#200 films of 1952 film 25
Text

Day 27- Film: The Pride of St. Louis
Release date: May 2nd
Studio: 20th Century Fox
Genre: Drama/sports
Director: Harmon Jones
Producer: Jules Schermer
Actors: Dan Dailey, Joanne Dru, Richard Crenna
Plot Summary: This is the life story of famous 1930s baseball pitcher Dizzy Dean. It covers his rise to fame, his marriage, his life-changing injury, and his struggles to find a post-baseball career.
My Rating (out of five stars): ***
I didn’t know anything about Dizzy Dean before I watched this movie, and I didn’t want to read up on him beforehand, fearing it would ruin any surprises. I almost wish I had looked, though, because I spent the whole movie waiting for something really dramatic to happen... and it never did. It ended up being just a simple story of the brief career of a baseball player who everyone remembered as quite a character.
The Good:
The baseball scenes were interesting and well shot. I thought they were some of the most entertaining parts of the film, and I’m someone who doesn’t enjoy baseball much at all.
Dan Dailey was a good combination of being an effective actor and an effective looking sportsman.
The Bad:
There just wasn’t really much drama. Even his career-ending injury wasn’t covered in a way that made the trauma of it real. I think the tone was often too lighthearted- it lowered the stakes for a lot of things.
The movie infantilized him a lot. He acted like a child, and those around him treated him like a child, including his wife. She finally threatened to leave him and refused to come back until he made an adult decision on his own. The film even ends with some neighborhood children coming to the door to ask his wife if he can come out and play with them!
Supposedly the real Dizzy was quite a memorable and colorful character, but the film didn’t show much of anything other than the fact that he was childish and he spoke in a thick uneducated rural southern drawl.
It seemed pretty sanitized. There were very short scenes hinting at the fact that he drank and gambled after his injury, but it was not a realistic portrayal of someone struggling with those issues.
I really did not understand why his wife married him. She was highly educated, he wasn’t educated at all, and he often acted more like her son than her husband.
There was a lot of attention paid in the beginning to his very close relationship with his brother Paul, but then Paul virtually disappeared for the last third of the movie.
0 notes
Text
Timeline
Alright, so, the difficulty I first ran into, is that I could not find an exact timeline for releases of Superman content, so through intensive googling, I managed to make a list of releases up to 1960.
1938
(Comics) Action Comics #1-8
1939
(Comics) Action Comics #9-19 | Superman #1-3
1940
(Comics) Action Comics #20-31 | Superman #4-7
(Radio) The Adventures of Superman "The Baby From Krypton" - "The Nitrate Shipment"
1941
(Comics) Action Comics #32-43 | Superman #7-13 | World's Finest Comics #1-4
(Radio) "Black Pearl of Osiris" - "The Pan-Am Highway"
(Film) Fleischer Animated Series 1-2
1942
(Comics) Action Comics #44-55 | Superman #14-19 | World's Finest Comics #5-8
(Film) Fleischer Animated Series 3-13
(Radio) "The Mechanical Man" - The Mystery Ship"
(Novel) Adventures of Superman by George Lowther
1943
(Comics) Action Comics #56-67 | Superman #20-25 | World's Finest Comics #9-12
(Film) Fleischer Animated Series 14-17
(Radio) ""The Tin Men" - "Stolen War Information"
1944
(Comics) Action Comics #56-79 | Superman #26-31 | World's Finest Comics #13-16
(Radio) "Lois and Jimmy Disappear" - "The Man in the Velvet Shoes"
1945
(Comics) Action Comics #80-91 | Superman #32-37 | More Fun Comics #101 | World's Finest Comics #17-20
(Radio) "The Mystery of the Sleeping Beauty" - "Looking for Kryptonite"
1946
(Comics) Action Comics #92-103 | Superman #38-43 | World's Finest Comics #21-24
(Radio) "The Talking Cat" - "The Phony Restaurant Racket"
"Clan of the Fiery Cross"
1947
(Comics) Action Comics #104-115 | Superman #44-49 | World's Finest Comics #25-28
(Radio) "The Phony Inheritance Racket" - "Pennies for Plunder"
1948
(Comics) Action Comics #116-127 | Superman #50-55 | World's Finest Comics #29-32
(Film) Superman Serial (Columbia Pictures starring Kirk Alyn)
(Radio) "Hunger Inc." - Superman's Secret"
1949
(Comics) Action Comics #128-139 | Superman #56-61 | Superboy #1-5 | World's Finest Comics #33-37
(Film) Keep Your School All-American
(Radio) "The Return of the Octopus" - "Diamond of Death"
1950
(Comics) Action Comics #140-151 | Superman #62-67 | Superboy #6-11 | World's Finest Comics #38-49
(Film) Atom Man vs. Superman (Kirk Alyn)
1951
(Comics) Action Comics #152-163 | Superman #68-73 | Superboy #12-17 | World's Finest Comics #50-
(Film) Superman and the Mole Men (George Reeves)
1952
(Comics) Action Comics #163-175 | Superman #74-79 | Superboy #18-23 | World's Finest Comics #
(TV) Adventures of Superman (George Reeves) Season 1
1953
(Comics) Action Comics #176-187 | Superman #80-85 | Superboy #24-29 | World's Finest Comics #
(Film) Adventures of Superman (George Reeves) Season 2
1954
(Comics) Action Comics #187-199 | Superman #86-93 | Superboy #30-37 | World's Finest Comics
(Film) Stamp Day for Superman
1955
(Comics) Action Comics #200-211 | Superman #94-101 | Superboy #38-45
(Film) Adventures of Superman (George Reeves) Season 3
1956
(Comics) Action Comics #212-223 | Superman #102-109 | Superboy #46-53
(Film) Adventures of Superman (George Reeves) Season 4
1957
(Comics) Action Comics #224-235 | Superman #110-117 | Superboy #54-61
(Film) Adventures of Superman (George Reeves) Season 5
1958
(Comics) Action Comics #236-247 | Superman #118-125 | Superboy #62-69
(Film) Adventures of Superman (George Reeves) Season 6
1959
(Comics) Action Comics #248-259 | Superman #126-133 | Superboy #70-77
(Film) George Reeve's death.
1960
(Comics) Action Comics #260-271 | Superman #134-141 | Superboy #78-85
(Film) Superman (Mohammed Hussain)
However, upon joining the Superman subreddit Discord, I was kindly referred to this link on the Superman Supersite:
Which, heh, could have saved me some time. tbh.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Here is a list of the top 25 notable UFO sightings in history, along with details about each event:
1. **Kenneth Arnold Sighting (1947)**
- **Location**: Mount Rainier, Washington, USA
- **Details**: Pilot Kenneth Arnold reported seeing nine crescent-shaped objects flying at high speed, coining the term "flying saucers."
2. **Roswell Incident (1947)**
- **Location**: Roswell, New Mexico, USA
- **Details**: W.W. "Mac" Brazel discovered debris from a crashed object, initially reported as a "flying disc" by the military before being reclassified as a weather balloon.
3. **Battle of Los Angeles (1942)**
- **Location**: Los Angeles, California, USA
- **Details**: Anti-aircraft artillery fired thousands of rounds at an unidentified object over Los Angeles during World War II, leading to widespread panic.
4. **The Phoenix Lights (1997)**
- **Location**: Phoenix, Arizona, USA
- **Details**: Thousands reported seeing a massive V-shaped craft with lights moving silently across the sky.
5. **Rendlesham Forest Incident (1980)**
- **Location**: Suffolk, England
- **Details**: U.S. Air Force personnel reported seeing strange lights and a craft near a military base, with one officer claiming to have touched the craft.
6. **Dyatlov Pass Incident (1959)**
- **Location**: Ural Mountains, Russia
- **Details**: Nine hikers died under mysterious circumstances, with reports of strange lights in the sky and unusual injuries.
7. **The Tic Tac UFO (2004)**
- **Location**: Off the coast of California, USA
- **Details**: U.S. Navy pilots encountered a fast-moving object resembling a Tic Tac during training exercises, later confirmed by military footage.
8. **The Travis Walton Abduction (1975)**
- **Location**: Arizona, USA
- **Details**: Logger Travis Walton claimed to have been abducted by a UFO for five days, leading to extensive media coverage and a film adaptation.
9. **Westall Sighting (1966)**
- **Location**: Melbourne, Australia
- **Details**: Over 200 students and teachers witnessed a flying saucer hovering near their school, with many reporting the incident to authorities.
10. **The Cash-Landrum Incident (1980)**
- **Location**: Texas, USA
- **Details**: Two women reported seeing a diamond-shaped craft emitting heat and light, leading to health issues attributed to radiation exposure.
11. **The Allagash Abductions (1976)**
- **Location**: Maine, USA
- **Details**: Four men on a camping trip reported being abducted by aliens after seeing strange lights in the sky.
12. **The Belgium Wave (1989-1990)**
- **Location**: Belgium
- **Details**: Numerous sightings of triangular UFOs over Belgium led to investigations by the military and police.
13. **The Voronezh Incident (1989)**
- **Location**: Voronezh, Russia
- **Details**: Children and adults reported seeing a giant alien creature and a UFO landing in a park.
14. **The McMinnville UFO Photographs (1950)**
- **Location**: Oregon, USA
- **Details**: A farmer took two famous photographs of a flying saucer, which became iconic in UFO lore.
15. **The Hudson Valley Sightings (1980s)**
- **Location**: New York, USA
- **Details**: Thousands reported seeing large, silent, V-shaped crafts over the Hudson Valley region.
16. **The Kecksburg Incident (1965)**
- **Location**: Pennsylvania, USA
- **Details**: Witnesses reported seeing a fireball and a crash, with military personnel recovering a mysterious object.
17. **The Flatwoods Monster (1952)**
- **Location**: West Virginia, USA
- **Details**: After seeing a bright object land, witnesses encountered a strange creature, leading to widespread media coverage.
18. **The Lubbock Lights (1951)**
- **Location**: Texas, USA
- **Details**: A series of lights in a V formation were observed by professors and photographed, leading to investigations.
19. **The Varginha Incident (1996)**
- **Location**: Brazil
- **Details**: Witnesses reported seeing a strange creature and a UFO, leading to military involvement and widespread speculation.
20. **The Rendlesham Forest Incident (1980)**
- **Location**: Suffolk, England
- **Details**: U.S. Air Force personnel reported seeing strange lights and a craft near a military base, with one officer claiming to have touched the craft.
21. **The Aurora, Texas Incident (1897)**
- **Location**: Texas, USA
- **Details**: A supposed UFO crash led to the burial of an alien in the local cemetery, marking one of the earliest UFO reports.
22. **The Socorro Incident (1964)**
- **Location**: New Mexico, USA
- **Details**: Police officer Lonnie Zamora reported seeing a craft and two small beings, leading to extensive investigations.
23. **The Belgium Wave (1989-1990)**
- **Location**: Belgium
- **Details**: Numerous sightings of triangular UFOs over Belgium led to investigations by the military and police.
24. **The Tic Tac UFO (2004)**
- **Location**: Off the coast of California, USA
- **Details**: U.S. Navy pilots encountered a fast-moving object resembling a Tic Tac during training exercises, later confirmed by military footage.
25. **The Val Johnson Incident (1979)**
- **Location**: Minnesota, USA
- **Details**: Deputy Sheriff Val Johnson reported a close encounter with a UFO that damaged his patrol car and left him disoriented.
These sightings span decades and highlight the diverse experiences and reports associated with UFO phenomena.
Sources
[1] Top 25 Alien Encounters: UFO Case Files Exposed (Video 2023) - IMDb https://www.imdb.com/title/tt26424550/
[2] List of reported UFO sightings - Wikipedia https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_reported_UFO_sightings
[3] Unidentified flying object (UFO) | History, Sightings, & Facts - Britannica https://www.britannica.com/topic/unidentified-flying-object
[4] 10 UFO Sightings Around the World - Google Arts & Culture https://artsandculture.google.com/story/10-ufo-sightings-around-the-world/BwVRe1UdReh-_w?hl=en
[5] See 10 Mysterious 'UFO Sighting' Photos From History - Time https://time.com/4232540/history-ufo-sightings/
[6] Top 4 UFO Sightings AROUND THE WORLD! | The Proof Is Out There https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6e7xu0y5ZrE
[7] 'Outlast' Review, Recap And Ending: Who Survives—The Fittest, Smartest, Or Most Aggressive? https://dmtalkies.com/outlast-season-1-review-recap-and-ending-2023-netflix-game-reality-show/
[8] Outlast Episode 8 Recap: And the Winner Is... https://outdoors.com/outlast-recap-episode-8-finale/
0 notes
Text
MAD MONEY!!!
Lucy & Cash: A Crypto-History
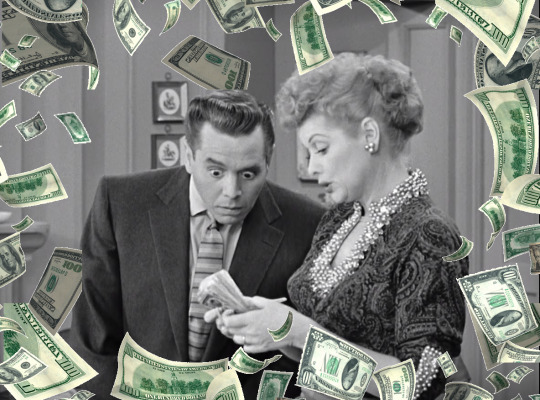

One of the great dramatic devices is the pursuit of money. The Lucy character was generally a middle class, working mother who was in pursuit of the American dream. Her entrepreneurial aspirations were only matched by her fiscal irresponsibility.

Blood Money (1934) ~ The metaphorical title of Lucille Ball’s 4th film.

“Trying to Cash the Prize Check” (1950) ~ Liz (Lucille Ball) goes on a radio quiz show and wins a check for $500, but she only gets to keep it if she can cash it within 25 minutes, and the banks are all closed!
I LOVE LU¢Y

“The Quiz Show” (1951) ~ With Lucy’s household accounts in arrears, she goes on a radio quiz show to win a $1,000!

Publicity photo showing Phil Ober handing Lucy the cash prize after dealing with a tramp (John Emery).

Lucy wins the prize, but after some quick accounting by Ricky, Lucy is left with just 25 cents!

“The Freezer” (1952)

“Job Switching” (1952)

“The Business Manager” (1954) ~ Lucy figures out how to ‘game the system’ and pay her bills as well! This is one of the best examples of money management gone wrong on all of television!

LUCY (to ETHEL): “They’re making the bills smaller, aren’t they?”

Lucy can’t think fast enough to answer Ricky’s financial questions about her windfall at the “market”.
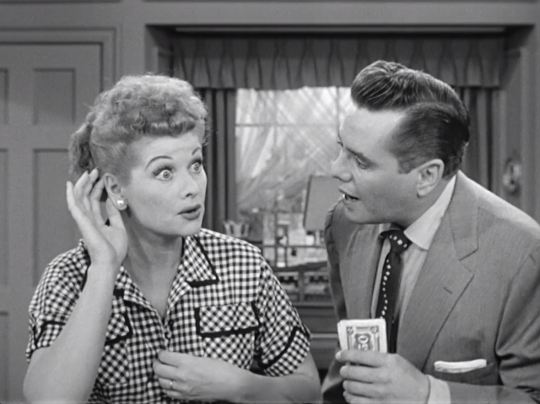

Lucy listens for her “little small voice” - which tells her what to buy at the “market”.

Lucy breezes out of the room after giving Ricky money for a haircut.

“The Girls Go Into Business” (1953) ~ Lucy and Ethel buy a dress shop they think is a gold mine! Lucy figures that based on the fact that she saw two customers buy $200 in merchandise in five minutes, they would make $2,400 an hour, and $19,000 a day! On the day this episode was filmed, September 11, 1953, hundreds of women took to the streets of New York City to track down bargains as part of 1953 Dollar Days. It was also the same day Lucille Ball was accused of being a Communist. Earning green paled compared to being called red!

MRS. HANSEN: Oh, you’re the dearest, sweetest girls in all the world and how do you want to handle the down payment?
LUCY: Uh, well, what did you have in mind?
MRS. HANSEN (bluntly): Money.
Mabel Paige (Mrs. Hansen) does a brilliant job of portraying a little old lady with the heart of a cash register!

Oops! Mrs. Hansen can’t need money all that much, since she leaves a bill lying on the floor!
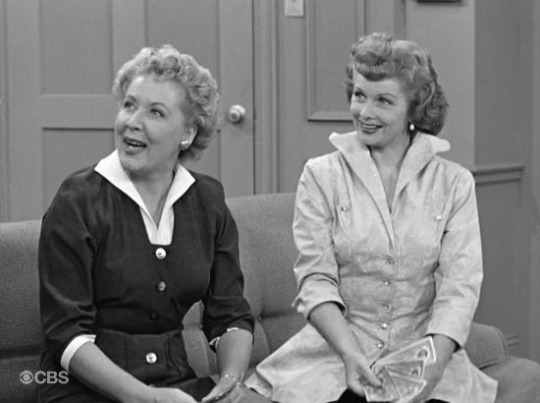

Lucy and Ethel sell the shop for $3,500. Lucy and Ethel think they’ve made a nifty profit – until they boys tell them the building sold to developers for $50,000!

“Bonus Bucks” (1954) ~ Lucy finds the winning dollar bill in the newspaper’s Bonus Buck contest, but lets it slip through her fingers. Now she has only a few hours left to get it back to qualify for the cash prize! This was another of the best of the money madness episodes. Everything revolves around the almighty dollar! In real life, contests like these were called Lucky Bucks, but since Lucky Strike was the largest competitor of “I Love Lucy’s” sponsor, Philip Morris, the writers were discouraged from using the word ‘lucky.’
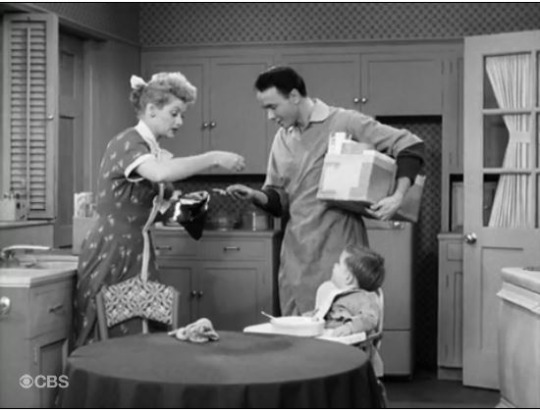

The episode begins with Lucy paying for her grocer delivery, careful not to pay with a buck whose serial number had not been checked.

Lucy and Ethel check their bills against the newspaper’s published seriel numbers to see if they are winners.

When they find one - they fight over who it belongs to - ripping it in half!

After ransacking the laundry to get the bill back, they are awarded the prize money. After expenses, they are left with one dollar - the same amount they started with! Fred gives the lone bill to a starched Lucy. End credits roll.

“The Diner” (1954) ~ After a price war over hamburgers reduces the price to a penny, A Little Bit of Cuba gives a drunk a dollar to buy 100 hamburgers from a Big Hunk of America.
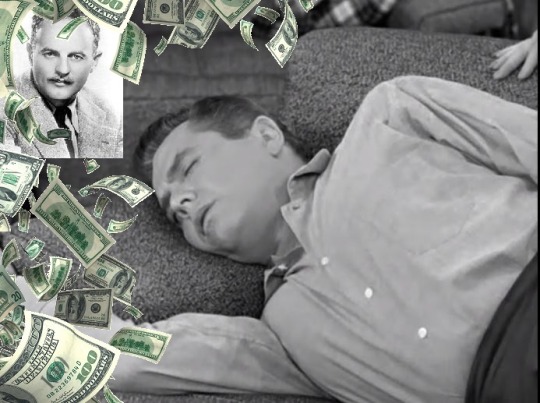

“Getting Ready” (1954) ~ Talking in his sleep during a nap on the sofa, Ricky is dreaming of Hollywood.
RICKY: “No. No, Mr. Zanuck. My price is a million dollars, Mr. Zanuck.”

“The Million Dollar Idea” (1954) ~ Lucy wants to sell her own salad dressing - until Ricky points out that she is losing money on every jar! Although this episode was all about making money, no money was ever made.

In April 2019, CBS colorized “Million Dollar Idea” and “Bonus Bucks” and aired them under the title Funny Mooney $pecial.

“Bon Voyage” (1956) ~ After missing the ship to Europe, Lucy arranges to be lowered to the deck by helicopter. Learning that the chopper can’t land on the ship, she tries to convince the pilot to fly her to Europe!
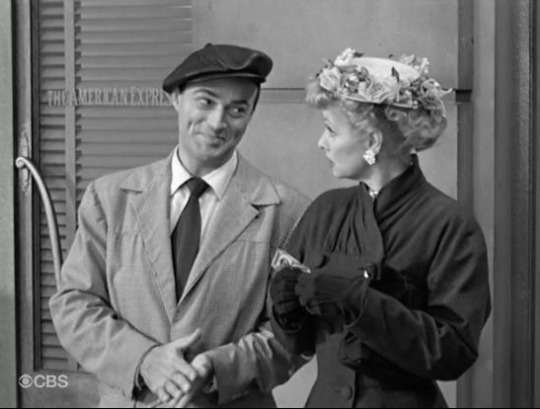

“Paris at Last!” (1955) ~ Lucy’s money trouble didn’t stop at the border. She exchanges American money for French Francs. Little does she know the man (Lawrence Dobkin) standing in front of the American Express Office is a forger!
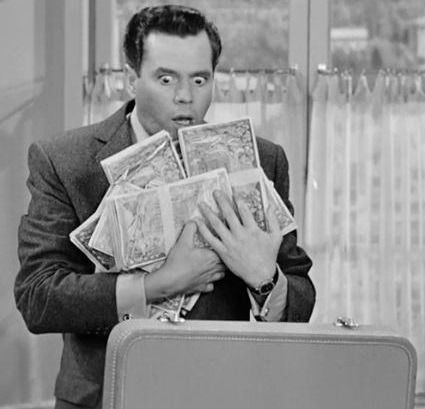

“Lucy Goes to Monte Carlo” (1956) ~ While traveling through the French Riviera, Lucy promises Ricky she won’t step foot inside a casino, but inadvertently gambles her way into a small fortune. Ricky finds the cash hidden in Ethel’s lingerie case. He thinks Fred is embezzling. The Desilu props department visited Earl Hays Press in Hollywood to have the money printed for this episode.
THE LU¢Y $HOW

When Mr. Mooney arrives in Danfield to work at the bank, he reads from Mr. Barnsdahl’s 27-page memo about Mrs. Carmichael:
“To get money from the bank, she will threaten, wheedle, cajole, cry, implore, jolly and stage tantrums.”

“Lucy Misplaces $2,000″ (1962) ~ The bank gives Lucy $2,000 instead of $20. Lucy gazes lovingly at the four $500 bills and remarks that President McKinley has a lovely smile. When it comes time to return the cash, it is missing. Lucy and Viv track down the money to a local carnival.

“Lucy, the Bird Sitter” (1964) ~ Mr. Mooney’s pet bird is a female cockatiel named Greenback for its coloration. “Greenback” is also a slang word for US paper currency due to its dark green color; an ideal name for a miserly banker’s bird!

“Lucy the Coin Collector” (1964) ~ When Jerry finds a rare penny worth $16.50, Lucy and Viv decide to search through thousands of pennies to find a rare one.

Lucy asks Mr. Mooney for change for a ten dollar bill - all pennies!

Viv volunteers to sing a couple of choruses from “Pennies from Heaven” or “Three Coins in the Fountain.” Both songs also were the titles of popular films.

“Lucy, the Meter Maid” (1964) ~ Viv volunteers to pay her parking fine rather than face a ticket, but Lucy thinks of it as a bribe.

“Lucy and the Great Bank Robbery” (1964) ~ When Lucy rents out Viv’s room to two gentlemen visiting for the World’s Fair, they turn out to be bank robbers who stash the loot in Viv’s mattress.
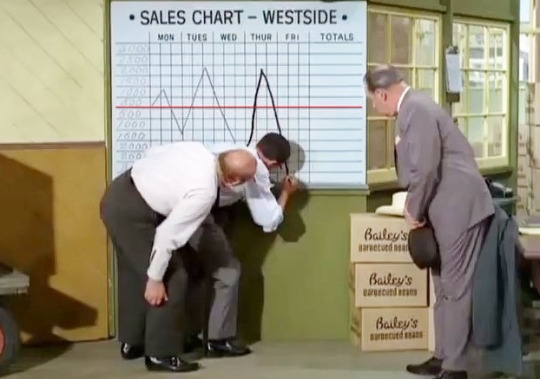
“Lucy, the Bean Queen” (1966) ~ Mr. Mooney partners with an enterprising southern colonel to market canned baked beans. Their sales are plunging until Lucy gets involved.
HERE’$ LUCY

“Lucy Makes a Few Extra Dollars” (1971) ~ Literally!
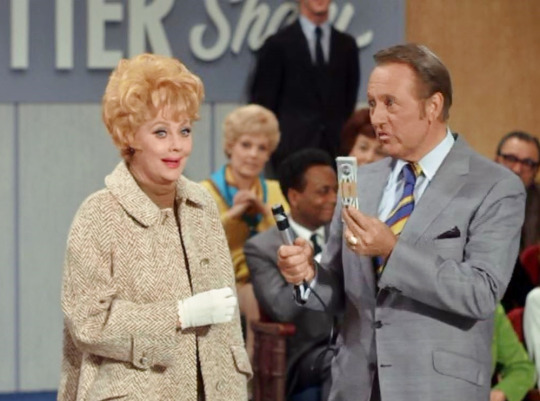

“Lucy Loses Her Cool” (1970) ~ Lucy goes on the Art Linkletter Show and is challenged not to lose her temper for 24 hours in order to win $500.
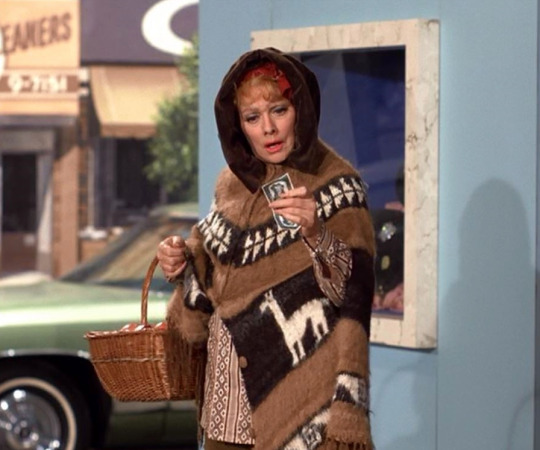

"Dirty Gertie” (1972)

“Lucy Takes Over” (1970) ~ Lucy finds her great grandmother's diary with an IOU from one of Harry's relatives tucked inside. With interest, Lucy estimates Harry owes her thousands of dollars and soon she's taken over his business!

“Lucy the Process Server” (1968) ~ Harry asks Lucy to deliver a summons and make a bank deposit. Lucy gets the two mixed-up and loses the envelope of $1,500 cash!
CA$H REGISTER$

“The Diner” (1954) ~ After the diner is divided in two, the cash register is left straddling the border between “Cuba” and “America”.
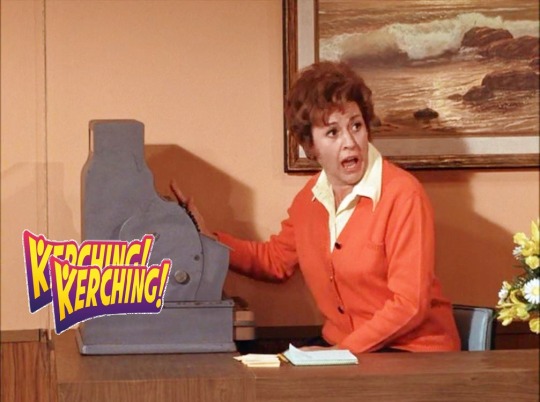

“Lucy Competes with Carol Burnett” (1970) ~ Frequent extra Vanda Barra has no lines, but a very funny bit of business with a cafeteria cash register.
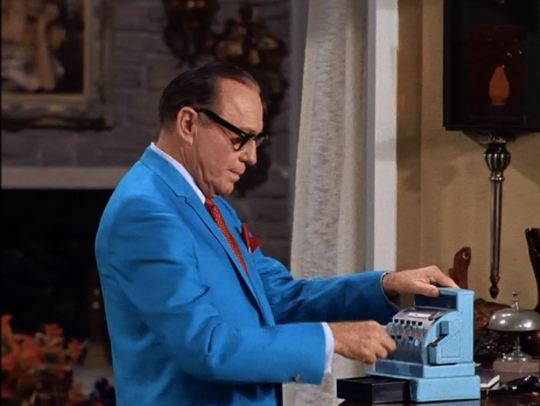

“Lucy Visits Jack Benny” (1968) ~ At Jack Benny’s home in Palm Springs, he makes change for Lucy on his toy cash register.

“Lucy and the Franchise Fiasco” (1973) ~ The same cash register was used at both the luncheonette and the custard stand (with a penguin sticker slapped on the side).
$TICKER $HOCK!

“Lucy is Matchmaker” (1953)

“Sentimental Anniversary” (1954) ~ The Mertzes give the Ricardos a silver cigarette lighter. Although Fred is shocked to see the price tag says $32.50, Ethel admits the real price was $4.95.

“The Fashion Show” (1955)
LUCY: “Doesn't Loper know any other numbers but 5-0-0?!”

Shopping for the best prices on furniture in “Lucy Bags a Bargain” (1966) and “Lucy Gets Chummy with the Neighbors” (1957).
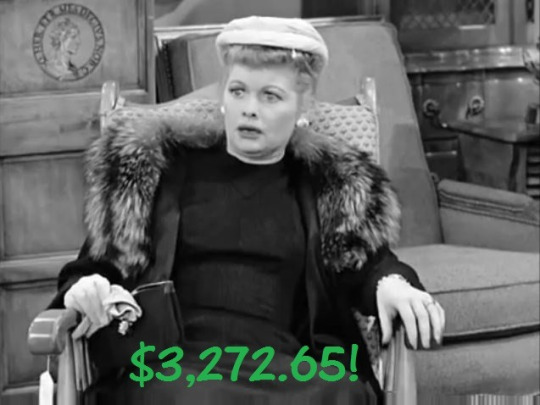

Mistaking price tags for stock numbers, Lucy has sticker shock realizing how much she spent on new furniture for the Connecticut house.
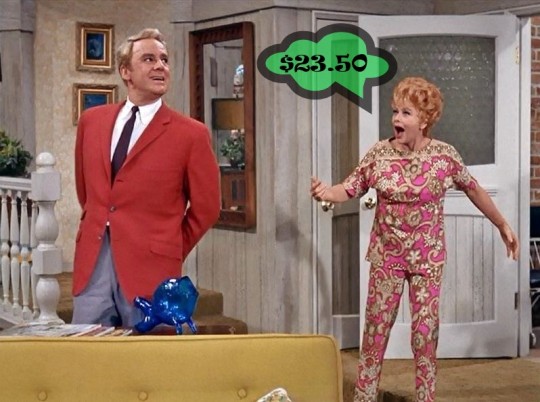

“Guess Who Owes Lucy $23.50?” (1968) ~ It’s Van Johnson! Or is it?

