#Big Data Security Market
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Big Data Security Market to be Worth $60.1 Billion by 2031
Meticulous Research®—a leading global market research company, published a research report titled, ‘Big Data Security Market by Component (Solutions [Data Encryption, Security Intelligence, Data Backup & Recovery], Services), Deployment Mode, Organization Size, End User (IT & Telecom, BFSI, Retail & E-commerce), and Geography - Global Forecast to 2031.’
According to this latest publication from Meticulous Research®, the big data security market is projected to reach $60.1 billion by 2031, at a CAGR of 13.2% from 2024 to 2031. The growth of the big data security market is driven by the emergence of disruptive digital technologies, the increasing demand for data security and privacy solutions due to the rise in data breaches, and the growing data generation in the e-commerce industry. However, the high implementation costs of big data security solutions restrain the growth of this market.
Furthermore, the growing need for cloud-based security solutions and the increasing integration of AI, ML, and blockchain technologies in security solutions are expected to generate growth opportunities for the stakeholders in this market. However, the lack of knowledge about big data security solutions and the shortage of skilled IT professionals are major challenges impacting the growth of the big data security market.
The big data security market is segmented by component (solutions [data discovery and classification, data encryption {data protection, tokenization, data masking, other data encryption solutions}, security intelligence, data access control & authentication, data governance & compliance, data backup & recovery, data auditing & monitoring, other solutions], services [professional services, managed services]), deployment mode (on-premise deployments, cloud-based deployments), organization size (large enterprises, small & medium-sized enterprises), end user (IT & telecom, healthcare & pharmaceutical, BFSI, retail & e-commerce, energy & utilities, government, manufacturing, media & entertainment, transportation & logistics, and other end users). The study also evaluates industry competitors and analyzes the market at the regional and country levels.
Based on component, the big data security market is segmented into solutions and services. The solutions segment is further segmented into data discovery and classification, data encryption, security intelligence, data access control & authentication, data governance & compliance, data backup & recovery, data auditing & monitoring, and other solutions. In 2024, the solutions segment is expected to account for the larger share of the big data security market. The large market share of this segment is attributed to the increasing concerns regarding data security and privacy, the increasing adoption of data security solutions by SMEs, and the rising demand for encryption solutions for data protection across IoT devices. Big data security solutions include tools and measures to process or safeguard data and analytics processes. In March 2024, CrowdStrike, Inc. (U.S.) partnered with Rubrik, Inc. (U.S.) to transform data security solutions and stop breaches of critical information. Moreover, this segment is also projected to register the highest CAGR during the forecast period.
Based on deployment mode, the big data security market is segmented into on-premise deployments and cloud-based deployments. In 2024, the on-premise deployments segment is expected to account for the larger share of the big data security market. The large market share of this segment is attributed to the higher preference for on-premise deployments among large enterprises and increasing data generation in large enterprises. The on-premise model of deployment is majorly adopted by well-established and large companies that are capable of making capital investments toward the required hardware and hosting environments. In addition, these organizations also have sufficient in-house IT expertise to maintain software efficiency. Internal big data security is one of the major benefits of on-premise deployments.
However, the cloud-based deployments segment is projected to register the higher CAGR during the forecast period. The growth of this segment is driven by the rapid evolution of new security avenues for cloud-based deployments, the superior flexibility offered by cloud-based deployments, and the increase in security breaches. Cloud-based security solutions provide social networking privacy, system optimization, online storage, regulatory compliance, and connected device security. The adoption of cloud computing and storage systems is gaining popularity among small and medium-scale enterprises, supporting the growth of this segment.
Based on organization size, the big data security market is segmented into large enterprises and small & medium-sized enterprises. In 2024, the large enterprises segment is expected to account for the larger share of the big data security market. The large market share of this segment is attributed to the strong IT infrastructure of large enterprises, the growing adoption of advanced technologies such as AI, IoT, and blockchain, and the availability of skilled IT personnel to manage data security platforms. With larger budgets and a keen focus on developing strategic IT initiatives, large enterprises have a competitive advantage over small and medium-scale enterprises in terms of technology adoption. Large enterprises have a stable financial backup and can easily procure customized data security solutions, contributing to this segment's growth.
However, the small & medium-sized enterprises segment is projected to register the higher CAGR during the forecast period. The growth of this segment is driven by increasing digital transformation, government initiatives to promote security solutions, and the rising incidence of data breaches. SMEs are also increasingly becoming targets of cybercrime and therefore adopting suitable and strong security solutions.
Based on end user, the big data security market is segmented into IT & telecom, healthcare & pharmaceutical, BFSI, retail & e-commerce, energy & utilities, government, manufacturing, media & entertainment, transportation & logistics, and other end users. In 2024, the IT & telecom segment is expected to account for the largest share of the big data security market. The large market share of this segment is attributed to the increasing data breaches in IT companies as they store a vast amount of customer data, strict regulatory compliance forcing companies to implement stricter data security measures, and the increasing adoption of cloud-based solutions in the IT industry. In March 2023, IBM Corporation (U.S.) collaborated with Cohesity, Inc. (U.S.) to address increased data security and resiliency issues in hybrid cloud environments. With this collaboration, IBM launched its new IBM Storage Defender solution, including Cohesity's data protection, cyber resilience, and data management capabilities in the offering.
However, the healthcare & pharmaceutical segment is projected to register the highest CAGR during the forecast period. The growth of this segment is driven by the rising adoption of telemedicine devices and remote healthcare services, growing cyberattacks on connected devices, and the increasing demand for secure medical connected devices. A vast amount of medical data is generated in the healthcare sector. It is stored to improve patient outcomes, personalize treatment plans, and develop new drugs, among other applications. However, this sensitive data requires robust security measures to protect patient privacy and prevent unauthorized access. In November 2021, Armis, Inc. (U.S.) partnered with Nuvolo (U.S.) to improve data interoperability and the overall risk posture of healthcare organizations.
Based on geography, the big data security market is segmented into North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and the Middle East & Africa. In 2024, North America is expected to account for the largest share of the big data security market. The market growth in North America is driven by the presence of prominent players offering advanced big data security solutions & services, the early adoption of disruptive technologies, and growing awareness regarding data security. North America is home to several major players that provide products and services to improve big data security measures for IT assets, data, and privacy across different domains. Thus, big data security companies operating in the North America region are investing heavily in R&D activities to develop new & advanced security solutions that can address rising security challenges. In February 2024, Cyberhaven, Inc. (U.S.) launched Linea AI, an AI platform designed to combat the critical insider risks threatening vital corporate data.
However, the Asia-Pacific region is projected to record the highest CAGR during the forecast period. The growth of this market is driven by the growing data breaches, supportive government initiatives, and growing awareness regarding data security among small and medium-scale organizations. In December 2023, Safetica a.s. (U.S.) partnered with Kaira Global (Singapore) to deliver Safetica's Data Loss Prevention (DLP) solutions for enterprises of all sizes to safeguard their data against insider risks and data breaches in Singapore. APAC is the fastest-growing big data security market due to rapid investments in IT infrastructure, extensive use of the Internet, and growing security challenges.
Key Players
The key players operating in the big data security market are Check Point Software Technologies, Ltd. (Israel), Cisco Systems, Inc. (U.S.), Fortinet, Inc. (U.S.), Oracle Corporation (U.S.), IBM Corporation (U.S.), Microsoft Corporation (U.S.), Hewlett Packard Enterprise Development LP (U.S.), Intel Corporation (U.S.), Palo Alto Networks, Inc. (U.S.), Thales Group (France), Juniper Networks, Inc. (U.S.), Broadcom, Inc. (U.S.), Dell Technologies, Inc. (U.S.), CyberArk Software Ltd. (U.S.), and Rapid7, Inc. (U.S.).
Download Sample Report Here @ https://www.meticulousresearch.com/download-sample-report/cp_id=4984
Key Questions Answered in the Report:
What are the high-growth market segments in terms of the component, deployment mode, organization size, and end user?
What is the historical market size for the global big data security market?
What are the market forecasts and estimates for 2024–2031?
What are the major drivers, restraints, opportunities, challenges, and trends in the global big data security market?
Who are the major players in the global big data security market, and what are their market shares?
What is the competitive landscape like?
What are the recent developments in the global big data security market?
What are the different strategies adopted by major market players?
What are the trends and high-growth countries?
Who are the local emerging players in the global big data security market, and how do they compete with the other players?
Contact Us: Meticulous Research® [email protected] Contact Sales- +1-646-781-8004 Connect with us on LinkedIn- https://www.linkedin.com/company/meticulous-research
#Big Data Security Market#Big Data Security Management#Big Data Security and Privacy#Big Data Security Technologies#Big Data Security Solutions#Big Data Security Platform
0 notes
Text
Unveiling the Machine Learning Market Dynamics: The AI Evolution
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is an emerging technology transforming how businesses and people operate. Through the development of several digital services and products, as well as supply chain optimization, these technologies have revolutionized the consumer experience. Machine Learning (ML), one of the AI approaches, is gaining a lot of momentum in the industry due to its quick progress. This facilitates the expansion of the machine learning market globally. While some startups concentrate on solutions for specialized domains, numerous technology firms invest in this area to create AI platforms.
