Text


a couple from my old home
#i remember fighting so hard to get my phone to pick these up correctly#it was so much more pink in person#i need to get on my computer and get my photos from there#i have none left on my phone bc of storage space#clouds#sunset#photography#my photos#field#cottagecore#astronaut.png
5 notes
·
View notes
Photo





Cloud computing is one of the most helpful platforms one may use within their organization. Get rid of servers for explosive business growth by switching to our cloud services.
For more information, Visit us: https://www.algoworks.com/blog/cloud-computing-important-to-business-success/
#cloud#computing#cloudComputing#platforms#office#business#growth#businessgrowth#cloud services#services#security#accessibility#storage#adaptability#algoworks#implementation#development
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
#cloud projects#cloud computing projects#cloud computing topics for project#Revocable Attribute-Based Data Storage in Mobile Clouds#Cloud Computing Projects Ideas for Beginners
0 notes
Text
Eric Landau, Co-Founder & CEO of Encord – Interview Series
New Post has been published on https://thedigitalinsider.com/eric-landau-co-founder-ceo-of-encord-interview-series/
Eric Landau, Co-Founder & CEO of Encord – Interview Series
Eric Landau is the CEO & Co-Founder of Encord, an active learning platform for computer vision. Eric was the lead quantitative researcher on a global equity delta-one desk, putting thousands of models into production. Before Encord, he spent nearly a decade in high-frequency trading at DRW. He holds an S.M. in Applied Physics from Harvard University, M.S. in Electrical Engineering, and B.S. in Physics from Stanford University.
In his spare time, Eric enjoys playing with ChatGPT and large language models and craft cocktail making.
What inspired you to co-found Encord, and how did your experience in particle physics and quantitative finance shape your approach to solving the “data problem” in AI?
I first started thinking about machine learning while working in particle physics and dealing with very large datasets during my time at the Stanford Linear Accelerator Center (SLAC). I was using software designed for physicists by physicists, which is to say there was a lot to be desired in terms of a pleasant user experience. With easier tools, I would have been able to run analyses much faster.
Later, working in quantitative finance at DRW, I was responsible for creating thousands of models that were deployed into production. Similar to my experience in physics, I found that high-quality data was critical in making accurate models and that managing complex, large-scale data is difficult. Ulrik had a similar experience visualizing large image datasets for computer vision.
When I heard about his initial idea for Encord, I was immediately on board and understood the importance. Together, Ulrik and I saw a huge opportunity to build a platform to automate and streamline the AI data development process, making it easier for teams to get the best data into models and build trustworthy AI systems.
Can you elaborate on the vision behind Encord and how it compares to the early days of computing or the internet in terms of potential and challenges?
Encord’s vision is to be the foundational platform that enterprises rely on to transform their data into functional AI models. We are the layer between a company’s data and their AI.
In many ways, AI mirrors previous paradigm shifts like personal computing and the Internet in that it will become integral to workflows for every individual, business, nation, and industry. Unlike previous technological revolutions, which have been largely bottlenecked by Moore’s law of compounded computational growth of 30x every 10 years, AI development has benefited from simultaneous innovations. It is thus moving at a much faster pace. In the words of NVIDIA’s Jensen Huang: “For the very first time, we are seeing compounded exponentials…We are compounding at a million times every ten years. Not a hundred times, not a thousand times, a million times.” Without hyperbole, we are witnessing the fastest-moving technology in human history.
The potential here is vast: by automating and scaling the management of high-quality data for AI, we’re addressing a bottleneck preventing broader AI adoption. The challenges are reminiscent of early-day hurdles in previous technological eras: silos, lack of best practices, limitations for non-technical users, and a shortage of well-defined abstractions.
Encord Index is positioned as a key tool for managing and curating AI data. How does it differentiate itself from other data management platforms currently available?
There are a few ways that Encord Index stands out:
Index is scalable: Allows users to manage billions, not millions, of data points. Other tools face scalability issues for unstructured data and are limited in consolidating all relevant data in an organization.
