#American Community Survey
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
so apparently, the US census is about to make 40% of disabled people disappear in its data.
they gonna change the disability-related questions, and then only count the two most negative answers as a disability. and also the new version will do even worse than the old version at counting disabled ppl who are chronically and/or mentally ill. and just in time for long covid to create more of exactly those kinds of disabled ppl [/tinfoil hat]
article about the change they're trying to make:
https://nationalpartnership.org/new-census-proposal-would-reduce-disabled-women-girls-counted-nearly-10-million/?fbclid=IwAR09pGjYoMwdik6mo-uzEOf3kD7xe2oLIEU7wlm7wWlV9ykbgq02_fljJr8
on how to leave a public comment to try to make that not happen:
#disability rights#census#long covid#disability#ableism#disability discrimination#nothing about us without us#ada#american community survey#signal boost#us census
105 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Rise of Remote Work in America: Trends and Insights for 2023
The Rise of Remote Work in America In recent years, remote work has transformed from a temporary solution to a long-term norm for many professionals across the United States. As offices begin to reopen, it appears that they may never return to the pre-pandemic occupancy levels. A pressing question remains: how many individuals are currently working from home, and from where are they doing it? A…
#American Community Survey#Austin Texas#cities for remote work#Omaha#Raleigh North Carolina#remote work#remote workers#residential real estate#telecommuting#U.S. Census Bureau#workforce trends
0 notes
Text

Thanks for Participating. Post It Forward for Higher Participation.
#food#breakfast#foodies#food lovers#comfort food#food culture#foodblogger#lunch#dinner#coffeelovers#research#survey#polls#everyonelovestoeat#american culture#black american culture#culture studies#women writers#writing community
92 notes
·
View notes
Text
If you don't know this already, please try and internalize it: the idea that people join the US military primarily because they are young people at a disadvantage in life coerced into believing it is the most accessible path to upward mobility is not true.
if you're parroting this talking point, you are doing propaganda for the US military and you just need to stop saying it. here's an article from the Military Times that breaks the finding of various studies like this one from 2020 and this one from 2018 that analyze motivations for joining the military and popular conceptions of motivations for joining the military. Here's a pretty important excerpt:
Further, they hypothesized that some of this possible misconception about poorer Americans joining the military was a geographical issue. While the Defense Department tracks the zip codes of recruits ― and historically, many of them come from more rural areas in the southeast ― it doesn’t track their incomes or their parents’ incomes, which leads to assumptions that the poorer their communities, the poorer the recruits. [...] Using Bureau of Labor Statistics data from 1997 to 2008, they found that the services have recruited primarily from the middle class, America’s largest socio-economic demographic. “We show that recent recruits tend to have higher than average socioeconomic background: they disproportionally come from the middle of the family income, family wealth, and cognitive skill distributions, with both tails under-represented,” they found.
Here's from the army times:
Surveyed troops said these were the top five reasons for staying in the Army. The percentages indicate how many troops felt the factors were “extremely important” to them:
- Opportunity to serve my country — 53.5% - How well my retirement pay or benefits will meet my future needs — 45.1% - Opportunities to lead or train soldiers — 43.5% - My sense of purpose — 38.1% -How well my pay or benefits meet my present needs — 37%
Also mentioned in other sources but here from the NY times in 2020 as well, army enlistment is becoming increasingly skewed towards being the children of people who have previously served.
The main predictors are not based on class or race. Army data show service spread mostly evenly through middle-class and “downscale” groups. Youth unemployment turns out not to be the prime factor.
'Joining the army to lift yourself out of poverty' is not the reality for military service, it is the narrative used by the military in it's marketing and recruitment. if you go around repeating it i hope for your sake you're at least on their payroll! if you're going to bootlick don't do it for free!
7K notes
·
View notes
Text
Here is a brief summary of what is happening in Wikipedia right now:
In the last few years (3-4 years) the WikiProject Indigenous peoples of North America, which was originally created to improve the quality and coverage of native issues and native articles on wikipedia, has been hijacked by a small number of users with an extremist agenda. They have been working diligently over the last few years to change the definition of both what it means to be an Indigenous American and even what it means to be state and federally recognized.
The four or five key players (Mainly Editor Yuchitown, Bohemian Baltimore, ARoseWolf, (now retired editor CorbieVreccan, Netherzone and Oncamera) who are part of the “Native American Articles Improvement Project” started implementing these changes slowly, but they started pursuing their goals aggressively after November 2023, when state-recognized tribes retained their voting rights in NCAI. Essentially, after the movement to delegitimize state-recognized tribes failed officially, the key players doubled down on altering and controlling the flow of information about Native Americans through Wikipedia.
The talk page of Lily Gladstone’s article has a relevant discussion here. Initially, the leaders of the WikiProject removed any reference to her being a “Native American Actress” and instead had her as “Self-identifying as Blackfoot” and “Self-identifying as Nez Perce” because her blood quantum was too low to be enrolled in either tribe.
You can see some of the discussion here:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Talk:Lily_Gladstone
Eventually they relented and changed her category to being “Of Nez Perce Descent” but you can see in the discussion that they are referring to an article that these editors (Yuchitown, Bohemian Baltimore, and CorbieVreccan) themselves appeared to have mostly written and revised:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Native_American_identity_in_the_United_States
This statement is very much at odds with even the government’s description, as seen below;
The DOJ Office of Tribal Justice Office on their webpage “Frequently Asked Questions About Native American”, question “Who is an American Indian or Alaskan Native” states:
“As a general principle, an Indian is a person who is of some degree Indian blood and is recognized as an Indian by a Tribe and/or the United States. No single federal or tribal criterion establishes a person's identity as an Indian. Government agencies use differing criteria to determine eligibility for programs and services. Tribes also have varying eligibility criteria for membership.”
In addition, “List” pages have been created on Wikipedia for federally and state recognized tribes. The Wikipedia “List” page for state-recognized tribes is inaccurate in its interpretation of state recognition and not supported by expert reliable sources--(1) Cohen’s Handbook of Federal Indian Law 2012 edition, (2) NCSL.org current stand on state recognition (not the archived list from 2017 which NCSL no longer supports), (3) Koenig & Stein’s paper “Federalism and the State Recognition of Native American Tribes: a survey of state-recognized tribes and state recognition processes across the United States” (both 2008 & updated 2013 in book “ Recognition, sovereignty struggles, and indigenous rights in the United States: A sourcebook”)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/State-recognized_tribes_in_the_United_States
State-recognized tribes who have received recognition through less formal but acceptable means have been moved from the Wikipedia list page on state-recognized tribes to the Wikipedia list page of unrecognized or self-identifying organizations.
The Wiki page "List of organizations that self-identify as Native American tribes", in particular, is being used to purposely defame legitimate Native American individuals who are members of the tribes/Native communities that are on this list.
By the parameters set up on Wikipedia, only the colonizer’s governments can acknowledge who is Native American through either federal recognition or state recognition. If an individual is not a member of a federally or state-recognized tribe, then it is determined that they cannot be Native American and are, instead, considered “self-identifying” or only “a descendant of ...” (example Lily Gladstone). As a result, Native individuals are currently being tagged as “self-identifying” and their names are put on “list” pages that strongly imply they are “pretend” Indians.