Significant growth in the information technology (IT) sector is driving the global market. Along with this, the rise in cyberattacks and data thefts worldwide has prompted many businesses to invest heavily in deploying effective security systems, which is boosting market growth. The widespread integration of machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence (AI) technologies with big data security solutions, is positively impacting market growth. Continuous technological advancements are creating a positive market outlook.
ML-powered recommendation engines and personalized services enhance customer experience and engagement, driving demand in various consumer-centric industries. ML technologies enable automation of processes, predictive analytics, and improved decision-making, enhancing operational efficiency and reducing costs for businesses.
Players have used partnerships, joint ventures, agreements, and expansions. They are producing new products with faster speeds and improved features to broaden their portfolio and maintain a dominant market position. Market players focus on hybrid models combining different ML techniques and federated learning approaches that enable training models across distributed networks without centralizing data.
1 note
·
View note
Text
The big data security market is forecasted to be worth US$ 20,418.4 million in 2023 and is projected to increase to US$ 72,652.6 million by 2033. Sales of big data security are anticipated to experience substantial growth, with a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 13.5% throughout the forecast period.
0 notes
Text
The big data security market is projected to be valued at US$ 20,418.4 million in 2023 and is expected to rise to US$ 72,652.6 million by 2033. The sales of big data security are expected to record a significant CAGR of 13.5% during the forecast period.
Storing personal data securely, in this fast-paced world has become the most daunting task for big organizations today. Especially with the advancements in technology even the cyber security attacks are becoming sophisticated day by day, eluding all the traditional security tools, leading to demand for advanced protection techniques such as Big Data security.
0 notes
Text
#Big Data Security Market#Big Data Security Market size#Big Data Security Market share#Big Data Security Market trends#Big Data Security Market analysis#Big Data Security Market forecast#Big Data Security Market outlook
0 notes
Text
Abathur

At Abathur, we believe technology should empower, not complicate.
Our mission is to provide seamless, scalable, and secure solutions for businesses of all sizes. With a team of experts specializing in various tech domains, we ensure our clients stay ahead in an ever-evolving digital landscape.
Why Choose Us? Expert-Led Innovation – Our team is built on experience and expertise. Security First Approach – Cybersecurity is embedded in all our solutions. Scalable & Future-Proof – We design solutions that grow with you. Client-Centric Focus – Your success is our priority.
#Software Development#Web Development#Mobile App Development#API Integration#Artificial Intelligence#Machine Learning#Predictive Analytics#AI Automation#NLP#Data Analytics#Business Intelligence#Big Data#Cybersecurity#Risk Management#Penetration Testing#Cloud Security#Network Security#Compliance#Networking#IT Support#Cloud Management#AWS#Azure#DevOps#Server Management#Digital Marketing#SEO#Social Media Marketing#Paid Ads#Content Marketing
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Nope now it’s at the point that i’m shocked that people off tt don’t know what’s going down. I have no reach but i’ll sum it up anyway.
SCOTUS is hearing on the constitutionality of the ban as tiktok and creators are arguing that it is a violation of our first amendment rights to free speech, freedom of the press and freedom to assemble.
SCOTUS: tiktok bad, big security concern because china bad!
Tiktok lawyers: if china is such a concern why are you singling us out? Why not SHEIN or temu which collect far more information and are less transparent with their users?
SCOTUS (out loud): well you see we don’t like how users are communicating with each other, it’s making them more anti-american and china could disseminate pro china propaganda (get it? They literally said they do not like how we Speak or how we Assemble. Independent journalists reach their audience on tt meaning they have Press they want to suppress)
Tiktok users: this is fucking bullshit i don’t want to lose this community what should we do? We don’t want to go to meta or x because they both lobbied congress to ban tiktok (free market capitalism amirite? Paying off your local congressmen to suppress the competition is totally what the free market is about) but nothing else is like TikTok
A few users: what about xiaohongshu? It’s the Chinese version of tiktok (not quite, douyin is the chinese tiktok but it’s primarily for younger users so xiaohongshu was chosen)
16 hours later:
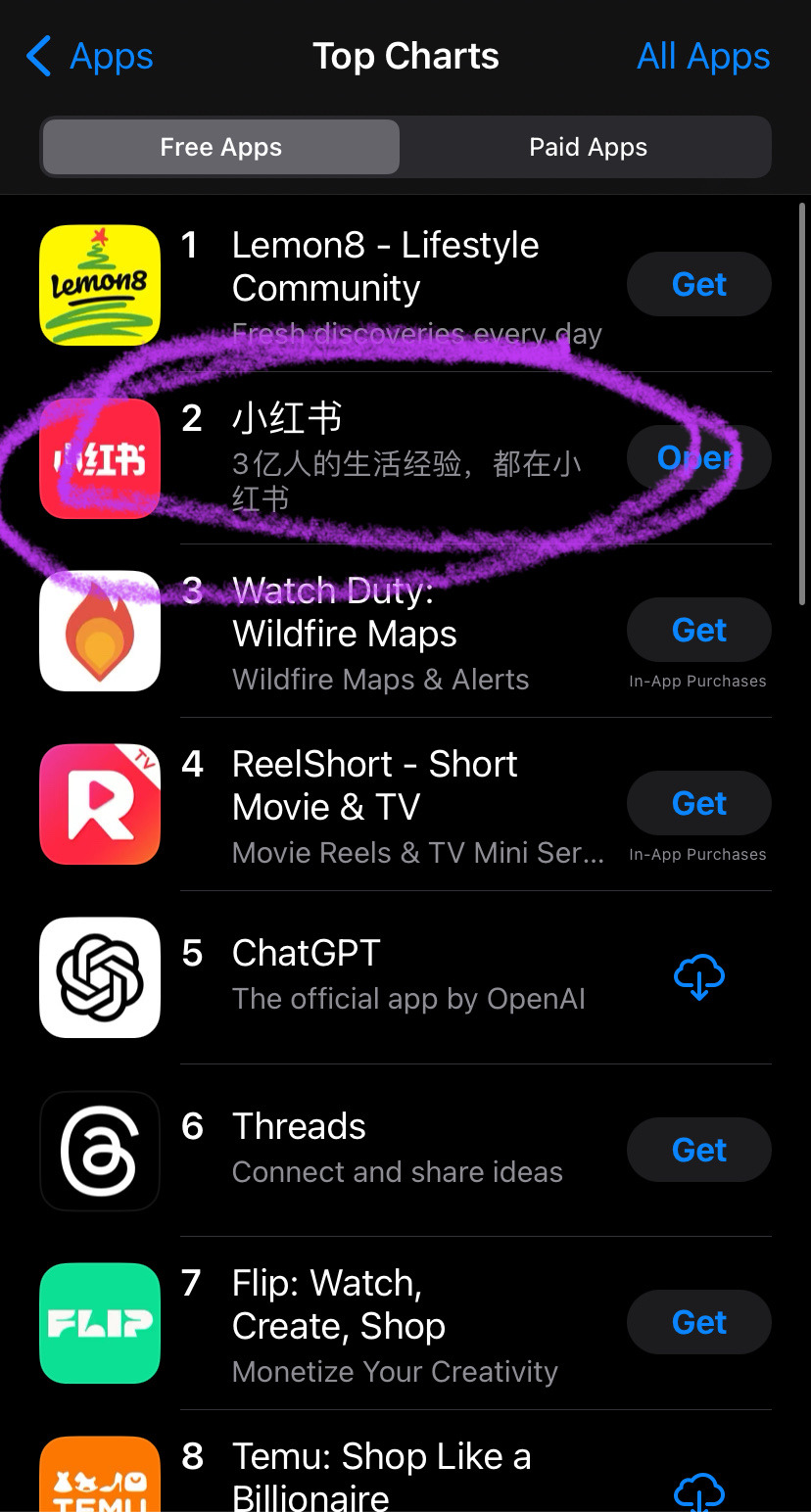
Tiktok as a community has chosen to collectively migrate TO a chinese owned app that is purely in Chinese out of utter spite and contempt for meta/x and the gov that is backing them.
My fyp is a mix of “i would rather mail memes to my friends than ever return to instagram reels” and “i will xerox my data to xi jinping myself i do not care i share my ss# with 5 other people anyway” and “im just getting ready for my day with my chinese made coffee maker and my Chinese made blowdryer and my chinese made clothing and listening to a podcast on my chinese made phone and get in my car running on chinese manufactured microchips but logging into a chinese social media? Too much for our gov!” etc.
So the government was scared that tiktok was creating a sense of class consciousness and tried to kill it but by doing so they sent us all to xiaohongshu. And now? Oh it’s adorable seeing this gov-manufactured divide be crossed in such a way.
