#Bomber Aircraft Operations
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
youtube
#youtube#militarytraining#2024#Whiteman Air Force Base#Night Operations#Aviation#Night Flight#Air Force#Fighter Jet#Advanced Warfare#Stealth Bomber#USAF#Air Force Base.#Warplane#Aircraft Operations#Military Aircraft#Bomber Aircraft#B-2 Spirit#Military Aviation#Bomber Aircraft Operations#Strategic Bomber#B-2 Stealth Bomber#Whiteman AFB#Military#Top Gun#Airplane#Night Ops#Stealth#Bomber#Aircraft
5 notes
·
View notes
Text

2 January 1967. 'MiG Sweep', by Keith Ferris, depicts “Olds 01” during Operation Bolo. McDonnell F-4C -21-MC Phantom II, s/no. 63-7680 flown by Colonel Robin Olds, USAF, with First Lieutenant Charles C. Clifton, USAF, as the Weapons System Operator.
@ron_eisele via X
#f-4c phantom#mcdonnell douglas aviation#fighter bomber#aircraft#usaf#aviation#vietnam war aircraft#cold war aircraft#operation bolo#Col Robin Olds
46 notes
·
View notes
Text

Douglas A-26 Invader - 609th Special Operations Squadron - South-East Asia - 1967
94 notes
·
View notes
Text

Fairey Albacore Mk I du 820 Naval Air Squadron opérant au large d'Alger depuis le porte-avions HMS Formidable – Opération Torch – Campagne d'Afrique du Nord – Novembre 1942
Photographe : Royal Navy official photographer
©Imperial War Museums - TR 296
#WWII#campagne d'afrique du nord#north african campaign#opération torch#operation torch#marine britannique#royal navy#820e escadron aéronaval#820 naval air squadron#aviation militaire#military aviation#bombardier-torpilleur#torpedo bomber#avion de reconnaissance#reconnaissance aircraft#fairey albacore#alger#algiers#algérie#algeria#11/1942#1942
9 notes
·
View notes
Text