Lucille Ball’s favorite gameshow “Password” added a new feature for their “Super Password” (1986) reboot called Cashword.
#I Love Lucy#Lucille Ball#Desi Arnaz#William Frawley#Vivian Vance#Gale Gordon#Here's Lucy#The Lucy Show#Password
1 note
·
View note
Text
Today is a very special day, it’s Marilyn’s Birthday! Can you believe that if she were still alive, Marilyn would have been turning 94 years old today – just two months younger than the Queen herself! With each year I always try and write a special post about this amazing woman, who has helped me so much and achieved more than anyone could have imagined in her 36 years. Therefore, I decided to write 94 facts about the Birthday Girl – some you may know, some you may not, all in the hope that genuine things will be learnt and the real Marilyn will be more understood and appreciated.
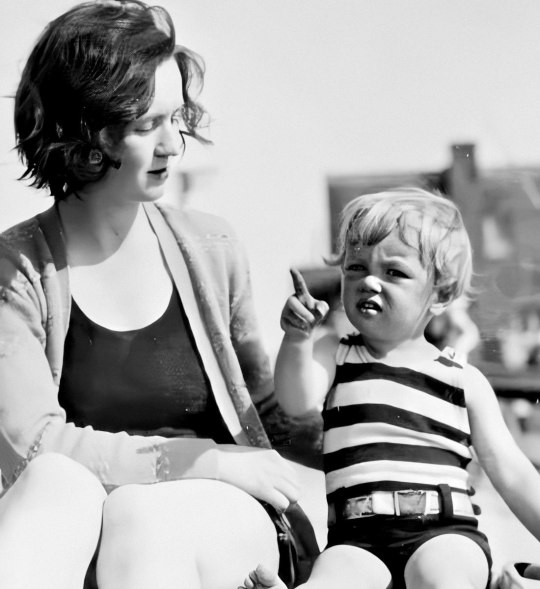

Gladys and baby Norma Jeane spend some quality time together on the beach in 1929.
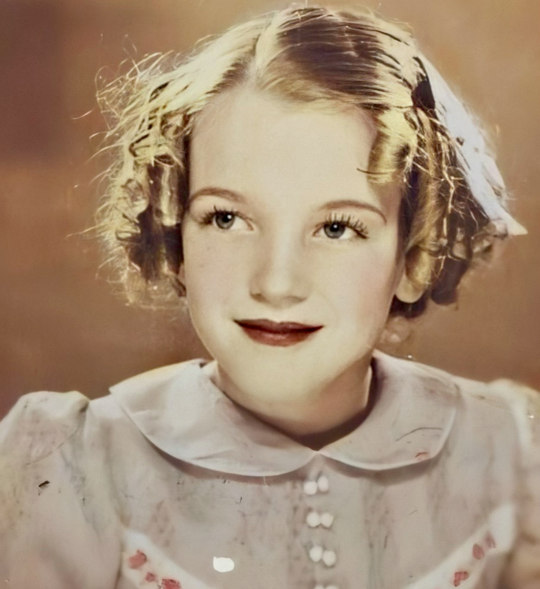
Little Norma Jeane, aged seven, in 1933.

Norma Jeane photographed by David Conover whilst working at the Radio Plane Munitions Factory in either the Fall of 1944 or Spring of 1945.
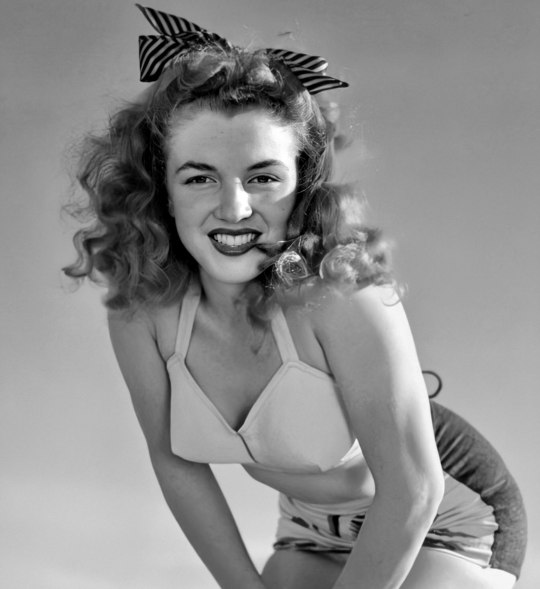

Norma Jeane by Andre de Dienes in late 1945.
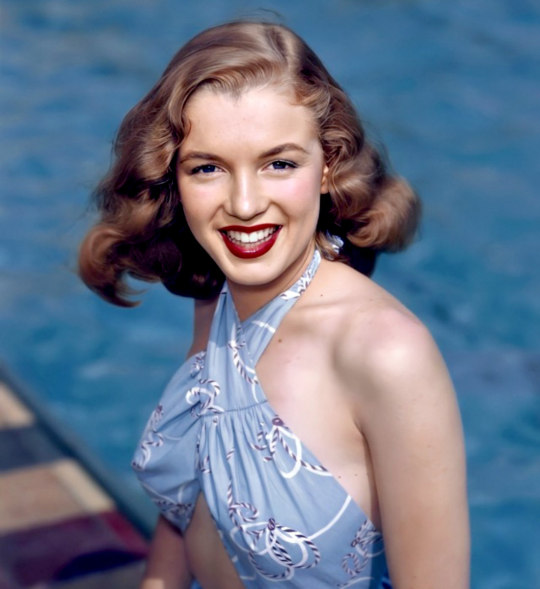

Marilyn by Richard Miller in 1946.
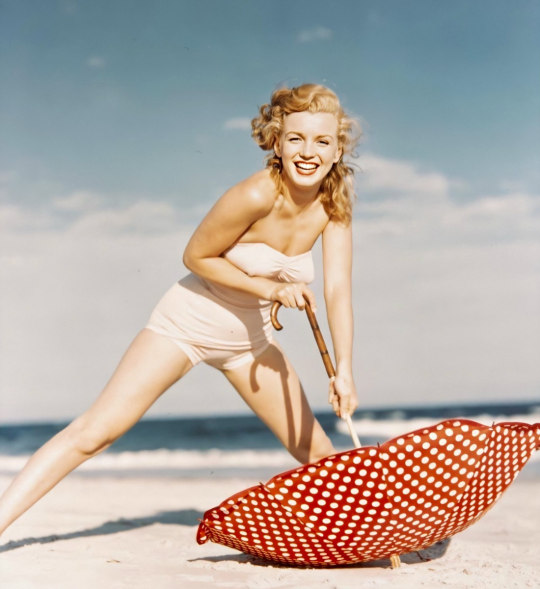

Marilyn on Tobey Beach by Andre de Dienes on July 23rd 1949.
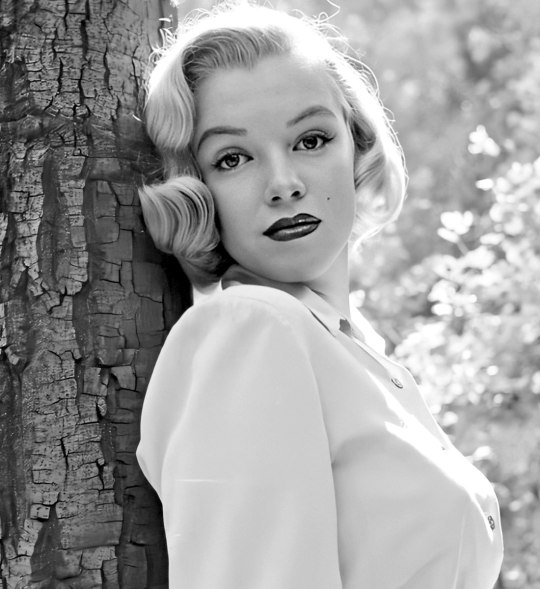

Marilyn by Ed Clark in Griffith Park in August 1950.
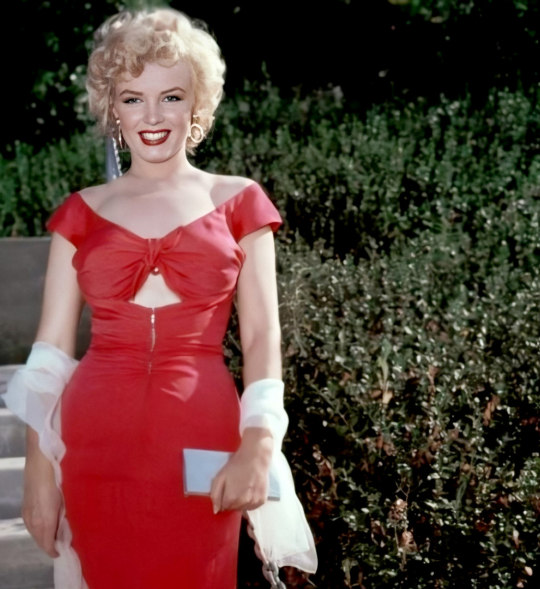

Marilyn attends a Party in Ray Anthony’s home, organized by 20th Century Fox on August 3rd 1952.
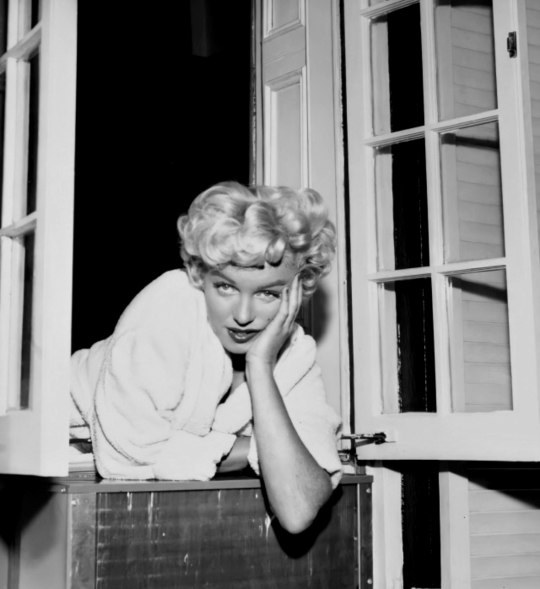

Marilyn filming The Seven Year Itch on location in New York City by Sam Shaw on September 13th 1954.
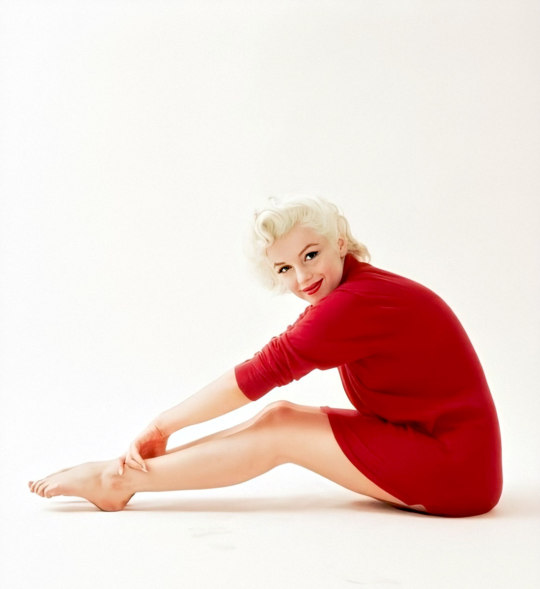

Marilyn by Milton Greene on January 28th 1955.
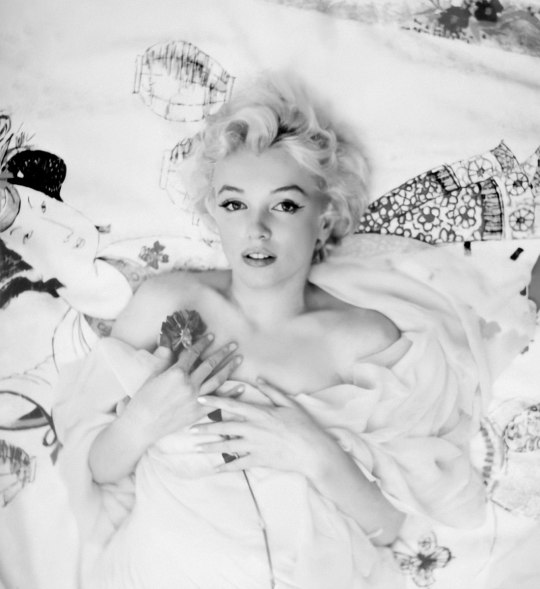

Marilyn by Cecil Beaton on February 22nd 1956. This was her favourite photo of herself.
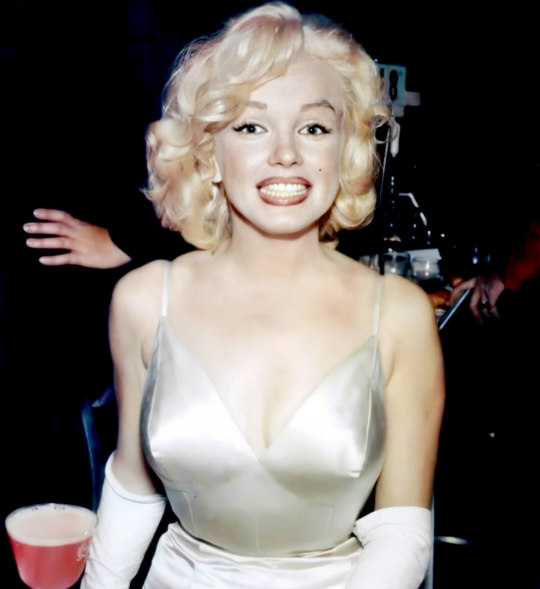

Marilyn attending the Premiere of The Prince In The Showgirl at the Radio City Music Hall on June 13th 1957.
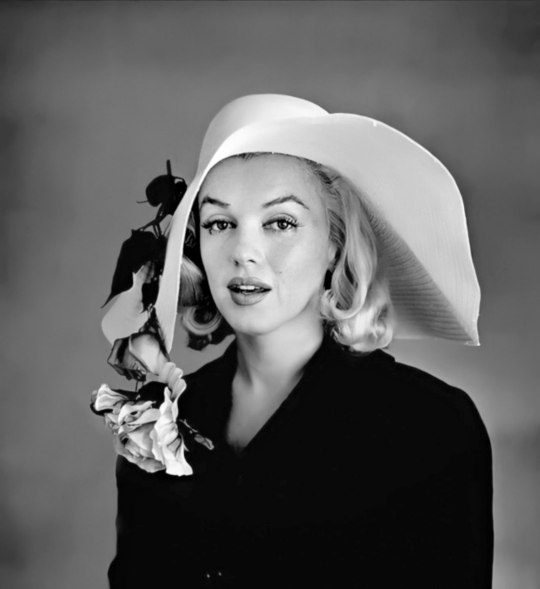

Marilyn by Carl Perutz on June 16th 1958.
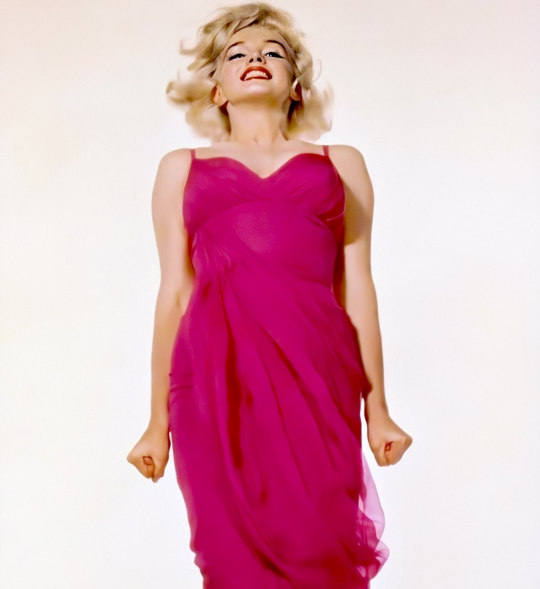

Marilyn by Philippe Halsman for LIFE Magazine in October 1959.
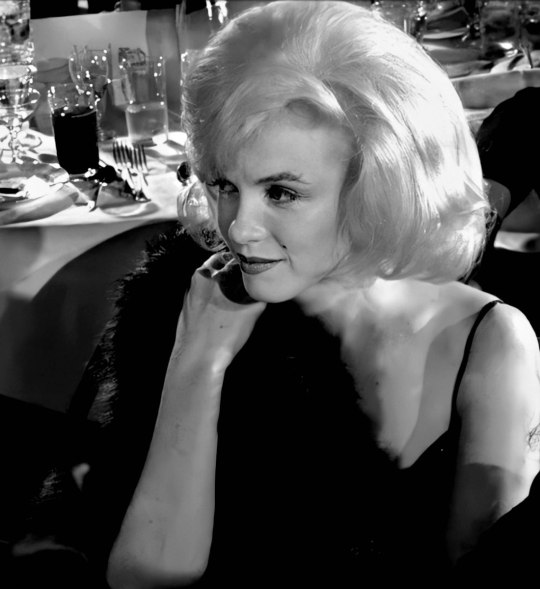

Marilyn attends a Benefit for The Actors Studio at the Roseland Dance City on March 13th 1961.
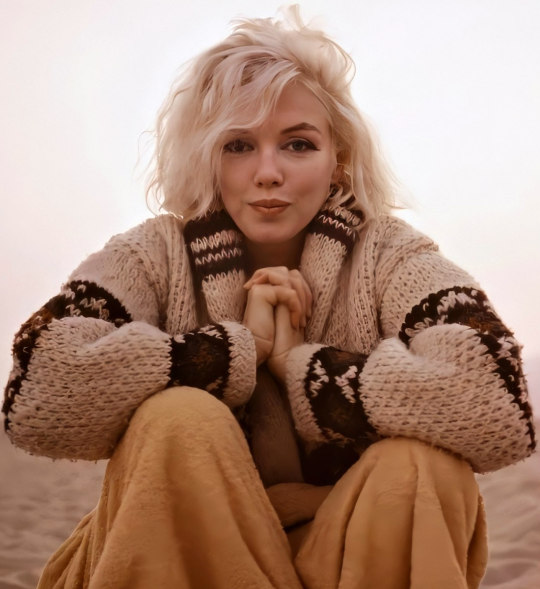

Marilyn on Santa Monica Beach for Cosmopolitan Magazine by George Barris on July 1st 1962.
______________________________________________________________________________
1. Stood at a height of 5’5½”
2. Born in the charity ward of the Los Angeles County Hospital at 9:30 AM on June 1st 1926.
3. Married three times;
– Jim Dougherty: (June 19th 1942 – September 13th 1946)
– Joe Dimaggio: (January 14th 1954 – 31st October 1955) (Temporary divorce granted on October 27th 1954)
– Arthur Miller: (June 29th 1956 – January 20th 1961).
4. Suffered two confirmed miscarriages; an ectopic pregnancy on August 1st 1957 and miscarriage in December 16th 1958.
5. Suffered with endometriosis very badly, so much so that she had a clause in her contract which stated she would be unable to work whilst menstruating.
6. Starred in 30 films – her last being uncompleted.
7. Favourite of her own performances was as Angela Phinlay in The Asphalt Jungle (1950)
8. Winner of three Golden Globes; two for World Film Favourite – Female in 1954 and 1962 and one for Best Actress in a Motion Picture – Comedy or Musical for her performance as Sugar Kane in Some Like It Hot (1959) in 1960.
9. Her idol was the first Platinum Blonde Bombshell, Jean Harlow.
10. Amassed a collection of over 400 books in her library, ranging from Russian Literature to Psychology.
11. Favourite perfume was Chanel No.5
12. Had two half siblings; Robert “Jackie” Baker (1918 – 1933) and Bernice Miracle (1919) – the former she would never have the chance to meet and Bernice was not informed about Marilyn until she was 19 years old.
13. Former Actor and 20th Century Fox Studio Executive, Ben Lyon created the name Marilyn Monroe in December 1946 – Marilyn after fellow Actress, Marilyn Miller and Monroe after Marilyn’s mother’s maiden name. Ironically enough, Ben starred with Jean Harlow, in her breakout movie, Hell’s Angels (1930).
14. Legally changed her name to Marilyn Monroe ten years later, on February 23rd 1956.
15. Attended The Actors Studio.
16. Third woman to start her own Film Production Company – the first being Lois Weber in 1917 and the second being Mary Pickford in 1919.
17. First had her hair bleached in January 1946 at the Frank & Joseph Salon by Beautician Sylvia Barnhart, originally intended for a Shampoo Advert.
18. Contrary to popular belief, she was technically a natural blonde, not a redhead or brunette. She was born with platinum hair and was very fair until just before her teen years. Her sister described her with having dark blonde hair upon their first meeting in 1944.
19. Another myth debunked – she had blue eyes, not brown.
20. Was one of the few women in the 1950s to use weights when exercising.
21. Wore jeans before it was considered acceptable for women.
22. Her famous mole was real – albeit skin coloured, so she emphasized it using a brown eye pencil.
23. Was a Step-Mother in two of her three marriages to three children – Joe Dimaggio Jr. and Bobby and Jane Miller.
24. Found out she landed the lead role in Gentlemen Prefer Blondes (1953) on her 26th Birthday.
25. Another huge myth dispelled – only actually met President Kennedy four times from 1961 – 1962. Three of them were at public events, with the last being her performance at Madison Square Garden. One of them was at Bing Crosby’s Palm Spring house with various people, so at most (which again, is very unlikely) they had a one night stand – nothing more and nothing less.
26. Was the first Playboy Cover Girl, although she did not actually pose for them, nor give permission for them to be used. Hugh Hefner bought the photograph from a Chicago Calendar Company for $500 and the two never met.
27. Speaking of Playboy, the photo was taken by Photographer Tom Kelley on May 27th 1951 and Marilyn made a total of $50 for the photo shoot. The most famous photo then went on to cause a national sensation after being sold to the Calendar Baumgarth Company and became known as, “Golden Dreams“.
28. In 1955 it was estimated that over four million copies of the Calendar had been sold.
29. Favourite singers were Frank Sinatra and Ella Fitzgerald.
30. Attended the Academy Awards Ceremony only once on March 29th 1951 and presented the award for “Best Sound Recording” to Thomas Moulton for All About Eve (1951) which she also starred in.
31. Performed ten shows over four days to over 100,000 soldiers and marines in Korea in February 1954 – she actually ended up catching pneumonia because it was so cold.
32. Was one of the few Stars who had Director Approval in their Contracts. Some of the names included were, John Huston, Elia Kazan, Alfred Hitchcock, George Stevens, William Wyler, Joshua Logan and Sir Carol Reed.
33. Was pregnant during the filming of Some Like It Hot (1959) – filming finished on November 7th 1958 and she miscarried the following month on December 16th.
34. Featured on the cover of LIFE Magazine seven times during her lifetime;
– April 7th 1952
– May 25th 1953
– July 8th 1957 (International Edition)
– April 20th 1959
– November 9th 1959
– August 15th 1960
– June 22nd 1962
35. Favourite bevarage was Dom Perignon 1953 Champagne.
36. By the time of her death, her films had grossed over $200 million, when adjusted for inflation that is the equivalent of $2 billion in 2019.
37. Designer, William Travilla dressed Marilyn for seven of her films, two (*) of them received Oscar Nominations in, “Best Costume/Design, Color“;
– Monkey Business (1952)
– Gentlemen Prefer Blondes (1953)
– How To Marry A Millionaire (1953) *
– River Of No Return (1954)
– There’s No Business Like Show Business (1954) *
– The Seven Year Itch (1955)
– Bus Stop (1956)
38. Spent 21 months of her childhood at the Los Angeles Orphanage, from September 13th 1935 until June 7th 1937.
39. Was one of the first Stars to speak out about child abuse, with her story appearing in movie magazines as early as 1954.
40. Fostered by her grandmother’s neighbours, Ida and Albert Bolender, for the first seven years of her life.
41. Lived in England for four months, during the period of filming for The Prince and The Showgirl (1957) from July 14th 1956 – November 20th 1956.
42. Her Production Company, Marilyn Monroe Productions produced only one film, The Prince and The Showgirl (1957) based on Terrance Rattigan’s play, The Sleeping Prince.
43. Was photographed by Earl Theisen in October 1952 wearing a potato sack dress after being criticized by the press for her outfit choice at The Henrietta Awards in January 1952. A journalist wrote that Marilyn was “insignificant and vulgar“and “even in a potato bag, it would have been more elegant.“
44. Was a huge supporter of LGBT+ rights, saying the following quote about fellow actor and friend, Montgomery Clift to journalist W.J. Weatherby in 1960,
“I was remembering Monty Clift. People who aren’t fit to open the door for him sneer at his homosexuality. What do they know about it? Labels–people love putting labels on each other. Then they feel safe. People tried to make me into a lesbian. I laughed. No sex is wrong if there’s love in it.”
45. Her measurements were listed as the following by her Dressmakers; 35-22-35 and 36-24-24 by The Blue Book Modelling Agency. For the majority of her life she weighed between 117-120 pounds, with her weight fluctuating around 15 pounds, during and after her pregnancies (1957-1960), although her waist never ventured past 28.5 inches and her dress size today would be a UK Size 6-8 and a US Size 2-4 as she was a vintage Size 12.
46. Her famous white halter dress from The Seven Year Itch (1955) sold for $4.6 million ($5.6 million including auction fees) on June 18th 2011, which was owned by Debbie Reynolds. The “Happy Birthday Mr. President Dress” originally held the record for the most expensive dress, when it was sold on October 27th 1999 for $1.26 million. It then went on to be resold for $4.8 million on November 17th 2016, thus regaining it’s original achievement.
47. Was discovered by Photographer, David Conover, whilst working in The Radio Plane Munitions Factory in the Fall of 1944 or Spring of 1945, depending on sources.
48. Now known as the, “Me Too” movement, Marilyn was one of the first Stars to speak out on the, “Hollywood Wolves” in a 1953 article for Motion Picture Magazine entitled, “Wolves I Have Known”. The most famous incident being with the Head of Columbia Studios, Harry Cohn, who requested Marilyn join him on his yacht for a weekend away in Catalina Island. Marilyn asked if his wife would be joining them, which, as you can imagine – did not go down well and her contract was not renewed with the Studio. Marilyn made only one film with Columbia during her six month contract, this being Ladies Of The Chorus (1948) which was shot in just ten days!
49. Loved animals dearly and adopted a variety of pets over the years. These included a basset hound called Hugo and parakeets, Clyde, Bobo and Butch with Husband Arthur Miller. A number of cats including a persian breed called Mitsou in 1955 and Sugar Finney in 1959. Her most famous pet was gifted to her in March or April of 1961 by friend, Frank Sinatra, a little white maltese named Maf. His full name was Mafia Honey, as a humorous reference to Sinatra’s alleged connections to the Mob. After Marilyn’s death, Maf went to live with Frank Sinatra’s secretary, Gloria Lovell.
50. The book she was reading at the time of her death was Harper Lee’s, To Kill A Mocking Bird.
51. One of the movies she starred in was nominated for the Academy Award for Best Picture and won, this being All About Eve (1950) at The 23rd Academy Awards on March 29th 1951. It ended up being nominated for 14 Oscars, a record at the time and has only been matched by Titanic (1997) and La La Land (2016).
52. Her first magazine cover was photographed by Andre de Dienes in December 1945 for Family Circle, released on April 26th 1946.
53. Joined The William Morris Agency on December 7th 1948.
54. Was right handed, not left as often believed.
55. Third Husband Arthur Miller wrote the screenplay for Marilyn’s last completed film, The Misfits (1961) which was originally written as a short story for Esquire Magazine in 1957. After the tragic ectopic pregnancy Marilyn endured in August of 1957, friend and Photographer, Sam Shaw suggested to Miller he alter his short story specifically for her. Ironically the making of this film culminated in their divorce and Marilyn stating,
“He could have written me anything and he comes up with this. If that’s what he thinks of me then I’m not for him and he’s not for me.”
56. Was Author, Truman Capote’s original choice for the role of Holly Golightly in Breakfast At Tiffany’s (1961) however, she was advised to turn it down by her Acting Coach, Paula Strasberg, who did not think the role of a prostitute would be good for her image. Writer George Axelrod, who wrote the Screenplay for Bus Stop (1956) and the play, The Seven Year Itch, ironically ended up being the Screenwriter for this movie.
Capote said this regarding Marilyn,
“I had seen her in a film and thought she would be perfect for the part. Holly had to have something touching about her . . . unfinished. Marilyn had that.”
57. Second Husband Joe Dimaggio had The Parisian Florists deliver red roses on Marilyn’s grave twice a week, for twenty years, from August 1962 until September 1982. Marilyn had told him how William Powell used to do this for Jean Harlow after her death and he reportedly vowed to do the same after their Wedding Ceremony. After the 20 years he then donated to a children’s charity, as he thought it would be a nice way to honour her memory. They also created the flower arrangements for her casket at her funeral.
58. The following five Directors directed Marilyn in more than one movie;
– John Huston; The Asphalt Jungle (1950) and The Misfits (1961)
– Richard Sale; A Ticket To Tomahawk (1950) and Let’s Make It Legal (1951)
– Howard Hawks; Monkey Business (1952) and Gentlemen Prefer Blondes (1953)
– Billy Wilder; The Seven Year Itch (1955) and Some Like It Hot (1959)
– George Cukor; Let’s Make Love (1960) and Something’s Got To Give (1962)
59. Was an illegitimate child, which unfortunately was attached with a lot of stigma in the 1920s. Her mother, Gladys, listed her then husband Edward Mortenson on the Birth Certificate, although it is commonly accepted that her real father was Charles Stanley Gifford, as Gladys left Edward on May 26th 1925. Gladys had an affair with him, which ended when she announced her pregnancy and he never acknowledged or met Marilyn, although she tried multiple times over the years to speak with him.
60. Stayed in a number of foster homes during her childhood,
– George and Emma Atkinson; February 1934 – September 1934
– Enid and Sam Knebelcamp; Fall of 1934
– Harvey and Elsie Giffen; January 1935 – March 1935
– Grace and “Doc” Goddard; April 1935 – September 1935 and June 1937 – November 1937 and end of 1940 – February 1942
– Ida Martin; November 1937 – August 1938
– “Aunt Ana” Lower; August 1938 – End of 1940 and February 1942
61. Had her hand and footprints immortalized in cement at Graumans Chinese Theatre on June 26th 1953, with Gentlemen Prefer Blondes (1953) co-star, Jane Russell. Marilyn would place a rhinestone in the dot of the letter “i” as a reference to her character, “Lorelei Lee” but it was sadly stolen. This was an incredibly special moment for her, as she often talked about placing her hands and feet in the many prints there, when she spent her weekends at the Theatre as a child, especially in 1933 and 1934.
“When I was younger, I used to go to Grauman’s Chinese Theatre and try to fit my foot in the prints in the cement there. And I’d say “Oh, oh, my foots too big. I guess that’s out.” I did have a funny feeling later when I finally put my foot down into that wet cement, I sure knew what it really meant to me, anything’s possible, almost.”
62. The famous gold lamé dress worn in Gentlemen Prefer Blondes (1953) and designed by William Travilla, was deemed too risqué by the censors. Unfortunately for fans, this meant that the musical number, “Down Boy” was cut from the film and we only glimpse a few seconds of the dress from behind, on screen.
63. Due to the censors, the original, “Diamond’s Are A Girl’s Best Friend” costume was changed to the now iconic pink dress with black bow. Originally it was to be a diamond encrusted two piece, which was extremely daring for the then Motion Picture Hays Code.
64. Loved Erno Lazlo Skin Cream, Vaseline and Nivea Moisturizer.
65. Had she completed Something’s Got To Give (1962), Marilyn would have been the first Star in a major Motion Picture to appear nude on film. As she passed before it was completed the achievement went to fellow Blonde Bombshell, Jayne Mansfield in, Promises! Promises (1963).
66. Met Queen Elizabeth II in England at the Empire Theater in Leicester Square whilst attending the Premiere of, “The Battle Of The River Plate“ on October 29th 1956.
67. The Misfits (1961) was both Marilyn and Clark Gable’s last completed films. Clark died 12 days after filming finished, on November 16th 1960. The film was released on Clark’s would be 60th Birthday, February 1st 1961 and Marilyn passed 18 months later.
68. As Marilyn died before the completion of Something’s Got To Give (1962) it ended up being remade with Doris Day and James Garner, entitled, Move Over Darling! (1963). The film was originally intended to be a remake of, My Favourite Wife (1940) which starred Cary Grant.
69. Signed a recording contract with RCA Records on September 1st 1953. One of her songs from River of No Return (1954) entitled, “File My Claim” sold 75,000 copies in its first three weeks of release.
70. Was admitted to the Payne Whitney Psychiatric Clinic on February 10th 1961 by her then Psychiatrist, Marianne Kris. Originally thought to be for rest and rehabilitation, following her divorce from Arthur Miller and the strain of filming The Misfits. However, Marilyn was placed on the security ring and held against her will. Thankfully, she was able to contact ex Husband, Joe Dimaggio, who stated he would, “Take the hospital apart brick by brick” if she was not released and after three days of emotional trauma, she left.
71. Visited the following Countries;
– Canada – (July – August 1953)
– Japan (February 1954)
– Korea (Feburary 1954)
– England (July – November 1956)
– Jamaica (January 1957)
– Mexico (February 1962)
72. Purchased her only home, 12305 Fifth Helena Drive on February 8th 1962, where she would tragically pass just under 6 months later.
73. The home had the following tile located on the front paving entrance saying, “cursum perficio” meaning, “my journey ends here.” The title is still there to this day.
74. Her final interview was published in LIFE Magazine on August 3rd 1962 and was written by Richard Meryman.
75. Aside from her millions of fans, had a staunch group of supporters affectionately known as, “The Monroe Six” who followed Marilyn around New York during her time there. Their nickname for Marilyn was, “Mazzie” and they became so acquainted that Marilyn actually once invited them for a picnic at her home.
76. First married at just sixteen years old, this was to avoid returning to the Orphanage she had spent almost two years in as a child.
77. Supported numerous charity events, most famously riding a pink elephant in Madison Square Garden, to support the Arthritis and Rheumatic Affections Association on March 30th 1955.
78. Left 25% of her Estate to her then Psychiatrist, Marianne Kris and 75% to mentor and friend, Lee Strasberg. For reference, her Will was last updated on January 1961 – a month before she entered the Payne Whitney Hospital on the advice of Marianne Kris.
79. At the time of it’s release, The Misfits (1961) turned out to be the most expensive black and white movie ever made, costing a budget of $4 million dollars.
80. The Premiere of The Seven Year Itch was held on her 29th Birthday, on June 1st 1955, she attended with ex Husband, Joe Dimaggio.
81. Laid to rest at Westwood Village Memorial Park Cemetery on August 8th 1962 at 1:00 PM, with friend and mentor Lee Strasberg delivering the Eulogy.
82. Although so often associated with diamonds, actually wasn’t that fond of jewellery stating, “People always ask me if I believe diamonds are a girl’s best friend. Frankly, I don’t.”
83. Spent her 36th Birthday filming Something’s Got To Give (1962) and then attending a Charity Event for muscular dystrophy at the Chavez Ravin Dodger Stadium, which also happened to be her last public appearance.
84. Whilst recovering in hospital from an appendectomy in April 1952, Marilyn asked long time Makeup Artist and friend, Allan “Whitey” Snyder to do her makeup, should she pass before him. She gave him a gold money clip with the inscription, “Whitey Dear, while I’m still warm, Marilyn” and he did fulfill this promise to her.
85. Converted to Judaism for third husband, Arthur Miller on July 1st 1956.
86. Despite appearing in 30 films, she only actually dies in one, that being her breakout movie, Niagara (1953) where her character Rose Loomis, is strangled by her Husband George, played by Joseph Cotten.
87. Moved to New York City in 1955 and attended The Actors Studio, after breaking her Film Contract with 20th Century Fox. This was for a number of reasons, mainly years of low pay, unsatisfactory scripts and lack of creative control. A new contract would finally be reinstated on December 31st.
88. Repurchased a white Baby Grand Piano that her mother, Gladys, owned during their time living together in 1933. After Marilyn passed it would then be sold at the Christies Auction of her Estate in 1999 to none other than, Mariah Carey for $632,500.
89. Wore long hair pieces in River of No Return (1954) and a medium length wig in The Misfits (1961). The first I can only assume was due to the time period and setting of a Western and the second was due to the bleach damage her hair had suffered. After the filming in 1960, she wore the wig a couple of times in public events and then reverted back to her normal hair.
90. Like all students, it was tradition to perform in front of each other in The Actors Studio and on February 17th 1955, Marilyn acted out a scene from “Anna Christie” with Maureen Stapleton. Although it was an unwritten rule that students were not meant to applaud one another, an eruption of cheers and clapping happened after Marilyn had finished.
“Everybody who saw that says that it was not only the best work Marilyn ever did, it was some of the best work ever seen at Studio, and certainly the best interpretation of Anna Christie anybody ever saw. She achieved real greatness in that scene.”
– Actor Ellen Burstyn, on recalling Marilyn’s performance.
91. Used the pseudonym, “Zelda Zonk“, when trying to remain incognito.
92. Marilyn’s mother, Gladys Baker, suffered from Paranoid Schizophrenia and after various stays in institutions, was declared insane on January 15th 1935, when Marilyn was just 8 years old. After 10 years she was released and managed to retain various cleaning jobs and had developed an intense interest in Christian Science. However, by 1951 she was back in various institutions and would stay in the Rockhaven Sanitarium until 1967. Even after death, Marilyn continued to cover her mother’s care payments and Gladys would go on to outlive her for 22 years.
93. Favourite photograph of herself was taken by Cecil Beaton on February 22nd 1956.
94. Last professional photos were taken by Bert Stern, famously known as “The Last Sitting” for Vogue Magazine on June 23rd, July 10th and 12th 1962. Allan Grant took the LIFE Magazine interview pictures in her home, on July 4th and 9th 1962. Whilst George Barris took his photos for Cosmopolitan Magazine, the previous weekend on the 29th and 30th of June, until July 1st 1962.
______________________________________________________________________________
To those of you who took the time to read through all 3000+ words, thank you! It truly means more to me than you know and I really hope it’s shed some light on the truly special person Marilyn was and made you hold a good thought for her on her big day.
Follow me at;
BLOGLOVIN
INSTAGRAM
TUMBLR
TWITTER
YOUTUBE
For inquiries or collaborations contact me at;
Happy 94th Birthday Marilyn! Today is a very special day, it's Marilyn's Birthday! Can you believe that if she were still alive, Marilyn would have been turning 94 years old today - just two months younger than the Queen herself!
#1940s#1950s#1960s#angel#blonde bombshell#classic hollywood#hollywood#icon#legend#marilyn#marilyn monroe#norma jeane#norma jeane baker#old hollywood
199 notes
·
View notes
Text
Sexy Little Me
This is how Hollywood turns a pretty Texas girl into Sharon Tate, the star.
By John Bowers for "The Saturday Evening Post"
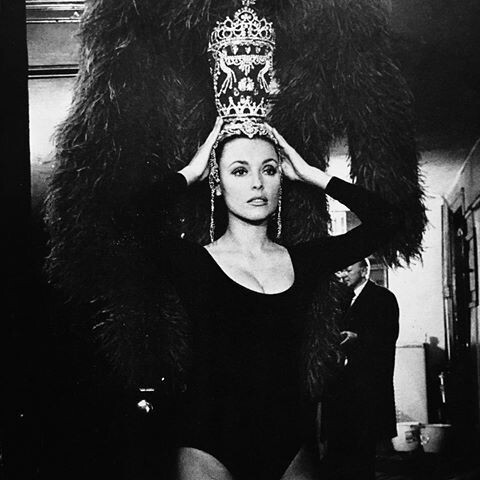
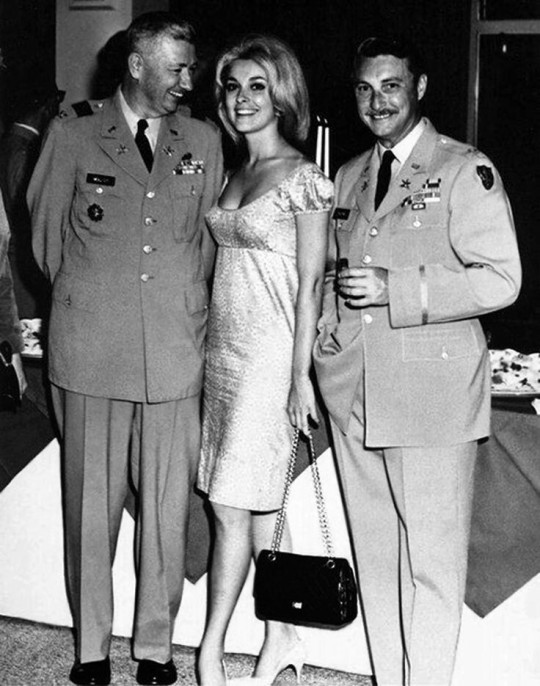
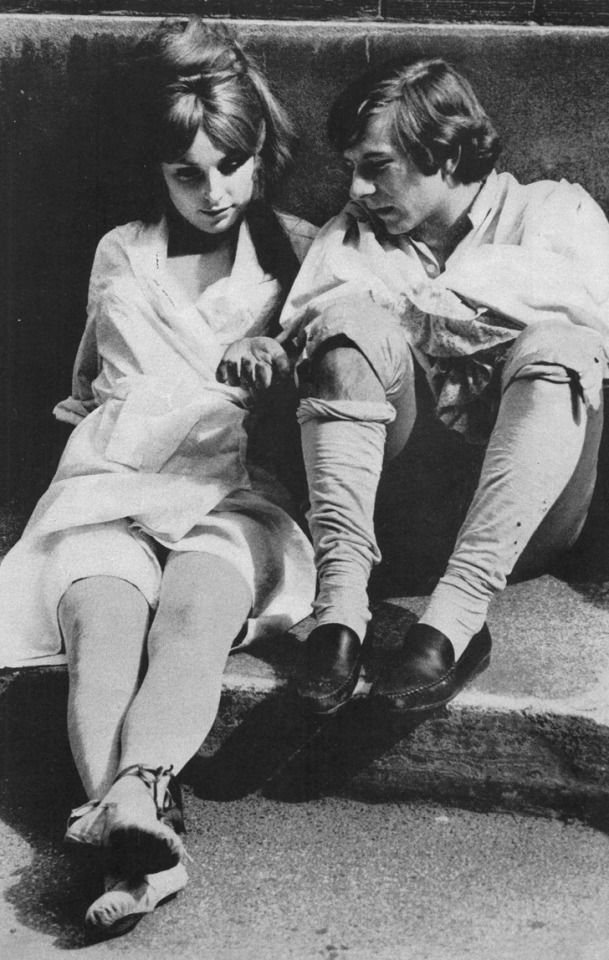