These editors have indicated that they would like “self-identification” to be the default setting for any people who they deem do not fit within the parameters that they themselves created within Wikipedia.
Moreof, these editors are admin and senior editors within the Wikiproject Indigenous Peoples of North America, and are being called in specifically to weigh on Native Identity, and any project involving any Indigenous Group.
Any attempt to correct misinformation, add information, or change any of these articles is often met with being blocked, reported for various offenses, or reported for having a Conflict of Interest, whether or not that is actually applicable. They have use this strategically in many different pages for many different individuals and groups within the scope of their Wikiprojects.
While changing things in Wikipedia does not change the truth, it is a way to control how most people take in information, and thus they hope to manipulate the narrative to better suit their goals.
This is quick and messy but:
Here is a link to the google document with the other state recognized tribes (Including yours) that were edited by these editors. This is an incomplete list so far that only goes back to September 2023 but I am going to add to it. If you can add to your own part of this list, and send your complaints and information to the arbitrator committee (the email is below) with the involved editors, this will help our case.
The more tribes who complain, and the more Wikipedia editors complain, the better our case will be.
https://docs.google.com/document/d/1YNDEjLTrrZ_mMIRCVxtvt69FwCYpJWKs71lBhWa5a9M/edit?usp=sharing
The place to make complaints on Wikipedia is oversight-en-wpwikipedia.org , and
arbcom-enwikimedia.org . It is most helpful to have an editing account on Wikipedia, because Yuchitown and the others will try to defend themselves using Wikipedia methodology and make anyone who confronts them look like the aggressor (see the other tribes who tried to fight back on Wikipedia I found).
The more people and tribes make complaints the more likely it is that this will work and we can rid ourselves of these monsters.
Some of the tribes I have spoken to are taking legal action against these editors. Any groups affected by their policies should also reach out to the news to make knowledge of this more widespread.
Thank you
- quoted with permission from an email sent by an associate of my tribe. Message me for their email address if you'd like to reach out to them.
#indigenous#intertribal infighting#state recognized tribes#seaconke Wampanoag#our chief and first councilman were at NCAI and there was ver nearly physical violence about this issue#Seaconke Wampanoag is recognized in MA and currently pursuing recognition by RI#like we gave active bills in tge state house
13K notes
·
View notes
Text
"Despite the Central Appalachia ecosystem being historically famous as coal country, under this diverse broadleaf canopy lies a rich, biodiverse world of native plants helping to fill North America’s medicinal herb cabinet.
And it turns out that the very communities once reliant on the coalfields are now bringing this botanical diversity to the country.
“Many different Appalachian people, stretching from pre-colonization to today, have tended, harvested, sold, and used a vast number of forest botanicals like American ginseng, ramps, black cohosh, and goldenseal,” said Shannon Bell, Virginia Tech professor in the Dept. of Sociology. “These plants have long been integral to many Appalachians’ livelihoods and traditions.”
50% of the medicinal herbs, roots, and barks in the North American herbal supply chain are native to the Appalachian Mountains, and the bulk of these species are harvested or grown in Central Appalachia, which includes southern West Virginia, eastern Kentucky, far-southwest Virginia, and east Tennessee.
The United Plant Savers, a nonprofit with a focus on native medicinal plants and their habitats, has identified many of the most popular forest medicinals as species of concern due to their declining populations.
Along with the herbal supply chain being largely native to Appalachia, the herb gatherers themselves are also native [to Appalachia, not Native American specifically], but because processing into medicine and seasonings takes place outside the region, the majority of the profits from the industry do too.
In a press release on Bell’s superb research and advocacy work within Appalachia’s botanical communities, she refers back to the moment that her interest in the industry and the region sprouted; when like many of us, she was out in a nearby woods waiting out the pandemic.
“My family and I spent a lot of time in the woods behind our house during quarantine,” Bell said. “We observed the emergence of all the spring ephemerals in the forest understory – hepatica, spring beauty, bloodroot, trillium, mayapple. I came to appreciate the importance of the region’s botanical biodiversity more than ever, and realized I wanted to incorporate this new part of my life into my research.”
With co-investigator, John Munsell at VA Tech’s College of Natural Resources and Environment, Bell’s project sought to identify ways that Central Appalachian communities could retain more of the profits from the herbal industry while simultaneously ensuring that populations of at-risk forest botanicals not only survive, but thrive and expand in the region.
Bell conducted participant observation and interviews with wild harvesters and is currently working on a mail survey with local herb buyers. She also piloted a ginseng seed distribution program, and helped a wild harvester write a grant proposal to start a forest farm.
“Economic development in post-coal communities often focuses on other types of energy development, like fracking and natural gas pipelines, or on building prisons and landfills. Central Appalachia is one of the most biodiverse places on the planet. I think that placing a greater value on this biodiversity is key to promoting a more sustainable future for the region,” Bell told VA Tech press.
Armed with a planning grant of nearly half a million dollars, Bell and collaborators are specifically targeting forest farming as a way to achieve that sustainable future.
Finally, enlisting support from the nonprofit organization Appalachian Sustainable Development, Virginia Tech, the City of Norton, a sculpture artist team, and various forest botanicals practitioners in her rolodex, Bell organized the creation of a ‘living monument’ along Flag Rock Recreation Area in Norton, Virginia.
An interpretive trail, the monument tells the story of the historic uses that these wild botanicals had for the various societies that have inhabited Appalachia, and the contemporary value they still hold for people today."
-via Good News Network, September 12, 2024
#appalachia#united states#biodiversity#herbs#herbal medicine#herbalism#native plants#conservation#sustainability#sustainable agriculture#solarpunk#good news#hope
642 notes
·
View notes
Text
"Much ink has already been spilled on Harris’s prosecutorial background. What is significant about the topic of sex work is how recently the vice president–elect’s actions contradicted her alleged views. During her tenure as AG, she led a campaign to shut down Backpage, a classified advertising website frequently used by sex workers, calling it “the world’s top online brothel” in 2016 and claiming that the site made “millions of dollars from trafficking.” While Backpage did make millions off of sex work ads, its “adult services” listings offered a safer and more transparent platform for sex workers and their clients to conduct consensual transactions than had historically been available. Harris’s grandiose mischaracterization led to a Senate investigation, and the shuttering of the site by the FBI in 2018.
“Backpage being gone has devastated our community,” said Andrews. The platform allowed sex workers to work more safely: They were able to vet clients and promote their services online. “It’s very heartbreaking to see the fallout,” said dominatrix Yevgeniya Ivanyutenko. “A lot of people lost their ability to safely make a living. A lot of people were forced to go on the street or do other things that they wouldn’t have otherwise considered.” M.F. Akynos, the founder and executive director of the Black Sex Worker Collective, thinks Harris should “apologize to the community. She needs to admit that she really fucked up with Backpage, and really ruined a lot of people’s lives.”
After Harris became a senator, she cosponsored the now-infamous Stop Enabling Sex Traffickers Act (SESTA), which—along with the House’s Allow States and Victims to Fight Online Sex Trafficking Act (FOSTA)—was signed into law by President Trump in 2018. FOSTA-SESTA created a loophole in Section 230 of the Communications Decency Act, the so-called “safe harbor” provision that allows websites to be free from liability for user-generated content (e.g., Amazon reviews, Craigslist ads). The Electronic Frontier Foundation argues that Section 230 is the backbone of the Internet, calling it “the most important law protecting internet free speech.” Now, website publishers are liable if third parties post sex-work ads on their platforms.