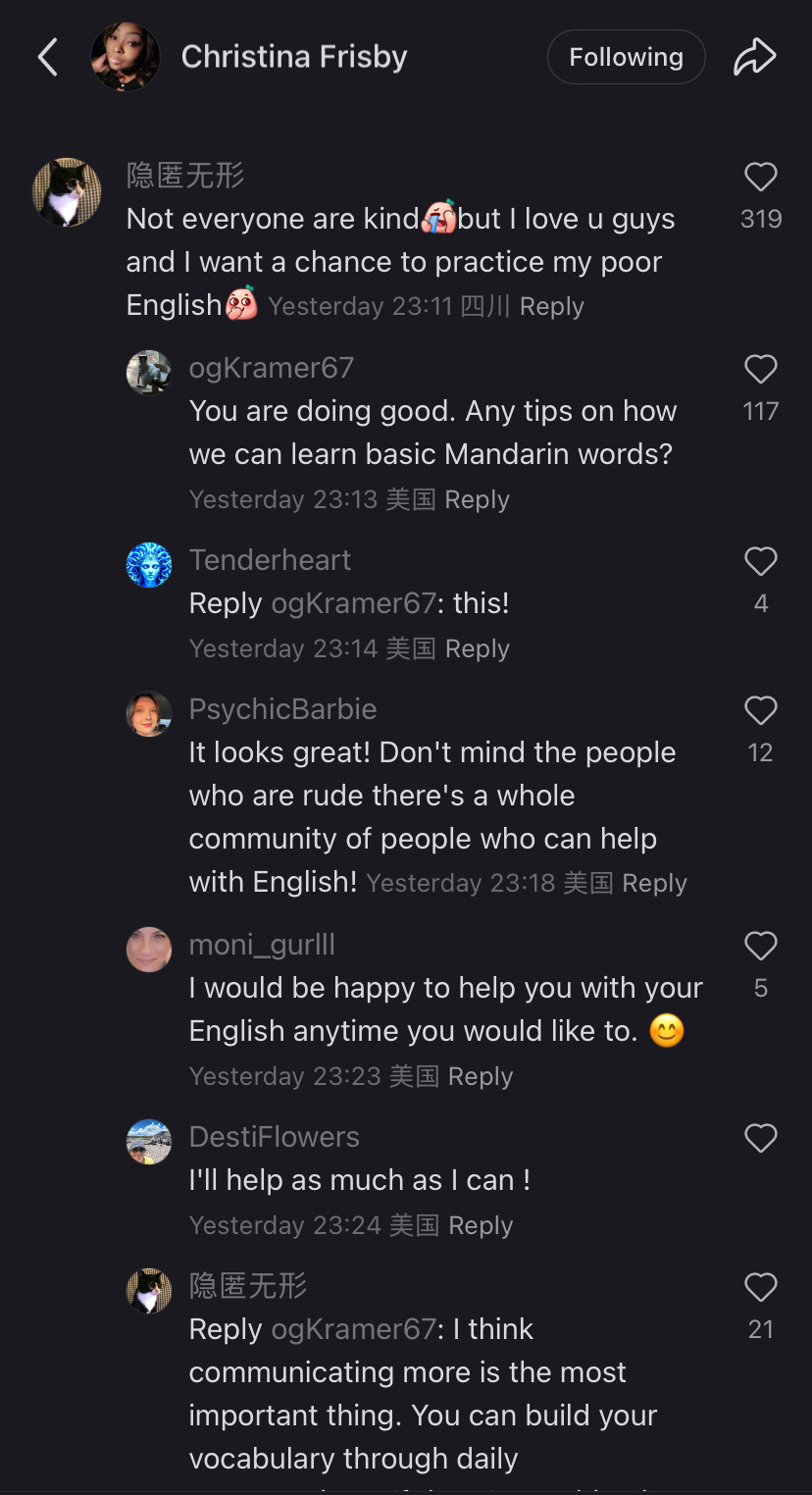
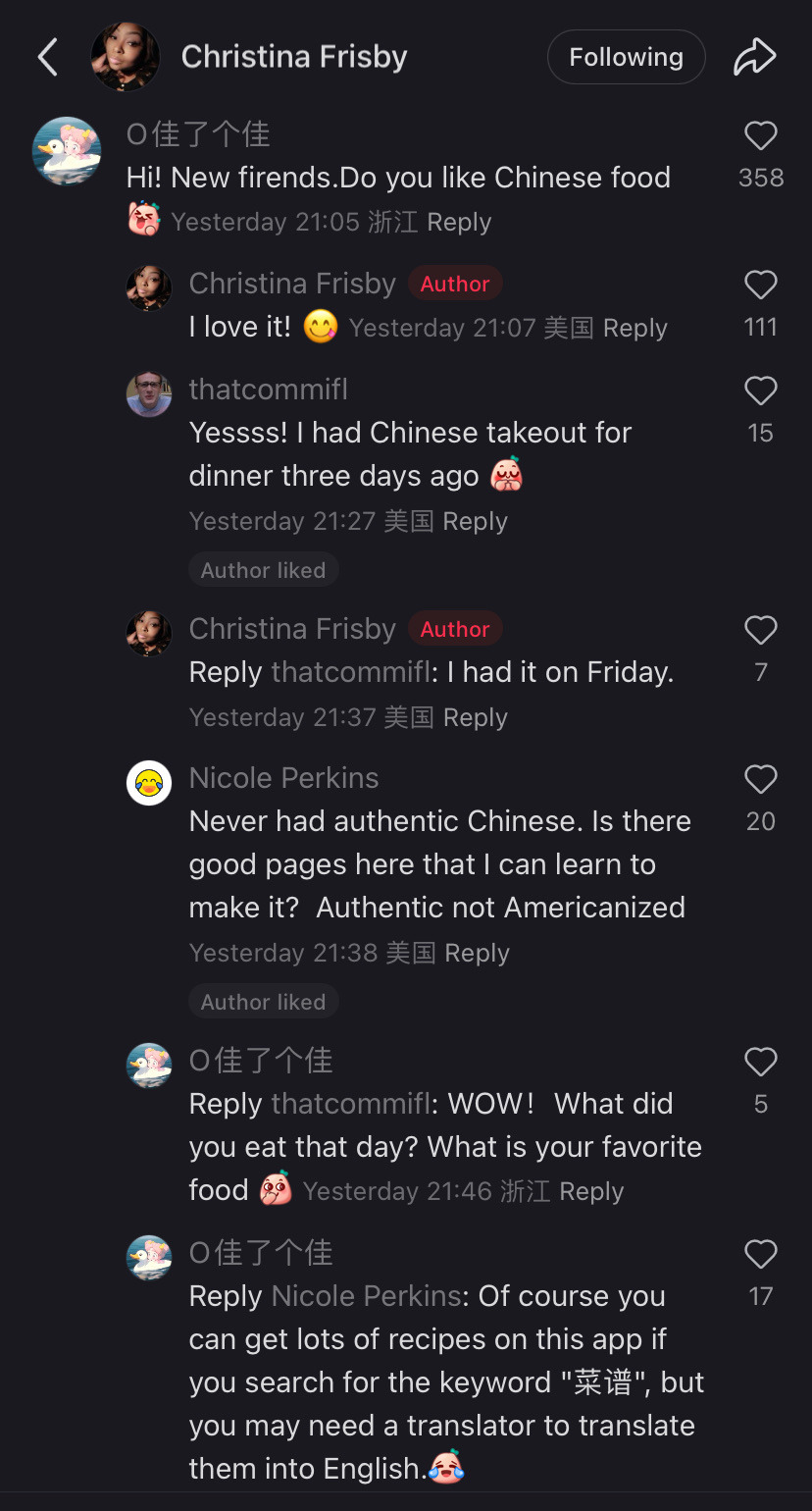
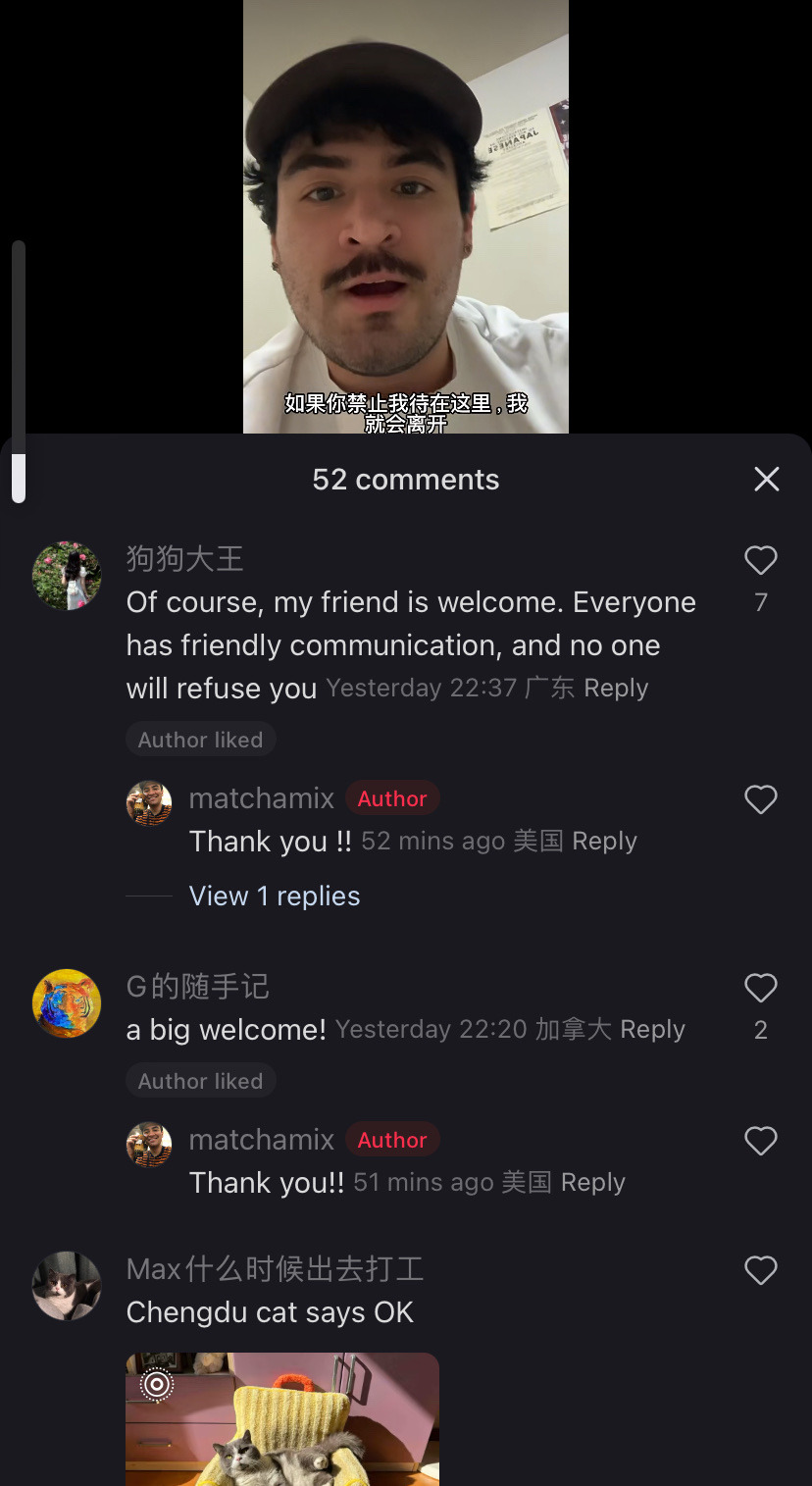

This is adorable and so not what they were expecting. Im sure they were expecting a reluctant return to reels and shorts to fill the void but tiktokers said fuck that, we will forge connections across the world. Who you tell me is my enemy i will make my friend. That’s pretty damn cool.
#tiktok ban#xiaohongshu#the great tiktok migration of 2025#us politics#us government#scotus#ftr tiktok is owned primarily by private investors and is not operated out of china#and all us data is stored on servers here in the us#tiktok also employs 7000 us employees to maintain the US side of operations#like they’re just lying to get us to shut up about genocide and corruption#so fuck it we’ll go spill all the tea to ears that wanna hear it cause this country is not what its cracked up to be#we been lied to and the rest of the world has been lied to#if scotus bans it tomorrow i can’t wait for their finding out#rednote
42K notes
·
View notes
Text
The Big Data Security Market Size, Share | CAGR 17.3% during 2025-2032

The global big data security market size was valued at USD 23.68 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 83.95 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 17.3% during the forecast period (2025–2032). The increasing sophistication of cyberattacks, growing regulatory compliance requirements, and rapid digital transformation across sectors are driving significant investment in big data protection.
Key Market Highlights
2024 Global Market Size: USD 23.68 billion
2025 Forecast Start Point: USD 27.40 billion
2032 Global Market Size: USD 83.95 billion
CAGR (2025–2032): 17.3%
Market Outlook: Rising demand for security solutions that protect structured and unstructured big data across hybrid and multi-cloud environments.
Key Players in the Global Big Data Security Market:
IBM Corporation
Oracle Corporation
McAfee LLC
Microsoft Corporation
Amazon Web Services (AWS)
Symantec (Broadcom Inc.)
Cloudera Inc.
Hewlett Packard Enterprise (HPE)
Check Point Software Technologies
Imperva
Palo Alto Networks
Talend
Splunk Inc.
Request for Free Sample Reports:
Market Dynamics:
Growth Drivers
Explosion in data volumes across enterprises, cloud platforms, and edge devices
Stringent compliance mandates (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA, CCPA)
Increased adoption of cloud and hybrid cloud models needing secure data movement and storage
Surge in cyberattacks targeting high-value data sets like PII and financial records
Growing implementation of AI/ML for security analytics and anomaly detection
Key Opportunities:
Development of AI-powered big data threat detection platforms
Integration of big data security with DevSecOps and data governance models
Expansion of managed security services (MSS) in data-heavy verticals
Customized solutions for healthcare, BFSI, retail, and energy sectors
Opportunities in edge and IoT security, especially for real-time big data use cases
Emerging Trends:
Adoption of AI and deep learning for automated data threat mitigation
Rise of unified data governance frameworks integrating security and compliance
Shift toward Zero Trust architectures for granular access control
Demand for real-time risk scoring and behavioral analytics
Cloud-native security solutions for containerized and serverless environments
Technology & Application Scope:
Core Solutions: Encryption, tokenization, firewall, antivirus/antimalware, SIEM, IAM, and data loss prevention
Deployment Models: On-premise, cloud-based, and hybrid
Data Types Secured: Personal Identifiable Information (PII), financial transactions, operational data, sensor data, unstructured business records