Index is flexible: Integrates directly with private data storage and cloud storage providers such as AWS, GCP, and Azure. Unlike other tools that are limited to a single cloud provider or internal storage system, Index is agnostic to where the data is located. It lets you manage data from many sources with appropriate governance and access controls that allow them to develop secure and compliant AI applications.
Index is multimodal: Supports multimodal AI, managing data in the form of images, videos, audio, text, documents and more. Index is not limited to a single form of data like many LLM tools today. Human cognition is multimodal, and we believe multimodal AI will be at the heart of the next wave of AI advancements, which will supplant chatbots and LLMs.
In what ways does Encord Index enhance the process of selecting the right data for AI models, and what impact does this have on model performance?
Encord Index enhances data selection by automating the curation of large datasets, helping teams identify and retain only the most relevant data while removing uninformative or biased data. This process not only reduces the size of datasets but also significantly improves the quality of the data used for training AI models. Our customers have seen up to a 20% improvement in their models while achieving a 35% reduction in dataset size and saving hundreds of thousands of dollars in compute and human annotation costs.
With the rapid integration of cutting-edge technologies like Meta’s Segment Anything Model, how does Encord stay ahead in the fast-evolving AI landscape?
We intentionally built the platform to be able to adapt to new technologies quickly. We focus on providing a scalable, software-first approach that easily incorporates advancements like SAM, ensuring that our users are always equipped with the latest tools to stay competitive.
We plan to stay ahead by focusing on multimodal AI. The Encord platform can already manage complex data types such as images, videos, and text, so as more advancements in multimodal AI come our way, we’re ready.
What are the most common challenges companies face when managing AI data, and how does Encord help address these?
There are 3 main challenges companies face:
Poor data organization and controls: As enterprises prepare to implement AI solutions, they are often met with the reality of siloed and unorganized data that is not AI-ready. This data often lacks strong governance around it, limiting much of it from being used in AI systems.
Lack of human experts: As AI models tackle increasingly complex problems, there will soon be a shortage of human domain experts to prepare and validate data. As a company’s AI demands increase, scaling that human workforce is challenging and costly.
Unscalable tooling: Performant AI models are very data-hungry in terms of data needed for fine-tuning, validation, RAG, and other workflows. The previous generation of tools is not equipped to manage the amount of data and types of data required for today’s production-grade models.
Encord fixes these problems by automating the process of curating data at scale, making it easy to identify impactful data from problematic data and ensuring the creation of effective training and validation datasets. It uses a software-first approach that is easy to scale up or down as data management needs change. Our AI-assisted annotation tools empower human-in-the-loop domain experts to maximize workflow efficiency. This process is particularly crucial in industries such as financial services and healthcare, where AI trainers are costly. We make it easy to manage and understand all of an organization’s unstructured data, reducing the need for manual labor.
How does Encord tackle the issue of data bias and under-represented areas within datasets to ensure fair and balanced AI models?
Tackling data bias is a critical focus for us at Encord. Our platform automatically identifies and surfaces areas where data might be biased, allowing AI teams to address these issues before they impact model performance. We also ensure that under-represented areas within datasets are properly included, which helps in developing fairer and more balanced AI models. By using our curation tools, teams can be confident that their models are trained on diverse and representative data.
Encord recently secured $30 million in Series B funding. How will this funding accelerate your product roadmap and expansion plans?
The $30 million in Series B funding will be used to drastically increase the size of our product, engineering, and AI research teams over the next six months and accelerate the development of Encord Index and other new features. We’re also expanding our presence in San Francisco with a new office, and this funding will help us scale our operations to support our growing customer base.
As the youngest AI company from Y Combinator to raise a Series B, what do you attribute to Encord’s rapid growth and success?
One of the reasons we have been able to grow quickly is that we have adopted an extremely customer-centric focus in all areas of the company. We are constantly communicating with customers, listening closely to their problems, and “bear hugging” them to get to solutions. By hyper-focusing on customer needs rather than hype, we’ve created a platform that resonates with top AI teams across various industries. Our customers have been instrumental in getting us to where we are today. Our ability to scale quickly and effectively manage the complexity of AI data has made us an attractive solution for enterprises.
We also owe much of our success to our teammates, partners, and investors, who have all worked tirelessly to champion Encord. Working with world-class product, engineering, and go-to-market teams has been enormously impactful in our growth.