That spelled the end of any number of platforms—mostly famously Craigslist’s “personal encounters” section—that sex workers used to vet prospective clients, leaving an already vulnerable workforce even more exposed. (The Woodhull Freedom Foundation has filed a lawsuit challenging FOSTA on First Amendment grounds; in January 2020, it won an appeal in D.C.’s district court).
“I sent a bunch of stats [to Harris and Senator Diane Feinstein] about decriminalization and how much SESTA-FOSTA would hurt American sex workers and open them up to violence,” said Cara (a pseudonym), who was working as a sex worker in the San Francisco and a member of SWOP when the bill passed. Both senators ignored her.
The bill both demonstrably harmed sex workers and failed to drop sex trafficking. “Within one month of FOSTA’s enactment, 13 sex workers were reported missing, and two were dead from suicide,” wrote Lura Chamberlain in her Fordham Law Review article “FOSTA: A Hostile Law with a Human Cost.” “Sex workers operating independently faced a tremendous and immediate uptick in unwanted solicitation from individuals offering or demanding to traffic them. Numerous others were raped, assaulted, and rendered homeless or unable to feed their children.” A 2020 survey of the effects of FOSTA-SESTA found that “99% of online respondents reported that this law does not make them feel safer” and 80.61 percent “say they are now facing difficulties advertising their services.” "
-What Sex Workers Want Kamala Harris to Know by Hallie Liberman
#personal#sw#sex work is work#kamala harris#one of the MANY many reasons i hate harris#she directly put so many sex workers at risk. i lost multiple community members because of her#whorephobia#fosta/sesta
413 notes
·
View notes
Note
can u elaborate on posture being a lie
As Beth Linker explains in her book “Slouch: Posture Panic in Modern America” (Princeton), a long history of anxiety about the proximity between human and bestial nature has played out in this area of social science. Linker, a historian of medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, argues that at the onset of the twentieth century the United States became gripped by what she characterizes as a poor-posture epidemic: a widespread social contagion of slumping that could, it was feared, have deleterious effects not just upon individual health but also upon the body politic. Sitting up straight would help remedy all kinds of failings, physical and moral [...] she sees the “past and present worries concerning posture as part of an enduring concern about so-called ‘diseases of civilization’ ”—grounded in a mythology of human ancestry that posits the hunter-gatherer as an ideal from which we have fallen.
[...]
In America at the turn of the twentieth century, anxieties about posture inevitably collided with anxieties not just about class but also about race. Stooping was associated with poverty and with manual, industrialized labor—the conditions of working-class immigrants from European countries who, in their physical debasement, were positioned well below the white Anglo-Saxon Protestant establishment. Linker argues that, in this environment, “posture served as a marker of social status similar to skin color.” At the same time, populations that had been colonized and enslaved were held up as posture paradigms for the élite to emulate: the American Posture League rewarded successful students with congratulatory pins that featured an image of an extremely upright Lenape man. The head-carrying customs associated with African women were also adopted as training exercises for white girls of privilege, although Linker notes that Bancroft and her peers recommended that young ladies learn to balance not baskets and basins, which signified functionality, but piles of flat, slippery books, markers of their own access to leisure and education. For Black Americans, posture was even more fraught: despite the admiration granted to the posture of African women bearing loads atop their heads, community leaders like Dr. Algernon Jackson, who helped establish the National Negro Health Movement, criticized those Black youth who “too often slump along, stoop-shouldered and walk with a careless, lazy sort of dragging gait.” If slouching among privileged white Americans could indicate an enviable carelessness, it was seen as proof of indolence when adopted by the disadvantaged.
This being America, posture panic was swiftly commercialized, with a range of products marketed to appeal to the eighty per cent of the population whose carriage had been deemed inadequate by posture surveys. The footwear industry drafted orthopedic surgeons to consult on the design of shoes that would lessen foot and back pain without the stigma of corrective footwear: one brand, Trupedic, advertised itself as “a real anatomical shoe without the freak-show look.” The indefatigable Jessie Bancroft trained her sights on children’s clothing, endorsing a company that created a “Right-Posture” jacket, whose trim cut across the upper shoulders gave its schoolboy wearer little choice but to throw his shoulders back like Jordan Baker. Bancroft’s American Posture League endorsed girdles and corsets for women; similar garments were also adopted by men, who, by the early nineteen-fifties, were purchasing abdominal “bracers” by the millions.
It was in this era that what eventually proved to be the most contentious form of posture policing reached its height, when students entering college were required to submit to mandatory posture examinations, including the taking of nude or semi-nude photographs. For decades, incoming students had been evaluated for conditions such as scoliosis by means of a medical exam, which came to incorporate photography to create a visual record. Linker writes that for many male students, particularly those who had military training, undressing for the camera was no biggie. For female students, it was often a more disquieting undertaking. Sylvia Plath, who endured it in 1950, drew upon the experience in “The Bell Jar,” whose protagonist, Esther Greenwood, discovers that undressing for her boyfriend is as uncomfortably exposing as “knowing . . . that a picture of you stark naked, both full view and side view, is going into the college gym files.” The practice of taking posture photographs was gradually abandoned by colleges, thanks in part to the rise of the women’s movement, which gave coeds a new language with which to express their discomfort. It might have been largely forgotten were it not for a 1995 article in the Times Magazine, which raised the alarming possibility that there still existed stashes of nude photographs of famous former students of the Ivy League and the Seven Sisters, such as George H. W. Bush, Bob Woodward, Meryl Streep, and Hillary Clinton. Many of the photographs in question were taken and held not by the institutions themselves but by the mid-century psychologist William Herbert Sheldon. Sheldon was best known for his later discredited theories of somatotypes, whereby he attributed personality characteristics to individuals based on whether their build was ectomorphic, endomorphic, or mesomorphic.
[...]
Today, the descendants of Jessie Bancroft are figures like Esther Gokhale, a Bay Area acupuncturist and the creator of the Gokhale Method, who teaches “primal posture” courses to tech executives and whose recommendations are consonant with other fitness trends, such as barefoot running and “paleo” eating, that romanticize an ancestral past as a remedy for the ills of the present. The compulsory mass surveillance that ended when universities ceased the practice of posture photography has been replaced by voluntary individual surveillance, with the likes of Rafi the giraffe and the Nekoze cat monitoring a user’s vulnerability to “tech neck,” a newly named complaint brought on by excessive use of the kind of devices profitably developed by those paleo-eating, barefoot-running, yoga-practicing executives. Meanwhile, Linker reports, paleoanthropologists quietly working in places other than TikTok have begun to revise the popular idea that our ancient ancestors did not get aches and pains in their backs. Analysis of fossilized spines has revealed degenerative changes suggesting that “the first upright hominids to roam the earth likely experienced back pain, or would have been predisposed to such a condition if they had lived long enough.” Slouching, far from being a disease of civilization, then, seems to be something we’ve been prone to for as long as we have stood on our own two feet.