The B-58 Hustler was the first operational bomber capable of sustained supersonic speeds. It could fly at Mach 2 (over 1,300 mph or 2,100 km/h), making it incredibly fast for its time and able to outrun most enemy aircraft and surface-to-air missiles.
510 notes
·
View notes
Text
December 3rd, 2031 – Sixty degrees, clear skies, and a nice southeasterly breeze. It was a beautiful day to lay siege to Dallas. It was a good thing the weather was nice, because everything else about the operation looked rough. Marian couldn’t wait.
Dallas was a classic Texan fortress-city, two rings of forty foot tall concrete walls with a killing field in between, bristling with anti-aircraft cannon. The ground-facing defenses were a little less thorough, but a few machine guns would make quick work of any infantry charge and Dallas had more than a few machine guns.
“We aren’t being paid enough,” Suzy griped. She was crouching in the shade, alternatingly blowing a bubble of gum and taking swigs out of a bottle whose contents were hidden by a paper bag.
“We’re mercenaries. Get used to it.” Marian hoisted her gun onto her shoulder. “Besides, they don’t exactly expect us to succeed.”
“Oh, are we leading a suicide charge? I wasn’t paying attention to the Duke.” Suzy was never paying attention, but the benefits of having her around outweighed the drawbacks. Most days, at least.
“Pretty much.”
“Did the guys we’re with know this was a suicide charge?”
Marion looked around at the Jeep the Duke of Austin had hastily assigned the duo to. The soldiers suddenly all looked a bit green around the gills. “I’m guessing not. Chin up, boys! Auntie Marian won’t let any harm come to you.”
One of the men, a lieutenant, managed to find his voice. “Why are we here?”
“The Duke hopes that we’ll die loud enough that Dallas won’t notice his bombers taking out the emplaced guns. Doesn’t strike me as very sound tactics, but hey, he’s got manpower to make up for what he lacks in brains.”
Silence in the back of the Jeep.
Marian continued, mostly to fuck with them. “And don’t think the tanks’ll be any help. See those big fancy guns up on the wall? Those are lonestar guns. You boys seen lonestar guns?”
“Yeah.”
“So you get the idea. But hey, cheer up! It’s not every day you get to storm the best-defended city in the state!”
The man slowly came to a revelation a long time coming. “You’re insane,” he said.
“Insane was my father’s name. Please, call me Marian Typhoon.”
Suzy cackled. “That was terrible.”
The soldiers looked between the two women, now realizing they were both mad. “How are you two so calm?”
Marian didn’t answer for a moment, looking out at the slowly-approaching walls of Dallas. The lonestar guns’ targeting algorithms would start flagging the vehicles soon. “Suzy, how far out are we?”
“About a mile and a half.” Suzy busied herself checking over her rifle.
“Now, boys, I’m gonna explain two concepts very quickly, so you’d best pay attention. The KL-90 fully automatic sniper rifle, sometimes called “Le Papillon,” was something of a failure, because for some reason those glorious Frenchmen decided to make it fire 1200 rounds per minute, giving it a tendency to dump the entire mag into one poor fucker. Only six were ever made, and nowadays they’re just museum pieces. In 2026, the American military plunged into the deep end of bioweaponry and concocted a little something known as the ‘vampire virus,’ which proved pretty damn lethal in 99.99% of cases. The 0.01% that survived were problematic enough that the program shut down, and all information about it was expunged from the record.”
Marion patted Suzy affectionately on the head. “Now you might be wondering how those two disparate pieces of information might happen to overlap, and if you boys just sit pretty for a moment I reckon you’ll be able to connect the dots. Suzy?”
The last surviving vampire, Suzy Nines, slotted the magazine into her KL-90 fully automatic sniper rifle, and squinted out at the Dallas walls. She squeezed the trigger, the barrel swinging into a wild blur of motion as the sound of gunfire filled the air. “Machine gunners down. Reloading.”
Marian patted the hapless lieutenant on the shoulder. “Come along, boys. Auntie Marian’s got a city to take.”
#ruin's architects#<- silly lil setting about a crew of superpowered mercenaries running around the shattered ruins of america having a good time#they get two more members later but idk if i'm going to actually write much of it#you get this bit tho!
223 notes
·
View notes
Text
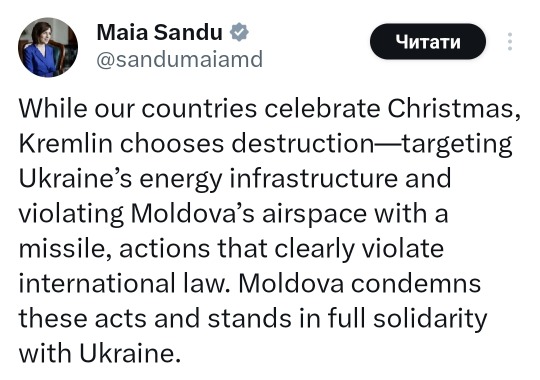
Merry Christmas?..
Today, on 25 December, the Russian occupiers launched another missile attack on Ukraine - the enemy again targeted critical infrastructure facilities: TPPs, CHPs, and power grids.
According to the command of the Ukrainian Air Force, 184 enemy air targets were recorded:
2 KN-23 ballistic missiles;
10 S-300/S-400 anti-aircraft guided missiles;
12 cruise Kalibr Missiles ;
50 X-101/X-55 cruise missiles from Tu-95MS strategic bombers;
4 X-59/X-69 guided missiles from tactical aircraft;
106 Shahed strike UAVs
The Ukrainian Air Defence Forces shot down 113 targets.
Kharkiv
The Russians launched 12 missiles at the city and targeted critical infrastructure: boiler houses, CHP plant, and electricity facilities.
So far, six people have been reported injured: five men and one woman.
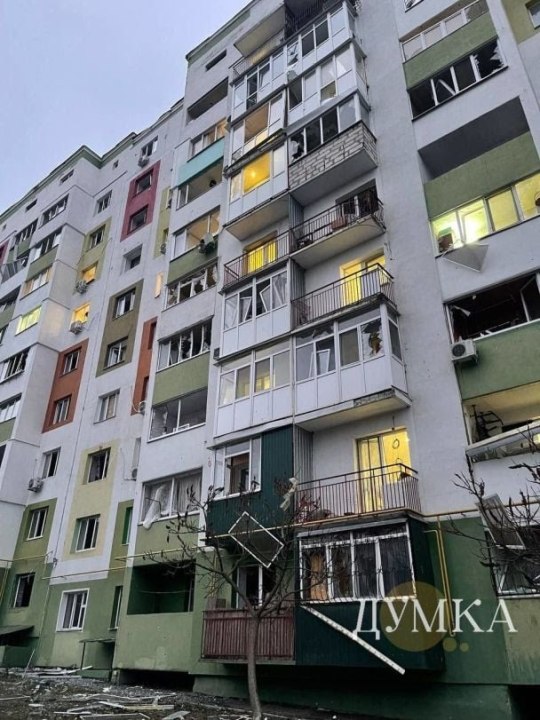