Industries Served: BFSI, government, healthcare, retail, telecom, manufacturing, and energy
Applications: Real-time risk analytics, compliance auditing, insider threat detection, and secure cloud analytics
Speak to analysts: https://www.fortunebusinessinsights.com/enquiry/speak-to-analyst/big-data-security-market-109528
Recent Developments:
March 2024 – IBM launched an updated Guardium Data Protection for Big Data, optimized for hybrid multicloud environments, offering AI-based anomaly detection and advanced auditing features.
September 2023 – Palo Alto Networks integrated advanced threat intelligence with big data processing platforms to deliver improved data security visibility and predictive breach detection.
December 2023 – Cloudera announced strategic collaboration with AWS to deliver secure big data analytics-as-a-service tailored for heavily regulated industries.
Conclusion:
The global big data security market is poised for substantial growth as organizations face mounting pressure to secure exponentially growing data ecosystems. Investments are accelerating across technologies that not only protect data but also ensure visibility, regulatory compliance, and resiliency in digital-first environments.
Vendors that offer scalable, cloud-native, and AI-enhanced big data security platforms will be best positioned to lead the market in the coming decade.
#Big Data Security Market Share#Big Data Security Market Size#Big Data Security Market Industry#Big Data Security Market Analysis#Big Data Security Market Driver#Big Data Security Market Research#Big Data Security Market Growth
0 notes
Text
China Telecom trains AI model with 1 trillion parameters on domestic chips
New Post has been published on https://thedigitalinsider.com/china-telecom-trains-ai-model-with-1-trillion-parameters-on-domestic-chips/
China Telecom trains AI model with 1 trillion parameters on domestic chips
.pp-multiple-authors-boxes-wrapper display:none; img width:100%;
China Telecom, one of the country’s state-owned telecom giants, has created two LLMs that were trained solely on domestically-produced chips.
This breakthrough represents a significant step in China’s ongoing efforts to become self-reliant in AI technology, especially in light of escalating US limitations on access to advanced semiconductors for its competitors.
According to the company’s Institute of AI, one of the models, TeleChat2-115B and another unnamed model were trained on tens of thousands of Chinese-made chips. This achievement is especially noteworthy given the tighter US export rules that have limited China’s ability to purchase high-end processors from Nvidia and other foreign companies. In a statement shared on WeChat, the AI institute claimed that this accomplishment demonstrated China’s capability to independently train LLMs and signals a new era of innovation and self-reliance in AI technology.
The scale of these models is remarkable. China Telecom stated that the unnamed LLM has one trillion parameters. In AI terminology, parameters are the variables that help the model in learning during training. The more parameters there are, the more complicated and powerful the AI becomes.
Chinese companies are striving to keep pace with global leaders in AI based outside the country. Washington’s export restrictions on Nvidia’s latest AI chips such as the A100 and H100, have compelled China to seek alternatives. As a result, Chinese companies have developed their own processors to reduce reliance on Western technologies. For instance, the TeleChat2-115B model has approximately 100 billion parameters, and therefore can perform as well as mainstream platforms.