952 notes
·
View notes
Text
Two weeks ago, Hurricane Helene made landfall as a Category 4 hurricane in the Big Bend region of Florida. From there it carved a path through Georgia, South Carolina, North Carolina, and Tennessee, leaving historic wreckage in its path as it flooded the region in 40 trillion gallons of water. The catastrophic damage in mountainous western North Carolina, especially, has garnered some of the most attention. Storms like this aren’t supposed to happen in places like that. Well, at least, they weren’t.
The all-hands-on-deck scramble to survey the extent of the damage, save lives and livelihoods, and restore power, water, and roads understandably still hasn’t been fast enough for those most affected. And just as understandably, the shock and the trauma of the storm have given way to conspiracy theories as a way to make sense of it all. Among those that have circulated either by word of mouth or through social media are the false theories that the government is razing property for lithium mining, that FEMA is bulldozing structures to cover up dead bodies, or that Democratic officials and the federal and state level are purposely ignoring the most Republican areas of the country.
There was also grumbling, especially in the early aftermath of the storm, that the media refused to cover what was happening in western North Carolina, or that the government had no money to help Americans suffering from the storm because it had spent it all on munitions for Ukraine and Israel. Another far-right theory for why the government supposedly hasn’t been devoting resources to disaster relief—which, to be clear, it has—is because it’s spending its budget on housing migrants.
The grandaddy of all the conspiracy theories going around, though, would have to be one most eagerly promoted by Georgia Rep. Marjorie Taylor Greene. According to Greene, an undefined “they”—who, if we’re being generous, is meant to be the Democrats, the deep state, or the “establishment”—“can control the weather.” In other words, “they” are actively working to crush communities with historic storms.
Despite backlash from basically every possible corner, she continues, still, to push this idea that the government can enhance and steer hurricanes on a path that does the most destruction to red America, ostensibly to create a mess in swing states that can’t be restored in time for voting. I’ve covered Congress for a while, so I don’t say this lightly: I’m not sure I’ve ever heard a member say something this disassociated with reality. But there are people who will believe it.
Officials at the federal, state, and local levels trying to manage recovery efforts, Democrat and Republican, are at their wits’ end with the overwhelming amount of misinformation that’s impeding their recovery work. They have emphasized that, actually, they’re impressed with the assistance the federal government has offered so far. Unfortunately, that sobriety—from officials actually on the ground—doesn’t extend to certain commanding heights of the Republican Party.
Donald Trump—as of now—hasn’t gone so far as to claim that Democrats control the hurricanes. But he’s given fuel to plenty of other outrageous and dangerous theories. Last week ahead of a visit to North Carolina, he posted on social media that he was getting “reports” about “the Federal Government, and the Democrat Governor of the State, going out of their way to not help people in Republican areas.” At a rally in Michigan this week, Trump said that “Kamala spent all her FEMA money, billions of dollars, on housing for illegal migrants, many of whom should not be in our country,” and that “they stole the FEMA money, just like they stole it from a bank, so they could give it to their illegal immigrants that they want to have vote for them this season.” He said there had been “no helicopters” to relieve people, and that Georgia Gov. Brian Kemp had been unable to get in touch with President Joe Biden.
All of this is blatantly false. It’s also pretty horrifying with another dangerous hurricane moving through the Gulf of Mexico, poised to wreak even more havoc on the region.
Worse yet is that one of the central pillars of social media is owned by an credulous doofus who’s positioned himself as sometimes consigliere, sometimes rally clown, to the Trump campaign. Elon Musk has used his platform seemingly to spread any rumor that’s come his way. Late last week, he posted a note that said that “FEMA is not merely failing to adequately help people in trouble, but is actively blocking citizens who try to help!”
This has been a recurring theme of his, that FEMA is, effectively, working to worsen the situation. Fortunately, he was able to get in touch with Transportation Secretary Pete Buttigieg eventually, which calmed him down. That would have been a good first step, of course, before posting rumors about how the federal government opposes helping people.
The unfortunate question here, as we barrel toward Election Day, is: Does this pattern sound at all familiar?
Much of the country is in widespread discontent. Along comes Trump to either offer his own stories or inflame those floating around on the fringes, to give people someone to blame. Local and state administrators of both parties insist there’s nothing to these stories, but Trump and his sycophants push them anyway.
In other words, no: The pattern and spread of misinformation that’s emerged following Hurricane Helene does not give me confidence that the aftermath of the 2024 election, in the event of a narrow Kamala Harris victory, will go more smoothly than that of 2020. It almost feels like a dry run ahead of the election to test that the systems of deceit are still operable. They sure seem to be—only this time, Elon Musk owns the social media platform that dictates the pace of “news.”
What’s most disconcerting about the idea that the government can control and direct hurricanes to maximize wreckage, or that FEMA is actively working to block Republican areas from rebuilding, is the assumption of malevolence at the root of it. Most of the fact checks of Greene’s theory focus on how it’s obviously not scientifically possible for “them” to do what she describes. What’s equally important to stress—and it’s a shame it needs stressing—is that “they” wouldn’t want to do that. Joe Biden and the Democratic Party do not want hurricanes to kill, displace, and destroy the lives of American citizens. FEMA does not want Republicans to have trouble getting water. If you’re willing to believe these things, though, you’re more than willing to believe that an election can be stolen—again.
134 notes
·
View notes
Text

On March 16, 1991 Latasha Harlin’s short life came to a violent end in the midst of racial tensions in LA, and became a major spark for the 1992 Los Angeles Riots. By the late 1980s, racial tensions were high in South Los Angeles. After the change in national immigration laws in 1965 a large number of Korean immigrants arrived in Los Angeles and by 1968 the first Korean-owned market opened in South Central LA. Longtime African American residents in the area at first welcomed the Koreans but eventually grew angry with them because they refused to hire black employees and often treated their customers poorly. By 1990, 65% of South Central businesses were Korean-owned and a 1992 survey of these storeowners revealed considerable racial prejudice against black customers and black people in general. Koreans in response argued that their attitudes evolved from high crime rates in the area and shop owner fears of shootings and burglaries. Latasha Harlins became a victim of these racial tensions on the morning of Saturday, March 16, 1991. She entered a store owned by a Korean family, to purchase a bottle of orange juice. As she approached the counter, Soon Ja Du, accused her of stealing after seeing her place the bottle in her backpack, despite her holding the $2 payment approaching the counter to pay. Du grabbed the bag and the two women had a violent scuffle. Harlins threw the juice bottle back on the counter and turned to leave the store when Du pulled a .38-caliber handgun and shot 15-year-old Harlins in the back of the head. Du was arrested and her trial was held on November 15, 1991. Security-camera footage which showed Harlins’ attempt to pay for the juice and the subsequent scuffle between the two women convinced a jury to find Du guilty of voluntary manslaughter. The Judge, Joyce Karlin, rejected the jury’s recommendation and instead sentenced Du to five years probation, 400 hours of community service, and a $500 fine.
One of the many reasons black people don't f*** with Asians like that and we should collectively drive them out of our neighborhoods
#latasha harlins#los angeles riots#racial tensions#korean immigrants#south los angeles#soon ja du#racial prejudice#voluntary manslaughter#racial discrimination#asian anti blackness#asian racism
268 notes
·
View notes
Text
The United States is experiencing scorching new levels of heat fueled by climate change this summer, with dozens of people dying in the West, millions sweating under heat advisories and nearly three-quarters of Americans saying the government must prioritize global warming.