Ivano-Frankivsk
The enemy strike left part of the Carpathian region without power supply - residents of Kalush, Burshtyn and Ivano-Frankivsk were without electricity.
Dnipro
The Ukrainian Air Defense Forces shot down 42 enemy missiles over the Dnipro region.
The missile attack damaged infrastructure in Dnipro. Unfortunately, a TPP worker, 51-year-old Dmitry Petlenko, was killed. His body was found under the rubble.
The windows of a nine-story building were also smashed, and a private house was damaged. An outbuilding caught fire, and rescuers extinguished the fire.

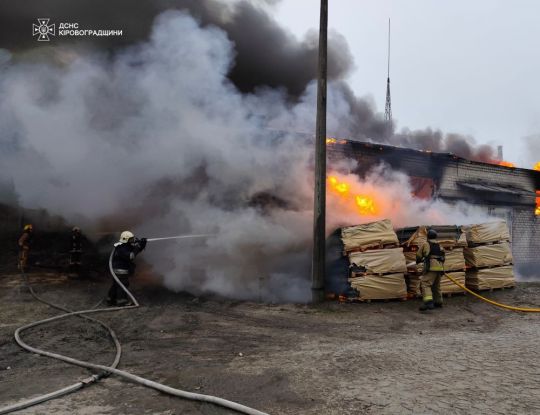
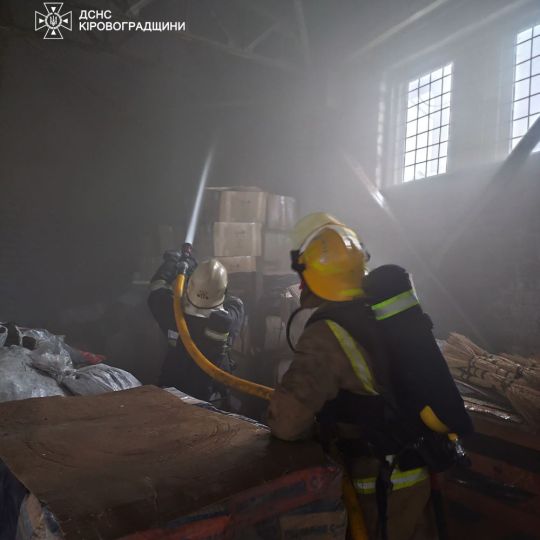
Kirovohrad region
Critical infrastructure in the Kirovohrad region was also targeted by the Russians.
The falling debris caused a fire in a warehouse.
As a result of the strike, the pumping stations of the Dnipro-Kirovohrad water pipeline were de-energized.


Vinnytsia region
At night, the enemy attacked the energy infrastructure. There is damage. As of the morning, thanks to the coordinated work of power engineers, all consumers are supplied with electricity.
Kyiv region
The air alert in the Kyiv region lasted all night. Air defense forces were working in the region. Some enemy targets were shot down. Fortunately, no people were hurt.
As a result of the falling debris of downed enemy targets in two districts of the region, 12 trucks, a cafe and three private houses were damaged.
Kryvyi Rih
An enemy missile strike killed one person and injured 17 others, including two children, the State Emergency Service of Ukraine reports.