1. Two of Sharon Tate's three pictures have been produced in Europe. Although Texas-born, Sharon spent her adolescence abroad, and much prefers London to Hollywood.
2. Sharon will be shown off to American audiences for the first time in DON’T MAKE WAVES. On the set, she reacts prettily to a compliment from co-star Tony Curtis.
3. At 6 months Sharon won Dallas’ “Miss Tiny Tot” award.
4. Portraying a Las Vegas showgirl who becomes a superstar in VALLEY OF THE DOLLS, Sharon had to wear a 10-pound jeweled headdress which “gave her a headache.”
5. This picture of Sharon and her father, Maj. Paul Tate, at a 1965 Fort MacArthur party is from a large “family events” scrapbook that Sharon dutifully keeps.
6. Relaxing on the set of YOUR TEETH IN MY NECK, Sharon listens attentively as the Polish-born Polanski explains how she can improve her performance in the next scene.
May 6, 1967 – Sharon Tate had finished her last scenes for The Vampire Killers (later to be called Your Teeth in My Neck), and had no film work for the moment. At 95 Eaton Mews West, London, she moved about in the late afternoon looking for something to do. She sat Buddah-style on the living room floor and put on fake eyelashes, one eyelash at a time. She worried that a sunlamp treatment, taken a few hours before, was going to make red cracks in her face. “Doesn’t it seem to be getting all red on the cheeks? Look close now.”
She wore a gray sweat suit and furry boots, having been to her daily gym class that afternoon. She didn’t like the gym class, but Roman Polanski, her director, had told her she must go. She frowned into a hand mirror, thinking she saw a red streak. She started to bite a fingernail, but stopped. Roman had forbidden any more fingernail biting; she had a tendency to bite them down to the nub. She went to the refrigerator, and amidst Wyborowa vodka and Carlsberg beer, brought out the makings for a salami sandwich. She would not drink a beer because it might bloat her, and Roman was taking her out for dinner.
There was no place in the apartment for her to settle back and relax now. Everything inside had a transient look, as if the tenants would only be there a short season. A complicated stereo set sat on crates; Bach on top of a stack of records, Cannonball Adderly on the bottom. There were no pictures, no pets, no cozy heat. Upstairs on the wall was a framed citation stating that Knife In The Water under the direction of Roman Polanski had been nominated for an Academy Award. As Sharon reached for a folder of still photographs from The Vampire Killers to show a male visitor, she stuck up her bottom in a way she has; as she went through the photos, she pooched out her bosom. But she did it by reflex. Her thoughts were totally on her director, who was not there. She had been in three unreleased films – 13, Don’t Make Waves and The Vampire Killers, all with different directors.
If she caught the public’s fancy in any of these pictures, she would become a movie star. And she was pleased with her work in The Vampire Killers. She was in a nude bathtub scene in it, and in a brief sequence in which she got spanked.
The phone rang; it was a strange female voice with a French accent. “Is Roman there?”
“No, I’m sorry he isn’t,” Sharon said, in her accent of the moment, which was English. “Who shall I say is calling, please?”
“Oh – I just wondered if he were in. Tell him Barbara. Thank you very much..”
The dull London afternoon turned dark, and still no Polanski. He could be cutting The Vampire Killers, or he could be tied up in London traffic or he could be sitting in a café. She took off her furry boots and put her feet into his house slippers, which rested at odd angels by a mammoth bed that cost over $600. The slippers were far too big for her. She wondered if tonight she would be thrown with people who would overwhelm her with their wit, their awesome knowledge, their self-confidence. When she was out in public with Roman, she never felt adequate enough to open her mouth. She could only talk to him alone. Her problem was that she had always been beautiful, and people were forever losing themselves in fantasy over her – electing her a beauty queen, imagining her as a wife, dreaming of a caress. Most people had fantasies. But a few people, like Polanski, took charge.
At the age of six months Sharon Tate was elected Miss Tiny Tot of Dallas, Tex. Her mother had sent in photos of the beautiful baby to contest officials. Sharon’s father was (and is) in the Regular Army, and was then stationed in Dallas. (Both her parents are natives of Houston.) As Sharon grew up, the family moved around in Army style, her father frequently absent from home. She remembers that when her father would return from an overseas tour, and she had reached a nubile age, her mother’s first command would be, “Now you, Sharon Marie, button up that night gown when you come out of your bedroom. Daddy’s home.” Her father was very strict with her as she budded through adolescence, turning thumbs down on potential boyfriends and making her stay in nights. He was very strong and knew how to take charge.
But most people continued to do things for Sharon without her lifting a finger. At 16 she was elected Miss Richland, Washington, and a short time later named Miss Autorama. At the age of 17 she was in Verona, Italy, where her father was stationed, and the prizes mounted. At Vicenza American High she was a cheerleader and baton twirler, and was chosen Homecoming Queen and Queen of the Senior Prom. The Vicenza yearbook for 1961 shows her as a very pretty, large-eyed girl, with hair somewhat darker and hips a little broader than now. She daydreamed at this time about becoming a psychiatrist and a ballerina, and had little to do with her classmates. Yet if any far-out stunts or fads were proposed, this terribly quiet girl was ready to lead the way. “If miniskirts had come in then, ” she says, “I’d have worn the shortest one.”
Today the fad among young girls in cosmopolitan circles is to use the old Anglo-Saxon words in everyday conversation, and Sharon Tate leads the way. But back in Italy at 17, she was just starting her worldly knowledge. She watched the on-location shooting of Barabbas, a film about ancient Rome, and the family scrapbook now includes still pictures of Jack Palance and Anthony Quinn in the movie costumers they wore in Italy. As she walked in Venice one day, she was spotted by the choreographer for the Pat Boone Show, which was being filmed in Italy. She next appeared very briefly in one of Boone’s TV shows, and his glossy smiling face now rests in the album with a fond inscription for Sharon.
When the Tate family moved from Italy to Southern California, Sharon decided it was time to live on her own. She was 18, and she paid a visit to Harold Gefsky, then agent for Richard Beymer, a young actor she met in Rome. “She was so young and beautiful,” Gefsky, a softly-spoken man, said in his Sunset Boulevard office, “that I didn’t know what to do with her. I think the first thing I did was take her to a puppet show.”
He also got her work because her father, in Calvinistic style, had only given her a few dollars to sink or swim. One of her first jobs was dressing up in an Irish costume and handing out Kelly-Kalani wine in Los Angeles restaurants at $25 a day. She also appeared in TV commercials for Chevy cars and Santa Fe cigars. People who knew her during this period agree on one thing. She was the most beautiful girl in the world. “Everywhere I took her she caused a sensation,” Gefsky said. “I would take her into a restaurant and the owner would pay for her meal. Photographers kept stopping her on the street. I’ve lived in Hollywood since the mid-Forties, but I’ve never seen anything like it before or since.”
But at this point no one, except perhaps Sharon, knew if she wanted to be an actress. Then one day Gefsky took her by to meet his friend Herbert Browar, who was connected with TV’s Petticoat Junction. He thought possibly Browar could fix her up with a minor role, something to tide her over. Browar took one look at her and rushed her in to see Martin Ransohoff, head of Filmways, Inc.
Ransohoff has a strand of hair combed over his bald dome. He wears loose sweaters, torn windbreakers and breeches that are baggy in the seat. He first started producing TV commercials in New York when food particles were glued onto Brand X’s plate to show the differences in detergents. He branched out into TV programs with such commercial winners as Mr. Ed, The Beverly Hillbillies and Petticoat Junction. He then tackled movies on the order of The Americanization of Emily and The Loved One, which got mixed reviews but generally made money. He founded the company in 1952 on $200, and today it operates on a budget of over $35 million. He will talk about Oswald Spengler or H. L. Mencken and then croon into his ever-present phone, “Helloooo, Bertie, baby. Where’s the action, kid?” He chews gum till his head rings, smokes two packs a day and sends everyone to the wall with his adrenaline. He can be gratuitously cruel in speaking of others – “She’s got a lunch pail for a mouth,” he said of an aging actress, “and if we take out insurance on her, it’ll have to be that she’ll die.” Then he can take his twin sons to a football game, clean up a dog’s mess in his Bel Air living room, and talk to anyone in the world who has guts enough to call him. A rich man’s son, he sold pots and pans from door to door while going to Colgate and claims the experience taught him what the public will or will not buy. He had little interest in films before he became involved in them, and his favorite actress in the old days was Deanna Durbin – who, coincidentally, was also Polanski’s favorite. Both vividly remember her pedaling a bicycle down a shady street and singing through a dimpled smile. Not everyone has had pleasant dealings with Ransohoff in Hollywood, but all agree he is a super salesman.
When he first saw Sharon Tate, he squinted his right eye and did something that was very impulsive, even for him. “Draw up a contract,” he shouted. “Get her mother. Get my lawyer. This is the girl I want!”
He had not seen a screen test, not even a still photograph. She had hardly opened her mouth. But Marty Ransohoff, like the rest of us, has his fantasies – and Sharon Tate walked into one of his fondest ones. “I have this dream,” Ransohoff said, “where I’ll discover a beautiful girl who’s a nobody and turn her into a star that everybody wants. I’ll do it like L. B. Mayer used to, only better. But once she’s successful, then I’ll loose interest. That’s how my dream goes. I don’t give two cents now for Tuesday Weld or Ann-Margret..”
“I think he’s just trying to pull one over on the public,” Gefsky said.
Sharon signed a seven-year contract, and Ransohoff took charge. Gefsky, a nice man, bowed out. At first she lived in complete fear of Ransohoff, and did as she was told. “She wouldn’t even eat a hamburger if he told her not to,” a friend from that period said. If Ransohoff said she was to appear on The Beverly Hillbillies disguised in a black wig, she appeared. If he told her to go on a moments notice to Big Sur, New York, London, she went. Off and on she studied acting.
Jeff Corey, one acting coach, said, “An incredibly beautiful girl, but a fragmented personality. I tried to get reactions out of her, though. Once I even gave her a stick, and said, ‘Hit me, do something, show emotion’ ..If you can’t tap who you are, you can never act.”
Charles Conrad, another acting teacher, said, “Such a beautiful girl, you would have thought she would have all the confidence in the world. But she had none.” Among her friends, however, she began to refer to herself as “sexy little me.”
Ransohoff tried to place Sharon in The Cincinnati Kid – his own movie – but failed when the director demanded Tuesday Weld. He packed her off to New York to study under the personal direction of Lee Strasberg at the Actors Studio. “She was only with me a few weeks,” Strasberg said, “but I remember her. She was a beautiful girl.” In New York Sharon had a romance with a young French star, who offered her relief from her Texas style, Puritan upbringing. The actor was tall, dark and very nice. When they broke up, the actor bungled a suicide attempt.
Sharon continued to fear Ransohoff. Once, while driving at a high speed near Big Sur, she turned her car over four and a half times, but somehow managed to crawl out with only minor injuries. Her first thought was that Marty would be mad. The first picture he finally placed her in was his French made 13, in which she plays a chillingly beautiful, expressionless girl who goes about putting the hex on people. Completed many months ago, ’13’ still rests in the can waiting for a 1967 release date. Ransohoff flew Sharon back to Hollywood for her second film, Don’t Make Waves, in which she plays a beautiful, deadpan skydiver. Sharon’s first two directors were older men. Britishers – very polite, very nice and understanding with a novice actress.
And then Ransohoff began dickering with Roman Polanski, the Polish director living in London, to make a picture. Polanski, a tiny, baby-faced man whose explosive manner and Beatle-like appearance belie his much-admired skill as a maker of art films, wanted to do something with Ransohoff called The Vampire Killers, a spoof of horror movies. He wanted to play in it himself, and, as in all his movies, he wanted a beautiful girl in a supporting role.
“How about Sharon Tate?” Ransohoff said. “I was thinking more in terms of Jill St. John,” Polanski said.
At Ransohoff’s instigation, Sharon and Polanski had dinner together. He looked at her from time to time, but said nothing. On a second dinner date he was painfully silent once more. Real weirdo, she thought. What’s he waiting on? She found out shortly. Walking in London’s Eaton Square, he suddenly put a bear hug on her and they fell to the ground, Polanski on the bottom. Sharon clouted him and stormed off. “That’s the craziest nut I ever saw,” she said. “I’ll never work for him.”
But Polanski apologized, and they saw each other again. One night he took her to his apartment which had even less furniture than it has now and no electricity. He lit a candle and excused himself, flying upstairs to don a Frankenstein mask. He crept up behind her, raised his arms, and whinnied like a madman. Sharon turned and emitted a terrible scream. It took over an hour for her hysterical weeping to subside. Not long afterward Polanski informed Ransohoff that Sharon would do fine for The Vampire Killers. On the set he treated her as if they never saw each other at night. He cajoled, flattered, got angry – which ever worked – and never had lunch with her. During the nude bathtub scene, he snapped still pictures of her. Still enthusiastic, he had her pose all over the set in the altogether, and then sent the results to Playboy. She plays a gorgeous redhead in The Vampire Killers – and she shows
Roman Polanski walked into his apartment in a sharp blue blazer and high-gloss shoes, carrying a briefcase. He had a good-sized nose and searching, deep-set eyes, and he nodded briskly to Sharon. “A Barbara called,” she let out daintily. “Do you know who that could be?”
“A Barbara?” he called from the kitchen, out of sight. A pause. “You didn’t get any last name? Always get last names. I don’t know any Barbara that would be calling. Sharon, Sharon. There’s no liquor here. Always see to it that we have enough whisky. Can’t you do that?”
Sharon went on the phone to order some, worrying about which brands to specify. She didn’t want to be embarrassed by asking Roman – although he would certainly tell her. He knew the correct whiskey brands in London, the good pastrami places in Manhattan, and the right topless spots in Hollywood. He learned a country’s customs and its language in a couple of weeks. He took a bath now upstairs, calling down for Sharon to fetch him some tea. Later he descended the stairs in a cowboy outfit and boots, ready for dinner. Some movie friends had shown up, and he led the party on foot toward Alvaro’s restaurant.
At the restaurant Sharon basked in the eyes that roved over her. She listened big-eyed to Polanski explain the difference between the sun’s heat and that on earth, apropos of Truffaut’s Fahrenheit 451. The only trouble was that it was difficult to digest pasta in such a giddy atmosphere, and she complained of her stomach. After Polanski figured out how to work the waiter’s ballpoint pen, he signed the check.
In a dreamlike state, Sharon began slipping into her fox fur coat in the foyer. Suddenly, out of nowhere, a tall Englishman with a prep-school tie and large teeth popped up and put his arm around her. “Ummm, you have a sexy feel, love. Don’t we all love to touch you now..” She squirmed away.
Out on the street, she said, “Roman, a complete stranger began hugging me in there.”
“Yeah? Really?” A short distance away he suddenly spied a blond in fox fur who had the same duck walk that Sharon has. “Hey, there goes Sharon,” he said. “Let’s get her and put the two of them together!”
“Don’t you dare,” she said, her anger flashing. Another day, away from Sharon, Polanski said, “I’m trying to get her to be a little meaner, She’s too nice, and she doesn’t believe in her beauty. Once when I was very poor in Poland I had got some beautiful shoes, and I immediately became very ashamed of them. All my friends had plain, ordinary shoes, and I was embarrassed to walk in front of them. That’s how Sharon feels about her beauty. She’s embarrassed by it.”
Sharon has a quarter-inch scar under her left eye and one beside the eye, the result of accidents which she keeps having. As Polanski drove with her one night in London, meticulously keeping on the left in the custom of the land, an Englishman with a couple of pints under his belt hit him from the right. The only one hurt was Sharon, whose head bounced off the dashboard, spraying blood on slacks, boots and fur. An angry red wound appeared at the start of her scalp, and it will leave another whitish scar on her head. With blond hair combed down over her forehead to hide it, she skied at St. Moritz. And then she caught a jet for Hollywood because Ransohoff had called. She must redo a few scenes for Don’t Make Waves. She grumbled a little. She found she could grumble to Ransohoff now. She hated Hollywood, and she didn’t want to leave Polanski. Also, she hated to fly. She had to be drugged to endure it.
And then she appeared beside Ransohoff at La Scala restaurant in Beverly Hills. She had a black costume that looked more like a slip than a dress, and her blond head caught glints of movie-star light as she turned this way and that. “Oh, there’s David! David Hemmings. David, David!”
David Hemmings, who had been featured with her in 13 and had gone on to star in Antonioni’s Blow-Up waved. Other celebrities flicked glances her way, at each other, to the door to see what majesty might enter next. Occasionally they looked down at food or drink. The place was as crowded as Alvaro’s in London, the customers practically the same. Ransohoff wore an open-neck sport shirt and shapeless coat, and he talked business. “Listen, sweetie, I’m going to have to cut some stuff out of The Vampire Killers. Your spanking scene has got to go.”
“Oh, don’t do that. Why would you do that?” “Because it doesn’t move the story. The story has got to move. Bang, bang, bang. No American audience is going to sit still while Polanski indulges himself.”
“But Europeans make movies differently than Americans, ” she explained to the producer she once feared. “Blow-Up moved slowly. But wasn’t it a great film!”
“I’ll tell you something, baby. I didn’t like it. If I’d have seen it before the reviews, I’d have said it’d never make it. It’s not my kind of picture. I want to be told a story without all that hocus-pocus symbolism going on.”
“But that one scene, Marty. When the girl show’s her, ah –” (only Sharon said the Anglo-Saxon word). In Hollywood, New York and London they all talked now about Blow-Up, dwelling on that scene.
“Yeah, I got to hand it to the guy for that one.” Ransohoff said, chuckling. “He pulled a good one off there.”
“Oh, I want to do a complete nude scene,” she said. “Say you’ll let me!”
“OK, OK,” Ransohoff said, bored, looking toward the door. “Yes, yes.”
“Do it now. Don’t just say it.” Then Sharon got bored.
Early in the morning Sharon appeared before the camera at Malibu Beach, redoing a scene for Don’t Make Waves. The sun had a hard time getting through the wisps of fog, and strong klieg lights helped out. In a sequence with an undraped David Draper, “Mr. Universe”, Sharon stuck out her backside and shot out her front. Magically, a button or two came undone on her polka-dot blouse, and after close examination of camera angle, director Sandy Mackendrick decided to leave it that way. He gave Sharon guidance in rubbing mineral oil over Draper’s bare back, as the scene called for. “Treat him like a horse,” he said. “Pat him just as you would an animal. That’s the way..”
She lovingly went over Draper’s muscled back, and then went “ugh” when the camera ceased to roll. The scene was done over and over. In her tiny trailer dressing room, she took a break and smoked daintily. “I’m happier when I’m working,” she said. “I don’t have time to think to much that way.”
One thing to think about was a visit to her parent’s home in Palos Verdes Estates, an hour’s drive away. (Her father was stationed in Korea, her mother and two younger sisters were at home.) Driving to the house one night in a heavy seaside fog, she became quieter and quieter, her words less Anglo-Saxon. A passenger beside her remarked, as the car neared its destination, that the fog reminded him of snow. “You know what it looks like to me?” she said. “Vomit.”
Her mother – a pleasant, plump, dark-haired woman – turned Sharon’s face this way and that. “Have you had your blood count recently, honey? You look so pale to me.” What did she think of Sharon’s becoming a movie star? What did she think of Roman Polanski? “You know,” she said, in the voice of every middle-class American mother, “I don’t care – just as long as she’s happy.”
Back in Hollywood Sharon moved from hotel to hotel, from one friend’s home to another. She talked to Polanski by phone. (It embarrassed him to try to write letters in English because of his mistakes.) So many things were unresolved, shadowy. Ransohoff was sore at Polanski because Polanski had gone way over the budget on The Vampire Killers (“Very un-Hollywood of him,” a Filmways executive said; another only referred to him as “the little–.”); Polanski was mad at Ransohoff because Ransohoff was cutting away at his film and postponing its release in the States. (Ransohoff had also had difficulties with Tony Richardson, the English director, over the budget and the cutting of The Loved One.) “The thing is,” said Sharon, “that Roman is an artist.”
At night Sharon went to The Daisy, a private discotheque in Beverly Hills. She wore an aviator’s leather jacket, slacks, and tinted Ben Franklin glasses. Seated near the dance floor, she silently watched young actresses her age go through their gyrations. Suzanne Pleshette and Patty Duke did subdued turns; Linda Ann Evans, in a miniskirt, did a much more spirited fling. Carolyn Jones, who only yesterday had played the ingénue, now looked like a chaperone. Sharon gave Linda Ann Evans the once over and said, “I’ve worn a much shorter mini in London. That’s nothing.”
From another table a slim, bronzed young man with a pampered black hair ambled confidently past Tina Sinatra, Patty Duke, Suzanne Pleshette – and hovered over this strange blond beauty in an aviator’s leather jacket. He had the air of a football star in a small town high school, who was used to having his pick. He showed his beautiful white teeth and said, “Let’s dance.”
“No,” she said, “let’s not.”
He kept the smile on his face as he backed away. He was now another who had tried to bring Sharon Tate into a private fantasy – but he didn’t know that she had passed his type long ago.
She was going to fly to London and get engaged to Roman Polanski. Then she was going to fly back to star in Valley of the Dolls. Ransohoff was lending her to 20th Century-Fox to play a sexy bombshell who goes to Europe to star in nudie movies and who bewitches the world with her improbable lushness.
#sharontate#sharon tate#sixties#1960s#vintage#hollywood#old hollywood#1967#sexy little me#john bowers#saturday evening post#article#cinema#fearless vampire killers#valley of the dolls#don't make waves#roman polanski#paul tate#fort macarthur
74 notes
·
View notes
Text
Canada Lee