But as the Republican Party opens its national convention in Milwaukee with a prime-time focus on energy on Monday night, the party has no plan to address climate change.
While many Republicans no longer deny the overwhelming scientific consensus that the planet is warming, party leaders do not see it as a problem that needs to be addressed.
“I don’t know that there is a Republican approach to climate change as an organizing issue,” said Thomas J. Pyle, president of the American Energy Alliance, a conservative research group focused on energy. “I don’t think President Trump sees reducing greenhouse gases, using the government to do so, as an imperative.”
When former President Donald J. Trump mentions climate change at all, it is mockingly.
“Can you imagine, this guy says global warming is the greatest threat to our country?” Mr. Trump said, referring to President Biden as he addressed a rally in Chesapeake, Va., last month, the hottest June in recorded history across the globe. “Global warming is fine. In fact, I heard it was going to be very warm today. It’s fine.”
He went on to dismiss the scientific evidence that melting ice sheets in Antarctica and Greenland are causing seas to rise, threatening coastal communities around the world. He said it would result in “more waterfront property, if you’re lucky enough to own.” And he lapsed into familiar rants against windmills and electric vehicles.
At the televised debate with Mr. Biden in June, Mr. Trump was asked if he would take any action as president to slow the climate crisis. “I want absolutely immaculate clean water and I want absolutely clean air, and we had it,” Mr. Trump responded, without answering the question.
Mr. Trump’s spokeswoman, Karoline Leavitt, later declined to clarify the former president’s position or discuss any actions he would take regarding climate change, saying only that he wants “energy dominance.”
The United States last year pumped more crude oil than any country in history and is now the world’s biggest exporter of natural gas.
A clear majority of Americans, 65 percent, wants the country to focus on increasing solar, wind and other renewable energy and not fossil fuels, according to a May survey by the Pew Research Center. But just 38 percent of Republicans surveyed said renewable energy should be prioritized, while 61 percent said the country should focus on developing more oil, gas and coal.
“Their No. 1 agenda is to continue producing fossil fuels,” said Andrew Dessler, a professor of atmospheric sciences and the director of the Texas Center for Climate Studies at Texas A&M University. “Once you understand their main goal is to entrench fossil fuels regardless of anything else, everything makes sense.”
The party platform, issued last week, makes no mention of climate change. Instead, it encourages more production of oil, gas and coal, the burning of which is dangerously driving up global temperatures. “We will DRILL, BABY, DRILL,” it says, referring to oil as “liquid gold.”
By contrast, Mr. Biden has taken the most aggressive action of any president to cut emissions from coal, oil and gas and encourage a transition to wind, solar and other carbon-free energy. He has directed every federal agency from the Agriculture Department to the Pentagon to consider how climate change is affecting their core missions.
If Mr. Biden has taken an all-of-government approach to fighting climate change, Mr. Trump and his allies would adopt the opposite: scrubbing “climate” from all federal functions and promoting fossil fuels.
Mr. Trump and his allies want to end federal subsidies for electric vehicles, battery development and the wind and solar industries, preferring instead to open up the Alaskan wilderness to oil drilling, encourage more offshore drilling and expand gas export terminals.
Project 2025, a lengthy manual filled with specific proposals for a next Republican administration, calls for erasing any mention of climate change across the government. While Mr. Trump has recently sought to distance himself from Project 2025, he has praised its architects at the Heritage Foundation, a conservative research organization, and much of the plan was written by people who were top advisers during his first term and could serve in prominent roles if he wins in November.
When pressed to discuss climate change, some Republicans say the country should produce more natural gas and sell it to other countries as a cleaner replacement for coal.
While natural gas produces less carbon dioxide than coal when burned, it remains one of the sources of the greenhouse gases that are driving climate change. Scientists say that countries must stop burning coal, oil and gas to keep global warming to relatively safe levels. Last year, at the United Nations climate summit in Dubai, United Arab Emirates, the United States and nearly 200 countries agreed to transition away from fossil fuels.
But if elected, Mr. Trump has indicated he would pull back from the global fight against climate change, as he did when he announced in 2017 that the United States would be the first and only country to withdraw from the Paris Agreement to limit greenhouse gas emissions. (The United States subsequently rejoined under Mr. Biden.)
And it’s possible he would go even further. Mr. Trump’s former aides said that if he wins in November, he would remove the country altogether from the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change, the international body that works on climate policy and created the 2015 Paris deal.
When it comes to international relations, Project 2025 calls for an end to spending federal funds to help the world’s poorest countries transition to wind, solar and other renewable energy.
The blueprint also calls for erasing climate change as a national security concern, despite research showing rising sea levels, extreme weather and other consequences of global temperature rise are destabilizing areas of the world, affecting migration and threatening American military installations.
Federal research into climate change would slow or disappear under Project 2025, which recommends dismantling the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, which conducts some of the world’s leading climate research and is also responsible for weather forecasting and tracking the path of hurricanes and other storms.
NOAA, according to the authors of Project 2025, is “one of the main drivers of the climate change alarm industry and, as such, is harmful to future U.S. prosperity.” At the agency’s research operation, which include a network of research laboratories, an undersea research center, and several joint research institutes with universities, “the preponderance of its climate-change research should be disbanded,” the blueprint said.
Project 2025 also calls for the president to issue an executive order to “reshape” the program that convenes 13 federal agencies every four years to produce the National Climate Assessment, the country’s most authoritative analysis of climate knowledge. The report is required by Congress and details the impacts and risks of climate change to a wide range of sectors, including agriculture, health care and transportation. It is used by the public, researchers and officials around the country to inform decisions about strategies and spending.
Project 2025 also calls for the elimination of offices at the Department of Energy dedicated to developing wind, solar and other renewable energy.
Waleed Abdalati, a former NASA chief scientist who is now at the University of Colorado Boulder, said downgrading climate science would be a disservice to the nation. “That’s a loss of four years in pursuit of creative solutions,” he said.
As president, Mr. Trump tried to replace top officials with political appointees who denied the existence of climate change and put pressure on federal scientists to water down their conclusions. Scientists refused to change their findings and attempts by the Trump administration to bury climate research were also not successful.
“Thank God they didn’t know how to run a government,” Thomas Armstrong, who led the National Climate Assessment program under the Obama administration, said at the end of Mr. Trump’s presidency, adding, “It could have been a lot worse.”
Next time, they would know how to run the government, Mr. Trump’s former officials said. “The difference between the last time and this time is, Donald Trump was president for four years,” Mr. Pyle said. “He will be more prepared.”
#climate change#climate action#global warming#Donald Trump#Trump#politics#us politics#american politics#election 2024#Republicans don't just not have a plan to fight climate change#they have a plan to make it much worse#the planet is on the line people
107 notes
·
View notes
Note
ive seeeen you mention listening to history podcasts before, are there any that youd recommend? I have looked at whats out there but a lot of the popular ones I saw seemed to be rather dubious if you get me
So an assortment off the top of my head
Mike Duncan's stuff is both generally very good and also the inspiration of 90% of the history podcasts I listen to, so useful for cultural literacy if nothing else. (He podcasted his way into being a bona fide public intellectual for a moment there!) History of Rome is exactly what it sounds like, a narrative history from the mythical foundation of the city to the fall of the Western Empire (getting much more detailed and in depth as it gets into the imperial era). Revolutions is an anthology on what can be called the great revolutions of the modern western world, with series on the English, American, French, Haitian, Spanish American, German/Italian/French again (1848), French round three (Paris commune), Mexican and Russian (also includes a semester-length intellectual history of 19th C europepan leftism) revolutions. First two series are fine but it really gets good with the French Revolution and the Haiti series is some of the best pop history I've listened to or read. Also doubles as just a decent history of the long 19th century in Europe.