"This is definitely not a global war"
Meanwhile, Poland again sent its military aircraft into the sky. As noted by the Operational Command of the Polish Armed Forces, this step was taken “because of the Russian air attack, which can hit objects located in the West of Ukraine, among other things.”
In addition, one of the Russian missiles entered Ukraine through the airspace of Moldova.
At 07:24, the Ukrainian Air Force reported a cruise missile flying toward Chernivtsi from Moldova. At the same time, monitoring Telegram channels claim that the Russian missile flew about 140 kilometers through the territories of Moldova and Romania.
Не забуваймо, завдяки кому ми зустрічаємо цьогоріч Різдво.
Слава Україні!
Героям слава!
Слава нації!
Смерть ворогам!
78 notes
·
View notes
Text
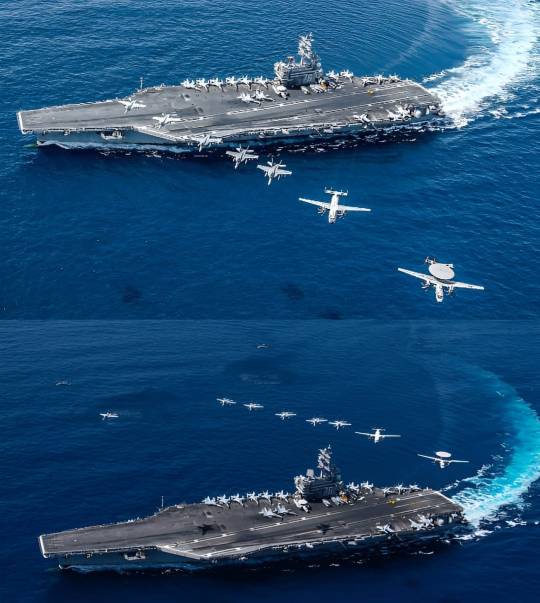

How powerful is a U.S. aircraft carrier?
A U.S. Navy aircraft carrier is a large warship designed to serve as a mobile airbase for naval aviation. It is the centerpiece of a carrier strike group (CSG) and plays a crucial role in projecting power, protecting maritime interests, and providing humanitarian assistance worldwide.
Key features of a U.S. Navy aircraft carrier include:
Flight Deck: The carrier's flight deck is where aircraft take off and land. It is equipped with catapults for launching fixed-wing aircraft and arresting gear to catch aircraft on landing. The flight deck is one of the busiest and most dangerous places on the ship during flight operations.
Hangar Deck: Below the flight deck is the hangar deck, where aircraft are stored, maintained, and prepared for flight operations. It provides sheltered storage for aircraft and equipment, as well as maintenance facilities and workshops.
Air Wing: The carrier's air wing typically consists of a mix of fighter jets, bombers, reconnaissance aircraft, early warning aircraft, and helicopters. These aircraft provide offensive and defensive capabilities, including strike missions, air superiority, surveillance, and search and rescue.
Command and Control Center: Aircraft carriers serve as command centers for naval task forces, with advanced communication and information systems to coordinate operations. They have the capability to direct air, surface, and subsurface assets in complex operations.
Defense Systems: Carriers are equipped with a variety of defense systems to protect against threats such as enemy aircraft, missiles, and submarines. These include radar systems, anti-aircraft missiles, close-in weapon systems, and electronic warfare capabilities.
Overall, U.S. Navy aircraft carriers are among the most powerful and versatile warships in the world, capable of projecting power, maintaining presence, and providing support in a wide range of military operations.
84 notes
·
View notes
Text

410th Bomb Wing, Desert Storm, 1991
A B-52G Stratofortress bomber aircraft of the 410th Bomb Wing, K.I. Sawyer Air Force Base, Mich., armed with Mark 82 500-pound bombs on the wing pylons, takes off from an air base during Operation Desert Storm.
... moins
41 notes
·
View notes
Text
youtube
#youtube#militarytraining#usmilitary#B-52 Stratofortress#aerial operations#defense operations#military news#homeland defense#airpower#defense strategy#global security#aviation#air force#bomber squadron#US Air Force#Cold War legacy#strategic bomber#military aircraft#military aviation#military mission#military aircraft video#B-52
3 notes
·
View notes
Text

@Harryelsucio via X
#f-4c phantom#mcdonnell douglas aviation#fighter bomber#aircraft#usaf#aviation#vietnam war aircraft#cold war aircraft#operation bolo
40 notes
·
View notes
Text