Given the increasing importance of data in AI, how do you see the role of AI data platforms like Encord evolving in the next five years?
As AI applications grow in complexity, the need for efficient and scalable data management solutions will only increase. I believe that every enterprise will eventually have an AI department, much like how IT departments exist today. Encord will be the only platform they need to manage the vast amounts of data required for AI and get models to production quickly.
Thank you for the great interview, readers who wish to learn more should visit Encord.
#adoption#ai#AI adoption#AI development#AI models#AI research#AI systems#amp#analyses#applications#approach#audio#AWS#azure#Bias#board#Business#CEO#change#chatbots#chatGPT#Cloud#cloud storage#cognition#Companies#complexity#computer#Computer vision#computing#craft
0 notes
Text
Get robust VPS solutions for your business from a top Virtual Private Server Provider in Nigeria! We, Layer3 Cloud, have the expertise to manage multiple VMs in a private environment. For more information, you can visit our website https://www.layer3.cloud/ or call us at 09094529373
0 notes
Text
youtube
#youtube#crypto#food and crypto#bitcoin#cryptocurrency#DePIN#storage#data#data storage#cloud computing#AI#wifi#cellular#mobile
1 note
·
View note
Text
Cloud vs On-Prem Data Warehouse: Making the Right Choice for Your Business
In today's data-driven world, businesses face a critical decision when it comes to choosing the right data warehouse solution. The debate between cloud and on-premise data warehouses has been ongoing, with each option offering distinct advantages and challenges. This article will delve into the practical differences between cloud and on-premise data warehouses, offering real-world examples and data-driven insights to help you make an informed decision.

What is a Cloud Data Warehouse?
A cloud data warehouse is a scalable and flexible data storage solution hosted on cloud platforms like AWS, Google Cloud, or Microsoft Azure. Unlike traditional on-premise data warehouses, cloud data warehouses eliminate the need for physical infrastructure, offering businesses the ability to store and manage data with ease and efficiency.
On-Premise Data Warehouse: A Legacy Approach
An on-premise data warehouse is a traditional data storage solution where the data is hosted on local servers within a company's own data center. This model offers complete control over the data and the infrastructure but comes with significant upfront costs and ongoing maintenance requirements.
Key Differences Between Cloud and On-Premise Data Warehouses
1. Cost Efficiency
Cloud Data Warehouse:
Pros: The pay-as-you-go model allows businesses to scale resources up or down based on demand, reducing unnecessary costs. There is no need for significant capital investment in hardware or software.
Cons: Long-term costs can add up if not managed properly, especially with increasing data volumes and computational needs.
On-Premise Data Warehouse:
Pros: Once the initial investment is made, ongoing costs can be more predictable. No recurring subscription fees.
Cons: High upfront costs for hardware, software, and skilled IT personnel. Ongoing maintenance, power, and cooling expenses add to the total cost of ownership (TCO).
2. Scalability
Cloud Data Warehouse:
Pros: Cloud solutions offer almost infinite scalability. Businesses can adjust their storage and processing power according to their needs without physical limitations.
Cons: Rapid scaling can lead to unexpectedly high costs if usage is not carefully monitored.
On-Premise Data Warehouse:
Pros: Customizable to specific business needs. Scaling is possible but requires additional hardware and can be time-consuming.
Cons: Scaling is limited by the physical infrastructure, often requiring significant time and financial investment.
3. Performance
Cloud Data Warehouse:
Pros: Advanced cloud architectures are optimized for performance, offering faster query processing and better data handling capabilities.
Cons: Performance can be affected by network latency and bandwidth limitations.
On-Premise Data Warehouse:
Pros: Performance is highly controlled, with low latency since data is processed on-site.
Cons: Performance improvements require hardware upgrades, which can be costly and time-consuming.
4. Security and Compliance
Cloud Data Warehouse:
Pros: Leading cloud providers offer robust security features, including encryption, access controls, and compliance with industry standards like GDPR, HIPAA, and SOC 2.
Cons: Data security in the cloud is a shared responsibility. Organizations must ensure that they implement proper security measures on their end.