Canada Lee (born Leonard Lionel Cornelius Canegata; March 3, 1907 – May 9, 1952) was an American actor who pioneered roles for African Americans. After careers as a jockey, boxer and musician, he became an actor in the Federal Theatre Project, most notably in a 1936 production of Macbeth adapted and directed by Orson Welles. Lee later starred in Welles's original Broadway production of Native Son (1941). A champion of civil rights in the 1930s and 1940s, Lee was blacklisted and died shortly before he was scheduled to appear before the House Un-American Activities Committee. He furthered the African-American tradition in theatre pioneered by such actors as Paul Robeson. Lee was the father of actor Carl Lee.
Biography
Canada Lee was born Leonard Lionel Cornelius Canegata on March 3, 1907, in the San Juan Hill neighborhood of Manhattan in New York City. His father, James Cornelius Lionel Canegata, was born on the Caribbean island of St. Croix, and as a youth had migrated to New York, where he married Lydia Whaley Gadsen. Raised by his parents in Harlem, Lee had an aptitude for music, and at age seven he began studying violin and piano with J. Rosamond Johnson at the Music School Settlement for Colored People. He made his concert debut at age 11, performing a student recital at Aeolian Hall. But after seven years of music studies, without explanation, he put away his violin and ran away from home. In 1921, aged 14, Lee went to Saratoga Springs, New York, and began a two-year career as a jockey.
Lee returned to his parents' home in Harlem in 1923 with no idea what he was going to do next. He considered returning to music, but an old school friend suggested that he try boxing. At one amateur match, fight announcer Joe Humphries saw the name "Canagata, Lee" on the card he was using. He tossed the card aside and instead announced "Canada Lee"—a name that Lee liked and adopted. In the amateur ring he won 90 out of 100 bouts and the national amateur lightweight title.
Lee turned pro at age 19, in October 1926, and became a favorite with audiences. At 5 feet 9 inches (1.75 m) and about 144 pounds (65 kg), he fought as a welterweight. His boxing statistics vary due to incomplete coverage and record keeping for the sport in the 1920s and 1930s. Boxing historian Donald R. Koss documents Lee having 60 bouts 1927–31, the majority of them taking place 1927–28. The New York Times reported that Lee had some 200 professional matches and lost only about 25.
During his victorious 10-round bout with Andy Divodi at Madison Square Garden on December 12, 1929, Lee was dealt a blow over his right ear that detached his retina. With treatment his vision could have been saved, but Lee feared losing his successful career and masked his injury. In time he lost all sight in his right eye. He quit professional boxing in 1933. Despite having made an estimated $90,000 during his boxing career (roughly equivalent to $1.7 million today), Lee was broke. "Just threw it away," Lee later said. Lee eventually lobbied for insurance, health care, financial consultation and retirement homes for fighters. "The average boxer possesses little education," he said in 1946. "If he winds up broke, he has no trade, no education and nobody to turn to."
As Lee's fighting career began to wind down, he put together a small dance band that played at obscure clubs. When an old friend, sportswriter Ed Sullivan, plugged him in his new entertainment column, Lee and his group began landing better engagements. His career as a bandleader peaked in 1933 when his group played at the Lafayette Theatre in Harlem. The following year he opened his own small club, The Jitterbug, which he managed to operate for six months. When it closed he had no prospects, and his mother convinced him to simply get a job.
Acting
All my life I've been on the verge of something. I'm almost becoming a concert violinist and I run away to the races. I'm almost a good jockey and I go overweight. I'm almost a champion prizefighter and my eyes go bad. Now I've got it, now I've got what I'm going to be.
Lee discovered a love for Broadway theatre during his years as a prizefighter. He remembered Show Boat as the first stage production he ever saw: "A big, tough fighter, all muscle, just sobbing," he recalled.
His acting career began by accident in 1934. While at a YMCA to apply for a job as a laborer, Lee stumbled upon an audition in progress and was recognized by playwright Augustus Smith. Lee was invited to try out, and won a supporting role in Brother Mose, directed by Frank H. Wilson. Sponsored by New York's Civil Works Administration, the show toured the boroughs, playing at community centers and city parks into the fall of the year. In October 1934 Lee succeeded Rex Ingram in the Theatre Union's revival of Stevedore, which toured to Chicago, Detroit and other U.S. cities after its run on Broadway. It was his first professional role.
Lee then was cast in his first major role, that of Banquo, in the legendary Federal Theatre Project production of Macbeth (1936), adapted and directed by Orson Welles.
"I never would have amounted to anything in the theatre if it hadn't been for Orson Welles," Lee recalled. "The way I looked at acting, it was interesting and it was certainly better than going hungry. But I didn't have a serious approach to it until … I bumped into Orson Welles. He was putting on a Federal Theatre production of Macbeth with Negro players and, somehow, I won the part of Banquo. He rehearsed us for six solid months, but when the play finally went on before an audience, it was right—and it was a wonderful sensation, knowing it was right. Suddenly, the theatre became important to me. I had a respect for it, for what it could say. I had the ambition—I caught it from Orson Welles—to work like mad and be a convincing actor."
Macbeth was sold out for ten weeks at the Lafayette Theatre. After an additional two weeks on Broadway it toured the nation, including performances at the Texas Centennial Exposition in Dallas.
After five months in a supporting role, Lee succeeded Rex Ingram as the lead in the stage production Haiti (1938), portraying Haitian slave turned emperor Henri Christophe. One of the Federal Theatre Project's most popular productions, Haiti was seen by some 90,000 people at the Lafayette Theatre in Harlem and at Boston's Copley Theatre.
In January 1939, with the end of the Federal Theatre Project, Lee won a role in Mamba's Daughters, a Broadway success that toured North America and returned to Broadway for another brief run in 1940. Lee took a break from the road tour to make his motion picture debut in Keep Punching (1939), a film about boxing. He made his radio debut as narrator of the weekly CBS jazz series Flow Gently, Sweet Rhythm (1940–41). As that regular series came to an end, he opened a restaurant at 102 West 136th Street, Canada Lee's Chicken Coop, which offered authentic South Carolina cuisine, jazz and blues. Lee kept it going despite chronic financial difficulties.
Lee played the lead role in the 1940 revival of Theodore Ward's Big White Fog. A 1938 Federal Theatre Project production, the play was remounted by the newly created Negro Playwrights Company, founded in New York by Ward, Langston Hughes, Paul Robeson, Theodore Browne, Richard Wright and Alain Locke.
Lee became a star overnight in his ultimate stage success, Native Son (1941), an adaptation of Richard Wright's novel staged on Broadway by Orson Welles. The show was a spectacular hit for both Welles and Lee, who starred in the initial New York run, a 19-month national tour, and a second run on Broadway with accessible ticket prices. "Mr. Lee's performance is superb," wrote Brooks Atkinson of The New York Times, who called him "certainly the best Negro actor of his time, as well as one of the best actors in this country." Wright also applauded the performance, noting the contrast between Lee's affable personality and his intensity as Bigger Thomas. The sympathetic portrayal of a black man driven to murder by racial hatred brought much criticism however, especially from the Catholic Diocese of Brooklyn and the Legion of Decency, and the ensuing pressure forced the play to close.
During World War II, Lee continued to act in plays and in films. In 1942, he played in two comedies by William Saroyan, and earned approving reviews despite the generally negative response to these plays. In 1943, his name was above the title on the marquee for South Pacific, a race-themed drama directed by Lee Strasberg that again was panned by critics but won Lee critical praise.
Perhaps Lee's most famous film role was in Alfred Hitchcock's Lifeboat (1944), in which he played ship’s steward Joe Spencer, one of 8 men and women who survive the sinking of the freighter carrying them from New York to London and are joined in their lifeboat by a survivor of the crew of the U-boat that destroyed their vessel.
According to a June 22, 1943, Hollywood Reporter news item, Lee was the first actor cast for the film. The script was criticized for making Joe "too stereotypical". Lee testified that he attempted to round out the character by revising dialogue, primarily eliminating repeated "yessir"s and "nossir"s that sounded subservient, and cutting some actions. An NAACP critique of the film condemned the role of Joe and praised Lee’s performance. The Baltimore Afro-American's review, while commenting on the character's shortcomings, praised Lee's portrayal. Historian Rebecca Sklaroff, while writing in 2009 that Joe's role was more "tokenistic" than black roles in the wartime films Sahara and Bataan, noted that Joe was depicted as compassionate, dependable and heroic. He is the only one who resists the impulse of mob fury that leads the other characters to kill the German. He is the only character who steps forward to disarm the wounded German sailor rescued at the end of the film.
Lee's successful radio career continued with New World A-Comin', which made its debut in March 1944. He narrated the first two seasons of the groundbreaking WMCA radio series that presented Negro history and culture to mainstream American audiences.
He became the first African American to play Caliban, in Margaret Webster’s 1945 Broadway rendition of The Tempest. Lee had admired Shakespeare since his turn in Macbeth; indeed, at the time of his death he was preparing to play Othello on film.
In 1946, Lee played a principal role in On Whitman Avenue, a drama about racial prejudice directed by Margo Jones. Lee produced the play, making him the first African-American producer on Broadway. The play spoke directly to the need for interracial housing following World War II and won the praise of former First Lady Eleanor Roosevelt, who wrote weekly columns encouraging readers to see it.
In the autumn of 1946, Lee made American theatre history when he portrayed the villain Daniel de Bosola in John Webster's The Duchess of Malfi. Presented in Boston and on Broadway, the production marked the first time a black actor had played a white role on the stage. Lee wore a special white paste that had been used medically, to cover burns and marks, but had never before been used in the theatre.
In 1947, he had a supporting role in Robert Rossen's Body and Soul, another boxing picture.
In 1948, Lee played his last stage role, that of a devoted slave in Set My People Free, Dorothy Heyward's drama based on the aborted 1822 slave revolt led by Denmark Vesey.
In 1949, he took a supporting role in Lost Boundaries, a drama based on William Lindsay White's book of the same title, a nonfiction account of Dr. Albert C. Johnston and his family, who passed for white while living in New England in the 1930s and 1940s.
Lee's last film appearance was the starring role of minister Stephen Kumalo in Cry, the Beloved Country (1951).
Civil rights activism
As an actor, Lee came into contact with many of the leading progressive figures in the country. Langston Hughes, for instance, wrote two brief plays for Lee; these were submitted to the Theater Project, but their criticism of racism in America was deemed too controversial, and neither was staged. Lee spoke to schools, sponsored various humanitarian events, and began speaking directly against the existing segregation in America's armed forces, while simultaneously acknowledging the need to win World War II. To this latter end, he appeared at numerous USO events; he won an award from the United States Recruiting Office and another from the Treasury Department for his help in selling war bonds. These sentiments would carry on throughout his life, culminating in his early firsthand account of apartheid in South Africa.
Lee was an early influence on physician and human rights activist H. Jack Geiger. They met in 1940 when Geiger, a 14-year-old middle-class Jewish runaway, was backstage at a Broadway production of Native Son. Lee agreed to take Geiger in when he showed up at his door in Harlem asking for a place to stay. With the consent of his parents, Geiger stayed with Lee for over a year. Lee took on the role of surrogate father and introduced Geiger to Langston Hughes, Billy Strayhorn, Richard Wright, and Adam Clayton Powell. Geiger eventually became a journalist, then a doctor who co-founded the first community health center in the United States, Columbia Point Health Center in Dorchester, Massachusetts. He became a founder of Physicians for Social Responsibility and Physicians for Human Rights, and established community health centers in Mississippi and South Africa. Geiger says he would never have moved so deeply in these worlds so quickly if not for his experiences with Canada Lee.
By the late 1940s, the rising tide of anti-communism had made many of Lee’s earlier contacts politically dangerous. In 1949, the trade journal Variety stated that under no circumstance was Lee to be used in American Tobacco’s televised production of a radio play he had recently starred in because he was "too controversial".
The same year, the FBI offered to clear Lee’s name if he would publicly call Paul Robeson a communist. Lee refused and responded by saying, "All you’re trying to do is split my race." According to newspaper columnist Walter Winchell, Lee stated that he intended to come out and "publicly blast Paul Robeson." However, the fact that the friendship between the two actors remained until Lee's death suggests that Robeson put no faith in Winchell's claim.
At the height of the Hollywood blacklist, Lee managed to find work in 1950 as the star of a British film Cry, The Beloved Country, for which both he and Sidney Poitier were smuggled into South Africa as indentured servants in order to play their roles as African ministers. During filming, Lee had his first heart attack, and he never fully recovered his health. The film’s message of universal brotherhood stands as Lee's final work towards this aim.
Being on the Hollywood blacklist prevented him from getting further work. Scheduled to appear in Italy to begin production on a filmed version of Othello, he was repeatedly notified that his passport "remained under review". Lee was reportedly to star as Bigger Thomas in the Argentine version of Native Son but was replaced in the role by Richard Wright, author of the novel, when Lee had to withdraw.
Family life
In December 1925, Lee married Juanita Eugenia Waller. On November 22, 1926, they had a son, Carl Vincent Canegata, who became actor Carl Lee. The couple separated while their son was young, and they were amicably divorced in 1942.
In 1934, Lee began a love affair with publisher and peace activist Caresse Crosby, despite the threat of miscegenation laws. They often had lunch in uptown New York in Harlem at the then-new restaurant "Franks", where they could maintain their secret relationship. When Lee was performing in Washington, D.C., during the 1940s, the only restaurant in the city where they could eat together was an African restaurant named the Bugazi. Crosby and Lee's intimate relationship continued into the mid-1940s.
In March 1951, Lee married Frances Pollack. They remained together until he died just over a year later.
Death
Lee died of a reported heart attack at the age of 45 on May 9, 1952, in Manhattan. It was later revealed by his widow, Frances Pollack, that he had been diagnosed with uremia and died of kidney disease, slipping into a coma and passing away 10 days after his diagnosis. He was buried at Woodlawn Cemetery in The Bronx.
5 notes
·
View notes
Photo

A "pioneer" of the deepest order
Donna M. Tobias (May 22, 1952 – September 21, 2010) was an American diver. She was the United States Navy's first female deep sea diver.
Upon enlisting in the Navy in March 1974, she inquired a Navy recruiter about the possibility of her becoming a diver. Her question was immediately shot down as “women can’t get in [to dive school],” and she chose to focus on shipfitting and hull technician.While working as a shipfitter and hull technician for the Navy, she applied for a waiver to attend dive school. She was required to get permission from The Pentagon before being assigned to training in Norfolk.
At the age of 21, she applied to the Navy 2nd Class Diving School and was accepted two days before the program started in January 1975.During training, she was required to dive while carrying more than 200 pounds of gear in dark, cold or turbulent water. Despite this, Tobias became the first woman to graduate from the Navy Deep Sea Diving School and went on to work with the Navy search and salvage operations. However, she was still limited opportunities due to her gender. She was unable to join sea duty billets so she accepted a position as an instructor at the Submarine Escape Training Tank at Submarine Naval Base in New London.Tobias also worked within the hyperbaric chamber to treat divers suffering embolisms and civilians suffering from carbon monoxide poisoning and gangrene. Retired Master Diver Steven Lechner believed Tobias was the first woman to teach in the escape tank. Her brother Gary was also enrolled in the army, and she was his instructor at the diving school on base.
After eight years in the Navy, Tobias earned her bachelor's degree in education and a master's in psychology and taught special-education classes at New London High School. In 2001, she was inducted into the Women Diver's Hall of Fame.However, at the age of 58, Tobias committed suicide due to depression on September 21, 2010.
In 2018, the Naval Submarine Base New London unveiled a dive locker named after Tobias
She was the first woman- and Carl Brashear was the first man of color


Carl Maxie Brashear (January 19, 1931 – July 25, 2006) was a highly decorated United States Navy sailor. He was a U.S. Navy master diver, rising to the position in 1970 having an amputated left leg. The film Men of Honor was based on his life.
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
TOP 10 WRITERS OF 2019′s REVIEWS
It is very hard to pick the best artists of the year, especially when you know in advance, they will not match anyone else’s list. And I say this because this list is based in all the reviews that scored a perfect 10 during 2019. And these reviews go from 1935 to 2020, so it is definitely not going to match anyone else’s.
There were other writers I would have loved to include in this list but they weren’t as prominent in my reviews as the one here. Those writers that are worth mentioning are: Bub Burden, Carl Potts, Denny O’Neil, Grant Morrison, Harlan Ellison, Jim Lawson, Jim Starlin, John Ostrander, Paul Dini, Peter Laird, Sam Humphries, Stan Sakai, Steve Darnall, Steve Murphy and Tom Taylor. To all of them, thank you for your work!
NUMBER TEN
JAMES ROBINSON / JAMES TYNION IV

James Robinson (1963 - present) has been writing for three decades, with an early comics work, "Grendel: The Devil's Whisper", appearing in the 1989 series of the British anthology A1. The series for which he is arguably most renowned is the DC Comics series Starman, where he took the aging Golden Age character of the same name and revitalized both the character and all those who had used the name over the decades, weaving them into an interconnected whole. In 1997, Robinson's work on the title garnered him an Eisner Award for "Best Serialized Story".
He is also known for his The Golden Age limited series, which, despite being an Elseworlds story, established much of the backstory he would later use in Starman. He has written the Batman: Legends of the Dark Knight series, and served as a consultant and co-writer in the first year of JSA and its subsequent spin-off Hawkman.
James Tynion IV was born December 14, 1987, and grew up in Milwaukee, Wisconsin, where he attended Marquette University High School. While studying creative writing at Sarah Lawrence College, Tynion met and began studying under Scott Snyder, in the nascent years of his comic book writing career. Following school, he became an intern for the Vertigo imprint of DC Comics, working under Editor Shelly Bond, among others.
After a few years working in advertising, Scott Snyder asked Tynion to co-write the back-up features for the New 52 relaunch of Batman, in the midst of the acclaimed "Night of the Owls" comic book storyline, starting with Batman #8. In this comic, he tied the Court of Owls mythology to Alfred Pennyworth's father, Jarvis Pennyworth, working with noted American Vampire artist, Rafael Albuquerque.
James Tynion IV is openly bisexual.
These two writers are sharing the number ten spot because they have pretty much the same “rank” in the list of the year. Robinson made it in the list because of his work in “Starman”, and Tynion IV made it because of his work with the “Witching Hour” crossover.
NUMBER NINE
SEAN MURPHY (1980 - PRESENT)

Sean Gordon Murphy is an American comic book creator known for work on books such as Joe the Barbarian with Grant Morrison, Chrononauts with Mark Millar, American Vampire: Survival of the Fittest and The Wake with Scott Snyder, and Tokyo Ghost with Rick Remender. He has also written and drawn the miniseries Punk Rock Jesus, as well as Batman: White Knight and its sequel Curse of the White Knight.
Sean Gordon Murphy was born in Nashua, New Hampshire in 1980. He showed an interest in comics during grade school. In Salem he apprenticed to local painter and cartoonist, Leslie Swank. He graduated from Pinkerton Academy high school in 1999, and attended Massachusetts College of Art in Boston, and then Savannah College of Art and Design.
Murphy lives in Portland, Maine with his wife Colleen, having moved there from Brooklyn in 2016. Murphy was raised a Catholic, but is now an atheist.
The reason Sean Murphy made it into the list was “Batman: White Knight”, which is an elseworld story loosely based in the Batman Animated Series.
NUMBER EIGHT
FRANK MILLER (1957 - PRESENT)

Frank Miller (born January 27, 1957) is an American comic book writer, penciller and inker, novelist, screenwriter, film director, and producer best known for his comic book stories and graphic novels such as Ronin, Daredevil: Born Again, The Dark Knight Returns, Batman: Year One, Sin City, and 300.
He also directed the film version of The Spirit, shared directing duties with Robert Rodriguez on Sin City and Sin City: A Dame to Kill For, and produced the film 300. His film Sin City earned a Palme d'Or nomination, and he has received every major comic book industry award. In 2015, Miller was inducted into the Will Eisner Award Hall of Fame.
He created the comic book characters Elektra for Marvel Comics' Daredevil series, and a female version of the Robin character, Carrie Kelley, for DC Comics.
Miller is noted for combining film noir and manga influences in his comic art creations. "I realized when I started Sin City that I found American and English comics be too wordy, too constipated, and Japanese comics to be too empty. So I was attempting to do a hybrid".
Miller was raised in Montpelier, Vermont, the fifth of seven children of a nurse mother and a carpenter/electrician father. His family was Irish Catholic.
Miller was married to colorist Lynn Varley from 1986 to 2005; she colored many of his most acclaimed works (from Ronin in 1984 through 300 in 1998), and the backgrounds to the 2007 movie 300.
Miller has since been romantically linked to New York-based Shakespearean scholar Kimberly Halliburton Cox, who had a cameo in The Spirit (2008).
You can think many different things about Frank Miller, especially on his political views. But his work includes some pieces that really changed the industry. In this case, he made it into the list because of “Ronin” and “The Dark Knight Returns”, both have been influencing comics until our days (with “Ronin” being one of the many influences of the “Teenage Mutant Ninja Turtles”).
NUMBER SEVEN
MIKE W. BARR (1952 - PRESENT)

Mike W. Barr (born May 30, 1952) is an American writer of comic books, mystery novels, and science fiction novels.
Barr's debut as a comics professional came in DC Comics' Detective Comics #444 (Dec. 1974-Jan. 1975), for which he wrote an eight-page back-up mystery feature starring the Elongated Man. Another Elongated Man story followed in Detective Comics #453 (Nov. 1975). He wrote text articles and editorial replies in letter columns for the next few years. By mid-1980 he was writing regularly for both DC and Marvel, including stories for Mystery in Space, Green Lantern, The Brave and the Bold, Marvel Team-Up, and a Spider-Man/Scarlet Witch team-up in Marvel Fanfare #6.
Legion of Super-Heroes #277 (July 1981) saw him take on editorial duties at DC, a position he would hold until 1987. In December 1982, he and artist Brian Bolland began Camelot 3000, a 12 issue limited series that was one of DC Comics' first direct market projects. Barr and artist Trevor Von Eeden produced the first Green Arrow limited series in 1983. When the long running The Brave and the Bold series came to its conclusion with issue #200 (July 1983), it featured a preview of a new Batman series, Batman and the Outsiders by Barr and artist Jim Aparo, which would be described by DC Comics writer and executive Paul Levitz as being "a team series more fashionable to 1980s audiences." The Masters of Disaster were among the supervillains created by Barr and Aparo for the series. Barr wrote every issue of the original series, and its Baxter paper spinoff, The Outsiders that did not include Batman and introduced Looker. After the series' cancellation in February 1988, it was revived in November 1993 by Barr and artist Paul Pelletier.
He was one of the contributors to the DC Challenge limited series in 1986 and wrote the "Batman: Year Two" storyline in Detective Comics #575-578 (June-Sept. 1987) which followed up on Frank Miller's "Batman: Year One". Barr introduced the Reaper in Detective Comics #575 (June 1987) and returned to the character in the Batman: Full Circle one-shot in 1991. Another project from 1987 was the Batman: Son of the Demon graphic novel which was drawn by Jerry Bingham, proceeds from which reputedly "restored DC Comics to first place in sales after fifteen years." This title, and Barr's work on Batman with artist Alan Davis have been cited by Grant Morrison as key inspirations for his own run on the Batman title. Barr's sequel, Batman: Bride of The Demon, was published in 1991.
Mike W. Barr has been only of the earliest comic-book writers I knew about, and he made it into this list because of his work in “Camelot 3000″ and “Batman and the Outsiders”.
NUMBER SIX
CHRIS CLAREMONT, WITH JOHN BYRNE (1950 - PRESENT)

Christopher S. Claremont (born November 25, 1950) is a British-born American comic book writer and novelist, known for his 1975–1991 stint on Uncanny X-Men, far longer than that of any other writer, during which he is credited with developing strong female characters as well as introducing complex literary themes into superhero narratives, turning the once underachieving comic into one of Marvel's most popular series.
During his tenure at Marvel, Claremont co-created numerous X-Men characters, such as Rogue, Psylocke, Kitty Pryde/Shadowcat, Phoenix, The Brood, Lockheed, Shi'ar, Shi'ar Imperial Guard, Mystique, Destiny, Selene, Reverend William Stryker, Lady Mastermind, Emma Frost, Tessa, Siryn, Jubilee, Rachel Summers, Madelyne Pryor, Moira MacTaggert, Lilandra, Shadow King, Cannonball, Warpath, Mirage, Wolfsbane, Karma, Cypher, Sabretooth, Empath, Sebastian Shaw, Donald Pierce, Avalanche, Pyro, Legion, Nimrod, Gateway, Strong Guy, Proteus, Mister Sinister, Marauders, Purifiers, Captain Britain, Sunspot, Forge and Gambit. Claremont scripted many classic stories, including "The Dark Phoenix Saga" and "Days of Future Past", on which he collaborated with John Byrne. He developed the character of Wolverine into a fan favorite. X-Men #1, the 1991 spinoff series premiere that Claremont co-wrote with Jim Lee, remains the best-selling comic book of all time, according to Guinness World Records. In 2015, Claremont and his X-Men collaborator John Byrne were entered into the Will Eisner Award Hall of Fame.
Claremont was born in London, England. His father was an internist and his mother was a pilot and caterer. Claremont is Jewish on his mother's side, and lived in a kibbutz in Israel during his youth. His family moved to the United States when he was three, and he was raised primarily on Long Island. Alienated by the sports-oriented suburbs, his grandmother purchased for him a subscription to Eagle when he was a child, and he grew up reading Dan Dare, finding them more exciting than the Batman and Superman comics of the 1950s and early 1960s. He read works by science fiction writers such as Robert Heinlein, as well as writers of other genres such as Rudyard Kipling and C. S. Forester.
In the mid-1970s, Claremont was married to Bonnie Wilford. Following the dissolution of that marriage, he married Beth Fleisher, with whom Claremont co-authored Dragon Moon. Fleisher is the cousin (through marriage) of editor Dan Raspler, who was the editor on JLA during the six-issue "Tenth Circle" story arc Claremont and John Byrne wrote in 2004. Claremont and Fleisher have twin sons.
So why not John Byrne? Well, the reason Claremont made it into this list was mostly the Dark Phoenix Saga, but also the Wolverine mini-series. It is hard to separate them from their work in X-Men, but in the end, it is his dialogue that we read. I still think it is worth mentioning Byrne in this spot, as we wouldn’t have one without the other. Perhaps Wolverine solo mini-series wouldn’t be possible without the work of Byrne with the character, but there is more influence from Miller in that one. I am pretty sure Byrne will be in the top 10 next year anyway ;)
NUMBER FIVE
NEIL GAIMAN (1960 - PRESENT)