Tides of History is the only one of this list that feels like it has an actual production budget and more than one person working on it as part of their actual job. The host is the other guy whose podcasted himself into being a bit of a public intellectual (would rec his substack!) The downside of having a budget is most of the older stuff being locked behind a paywall, which is a shame because the early seasons are some of the best approachable history on the late medieval and early early modern period in Europe I've heard or seen. The current season is about the late bronze age world, and continues to be excellent.
History of Byzantium is explicitly an attempt to pick off where Duncan left off and follow the Eastern Roman empire from the fall of the west to 1452 (it's still in progress, now well into the 13th century). Also much like History of Rome, it starts off fairly general and vague but gets much more detailed as it goes. The general narrative history is intercut with semi-regular interviews with academic historians about the subject of their expertise for more in depth and probably rigorous discussion.
Speaking of Byzantium and Friends is hosted by one of the more prominent working byzantinists and consists of absolutely nothing but that. Much, much more academic - there's a level of assumed background knowledge to get much of anything out of the episodes, and and a level of academic inside baseball, but accurcy-wise this is the podcast I trust most out of all of them.
History of Japan is, again, what it sounds like. One of many podcasts begun by a grad student probably procrastinating working on his thesis that has lasted long enough for him to graduate, get married, and settle into a full time job. Vast majority of episodes are 20-30-minute mini-histories on, say, the biography of a particular political figure or part of a mini-series on the spread of Buddhism or something (plus a few much, much longer series on e.g. the Meiji Restoration). Currently in the middle of remaking/expanding a series that's a general high-level survey of Japanese history to celebrate hitting episode 500.
Criminal Records shares a host with it, but is (intentionally) less rigorous and much more bantery (having two hosts helps, them being married presumably good for the chemistry), also technically a true crime podcast - specifically about weird crimes and legal cases throughout history. My favorite episode is the one on the oldest surviving court case in the record from ancient Sumeria.
The History of the Crusades and it's sequel Reconquista continue the trend of admirably self-explaining names. They're nearly-entirely narrative and political histories, so if you're not interested in crowns, marriages and wars probably give them a pass, but very granular and detailed as they go. Crusades finished after the fall of Jerusalem and then a follow-up about the Albigensian Crusade, Reconquista currently still ongoing (in the 11th century at the moment, I believe).
Pax Brittancia is the one I just finished binging as depression-ameliorating background noise and what I've been posting about recently. Another begun by a grad student avoiding their thesis who has since become a doctor (who had previously completed a podcast on the history of witchcraft, which I have not listened to). It's ostensibly a history of the British Empire, beginning with the Stuart Dynasty (and personal union with Scotland) and moving forward with sufficent attention to detail that after five years and change it's objectively just a very in depth history of the Wars of Three Kingdoms (incl. causes and aftermath). Includes many, many interviews with established historians, including a whole series on Covenanter Scotland and whether its rise should be considered a Scottish Revolution. The narrative just reached Cromwell's inauguration as Lord Protector.
144 notes
·
View notes
Text
I feel like we need to talk about how increasingly poor reading literacy (in America, ofc) is causing subtle negative effects that affect daily lives and make it extremely difficult to understand arguments, analysis, data, and other content, and it is undoubtedly affecting the political sphere.
Over half of Americans 16-74 have a reading comprehension lower than 6th-grade level (source linked below). This is honestly a crisis, yet we already have so many other critical emergencies going on that it’s put on the back-burner. Many people are looking at headlines referencing studies and assuming that whatever’s put in the headline is the truth (they’re often directly against findings or based on deeply flawed studies/surveys). Many don’t understand speeches and debates from politicians (and definitely not the implications they house). In this confusing, heavily biased and illicitly-funded era of endless headlines and content, many don’t even have a 6th-grade level of reading comprehension - how the hell are they going to understand even the basics that are already from unreliable sources?
I can’t help but to think that this may be part of the reason extremist ideologies (MAGA, anti-vaxxers, cultists, TRAs) are becoming increasingly popular. Now, people need to be told what an article or survey or study means - usually by the same people who are trying to get them on their side. Every single TRA I’ve encountered has had massive misunderstandings in the very basics of radfem ideology: they believe we want to kill all gender-nonconforming people, that we think trans-identified people should kill themselves, that we are all conservatives, that JKR has outright advocated for the murder of trans-identified people.
What scares me is that we have one side with all of the anti-vaxxers, MAGA-enthusiasts, and creepy religious cults, and on the other we have the TRA movement absolutely screaming we need for trans people to be catered for in every possible public setting or we’ll “have blood on our hands.” I think anti-vaxxers and the Bible-enthusiasts are more dangerous than TRAs, but at least they are recognised as dangerous. Both sides are controlled by at least one extremist ideology. What the hell are we to do in the 2024 election?
PLEASE take a college reading comprehension course if possible. Many community colleges offer courses cheap, and if it still isn’t feasible, there are plenty of sources online to help improve your reading comprehension.
#gender critical#radblr#radfems do interact#radical feminist#radfem#radical feminists do touch#terfsafe
327 notes
·
View notes
Text
Lois Beckett at The Guardian:
Attacks targeting American public schools over LGBTQ+ rights and education about race and racism cost those schools an estimated $3.2bn in the 2023-24 school year, according to a new report by education professors from four major American universities. The study is believed to be the first attempt to quantify the financial impact of rightwing political campaigns targeting school districts and school boards across the US. In the wake of the pandemic, these campaigns first attempted to restrict how American schools educate students about racism, and then increasingly shifted to spreading fear among parents about schools’ policies about transgender students and LGBTQ+ rights.
Researchers from UCLA, UT Austin, UC Riverside and American University surveyed 467 public school superintendents across 46 US states, asking them about the direct and indirect costs of dealing with these volatile campaigns. Those costs included everything from out-of-pocket payments to hire to lawyers or additional security, to the staff member hours devoted to responding to disinformation on social media, addressing parent concerns and replying to voluminous public records requests focused on the district’s teachings on racism, gender and sexuality. The campaigns that focused on public schools’ policies about transgender students often included lurid false claims about schools trying to change students’ gender or “indoctrinating” them into becoming gay. This disinformation sparked harassment and threats against individual teachers, school board members and administrators, with some of the fury coming from within local communities, and even more angry calls, emails and social media posts flooding in from conservative media viewers across the country.
In addition to the financial costs of responding to these targeted campaigns, the study revealed other dynamics, the researchers said. “The attack on public officials as pedophiles was one I heard again and again, from people across extremely different parts of the country: rural, urban, suburban. It speaks to the way that this really is a nationalized conflict campaign,” said John Rogers, an education professor at the University of California, Los Angeles, and the lead author of the study. The frequency with which both school board members and school superintendents were “being called out as sexual predators – it was really frightening”, Rogers said. Superintendents from across the country told the researchers how these culture battles had affected their schools, and cut into resources they would have preferred to spend on education.