On-Premise Data Warehouse:
Pros: Complete control over security policies and compliance with regulatory requirements. Data remains within the company's own environment.
Cons: Higher responsibility for maintaining security, requiring dedicated IT staff and resources.
Live Examples: Cloud vs On-Premise in Action
Cloud Data Warehouse: Netflix
Netflix is a prime example of a company leveraging cloud data warehouses to manage its massive data volumes. By using AWS Redshift, Netflix can analyze petabytes of data in real-time, optimizing its recommendation algorithms and improving user experience. The scalability and performance of cloud data warehouses allow Netflix to handle peak loads, such as during new content releases, without compromising speed or reliability.
On-Premise Data Warehouse: Bank of America
Bank of America relies on an on-premise data warehouse to maintain full control over its sensitive financial data. By keeping data in-house, the bank ensures that all security and compliance requirements are met without relying on external cloud providers. While the costs and complexity of managing an on-premise solution are higher, the bank prioritizes control and security over the flexibility offered by cloud solutions.
Data-Driven Insights: Market Trends and Future Outlook
Market Growth: According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the global cloud data warehouse market is expected to grow from $4.7 billion in 2021 to $12.9 billion by 2026, at a CAGR of 23.8%. This growth is driven by the increasing adoption of cloud technologies, the need for real-time analytics, and the flexibility offered by cloud solutions.
Hybrid Approaches: Many organizations are adopting hybrid models, combining both cloud and on-premise data warehouses to balance the benefits of both. For instance, sensitive data may be stored on-premise, while less critical data is managed in the cloud.
AI and Machine Learning Integration: Cloud data warehouses are increasingly integrating AI and machine learning tools to enhance data processing capabilities. This trend is expected to accelerate, with cloud providers offering more advanced analytics and automation features.
Making the Right Choice: Key Considerations
Business Needs: Assess your organization’s specific needs, including data volume, security requirements, budget, and long-term goals.
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider both the short-term and long-term costs associated with each solution, including maintenance, upgrades, and scalability.
Security and Compliance: Ensure that your chosen solution meets all regulatory requirements and provides the necessary security features to protect your data.
Scalability and Performance: Evaluate the scalability and performance needs of your organization, and choose a solution that can grow with your business.
Conclusion
Choosing between a cloud and an on-premise data warehouse is a decision that requires careful consideration of various factors, including cost, scalability, performance, and security. While cloud data warehouses offer flexibility, scalability, and advanced analytics, on-premise solutions provide greater control and security. By understanding your organization’s unique needs and long-term goals, you can make an informed decision that will support your data management strategy for years to come.
#Cloud Data Warehouse#On Premise Data Warehouse#Data Storage#Data Management#Cloud Computing#Enterprise Data#Hybrid Cloud#Data Analytics#Data Security#Digital Transformation#Data Infrastructure#Business Intelligence
0 notes
Text
Smart Manufacturing: Market Trends and Growth Insights
The global landscape of manufacturing is undergoing a significant transformation driven by technological advancements and evolving industry needs. The concept of smart manufacturing has emerged as a critical component in this transformation, integrating advanced technologies like the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), artificial intelligence (AI), and machine learning (ML) into production processes. According to a recent publication by Meticulous Research®, the smart manufacturing market is expected to reach $733.4 billion by 2031, growing at a robust CAGR of 24.6% from 2024 to 2031. This article delves into the factors driving this market growth, the key technologies involved, and the challenges that industries face in adopting smart manufacturing practices.
Download Sample Report Here @ https://www.meticulousresearch.com/download-sample-report/cp_id=5265
The Growth Drivers of the Smart Manufacturing Market
The rise of smart manufacturing is largely driven by the need to optimize production processes, reduce operational costs, and enhance overall efficiency. Several key factors contribute to the growth of the smart manufacturing market:
Predictive Maintenance and Cost Reduction: One of the primary drivers of smart manufacturing is the increasing demand for predictive maintenance. Predictive maintenance leverages data analytics and machine learning to predict equipment failures before they occur, allowing manufacturers to perform maintenance only when necessary. This approach significantly reduces downtime and operational costs, enhancing productivity.