Flying Officer B.P. “Squirrel” Nutkin of 266 Squadron RAF, seen here in a Hawker Hurricane Mk I flown by 266 during the Fall of France.
As the British Expeditionary Force were driven back by Guderian’s Blitzkrieg, 266 was badly mauled while keeping Luftwaffe bombers away from the Dunkirk beaches, losing enough Hurricanes that it re-equipped with the Supermarine Spifire Mk Ia just in time for the Battle of Britain.
Nutkin, resisting what was already becoming known as "Spitfire Snobbery", was one of the last 266 Squadron pilots to convert from his Hurricane. This snapshot, therefore, must have been taken at some time in mid-June 1940, between the end of Operation Dynamo on 4th June and the official start of the Battle of Britain on 10th July.
*****
It was during the BEF’s final withdrawal from Dunkirk that Flying Officer Nutkin, already with two kills to his credit, made ace in an afternoon and won his first DFC.
He was section leader of Red Section - comprising himself, Pilot Officer Tom E. Brock and Pilot Officer J.R.M.E. Fisher - providing top cover for the evacuation, when on 2nd June 1940 they found themselves up-sun from a raid directed against several of the “Little Ships” (civilian vessels with volunteer crews).
Red Section executed a perfect “bounce” that caught the enemy completely off guard, six Luftwaffe aircraft were shot down, and Nutkin personally accounted for two Junkers Ju.87-B Stuka dive-bombers as well as one Messerschmitt Bf.109-E4 from their escort.


(Representative images, not actual footage)
“Squirrel” Nutkin finished his RAF service in 1946 with the rank of Wing Commander. It’s widely believed he was promoted no higher after saying “Nuts!” to Air Vice-Marshal Trafford Leigh-Mallory, even though this turned out not to have been an insult, merely a misheard comment about which bar snacks were running short in the Officers' Mess.
Regardless of explanation, Leigh-Mallory - always notoriously pompous about his own image and reputation - made a disparaging entry in Nutkin’s file and refused to amend it. His later death in an accident meant the unwarranted black mark was never deleted.
This didn't concern post-war fledgling new airline BEA (British European Airways), and Nutkin joined them directly he left the Air Force…

…going on to become one of their senior captains before transferring to Transatlantic service with BOAC (British Overseas Airways Corporation).


During a layover in New York he met and later married Cicely van Gopher of the New Hampshire van Gophers, and on retirement from flying made a fortune in forestry.
“Some people can’t see the wood for the trees, but for some reason I'm quite good at both.”
106 notes
·
View notes
Text

1942 11 09 Morocco, Operation Torch, Clawed by a Wildcat - Roy Grinnell
https://mikesresearch.com/2022/03/27/air-battle-over-morocco-1942/
November 9 The battered but plucky pilots of GC II/5 were airborne at dawn with only five aircraft. They strafed landing craft at Fedhala and received such intense US Navy AA fire that three of the French Hawks were damaged severely, although all the planes returned.At 0645 hours, Tom Booth leading 7 Red Ripper Wildcats took off from the RANGER bound for Port Lyautey. John Raby’s VF-9 was close behind with eight F4F-4s ordered to patrol over Fedhala. The VF-41 pilots were straining to locate enemy targets and waiting for some direction when an air control officer with US troops radioed that a lone French plane was strafing them. Tom Booth replied to the distress call but was immediately countermanded by the ship and ordered to attack an enemy transport column on the Fedhala-Casablanca Road. In screaming dives, the Wildcats descended on the enemy truck convoy spraying it with .50 Cal machine gun fire. Booth ordered the stubby Wildcats to strafe the column again. While pulling up, they observed 6 to 8 trucks burning and another half dozen sitting at odd angles in the ditches along the chaotic road.John Raby’s VF-9 had barely reached their patrol altitude at 10,000 feet when French aircraft were spotted. A motley group of 15 LeO 451s, DB-7s and Martin 167s had just bombed landing craft on the Fedhala beachhead from high altitude with poor results. They were escorted by 16 Hawk 75s from GC I/5. Without the slightest hesitation, Raby led his 8 Wildcats against the enemy force. The French bombers got away as the fighters became embroiled in a massive dogfight.In the air battle, Wildcats and Hawks alternately became the hunter and were the hunted. The French fought and flew courageously, but the Curtiss fighters were unable to cause decisive damage to the Wildcats. On the other hand, the six .50 Cal machine guns of the F4F-4s had a devastating effect on the French fighters. Some of the French pilots had out flown the Wildcats, but they did not ready had a chance. The main reason may have been that their aerial combat tactics were those from WWI. Four planes of the Champagne Escadrille were destroyed, two pilots KIA and two other survived crash landings. Another four Hawks were damaged. VF-9 claimed 5 destroyed and 4 probables.
24 notes
·
View notes
Text

