#Civil Service Reform
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

"Damn the President! He is a cold-blooded, narrow-minded, prejudiced, obstinate, timid old-psalm singing Indianapolis politician."
-- Theodore Roosevelt, after an uncomfortable meeting with President Benjamin Harrison, who had appointed him to the United States Civil Service Commission, but who Roosevelt felt was no longer supportive of the Commission's reform work when it began to investigate certain officials close to President Harrison, letter to Congressman Henry Cabot Lodge, October 4, 1890.
#History#Presidents#Presidential History#Benjamin Harrison#President Harrison#Harrison Administration#Theodore Roosevelt#President Roosevelt#TR#Quotes by Presidents#Quotes About Presidents#Presidential Quotes#U.S. Civil Service Commission#Politics#Political History#Henry Cabot Lodge#Civil Service Commission#Civil Service#Civil Service Reform#Presidential Rivals#Presidential Rivalries
90 notes
·
View notes
Text
Trump Officials Initiate Extensive Job Cuts Across Multiple Federal Agencies
Trump Officials Initiate Extensive Job Cuts Across Multiple Federal Agencies Over 9,500 Federal Employees Terminated as Part of Government Downsizing Effort In a sweeping move to reduce the size of the federal government, the Trump administration has terminated over 9,500 federal employees across various agencies. This action is part of a broader initiative led by President Donald Trump and…
0 notes
Text
The Tammany Machine And The Evolution of Machine Politics
The “Tammany Machine,” also known as Tammany Hall, was a powerful and notorious political organization that operated in New York City for much of the 19th and early 20th centuries. It played a significant role in shaping the city’s politics and had a reputation for corruption, patronage, and machine politics. Here are some key points about the Tammany Machine: Origins: Tammany Hall was founded…

View On WordPress
#Campaign Finance Reform#Civic Engagement#Civil Service Reform#corruption#Democratic Party#Electoral Reforms#Graft#Immigrant Vote Bank#machine politics#patronage#political machines#Republican Party#tammany#tammany hall#tammany machine#voter fraud#Whistleblower Protections#workers&039; rights
0 notes
Text

"$700 A YEAR WAGES RIDICULOUS---CONBOY," Toronto Star. October 9, 1942. Page 2. ---- Declares "People Can't Work for That Kind of Money" ---- "It seems to me a salary of $700 a year is ridiculous." Mayor Con- boy remarked yesterday.
Board of control had before it a recommendation for temporary appointment of a junior clerk in the accounting branch. finance department. at a salary of $700 a year. The applicant is 19 and has been rejected for military service.
"Let us set this over." said the mayor. "We'll have to do something about this kind of thing."
"The previous occupant of the post received only $624." said Secretary Norris.
"It's still ridiculous." said the mayor. "People can't work for that kind of money."
"We have heads of departments receiving far too much money and staying on far beyond the time when their usefulness has expired." Con. Duncan stated. "We also have other people receiving too much money and staying too long. It keeps other salaries down and holds other employees back from deserved advancement. "We need a survey of all departments to see who are the drones and who are not the drones. Some form of civil service commission is the answer. It is time we did something for the people who are really doing the work." The same question arose again when a letter was presented from the City Hall Employees' association regarding recent appointment of a stenographer at a salary of $1.450. The letter was not read.
"Have copies made for all members," the mayor instructed. "We will deal with all these things when the heads of departments bring in their report. They will have it ready very shortly."
#toronto#city council#municipal government#municipal workers#high cost of living#poverty wages#wage demand#wage increase#civil service commission#civil service reform#canada during world war 2#union demands
0 notes
Text
📨 An open letter to the President & U.S. Congress
🪖 Don't Ask, Don't Tell 2.0: The Trans Military Ban Violates Equality & Readiness
✍️ 193 so far! Help us get to 250 signers!
The open letter calls for the repeal of the transgender military ban, emphasizing that discrimination undermines unit cohesion, military readiness, and the equality of service members. It highlights historical parallels with the "Don't Ask, Don't Tell" policy and advocates for equal treatment, access to gender-affirming healthcare, and a merit-based military system. The letter demands immediate action to end discriminatory policies and restore the rights of transgender Americans to serve openly in the military.
📱 Text SIGN PRSOMP to 50409
🤯 Liked it? Text FOLLOW IVYGORGON to 50409
#PRSOMP#IVYGORGON#resistbot#petition#us politics#Don't Ask Don't Tell#transgender#LGBTQ#LGBTQ+ Rights#Human Rights#Military Policy#Equality#Civil Rights#Transgender Rights#Military Readiness#Armed Forces#Unit Cohesion#Discrimination#Workplace Equity#Diversity & Inclusion#Gender Identity#LGBTQ+ Advocacy#Military Service#Trans Troops#Policy Reform#Veterans’ Rights#Healthcare Access#Gender-Affirming Care#Psychological Readiness#Medical Standards
3 notes
·
View notes
Text

corruption and the need for a scientific approach to governance... very intriguing! someone should look into this
#once we invent the civil service we should get some civil service reformers to deal with this stuff#isn't khum what dj khaled left in that elevator
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Halloween 2024: Five Years of Pumpkins
I am sorry it has taken so long to get this published. If you've been waiting for it, here it is! PART ONE of the story behind my Halloween 2024 Pumpkins.
Five Years. It’s coming up on the five year anniversary since I said goodbye to my children. It’s hard to believe. It doesn’t seem right, and I’ve had to count the years out on my fingers several times. 2020. 2021. 2022. 2023… 2024. I have reflected on years past in previous posts, so if you are just tuning in, the links above will get you all caught up. This article will be long enough,…
#4#5#child abuse#child welfare#children#Civil Rights#department of human services#foster care#government spending#iowa#Iowa DHHS#kids#Libertarian#Me+3#Mental Health#reform#s#subsidies#United we stand#welfare reform
0 notes
Text
I'm gonna say it until I'm blue in the face
Right now, it doesn't matter that our federal programs and institutions need reform. YOU CAN'T REFORM SOMETHING ONCE IT'S GONE. It will take WAY more work (and harm way more people in the meantime) to rebuild from scratch than to work to save these programs now.