Integration of AI and ML Technologies: The incorporation of AI and ML into manufacturing processes is revolutionizing how industries operate. AI and ML enable manufacturers to analyze vast amounts of data in real time, optimizing production processes and improving decision-making. These technologies also play a crucial role in quality management, resource optimization, and energy management, further driving the adoption of smart manufacturing.
Expansion of 3D Printing and Additive Manufacturing: Additive manufacturing, particularly 3D printing, is another critical component of the smart manufacturing landscape. 3D printing allows for the creation of complex and customized products with reduced waste and shorter lead times. As the technology continues to advance, it is increasingly being integrated into mainstream manufacturing processes, contributing to the market's growth.
Introduction of 5G Connectivity: The rollout of 5G technology is expected to have a profound impact on the smart manufacturing market. 5G offers faster data transmission speeds and lower latency, enabling real-time communication between machines, sensors, and control systems. This enhanced connectivity supports the deployment of advanced applications such as augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and digital twins in manufacturing environments.
Adoption in Developing Countries: While smart manufacturing has seen significant adoption in developed regions, its expansion into developing countries presents a substantial growth opportunity. Countries in Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Africa are increasingly investing in smart manufacturing technologies to enhance their industrial capabilities and compete on a global scale. This trend is expected to drive market growth in these regions over the forecast period.
Key Technologies in Smart Manufacturing
Smart manufacturing is an umbrella term that encompasses various advanced technologies aimed at improving the efficiency, flexibility, and sustainability of manufacturing processes. Some of the key technologies driving the smart manufacturing market include:
Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT): The IIoT is a network of interconnected devices, sensors, and machines that communicate with each other and exchange data. In a smart manufacturing environment, IIoT enables real-time monitoring and control of production processes, leading to increased efficiency and reduced waste. IIoT is expected to account for the largest share of the smart manufacturing market, with a significant focus on improving operational visibility and process optimization.
Cloud Computing and Storage: Cloud computing provides manufacturers with the ability to store and process large amounts of data remotely, offering scalability and flexibility. By leveraging cloud-based solutions, manufacturers can access real-time data from multiple locations, streamline operations, and enhance collaboration across different departments.
Robotics and Automation: Robotics and automation are integral to smart manufacturing, enabling manufacturers to automate repetitive tasks and improve precision and speed. The integration of robotics with AI and ML further enhances the capabilities of automated systems, allowing them to perform complex tasks with minimal human intervention.
Industrial Cybersecurity: As manufacturing processes become more interconnected, the need for robust cybersecurity measures becomes increasingly critical. Industrial cybersecurity solutions are designed to protect manufacturing systems from cyber threats, ensuring the integrity and confidentiality of data. With the rising adoption of smart manufacturing technologies, the demand for advanced cybersecurity solutions is expected to grow.
Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing): Additive manufacturing, or 3D printing, allows manufacturers to produce parts and products layer by layer, offering greater design flexibility and reduced material waste. This technology is particularly valuable for producing customized and complex components, making it a key driver of innovation in the smart manufacturing market.
Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR): AR and VR technologies are increasingly being used in smart manufacturing for applications such as training, maintenance, and quality control. AR can overlay digital information onto the physical world, helping workers perform tasks more accurately, while VR can simulate real-world environments for training purposes.
Digital Twin Technology: A digital twin is a virtual replica of a physical object or system, used to simulate and analyze its performance in real-time. In smart manufacturing, digital twins enable manufacturers to monitor production processes, predict potential issues, and optimize operations. The use of digital twins is expected to grow as manufacturers seek to enhance their operational efficiency and reduce downtime.
Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI is at the core of smart manufacturing, driving innovations in automation, predictive analytics, and process optimization. AI-powered systems can analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns, predict outcomes, and make informed decisions, helping manufacturers improve their productivity and reduce costs.
Blockchain: Blockchain technology offers a decentralized and secure way to record transactions and track assets in a manufacturing environment. It is particularly valuable for ensuring transparency and traceability in supply chains, reducing the risk of fraud and improving trust among stakeholders.