China Telecom did not specify which company supplied the domestically-designed chips used to train its models. However, as previously discussed on these pages, Huawei’s Ascend chips play a key part in the country’s AI plans.
Huawei, which has faced US penalties in recent years, is also increasing its efforts in the artificial intelligence field. The company has recently started testing its latest AI processor, the Ascend 910C, with potential clients waiting in the domestic market. Large Chinese server companies, as well as internet giants that have previously used Nvidia chips, are apparently testing the new chip’s performance. Huawei’s Ascend processors, as one of the few viable alternatives to Nvidia hardware, are viewed as a key component of China’s strategy that will lessen its reliance on foreign technology.
In addition to Huawei, China Telecom is collaborating with other domestic chipmakers such as Cambricon, a Chinese start-up specialising in AI processors. The partnerships reflect a broader tendency in China’s tech industry to build a homegrown ecosystem of AI solutions, further shielding the country from the effects of US export controls.
By developing its own AI chips and technology, China is gradually reducing its dependence on foreign-made hardware, especially Nvidia’s highly sought-after and therefore expensive GPUs. While US sanctions make it difficult for Chinese companies to obtain the latest Nvidia hardware, a black market for foreign chips has emerged. Rather than risk operating in the grey market, many Chinese companies prefer to purchase lower-powered alternatives such as previous-gen models to maintain access to Nvidia’s official support and services.
China’s achievement reflects a broader shift in its approach to AI and semiconductor technology, emphasising self-sufficiency and resilience in an increasingly competitive global economy and in face of American protectionist trade policies.
(Photo by Mark Kuiper)
See also: Has Huawei outsmarted Apple in the AI race?
Want to learn more about AI and big data from industry leaders? Check out AI & Big Data Expo taking place in Amsterdam, California, and London. The comprehensive event is co-located with other leading events including Intelligent Automation Conference, BlockX, Digital Transformation Week, and Cyber Security & Cloud Expo.
Explore other upcoming enterprise technology events and webinars powered by TechForge here.
Tags: artificial intelligence, chip, huawei, llm, Nvidia
#ai#ai & big data expo#AI chips#ai model#AI Race#American#amp#apple#applications#approach#artificial#Artificial Intelligence#automation#background#Big Data#billion#black market#california#China#chip#chips#Cloud#cloud computing#Companies#comprehensive#computing#conference#content#cyber#cyber security
0 notes
Text
The Illusion of Influence: An Examination of the Media, Security Agencies, and Technological Power in Shaping Public Perception
Introduction In today’s digital age, the boundary between reality and illusion has blurred significantly. This essay explores how the perception of magical influence, akin to saying “hocus pocus” and seeing changes unfold, mirrors the intricate interplay between journalism, security agencies, state agencies, and information specialists in contemporary society. By examining these mechanisms and…
#Advanced Analytics#augmented reality#behavioral analysis#Behavioral Insights#Big Data#control mechanisms#data analysis#data collection#Data Management#data mining#Data Privacy#data security#Design#digital age#digital culture#Digital Design#Digital Dynamics#Digital Dynamics Research#digital identity#Digital Impact#Digital Influence#Digital Influence Factors#Digital Information#Digital Innovations#Digital Marketing#digital media#Digital Media Influence#Digital Perception#digital surveillance#digital technology
0 notes
Text
Big Data Security Market by Size, Share, Forecast, & Trends Analysis
Meticulous Research®—a leading global market research company, published a research report titled, ‘Big Data Security Market by Component (Solutions [Data Encryption, Security Intelligence, Data Backup & Recovery], Services), Deployment Mode, Organization Size, End User (IT & Telecom, BFSI, Retail & E-commerce), and Geography - Global Forecast to 2031.’
According to this latest publication from Meticulous Research®, the big data security market is projected to reach $60.1 billion by 2031, at a CAGR of 13.2% from 2024 to 2031. The growth of the big data security market is driven by the emergence of disruptive digital technologies, the increasing demand for data security and privacy solutions due to the rise in data breaches, and the growing data generation in the e-commerce industry. However, the high implementation costs of big data security solutions restrain the growth of this market.
Furthermore, the growing need for cloud-based security solutions and the increasing integration of AI, ML, and blockchain technologies in security solutions are expected to generate growth opportunities for the stakeholders in this market. However, the lack of knowledge about big data security solutions and the shortage of skilled IT professionals are major challenges impacting the growth of the big data security market.
The big data security market is segmented by component (solutions [data discovery and classification, data encryption {data protection, tokenization, data masking, other data encryption solutions}, security intelligence, data access control & authentication, data governance & compliance, data backup & recovery, data auditing & monitoring, other solutions], services [professional services, managed services]), deployment mode (on-premise deployments, cloud-based deployments), organization size (large enterprises, small & medium-sized enterprises), end user (IT & telecom, healthcare & pharmaceutical, BFSI, retail & e-commerce, energy & utilities, government, manufacturing, media & entertainment, transportation & logistics, and other end users). The study also evaluates industry competitors and analyzes the market at the regional and country levels.
Based on component, the big data security market is segmented into solutions and services. The solutions segment is further segmented into data discovery and classification, data encryption, security intelligence, data access control & authentication, data governance & compliance, data backup & recovery, data auditing & monitoring, and other solutions. In 2024, the solutions segment is expected to account for the larger share of the big data security market. The large market share of this segment is attributed to the increasing concerns regarding data security and privacy, the increasing adoption of data security solutions by SMEs, and the rising demand for encryption solutions for data protection across IoT devices. Big data security solutions include tools and measures to process or safeguard data and analytics processes. In March 2024, CrowdStrike, Inc. (U.S.) partnered with Rubrik, Inc. (U.S.) to transform data security solutions and stop breaches of critical information. Moreover, this segment is also projected to register the highest CAGR during the forecast period.
Based on deployment mode, the big data security market is segmented into on-premise deployments and cloud-based deployments. In 2024, the on-premise deployments segment is expected to account for the larger share of the big data security market. The large market share of this segment is attributed to the higher preference for on-premise deployments among large enterprises and increasing data generation in large enterprises. The on-premise model of deployment is majorly adopted by well-established and large companies that are capable of making capital investments toward the required hardware and hosting environments. In addition, these organizations also have sufficient in-house IT expertise to maintain software efficiency. Internal big data security is one of the major benefits of on-premise deployments.
However, the cloud-based deployments segment is projected to register the higher CAGR during the forecast period. The growth of this segment is driven by the rapid evolution of new security avenues for cloud-based deployments, the superior flexibility offered by cloud-based deployments, and the increase in security breaches. Cloud-based security solutions provide social networking privacy, system optimization, online storage, regulatory compliance, and connected device security. The adoption of cloud computing and storage systems is gaining popularity among small and medium-scale enterprises, supporting the growth of this segment.
Based on organization size, the big data security market is segmented into large enterprises and small & medium-sized enterprises. In 2024, the large enterprises segment is expected to account for the larger share of the big data security market. The large market share of this segment is attributed to the strong IT infrastructure of large enterprises, the growing adoption of advanced technologies such as AI, IoT, and blockchain, and the availability of skilled IT personnel to manage data security platforms. With larger budgets and a keen focus on developing strategic IT initiatives, large enterprises have a competitive advantage over small and medium-scale enterprises in terms of technology adoption. Large enterprises have a stable financial backup and can easily procure customized data security solutions, contributing to this segment's growth.
However, the small & medium-sized enterprises segment is projected to register the higher CAGR during the forecast period. The growth of this segment is driven by increasing digital transformation, government initiatives to promote security solutions, and the rising incidence of data breaches. SMEs are also increasingly becoming targets of cybercrime and therefore adopting suitable and strong security solutions.
Based on end user, the big data security market is segmented into IT & telecom, healthcare & pharmaceutical, BFSI, retail & e-commerce, energy & utilities, government, manufacturing, media & entertainment, transportation & logistics, and other end users. In 2024, the IT & telecom segment is expected to account for the largest share of the big data security market. The large market share of this segment is attributed to the increasing data breaches in IT companies as they store a vast amount of customer data, strict regulatory compliance forcing companies to implement stricter data security measures, and the increasing adoption of cloud-based solutions in the IT industry. In March 2023, IBM Corporation (U.S.) collaborated with Cohesity, Inc. (U.S.) to address increased data security and resiliency issues in hybrid cloud environments. With this collaboration, IBM launched its new IBM Storage Defender solution, including Cohesity's data protection, cyber resilience, and data management capabilities in the offering.