Did the grant freeze scare anyone?? It should have!! Yes, it's been temporarily blocked, BUT EVEN IF IT STAYS BLOCKED, IF THERE'S NO ONE TO ADMINISTER THE GRANTS, WE STILL DON'T GET FUNCTIONING PROGRAMS
Snyder's On Tyranny, #2: DEFEND INSTITUTIONS. All Americans should be throwing their backs behind civil service right now and calling their reps until the reps actually DO something to keep our workers in their jobs. We NEED good people in the agencies and offices that are being targeted!! Or we are going to lose programs, resources, and data we worked for generations to build!

Don't think for one second it's going to be fucking ICE that shuts down because of this... ICE won't be touched. It'll be research, welfare, disaster assistance, land protections, environmental protections, even access to core data that we take for granted, is what we're going to lose. With the grant freeze, and the DEI purge, we've already seen just how FAST resources can be ripped away
FEDERAL WORKERS ARE NOT YOUR ENEMY. We need to stand together on this, as they are building a resistance to defend the constitution against ALL ENEMIES, FOREIGN AND DOMESTIC, because if anyone's the enemy here it's the fucking fascists. And, like it or not, bureaucracy (filled with stubborn, dedicated people) is our first line of defense.
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
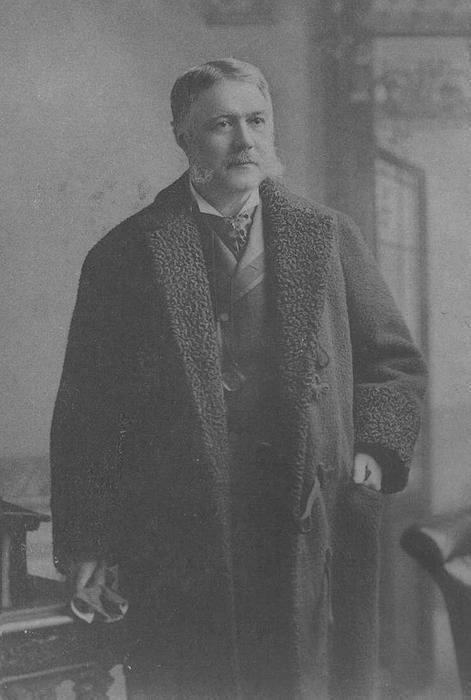
The Elegant Mr. Arthur

It was about two hours after midnight on September 20, 1881, and not unusual for the resident of 123 Lexington Avenue in New York City to be awake at such a late hour or to have plenty of guests. In fact, he preferred to keep late hours, entertaining friends deep into the night with late-night dinner, drinks, and endless conversation. Yet, on this night, 123 Lexington Avenue was somber and the mood was grave. Just a few hours earlier -- at 11:30 PM -- a messenger knocked on the door of Vice President Chester Alan Arthur's Manhattan brownstone and handed Arthur a telegram. Surrounded by a few friends and colleagues, Arthur read that President James Garfield, just 49 years old and in office for almost exactly 200 days, had died at a beach cottage rough 60 miles away, in Elberon, New Jersey. Turning to his friends in his sitting room, Arthur said, "I hope -- my God, I do hope it is a mistake."
On July 2nd, President Garfield was shot twice and seriously wounded by Charles Guiteau as he walked through the Baltimore & Potomac Railroad Station in Washington, D.C. with Secretary of State James G. Blaine and Secretary of War Robert Todd Lincoln (son of Abraham Lincoln), en route to a speaking engagement at his alma mater, Williams College in Massachusetts. Guiteau was a disgruntled, disturbed, and delusional office-seeker who had been pleading for an appointment as consul to Paris despite an absence of diplomatic or political experience and a complete lack of qualifications. Hounding Garfield throughout the early months of an Administration that had just begun on March 4, 1881, Guiteau's constant harassment of the new President finally resulted in Secretary Blaine ordering Guiteau to never return to the White House again. Guiteau felt that he had been entitled to some office, particularly a high-profile ambassadorship, and was terribly upset that Garfield and his Cabinet members refused to consider his requests. Blaine's order to stay away drove Guiteau to purchase an ivory-handled .44 British Bulldog revolver (specifically chosen because Guiteau felt that particular firearm would look good in a museum) and he began stalking Garfield throughout Washington before finally shooting him in the rail station two days before Independence Day 1881. As police arrested him, Guiteau shouted, "I am a Stalwart of the Stalwarts...Arthur is President now!"
But, Arthur wasn't President; not yet at least. Garfield was a physically robust man and relatively young in comparison to most Presidents. Although one bullet had lodged in Garfield's spine, the other bullet grazed his arm and caused no significant damage. While it appeared that he was gravely immediately following the shooting, Garfield's vital signs soon started to improve and the American people began to get their hopes up about a full recovery. A vigil of sorts was underway as President Garfield convalesced in the White House, and his doctors issued regular bulletins updating his condition. Garfield's doctors also poked and prodded with unsterilized instruments and dirty fingers to attempt to locate the bullet still inside of the President's body. Had they left it alone, Garfield almost certainly would have survived; his wounds were significantly less dangerous than those survived by Ronald Reagan 100 years later. However, the unnecessary poking and prodding resulted in a serious infection that ravaged Garfield's body, weakened his heart, and left the muscular, 215-pound President emaciated and weighing less than 135 pounds. After fighting for his life in the sweltering summer heat of Washington, on September 6th it was finally decided to transport Garfield to a cottage on the Jersey Shore in hopes that he could benefit from the fresh ocean air. Sadly, it was too late. The infections were accompanied by blood poisoning and pneumonia, among other ailments. On September 19th, at 10:35 PM, Garfield suffered a massive heart attack and was pronounced dead. In the 79 days since he had been shot, Garfield had lost over 80 pounds and the 49-year-old President's dark brown hair and beard had turned a ghastly white color. An hour later, the messenger arrived at 123 Lexington Avenue.