Neil Richard MacKinnon Gaiman (born Neil Richard Gaiman, 10 November 1960) is an English author of short fiction, novels, comic books, graphic novels, nonfiction, audio theatre, and films. His works include the comic book series The Sandman and novels Stardust, American Gods, Coraline, and The Graveyard Book. He has won numerous awards, including the Hugo, Nebula, and Bram Stoker awards, as well as the Newbery and Carnegie medals. He is the first author to win both the Newbery and the Carnegie medals for the same work, The Graveyard Book (2008). In 2013, The Ocean at the End of the Lane was voted Book of the Year in the British National Book Awards.
Gaiman's family is of Polish Jewish and other Eastern European Jewish origins. His great-grandfather emigrated from Antwerp, Belgium, to the UK before 1914 and his grandfather eventually settled in the south of England in the Hampshire city of Portsmouth and established a chain of grocery stores. Gaiman's grandfather changed his original family name of Chaiman to Gaiman. His father, David Bernard Gaiman, worked in the same chain of stores; his mother, Sheila Gaiman (née Goldman), was a pharmacist. He has two younger sisters, Claire and Lizzy.
After living for a period in the nearby town of Portchester, Hampshire, where Neil was born in 1960, the Gaimans moved in 1965 to the West Sussex town of East Grinstead, where his parents studied Dianetics at the Scientology centre in the town; one of Gaiman's sisters works for the Church of Scientology in Los Angeles. His other sister, Lizzy Calcioli, has said, "Most of our social activities were involved with Scientology or our Jewish family. It would get very confusing when people would ask my religion as a kid. I'd say, 'I'm a Jewish Scientologist.'" Gaiman says that he is not a Scientologist, and that like Judaism, Scientology is his family's religion. About his personal views, Gaiman has stated, "I think we can say that God exists in the DC Universe. I would not stand up and beat the drum for the existence of God in this universe. I don't know, I think there's probably a 50/50 chance. It doesn't really matter to me."
Gaiman was able to read at the age of four. He said, "I was a reader. I loved reading. Reading things gave me pleasure. I was very good at most subjects in school, not because I had any particular aptitude in them, but because normally on the first day of school they'd hand out schoolbooks, and I'd read them—which would mean that I'd know what was coming up, because I'd read it." When he was about ten years old, he read his way through the works of Dennis Wheatley, where especially The Ka of Gifford Hillary and The Haunting of Toby Jugg made an impact on him. One work that made a particular impression on him was J. R. R. Tolkien's The Lord of the Rings from his school library, although it only had the first two volumes of the novel. He consistently took them out and read them. He would later win the school English prize and the school reading prize, enabling him to finally acquire the third volume.
For his seventh birthday, Gaiman received C. S. Lewis's The Chronicles of Narnia series. He later recalled that "I admired his use of parenthetical statements to the reader, where he would just talk to you ... I'd think, 'Oh, my gosh, that is so cool! I want to do that! When I become an author, I want to be able to do things in parentheses.' I liked the power of putting things in brackets." Narnia also introduced him to literary awards, specifically the 1956 Carnegie Medal won by the concluding volume. When Gaiman won the 2010 Medal himself, the press reported him recalling, "it had to be the most important literary award there ever was" and observing, "if you can make yourself aged seven happy, you're really doing well – it's like writing a letter to yourself aged seven."
Gaiman attended Ardingly College in Ardingly, West Sussex
Lewis Carroll's Alice's Adventures in Wonderland was another childhood favourite, and "a favourite forever. Alice was default reading to the point where I knew it by heart." He also enjoyed Batman comics as a child.
Gaiman was educated at several Church of England schools, including Fonthill School in East Grinstead, Ardingly College (1970–74), and Whitgift School in Croydon (1974–77). His father's position as a public relations official of the Church of Scientology was the cause of the seven-year-old Gaiman being forced to withdraw from Fonthill School and remain at the school that he had previously been attending. He lived in East Grinstead for many years, from 1965 to 1980 and again from 1984 to 1987. He met his first wife, Mary McGrath, while she was studying Scientology and living in a house in East Grinstead that was owned by his father. The couple were married in 1985 after having their first child, Michael.
As a child and a teenager, Gaiman read the works of C. S. Lewis, J. R. R. Tolkien, Lewis Carroll, Mary Shelley, Rudyard Kipling, Edgar Allan Poe, Michael Moorcock, Alan Moore, Steve Ditko, Will Eisner, Ursula K. Le Guin, Harlan Ellison, Lord Dunsany and G. K. Chesterton. A lifetime fan of the Monty Python comedy troupe, as a teenager he owned a copy of Monty Python's Big Red Book. When he was 19–20 years old, he contacted his favourite science fiction writer, R. A. Lafferty, whom he discovered when he was nine, and asked for advice on becoming an author along with a Lafferty pastiche he had written. The writer sent Gaiman an encouraging and informative letter back, along with literary advice.
In the early 1980s, Gaiman pursued journalism, conducting interviews and writing book reviews, as a means to learn about the world and to make connections that he hoped would later assist him in getting published. He wrote and reviewed extensively for the British Fantasy Society. His first professional short story publication was "Featherquest", a fantasy story, in Imagine Magazine in May 1984.
When waiting for a train at London's Victoria Station in 1984, Gaiman noticed a copy of Swamp Thing written by Alan Moore, and carefully read it. Moore's fresh and vigorous approach to comics had such an impact on Gaiman that he would later write "that was the final straw, what was left of my resistance crumbled. I proceeded to make regular and frequent visits to London's Forbidden Planet shop to buy comics".
In 1984, he wrote his first book, a biography of the band Duran Duran, as well as Ghastly Beyond Belief, a book of quotations, with Kim Newman. Even though Gaiman thought he had done a terrible job, the book's first edition sold out very quickly. When he went to relinquish his rights to the book, he discovered the publisher had gone bankrupt. After this, he was offered a job by Penthouse. He refused the offer.
He also wrote interviews and articles for many British magazines, including Knave. During this he sometimes wrote under pseudonyms, including Gerry Musgrave, Richard Grey, and "a couple of house names". Gaiman has said he ended his journalism career in 1987 because British newspapers regularly publish untruths as fact. In the late 1980s, he wrote Don't Panic: The Official Hitchhiker's Guide to the Galaxy Companion in what he calls a "classic English humour" style. Following this he wrote the opening of what would become his collaboration with fellow English author Terry Pratchett on the comic novel Good Omens, about the impending apocalypse.
After forming a friendship with comic-book writer Alan Moore, Gaiman started writing comic books, picking up Miracleman after Moore finished his run on the series. Gaiman and artist Mark Buckingham collaborated on several issues of the series before its publisher, Eclipse Comics, collapsed, leaving the series unfinished. His first published comic strips were four short Future Shocks for 2000 AD in 1986–87. He wrote three graphic novels with his favourite collaborator and long-time friend Dave McKean: Violent Cases, Signal to Noise, and The Tragical Comedy or Comical Tragedy of Mr. Punch. Impressed with his work, DC Comics hired him in February 1987, and he wrote the limited series Black Orchid. Karen Berger, who later became head of DC Comics's Vertigo, read Black Orchid and offered Gaiman a job: to re-write an old character, The Sandman, but to put his own spin on him.
The Sandman tells the tale of the ageless, anthropomorphic personification of Dream that is known by many names, including Morpheus. The series began in January 1989 and concluded in March 1996. In the eighth issue of The Sandman, Gaiman and artist Mike Dringenberg introduced Death, the older sister of Dream, who would become as popular as the series' title character. The limited series Death: The High Cost of Living launched DC's Vertigo line in 1993. The 75 issues of the regular series, along with an illustrated prose text and a special containing seven short stories, have been collected into 12 volumes that remain in print. The series became one of DC's top selling titles, eclipsing even Batman and Superman. Comics historian Les Daniels called Gaiman's work "astonishing" and noted that The Sandman was "a mixture of fantasy, horror, and ironic humor such as comic books had never seen before". DC Comics writer and executive Paul Levitz observed that "The Sandman became the first extraordinary success as a series of graphic novel collections, reaching out and converting new readers to the medium, particularly young women on college campuses, and making Gaiman himself into an iconic cultural figure."
Gaiman has lived near Menomonie, Wisconsin, since 1992. Gaiman moved there to be close to the family of his then-wife, Mary McGrath, with whom he has three children. As of 2013, Gaiman also resides in Cambridge, Massachusetts. In 2014, he took up a five-year appointment as professor in the arts at Bard College, in Annandale-on-Hudson, New York.
Gaiman is married to songwriter and performer Amanda Palmer, with whom he has an open marriage. The couple announced that they were dating in June 2009, and announced their engagement on Twitter on 1 January 2010. On 16 November 2010, Palmer hosted a non-legally binding flash mob wedding for Gaiman's birthday in New Orleans. They were legally married on 2 January 2011. The wedding took place in the parlour of writers Ayelet Waldman and Michael Chabon. On marrying Palmer, he took her middle name, MacKinnon, as one of his names. In September 2015 they had a son.
I am sure Gaiman will make it to next year’s list as well, but in this year in particular, the main reason he made it was “The Sandman”, which had so much quality, almost all the issues I reviewed scored a 10.
NUMBER FOUR
MARK MILLAR (1969 - PRESENT)

Mark Millar MBE is a Scottish comic book writer, best known for his work on The Authority, The Ultimates, Marvel Knights Spider-Man, Ultimate Fantastic Four, Civil War, Kingsman: The Secret Service, Wanted, Chrononauts, Superior and Kick-Ass, the latter seven of which have been, or are planned to be, adapted into feature films.
Millar was born 24 December 1969 in Coatbridge, Scotland. His parents were also born in Coatbridge, and Millar spent the first half of his life in the town's Townhead area, attending St Ambrose High. He has four older brothers, and one older sister, who are 22, 20, 18, 16 and 14 years older than him, respectively. His brother Bobby, who today works at a special needs school, introduced him to comics at age 4 while attending university by taking him to shops and purchasing them for him. Still learning to read, Millar's first comic was the seminal The Amazing Spider-Man #121 (1973), which featured the death of Gwen Stacy. He purchased a Superman comic that day as well. Black and white reprinted comics purchased by his brothers for him would follow, cementing his interest in the medium so much that Millar drew a spider web across his face with indelible marker that his parents were unable to scrub off in time for his First Communion photo a week later. Millar has named Alan Moore and Frank Miller as the two biggest influences on his career, characterizing them as "my Mum and Dad." Other writers he names as influences include Grant Morrison, Peter Milligan, Warren Ellis and Garth Ennis. More recent writers that have impressed him include Jason Aaron and Scott Snyder.
Millar's mother died of a heart attack at age 64, when Millar was 14, and his father died four years later, aged 65. Although Millar enjoyed drawing comics, he was not permitted to go to art school because his family frowned upon such endeavours as a waste of time for the academic Millar, who studied subjects like chemistry, physics and advanced maths. He initially planned to be a doctor, and subsequently decided that becoming an economist would be a viable alternate plan, but later decided that he "couldn't quite hack it" in that occupation. He attended Glasgow University to study politics and economics, but dropped out after his father's death left him without the money to pay his living expenses.
When Millar was 18, he interviewed writer Grant Morrison, who was doing his first major American work on Animal Man, for a fanzine. When he told Morrison that he wanted to be both a writer and an artist, Morrison suggested that he focus on one of those career paths, as it was very hard to be successful at both, which Millar cites as the best advice he has received.
Millar's first job as a comic book writer came when he was still in high school, writing Trident's Saviour with Daniel Vallely providing art. Saviour combined elements of religion, satire and superhero action. During the 1990s, Millar worked on titles such as 2000 AD, Sonic the Comic and Crisis. In 1993, Millar, Grant Morrison and John Smith created a controversial eight-week run on 2000 AD called The Summer Offensive. It was during this run that Millar and Morrison wrote their first major story together, Big Dave.
Millar's British work brought him to the attention of DC Comics, and in 1994 he started working on his first American comic, Swamp Thing. The first four issues of Millar's run were co-written by Grant Morrison, allowing Millar to settle into the title. Although his work brought some critical acclaim to the ailing title, the book's sales were still low enough to warrant cancellation by the publisher. From there, Millar spent time working on various DC titles, often co-writing with or under the patronage of Morrison as in the cases of his work on JLA, The Flash and Aztek: The Ultimate Man, and working on unsuccessful pitches for the publisher.
In 2000, Millar replaced Warren Ellis on The Authority for DC's Wildstorm imprint. Millar announced his resignation from DC in 2001, though his miniseries Superman: Red Son was printed in 2003.
In 2001, Millar launched Ultimate X-Men for Marvel Comics' Ultimate Marvel imprint. The following year he collaborated with illustrator Bryan Hitch on The Ultimates, the Ultimate imprint's equivalent of The Avengers. Millar's work on The Ultimates was later adapted into two Marvel Animated Features and the subsequent 2012 Hollywood box office smash Marvel's The Avengers.
In 2006, Millar, joined by artist Steve McNiven, began writing the Marvel miniseries Civil War a seven-issue limited series revolving around the passing of Superhuman Registration Act as a result of the death and destruction unintentionally caused by superheroes and turned Captain America and Iron Man onto opposing sides, the book formed the basis for the film Captain America: Civil War. In 2009 Millar wrote the dystopian "Old Man Logan" storyline, which appeared in the Wolverine series, and was set in a possible future in which Wolverine, having been traumatized by his murder of the X-Men (an event prompted by Mysterio's illusions), became a recluse, after which the United States government collapsed, and the country fell under the control of various supervillain enclaves. Needing rent money for his family's farm, Wolverine comes out of retirement when called upon by Hawkeye.
Millar supports British withdrawal from the European Union.
While Millar is usually not my cup of tea, mostly because of his toxic depictions of masculinity in his stories (this may or may not be on purpose), he did write a lot of sophisticated comics in the reviews I did this year (”The Ultimates” and “Marvel Knights: Spider-man”).
NUMBER THREE
GEOFF JOHNS (1973 - PRESENT)

Geoffrey Johns (born January 25, 1973) is an American comic book writer, screenwriter and film and television producer. He served as the President and Chief Creative Officer (CCO) of DC Entertainment from 2016 to 2018 after his initial appointment as CCO in 2010. Some of his most notable work has used the DC Comics characters Green Lantern, Aquaman, Flash and Superman.
In 2018, he stepped down from his executive role at DC Entertainment to open a production company, Mad Ghost Productions, to focus on writing and producing film, television and comic book titles based on DC properties. Some of his work in television includes the series Blade, Smallville, Arrow and The Flash. He was a co-producer on the film Green Lantern (2011) and a producer on Justice League (2017). He co-wrote the story for Aquaman (2018) and the screenplay for Wonder Woman 1984 (2020).
Geoff Johns was born in Detroit, Michigan, the son of Barbara and Fred Johns. He is of half Lebanese ancestry and grew up in the suburbs of Grosse Pointe and Clarkston. As a child, Johns and his brother first discovered comics through an old box of comics they found in their grandmother's attic, which included copies of The Flash, Superman, Green Lantern, and Batman from the 1960s and 1970s. Johns eventually began to patronize a comics shop in Traverse City, recalling that the first new comics he bought were Crisis on Infinite Earths #3 or 4 and The Flash #348 or 349, as the latter was his favorite character. As Johns continued collecting comics, he gravitated toward DC Comics and later Vertigo, and drew comics. After graduating from Clarkston High School in 1991, he studied media arts, screenwriting, film production and film theory at Michigan State University. He graduated from Michigan State in 1995, and then moved to Los Angeles, California.
In Los Angeles, Johns cold-called the office of director Richard Donner looking for an internship, and while Johns was being transferred to various people, Donner picked up the phone by accident, leading to a conversation and the internship. Johns started off copying scripts, and after about two months, was hired as a production assistant for Donner, whom Johns regards as his mentor.
While working on production of Donner's 1997 film Conspiracy Theory, Johns visited New York City, where he met DC Comics personnel such as Eddie Berganza, reigniting his childhood interest in comics.
Berganza invited Johns to tour the DC Comics offices, and offered Johns the opportunity to suggest ideas, which led to Johns pitching Stars and S.T.R.I.P.E., a series based on the second Star-Spangled Kid and her stepfather, to editor Chuck Kim a year later. Johns expected to write comics "on the side", until he met David Goyer and James Robinson, who were working on JSA. After looking at Stars and S.T.R.I.P.E., Robinson offered Johns co-writing duties on JSA in 2000, and Johns credits both him and Mike Carlin with shepherding him into the comics industry. That same year, Johns became the regular writer on The Flash ongoing series with issue 164. John's work on The Flash represents one example of his modeling of various elements in his stories after aspects of his birth town, explaining, "When I wrote The Flash, I turned Keystone City into Detroit, made it a car town. I make a lot of my characters from Detroit. I think self-made, blue-collar heroes represent Detroit. Wally West's Flash was like that. I took the inspiration of the city and the people there and used it in the books." John's Flash run concluded with #225.
His younger sister, Courtney, was a victim of the TWA Flight 800 crash. The DC Comics character Courtney Whitmore, whom Johns created, is based on her.
In a 2010 interview, Johns named Steve McNiven as an artist he would like to collaborate with, J. Michael Straczynski's run on Thor as his then-favorite ongoing comic book, and The Flash as his favorite of all time, stating that he owns every issue of it. He credits reading James Robinson's The Golden Age as the book responsible for his love of the characters featured in the book, and for his decision to accept writing duties on JSA. He is also a comic book retailer who co-owns Earth-2 Comics in Northridge, California, with Carr D'Angelo and Jud Meyers.
There are plenty of reasons for Geoff Johns to be in this list, this year. But the main ones are his Justice League and Shazam Origin. At the moment of this writing, Doomsday Clock is not included in these reviews, but his writing there is also very, very good.
NUMBER TWO
MARV WOLFMAN, WITH GEORGE PEREZ (1946 - PRESENT)

Marvin Arthur Wolfman (born May 13, 1946) is an American comic book and novelization writer. He worked on Marvel Comics's The Tomb of Dracula, for which he and artist Gene Colan created the vampire-slayer Blade, and DC Comics's The New Teen Titans and the Crisis on Infinite Earths limited series with George Pérez.
Marv Wolfman was born in Brooklyn, New York City, the son of police officer Abe and housewife Fay. He has a sister, Harriet, 12 years older. When Wolfman was 13, his family moved to Flushing, Queens, in New York City, where he attended junior high school. He went on to New York's High School of Art and Design, in Manhattan, hoping to become a cartoonist. Wolfman is Jewish.
Marvin Wolfman was active in fandom before he began his professional comics career at DC Comics in 1968. Wolfman was one of the first to publish Stephen King, with "In A Half-World of Terror" in Wolfman's horror fanzine Stories of Suspense No. 2 (1965). This was a revised version of King's first published story, "I Was a Teenage Grave Robber", which had been serialized over four issues (three published and one unpublished) of the fanzine Comics Review that same year.
Wolfman's first published work for DC Comics appeared in Blackhawk No. 242 (Aug.–Sept. 1968). He and longtime friend Len Wein created the character Jonny Double in Showcase No. 78 (Nov. 1968) scripted by Wolfman. The two co-wrote "Eye of the Beholder" in Teen Titans No. 18 (Dec. 1968), which would be Wein's first professional comics credit. Neal Adams was called upon to rewrite and redraw a Teen Titans story which had been written by Wein and Wolfman. The story, titled "Titans Fit the Battle of Jericho!", would have introduced DC's first African American superhero, but was rejected by publisher Carmine Infantino. The revised story appeared in Teen Titans No. 20 (March–April 1969). Wolfman and Gil Kane created an origin for Wonder Girl in Teen Titans No. 22 (July–Aug. 1969) which introduced the character's new costume.
Wolfman is married to Noel Watkins. Wolfman was previously married to Michele Wolfman, for many years a colorist in the comics industry. They have a daughter, Jessica Morgan.
There are also many reasons for Wolfman to be in this list. Among them there is: “Man and Superman”, “New Teen Titans”, “Tales of the Teen Titans”, “The Judas Contract”, “Vigilante” and “Crisis on Infinite Earths”. Many of these, were collaborations with George Pérez and that is why he gets a mention in this space (don’t worry, he is in another TOP 10 this year). Not only he destroyed a multiverse and created one of the most stable runs of DC Continuity ever, he also “created” Nightwing and Vigilante and finally published “Man and Superman” this year.
NUMBER ONE
ALAN MOORE (1953 - PRESENT)

Alan Moore (born 18 November 1953) is an English writer known primarily for his work in comic books including Watchmen, V for Vendetta, The Ballad of Halo Jones, Swamp Thing, Batman: The Killing Joke and From Hell. Regarded by some as the best comics writer in the English language, he is widely recognized among his peers and critics. He has occasionally used such pseudonyms as Curt Vile, Jill de Ray, and Translucia Baboon; also, reprints of some of his work have been credited to The Original Writer when Moore requested that his name be removed.
Moore started writing for British underground and alternative fanzines in the late 1970s before achieving success publishing comic strips in such magazines as 2000 AD and Warrior. He was subsequently picked up by the American DC Comics, and as "the first comics writer living in Britain to do prominent work in America", he worked on major characters such as Batman (Batman: The Killing Joke) and Superman (Whatever Happened to the Man of Tomorrow?), substantially developed the character Swamp Thing, and penned original titles such as Watchmen. During that decade, Moore helped to bring about greater social respectability for comics in the United States and United Kingdom. He prefers the term "comic" to "graphic novel". In the late 1980s and early 1990s he left the comic industry mainstream and went independent for a while, working on experimental work such as the epic From Hell and the prose novel Voice of the Fire. He subsequently returned to the mainstream later in the 1990s, working for Image Comics, before developing America's Best Comics, an imprint through which he published works such as The League of Extraordinary Gentlemen and the occult-based Promethea. In 2016, he published Jerusalem: a 1266-page experimental novel set in his hometown of Northampton, UK.
Moore is an occultist, ceremonial magician, and anarchist, and has featured such themes in works including Promethea, From Hell, and V for Vendetta, as well as performing avant-garde spoken word occult "workings" with The Moon and Serpent Grand Egyptian Theatre of Marvels, some of which have been released on CD.
Despite his own personal objections, his works have provided the basis for a number of Hollywood films, including From Hell (2001), The League of Extraordinary Gentlemen (2003), V for Vendetta (2005), and Watchmen (2009). Moore has also been referenced in popular culture, and has been recognized as an influence on a variety of literary and television figures including Neil Gaiman, Joss Whedon, and Damon Lindelof. He has lived a significant portion of his life in Northampton, England, and he has said in various interviews that his stories draw heavily from his experiences living there.
Abandoning his office job, he decided to instead take up both writing and illustrating his own comics. He had already produced a couple of strips for several alternative fanzines and magazines, such as Anon E. Mouse for the local paper Anon, and St. Pancras Panda, a parody of Paddington Bear, for the Oxford-based Back Street Bugle. His first paid work was for a few drawings that were printed in NME, and not long after he succeeded in getting a series about a private detective known as Roscoe Moscow published using the pseudonym of Curt Vile (a pun on the name of composer Kurt Weill) in the weekly music magazine Sounds, earning £35 a week. Alongside this, he and Phyllis, with their newborn daughter Leah, began claiming unemployment benefit to supplement this income. Not long after this, in 1979 he also began publishing a new comic strip known as Maxwell the Magic Cat in the Northants Post, under the pseudonym of Jill de Ray (a pun on the Medieval child murderer Gilles de Rais, something he found to be a "sardonic joke"). Earning a further £10 a week from this, he decided to sign off of social security, and would continue writing Maxwell the Magic Cat until 1986. Moore has stated that he would have been happy to continue Maxwell's adventures almost indefinitely, but ended the strip after the newspaper ran a negative editorial on the place of homosexuals in the community. Meanwhile, Moore decided to focus more fully on writing comics rather than both writing and drawing them, stating that "After I'd been doing [it] for a couple of years, I realised that I would never be able to draw well enough and/or quickly enough to actually make any kind of decent living as an artist."
To learn more about how to write a successful comic-book script, he asked advice from his friend, comic-book writer Steve Moore, whom he had known since he was fourteen. Interested in writing for 2000AD, one of Britain's most prominent comic magazines, Alan Moore then submitted a script for their long running and successful series Judge Dredd. While having no need for another writer on Judge Dredd, which was already being written by John Wagner, 2000AD's editor Alan Grant saw promise in Moore's work – later remarking that "this guy's a really fucking good writer" – and instead asked him to write some short stories for the publication's Future Shocks series. While the first few were rejected, Grant advised Moore on improvements, and eventually accepted the first of many. Meanwhile, Moore had also begun writing minor stories for Doctor Who Weekly, and later commented that "I really, really wanted a regular strip. I didn't want to do short stories ... But that wasn't what was being offered. I was being offered short four or five-page stories where everything had to be done in those five pages. And, looking back, it was the best possible education that I could have had in how to construct a story."
From 1980 through to 1984, Moore maintained his status as a freelance writer, and was offered a spate of work by a variety of comic book companies in Britain, namely Marvel UK, and the publishers of 2000AD and Warrior. He later remarked that "I remember that what was generally happening was that everybody wanted to give me work, for fear that I would just be given other work by their rivals. So everybody was offering me things." It was an era when comic books were increasing in popularity in Britain, and according to Lance Parkin, "the British comics scene was cohering as never before, and it was clear that the audience was sticking with the title as they grew up. Comics were no longer just for very small boys: teenagers – even A-level and university students – were reading them now."
During this three-year period, 2000AD would accept and publish over fifty of Moore's one-off stories for their Future Shocks and Time Twisters science fiction series. The editors at the magazine were impressed by Moore's work and decided to offer him a more permanent strip, starting with a story that they wanted to be vaguely based upon the hit film E.T. the Extra-Terrestrial. The result, Skizz, which was illustrated by Jim Baikie, told the story of the titular alien who crashes to Earth and is cared for by a teenager named Roxy, and Moore later noted that in his opinion, this work "owes far too much to Alan Bleasdale." Another series he produced for 2000AD was D.R. and Quinch, which was illustrated by Alan Davis. The story, which Moore described as "continuing the tradition of Dennis the Menace, but giving him a thermonuclear capacity", revolved around two delinquent aliens, and was a science-fiction take on National Lampoon's characters O.C. and Stiggs. The work widely considered to be the highlight of his 2000AD career, and that he himself described as "the one that worked best for me" was The Ballad of Halo Jones. Co-created with artist Ian Gibson, the series was set in the 50th century. The series was discontinued after three books due to a dispute between Moore and Fleetway, the magazine's publishers, over the intellectual property rights of the characters Moore and Gibson had co-created.
Another comic company to employ Moore was Marvel UK, who had formerly purchased a few of his one-off stories for Doctor Who Weekly and Star Wars Weekly. Aiming to get an older audience than 2000AD, their main rival, they employed Moore to write for the regular strip Captain Britain, "halfway through a storyline that he's neither inaugurated nor completely understood." He replaced the former writer Dave Thorpe, but maintained the original artist, Alan Davis, whom Moore described as "an artist whose love for the medium and whose sheer exultation upon finding himself gainfully employed within it shine from every line, every new costume design, each nuance of expression."
Guy Fawkes serves as physical and philosophical inspiration for the titular protagonist of V for Vendetta.
The third comic company that Moore worked for in this period was Quality Communications, publishers of a new monthly magazine called Warrior. The magazine was founded by Dez Skinn, a former editor of both IPC (publishers of 2000 AD) and Marvel UK, and was designed to offer writers a greater degree of freedom over their artistic creations than was allowed by pre-existing companies. It was at Warrior that Moore "would start to reach his potential". Moore was initially given two ongoing strips in Warrior: Marvelman and V for Vendetta, both of which debuted in Warrior's first issue in March 1982. V for Vendetta was a dystopian thriller set in a future 1997 where a fascist government controlled Britain, opposed only by a lone anarchist dressed in a Guy Fawkes costume who turns to terrorism to topple the government. Illustrated by David Lloyd, Moore was influenced by his pessimistic feelings about the Thatcherite Conservative government, which he projected forward as a fascist state in which all ethnic and sexual minorities had been eliminated. It has been regarded as "among Moore's best work" and has maintained a cult following throughout subsequent decades.
Marvelman (later retitled Miracleman for legal reasons) was a series that originally had been published in Britain from 1954 through to 1963, based largely upon the American comic Captain Marvel. Upon resurrecting Marvelman, Moore "took a kitsch children's character and placed him within the real world of 1982". The work was drawn primarily by Garry Leach and Alan Davis. The third series that Moore produced for Warrior was The Bojeffries Saga, a comedy about a working-class English family of vampires and werewolves, drawn by Steve Parkhouse. Warrior closed before these stories were completed, but under new publishers both Miracleman and V for Vendetta were resumed by Moore, who finished both stories by 1989. Moore's biographer Lance Parkin remarked that "reading them through together throws up some interesting contrasts – in one the hero fights a fascist dictatorship based in London, in the other an Aryan superman imposes one."
Although Moore's work numbered amongst the most popular strips to appear in 2000 AD, Moore himself became increasingly concerned at the lack of creator's rights in British comics. In 1985, he talked to fanzine Arkensword, noting that he had stopped working for all British publishers bar IPC, "purely for the reason that IPC so far have avoided lying to me, cheating me or generally treating me like shit." He did join other creators in decrying the wholesale relinquishing of all rights, and in 1986 stopped writing for 2000 AD, leaving mooted future volumes of the Halo Jones story unstarted. Moore's outspoken opinions and principles, particularly on the subject of creator's rights and ownership, would see him burn bridges with a number of other publishers over the course of his career.
Meanwhile, during this same period, he – using the pseudonym of Translucia Baboon – became involved in the music scene, founding his own band, The Sinister Ducks, with David J (of goth band Bauhaus) and Alex Green, and in 1983 released a single, March of the Sinister Ducks, with sleeve art by illustrator Kevin O'Neill. In 1984, Moore and David J released a 12-inch single featuring a recording of "This Vicious Cabaret", a song featured in V for Vendetta, which was released on the Glass Records label. Moore would write the song "Leopardman at C&A" for David J, and it would be set to music by Mick Collins for the album We Have You Surrounded by Collins' group The Dirtbombs.
Moore's work in 2000 AD brought him to the attention of DC Comics editor Len Wein, who hired him in 1983 to write The Saga of the Swamp Thing, then a formulaic and poor-selling monster comic. Moore, with artists Stephen R. Bissette, Rick Veitch, and John Totleben, deconstructed and reimagined the character, writing a series of formally experimental stories that addressed environmental and social issues alongside the horror and fantasy, bolstered by research into the culture of Louisiana, where the series was set. For Swamp Thing he revived many of DC's neglected magical and supernatural characters, including the Spectre, the Demon, the Phantom Stranger, Deadman, and others, and introduced John Constantine, an English working-class magician based visually on the British musician Sting; Constantine later became the protagonist of the series Hellblazer, which became Vertigo's longest running series at 300 issues. Moore would continue writing Swamp Thing for almost four years, from issue No. 20 (January 1984) through to issue No. 64 (September 1987) with the exception of issues No. 59 and 62. Moore's run on Swamp Thing was successful both critically and commercially, and inspired DC to recruit British writers such as Grant Morrison, Jamie Delano, Peter Milligan, and Neil Gaiman to write comics in a similar vein, often involving radical revamps of obscure characters. These titles laid the foundation of what became the Vertigo line.
Moore began producing further stories for DC Comics, including a two-part story for Vigilante, which dealt with domestic abuse. He was eventually given the chance to write a story for one of DC's best-known superheroes, Superman, entitled "For the Man Who Has Everything", which was illustrated by Dave Gibbons and published in 1985. In this story, Wonder Woman, Batman, and Robin visit Superman on his birthday, only to find that he has been overcome by an alien organism and is hallucinating about his heart's desire. He followed this with another Superman story, "Whatever Happened to the Man of Tomorrow?", which was published in 1986. Illustrated by Curt Swan, it was designed as the last Superman story in the pre-Crisis on Infinite Earths DC Universe.
The threat of Nuclear war during the Cold War influenced the setting and tone of Watchmen.
The limited series Watchmen, begun in 1986 and collected as a trade paperback in 1987, cemented Moore's reputation. Imagining what the world would be like if costumed heroes had really existed since the 1940s, Moore and artist Dave Gibbons created a Cold War mystery in which the shadow of nuclear war threatens the world. The heroes who are caught up in this escalating crisis either work for the US government or are outlawed, and are motivated to heroism by their various psychological hang-ups. Watchmen is non-linear and told from multiple points of view, and includes highly sophisticated self-references, ironies, and formal experiments such as the symmetrical design of issue 5, "Fearful Symmetry", where the last page is a near mirror-image of the first, the second-last of the second, and so on, and in this manner is an early example of Moore's interest in the human perception of time and its implications for free will. It is the only comic to win the Hugo Award, in a one-time category ("Best Other Form"). It is widely seen as Moore's best work, and has been regularly described as the greatest comic book ever written. Alongside roughly contemporary works such as Frank Miller's Batman: The Dark Knight Returns, Art Spiegelman's Maus, and Jaime and Gilbert Hernandez's Love and Rockets, Watchmen was part of a late 1980s trend in American comics towards more adult sensibilities. Comics historian Les Daniels noted that Watchmen "called into question the basic assumptions on which the super hero genre is formulated". DC Comics writer and executive Paul Levitz observed in 2010 that "As with The Dark Knight Returns, Watchmen set off a chain reaction of rethinking the nature of super heroes and heroism itself, and pushed the genre darker for more than a decade. The series won acclaim ... and would continue to be regarded as one of the most important literary works the field ever produced." Moore briefly became a media celebrity, and the resulting attention led to him withdrawing from fandom and no longer attending comics conventions (at one UKCAC in London he is said to have been followed into the toilet by eager autograph hunters).
Since his teenage years Moore has had long hair, and since early adulthood has also had a beard. He has taken to wearing a number of large rings on his hands, leading him to be described as a "cross between Hagrid and Danny from Withnail and I" who could be easily mistaken for "the village eccentric". Born and raised in Northampton, he continues to live in the town, and used its history as a basis for his novels Voice of the Fire and Jerusalem. His "unassuming terraced" Northampton home was described by an interviewer in 2001 as "something like an occult bookshop under permanent renovation, with records, videos, magical artifacts and comic-book figurines strewn among shelves of mystical tomes and piles of paper. The bathroom, with blue-and-gold décor and a generous sunken tub, is palatial; the rest of the house has possibly never seen a vacuum cleaner. This is clearly a man who spends little time on the material plane." He likes to live in his home town, feeling that it affords him a level of obscurity that he enjoys, remarking that "I never signed up to be a celebrity." He has spoken in praise of the town's former Radical MP, Charles Bradlaugh at the annual commemoration. He is also a vegetarian.
With his first wife Phyllis, whom he married in the early 1970s, he has two daughters, Leah and Amber. The couple also had a mutual lover, Deborah, although the relationship between the three ended in the early 1990s as Phyllis and Deborah left Moore, taking his daughters with them. On 12 May 2007, he married Melinda Gebbie, with whom he has worked on several comics, most notably Lost Girls.
It was pretty clear that Alan Moore was going to end up being in the Top 10 this year. Mostly because I read a lot of his material from DC. The reason he made it into the top 10 is “V for Vendetta” with David Lloyd, “Swamp Thing”, “Whatever Happened to the Man of Tomorrow?”, “Tom Strong”, Batman: The Killing Joke” and “Watchmen”.
Most of these writers have also done something good, not only for the comic-book industry, but also for the world. And this TOP 10 is a way of celebrating them, because their work really inspired most of the pop-culture we consume today.
#writers#comics#reviews#2019#alan moore#marv wolfman#geoff johns#mark millar#neil gaiman#chris claremont#mike w barr#frank miller#sean murphy#james robinson#james tynion iv
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
“James Bond: Los superhombres están entre nosotros” [Primera Plana, 19.04.1966]