• Satoru Anabuki (Japanese IJAAF Ace)
Lieutenant Colonel Satoru Anabuki 穴吹 智, Anabuki Satoru, was depending on the source, the second or third highest-scoring flying ace of the Imperial Japanese Army Air Force in World War II, with 39 victories (51 claimed).
Born into a farming family in the Kagawa Prefecture, he graduated high school to take the entrance examination for the Juvenile Flying Soldier School and entered the Tokyo Army Aviation School in April 1938, In Oct 1940, he was enrolled in Tachi'arai flight school in Fukuoka Prefecture graduating in March 1941 in the 6th Juvenile Soldier Course and receiving a promotion to corporal in October. He was assigned to the 3rd Company of the 50th Air Squadron, stationed on Formosa in 1941. With the outbreak of the Pacific War, he fought in the conquest of the Philippines, where he claimed his first victory, a Curtiss P-40, on December 22nd, 1941 flying a Ki-27 aircraft. On February 9th, 1942, he shot down two more.
He returned to Japan with his squadron in Apr 1942, where the squadron was re-equipped with Ki-43 Hayabusa aircraft; Anabuki named his new fighter "Fubuki", partially based on his own surname. In Jun 1942, his squadron was transferred to Burma, where he would see combat over Burma, India, and southwestern China. He was promoted to the rank of sergeant in Dec 1942. On December 20th, 1942, he shot down a Blenheim bomber over Magwe, Burma, the first of many bomber victories. On December 24th, he shot down three British Hurricane fighters in combat over Magwe, Burma. In May 1943, he received a new Ki-43 fighter; he named this new aircraft "Kimikaze" after his wife Kimiko. He was seriously wounded in combat while flying "Kimikaze" over Rangoon, Burma on October 8th, 1943; after initial recuperation, he was transferred to the Akeno Army Flying School in Ibaraki Prefecture, Japan in Feb 1944.
In late 1944, after being cleared to fly once again, he shot down four US F6F Hellcat fighters over Takao, Taiwan and the Philippine Islands while ferrying Ki-84 Hayate fighters from Japan southwards. In December 1944, he was promoted to the rank of sergeant major. In the final months of the war, he was an instructor at Akeno with frequent combat assignments; in this role, he scored his 39th and final confirmed victory (53rd claimed victory), a B-29 bomber, over Japan while flying a Ki-100 fighter. After the war, he joined the Police Reserve in 1950, eventually reaching the rank of captain. Later, he joined the Japan Ground Self-Defense Force, becoming a helicopter pilot stationed in northeastern Japan; he retired from his military career in 1971 at the rank of lieutenant colonel. He worked for Japan Airlines before retiring in 1984. Many of Anabuki's victory claims during the Burma Campaign have been contested by comparing them to Allied records of lost aircraft on particular occasions. In several cases, there were no records of Allied planes even operating in the area where the claims were made. Anabuki passed away on an unknown date in June of 2005 at the age of 83 years old.
#second world war#world war 2#world war ii#wwii#military history#aviation#aviation history#ww2 aces#japanese history#imperial japan#airforce history
29 notes
·
View notes
Text