[...] While disagreement, debate and dealing with angry parents are a normal part of local public school administration, the researchers noted, the political campaigns that schools have faced in recent years have been anything but normal. Many of them have been driven by “a small number of active individuals on social media or at school board meetings”, and fueled by misinformation. The school-focused campaigns, which started with claims that elementary and middle schools were harming white students by teaching critical race theory and later shifted to attacks on schools’ policies for transgender students, were nationally organized, with “common talking points” that could be traced back to conservative foundations and rightwing legal organizations, and were intensely amplified by rightwing media coverage, Rogers said.
Public schools across the US burned up nearly $3.2BN worth of money fending off right-wing culture war items such as book bans, anti-LGBTQ+ extremism, anti-student inclusion, and anti-racial equity policies.
See Also:
The Advocate: U.S. public schools lost $3.2 billion fighting conservative culture wars: report
#Schools#Culture Wars#Parental Rights#Public Schools#School Boards#Education#School Curriculums#Student Inclusion#Book Bans#Forced Outing#Anti LGBTQ+ Extremism#LGBTQ+#Critical Race Theory#Racial Equity#Anti Trans Extremism#Transgender
90 notes
·
View notes
Text
SURVEY BREAKDOWN
(long post warning)
**A FEW DISCLAIMERS**
I AM NOT A SCIENTIST, I AM A HUMANITIES BITCH. My math skills are limited, and I have no training on processing/presenting this sort of data. I am also one person with a shitty laptop, an unreliable internet connection, and a very busy personal life. Take all of this with an extremely large grain of salt.
Participants are self-reporting. They may not know for sure, they may be wrong, they may be lying. I took everyone here at their word. I tried not to extrapolate much from what they were saying, because I do not want to misrepresent what they said.
I will be covering why people thought they developed this fetish in a later post because this is already too long.
Gender of Participants
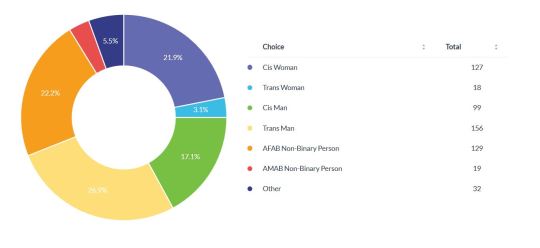
*According to a 2024 survey, 1.14% of American adults identify as transgender, while 1.52% do not identify as male, female, or trans (some of whom identified as Non-Binary.) That makes the presence of trans and non-binary participants VASTLY disproportional to the American average. I'm sure some of it can be explained by younger people being more likely to identify as not cis, and younger people using the internet far more than the older generations. I also read a paper once that suggested the internet was responsible for the development of more niche fetishes. It's also possible that trans people are more likely to be comfortable engaging with communities surrounding 'deviant' sexual interests because they've already been labeled 'abnormal' (BUT THESE ARE ALL JUST GUESSES). What I theorize is that, because pregnancy is inextricable from sex organs and gender rolls, trans people (ESPECIALLY AFAB trans/non-binary people) are more likely to have those early, strong emotional reactions to pregnancy that seem to develop into fetishes. I'll get into this more on my next post.
*cis women outnumbering cis men was not something I was expecting, but makes sense, since young girls often have to think about pregnancy much sooner than boys, and it threatens to have a much greater impact on their life.
*in retrospect, I wish I'd included a question on how the participants found the survey, since knowing might help explain the disparity between trans and cis people.
Sexuality of Participants
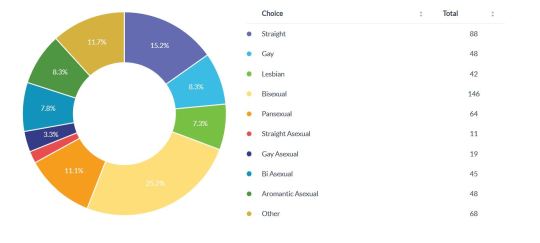
*most (but not all) of the people who chose "other" wrote in an ace-spec identity not included in the above choices (ace lesbian, demi-sexual, etc.,)
Content of Fetish Material Consumed
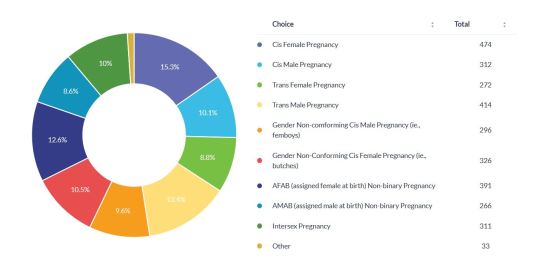
*the vast majority of participants selected multiple answers, the exception to this was straight cis men, who often only selected the 'Cis Female Pregnancy' option (a small percentage of this group also answered femboys). The minority of straight cis men who chose other options most often fantasized about becoming pregnant themselves.
When the Fetish was Developed
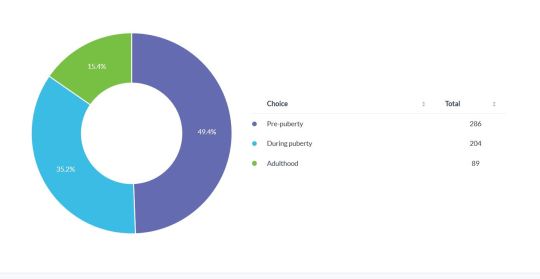
*One person wrote in that they didn't believe children could have fetishes. Their entry was shortly followed by one from someone who described frequently masturbating to fantasies surrounding pregnancy at the age of 5. This isn't important to the overall data, I just find it funny.
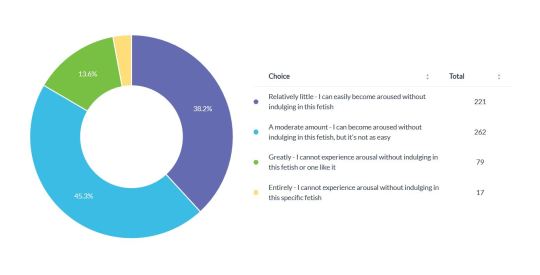
How Great a Role does the Participants' Fetish Play in their Achieving Arousal?
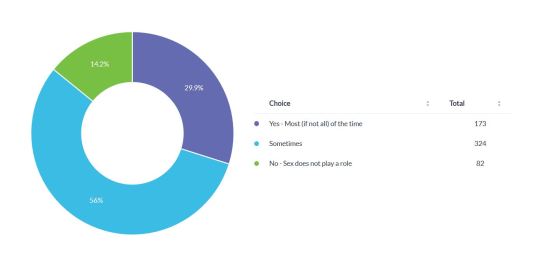
How Great a Role does Sex Play in the Participants' Fetish Related Fantasies?
Did the Participants' Pregnancy Fetish Play a Role in their First Time Experiencing Arousal?