Applications of Smart Manufacturing
Smart manufacturing technologies are being applied across various industries to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and improve product quality. Some of the key applications of smart manufacturing include:
Surveillance and Safety: Surveillance and safety are critical components of smart manufacturing, particularly in industries where worker safety is a priority. The integration of smart cameras, motion detection, and facial recognition technologies allows manufacturers to monitor worker behavior, machinery compliance, and safety anomalies in real-time. This not only enhances productivity but also ensures a safer working environment.
Quality Management: Quality management is essential in manufacturing to ensure that products meet the required standards and specifications. Smart manufacturing technologies, such as AI and machine learning, enable manufacturers to monitor and control quality throughout the production process, reducing the risk of defects and improving overall product quality.
Resource Optimization: Resource optimization involves maximizing the efficiency of resources such as materials, energy, and labor. Smart manufacturing technologies, such as IIoT and AI, enable manufacturers to monitor resource usage in real-time, identify inefficiencies, and implement corrective measures to reduce waste and lower costs.
Inventory and Warehouse Management: Effective inventory and warehouse management are crucial for ensuring that materials and products are available when needed. Smart manufacturing technologies, such as robotics and automation, enable manufacturers to streamline inventory management processes, reduce errors, and improve order fulfillment times.
Machine Inspection and Maintenance: Regular machine inspection and maintenance are essential for preventing equipment failures and reducing downtime. Smart manufacturing technologies, such as predictive maintenance and digital twins, enable manufacturers to monitor the condition of machines in real-time, predict potential issues, and perform maintenance only when necessary.
Production Planning: Production planning involves determining the most efficient way to produce products while meeting demand and minimizing costs. Smart manufacturing technologies, such as AI and machine learning, enable manufacturers to optimize production schedules, reduce lead times, and improve overall efficiency.
Energy Management: Energy management is a key consideration for manufacturers looking to reduce their environmental impact and lower operating costs. Smart manufacturing technologies, such as IIoT and AI, enable manufacturers to monitor energy usage in real-time, identify inefficiencies, and implement energy-saving measures.
Challenges in Smart Manufacturing
Despite the many benefits of smart manufacturing, several challenges must be addressed to ensure its successful adoption. Some of the key challenges include:
High Capital and Operating Expenses: Implementing smart manufacturing technologies requires significant capital investment in equipment, software, and infrastructure. Additionally, the ongoing operating costs associated with maintaining and updating these technologies can be substantial. These financial barriers can be a major obstacle for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) looking to adopt smart manufacturing practices.
Need for Skilled Personnel: Smart manufacturing technologies require a workforce with specialized skills in areas such as data analysis, machine learning, and industrial cybersecurity. However, there is a shortage of skilled personnel in these areas, making it difficult for manufacturers to fully leverage the benefits of smart manufacturing.
Privacy and Data Protection Concerns: As manufacturing processes become more interconnected and data-driven, concerns about privacy and data protection have become increasingly important. Manufacturers must ensure that sensitive data is securely stored and transmitted to protect against cyber threats and data breaches.
Integration with Legacy Systems: Many manufacturers still rely on legacy systems that may not be compatible with modern smart manufacturing technologies. Integrating these systems with new technologies can be complex and costly, posing a challenge for manufacturers looking to transition to smart manufacturing.
Conclusion
The smart manufacturing market is poised for significant growth in the coming years, driven by the increasing adoption of advanced technologies such as IIoT, AI, and 3D printing. While there are challenges to overcome, including high costs and the need for skilled personnel, the benefits of smart manufacturing are undeniable. As more industries recognize the value of these technologies in improving efficiency, reducing costs, and enhancing product quality, the smart manufacturing market is expected to continue its upward trajectory, reaching an estimated $733.4 billion by 2031.
Contact Us:
Meticulous Research®
Email- [email protected]
Contact Sales- +1-646-781-8004
Connect with us on LinkedIn- https://www.linkedin.com/company/meticulous-research
#Smart Manufacturing Market#Industrial Internet of Things#Cloud Computing & Storage#Robotics & Automation#Industrial Cybersecurity#Augmented Reality (AR)/Virtual Reality (VR)#Digital Twin#Surveillance & Safety#Inventory & Warehouse Management#Machine Inspection & Maintenance#Production Planning#Resource Optimization
0 notes