However, the healthcare & pharmaceutical segment is projected to register the highest CAGR during the forecast period. The growth of this segment is driven by the rising adoption of telemedicine devices and remote healthcare services, growing cyberattacks on connected devices, and the increasing demand for secure medical connected devices. A vast amount of medical data is generated in the healthcare sector. It is stored to improve patient outcomes, personalize treatment plans, and develop new drugs, among other applications. However, this sensitive data requires robust security measures to protect patient privacy and prevent unauthorized access. In November 2021, Armis, Inc. (U.S.) partnered with Nuvolo (U.S.) to improve data interoperability and the overall risk posture of healthcare organizations.
Based on geography, the big data security market is segmented into North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and the Middle East & Africa. In 2024, North America is expected to account for the largest share of the big data security market. The market growth in North America is driven by the presence of prominent players offering advanced big data security solutions & services, the early adoption of disruptive technologies, and growing awareness regarding data security. North America is home to several major players that provide products and services to improve big data security measures for IT assets, data, and privacy across different domains. Thus, big data security companies operating in the North America region are investing heavily in R&D activities to develop new & advanced security solutions that can address rising security challenges. In February 2024, Cyberhaven, Inc. (U.S.) launched Linea AI, an AI platform designed to combat the critical insider risks threatening vital corporate data.
However, the Asia-Pacific region is projected to record the highest CAGR during the forecast period. The growth of this market is driven by the growing data breaches, supportive government initiatives, and growing awareness regarding data security among small and medium-scale organizations. In December 2023, Safetica a.s. (U.S.) partnered with Kaira Global (Singapore) to deliver Safetica's Data Loss Prevention (DLP) solutions for enterprises of all sizes to safeguard their data against insider risks and data breaches in Singapore. APAC is the fastest-growing big data security market due to rapid investments in IT infrastructure, extensive use of the Internet, and growing security challenges.
Key Players
The key players operating in the big data security market are Check Point Software Technologies, Ltd. (Israel), Cisco Systems, Inc. (U.S.), Fortinet, Inc. (U.S.), Oracle Corporation (U.S.), IBM Corporation (U.S.), Microsoft Corporation (U.S.), Hewlett Packard Enterprise Development LP (U.S.), Intel Corporation (U.S.), Palo Alto Networks, Inc. (U.S.), Thales Group (France), Juniper Networks, Inc. (U.S.), Broadcom, Inc. (U.S.), Dell Technologies, Inc. (U.S.), CyberArk Software Ltd. (U.S.), and Rapid7, Inc. (U.S.).
Download Sample Report Here @ https://www.meticulousresearch.com/download-sample-report/cp_id=4984
Key Questions Answered in the Report:
What are the high-growth market segments in terms of the component, deployment mode, organization size, and end user?
What is the historical market size for the global big data security market?
What are the market forecasts and estimates for 2024–2031?
What are the major drivers, restraints, opportunities, challenges, and trends in the global big data security market?
Who are the major players in the global big data security market, and what are their market shares?
What is the competitive landscape like?
What are the recent developments in the global big data security market?
What are the different strategies adopted by major market players?
What are the trends and high-growth countries?
Who are the local emerging players in the global big data security market, and how do they compete with the other players?
Contact Us: Meticulous Research® [email protected] Contact Sales- +1-646-781-8004 Connect with us on LinkedIn- https://www.linkedin.com/company/meticulous-research
#Big Data Security Market#Big Data Security Management#Big Data Security and Privacy#Big Data Security Technologies#Big Data Security Solutions#Big Data Security Platform
0 notes
Text
If anyone wants to know why every tech company in the world right now is clamoring for AI like drowned rats scrabbling to board a ship, I decided to make a post to explain what's happening.
(Disclaimer to start: I'm a software engineer who's been employed full time since 2018. I am not a historian nor an overconfident Youtube essayist, so this post is my working knowledge of what I see around me and the logical bridges between pieces.)
Okay anyway. The explanation starts further back than what's going on now. I'm gonna start with the year 2000. The Dot Com Bubble just spectacularly burst. The model of "we get the users first, we learn how to profit off them later" went out in a no-money-having bang (remember this, it will be relevant later). A lot of money was lost. A lot of people ended up out of a job. A lot of startup companies went under. Investors left with a sour taste in their mouth and, in general, investment in the internet stayed pretty cooled for that decade. This was, in my opinion, very good for the internet as it was an era not suffocating under the grip of mega-corporation oligarchs and was, instead, filled with Club Penguin and I Can Haz Cheezburger websites.
Then around the 2010-2012 years, a few things happened. Interest rates got low, and then lower. Facebook got huge. The iPhone took off. And suddenly there was a huge new potential market of internet users and phone-havers, and the cheap money was available to start backing new tech startup companies trying to hop on this opportunity. Companies like Uber, Netflix, and Amazon either started in this time, or hit their ramp-up in these years by shifting focus to the internet and apps.
Now, every start-up tech company dreaming of being the next big thing has one thing in common: they need to start off by getting themselves massively in debt. Because before you can turn a profit you need to first spend money on employees and spend money on equipment and spend money on data centers and spend money on advertising and spend money on scale and and and
But also, everyone wants to be on the ship for The Next Big Thing that takes off to the moon.
So there is a mutual interest between new tech companies, and venture capitalists who are willing to invest $$$ into said new tech companies. Because if the venture capitalists can identify a prize pig and get in early, that money could come back to them 100-fold or 1,000-fold. In fact it hardly matters if they invest in 10 or 20 total bust projects along the way to find that unicorn.
But also, becoming profitable takes time. And that might mean being in debt for a long long time before that rocket ship takes off to make everyone onboard a gazzilionaire.
But luckily, for tech startup bros and venture capitalists, being in debt in the 2010's was cheap, and it only got cheaper between 2010 and 2020. If people could secure loans for ~3% or 4% annual interest, well then a $100,000 loan only really costs $3,000 of interest a year to keep afloat. And if inflation is higher than that or at least similar, you're still beating the system.
So from 2010 through early 2022, times were good for tech companies. Startups could take off with massive growth, showing massive potential for something, and venture capitalists would throw infinite money at them in the hopes of pegging just one winner who will take off. And supporting the struggling investments or the long-haulers remained pretty cheap to keep funding.
You hear constantly about "Such and such app has 10-bazillion users gained over the last 10 years and has never once been profitable", yet the thing keeps chugging along because the investors backing it aren't stressed about the immediate future, and are still banking on that "eventually" when it learns how to really monetize its users and turn that profit.
The pandemic in 2020 took a magnifying-glass-in-the-sun effect to this, as EVERYTHING was forcibly turned online which pumped a ton of money and workers into tech investment. Simultaneously, money got really REALLY cheap, bottoming out with historic lows for interest rates.
Then the tide changed with the massive inflation that struck late 2021. Because this all-gas no-brakes state of things was also contributing to off-the-rails inflation (along with your standard-fare greedflation and price gouging, given the extremely convenient excuses of pandemic hardships and supply chain issues). The federal reserve whipped out interest rate hikes to try to curb this huge inflation, which is like a fire extinguisher dousing and suffocating your really-cool, actively-on-fire party where everyone else is burning but you're in the pool. And then they did this more, and then more. And the financial climate followed suit. And suddenly money was not cheap anymore, and new loans became expensive, because loans that used to compound at 2% a year are now compounding at 7 or 8% which, in the language of compounding, is a HUGE difference. A $100,000 loan at a 2% interest rate, if not repaid a single cent in 10 years, accrues to $121,899. A $100,000 loan at an 8% interest rate, if not repaid a single cent in 10 years, more than doubles to $215,892.
Now it is scary and risky to throw money at "could eventually be profitable" tech companies. Now investors are watching companies burn through their current funding and, when the companies come back asking for more, investors are tightening their coin purses instead. The bill is coming due. The free money is drying up and companies are under compounding pressure to produce a profit for their waiting investors who are now done waiting.
You get enshittification. You get quality going down and price going up. You get "now that you're a captive audience here, we're forcing ads or we're forcing subscriptions on you." Don't get me wrong, the plan was ALWAYS to monetize the users. It's just that it's come earlier than expected, with way more feet-to-the-fire than these companies were expecting. ESPECIALLY with Wall Street as the other factor in funding (public) companies, where Wall Street exhibits roughly the same temperament as a baby screaming crying upset that it's soiled its own diaper (maybe that's too mean a comparison to babies), and now companies are being put through the wringer for anything LESS than infinite growth that Wall Street demands of them.
Internal to the tech industry, you get MASSIVE wide-spread layoffs. You get an industry that used to be easy to land multiple job offers shriveling up and leaving recent graduates in a desperately awful situation where no company is hiring and the market is flooded with laid-off workers trying to get back on their feet.
Because those coin-purse-clutching investors DO love virtue-signaling efforts from companies that say "See! We're not being frivolous with your money! We only spend on the essentials." And this is true even for MASSIVE, PROFITABLE companies, because those companies' value is based on the Rich Person Feeling Graph (their stock) rather than the literal profit money. A company making a genuine gazillion dollars a year still tears through layoffs and freezes hiring and removes the free batteries from the printer room (totally not speaking from experience, surely) because the investors LOVE when you cut costs and take away employee perks. The "beer on tap, ping pong table in the common area" era of tech is drying up. And we're still unionless.