Humans are weird: Hubris before the fall
( Please come see me on my new patreon and support me for early access to stories and personal story requests :D https://www.patreon.com/NiqhtLord Every bit helps)
A decade ago there was a powerful world by the name of Oma that was the crown jewel of the Omak Domain. Rich with natural resources and rare metals, it was able to establish a powerful trade network that generated billions of credits monthly leading to the people of Oma to grow fat with decadence. This led to a rapid degradation of their societal values to such an extent that they believed that they and only they were truly worthy of running galactic trade and began pressuring their neighboring governments to relinquish trade control of their domains to them.
When they finally approached the humans they sent forth a trade delegation to their parliament. This delegation did not present a sympathetic view of their stewardship, nor a presentation outlining the benefits of their management skills in intergalactic trade. No; this delegation strode into the terran parliament and denounced human trade standards as inferior and unworthy implementation between galactic powers.
No strangers to prideful boasting, the humans naturally took great offense to the grand standing of the delegation and cast them out without even hearing their full proposal. In response, the Oma began sanctioning the terran domain; isolating its trade routes and starving it off much needed resources.
For months the human diplomats tried to reach out to the Oma to find a political solution, but each attempt was met with the repeated message “Submit”.
As time passed and riots began to break out across human worlds from the lack of materials, the terran government finally had enough and dispatched a war fleet to Oma. The fleet was comprised of nearly three fifths of their entire naval power and was spear headed by the latest Herald class battleship “Saladin” with the equally famous Admiral Timmins in command.
Being comprised of mainly trade ships; the Omak Domain navy was primarily built around fast moving frigates, destroyers, and smaller patrol craft capable of catching pirates that preyed upon their shipping lanes. They were little more than a speed bump to the well-disciplined prowess of terran armada and was swept aside easily as the human ships made for orbit directly above Oma. Yet even with this encroaching ring of steel the Oma public did not panic.
Unlike their navy, the Omak Domain’s ground forces were substantially better in comparison. They had fought many ground wars to secure trade outposts, mining operations, and subjugation camps and were thusly made up of a hardened collective of veteran soldiers and automated war machines that were capable to five terran soldiers. So when the human fleet finally did position itself in orbit above Oma, the Omak military was confident they would repel any invasion attempts made by the humans; even going so far as to openly mock Admiral Timmins in a direct communique that not one human soldier would live to set foot on their world.
To their surprise Admiral Timmins agreed to those terms and began the battle.
From the launch bays of every terran ship came hundreds of heavily armed fighters, bombers, drones, and reconnaissance craft that swarmed through Oma’s atmosphere. Not a single lander or ground soldier was deployed as the Admiral coordinated a planet wide devastating air campaign of destruction.
The Omak air force was overwhelmed in a matter of hours by the constant waves of enemy aircraft and found itself further crippled as their launch sites were surgically struck from orbit by human warships. When the last of the Omak air power was expended the human air power had complete control over the skies of the planet.
Civilian targets such as cities and towns were ignored; but the precious foundries, factories, and mining complexes that had given the Omak people such wealth were reduced to little more than burnt pieces of metal and ash. The Omak rulers watched as their life blood of commerce was taken from them one continent at a time and sent countless messages to the human fleet for peace. Their reply was always a single word that none of the Omak would agree to.
“Submit.”
By a month’s end the world of Oma was little more than a smoldering crater. Gleaming cities now stood as silent watchers over miles of burnt landscapes and wasted industrial complexes. The people who had only known wealth and power were now left to wander the ruins of their former trade empire as the human fleet still held orbit over the world. Fragments of the Omak Domain attempted to bypass the human fleet to deliver supplies but each attempt was met with the humans either seizing the ship and the valuable cargo or destroying it just as it was about to land.
It didn’t take long for the previously subjugated peoples that had relinquished control to the Omak to begin rising up once more and regaining their sovereignty. Some the newly freed powers sent their own delegations to the human fleet and kneeled before Admiral Timmins; thanking the humans for bringing their oppressors low. Each time the Admiral would thank the aliens and invite them to the viewing decks so they could look down at the burnt world that had once held them so firmly under its thumb.
In a way it was both a gesture of friendship and a warning to all those that would come after; that the realms of man would never take kindly to the hubris of fools.
#humans are space oddities#humans are space orcs#humans are insane#humans are weird#scifi#story#writing#original writing#niqhtlord01#ai generated art#bing image creator
99 notes
·
View notes
Text

1942 06 04 Midway IJN Aircraft Carrier Akagi vs B-26 Marauder - Randall Wilson
Having taken off prior to the Japanese attack, American bombers based on Midway made several attacks on the Japanese carrier force. These included (…) four USAAF B-26s of the 18th Reconnaissance and 69th Bomb Squadrons armed with torpedoes.
One B-26, piloted by Lieutenant James Muri, after dropping his torpedo and searching for an escape route, flew directly down the length of Akagi while being fired upon by fighters and anti-aircraft fire, which had to hold their fire to avoid hitting their own flagship; the B-26 strafed Akagi, killing two men. Another B-26, piloted by Lieutenant Herbert Mayes, did not pull out of its run after being seriously damaged by anti-aircraft fire, and instead flew directly at Akagi's bridge. Either attempting a suicide ramming or out of control, the plane narrowly missed striking the bridge, which could have killed Nagumo and his staff, crashing into the ocean. This experience may well have contributed to Nagumo's determination to launch another attack on Midway in direct violation of Yamamoto's order to keep the reserve strike force armed for anti-ship operations.
28 notes
·
View notes