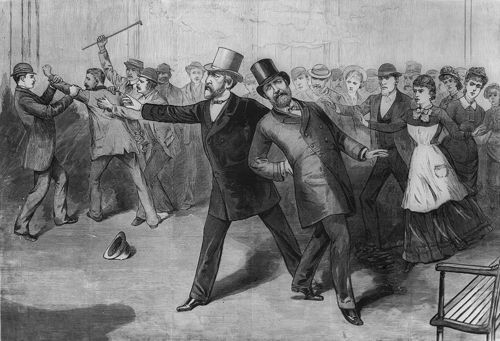
•••
The Vice Presidency was a stretch. Chet Arthur of New York as Vice President? When offered the Republican Vice Presidential nomination by James Garfield in 1880, Chester Arthur was urged by his political mentor, the leader of the Stalwart branch of the Republican Party, Senator Roscoe Conkling of New York, to decline the appointment. Arthur, a man who had never spent a day in Congress or been elected to any office at any level, couldn't turn down such an unexpected opportunity. He accepted the nomination and was elected alongside Garfield in November 1880, but most of the country (rightfully) saw Arthur as the poster boy for a machine politician elevated by the spoils system. The Vice Presidency was certainly a stretch for Chester Arthur, but President of the United States? That was an almost frightening thought to a nation still recovering from Civil War and desperately seeking civil service reform, especially now that a disgruntled office-seeker has assassinated the President. The idea of Arthur as President left a lot of Americans worried -- some because Arthur's political background was as the powerful and somewhat shady Collector of the Port of New York, appointed during the controversial Administration of President Ulysses S. Grant and eventually fired by President Rutherford B. Hayes during a housecleaning of corrupt institutions; and some because James Garfield's murderer had claimed to be a Stalwart and, by his own words, insinuated that Garfield's shooting might be a conspiracy on behalf of Arthur's faction of the divided Republican Party.
Chester Arthur was a creature of the era known as the "Gilded Age" and was the symbolic mascot for the widespread corruption of the 1870's due to his position at the Port of New York. Born in Vermont in 1829, Arthur was the son of a preacher and grew up mostly in upstate New York, graduated from Schenectady's Union College in 1848, briefly taught school was studying law, and was admitted to the bar in 1854. As his law practice grew in the 1850's, Arthur immersed himself in New York Republican politics yet never ran for office. A political appointee to the New York State Militia, he found himself serving during the Civil War and his superb organizational skills led to quick promotions all the way to quartermaster general in 1862, a position which carried the rank of brigadier. As a political appointee to the militia, however, Arthur served at the pleasure of the Governor of New York and was forced to resign in 1862 when a Democratic Governor took office. Returning to New York City, Arthur resumed his law practice and political gamesmanship. More appointments came his way as he supported Republican candidates throughout the state and worked on national campaigns such as President Lincoln's 1864 bid for re-election and Ulysses S. Grant's 1868 Presidential campaign.
In 1871, President Grant appointed Arthur as Collector of customs at the Port of New York, which gave Arthur responsibility for about 75% of the nation's customs duties and was one of the most powerful patronage positions available in the United States government. Arthur used his office to efficiently raise money for Republican campaigns and candidates, supporting President Grant's 1872 re-election campaign by seeking contributions from his employees at the customhouse. In 1876, Arthur championed his political mentor, Roscoe Conkling, for the Republican Presidential nomination, but supported Rutherford B. Hayes in the general election, once again using the employees at the customhouse to help raise money to finance the successful Republican campaign. However, once Hayes was elected, the new President made it clear that he was serious about civil service reform and that meant reforming Arthur's customhouse, too. In 1877, Arthur testified before the Jay Commission, which was formed to investigate charges of corruption and eventually recommended that President Hayes reduce the workforce of the customhouse and eliminate the corrupt elements that had worked there for so long. Due to Arthur's longtime support of the Republican Party, President Hayes offered him an appointment as consul in Paris in order to quietly remove him from the Port of New York. When Arthur refused the appointment, the President fired him and Arthur resumed his law practice in New York City (Hayes intended to replace Arthur with Theodore Roosevelt, Sr. -- father of the future President -- but Conkling felt insulted by Hayes's termination of Arthur and worked to kill Roosevelt's appointment during his Senate confirmation ).
When Arthur headed to the 1880 Republican National Convention at the Interstate Exposition Building in Chicago, it was as a New York delegate supporting the aspirations of former President Ulysses S. Grant who was coming out of retirement to seek an unprecedented third term. However, neither of the front-runners for the nomination -- Grant and Senator James G. Blaine of Maine -- could capture enough votes from delegates to clinch the nomination. After thirty-five ballots, Blaine and another prospective candidate, John Sherman of Ohio, threw their support behind a dark horse candidate -- Ohio Congressman James A. Garfield. On the next ballot, Garfield clinched the nomination and reached out to the opposing wing of the Republican Party for his Vice Presidential choice. The first choice, Levi P. Morton of New York (who would later serve as President Benjamin Harrison's Vice President) declined Garfield's offer, and Arthur -- who had never previously held an elective office -- excitedly accepted, much to the chagrin of his angry political mentor, Roscoe Conkling. Not confident in Garfield's chances for election, Conkling told Arthur, "You should drop it as you would a red hot shot from the forge." Arthur replied, "There is something else to be said," and Conkling asked in disbelief, "What, sir, you think of accepting?" Despite the complaints and anger of Conkling, Arthur told him, "The office of Vice President is a greater honor than I have ever dreamed of attaining. I shall accept. In a calmer moment you will look at this differently."
Following the election, Arthur prepared to settle into the quiet role of Vice President during the 19th Century. The Vice President of the United States has only one real Constitutional responsibility -- to preside over the Senate, and even that responsibility is normally delegated to Senators who rotate as presiding officer almost daily. The powerful or even influential American Vice Presidency is a fairly recent evolution, not even 50 years old. While some Vice Presidents were relied upon for advice or counsel or given larger duties than others, most Vice Presidents were so far removed from the Executive Branch that they were not only kept out of the decision-making process but also kept in the dark about certain information. For example, when President Franklin D. Roosevelt died towards the end of World War II in April 1945 and was succeeded by his Vice President, Harry S. Truman, the new President Truman had to be quickly briefed about the existence of the Manhattan Project to develop atomic weaponry. The first Vice President to have an office in the White House was Walter Mondale and that didn't occur until 1977, so in 1881, a Vice President was expected to preside over the Senate on special occasions, cast a tie-breaking vote when necessary, and be available to take the oath of office if the President happened to die or resign.
Like most 19th Century Vice Presidents, Chester Arthur didn't even spend much time in Washington, and he was returning to his regular home in New York City on July 2, 1881 when he stepped off a steamship with Roscoe Conkling and was told that President Garfield had been shot. In fact, the first message that Arthur received erroneously reported that Garfield was already dead and at the request of Garfield's Cabinet, the stunned Vice President immediately returned to Washington, D.C. to proceed with the next steps necessary for maintaining the continuity of government. When Arthur arrived in Washington, President Garfield's condition had improved and his recovery continued to show signs of promise as the Vice President and the nation prayed for him and held vigil throughout the summer. Shaken by rumors that he and his "Stalwart" wing of the Republican Party conspired to assassinate Garfield, Arthur returned home to New York City, hesitant to invite criticism that his continued presence in Washington was merely an eager deathwatch so that he could grab power.