Cinco mil años atrás, los egipcios organizaron un óptimo servicio secreto e incluyeron el espionaje entre las ciencias ocultas. Durante el reinado del faraón Thutmose III, un capitán llamado Thute introdujo 200 soldados en Jafa, disimulándolos bajo un cargamento de harina, gracias a los informes de sus agentes. En la Ilíada, Homero canta a una de las obras maestras del espionaje: el Caballo de Troya. En el siglo XV, Juana de Arco fue traicionada por el Obispo Pierre Cauchon de Beauvais, un espía pagado por los ingleses. Pero las complejidades de la guerra moderna crearon divisiones dentro de esa ciencia vasta y deleznable.
El espionaje político, por ejemplo, persigue informaciones sobre industria, agricultura, comercio, trabajo, transportes y, por supuesto, política. En su ensayo La sociedad desnuda, Vance Packard analiza cómo las grandes corporaciones de USA establecieron hasta con los baños una vigilancia de sus empleadas y obreras a través de micrófonos ocultos. Pero fue Joseph Fouché, ministro de Policía de Napoleón, el verdadero inventor de la estrategia que luego heredaría James Bond: durante el Consulado y el Imperio consiguió desbaratar todos los complots contra su príncipe.
En el terreno militar, el privilegio de la creación suele adjudicarse a Federico el Grande, quien estableció un sólido cuerpo de agentes separado en cuatro categorías: los espías comunes, proletarios y campesinos que pretendían así ganarse algún dinero extra; los espías dobles, que trabajaban simultáneamente para potencias enemigas y cuya misión era confundir al adversario; los de alto rango, oficiales del Ejército, nobles y embajadores, que cobraban sueldos altísimos; y los espías a la fuerza, por lo general jefes de pueblos conquistados que debían pasar datos contra su voluntad. Federico solía decir: "El mariscal de Soubise es siempre seguido por cien cocineros; a mí me preceden cien espías".
La Primera Guerra tuvo su heroína del espionaje, Mata Hari, glorificada después por Greta Garbo y Jeanne Moreau; es curioso que su entregador fuera el agente alemán Walter W. Canaris a quien Hitler concedió el rango de almirante y designó jefe de la Inteligencia Exterior, a las órdenes de von Ribbentrop.
A fines de la Segunda Guerra, los escarceos bélicos entre la Unión Soviética y los Estados Unidos se concentraron en sus propias centrales de espionaje: la terrible NKVD, con sede En Moscú, era conducida por el mariscal Beba (a su muerte, en 1953, fue reorganizada y rebautizada como KVD); la CIA (Central Intelligence Agency) se fundó en 1947 y prosperó luego a las órdenes de Allen Dulles; un año después de su nacimiento, un sensacional caso de espionaje se ventiló en USA: Whittaker Chambers, ex comunista, denunció que Alger Hiss, funcionario del Departamento de Estado, pasaba informes a la NKVD.
Nace el Superhombre

Toda esa rara secta de próceres más o menos embozados encontró, por fin, hace 14 años, un semidiós que los resumía: fue en la primavera de 1952 cuando Ian Lancaster Fleming, ex agente del Naval Intelligence británico, escribía las páginas iniciales de Casino Royale e introducía al personaje James Bond en el universo de los mitos. El parto se consumó apaciblemente en una de las islas del Caribe: Ocarabesa, en Jamaica.
La semana pasada, Buenos Aires se sacudía a su vez con las consecuencias de ese acto sereno pero artero: en la sala del Gran Rex se estrenaba Operación Trueno, el cuarto film de la serie Bond, y los 83 mil espectadores convocados durante los primeros siete días de exhibición festejaban con carcajadas o silbidos la indemnidad de este nuevo Superhombre. Más de doce años tardó esa glorificación en trasladarse de Londres a las playas sudamericanas: en 1953, uno de los clubes londinenses consagrados a la adoración de Bond —con 1.200 socios— libró batalla En Sobo contra una banda de eduardianos que hablan tratado de mancillar al héroe; treinta muchachos terminaron en el hospital. El 17 de abril de 1963, el Gran Rex de Buenos Aires cerraba la primera semana de exhibiciones de El satánico doctor No con una recaudación apenas superior al medio millón de pesos y un total de 10.803 espectadores; Bond se reivindicó el 22 de mayo de 1965, cuando el primer balance semanal de Goldfinger (Dedos de oro, tercer film del ciclo) reveló la asistencia de 52.429 personas y un ingreso de 5.429.022 pesos, excluidos los impuestos.
Entre el sábado y el domingo últimos, no menos de sesenta espectadores consultados por esta revista parecían estar dispuestos a fundar un Club de Amor a Bond o a inscribirse en los que hubiera. Todavía extasiada por los recursos que acaba de exponer el ídolo, Adriana Divarian, de 45 años, madre de tres hijos, admitió que Sean Connery, el escocés que encarna a Bond, "representa el ideal masculino" y que el propio personaje es algo así como un soplo de Dios. "Lástima que trate tan mal a las mujeres —suspiró—. Ojalá cambie algún día." Miguel Bersaiz, un estudiante de arquitectura de 20 años, explicó: "Admiro su seducción. Pero lo que más me fascina son sus rasgos de sadismo". Tulio Suárez, de 31 años, agente publicitario, opinó que Bond "sintetizaba todas nuestras ansias, pese a lo sobrenatural e increíble que es, pensándolo un poco".
Es posible que nadie lo piense demasiado; de otro modo no podría explicarse que la ficción propuesta por Ian Lancaster Fleming golpee tanto la realidad, se entronque con ella en un juego de siniestros mimetismos. Cuando en 1957 un periódico inglés que folletinizó la novela De Rusia con amor incluyó una variante en el final e insinuó que James Bond habla muerto, la redacción del diario fue acosada por centenares de iracundos que exigían una retractación. Asediado por las protestas, Fleming tuvo que demandar al periódico por daños, y dar fe de que 007 estaba sano y salvo. Desde que Arthur Conan Doyle decidió eliminar a Sherlock Holmes (a manos de Moriarty, un símil del señor Goldfinger), no se repetía un fenómeno semejante. Esta vez, en cambio, los admiradores de Bond no se contentan con su supervivencia: se apoyan en él para extraer sus propios beneficios.
Los provechos no consisten sólo en copiar sus desplantes y en drogarse a su conjuro. Los security men de Inglaterra pidieron aumento de sueldos invocando los riesgos a que están expuestos. En una revista del sindicato de empleados estatales escribieron: "Se debe pensar que verdaderamente estos hombres viven una vida de James Bond y que están de servicio incluso cuando descansan. Cobran actualmente 900 libras esterlinas al año como máximo; deben vestir con mucho decoro, si no tan rebuscadamente como el famoso personaje de Fleming; deben también afrontar gastos excepcionales y están expuestos a continuas insidias".
Otro ejemplo: Allen Dulles, jefe de la Central Intelligence Agency, confesó a un redactor de Life que desde que Jacqueline Kennedy puso en sus manos un libro de Fleming, se interesó cada vez más en los ingenios técnicos de 007: "Por ejemplo —reconoció—, el artefacto que Bond instala en los automóviles de sus adversarios para seguir su itinerario, inclusive a muchos kilómetros de distancia. Encomendé a nuestros expertos el estudio en el laboratorio de un aparejo semejante".
Los comerciantes, a su vez, no vacilan en exprimir la historia bondista, y, en París y Nueva York, abarrotan el mercado con batas celestes —el color que más sienta a Connery— y nuevos modelos de prendas sport. Con todo, el regalo más apreciado por los neoyorquinos, en la Navidad de 1964, resultó una réplica de la valija diplomática que Bond lució en De Rusia, y que Macy's vendió por centenares. A mediados del 65, cuando su fama había impregnado todos los estratos sociales y atrapado a los fanáticos del cine, la marca del champagne preferido de Bond, Taittinger, aumentó su venta en un 40 por ciento con respecto al año anterior, y en un 30 por ciento las importaciones de su vodka favorito. Los cuerpos casi desnudos de sus amigas (Ursula Andress, Daniella Bianchi) ilustraron las páginas de las lujosas publicaciones que exaltaban el fiction's sexiest Bond.
El éxito de las películas de Bond no es, sin embargo, sino el efecto directo que provocaron las trece novelas de la serie, clausurada por la muerte de su autor en 1964. Hasta el año pasado se habían vendido 25 millones de ejemplares de esas trece novelas, traducidas a dieciocho lenguas, incluidas el catalán y el turco. La cifra equivale a la edición total de las obras de Balzac y a todas las de Hemingway. En mitad de ese boom, es posible que John F. Kennedy haya contribuido a engrosar el torrente de adeptos cuando, en conferencia de prensa, situó a Fleming entre sus autores de cabecera y a From Russia entre las diez obras que salvarían a la humanidad del desastre atómico. Curiosamente, Kennedy y Lee Oswald, su presunto asesino, tenían gustos análogos. Semanas antes del crimen, Oswald tomó prestadas de la biblioteca pública de Dallas todas las historias de 007.
La semana pasada, en el vestíbulo del Gran Rex, la mitad de los espectadores confrontados no habían leído una sola novela de Fleming, pero casi todos prometieron una inmediata adhesión literaria, Cabría determinar, pues, los niveles de predominio: hasta qué punto Connery es Bond, o Bond es Connery.
El vicario de 007
Pero no, Connery y Bond no se parecen realmente, salvo por sus ascendentes escoceses. Hijo de un obrero textil de Edimburgo, Sean Connery abandonó la escuela a los 13 años para ganarse una vida muy dura como lustrador de ataúdes, salvavidas, marinero, modelo, boxeador de peso liviano, aprendiz de impresor y, finalmente, como comediante de cuarto orden en una compañía de comedias musicales que cantaba South Pacific. En 1957 tuvo que optar entre ser un centro delantero profesional o un actor aceptable. Resolvió inscribirse en una escuela de arte dramático y estudiar esforzadamente: al cabo de un año, lo citaron para pequeños papeles y luego consiguió encaramarse como primera figura en los teatros provinciales de Inglaterra. Los fantasmas de Shakespeare (Macbeth, Hotspur) vivieron bajo su piel más veces que James Bond.
A los 26 años recaló por fin en el cine, contratado por la Fox, pero sólo para languidecer en una retahíla de films mediocres que culminaron con una pequeña parte en El día más largo.
Poco antes, Fleming había cedido, por fin, a las melosas presiones de los productores Harry Saltzman, canadiense, y Albert Cubby Broccoli, norteamericano, y consintió en venderles los derechos de sus novelas. Elegido en un referéndum, esa mera debilidad del novelista, ante el dinero que le prometía el cine, cambió la vida de Connery. Desde entonces trató de entender quién era Bond: "Fleming me contó —dijo el actor— que, al concebir el personaje, 007 era un simple instrumento de la policía, muy recto, sencillo, distante de cualquier forma de ingenio; en suma, un funcionario capaz de cumplir con su trabajo al pie de la letra. El snobismo del autor, sin embargo, acabó por transferirse al héroe".
La vida de Connery no cambió demasiado desde entonces, salvo por el hecho de que sus ingresos ascendieron de 18 mil dólares (la cifra que le pagaron por El satánico doctor No) a un millón. Sigue casado con Diane Cilento, conviviendo con un hijo de ella y otro hijo de los dos, cocinando su goulash y ensillando sus caballos. Pero mientras tanto, los imitadores cundieron.
Los hijos de Bond

A fines de 1964, la certeza de que Bond era sinónimo de oro tentó irresistiblemente a los productores de Cinecittá, en Roma: con apuro, encomendaron algunos plagios paródicos y se los endilgaron a Totó (007, de China con tenor) y a Vittorio Gassman (Slalom). En esas dos empresas invirtieron medio millón de dólares, pero los artefactos de cartón que montaron en torno de sus personajes ahuyentaron al público. El negocio resultó un fiasco, y los pequeños Bond que nacieron en los meses siguientes ya no se exportaron de Italia. Por entonces, Saltzman y Broccoli gastaron tres millones de dólares en la filmación de Goldfinger, y eso convenció a los competidores de que para acabar con Bond hacían falta juguetes caros y actores caros. Sólo Hollywood estaba en condiciones de librar semejante batalla.
En la primavera de 1965, por lo menos cuatro imitadores ingratos de 007 ya parecían listos para salir a estrangularlo: sus nombres eran Napoleon Solo, Derek Flint, Matt Helm y Modesty Blaise. Un detalle los unía al Padre Todopoderoso: o defendían una sigla, o combatían contra una sigla. El enemigo de Bond era SPECTRE; Solo, agente de la UNCLE, enfrentaba al agente TRUSH; Flint, miembro de ZOWIE, se oponía a GALAXIE; Modesty Blaise ponía los bandidos de su equipo FILET al servicio de Su Graciosa Majestad. Sólo Matt Helm sigue oscilante, todavía, entre depender de la CIA o fundar su clan propio.
Los otros elementos comunes son el sexo y las armas secretas; al Aston Martin de usos múltiples imaginado por el novelista Ian Fleming, los creadores de Flint oponen un encendedor que cumple 82 funciones (revólver, máquina fotográfica, soplete, contador geiger, microscopio, rayo laser, radio-emisora) y hasta una función extra, si el caso lo exige: la de encendedor propiamente dicho. Helm dispone de un revólver que dispara hacia atrás y viste un saco cuyos botones son cartuchos de dinamita; Modesty Blaise, extraída por el realizador Joseph Losey de una tira cómica que se publica en The Evening Standard, emplea un encendedor lanzallamas, un vaporizador de perfume que puede convertirse en máscara de oxígeno y un lápiz de labios que dispara flechas; pero ninguno de sus argumentos es más fuerte que the Nailer, el Inmovilizador, un cierre relámpago en el rompevientos de Modesty, que al abrirse deja sus pechos al descubierto e inmoviliza a los enemigos.
Es en el territorio sexual donde se despliegan los mayores refinamientos: a gloria de Bond consiste en su aptitud para vencer la resistencia de mujeres asexuadas o francamente lesbianas (como la Pussy Galore de Goldfinger); sus herederos no parecen tener otro remedio que apelar a la mecanización del amor. La eficacia de Napoleon Solo se mide por el número de mujeres que se le rinden (una decena en su última aventura, El espía con mi cara); la de Flint, por una cama de cinco plazas donde se tiende con cuatro fidelísimas amigas. Matt Helm, en cambio, duerme en un vasto diván circular y móvil que le permite estar siempre cerca de sus juguetes mecánicos: al despertarse, el diván atraviesa el cuarto, y el tabique que da a un jardín desaparece; luego, el colchón se levanta y desliza a Helm hacia una piscina cuidada por una graciosa náyade. Es la apoteosis del reposo del guerrero. Pero además, como Modesty Blaise, Helm confía en sus talentos naturales: lava y cepilla a su enjambre de admiradoras, las divierte con un sofisticado strip-tease y les canta en voz baja. Como se define a sí mismo, es el espía que viene del show.
Sin embargo, la erudición de estos semidioses en disciplinas aparentemente inútiles es lo que más impresiona al público. Bond puede reconocer hasta por el tacto el año de cosecha de un Dom Périgord o de un Pommery; Flint distingue la diferencia que hay entre dos platos de bouillabaisse por los miligramos extra de ajo que le añaden los taberneros marselleses; Modesty Blaise conoce al dedillo las fórmulas químicas de todos los perfumes posibles.
Los presupuestos bajos que el cine francés o el italiano consagraban a estos devoradores superhombres acabó por excluirlos de ese nuevo Mercado Común que se llama Club Atómico, Club de Vuelos Espaciales o Club de los Grandes Espías. Tampoco la estrategia de resucitar a Fantomas o de armar a Lemmy Caution con versos de Paul Eluard (en Alohaville) dio el menor resultado. Pero el combate de los hijos de Bond contra su Padre Todopoderoso no se libraba sólo en el campo de los efectos especiales, de las escenografías gigantescas o del lujo visual. A principios del 85, se convirtió también en un problema de estrategia empresaria.
El actor que iba a encarnar a Bond fue elegido por Saltzman y Cubby Broccoli mediante un referéndum que propició el Daily Express en Londres: se publicaron las fotografías de diez jóvenes comediantes británicos y se instó a los lectores a elegir. Una mayoría del 62 por ciento optó por Sean Connery; el segundo clasificado, un tal Terence Cooper, consiguió sólo el 7 por ciento. Cuando tuvo que designar al intérprete de su primer semidiós, Derek Flint, la Columbia concentró su referéndum en Los Angeles y aceptó al sofisticado cowboy que habían seleccionado los diez mil californianos encuestados: James Coburn. Los expertos habían decidido que Flint fuese un personaje paródico, capaz de ridiculizar a Bond con sus propias armas. Pero los resultados fueron inesperados: en el primer mes de exhibición, el éxito de Flint era arrasador, casi igual al de Bond. Pero después de ese tope, el público parecía fatigarse. Fue entonces cuando se pensó en Matt Helm, un play-boy del espionaje creado por Donald Hamilton. La Columbia eligió el cuarto libro de la serie Helm, The Silencers (Los silenciadores), y encomendó el papel a Dean. Martin. Como explicaron sus agentes de relaciones públicas, la lucha contra Bond iba a librarse ahora en todos los campos: un actor famoso contra otro, un presupuesto de 6 millones de dólares contra los 5 y medio de Operación trueno. Pero el punto de partida para el ataque no se había modificado: Helm salía con la misma consigna de Flint, derrotar a Bond por el ridículo.
Más miel para los dioses
En los tiempos de Dashiell Hammett y de Eric Ambler —poco antes de la Segunda Guerra—, el espía o el detective privado eran apenas seres duros, capaces de incurrir en el Mal. Ian Fleming agregó a esas cualidades la certidumbre de que un espía puede ser todopoderoso, salvo ante la Reina o ante su jefe. La omnipotencia encandiló a los lectores, les despertó una sed que ni siquiera James Bond podía saciar: según los sociólogos, la avalancha de espías-semidioses se debió no tanto a que encarnaban los Sueños de las Masas sino a una simple condición humana, el hubris o ciega seguridad de uno mismo.
Los ojos devoradores de aventuras consiguieron que el género del espionaje prosperara y arrasara el mercado. El más importante de los novelistas que surgió a la zaga de Fleming (y su real contracara) es el británico John Le Carré, seudónimo de David John Moore Cornwell, un funcionario del Foreign Office que nació en 1931. La fama de Le Carré se consolidó con su tercera novela, The Spy Who Came in From the Cold (El espía que no vuelve, 1963), una historia ambientada en el Berlín de la Guerra Fría, cuya versión cinematográfica acaba de estrenarse en los Estados Unidos. El clima de sordidez y desvalimiento en que se mueve Alee Leamas, el viejo agente de Spy, quizá tenga dos antecedentes: Raíces en el fango (Confidential Report, 1956, de Orson Welles), y Los espías (Les espions, 1957, de H. G. Clouzot).
Para Le Carré, el espía es un hombre común, ni atleta ni buen mozo, ni patriótico ni buscador de gloria. Elige su oficio por rutina, por necesidad de dinero. Son parte de ese suburbio de la sociedad en el que también entran los delincuentes. En el caso inglés (los antihéroes de Le Carré están, como Bond, al servicio de la Reina), esos espías denostados, arrojados al infierno por la sociedad, sometidos a la soledad y al miedo, desvalidos de armas electrónicas o complicados equipos, trabajan para God, King and Country. Las culpas no son transferidas a los espías, simples empleados del Mal, sino a quienes fabrican, inventan y mantienen las redes del espionaje. El espejo de los espías (1965, su última novela; las otras fueron Llamada para el muerto, 1961, y A Murder of Quality. 1962) es el más violento anatema contra el espionaje, como institución, que se haya escrito. Para Le Cerré, cada caso es una auténtica tragedia, y por lo tanto se niega a toda trampa. Su grandeza debe buscarse, ante todo, en el hecho de que el Mal asume la forma de un laberinto del que es imposible escapar: y en tal sentido, más que un heredero de Fleming, Le Carré puede ser visto como un epígono de Kafka.
Otro de los novelistas uncidos al aluvión es Len Deighton, cuya columna sobre recetas de cocinas aparece en The Observen de Londres. Menos afecto que Le Cerré a la disciplina que exige el oficio de narrar en serio, Deighton ya ha vendido un millón y medio de ejemplares de sus cuatro novelas y sus das recetarios. El dúo de productores Saltzman-Broccoli (que monopolizó definitivamente el mercado del espionaje al lanzar también al actor Michael Caine en The Ipcress File, otra obra de Deighton) acaba de comprar en un cuarto de millón de dólares los derechos cinematográficos de The BiIlion Dolar Brain, una novela que el Daily Express está publicando en folletín.
Los esquemas de Deighton son siempre iguales: un agente bohemio, joven, que ejerce el espionaje por azar y cuya apariencia es la de un tonto, se ve envuelto en casos importantes, y lo que es más grave, los esclarece. Deighton enfila su humor contra los jefes de los servicios secretos, flemáticos caballeros ingleses que dirigen sus oficinas como empleos burocráticos y que obligan a los espías a llenar fatigosas planillas diarias, con el resumen cronológico de sus movimientos, sólo para que justifiquen los horarios asignados. Deighton escribe con tres máquinas a la vez, en su casa de Southwark, y ha terminado por convertirse en un empresario: tiene una compañía de viajes (la Trinity Travel Co.), una casa en Portugal que suele prestar a otros escritores cuando él no la ocupa, y una editorial en formación, la Hemisphere Publications, cuyo primer volumen será el Deighton Dictionary, una enciclopedia con voces cockney y hasta malas palabras del slang vietnamita.
Dentro de este cortejo gigantesco, cuyo primer Padre fue Mickey Spillane (un narrador lleno de una fuerza grosera, elemental), son los burladores, los parodistas, quienes parecen alcanzar la mayor repercusión. Hace una década, Graham Greene ocupaba los ocios de un espía haciéndolo copiar los planos de una aspiradora (en Nuestro hombre en La Habana); en 1936, el detective Sam Spade, inventado por Dashiell Hammett, se farsaba de los expedientes policiales y convenía en que la única arma posible contra el mal era el mal. El intento de Greene era francamente satírico, un áspero dardo contra los servicios de Inteligencia británicos; de la misma manera, los personajes de Flint o Matt Helm son ridiculizaciones de Bond. Pero el caso de Sam Spade, el de los espías de Le Carré, es de un orden moral: luchan por quien les paga o por interés propio, no por obedecer a una abstracta idea de justicia. En la práctica, son agudamente asociales.
Bond se les distingue por su extrema insensibilidad, salvo ante el alcohol; por su increíble fortuna sexual, por sus contactos frecuentes con la alta burguesía. Sólo Spillane sobrelleva juegos parecidos con las mujeres: en The Flier, el violento Mickey dispone de una joven morena, vista de espalda, que se cubre apenas con un corpiño y una falda a punto de caer; en Dedos de oro, Bond asiste a la muerte de una amante dorada, desnuda, yaciendo boca abajo. Es verdaderamente el sexo lo que mejor prueba la calidad de la miel segregada por estos semidioses.
Las mujeres de Bond

En una entrevista para Playboy, el actor Sean Connery admitió que tenía "sólo cierta experiencia con las mujeres. Pero nunca las perseguí sádicamente, como James Bond. Por supuesto, el apetito por las chicas lindas es algo que no se pierde, aunque ahora también me fascina la conversación de los hombres. Y algo más: no siento una avidez retrospectiva por las mujeres de mi pasado". Esa imagen de buen burgués británico está en las antípodas del semidiós 007, con quien Connery suele, (muy a su pesar) ser confundido.
Para Bond, el único entendimiento posible con las mujeres es de índole sexual. Sus tres amantes casadas abastecen semanalmente todas sus exigencias sádicas: toleran que las abandone, que las castigue, que les dispense una melancólica frase de despedida. Pero el Bond típico se revela en sus relaciones ocasionales: la historia que él quisiera vivir le fue narrada por su amigo Darko Kerim, y está transcripta en De Rusia con amor. Cuenta la captura de una muchacha en Besarabia:
La había ganado en una pelea con algunos gitanos, aquí, en las colinas que crecen a, espaldas de Estambul. Me persiguieron, pero conseguí meterla en un bote. Primero tuve que desmayarla de un golpe. Todavía trataba de matarme cuando volvimos a Trebizonda, de modo que la llevé a mi casa, le quité toda la ropa y la mantuve encadenada, desnuda, debajo de la mesa. Cuando comía, me acostumbré a tirarle algunas sobras, como se hace con los perros. Ella tenía que aprender quién era el amo...
Siempre las mujeres de Bond irrumpen imprevistamente, desde un lugar lejano, y desaparecen de modo misterioso, como un desprendimiento de la carne. Los dos ejemplos extremos son Honeychile, la pescadora de caracoles de El satánico doctor No, cuyo magnetismo se concentraba íntegramente en su nariz quebrada, y Solitaire, de Vivir y dejar morir, que, oculta bajo sus tocas negras, puede leer el pensamiento y sentir el pasado y el futuro de los hombres a través del vudú.
Las únicas excepciones a las relaciones lascivas de Bond con las mujeres son las secretarias del Servicio Secreto. Llevan nombres plausibles: Leolia Ponsonby, Mary Goddnight, Moneypenny. Todas son hijas de familias honorables, que se sacrificaron durante la guerra, y por lo tanto no hay el menor riesgo de que traicionen a la Madre Inglaterra, vendiendo secretos al enemigo. La idea británica al respecto señala que si provinieran de hogares más humildes, la tentación no podría resistirse.
Según Kingsley Amis, autor de The James Bond Dossier, el agente no trata de seducir a estas ejemplares matronas porque delante de M, jefe del Servicio Secreto, siente que se reduce "su normalmente alta potencia sexual". Amis también conjetura que Bond es un adulador de M, y por lo tanto no se atrevería a contrariarlo. En el fondo, el agente 007 intuye que su jefe ejerce droits de seigneur sobre las secretarias y no toleraría ninguna usurpación de sus predios.
Esa falta de autenticidad en las relaciones del personaje con las mujeres acaban por minarlo: los rastros de pesadumbre ya son muy acentuados en You Only Live Twice, el penúltimo libro escrito por Fleming. La historia acontece en Japón, luego de un período en el que Bond vivió borracho todo el tiempo. Sin insistir demasiado en la descripción, el novelista desliza la idea de un semidiós caído, cuyas manos temblorosas sólo se ocupan de mezclar whiskies y vodkas. Su ropa está descuidada y su camisa llena de arrugas. No sólo tiene muy poco dinero: también las mujeres ya no lo toman en cuenta.
Para vencer el miedo
Bond es un hombre sin identidad y sin proyecto, con la impostura típica del psicópata en el que todo afecto es congelado. En plena Guerra Fría, aparece como uno de los pocos personajes capaces de mantener un inestable equilibrio entre dos mundos en tensión. En el contexto de la llamada revolución capitalista o neocapitalismo (una ideología que se estructura al amparo de la automación, aunque mantiene el carácter monopolista del capitalismo tradicional), Bond asume tres papeles: agente secreto, saboteador y depositario de un permiso para matar. En el fondo es también un funcionario contratado para inmovilizar el capital de un grupo contrario a su bloque (sean norteamericanos, franceses o soviéticos). Esa actitud de mero funcionario se esclarece al advertir que Bond trabaja en el área de pequeños grupos, siempre con un líder o jefe (M), con una estrategia, una táctica, una técnica y una logística en forma de código: su papel no está del todo institucionalizado, y se le permite sólo un escaso índice de espontaneidad y creatividad.
Tanto él como su mundo inmediato son manejados a distancia: vive en un clima cibernético, esto es, enajenado, reducido a la función de un instrumento. Si deja crecer su iniciativa personal tiende invariablemente al fracaso. Detrás de todo ese andamiaje subyace el gran miedo a un enfrentamiento atómico entre USA y la URSS, cuyas consecuencias catastróficas son imprevisibles. El sociólogo C. Wright Milis había sostenido que "la Tercera Guerra Mundial está en preparación y será librada fríamente en nombre del Estado soberano, por las élites mandatarias de las dos superpotencias, con la aquiescencia del público y las masas y las abstenciones de los políticos e intelectuales". Así, pues, Bond no sólo trabaja en la Guerra Fría sino también en el incubamiento de la otra: quizá sea su imagen, con la Beretta pegada al rostro, la señal más rotunda de esta época temerosa, una imagen más sádica y abominable que la del hongo atómico que la engendró.
¿Quién es James Bond?