Never mind that last part.
And then in early 2023, AI (more specifically, Chat-GPT which is OpenAI's Large Language Model creation) tears its way into the tech scene with a meteor's amount of momentum. Here's Microsoft's prize pig, which it invested heavily in and is galivanting around the pig-show with, to the desperate jealousy and rapture of every other tech company and investor wishing it had that pig. And for the first time since the interest rate hikes, investors have dollar signs in their eyes, both venture capital and Wall Street alike. They're willing to restart the hose of money (even with the new risk) because this feels big enough for them to take the risk.
Now all these companies, who were in varying stages of sweating as their bill came due, or wringing their hands as their stock prices tanked, see a single glorious gold-plated rocket up out of here, the likes of which haven't been seen since the free money days. It's their ticket to buy time, and buy investors, and say "see THIS is what will wring money forth, finally, we promise, just let us show you."
To be clear, AI is NOT profitable yet. It's a money-sink. Perhaps a money-black-hole. But everyone in the space is so wowed by it that there is a wide-spread and powerful conviction that it will become profitable and earn its keep. (Let's be real, half of that profit "potential" is the promise of automating away jobs of pesky employees who peskily cost money.) It's a tech-space industrial revolution that will automate away skilled jobs, and getting in on the ground floor is the absolute best thing you can do to get your pie slice's worth.
It's the thing that will win investors back. It's the thing that will get the investment money coming in again (or, get it second-hand if the company can be the PROVIDER of something needed for AI, which other companies with venture-back will pay handsomely for). It's the thing companies are terrified of missing out on, lest it leave them utterly irrelevant in a future where not having AI-integration is like not having a mobile phone app for your company or not having a website.
So I guess to reiterate on my earlier point:
Drowned rats. Swimming to the one ship in sight.
36K notes
·
View notes
Text
https://www.htfmarketintelligence.com/report/global-big-data-security-market
0 notes
Text
Bossware is unfair (in the legal sense, too)

You can get into a lot of trouble by assuming that rich people know what they're doing. For example, might assume that ad-tech works – bypassing peoples' critical faculties, reaching inside their minds and brainwashing them with Big Data insights, because if that's not what's happening, then why would rich people pour billions into those ads?
https://pluralistic.net/2020/12/06/surveillance-tulip-bulbs/#adtech-bubble
You might assume that private equity looters make their investors rich, because otherwise, why would rich people hand over trillions for them to play with?
https://thenextrecession.wordpress.com/2024/11/19/private-equity-vampire-capital/
The truth is, rich people are suckers like the rest of us. If anything, succeeding once or twice makes you an even bigger mark, with a sense of your own infallibility that inflates to fill the bubble your yes-men seal you inside of.
Rich people fall for scams just like you and me. Anyone can be a mark. I was:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/02/05/cyber-dunning-kruger/#swiss-cheese-security
But though rich people can fall for scams the same way you and I do, the way those scams play out is very different when the marks are wealthy. As Keynes had it, "The market can remain irrational longer than you can remain solvent." When the marks are rich (or worse, super-rich), they can be played for much longer before they go bust, creating the appearance of solidity.
Noted Keynesian John Kenneth Galbraith had his own thoughts on this. Galbraith coined the term "bezzle" to describe "the magic interval when a confidence trickster knows he has the money he has appropriated but the victim does not yet understand that he has lost it." In that magic interval, everyone feels better off: the mark thinks he's up, and the con artist knows he's up.
Rich marks have looong bezzles. Empirically incorrect ideas grounded in the most outrageous superstition and junk science can take over whole sections of your life, simply because a rich person – or rich people – are convinced that they're good for you.
Take "scientific management." In the early 20th century, the con artist Frederick Taylor convinced rich industrialists that he could increase their workers' productivity through a kind of caliper-and-stopwatch driven choreographry:
https://pluralistic.net/2022/08/21/great-taylors-ghost/#solidarity-or-bust
Taylor and his army of labcoated sadists perched at the elbows of factory workers (whom Taylor referred to as "stupid," "mentally sluggish," and as "an ox") and scripted their motions to a fare-the-well, transforming their work into a kind of kabuki of obedience. They weren't more efficient, but they looked smart, like obedient robots, and this made their bosses happy. The bosses shelled out fortunes for Taylor's services, even though the workers who followed his prescriptions were less efficient and generated fewer profits. Bosses were so dazzled by the spectacle of a factory floor of crisply moving people interfacing with crisply working machines that they failed to understand that they were losing money on the whole business.
To the extent they noticed that their revenues were declining after implementing Taylorism, they assumed that this was because they needed more scientific management. Taylor had a sweet con: the worse his advice performed, the more reasons their were to pay him for more advice.
Taylorism is a perfect con to run on the wealthy and powerful. It feeds into their prejudice and mistrust of their workers, and into their misplaced confidence in their own ability to understand their workers' jobs better than their workers do. There's always a long dollar to be made playing the "scientific management" con.
Today, there's an app for that. "Bossware" is a class of technology that monitors and disciplines workers, and it was supercharged by the pandemic and the rise of work-from-home. Combine bossware with work-from-home and your boss gets to control your life even when in your own place – "work from home" becomes "live at work":
https://pluralistic.net/2021/02/24/gwb-rumsfeld-monsters/#bossware
Gig workers are at the white-hot center of bossware. Gig work promises "be your own boss," but bossware puts a Taylorist caliper wielder into your phone, monitoring and disciplining you as you drive your wn car around delivering parcels or picking up passengers.
In automation terms, a worker hitched to an app this way is a "reverse centaur." Automation theorists call a human augmented by a machine a "centaur" – a human head supported by a machine's tireless and strong body. A "reverse centaur" is a machine augmented by a human – like the Amazon delivery driver whose app goads them to make inhuman delivery quotas while punishing them for looking in the "wrong" direction or even singing along with the radio:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/08/02/despotism-on-demand/#virtual-whips
Bossware pre-dates the current AI bubble, but AI mania has supercharged it. AI pumpers insist that AI can do things it positively cannot do – rolling out an "autonomous robot" that turns out to be a guy in a robot suit, say – and rich people are groomed to buy the services of "AI-powered" bossware:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/01/29/pay-no-attention/#to-the-little-man-behind-the-curtain
For an AI scammer like Elon Musk or Sam Altman, the fact that an AI can't do your job is irrelevant. From a business perspective, the only thing that matters is whether a salesperson can convince your boss that an AI can do your job – whether or not that's true:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/07/25/accountability-sinks/#work-harder-not-smarter
The fact that AI can't do your job, but that your boss can be convinced to fire you and replace you with the AI that can't do your job, is the central fact of the 21st century labor market. AI has created a world of "algorithmic management" where humans are demoted to reverse centaurs, monitored and bossed about by an app.
The techbro's overwhelming conceit is that nothing is a crime, so long as you do it with an app. Just as fintech is designed to be a bank that's exempt from banking regulations, the gig economy is meant to be a workplace that's exempt from labor law. But this wheeze is transparent, and easily pierced by enforcers, so long as those enforcers want to do their jobs. One such enforcer is Alvaro Bedoya, an FTC commissioner with a keen interest in antitrust's relationship to labor protection.
Bedoya understands that antitrust has a checkered history when it comes to labor. As he's written, the history of antitrust is a series of incidents in which Congress revised the law to make it clear that forming a union was not the same thing as forming a cartel, only to be ignored by boss-friendly judges:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/04/14/aiming-at-dollars/#not-men
Bedoya is no mere historian. He's an FTC Commissioner, one of the most powerful regulators in the world, and he's profoundly interested in using that power to help workers, especially gig workers, whose misery starts with systemic, wide-scale misclassification as contractors:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/02/02/upward-redistribution/
In a new speech to NYU's Wagner School of Public Service, Bedoya argues that the FTC's existing authority allows it to crack down on algorithmic management – that is, algorithmic management is illegal, even if you break the law with an app:
https://www.ftc.gov/system/files/ftc_gov/pdf/bedoya-remarks-unfairness-in-workplace-surveillance-and-automated-management.pdf
Bedoya starts with a delightful analogy to The Hawtch-Hawtch, a mythical town from a Dr Seuss poem. The Hawtch-Hawtch economy is based on beekeeping, and the Hawtchers develop an overwhelming obsession with their bee's laziness, and determine to wring more work (and more honey) out of him. So they appoint a "bee-watcher." But the bee doesn't produce any more honey, which leads the Hawtchers to suspect their bee-watcher might be sleeping on the job, so they hire a bee-watcher-watcher. When that doesn't work, they hire a bee-watcher-watcher-watcher, and so on and on.