Garfield clung to life for eighty excruciating days with doctors probing him in an effort to remove the bullet in his body, causing infections and leaving the President suffering from blood poisoning which led him to hallucinate at times. The Navy helped rig together an early form of air conditioning in Garfield's White House sickroom in order to give him relief from Washington's stifling summer conditions. When Garfield was taken by train to New Jersey in early-September, it was clear to many that the long vigil was nearly over. More infections set in, along with pneumonia and painful spasms of angina. When the messenger arrived at 123 Lexington Avenue just before midnight on September 20, 1881 to inform Arthur that President Garfield had died just 60 miles away, the new President wasn't surprised, but he also wasn't quite prepared. The nation worried about the lifetime political operative stepping into the position vacated by the promising President assassinated before he could enact the civil service reforms promised in his Inaugural Address. What would Arthur -- the quintessential patronage politician -- do as President? Nobody knew, but Chester Alan Arthur had an idea.
•••

It was fitting that Arthur was surrounded by friends when he took the oath of office at his home in Manhattan at 2:15 AM on September 20, 1881. Arthur's beautiful wife, Nell, died of pneumonia in January 1880 and he was inconsolable for months, regretting for the rest of the life the fact that she never saw his election as Vice President or ascendancy to the Presidency. People who knew Arthur stated that he clearly never fully recovered from her death, and that as a "deeply emotional...romantic person," it was no surprise that he ordered that fresh flowers were placed before her portrait in the White House every day while he was President.
Chester Arthur had a lot of friends. That's what happens when you control as many patronage positions as Arthur controlled for as long as Arthur controlled them. But it wasn't just his political position that gained him friends. Arthur was a great storyteller, a man who loved to hunt and fish, kind, easy-going, charming, graceful, and smooth. During his life he was nicknamed "Elegant Arthur" and is considered one of the most stylish of Presidents. Photographs of Presidents from the 19th Century show us men no different than statues. They dressed the same, they looked the same, and when portrayed in the black and white photos of the time, we feel no differently when we see their pictures than when we see a slab of marble carved in their image. Arthur leaps out of his photographs, however. He was a very large man for his era, standing 6'2" and weighing around 220 pounds during his Presidency. Large muttonchops connected to a bushy mustache and his close-cropped, wavy brown hair seemed to pull back his forehead and place more emphasis on expressive black eyes that easily reflected his moods. While it seems that most Presidents of the 19th Century wore the same boring black suit and black tie like a uniform, Arthur's ties are patterned, his jewelry is visible, collars are crisp, handkerchiefs are folded creatively, and his lapels shine as if they were polished along with his shoes. We see photographs of Arthur in fashionable overcoats, a wide variety of hats, and he employed a personal valet who helped the President change clothes for every occasion and multiple times a day -- he was said to have over 80 pairs of pants.
Most apparent of all is that Arthur was a gentleman -- an interesting man with superb social skills and fastidious manners. Even as one of the top operatives in New York's Republican political machine of the corrupt 1870's, he was nicknamed the "Gentleman Boss." As President, he brought entertainment back to the White House -- something that had been missing on a large scale since before the Civil War twenty years earlier. One of his recent predecessors, Rutherford B. Hayes, was one of the few critics of this development, stating that there was "nothing like it before in the Executive Mansion -- liquor, snobbery, and worse." Arthur also redecorated the White House, hiring Louis Comfort Tiffany to help with the design. To help raise money for the redecoration, Arthur basically held a White House yard sale. On the lawn of the mansion, twenty-four wagons full of history (including a pair of Abraham Lincoln's pants that were left behind in a closet) were sold to citizens. To some, the items were priceless; to President Arthur, they were ugly and a man like Chester Arthur did not live in an ugly home. Several weeks after Garfield died, Arthur got his first look at his new home and quickly stated, "I will not live in a house like this." He didn't end up moving into the White House until three months into his Presidency.
•••

After taking the oath of office at home in Manhattan in the early hours of September 20, 1881, now-President Arthur proceeded to Washington, D.C., stopping in Long Branch, New Jersey to pay respects to the late President Garfield and his grieving family. Once Arthur succeeded to the Presidency upon Garfield's death, there was no Vice President, no president pro tempore of the Senate, and no Speaker of the House because Congress had not elected its leadership yet, thus, there was no Constitutional line of succession. If something had happened to Arthur at that moment, the United States would have faced an unprecedented Constitutional crisis. As his first act as President, Arthur immediately called the Senate into session in order to select their leadership positions and place someone in the line of succession. Upon arriving in Washington, Attorney General Wayne MacVeagh suggested that Arthur take a second oath of office and he did so at the U.S. Capitol on September 22nd in the presence of Garfield's Cabinet, members of Congress, Supreme Court Justices, and former Presidents Grant and Hayes.
Americans worried about the former machine politician's integrity were transformed quickly as Chester Arthur underwent somewhat of a transformation himself. Widely considered a lapdog of New York's Roscoe Conkling, Arthur broke ranks with the party boss and pushed for the same civil service reform championed by James Garfield prior to the assassination. Arthur's former associates in the New York Republican Party were disappointed when he declined their requests for political favors. One former colleague sadly reported, "He isn't 'Chet' Arthur anymore. He's the President." Arthur found that the transformation was almost automatic and out of his control, noting that "Since I came here I have learned that Chester A. Arthur is one man and the President of the United States is another." His old benefactor, Conkling, was one critic of the new President, complaining "I have but one annoyance with the Administration of President Arthur and that is, in contrast with it, the Administration of Hayes becomes respectable, if not heroic." Arthur signed the Pendleton Act in 1883 which created a modern civil service system and eliminated the spoils system that had long dominated American politics. The reform, which Conkling called "snivel service" was the final break between the longtime friends and colleagues.