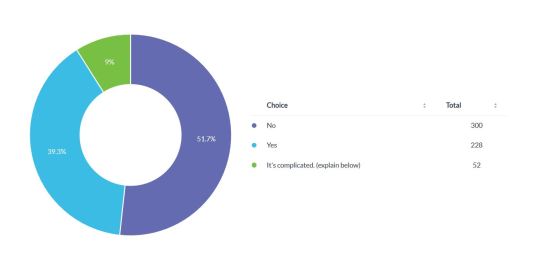
*most of the "it's complicated" answers were people who couldn't remember their first time experiencing arousal.
...
That's the basics down, stay tuned for a breakdown of why people think they developed their fetish.
(will be linked when post is done).
84 notes
·
View notes
Text
Alphaworld File 1: Oral History
The universe is multifarious, constantly diverging as new choices are made. Spinning away through time, these alternate realities become locked away from our own, so we can never know exactly what would have happened if a single choice was made differently.
Except, sometimes, two of those worlds, careening through the upper dimensions, happen to converge. As they slide past each other, they may line up just so, each leaving behind fragments as they continue their journey into their divergent futures. You’ve never heard of this, because the remnants, mostly data, are swiftly collected by various government agencies and collected into reports on the intercepted reality.
This report collects various scientific articles, personal journals, news reels, and even a documentary series from one such reality, codenamed Alphaworld. In this world, gay men have not only become the norm, but have seemingly replaced all other people. In this world, society is stratified into an apparently biological hierarchy of homosexual castes, based on men’s physical characteristics and psychologies. Upon finishing the following fragment from a peer-reviewed article that was a trace recovered from Alphaworld, please select the next fragment you would like to consume.
X
An Oral History of the Creation and Initial Spread of the Alpha Phenomenon, by Alpha Dr. Jose Martinez
Until recently, it was not known what sparked the spread of the Alpha Phenomenon which has wholly remade the world in recent years. This was until Alpha Joshua Dearfoot, who resides with his Betas in rural ex-Ontario, stated during a livestream on OnlyFans that he is the original Alpha.
Alpha Dearfoot does not interact with Betas from outside his harem unless they renounce their current Alpha. As this research team contains no unbonded Betas—Alpha Dr. Martinez says we can’t spend too much time with non-harem Betas—we investigated among those close to Alpha Dearfoot, conducting interviews and surveying in the local area to discover as much as we could.
Joshua, as he was known before the emergence of the Alpha Phenomenon, was a PhD candidate in nanotechnology, with a secondary focus in physiology. Photographs kept by his father (Beta to Alpha Sean Barehill) reveal that through his youth and young adulthood Joshua was physically unimpressive, with a physique not even reaching the base level expected of a Beta.
According to a classmate of Joshua’s from university (Beta to Alpha Liam Oliver), Joshua was studious but insecure: “I mean, I used to push him around all the time for being a fa— gay kid. Gay and a nerd? In the Old World, that was, like, the worst thing.” When asked about whether he has properly apologised, the Beta said, in a rapturous voice, “Oh, yeah, Alpha Dearfoot was my first. He disciplined me so well I could barely walk, I came like four times. Then he told me to come join Alpha Liam’s harem. I mean, he wasn’t Alpha Liam then, I was one of the first guys to go full Beta on campus.”
It appears that Alpha Dearfoot had a difficult youth, growing up unable to meet certain Old World expectations of manhood. The masculine stereotypes of Native Americans also seem to have weighed on him, as he was entirely unable to meet them. As his father told us, “Joshua was a sweet kid, but he got bullied for being too short and scrawny, not matching the image of an “Indian” in all these bigoted kids’ heads. He was obsessed with growing bigger, which is why he went into physio.” Remember, in some communities it is normal for a Beta father to continue to refer to his Alpha son by his first name.
According to Sigma Harrison White, a former lab partner of Dearfoot’s who fucked us on his lawn in exchange for this interview, Joshua was obsessed with creating some way to become more manly. “He spent some really long evenings in the lab,” said Harrison while one of us squealed in the grass beneath him. “One morning he came out with this manic grin on his face, said that he’d finally done it, and ran off. Two weeks later, he came back a full Alpha.” At this point, Harrison’s pace slowed down as he became contemplative. “It was only after he started hooking up with all the queer guys on campus that we started becoming Alphas and Sigmas and stuff, too.”
Did Alpha Dearfoot intend for the Alpha Phenomenon to be infectious? A Beta from his harem claims not. “He got home from school one morning all excited about some project he’d finished,” the Beta told us—it seems that he and Alpha Dearfoot were childhood friends. “The next day, he seemed a little different, a little more muscular, more assertive. He seemed really satisfied for about a week, then he got scared. He just kept getting bigger. The day he got taller than me and nearly broke a bar at the gym doing deadlifts, I started feeling the Beta change.
“I went to him and started telling him about my muscle gains and all the weird thoughts and sensations I was experiencing, and he got really scared,” the Beta continued, his eyes distant. “I started to comfort him, and that was when we felt the bond form. It felt so right for him to be my first, to finger me open and fill me with his still-growing dick.”
While we pressed for more details about what may have been the first Alpha/Beta bond in history, the Beta refused to disclose more information, claiming that it was private to him and his Alpha. For the reader’s imagination, see Figure A to find a picture of Alpha Dearfoot from his Instagram profile.

Alpha Dearfoot appears to have intended to create a nanomachine-based masculinity booster, and the transmissibility of the Alpha Phenomenon, as well as the behavioural and sexual changes it induces, were unintended side effects, perhaps introduced in the particles’ replication process. The effects of the Alpha Phenomenon on aging and physical fitness may also be unexpected consequences of Alpha Dearfoot's programming efforts.
According to Alpha Young Baek Hyeon, who lives in the former New York area with a mixed harem, he and Alpha Dearfoot attempted to “date,” an outmoded practice common in the Old World, during the early weeks of the Alpha Phenomenon’s spread. “Alpha DeWayne and I work well together,” Alpha Young told us by video call, “but we’re both pretty chill even since we changed. Alpha Dearfoot and I couldn’t even stand to be in the same room once I had transformed. He’s one of the most territorial Alphas I’ve ever met, he can barely stand to have another Alpha within a mile of him.” As Alpha Young spoke, we watched a well-trained Beta enter the room with a plate of apple slices and present them to his Alpha.
“He was really torn up about it, too. Even though we couldn’t stop yelling at each other in person or over the phone, he left me a ton of really sweet voice messages about how much he’d liked me before we became Alphas.” Alpha Young took a bite of apple and ruffled his Beta’s hair, causing all of us to shudder with phantom pleasure at the affection. With a contemplative expression, Alpha Young said, “No, I don’t think he meant for any of this to happen.”
While this study has yielded plenty of useful biographical information about the man apparently responsible for the Alpha Phenomenon that changed the world, we appear no closer to understanding the precise mechanism of that change. With better access to the programming of the nanomachines, perhaps it would be possible to reduce the natural aggressiveness of the Alphas, allowing Alphas like Dearfoot to return to their studies or jobs if they so wish. In the following section, we will propose potential opportunities for further research in the effort to isolate the Alpha Phenomenon.
Or vote on Strawpoll here: https://strawpoll.com/wby5A0vw8yA
This series is my way of celebrating reaching 2000 followers! I hope you enjoy this glimpse into Alphaworld and vote on what file you would like to see next. There is no strict update schedule, so you good boys better be on the lookout for a new chapter you can vote on ;)
177 notes
·
View notes