For gig workers, it's bee-watchers all the way down. Call center workers are subjected to "AI" video monitoring, and "AI" voice monitoring that purports to measure their empathy. Another AI times their calls. Two more AIs analyze the "sentiment" of the calls and the success of workers in meeting arbitrary metrics. On average, a call-center worker is subjected to five forms of bossware, which stand at their shoulders, marking them down and brooking no debate.
For example, when an experienced call center operator fielded a call from a customer with a flooded house who wanted to know why no one from her boss's repair plan system had come out to address the flooding, the operator was punished by the AI for failing to try to sell the customer a repair plan. There was no way for the operator to protest that the customer had a repair plan already, and had called to complain about it.
Workers report being sickened by this kind of surveillance, literally – stressed to the point of nausea and insomnia. Ironically, one of the most pervasive sources of automation-driven sickness are the "AI wellness" apps that bosses are sold by AI hucksters:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/03/15/wellness-taylorism/#sick-of-spying
The FTC has broad authority to block "unfair trade practices," and Bedoya builds the case that this is an unfair trade practice. Proving an unfair trade practice is a three-part test: a practice is unfair if it causes "substantial injury," can't be "reasonably avoided," and isn't outweighed by a "countervailing benefit." In his speech, Bedoya makes the case that algorithmic management satisfies all three steps and is thus illegal.
On the question of "substantial injury," Bedoya describes the workday of warehouse workers working for ecommerce sites. He describes one worker who is monitored by an AI that requires him to pick and drop an object off a moving belt every 10 seconds, for ten hours per day. The worker's performance is tracked by a leaderboard, and supervisors punish and scold workers who don't make quota, and the algorithm auto-fires if you fail to meet it.
Under those conditions, it was only a matter of time until the worker experienced injuries to two of his discs and was permanently disabled, with the company being found 100% responsible for this injury. OSHA found a "direct connection" between the algorithm and the injury. No wonder warehouses sport vending machines that sell painkillers rather than sodas. It's clear that algorithmic management leads to "substantial injury."
What about "reasonably avoidable?" Can workers avoid the harms of algorithmic management? Bedoya describes the experience of NYC rideshare drivers who attended a round-table with him. The drivers describe logging tens of thousands of successful rides for the apps they work for, on promise of "being their own boss." But then the apps start randomly suspending them, telling them they aren't eligible to book a ride for hours at a time, sending them across town to serve an underserved area and still suspending them. Drivers who stop for coffee or a pee are locked out of the apps for hours as punishment, and so drive 12-hour shifts without a single break, in hopes of pleasing the inscrutable, high-handed app.
All this, as drivers' pay is falling and their credit card debts are mounting. No one will explain to drivers how their pay is determined, though the legal scholar Veena Dubal's work on "algorithmic wage discrimination" reveals that rideshare apps temporarily increase the pay of drivers who refuse rides, only to lower it again once they're back behind the wheel:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/04/12/algorithmic-wage-discrimination/#fishers-of-men
This is like the pit boss who gives a losing gambler some freebies to lure them back to the table, over and over, until they're broke. No wonder they call this a "casino mechanic." There's only two major rideshare apps, and they both use the same high-handed tactics. For Bedoya, this satisfies the second test for an "unfair practice" – it can't be reasonably avoided. If you drive rideshare, you're trapped by the harmful conduct.
The final prong of the "unfair practice" test is whether the conduct has "countervailing value" that makes up for this harm.
To address this, Bedoya goes back to the call center, where operators' performance is assessed by "Speech Emotion Recognition" algorithms, a psuedoscientific hoax that purports to be able to determine your emotions from your voice. These SERs don't work – for example, they might interpret a customer's laughter as anger. But they fail differently for different kinds of workers: workers with accents – from the American south, or the Philippines – attract more disapprobation from the AI. Half of all call center workers are monitored by SERs, and a quarter of workers have SERs scoring them "constantly."
Bossware AIs also produce transcripts of these workers' calls, but workers with accents find them "riddled with errors." These are consequential errors, since their bosses assess their performance based on the transcripts, and yet another AI produces automated work scores based on them.
In other words, algorithmic management is a procession of bee-watchers, bee-watcher-watchers, and bee-watcher-watcher-watchers, stretching to infinity. It's junk science. It's not producing better call center workers. It's producing arbitrary punishments, often against the best workers in the call center.
There is no "countervailing benefit" to offset the unavoidable substantial injury of life under algorithmic management. In other words, algorithmic management fails all three prongs of the "unfair practice" test, and it's illegal.
What should we do about it? Bedoya builds the case for the FTC acting on workers' behalf under its "unfair practice" authority, but he also points out that the lack of worker privacy is at the root of this hellscape of algorithmic management.
He's right. The last major update Congress made to US privacy law was in 1988, when they banned video-store clerks from telling the newspapers which VHS cassettes you rented. The US is long overdue for a new privacy regime, and workers under algorithmic management are part of a broad coalition that's closer than ever to making that happen:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/12/06/privacy-first/#but-not-just-privacy
Workers should have the right to know which of their data is being collected, who it's being shared by, and how it's being used. We all should have that right. That's what the actors' strike was partly motivated by: actors who were being ordered to wear mocap suits to produce data that could be used to produce a digital double of them, "training their replacement," but the replacement was a deepfake.
With a Trump administration on the horizon, the future of the FTC is in doubt. But the coalition for a new privacy law includes many of Trumpland's most powerful blocs – like Jan 6 rioters whose location was swept up by Google and handed over to the FBI. A strong privacy law would protect their Fourth Amendment rights – but also the rights of BLM protesters who experienced this far more often, and with far worse consequences, than the insurrectionists.
The "we do it with an app, so it's not illegal" ruse is wearing thinner by the day. When you have a boss for an app, your real boss gets an accountability sink, a convenient scapegoat that can be blamed for your misery.
The fact that this makes you worse at your job, that it loses your boss money, is no guarantee that you will be spared. Rich people make great marks, and they can remain irrational longer than you can remain solvent. Markets won't solve this one – but worker power can.

Image: Cryteria (modified) https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:HAL9000.svg
CC BY 3.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/deed.en
#pluralistic#alvaro bedoya#ftc#workers#algorithmic management#veena dubal#bossware#taylorism#neotaylorism#snake oil#dr seuss#ai#sentiment analysis#digital phrenology#speech emotion recognition#shitty technology adoption curve
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
Since Lando is involved, there's of course a particular narrative that has popped up around his Monster release and which other drivers deserve it more, so I'm going to get on my professional soap box once again because oh my god shut the fuck up already.
My creds: dual BS in Business Analytics and Marketing. MA in Strategic Communication (thesis on sports PR in the social media age). MBA with a sports economics coursework emphasis. Consultant working in corporate partnerships in a variety of sports, including motorsport.
Based on what I've seen today, people have no idea how much work goes into securing personal sponsors. In order to get a personal sponsorship deal, you and your team have to pitch the sponsor and demonstrate the value that it will bring to their business through things like DATA and RESEARCH. Engagement metrics, impressions, reach, products sold, brand recognition, return on investment, etc.
If a McLaren sponsor does a personal sponsorship of Lando as well, it's because his team pitched and demonstrated that the metrics bear out that it would be worth their money. It's not like oh let's throw money at this kid bc VIBES. Or bc Zak Brown says we had to. I keep seeing people implying that they just picked him on a whim, when things like this take ages to decide, with a ton of data, a ton of research, and a ton of really smart people analyzing it before making the call.
You have to show a sponsor the reasons that they should work with you and why it's worth their money. Lando and Quadrant have done that. And it's a fuckton of work to not only get them, but to deliver the results to retain them. Some of those results are in the form of social media engagement that they've gotten from Lando and his brands likely before the drink was even contracted.
Identifying sponsors, pitching and securing their money, etc. is a multi-billion dollar industry that requires a ton of work, data analysis, content testing, focus group testing, etc. The people saying "it should have been _____" clearly either have a personal bias or don't understand the level of personal brand you have to have to get this sort of a deal.
Lando has larger reach, more engagement, recognizable brands with very passionate followings, etc. when compared to some of the other drivers people are bringing up here. He's selling out merch collection after merch collection after merch collection, and that is not true of 90% of the other drivers on the grid. He sold so many tickets to Landostand that they quite literally BUILT ANOTHER GRANDSTAND. And sold that one out, too! These are things that come with a ton of value to sponsors. Sponsors are seeking out his audience based on demographics. It's not some sort of conspiracy, it's business.
Right now, there are a couple of drivers that are LEAGUES above the others when it comes to the effort they've put into developing their personal brand, ability to drive product, and relevancy within high disposable income and retail-spending fan demographics (Lando over indexes with four key demos: young women, highly educated women, queer men, families with children). Averaged across these "big spender demos," Lando is in the top 2. I can say that based on the data I have at my fingertips.
tl;dr - Monster is looking to sell product. Data says Lando Norris sells product because people actually like him very much.
#lando norris#lando x monster#please do not make me have to get on my soapbox again#normally i charge people a billable hourly rate for this shit
161 notes
·
View notes