To the American people, the great surprise of the Arthur Administration was the fact that it was clean, honest, and efficient. Arthur helped lift the gloomy moods that had shadowed Washington through the Civil War, Lincoln's assassination, Andrew Johnson's Impeachment, Reconstruction, the corruption of the Gilded Age, and Garfield's assassination. His popularity rose throughout his term and most critics focused on his lavish entertainment or the fact that he was notoriously late for meetings and seemed bored or lethargic at times. He often procrastinated -- as a White House clerk once said, "President Arthur never did today what he could put off until tomorrow." Still, most Americans were happy with President Arthur and echoed the thoughts of Mark Twain who said, "I am but one in 55 million; still, in the opinion of those one-fifty-five-millionth of the country's population, it would be hard to better President Arthur's Administration."
He was bored, though. President Arthur didn't like being President. He enjoyed the entertaining dinners that he could throw and loved public events or ceremonies that allowed him to meet the people of the United States, but the desk work was tedious and he wasn't interested in policy. Arthur stayed up late and seemed to vacation often, which perplexed many people because it was said that he was constantly exhausted. What they didn't know was that from almost the time he became President, Chester Arthur was dying. In 1882, he was diagnosed with Bright's disease, a fatal kidney ailment at the time. Despite reports that he was suffering from the disease, Arthur hid it from the public, desperately protecting his privacy, as always. Arthur's distaste for the Presidency probably stemmed in part from depression triggered by the Bright's disease. At times, Arthur suffered from debilitating illness and it was always covered with a story about the President catching a cold during a fishing trip or spending too much time in the sun while hunting. In a letter to his son Alan in 1883, the President confided, "I have been so ill that I have hardly been able to dispose of the...business before me."
Despite his popularity, Republican leaders opposed Arthur's nomination as President in his own right in 1884. The man who opposed it most, however, was the President himself, who stated "I do not want to be re-elected." Not only was he disinterested in a second term, but he knew very well that there was a possibility he might not even survive to the end of his current term. He did, and after attending the inauguration of his successor, Grover Cleveland, on March 4, 1885, Arthur returned home to New York City where his health rapidly declined. The former President was aware that he was dying and made plans for a relatively quiet retirement, deciding to practice law, but doing very little work due to his health. When asked about his future, Arthur said, "There doesn't seem anything for an ex-President to do but to go out in the country and raise big pumpkins." On November 16, 1886, Arthur suffered a stroke that paralyzed his left side. Gravely ill, he called his son to his bedside the day before his death and had all of his public and private papers stuffed into trash cans and burned. On November 18, 1886, the 57-year-old former President died in the same place he became President just five years earlier, 123 Lexington Avenue in New York City. After a quiet funeral at the Church of Heavenly Rest on Fifth Avenue in New York, Arthur's remains were buried next to his beloved wife at Rural Cemetery in Albany, New York.
•••
When President Arthur had many of his personal papers burned prior to his death, he eliminated one of the best sources of information for future historians. With a thin resume and a fairly uneventful Presidency, there wasn't much public information about his career, either. This leaves us with very little to remember Chester Alan Arthur by. Research on his life -- particularly his personal life -- is difficult, and Arthur would have appreciated that. During his Presidency, leaders of the temperance movement called on Arthur and urged him to follow the non-alcoholic lifestyle led by President Hayes and his teetotaler wife, who was known as "Lemonade Lucy."
Arthur's response: "Madam, I may be President of the United States, but my private life is nobody's damn business."
And so it isn't.
#History#Presidents#Chester Arthur#Chester A. Arthur#Chester Alan Arthur#President Arthur#Arthur Administration#Presidential History#The Elegant Mr. Arthur#James A. Garfield#President Garfield#Assassination of James Garfield#Garfield Assassination#Charles Guiteau#Inauguration of Chester Arthur#Presidential Assassinations#Presidential Succession#Roscoe Conkling#Gilded Age#Civil Service Reform#Pendleton Act#1880 Election#1884 Election#Politics#Political History#Gentleman Boss#Presidential Personalities#Presidency#Vice Presidents#Vice President Arthur
26 notes
·
View notes
Text
Trump Administration Offers Buyouts to Federal Employees in Effort to Downsize Government Initiative Aims to Reduce Federal Workforce by Offering Eight Months’ Salary to Voluntary Resignees In a significant move to reshape the federal workforce, the Trump administration has announced a “deferred resignation program” offering federal employees approximately eight months of salary to voluntarily…
1 note
·
View note
Text

"The Penitentiary Act," Kingston Whig Standard. March 31, 1933. Editorial ==== The Hon. Hugh Guthrie is on the right track in endeavoring to take the administration of our penitentiaries out of the hands of the Civil Service Commission. For if the Civil Service is to continue to make the appointments to the penitentiary staffs, then it is practically administering our penitentiaries. We have just had a series of riots in our Canadian penitentiaries and, when these riots were on, we did not look to the Civil Service Commission to quell them, rather to the Superintendent of Penitentiaries and his staff. It seems only fair. therefore, that if the Superintendent of Penitentiaries is to be responsible for the administration, he should have the final say in the choosing of his officials. So far as this newspaper is concerned, we are not unduly worried about abusive. patronage. If the Department of Justice chooses the right man for superintendent, and the superintendent places picked men at the heads of these institutions, we do not think there is any great danger. A warden with six or seven hundred convicts under his care, and with his own position and prestige to maintain, is not going to appoint an incompetent guard or instructor, simply because he happens to be of some particular political stripe. He is going to pick the best men he can possibly get. We are quite willing to admit that under the old patronage system there were some abuses, but we do not think they were any worse than the abuses that have crept in under our wonderful Civil Service Commission. We agree with Mr. Guthrie a man may be able to pass all the examinations in the world, and still not make a capable penitentiary official. What we want on our penitentiary staffs are men who are capable, efficient and courageous. We believe that our penitentiaries will be better managed by a staff chosen and trained by a capable, conscientious warden a staff that has had to prove itself worthy under his ever-watchful eye than a staff appointed by the Civil Service Commission. Mr. Guthrie's amendment is a good one. and in the interests of penitentiary management it should be adopted.
#kingston ontario#editorial#civil service commission#civil service of canada#civil service reform#patronage politics#reactionary reform#bennett government#hugh guthrie#prison guards#prison management#convict revolt#great depression in canada#history of crime and punishment in canada#crime and punishment in canada
0 notes
Text
Prison-tech company bribed jails to ban in-person visits

I'm on tour with my new, nationally bestselling novel The Bezzle! Catch me in BOSTON with Randall "XKCD" Munroe (Apr 11), then PROVIDENCE (Apr 12), and beyond!