El cine y las tiras cómicas —pero sobre todo las biografías apócrifas— han disuelto en una especie de confusa nube la historia de James Bond, su carácter, sus gustos, el dinero que gana y hasta las cosechas de vino que prefiere. Como ocurre con todo mito, 1a anatomía de un semidiós se modifica siempre según la interpretación de sus adoradores. En este caso, mientras sobrevivan los trece libros que lan Lancaster Fleming escribió entre 1952 y 1964, siempre será posible peregrinar hasta las fuentes y establecer la verdadera anatomía del personaje.
En De Rusia con amor se determina, la edad de Bond, 35 años. El último libro de la serie, The Man of the Golden Gun, dice, sin precisar demasiado, que "anda entre los 38 ó 37". Mide un metro 83, pesa 76 kilos.
Se parece mucho a Hoagy Carmichael, el autor de "Polvo de estrellas” (Sabotaje). Tiene los ojos de un clarísimo gris azulado, un mechón que tiende a caer sobre la ceja derecho (Sabotaje) y una cicatriz blanca qui le atraviesa la mejilla izquierda (The Spv Who Loved Me).
Su padre era un escocés del Glencoe; la madre, Monique Delacroix, había nacido en el cantón suizo de Vaud. Bond fue educado por una tía de gran cultura —según la define M, jefe de Servicio Secreto— y gracias a ella pudo ingresar en Eton, donde su padre lo había inscripto desde su nacimiento A los 17 años, James ya habla representado a su colegio como boxeador de peso liviano y especialista en judo. Durante la Segunda Guerra, alcanzó el grado de comandante en la Marina.
Su renta anual es de 1.500 libras esterlinas, más mil libras exentas de impuestos (Sabotaje). Cuando está de servicio, puede gastar todo lo que quiere. Vive en un departamento pequeño en Kings Road, un barrio elegante dc Londres. Lo atiende una vieja ama de llaves escocesa, May.
Es vivamente racista. Siente horror por los negros y los chinos, detesta a los soviéticos y a los balcánicos, considera ridículos a los franceses y una de sus mejores satisfacciones es insultar a los italianos. "Los italianos son inútiles para todo —reflexiona en Diamantes eternos—. Llevan camisas bordada y pasan el dia perfumándose y comiendo spaghetti."
Cuando no le encomiendan alguna misión, su vida es opaca, tediosa. Trabaja de diez de la mañana a seis de la tarde en las oficinas del Servicio Secreto; almuerza en el restaurante de edificio: por las tardes, juega a las cartas con algún amigo o se dedica con escaso entusiasmo amoroso a una de las tres mujeres —casadas— que lo perturban. Carece de vacaciones, pero 1e conceden dos semanas libres al término de cada misión: M le encarga la solución de un caso sólo dos o tres veces año. No tiene nadie a quien mantener. Es huérfano y viudo. Se casó el 1º de enero de 1962, en el Consulado inglés de Mónaco, con la condesa corsa Teresa de Vincenzo; según se narra en Al Servicio de Su Majestad, su mujer es asesinada dos horas después del casamiento.
Muchos de estos rasgos coinciden con los del propio Ian Fleming. El escritor había estudiado en Eton, fue corresponsal de Reuter en Moscú y redactor de The Sunday Times; combatió en la Segunda Guerra como asistente del contraalmirante Goodfrey, jefe del Ser-vicio Secreto de la Marina, y logró ser admitido como socio del Elides, el más exclusivo de los clubes londinenses. Su pasión por los automóviles llegaba casi al delirio: más rico que Bond, Fleming había conseguido cambiar un Standard caqui por un Lancia Gran Turismo; un Morris Oxford caqui por un Thunderbird de diez mil dólares. En 1941, el espía Fleming intentó ganar en el juego todos los fondos de que disponía el espionaje alemán; convocó a seis agentes del almirante Canaris ante una mesa de punto y banca en el casino de Estoril, Portugal, y fue aniquilado: los nazis le arrancaron ocho mil dólares. El espía Bond lo vengó once años después: pudo limpiar los bolsillos de Le Chiffre, uno de los jefes del SMERSH, en el casino de Royale-les-Eaux. Pero quedan todavía otras dos identificaciones claves entre el autor y su semidiós: Bond es un prodigio como hombre-rana; Fleming se lució en algunas incursiones submarinas junto al comandante Jacques-Yves Cousteau; el escritor había imaginado un coctel afrodisíaco, compuesto de tres partes de Gordon, una de vodka y media de China Lillet; en De Rusia con amor, esa receta aparece como una invención de Bond.
El agente secreto no es nada excéntrico en sus gustos. Su encendedor es un Ronson de gas, su máquina de afeitar una Gillette, su pistola una Beretta, su reloj un Rolex Oyster Perpetual, sus palos de golf son Penfold.
Fuma de 60 a 70 cigarrillos diarios: la casa Morland, de Grosvenor Street, en Londres, se los prepara expresamente para él con mezclas muy fuertes de tabacos turcos y griegos. Cuando está demasiado intoxicado, se inclina por los Senior Service (en Operación Trueno) o los Chesterfield King Size (en Dedos de oro). También en esto es idéntico a Fleming.
Demuestra un arrasador convencionalismo en sus viajes, y eso es casi previsible si se advierte que su consejera era la Guía Michelin (For Your Eyes Only). Sólo con los automóviles y las bebidas se revela como un experto de increíble refinamiento. En Casino Royale maneja uno de los últimos Bentley modelo 1933, de 4 cilindros, color gris oscuro. Esta espléndida joya, capaz de correr a 190 kilómetros por hora, se incendia en un accidente: M, el jefe de Bond, le regala entonces un Mark VI de 1933, deportivo, color gris perla. El famoso Aston Martin de Dedos de oro (guardabarros reforzados con acero, emisor y receptor de radio, radar, patentes intercambiables, etcétera) carece de importancia en la vida de Bond: es en verdad un DB III, pro-piedad del Servicio Secreto.
Con el alcohol, Bond llega a limites casi orgiásticos: adora el champagne y el vodka, pero su sabiduría esplende al elegir Taittinger Blanc de Blancs brut, cosecha 1943, o whisky Haig & Haig Pinch-Bottle. A menudo se equivoca: el Dom Perigon es un champagne mediocre, y por lo demás, la cosecha 1948 (su predilecta) es la peor; el Pommery 1950 resulta absolutamente trivial para los expertos. Esos deslices no son demasiado frecuentes, sin embargo.
Sus menús son absolutamente ejemplares, aunque Bond no gaste en comida todo su precioso sibaritismo. En Inglaterra, se inclina por el lenguado a la parrilla, ensalada mixta con mostaza, una tostada con queso y café (Sabotaje); en la Florida prefiere los cangrejos de roca frescos, rociados con manteca fundida (Dedos de oro); en Italia, tallarines verdes al pesto y café (For Your Eyes Only); en Francia, pate de foie gras, langosta con mayonesa, frutillas con nata y café (Casino Royale).
Bond acabó por sembrar una aluvional moda, pero según el sastre italiano Caraceni, la manera de vestir del agente "es absolutamente sin errores, en todo de acuerdo con los cánones anglosajones". Jamás lleva zapatos acordonados: se consuela con mocasines cuya punta está reforzada por un bloquecito de hierro; sus camisas son de manga corta, inclusive cuando no viste de sport; su corbata es siempre negra y tejida; prefiere los trajes livianos, de alpaca o telas tropicales y de tonos azules profundos; los combina con camisas de seda, blancas o crema. En Operación Trueno incurrió en la osadía de mezclar esas camisas con sandalias negras: en The Spy Who Loved Me, descendió a la vulgaridad de ponerse un impermeable azul oscuro, con cinturón.
Todos los indicios parecen señalar que Bond es un hidalgo, como Fleming. Sólo resta averiguar hasta qué punto la hidalguía de un agente secreto se parece a la de los ladrones de guante blanco que proliferaron en el siglo XIX, a la sombra de Rediles y Arsène Lupin. En el fondo, a Bond lo acongojaban sus constantes acercamientos a la vileza. No por nada debía tomar píldoras de bencedrina para mantenerse en pie y una fuerte dosis de seconal para dormirse.
Versión original:
Descargar PDF (5,16 MB - Google Drive)
4 notes
·
View notes
Text

Day 25- Film: Macao
Release date: April 30th
Studio: RKO
Genre: Adventure Noir
Director: Josef von Sternberg, Nicholas Ray
Producer: Howard Hughes, Samuel Bischoff, Alex Gottlieb
Actors: Robert Mitchum, Jane Russell, William Bendix, Gloria Grahame
Plot Summary: Three American strangers with mysterious pasts end up on the island of Macao, just off the coast from Hong Kong. An American criminal who runs a casino there keeps his eyes on all three of them. Is one of them the Law coming after him?
My Rating (out of 5 stars): ***
When this film began, I thought, “The style really reminds me of Shanghai Express.” Then I saw von Sternberg’s name come on the screen and it made total sense! Unfortunately, this film does not live up to that earlier masterpiece. It’s another film in this project where a lot of elements are there to create something great, but it is ultimately just missing something. It was still generally an enjoyable movie, though, even if it was not great.
The Good:
Some of the Shanghai Express style. Von Sternberg can create a palpable mood/backdrop of exoticism in his films, and this has some of that. It’s also in an exotic locale where there are many different cultures coexisting together: Chinese, Portuguese, American, Japanese, etc.
The way the mystery about who these people are unravels slowly as we learn more about their pasts. And the fact that the mystery is never totally solved.
Jane Russell. She was subjected to constant catcalls and objectification by men, so I want to be very aware of that. Suffice it to say, she is stunning. She may not be the world’s greatest actor or singer, but you still want to drink in every opportunity to look at her.
The plot was efficient and well-paced. At under 90 minutes, there was no time for it to get bloated and mind-numbing.
The Bad:
The characters weren’t developed much beyond the surface.
Everybody looked so heavy-lidded, like they were so relaxed (jaded?) they could barely keep their eyes open. Russell, Mitchum, Grahame, and Dexter... they all had this. Was this a specific direction from von Sternberg? There is the famous story of him telling the cast of Shanghai Express to speak in monotone to mimic the train. Was this a similar kind of case? I can’t say I disliked it, exactly, but it could be distracting.
It was hard not to compare it to von Sternberg’s more famous films with Marlene Dietrich. She is a seductive sex symbol like Russell, but Dietrich has a lot more charisma and skill as an actress. She knows how to walk into a room and make a bomb go off. It’s more than just her looks that achieve this. You always get this sparkle and sense of a full and complex person under the surface. Russell just doesn’t have this quality. Dietrich is never heavy-lidded!
2 notes
·
View notes
Link
After enjoying an incredible amateur boxing career, Sugar Ray Robinson fought professionally from 1940 until 1965 and is often heralded as one of the sport’s best fighters of all-time. In 1990, he was inducted into the International Boxing Hall of Fame. On June 25, 1952, after a fight at Yankee Stadium against Joey Maxim, where in the extreme heat (103°F or 39°C) Robinson collapsed in Round 13 - suffering the only knockout of his career by not answering the bell for the next round - he gave up his title and retired with a record of 131–3–1–1. But he returned to the ring in 1955 before retiring, for good, in 1965, compiling an incredible record of 173–19–6 (2 no contests) with 109 knockouts in 200 professional bouts, ranking him among the all-time leaders in knockouts. Robinson then moved to the West Coast and appeared in several television shows and films. In 1969, he founded the Sugar Ray Robinson Youth Foundation for the inner-city Los Angeles area. He was diagnosed with Alzheimer's disease and died in Los Angeles on April 12, 1989 at the age of 67. The Bright Lights and Dark Shadows - a documentary about Sugar Ray Robinson: https://youtu.be/4QVwmuHZY84 https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sugar_Ray_Robinson for more information on his life and legacy. #talkinfight #happytomeet #sugarrayrobinson Watch more on TalkinFight.com or YouTube.com/c/TalkinFight
0 notes
Link
via Politics – FiveThirtyEight
Pretend I’m the owner of a polling company that surveys political races. I prominently advertise my results: According to a Walt Hickey Polling Inc. survey of 600 likely voters, John Doe is beating Jane Doe 58 percent to 40 percent — John Doe will likely win the election. (Let’s say it’s a race for the U.S. Senate.)
But then you keep reading and you notice that the sample on which my poll is based consists of 400 men and 200 women. You can’t really tell whether I’m adjusting the numbers, and if so, how. Would you trust that number? Unless there’s some state I don’t know about where men outnumber women 2-to-1, you shouldn’t.
So why aren’t we more skeptical of movie ratings that do the same thing?
It’s a worthwhile question, and lately it’s made it pretty hard for us to take the ratings provided on IMDb, the largest and most popular movie site on the internet, at face value. The Academy Awards rightly get criticized for reflecting the preferences of a small, unrepresentative sample of the population, but online ratings have the same problem. Even the vaunted IMDb Top 250 — nominally the best-liked films ever — is worth taking with 250 grains of salt. Women accounted for 52 percent of moviegoers in the U.S. and Canada in 2016, according to the most recent annual study by the Motion Picture Association of America. But on the internet, and on ratings sites, they’re a much smaller percentage.
“If you see any number that is a rating number or a number with a percentage sign, it may be compelling or meaningful and it may not be,” said Gary Langer, the president of Langer Research Associates, the polling firm that has long conducted surveys for ABC News. “And what we need to do rather than be seduced by the number is to subject it to meaningful inquiry as to how it was obtained.”
OK, but how skeptical should we be? To figure that out, I wanted to see how strong the male skew of raters is on IMDb and how big an effect that skew has on movies’ scores.
We’ll start with every film that’s eligible for IMDb’s Top 250 list. A film needs 25,000 ratings from regular IMDb voters to qualify for the list. As of Feb. 14, that was 4,377 titles. Of those movies, only 97 had more ratings from women than men. The other 4,280 films were mostly rated by men, and it wasn’t even close for all but a few films. In 3,942 cases (90 percent of all eligible films), the men outnumbered the women by at least 2-to-1. In 2,212 cases (51 percent), men outnumbered women more than 5-to-1. And in 513 cases (12 percent), the men outnumbered the women by at least 10-to-1.
Looking strictly at IMDb’s weighted average — IMDb adjusts the raw ratings it gets “in order to eliminate and reduce attempts at vote stuffing,” but it does not disclose how — the male skew of raters has a pretty significant effect. In 17 percent of cases, the weighted average of the male and female voters was equal, and in another 26 percent of cases, the votes of the men and women were within 0.1 points of one another. But when there was bigger disagreement — i.e. men and women rated a movie differently by 0.2 points or more, on average — the overall score overwhelmingly broke closer to the men’s rating than the women’s rating. The score was closer to the men’s rating more than 48 percent of the time and closer to the women’s rating less than 9 percent of the time, meaning that when there was disagreement, the male preference won out about 85 percent of the time.
That male skew of raters is also apparent in the 250 movies that make IMDb’s top list, which we pulled on Feb. 16:
So, what’s the issue here? If IMDb is content with its ratings being intended almost solely for men, then there isn’t one. (We reached out to IMDb for comment and for more information on how the site adjusts its ratings, but we received no response. So we don’t know, for example, if IMDb is already doing something to the data that accounts for the gender disparity in raters.) But if IMDb seeks to reflect the opinions of the actual movie-going population, the situation is grave.
Can we fix that? Langer is skeptical. Mainly, besides how simple it is for a dedicated individual or group to “manufacture” results, online data from a self-selected group of people is so inherently dubious that any reweighting of that data is also inherently dubious. You can’t just adjust troublesome data to make it reflect the world, he said.
“The notion that you can take bad data and weight it to be OK is … hazardous to your health,” Langer cautioned.
That said, since the scores of the most popular movie site on the internet are already being calculated based on an entirely self-selected sample, would it destroy the IMDb Top 250 to try to mimic actual movie audiences more? I don’t really think so. As a thought experiment, I used everything we know about IMDb’s rating adjustments — which is far from the full picture — and ran them on the ratings of the 4,377 eligible films after I adjusted the raw ratings to weight men’s and women’s views equally.
We can’t do an adjustment that allows us to perfectly replicate the top 250 — again, we don’t know what’s in the black box, so we can’t re-create it — but to approximate it, I excluded any film that didn’t either a) make the IMDb top 1,000 movies list or b) have a rating from the site’s top 1,000 users within 0.87 points1 of the rating from its users overall. This allows us to sidestep films that would have made the top 250 through vote-stuffing.
My main point is that overall, the naive reweighting didn’t destroy the general look of the 250, and if anything, it elevated films that may have been overlooked because one gender is vastly outnumbered.2
What if IMDb adjusted ratings toward gender parity?
Estimated highest-ranking films on IMDb if the men’s and women’s ratings were weighted toward 50-50 vs. IMDb’s actual rank as of Feb. 16, 2018
Rankings Year▲▼
Film▲▼
Actual▲▼
Women only▲▼
Men only▲▼
Gender- weighted▲▼
1994 The Shawshank Redemption 1 1 1 1 1972 The Godfather 2 10 2 2 2008 The Dark Knight 4 3 3 3 2003 The Lord of the Rings: The Return of the King 8 2 4 4 1993 Schindler’s List 6 6 11 5 1999 Fight Club 10 5 8 6 2001 The Lord of the Rings: The Fellowship of the Ring 11 7 10 7 1957 12 Angry Men 5 27 7 8 1974 The Godfather: Part II 3 22 5 9 2010 Inception 14 8 6 10 1994 Forrest Gump 12 9 13 11 2002 The Lord of the Rings: The Two Towers 15 11 14 12 1994 The Lion King 47 4 29 13 1994 Pulp Fiction 7 15 9 14 2014 Interstellar 30 25 15 15 1999 The Green Mile 32 12 28 16 1975 One Flew Over the Cuckoo’s Nest 16 24 19 17 1966 The Good, the Bad and the Ugly 9 115 12 18 2006 The Prestige 48 26 16 19 1998 American History X 31 17 27 20 2012 The Dark Knight Rises 65 23 22 21 1997 Life Is Beautiful 25 16 41 22 1980 Star Wars: Episode V – The Empire Strikes Back 13 41 17 23 1994 Leon: The Professional 27 21 37 24 2002 City of God 21 64 20 25 1995 Se7en 22 28 23 26 2001 Spirited Away 28 13 56 27 1991 The Silence of the Lambs 23 20 33 28 2006 The Departed 40 35 26 29 1990 Goodfellas 17 71 18 30 2011 The Intouchables 37 19 52 31 2014 Whiplash 45 54 30 32 2000 Gladiator 46 44 24 33 2012 Django Unchained 60 29 31 34 2002 The Pianist 39 31 53 35 1946 It’s a Wonderful Life 24 56 51 36 1960 Psycho 34 55 40 37 1977 Star Wars: Episode IV – A New Hope 20 48 32 38 2009 Inglourious Basterds 97 32 43 39 1998 Saving Private Ryan 29 70 25 40 1995 The Usual Suspects 26 58 36 41 1999 The Matrix 18 62 21 42 2000 Memento 49 57 34 43 1942 Casablanca 36 73 42 44 1999 American Beauty 63 51 35 45 1985 Back to the Future 44 49 46 46 2001 A Beautiful Mind 144 34 68 47 1954 Rear Window 43 80 60 48 2000 Requiem for a Dream 80 50 49 49 2011 Harry Potter and the Deathly Hallows: Part 2 218 14 126 50 2006 The Lives of Others 58 86 78 51 2010 Shutter Island 177 39 59 52 2008 WALL-E 62 42 62 53 2004 Eternal Sunshine of the Spotless Mind 87 38 66 54 1980 The Shining 61 61 47 55 1997 Good Will Hunting 102 60 48 56 1971 A Clockwork Orange 84 79 50 57 2001 Amelie 82 30 90 58 1954 Seven Samurai 19 336 39 59 1983 Star Wars: Episode VI – Return of the Jedi 76 87 63 60 1992 Reservoir Dogs 77 94 64 61 2017 Coco 51 209 166 62 1988 Cinema Paradiso 54 165 97 63 1979 Apocalypse Now 50 219 38 64 1940 The Great Dictator 53 262 101 65 1950 Sunset Boulevard 55 190 108 66 1931 City Lights 35 294 92 67 1997 Princess Mononoke 64 118 100 68 2015 Room 143 82 139 69 2003 Pirates of the Caribbean: The Curse of the Black Pearl > 250 36 113 70 2004 Howl’s Moving Castle 137 43 216 71 1962 To Kill a Mockingbird 89 102 135 72 2009 Up 115 37 117 73 2014 Gone Girl 179 81 70 74 2010 Toy Story 3 98 66 82 75 1936 Modern Times 38 248 96 76 1988 Grave of the Fireflies 57 159 133 77 2006 Pan’s Labyrinth 130 74 91 78 2016 Hacksaw Ridge 175 161 124 79 1968 2001: A Space Odyssey 91 195 54 80 2007 Into the Wild 181 84 95 81 1958 Vertigo 72 154 87 82 2015 Inside Out 140 78 107 83 2005 Batman Begins 116 106 58 84 1975 Monty Python and the Holy Grail 103 123 104 85 2009 3 Idiots 93 203 93 86 2003 Oldeuboi 67 171 73 87 1964 Dr. Strangelove or: How I Learned to Stop Worrying and Love the Bomb 56 236 57 88 1991 Terminator 2 42 178 44 89 1959 North by Northwest 74 205 99 90 1968 Once Upon a Time in the West 33 447 55 91 1981 Raiders of the Lost Ark 41 131 65 92 1995 Toy Story 94 85 80 93 1952 Singin’ in the Rain 90 110 170 94 2016 La La Land 207 122 86 95 1979 Alien 52 151 67 96 1941 Citizen Kane 71 188 74 97 2002 Catch Me if You Can 219 97 81 98 1983 Scarface 105 181 69 99 1976 Taxi Driver 88 164 71 100 2014 The Grand Budapest Hotel 194 65 128 101 1987 Full Metal Jacket 92 177 83 102 2010 How to Train Your Dragon 176 47 165 103 1984 Amadeus 83 128 121 104 2007 There Will Be Blood 165 212 72 105 2012 The Avengers > 250 52 144 106 1984 Once Upon a Time in America 69 337 88 107 2013 The Wolf of Wall Street 150 158 45 108 2005 V for Vendetta 151 76 112 109 1939 Gone With the Wind 157 46 279 110 2003 Kill Bill: Vol. 1 174 89 114 111 1995 Braveheart 75 141 61 112 2003 Finding Nemo 166 53 151 113 1999 The Sixth Sense 160 75 116 114 2011 The Help 241 33 245 115 2015 Star Wars: The Force Awakens > 250 92 154 116 2015 Mad Max: Fury Road 204 135 79 117 2000 Snatch 100 144 76 118 2016 Dangal 73 649 195 119 2016 Zootopia > 250 95 187 120 2001 Donnie Darko 226 91 122 121 2008 Gran Torino 158 121 120 122 1989 Indiana Jones and the Last Crusade 112 156 84 123 2012 Jagten 101 183 141 124 1988 My Neighbor Totoro 132 112 183 125 1996 Trainspotting 156 107 127 126 2013 12 Years a Slave 201 100 131 127 1959 Some Like It Hot 118 124 186 128 1973 The Sting 95 284 143 129 2013 Prisoners 215 148 98 130 2017 Logan 202 193 103 131 2016 Your Name 79 399 190 132 2007 Taare Zameen Par 81 448 138 133 2011 A Separation 109 242 125 134 1997 Titanic > 250 45 188 135 2011 Warrior 154 213 134 136 2017 Dunkirk 236 192 145 137 2015 Spotlight 205 155 152 138 1986 Stand by Me 192 125 184 139 2014 X-Men: Days of Future Past > 250 113 159 140 2004 Kill Bill: Vol. 2 > 250 116 157 141 2014 The Imitation Game > 250 69 209 142 2010 The King’s Speech > 250 59 206 143 1986 Aliens 68 217 85 144 2004 Downfall 121 288 115 145 1998 Lock, Stock and Two Smoking Barrels 142 199 130 146 1997 L.A. Confidential 106 225 94 147 2016 Arrival > 250 169 137 148 1957 Paths of Glory 59 704 109 149 2017 Blade Runner 2049 147 368 102 150 1991 Beauty and the Beast 247 40 379 151 2014 Guardians of the Galaxy > 250 111 147 152 1962 Lawrence of Arabia 85 396 105 153 1993 Jurassic Park 198 150 118 154 1927 Metropolis 108 331 182 155 2016 Deadpool > 250 126 155 156 2012 The Hobbit: An Unexpected Journey > 250 90 192 157 2001 Monsters, Inc. 224 77 196 158 1988 Die Hard 122 220 77 159 1989 Dead Poets Society 238 103 239 160 2010 Black Swan > 250 98 161 161 2015 The Martian > 250 134 160 162 1957 Witness for the Prosecution 66 476 229 163 2004 Hotel Rwanda 190 176 181 164 2009 Star Trek > 250 117 199 165 2013 The Hobbit: The Desolation of Smaug > 250 109 205 166 2009 Hachi: A Dog’s Tale 212 127 288 167 2017 Three Billboards Outside Ebbing, Missouri 111 351 204 168 1981 Das Boot 70 603 111 169 1995 Heat 123 332 89 170 1978 The Deer Hunter 159 346 153 171 1980 The Elephant Man 148 261 177 172 1931 M 78 465 167 173 1950 All About Eve 114 227 302 174 1921 The Kid 99 459 249 175 1944 Double Indemnity 86 433 169 176 2013 Her > 250 194 106 177 2009 Mary and Max 178 175 274 178 2017 Thor: Ragnarok > 250 200 260 179 2013 Dallas Buyers Club > 250 146 175 180 1960 The Apartment 107 322 189 181 2008 In Bruges > 250 239 140 182 1998 The Truman Show 206 132 149 183 2010 Incendies 131 300 253 184 1939 The Wizard of Oz 232 119 241 185 2008 Slumdog Millionaire > 250 99 191 186 2007 No Country for Old Men 162 244 75 187 1999 The Boondock Saints > 250 254 250 188 2009 The Secret in Their Eyes 135 265 198 189 2016 Lion > 250 170 332 190 2017 Baahubali 2: The Conclusion > 250 1170 343 191 2015 The Revenant > 250 214 129 192 2004 Million Dollar Baby 203 163 162 193 2005 Babam ve Oglum 117 526 291 194 1963 The Great Escape 126 479 174 195 1948 Bicycle Thieves 96 458 202 196 2004 Harry Potter and the Prisoner of Azkaban > 250 72 339 197 2006 Blood Diamond > 250 172 212 198 1993 The Nightmare Before Christmas > 250 105 318 199 1974 Chinatown 129 360 158 200 2012 The Perks of Being a Wallflower > 250 108 232 201 1990 Edward Scissorhands > 250 67 357 202 1949 The Third Man 127 484 224 203 2003 Big Fish > 250 133 226 204 2013 Rush 193 252 172 205 1954 Dial M for Murder 155 352 233 206 1995 Before Sunrise 211 179 228 207 1940 Rebecca 173 250 350 208 1992 Unforgiven 120 543 110 209 1979 Life of Brian 183 266 179 210 1998 The Big Lebowski 167 256 123 211 1992 Aladdin > 250 120 308 212 2000 Amores Perros 209 260 225 213 2007 The Bourne Ultimatum 234 235 156 214 2007 Ratatouille > 250 138 211 215 1996 Fargo 161 230 164 216 1995 Twelve Monkeys 245 238 163 217 1965 For a Few Dollars More 104 792 142 218 1980 Raging Bull 124 599 119 219 2005 Serenity > 250 208 295 220 1967 Cool Hand Luke 172 539 215 221 1969 Butch Cassidy and the Sundance Kid 210 421 231 222 1957 The Bridge on the River Kwai 138 581 180 223 1988 Rain Man > 250 182 217 224 1965 The Sound of Music > 250 101 516 225 1957 The Seventh Seal 141 462 223 226 1993 In the Name of the Father 188 408 268 227 2014 Wild Tales 185 323 282 228 1939 Mr. Smith Goes to Washington 145 466 297 229 2006 The Pursuit of Happyness > 250 185 220 230 1995 Casino 146 419 136 231 1987 The Princess Bride 214 136 298 232 1950 Rashomon 110 626 185 233 2008 Iron Man > 250 140 244 234 1975 Dog Day Afternoon > 250 417 252 235 2014 PK > 250 646 246 236 2005 Sin City > 250 231 148 237 1954 On the Waterfront 139 546 237 238 1982 Gandhi 227 370 221 239 2017 Call Me by Your Name 186 347 528 240 2011 X: First Class > 250 157 248 241 1948 The Treasure of the Sierra Madre 119 786 230 242 2014 Kingsman: The Secret Service > 250 174 259 243 2012 Life of Pi > 250 152 257 244 2016 Captain America: Civil War > 250 215 265 245 2005 Harry Potter and the Goblet of Fire > 250 96 431 246 2004 The Notebook > 250 63 452 247 1976 Rocky 220 442 132 248 2013 About Time > 250 189 269 249 1977 Annie Hall 233 289 218 250 2003 Mystic River > 250 245 219 251 2011 The Girl With the Dragon Tattoo > 250 216 222 252 1992 Scent of a Woman > 250 276 255 253 2007 Atonement > 250 139 366 254 2011 The Artist > 250 197 325 255 2014 Big Hero 6 > 250 129 462 256 1986 Platoon 187 490 176 257 1984 Nausicaa of the Valley of the Wind 213 378 301 258 1973 The Exorcist > 250 309 178 259 1925 The Gold Rush 136 684 306 260 1953 Roman Holiday > 250 206 426 261 1982 The Thing 163 528 146 262 1984 The Terminator 229 318 150 263 1985 The Breakfast Club > 250 137 391 264 2007 Persepolis > 250 291 477 265 2004 Before Sunset > 250 263 240 266 1959 Ben-Hur 195 481 227 267 1961 Judgment at Nuremberg 134 752 375 268 2013 The Hunger Games: Catching Fire > 250 83 525 269 2004 The Incredibles > 250 222 208 270 2000 Remember the Titans > 250 312 346 271 2001 Shrek > 250 143 323 272 1934 It Happened One Night 184 366 424 273 2001 Harry Potter and the Sorcerer’s Stone > 250 88 530 274 2006 Casino Royale > 250 282 200 275 2014 Edge of Tomorrow > 250 293 203 276 2014 How to Train Your Dragon 2 > 250 186 395 277 1941 The Maltese Falcon 216 541 271 278 2014 Birdman or (The Unexpected Virtue of Ignorance) > 250 299 168 279 1974 Young Frankenstein > 250 443 334 280 1957 Wild Strawberries 152 609 329 281 2001 Ocean’s Eleven > 250 221 262 282 2004 Shaun of the Dead > 250 233 261 283 1967 The Graduate > 250 285 254 284 2006 The Fall > 250 223 594 285 1995 La Haine 231 561 276 286 2006 Little Miss Sunshine > 250 149 349 287 2003 Dogville > 250 328 365 288 2015 The Hateful Eight > 250 411 171 289 2005 Pride & Prejudice > 250 68 754 290 2014 Nightcrawler > 250 380 173 291 1990 Dances With Wolves > 250 375 264 292 1986 Castle in the Sky 250 379 310 293 2010 Tangled > 250 93 599 294 1999 The Iron Giant > 250 418 312 295 2000 In the Mood for Love 240 358 423 296 2016 Hidden Figures > 250 180 651 297 2008 Yip Man > 250 744 214 298 1951 Strangers on a Train > 250 478 371 299 1948 Rope > 250 503 369 300 2009 Moon > 250 350 284 301 2016 Manchester by the Sea > 250 427 243 302 1951 A Streetcar Named Desire > 250 348 448 303 1986 Ferris Bueller’s Day Off > 250 255 303 304 2001 Mulholland Drive > 250 349 242 305 2014 Captain America: The Winter Soldier > 250 204 316 306 2009 District 9 > 250 324 193 307 1982 Blade Runner 149 341 197 308 1999 Magnolia > 250 444 194 309 1985 Brazil > 250 554 287 310 2002 The Bourne Identity > 250 298 256 311 2002 Hero > 250 492 355 312 2005 Cinderella Man > 250 495 286 313 2000 Crouching Tiger, Hidden Dragon > 250 354 313 314 1999 Toy Story 2 > 250 249 266 315 2013 Star Trek: Into Darkness > 250 191 417 316 1968 Rosemary’s Baby > 250 343 304 317 1946 Notorious > 250 500 450 318 1976 Network 191 720 273 319 2016 Rogue One > 250 283 337 320 1997 Children of Heaven 128 678 519 321 2007 Hot Fuzz > 250 259 331 322 1983 A Christmas Story > 250 415 377 323 2004 Crash > 250 226 336 324 2010 Harry Potter and the Deathly Hallows: Part 1 > 250 104 696 325 1995 Dilwale Dulhania Le Jayenge > 250 902 437 326 2013 Captain Phillips > 250 270 340 327 2005 Walk the Line > 250 224 418 328 2017 Guardians of the Galaxy Vol. 2 > 250 241 446 329 2007 Elite Squad > 250 974 307 330 1982 E.T. the Extra-Terrestrial > 250 246 370 331 2000 Dancer in the Dark > 250 400 447 332 1966 Persona 196 548 400 333 2009 The Girl With the Dragon Tattoo > 250 269 412 334 2008 Let the Right One In > 250 384 270 335 2014 Boyhood > 250 335 238 336 2012 Barfi! > 250 877 440 337 2009 Mr. Nobody > 250 253 434 338 1993 True Romance > 250 557 280 339 2010 My Name Is Khan > 250 535 517 340 2009 The Hangover > 250 258 247 341 1926 The General 153 891 381 342 2012 Moonrise Kingdom > 250 232 386 343 2012 Les Miserables > 250 168 499 344 1979 Stalker 197 767 347 345 2017 Baby Driver > 250 389 305 346 2012 Silver Linings Playbook > 250 237 251 347 2016 Contratiempo > 250 589 561 348 2004 The Sea Inside > 250 428 507 349 2006 Apocalypto > 250 364 373 350 1959 The 400 Blows 200 637 374 351 2017 Get Out > 250 344 314 352 1988 Akira > 250 882 267 353 1964 Fistful of Dollars > 250 950 278 354 2009 The Blind Side > 250 198 488 355 2008 Taken > 250 257 315 356 2008 The Curious Case of Benjamin Button > 250 211 320 357 2007 The Diving Bell and the Butterfly > 250 432 397 358 2011 Drive > 250 361 207 359 2003 Spring, Summer, Fall, Winter… and Spring > 250 572 416 360 1987 The Untouchables > 250 604 300 361 1944 Arsenic and Old Lace > 250 464 617 362 1996 Sling Blade > 250 715 464 363 2008 The Boy in the Striped Pajamas > 250 207 601 364 2002 Talk to Her > 250 394 430 365 1979 Manhattan > 250 508 359 366 2013 Short Term 12 > 250 474 529 367 2015 Straight Outta Compton > 250 513 459 368 2010 Despicable Me > 250 145 543 369 2000 Almost Famous > 250 320 322 370 1982 Pink Floyd: The Wall > 250 656 510 371 2006 Children of Men > 250 355 263 372 2014 Ex Machina > 250 362 272 373 1997 Boogie Nights > 250 660 213 374 2013 Queen > 250 1005 484 375 1973 Papillon > 250 831 354 376 2010 Elite Squad: The Enemy Within > 250 1116 352 377 2014 The Theory of Everything > 250 173 591 378 1940 The Philadelphia Story > 250 393 766 379 1940 The Grapes of Wrath 221 728 403 380 1971 Harold and Maude > 250 436 685 381 2016 Captain Fantastic > 250 363 505 382 1993 What’s Eating Gilbert Grape > 250 202 574 383 2003 Memories of Murder 199 916 330 384 2009 Avatar > 250 228 296 385 2002 Infernal Affairs 243 875 292 386 1994 Three Colors: Red > 250 644 415 387 1976 All the President’s Men > 250 755 420 388 2016 The Handmaiden 246 595 549 389 1955 The Night of the Hunter > 250 737 471 390 1995 Underground > 250 751 541 391 1990 The Godfather: Part III > 250 440 358 392 1984 Paris, Texas 244 736 455 393 2010 The Fighter > 250 452 283 394 1966 Who’s Afraid of Virginia Woolf? > 250 537 565 395 2014 The Fault in Our Stars > 250 187 513 396 2005 Brokeback Mountain > 250 162 611 397 2007 Chak de! India > 250 1278 317 398 2006 Lucky Number Slevin > 250 416 363 399 1991 JFK > 250 847 324 400 1998 The Legend of 1900 242 608 607 401 2017 The Greatest Showman > 250 272 972 402 2000 O Brother, Where Art Thou? > 250 401 387 403 2010 The Social Network > 250 414 201 404 1997 Gattaca > 250 356 390 405 2012 Argo > 250 243 409 406 1993 Groundhog Day 230 457 210 407 1962 The Manchurian Candidate > 250 849 506 408 1984 This Is Spinal Tap > 250 762 348 409 2013 Frozen > 250 130 692 410 1990 Misery > 250 402 466 411 2007 The Man From Earth > 250 764 290 412 1968 Planet of the Apes > 250 789 294 413 2000 Cast Away > 250 314 328 414 1998 Black Cat, White Cat > 250 676 605 415 1971 Willy Wonka & the Chocolate Factory > 250 333 496 416 1985 Ran 133 1207 234 417 2008 Changeling > 250 296 405 418 2006 Rang De Basanti 180 1218 236 419 1989 Glory > 250 768 427 420 1989 Back to the Future Part II > 250 374 338 421 2004 The Bourne Supremacy > 250 413 333 422 2006 Letters From Iwo Jima > 250 791 364 423 1952 High Noon > 250 890 407 424 1997 The Fifth Element > 250 247 546 425 2017 Wonder Woman > 250 196 706 426 1995 Ghost in the Shell > 250 917 361 427 1961 Yojimbo 113 1281 235 428 2015 Bahubali: The Beginning > 250 1491 393 429 2007 Zodiac > 250 435 275 430 1990 Awakenings > 250 467 559 431 1993 Three Colors: Blue > 250 552 603 432 1950 Harvey > 250 645 680 433 2014 Fury > 250 449 341 434 1993 Philadelphia > 250 277 644 435 1998 The Celebration > 250 785 404 436 1946 The Big Sleep > 250 750 489 437 1987 Wings of Desire > 250 622 638 438 2016 Hunt for the Wilderpeople > 250 605 701 439 1994 Chungking Express > 250 712 600 440 2012 Kahaani > 250 1212 478 441 1958 Touch of Evil 228 1008 356 442 2004 Finding Neverland > 250 240 570 443 2004 The Machinist > 250 330 438 444 1987 Empire of the Sun > 250 530 668 445 2012 Wreck-It Ralph > 250 281 458 446 1968 Night of the Living Dead > 250 837 385 447 1993 Carlito’s Way > 250 876 326 448 1996 The Bandit 171 1181 362 449 1997 The Game > 250 441 367 450 1946 The Best Years of Our Lives 239 772 604 451 2004 Man on Fire > 250 406 444 452 2014 The Lego Movie > 250 397 380 453 1964 Mary Poppins > 250 234 806 454 1959 Anatomy of a Murder > 250 864 515 455 1999 Being John Malkovich > 250 392 383 456 2015 The Big Short > 250 515 299 457 2008 The Wrestler > 250 621 289 458 1954 La Strada > 250 748 623 459 1999 All About My Mother > 250 405 712 460 2007 3:10 to Yuma > 250 511 456 461 1975 Barry Lyndon 225 991 281 462 2009 Fantastic Mr. Fox > 250 423 445 463 1922 Nosferatu > 250 716 468 464 2017 Wonder > 250 577 862 465 2006 The Last King of Scotland > 250 455 535 466 1980 The Blues Brothers > 250 687 372 467 2012 Skyfall > 250 295 401 468 1997 As Good as It Gets > 250 367 396 469 1955 Diabolique 223 910 534 470 2016 Kubo and the Two Strings > 250 600 616 471 1972 Solaris > 250 996 429 472 2013 Before Midnight > 250 453 449 473 1989 Kiki’s Delivery Service > 250 357 674 474 1994 Ed Wood > 250 545 384 475 1960 La Dolce Vita > 250 793 512 476 1993 The Fugitive > 250 569 392 477 1967 Bonnie and Clyde > 250 648 501 478 1996 Primal Fear > 250 426 578 479 2002 Harry Potter and the Chamber of Secrets > 250 142 831 480 1999 The Insider > 250 863 378 481 2004 3-Iron > 250 651 719 482 1965 Doctor Zhivago > 250 714 577 483 1927 Sunrise 164 995 633 484 2009 Zombieland > 250 329 414 485 2001 Lagaan: Once Upon a Time in India 249 1190 293 486 1993 Tombstone > 250 794 526 487 2008 Departures > 250 731 613 488 2009 (500) Days of Summer > 250 310 345 489 1969 Midnight Cowboy > 250 818 502 490 1961 Breakfast at Tiffany’s > 250 210 802 491 2007 Harry Potter and the Order of the Phoenix > 250 147 837 492 2004 The Butterfly Effect > 250 303 428 493 2003 21 Grams > 250 410 500 494 2016 Doctor Strange > 250 287 556 495 2009 Harry Potter and the Half-Blood Prince > 250 160 846 496 1953 Stalag 17 > 250 1059 642 497 1962 What Ever Happened to Baby Jane? > 250 585 793 498 2007 Once > 250 463 487 499 2013 Mandariinid > 250 666 865 500
IMDb makes adjustments to its raw ratings but does not disclose its methodology. Therefore, these rankings — which start with the raw ratings — may not match a gender-weighted version of a list made by IMDb itself because we can’t re-create the site’s adjustments.
Source: IMDb
The top 100 largely includes films from the original list of 250, and the additions to the list — there are a lot of best picture winners among the newbies — appear mainly in the back half of the 250.
Attempting to reflect a target population is a common practice in many fields that use surveys. It’s not clear to me why movie rating sites don’t do it — or, at the least, why they don’t indicate that their scores are almost all based mostly on the opinions of male users.
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
2017 Movie Odyssey
So ends the 2017 Movie Odyssey. Last year, I wrote that I did not foresee ever surpassing the 200+ movie mark for a long, long time. But look what happened here (outside of May because that was a hectic time in the Master’s program for sure). The 2017 Movie Odyssey consisted of 232 films - 180 feature-length films and fifty-two shorts. A century of filmmaking was covered this year, from 1917 to 2017. If I do have one regret this year... it’s that African films were not featured this year (due to availability issues and me not having enough money; I tend to watch things legally if possible). I hope to assuage that next year for a more representative Movie Odyssey.
For all of you out there who supported the Movie Odyssey in your own ways – whether reading, liking, commenting, or reblogging a write-up or sitting down with me to a new movie or talking to me about any movie... my thanks to all of you. None of this possible without you, and I hope you find that, through this blog, classic movies seem more approachable and welcoming and you are inspired to see some and learn about them yourself. A Happy New Year to all, and I’ll see you for the 2018 leg of the Movie Odyssey very soon (oh boy the Winter Olympics and World Cup are gonna chip away at the final count next year)!
As many know, all ratings are based on my imdb rating and half-points are always rounded down. My interpretation of that ratings system can be found here. A 6/10 is considered the borderline between “passing” and “failing”. Feature-length narrative films, short films, and documentaries are rated within their respective spectrums.
JANUARY
1. Marnie (1964) – 6/10
2. The Moon Is Down (1943) – 7/10
3. Sense and Sensibility (1995) – 8.5/10
4. The Big House (1930) – 7.5/10
5. Manchester by the Sea (2016) – 7/10
6. The Far Country (1954) – 7/10
7. Kung Fu Hustle (2004, Hong Kong/China) – 7/10
8. Road to Singapore (1940) – 6/10
9. A Clever Dummy (1917 short) – 5/10
10. Hidden Figures (2016) – 7.5/10
11. Teddy at the Throttle (1917 short) – 7.5/10
12. The Last of the Mohicans (1920) – 7/10
13. Sweet Smell of Success (1957) – 10/10
14. The Red Turtle (2016, France/Belgium/Japan) – 9/10
15. Life, Animated (2016) – 7.5/10
16. In the Mood for Love (2000, Hong Kong) – 10/10
FEBRUARY
17. Lion (2016) – 7/10
18. It’s Always Fair Weather (1955) – 7.5/10
19. Fences (2016) – 8.5/10
20. Shenandoah (1965) – 7/10
21. Caged (1950) – 8/10
22. Pearl (2016 short) – 7.5/10
23. Blind Vaysha (2016 short) – 8/10
24. Asteria (2016 short) – 6/10
25. The Head Vanishes (2016 short) – 6/10
26. Once Upon a Line (2016 short) – 7/10
27. Pear Cider and Cigarettes (2016 short) – 8/10
28. Sing (2016 short, Hungary) – 7.5/10
29. Silent Nights (2016 short, Denmark) – 6/10
30. Timecode (2016 short, Spain) – 7/10
31. Ennemis intérieurs (2016 short, France) – 8.5/10
32. La femme et le TGV (2016 short, Switzerland) – 8/10
33. Joe’s Violin (2016 short) – 7/10
34. Extremis (2016 short) – 8/10
35. 4.1 Miles (2016 short, Greece) – 9/10
36. Nashville (1975) – 7.5/10
37. The Romance of Transportation in Canada (1952 short) – 7/10
MARCH
38. My Life as a Zucchini (2016, Switzerland) – 8/10
39. Lili (1953) – 7/10
40. The Man from U.N.C.L.E. (2015) – 6/10
41. Captain Blood (1935) – 9.5/10
42. Logan (2017) – 7/10
43. Friendly Persuasion (1956) – 9/10
44. Ducks and Drakes (1921) – 7/10
45. What Dreams May Come (1998) – 6/10
46. Bright Road (1953) – 6/10
47. Snow Gets in Your Eyes (1938 short) – 5/10
48. Jungle Cat (1959) – 6.5/10
49. The Salesman (2016, Iran) – 8.5/10
50. Good Scouts (1938 short) – 7.5/10
51. All in a Nutshell (1949 short) – 8/10
52. The Hound That Thought He Was a Raccoon (1960) – 7/10
53. Winter Storage (1949 short) – 7/10
54. Out of Scale (1951 short) – 8/10
55. The Incredible Journey (1963) – 7/10
56. Follow Me, Boys! (1966) – 7/10
57. Charlie, the Lonesome Cougar (1967) – 5.5/10
58. Belladonna of Sadness (1973, Japan) – 6/10
59. Ponyo (2008, Japan) – 7/10
60. My Cousin Rachel (1952) – 7.5/10
61. Road to Perdition (2002) – 9/10
APRIL
62. The X from Outer Space (1967, Japan) – 3/10
63. The Blue Gardenia (1953) – 6.5/10
64. Get Out (2017) – 7.5/10
65. Fantastic Planet (1973, France/Czechoslovakia) – 8/10
66. 5 Centimeters Per Second (2007, Japan) – 6/10
67. Your Name (2016, Japan) – 7.5/10
68. The Outlaw and His Wife (1918, Sweden) – 7/10
69. Mail Early (1941 short) – experimental film, score withheld
70. Boogie-Doodle (1948 short) – experimental film, score withheld
71. A Chairy Tale (1957 short) – 9/10
72. Very Nice, Very Nice (1961 short) – experimental film, score withheld
73. Fine Feathers (1968) – 7/10
74. What on Earth! (1967 short) – 8/10
75. Walking (1968 short) – 7/10
76. Notes on a Triangle (1966 short) – experimental film, score withheld
77. The Three Faces of Eve (1957) – 7.5/10
78. Peeping Tom (1960) – 7.5/10
79. Porco Rosso (1992, Japan) – 8/10
80. MacArthur (1977) – 6/10
MAY
81. Dr. Goldfoot and the Bikini Machine (1965) – 4/10
82. Scarlet Street (1945) – 8.5/10
83. Tremors (1990) – 7/10
84. The Crucified Lovers (1954, Japan) – 7.5/10
85. Akeelah and the Bee (2006) – 8/10
JUNE
86. Wonder Woman (2017) – 7/10
87. Pollyanna (1960) – 7.5/10
88. Mickey’s Polo Team (1936 short) – 8/10
89. Tales of Manhattan (1942) – 7/10
90. The Horse with the Flying Tale (1960) – 7/10
91. Sound of the Mountain (1954, Japan) – 9/10
92. Return of the Fly (1959) – 4/10
93. Friday the 13th (1980) – 4/10
94. The Tattooed Police Horse (1964) – 6/10
95. Dr. Jack (1922) – 7/10
96. Pat Garrett and Billy the Kid (1973) – 7/10
97. Friday the 13th Part 2 (1981) – 5/10
98. The Great Man (1956) – 8/10
99. Sparrows (1926) – 7.5/10
100. Seven Days to Noon (1950) – 9/10
101. My Neighbor Totoro (1988, Japan) – 8.5/10
102. The Pocket Man (2016 short, France) – 7/10
103. Snack Attack (2012 short) – 7/10
104. You Were Never Lovelier (1942) – 7/10
105. San Francisco (1936) – 7.5/10
106. Eraserhead (1977) – 6.5/10
JULY
107. The Beguiled (2017) – 7/10
108. Summer Magic (1963) – 6/10
109. The Southerner (1945) – 9/10
110. The Statue of Liberty (1985) – 6/10
111. They Live by Night (1948) – 8/10
112. A Little Romance (1979) – 6/10
113. Conflagration (1958, Japan) – 6.5/10
114. The Naughty Twenties (1951 short) – 5/10
115. The Fastest Gun Alive (1956) – 7/10
116. For Your Eyes Only (1981) – 6/10
117. A Man There Was (1917, Sweden) – 9.5/10
118. His Royal Slyness (1920 short) – 6/10
119. Now or Never (1921 short) – 6.5/10
120. Among Those Present (1921 short) – 6/10
121. Dawn of the Planet of the Apes (2014) – 7.5/10
122. Independence Day (1996) – 5/10
123. Yoyo (1965, France) – 8/10
124. The Man Who Knew Too Much (1934) - 6.5/10
125. War for the Planet of the Apes (2017) – 7.5/10
126. The Lady Vanishes (1938) – 10/10
127. Funny Face (1957) – 9/10
128. A Brighter Summer Day (1991, Taiwan) – 9.5/10
129. A Sailor-Made Man (1921) – 6/10
130. Much Ado About Nothing (1993) – 8/10
131. Dunkirk (2017) – 8.5/10
132. Lost Horizon (1937) – 8/10
133. The Man from Snowy River (1982) – 7.5/10
134. A Touch of Zen (1971, Taiwan) – 10/10
AUGUST
135. A Double Life (1947) – 6/10
136. Tokyo Chorus (1931, Japan) – 7/10
137. In a Heartbeat (2017 short) – 7.5/10
138. Valerian and the City of a Thousand Planets (2017) – 4.5/10
139. Twelve O’Clock High (1949) – 9/10
140. The Big Clock (1948) – 7/10
141. Pink Floyd – The Wall (1982) – 8/10
142. Record of a Tenement Gentleman (1947, Japan) – 9/10
143. Octopussy (1983) – 6/10
144. West of Zanzibar (1928) – 6/10
145. Take Me Out to the Ball Game (1949) – 7/10
146. Detroit (2017) – 5.5/10
147. That Funny Feeling (1965) – 6/10
148. Kid Galahad (1962) – 6/10
149. Tokyo Twilight (1957, Japan) – 10/10
150. In This Corner of the World (2016, Japan) – 7/10
151. The Bedford Incident (1965) – 7.5/10
152. Johnny Express (2014 short) – 6/10
153. Carpark (2013 short) – 6/10
154. Castle in the Sky (1986, Japan) – 8/10
155. The Goonies (1985) – 7.5/10
156. State of the Union (1948) – 6/10
SEPTEMBER
157. Beyond the Poseidon Adventure (1979) – 3/10
158. Muscle Beach Party (1964) – 4/10
159. The Nutty Professor (1963) – 7/10
160. Camille (1921) – 6.5/10
161. Aguirre, the Wrath of God (1972, West Germany) – 8/10
162. Independence Day: Resurgence (2016) – 2/10
163. It (2017) – 7/10
164. Ocean Waves (1993, Japan) – 6/10
165. Monterey Pop (1968) – 8/10
166. Don’t Look Back (1967) – 9/10
167. Tyrus (2015) – 8.5/10
OCTOBER
168. A Star Is Born (1937) – 8/10
169. Swiss Family Robinson (1960) – 6/10
170. Revenge of the Nerds (1984) – 5/10
171. Horton Hears a Who! (2008) – 6/10
172. Freaky Friday (1976) – 6/10
173. The Great Muppet Caper (1981) – 7.5/10
174. Mr. & Mrs. ’55 (1955, India) – 8/10
175. Island of Lost Souls (1932) – 9.5/10
176. The Little Broadcast (1943 short) – 6.5/10
177. Hoola Boola (1941 short) – 6/10
178. The Sleeping Beauty (1935 short) – 7/10
179. Tulips Shall Grow (1942 short) – 8.5/10
180. Charulata (1964, India) – 8/10
181. Together in the Weather (1946 short) – 6/10
182. John Henry and the Inky-Poo (1946 short) – 7.5/10
183. Philips Cavalcade (1934 short) – 7/10
184. Jasper in a Jam (1946 short) – 8/10
185. Tubby the Tuba (1947 short) – 9/10
186. The Puppetoon Movie (1987) – 7/10
187. Brides of Dracula (1960) – 7/10
188. Blackbeard’s Ghost (1968) – 7/10
189. Candleshoe (1977) – 6/10
190. Jigoku (1960, Japan) – 5.5/10
191. Blacula (1972) – 6/10
192. Willard (1971) – 4/10
193. Ben (1972) – 4.5/10
NOVEMBER
194. The Coward (1965, India) – 7/10
195. The Happening (2008) – 2/10
196. Tom Thumb (1958) – 6.5/10
197. Strike (1925, Soviet Union) – 7.5/10
198. Loving Vincent (2017) – 7/10
199. Destry Rides Again (1939) – 7.5/10
200. The Master Race (1944) – 6/10
201. Justice League (2017) – 6/10
202. Sissi (1955, Austria) – 7.5/10
203. Sissi: The Young Empress (1956, Austria) – 7/10
204. The Sandlot (1993) – 7/10
205. Olaf’s Frozen Adventure (2017 short) – 4/10
206. Coco (2017) – 8/10
207. Sissi – Fateful Years of an Empress (1957, Austria) – 7/10
208. The Florida Project (2017) – 8.5/10
209. The Mortal Storm (1940) – 7/10
210. The Breadwinner (2017) – 8/10
211. Spencer’s Mountain (1963) – 6/10
212. Lady Bird (2017) – 9/10
DECEMBER
213. The Four Horsemen of the Apocalypse (1921) – 8.5/10
214. The Secret Life of Bees (2008) – 7/10
215. Murder on the Orient Express (2017) – 5.5/10
216. So You Think You’re Allergic (1945 short) – 5/10
217. Three Billboards Outside Ebbing, Missouri (2017) – 7.5/10
218. The Shape of Water (2017) – 8.5/10
219. Lonely Are the Brave (1962) – 9.5/10
220. Star Wars: The Last Jedi (2017) – 7/10
221. They Won’t Forget (1937) – 8/10
222. It Came from Outer Space (1953) – 6.5/10
223. Brave Little Tailor (1938 short) – 8/10
224. The Story of Robin Hood and His Merrie Men (1952) – 6/10
225. The Sign of Zorro (1958) – 5/10
226. Kong: Skull Island (2017) – 6.5/10
227. Flipped (2010) – 6/10
228. Bardelys the Magnificent (1926) – 7.5/10
229. There’s No Business Like Show Business (1954) – 7/10
230. Swim Team (2016) – 7/10
231. Toby Tyler (1960) – 5/10
232. The Liberator (2013, Venezuela) – 6/10
All scores are subject to change (upgrades and downgrades) upon a rewatch.
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Online Trademark Consultants in US
TRADEMARK OF THE WEEK- FOX
Fox Entertainment Group, an empire started with William Fox’s vision, today it is one of the world’s biggest player in the entertainment industry. The first brick was laid by buying of New York nickelodeon for $1,600 turning it into a booming entertaining company, expanding with ownership of further 25 theaters in New York.