Beware of geeks bearing gifts. When prison-tech companies started offering "free" tablets to America's vast army of prisoners, it set off alarm-bells for prison reform advocates – but not for the law-enforcement agencies that manage the great American carceral enterprise.
The pitch from these prison-tech companies was that they could cut the costs of locking people up while making jails and prisons safer. Hell, they'd even make life better for prisoners. And they'd do it for free!
These prison tablets would give every prisoner their own phone and their own video-conferencing terminal. They'd supply email, of course, and all the world's books, music, movies and games. Prisoners could maintain connections with the outside world, from family to continuing education. Sounds too good to be true, huh?
Here's the catch: all of these services are blisteringly expensive. Prisoners are accustomed to being gouged on phone calls – for years, prisons have done deals with private telcos that charge a fortune for prisoners' calls and split the take with prison administrators – but even by those standards, the calls you make on a tablet are still a ripoff.
Sure, there are some prisoners for whom money is no object – wealthy people who screwed up so bad they can't get bail and are stewing in a county lockup, along with the odd rich murderer or scammer serving a long bid. But most prisoners are poor. They start poor – the cops are more likely to arrest poor people than rich people, even for the same crime, and the poorer you are, the more likely you are to get convicted or be suckered into a plea bargain with a long sentence. State legislatures are easy to whip up into a froth about minimum sentences for shoplifters who steal $7 deodorant sticks, but they are wildly indifferent to the store owner's rampant wage-theft. Wage theft is by far the most costly form of property crime in America and it is almost entirely ignored:
https://www.theguardian.com/us-news/2023/jun/15/wage-theft-us-workers-employees
So America's prisons are heaving with its poorest citizens, and they're certainly not getting any richer while they're inside. While many prisoners hold jobs – prisoners produce $2b/year in goods and $9b/year in services – the average prison wage is $0.52/hour:
https://www.dollarsandsense.org/archives/2024/0324bowman.html
(In six states, prisoners get nothing; North Carolina law bans paying prisoners more than $1/day, the 13th Amendment to the US Constitution explicitly permits slavery – forced labor without pay – for prisoners.)
Likewise, prisoners' families are poor. They start poor – being poor is a strong correlate of being an American prisoner – and then one of their breadwinners is put behind bars, taking their income with them. The family savings go to paying a lawyer.
Prison-tech is a bet that these poor people, locked up and paid $1/day or less; or their families, deprived of an earner and in debt to a lawyer; will somehow come up with cash to pay $13 for a 20-minute phone call, $3 for an MP3, or double the Kindle price for an ebook.
How do you convince a prisoner earning $0.52/hour to spend $13 on a phone-call?
Well, for Securus and Viapath (AKA Global Tellink) – a pair of private equity backed prison monopolists who have swallowed nearly all their competitors – the answer was simple: they bribed prison officials to get rid of the prison phones.
Not just the phones, either: a pair of Michigan suits brought by the Civil Rights Corps accuse sheriffs and the state Department of Corrections of ending in-person visits in exchange for kickbacks from the money that prisoners' families would pay once the only way to reach their loved ones was over the "free" tablets:
https://arstechnica.com/tech-policy/2024/03/jails-banned-family-visits-to-make-more-money-on-video-calls-lawsuits-claim/
These two cases are just the tip of the iceberg; Civil Rights Corps says there are hundreds of jails and prisons where Securus and Viapath have struck similar corrupt bargains:
https://civilrightscorps.org/case/port-huron-michigan-right2hug/
And it's not just visits and calls. Prison-tech companies have convinced jails and prisons to eliminate mail and parcels. Letters to prisoners are scanned and delivered their tablets, at a price. Prisoners – and their loved ones – have to buy virtual "postage stamps" and pay one stamp per "page" of email. Scanned letters (say, hand-drawn birthday cards from your kids) cost several stamps:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/02/14/minnesota-nice/#shitty-technology-adoption-curve
Prisons and jails have also been convinced to eliminate their libraries and continuing education programs, and to get rid of TVs and recreational equipment. That way, prisoners will pay vastly inflated prices for streaming videos and DRM-locked music.
The icing on the cake? If the prison changes providers, all that data is wiped out – a prisoner serving decades of time will lose their music library, their kids' letters, the books they love. They can get some of that back – by working for $1/day – but the personal stuff? It's just gone.
Readers of my novels know all this. A prison-tech scam just like the one described in the Civil Rights Corps suits is at the center of my latest novel The Bezzle:
https://us.macmillan.com/books/9781250865878/thebezzle
Prison-tech has haunted me for years. At first, it was just the normal horror anyone with a shred of empathy would feel for prisoners and their families, captive customers for sadistic "businesses" that have figured out how to get the poorest, most desperate people in the country to make them billions. In the novel, I call prison-tech "a machine":
a million-armed robot whose every limb was tipped with a needle that sank itself into a different place on prisoners and their families and drew out a few more cc’s of blood.
But over time, that furious empathy gave way to dread. Prisoners are at the bottom of the shitty technology adoption curve. They endure the technological torments that haven't yet been sanded down on their bodies, normalized enough to impose them on people with a little more privilege and agency. I'm a long way up the curve from prisoners, but while the shitty technology curve may grind slow, it grinds fine:
https://pluralistic.net/2021/02/24/gwb-rumsfeld-monsters/#bossware
The future isn't here, it's just not evenly distributed. Prisoners are the ultimate early adopters of the technology that the richest, most powerful, most sadistic people in the country's corporate board-rooms would like to force us all to use.

If you'd like an essay-formatted version of this post to read or share, here's a link to it on pluralistic.net, my surveillance-free, ad-free, tracker-free blog:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/04/02/captive-customers/#guillotine-watch

Image: Cryteria (modified) https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:HAL9000.svg
CC BY 3.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/deed.en
--
Flying Logos https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Over_$1,000,000_dollars_in_USD_$100_bill_stacks.png
CC BY-SA 4.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/deed.en
--
KGBO https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Suncorp_Bank_ATM.jpg
CC BY-SA 3.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/deed.en
#pluralistic#prison#prison-tech#marty hench#the bezzle#securus#captive audiences#St Clair County#human rights#prisoners rights#viapath#gtl#global tellink#Genesee County#michigan#guillotine watch#carceral state#corruption
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
Despite its public portrayal of itself, the ADL isn’t a civil rights group in any meaningful sense, but rather, a veiled pro-Israel lobbying organization that uses superficial language of inclusiveness and anti-racism to defend Israel from criticism from the left. The ADL has made it clear on a number of occasions that it considers the entire basis of the peaceful Boycott, Divestment, Sanctions (BDS) movement — embraced by virtually all of Palestinian civil society — to be hate speech, specifically any claim that denies Israel’s “existence as a Jewish state” (e.g. its claim to ethnonational supremacy over non-Jews living in Palestine). The ADL’s website clearly states, “Anti-Israel activity crosses the line to anti-Semitism” with any statement that “Israel is denied the right to exist as a Jewish state,” and that “the founding goals of the BDS movement and many of the strategies used by BDS campaigns are anti-Semitic.” The ADL smearing Black activists who oppose Israel isn’t new. In the 1960s, the ADL harshly criticized the Black-led Student Nonviolent Coordinating Committee (SNCC) and the Black Panthers for their criticisms of Israel, equating these “negro extremists” with the KKK and American Nazi Party. The ADL also worked with the Israeli government in the 1960s, ‘70s and ‘80s to spy on Arab groups, as well as leftwing anti-South African apartheid activists. As Pulitzer Prize-winning author Glenn Frankel noted in Foreign Policy magazine in 2010, “The Anti-Defamation League participated in a blatant propaganda campaign against Nelson Mandela and the ANC in the mid 1980s and employed an alleged ‘fact-finder’ named Roy Bullock to spy on the anti-apartheid campaign in the United States — a service he was simultaneously performing for the South African government. The ADL defended the white regime’s purported constitutional reforms while denouncing the ANC as ‘totalitarian anti-humane, anti-democratic, anti-Israel, and anti-American.’”
297 notes
·
View notes
Text
President Trump has signed an executive order ending collective bargaining for wide swaths of federal employees, as part of his broader campaign to reshape the U.S. government's workforce. The largest federal employee union says the order affects over 1 million workers. In a fact sheet, the White House says the Civil Service Reform Act of 1978 (CSRA) gives him the authority to halt collective bargaining at agencies with national security missions. This provision has traditionally applied to certain employees at agencies such as the CIA, the FBI or the National Security Agency. But Trump's order, signed late Thursday, is more far-reaching, and includes employees whose jobs touch on national defense, border security, foreign relations, energy security, pandemic preparedness, the economy, public safety and cybersecurity. It notably excludes law enforcement. "Police and firefighters will continue to collectively bargain," the White House fact sheet states. Unions are roundly condemning the move.
28 March 2025
140 notes
·
View notes
Text
So is the Civil Service Reform Act of 1978 no longer the law?
Or has everyone just agreed to allow Trump to violate every law on the books?
182 notes
·
View notes
Text
Conspiracy theories that turned out as true

Here is a list of theories that were initially labeled as conspiracy theories by the mass media but later turned out to be true:
MKUltra: A secret CIA program that conducted mind control experiments using LSD and other methods on unsuspecting individuals. Initially dismissed as a far-fetched conspiracy theory, its existence was later confirmed through declassified documents released in the 1970s, revealing the extent of the unethical experiments.
Tuskegee Syphilis Study: A U.S. Public Health Service experiment where hundreds of Black men with syphilis were left untreated to study the disease’s natural progression. Initially denied and considered a conspiracy theory, it was confirmed in 1972 after a whistleblower exposed the study, leading to widespread outrage and reforms in medical ethics.
Operation Snow White: A conspiracy orchestrated by the Church of Scientology to infiltrate U.S. government agencies and steal sensitive documents. Dismissed as an unlikely plot, it was proven true in the late 1970s when investigations led to the conviction of several Scientology members.
CIA’s Involvement in the Crack Cocaine Epidemic: Allegations that the CIA facilitated the spread of crack cocaine in the 1980s to fund covert operations were initially rejected as conspiracy theories. Investigative journalism, notably by Gary Webb in the 1990s, and subsequent inquiries confirmed some level of CIA complicity or negligence in drug trafficking networks.
NSA’s Mass Surveillance Program: Claims of widespread government surveillance of citizens were dismissed as paranoid theories until 2013, when Edward Snowden leaked documents revealing the NSA’s extensive PRISM program, confirming the scope of global surveillance activities.
FBI’s COINTELPRO Program: A secret FBI initiative to surveil, infiltrate, and disrupt political groups, including civil rights organizations, was initially denied and labeled a conspiracy theory. It was confirmed in 1971 after activists stole and released FBI documents exposing the program’s illegal activities.
Project Sunshine: A U.S. government project that collected tissue samples from deceased children without parental consent to study the effects of radioactive fallout. Initially dismissed as a gruesome conspiracy theory, it was later confirmed through declassified records in the 1990s.
Operation Mockingbird: A CIA effort to influence and control media outlets and journalists during the Cold War. Long considered a conspiracy theory, it was substantiated by declassified documents and congressional investigations in the 1970s, revealing the agency’s manipulation of public narratives.
CIA’s Involvement in the 1953 Iranian Coup: The CIA’s role in orchestrating the overthrow of Iran’s democratically elected government was initially denied and dismissed as a conspiracy theory. It was officially confirmed in 2013 when declassified documents detailed the agency’s collaboration with British intelligence.
FBI’s Spying on Martin Luther King Jr.: Allegations that the FBI surveilled and attempted to discredit Martin Luther King Jr. were initially rejected as conspiratorial. The program’s existence was confirmed in the 1970s through released documents, exposing the extent of the FBI’s efforts to undermine the civil rights leader.
These examples demonstrate that while many conspiracy theories lack evidence, some dismissed by the mass media have been validated over time through investigations, leaks, and declassified records, revealing hidden truths about government and institutional actions.
These are less obvious, often overlooked incidents that still carry the weight of confirmed conspiracies:
The Business Plot (1933) Okay, this one stretches just before the post-WWII mark, but it’s modern enough and obscure today. Rumors swirled that a group of wealthy American businessmen planned to overthrow President Franklin D. Roosevelt and install a fascist regime. Marine Corps General Smedley Butler blew the whistle, claiming he’d been recruited to lead the coup. People dismissed it as a wild tale—until a congressional investigation confirmed there was indeed a plot. Big names like DuPont and J.P. Morgan were linked, though no one faced charges. It’s a chilling “what if” that doesn’t get much airtime today.