In the span of nearly 10 years, William Fox consolidated into Fox Film Corporation and moved to Los Angeles, which marked the beginning of his movie-making career. By the end of the decade, Fox studio was the major provider of films across the globe, producing 50 films a year and approximate worth of $200 million. In 1936, after the merger of Fox Film Corporation with Twentieth Century Pictures, named Twentieth Century Fox, William was forced to declare bankruptcy. Later he was injured in a car crash and died of heart failure in 1952.
In the 1940’s the company experienced financial boon with movies like The Sound of Music, The French Connection and Star Wars. In subsequent years, Oliman Marvin Davis bought the company which was later purchased by Rupert Murdoch’s News Corporation Ltd. The company expanded like wildfire branching out to the news network, sports, children radio and tv broadcast, cable networks, etc.
Fox Entertainment Group Inc, is the fourth network television channel and movie producer worldwide. The company is persistent towards delivering blockbuster movies, expanding its cable services, producing hit television shows, preserving its sports and news interests.
If you need assistance in Trademark Service contact Lex Protector.We offer a full range of trademark, copyright and trademark services to entrepreneurs, established businesses and other attorneys.We are prominent as the Online Trademark Consultants in US.
#Online Trademark Consultants#Online Trademark#Trademark Consultants#Trademark Consultants in US#Trademark Service
0 notes
Photo

https://youtu.be/nSR7YAdqurU
Ella Fitzgerald was the First African-American to Win Grammy Award in 1958. She won 14 Grammys. Here is her fascinating life story:
Born on April 25, 1917 in Newport News, Virginia, singer Ella Fitzgerald was the product of a common-law marriage between William Fitzgerald and Temperance "Tempie" Williams Fitzgerald. Ella experienced a troubled childhood that began with her parents separating shortly after her birth.
With her mother, Fitzgerald moved to Yonkers, New York. They lived there with her mother's boyfriend, Joseph Da Silva. The family grew in 1923 with the arrival of Fitzgerald's half-sister Frances. Struggling financially, the young Fitzgerald helped her family out by working as a messenger "running numbers" and acting as a lookout for a brothel. Her first career aspiration was to become a dancer.
After her mother's death in 1932, Fitzgerald ended up moving in with an aunt. She started skipping school. Fitzgerald was then sent to a special reform school but didn't stay there long. By 1934, Ella was trying to make it on her own and living on the streets. Still harboring dreams of becoming an entertainer, she entered an amateur contest at Harlem's Apollo Theater. She sang the Hoagy Carmichael tune "Judy" as well as "The Object of My Affection," wowing the audience. Fitzgerald went on to win the contest's $25 first place prize.
That unexpected performance at the Apollo helped set Fitzgerald's career in motion. She soon met bandleader and drummer Chick Webb and eventually joined his group as a singer. Fitzgerald recorded "Love and Kisses" with Webb in 1935 and found herself playing regularly at one of Harlem's hottest clubs, the Savoy. Fitzgerald also put out her first No. 1 hit, 1938's "A-Tisket, A-Tasket," which she co-wrote. Later that year Ella recorded her second hit, "I Found My Yellow Basket."
In addition to her work with Webb, Fitzgerald performed and recorded with the Benny Goodman Orchestra. She had her own side project, too, known as Ella Fitzgerald and Her Savoy Eight. Following Webb's death in 1939, Ella became the leader of the band, which was renamed Ella Fitzgerald and Her Famous Orchestra. (Some sources refer to the group as Ella Fitzgerald and Her Famous Band.) Around this time, Fitzgerald was briefly married to Ben Kornegay, a convicted drug dealer and hustler. They wed in 1941, but she soon had their union annulled.
Going out on her own, Fitzgerald landed a deal with Decca Records. She recorded some hit songs with the Ink Spots and Louis Jordan in the early 1940s. Fitzgerald also made her film debut as Ruby in 1942's comedy western Ride 'Em Cowboy with Bud Abbott and Lou Costello. Her career really began to take off in 1946 when she started working with Norman Granz, the future founder of Verve Records. In the mid-1940s, Granz had started Jazz at the Philharmonic, a series of concerts and live records featuring most of the genre's great performers. Fitzgerald also hired Granz to become her manager. Around this time, Fitzgerald went on tour with Dizzy Gillespie and his band. She started changing her singing style, incorporating scat singing during her performances. Fitzgerald also fell in love with Gillespie's bass player Ray Brown. The pair wed in 1947, and they adopted a child born to Fitzgerald's half-sister whom they named Raymond "Ray" Brown Jr. The marriage ended in 1952.
The 1950s and '60s proved to be a time of great critical and commercial success for Fitzgerald, and she earned the moniker "First Lady of Song" for her mainstream popularity and unparalleled vocal talents. Her unique ability to mimic instrumental sounds helped popularize the vocal improvisation of scatting, which became her signature technique.
In 1956, Fitzgerald began recording for the newly created Verve. She made some of her most popular albums for the label, starting out with 1956's Ella Fitzgerald Sings the Cole Porter Song Book. At the very first Grammy Awards in 1958, Fitzgerald picked up her first two Grammys—and made history as the first African-American woman to win the award—for best individual jazz performance and best female vocal performance for the two songbook projects Ella Fitzgerald Sings the Duke Ellington Song Book and Ella Fitzgerald Sings the Irving Berlin Song Book, respectively. (She worked directly with Ellington on the former album.)
A truly collaborative soul, Fitzgerald produced great recordings with such artists as Louis Armstrong and Count Basie. She also performed several times with Frank Sinatra over the years as well. In 1960, Fitzgerald broke into the pop charts with her rendition of "Mack the Knife." She was still going strong well into the '70s, playing concerts across the globe. One especially memorable concert series from this time was a two-week engagement in New York City in 1974 with Sinatra and Basie.
By the 1980s, Fitzgerald experienced serious health problems. She had heart surgery in 1986 and had been suffering from diabetes. The disease left her blind, and she had both legs amputated in 1994. She made her last recording in 1989 and her last public performance in 1991 at New York's Carnegie Hall. Ella Fitzgerald died on June 15, 1996, at her home in Beverly Hills. In all, Fitzgerald recorded more than 200 albums and some 2,000 songs in her lifetime. Her total record sales exceeded 40 million. Her many accolades included 14 Grammy Awards, the NAACP Image Award for Lifetime Achievement and the Presidential Medal of Freedom.
While some critics complained that her style and voice lacked the depth of some her more bluesy counterparts, her success and the respect she garnered from the biggest names in the music industry showed that Fitzgerald was in a class all her own. Mel Torme described her as "the High Priestess of Song" and Pearl Bailey called her "the greatest singer of them all," according to Fitzgerald's official website. And Bing Crosby once said, "Man, woman or child, Ella is the greatest of them all."
Since her passing, Fitzgerald has been honored and remembered in many ways. The United States Postal Service honored the late singer with an Ella Fitzgerald commemorative stamp celebrating the 90th anniversary of her birth. That same year, the tribute album We All Love Ella: Celebrating the First Lady of Song featured such artists as Gladys Knight, Etta James and Queen Latifah performing some of Fitzgerald's classics.
Sources: YouTube and biography.com
#ella fitzgerald#grammy winner#First Lady of Song#black history month#ride em cowboy#verve#mack the knife#louis armstrong#count basie
17 notes
·
View notes