Operation Paperclip’s Darker Edges You might’ve heard of Operation Paperclip—the U.S. recruiting Nazi scientists after WWII—but the conspiracy angle is less known. Beyond the famous ones like Wernher von Braun, whispers persisted that war criminals with horrific pasts were smuggled in. The government insisted they were just harmless tech experts. Declassified files later showed otherwise: many were high-ranking Nazis whose records were scrubbed to dodge immigration laws. It’s not just about rockets; some worked on biological and chemical weapons projects, a detail that stayed buried for decades.
The Nayirah Testimony Hoax (1990) In the lead-up to the Gulf War, a girl named Nayirah testified to Congress that Iraqi soldiers in Kuwait were ripping babies from incubators and leaving them to die. It was a gut-wrenching story that helped justify military action. Skeptics called it propaganda, but they were shouted down—until it unraveled. Nayirah was the Kuwaiti ambassador’s daughter, coached by PR firm Hill & Knowlton (hired by Kuwait’s government) to sell the war. Investigative journalists exposed the lie, proving it was a fabricated conspiracy to sway opinion.
The CIA’s Heart Attack Gun (1970s) Ever hear rumors of a gun that could silently kill with no trace? In the ‘70s, people speculated the CIA had a dart gun that triggered heart attacks using frozen toxins. It sounded like James Bond nonsense—until the 1975 Church Committee hearings. The CIA fessed up: they’d built it. The dart dissolved in the body, leaving no evidence. It’s a spy gadget turned real, and while it’s niche, it’s not a household name like Snowden’s leaks.
The Ford Pinto Scandal (1970s) This one’s corporate, not governmental. Word got around that Ford knew their Pinto car could explode in rear-end crashes due to a faulty fuel tank. Ford denied it, insisting the car was safe. Then internal memos leaked: they’d calculated it was cheaper to settle lawsuits from burn victims than fix the design. Court cases confirmed it—a cold-blooded conspiracy of profit over lives. It’s a grim footnote in automotive history that doesn’t get the spotlight it deserves.
Project SHAMROCK (1940s–1970s) Before the NSA’s modern surveillance scandals, there were whispers they’d been snooping on Americans’ telegrams for years. Critics were labeled paranoid—until the Church Committee (again, busy folks) uncovered Project SHAMROCK. Starting in the ‘40s, the NSA collected millions of telegrams without warrants, sharing them with other agencies. It ran for decades before exposure in the ‘70s, a precursor to today’s privacy debates that’s faded from public chatter.
Bohemian Grove’s Real Rituals (Ongoing) For years, people murmured about Bohemian Grove—a secretive retreat in California where elites like politicians and CEOs allegedly held weird rituals, including mock sacrifices to an owl statue. It sounded absurd, a fever dream of conspiracy buffs. Then, in 2000, Alex Jones snuck in and filmed the “Cremation of Care” ceremony, proving it happens. The meetings are real; what they mean—powerful networking or something darker—is still up for debate. It’s not a headliner like Watergate, but it’s verified and eerie.
These cases flew under the radar compared to the big-name conspiracies, yet they all started as dismissed theories before evidence—documents, testimony, or footage—proved them true. They’re snapshots of modern history where secrecy and power collided, only to be dragged into the light later!
1. 9/11 and Government Foreknowledge (2001)
Initial Dismissal: After the September 11, 2001 attacks, claims that the U.S. government had prior knowledge or was complicit were widely rejected as baseless conspiracy theories by officials and mainstream media.
Later Validation: The 9/11 Commission Report (2004) revealed significant intelligence failures, including missed warnings from agencies like the FBI and CIA. While it didn’t prove intentional involvement, it confirmed that critical information was overlooked, lending some credibility to theories of negligence or mishandling.
2. Iraq War and Weapons of Mass Destruction (2003)
Initial Dismissal: Before the 2003 invasion of Iraq, the idea that the U.S. and its allies exaggerated or fabricated evidence of weapons of mass destruction (WMDs) to justify war was dismissed as anti-government propaganda.
Later Validation: The Iraq Survey Group report (2004) found no active WMD programs, and subsequent inquiries, like the U.K.’s Chilcot Report (2016), confirmed that intelligence was flawed or manipulated, validating the core claim that the war’s premise was shaky.
3. Mass Surveillance Programs (2013)
Initial Dismissal: For years, suggestions that governments were conducting widespread surveillance of citizens via technology were brushed off as paranoid delusions.
Later Validation: Edward Snowden’s 2013 leaks exposed programs like PRISM, run by the NSA, showing that the U.S. and other governments were monitoring communications on an unprecedented scale, confirming the reality of mass surveillance.
4. Financial Crisis and Banking Misconduct (2008)
Initial Dismissal: Before the 2008 financial crisis, theories that major banks were engaging in reckless or fraudulent practices—like predatory lending and creating risky financial products—were often dismissed as exaggerated or alarmist.
Later Validation: The crisis exposed widespread misconduct, with investigations and settlements (e.g., the 2010 Dodd-Frank Act and billions in fines) confirming that banks had indeed acted irresponsibly, validating earlier suspicions.
5. COVID-19 Lab Leak Hypothesis (2020)
Initial Dismissal: Early in the COVID-19 pandemic, the notion that the virus originated from a lab in Wuhan, China, was labeled a conspiracy theory and dismissed by many scientists, media outlets, and organizations like the WHO.
Later Validation: By 2021, intelligence reports and scientific discussions (e.g., U.S. government assessments and WHO revisits) deemed the lab leak a plausible scenario, shifting it from fringe theory to a legitimate hypothesis, though conclusive evidence is still lacking.
6. Social Media Manipulation and Data Misuse (2018)
Initial Dismissal: Claims that social media platforms like Facebook were exploiting user data for political or financial gain were often downplayed as speculative before 2018.
Later Validation: The Cambridge Analytica scandal (2018) revealed that data from millions of users was harvested without consent and used to influence elections, confirming that such manipulation was occurring on a large scale.
#republicans#donald trump#jd vance#robert kennedy jr#tulsi gabbard#maga#democrats#joe biden#kamala harris#conspiracy theories#qanon conspiracy#conspiracy#mass media#fake news#propaganda#cia#nsa
131 notes
·
View notes