#1908 politics
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

History & Trivia Buffs! Check this out :)
Wonder what mascots our current presidential candidates would adopt?
#opossum#1908 politics#teddy bear#teddy roosevelt#william h taft#us presidents#animal mascot#billy possum
2 notes
·
View notes
Text

Untitled-Political Cartoon
Record Group 46: Records of the U.S. SenateSeries: Berryman Political Cartoon Collection
This untitled illustration by cartoonist Clifford Berryman, which appeared in the Washington Evening Star on November 8, 1908, depicts the feeling of many that William Howard Taft would bring prosperity to the country.
It shows President Taft walking hand-in-hand with a female figure labeled “Prosperity” who holds a cornucopia. The teddy bear is introducing them to Uncle Sam, saying “Oh, see who’s here!” Uncle Sam is taking off his hat and bowing to the couple. A factory with many smokestacks is in the background.
155 notes
·
View notes
Text

I dare you to find a better Presidential campaign poster than this one for William Howard Taft. Good luck.
#History#Presidents#William Howard Taft#President Taft#1908 Election#1912 Election#Presidential Campaigns#Politics#Political Campaigns#Campaign Posters#Political History
156 notes
·
View notes
Text

Freedom. A Journal of Anarchist Communism, 1908
52 notes
·
View notes
Text

A Strange Bed-Fellow, Indeed
September 28, 1908
AFL president Samuel Gompers puts the Democratic Donkey into bed with Labor, who looks alarmed.
The caption reads "Mr. Gompers has some new ideas about politics, but what does Labor think about it?"
Gompers had made a surprise endorsement of Democratic Candidate William Jennings Bryan in the 1908 election, according to the September 24th edition of the New York Times.
From Hennepin County Library
Original available at: https://digitalcollections.hclib.org/digital/collection/Bart/id/6595/rec/2085
#charles bartholomew#political cartoon#democratic party#1908 presidential election#samuel gompers#labor#american history
3 notes
·
View notes
Text

Following the Political Leader — One of the most pitiful sights of our present age, is the manner in which the masses of voters are tricked by campaign promises. They follow the leader like slaves into deeper darkness. Hell Before Death, Rev. W. S. Harris, illustrated by Paul Kraft, 1908
#socialism#anarchy#politics#democracy#vote#hell before death#paul kraft#rev. w. s. harris#1908#1900s#00s
1 note
·
View note
Text
Tongoa Media Weekly Review
1.Embakasi Tragedy: Gas Plant Owner and Officials Arrested Following Fatal Explosion2.Former Treasury Chief Henry Rotich Declines Senior Advisor Role in Ruto’s Office3.Joseph Irungu Convicted of Monica Kimani Murder; Jacque Maribe Acquitted4.Mbeere North Shocked as Teacher’s Love Tragedy Ends in Suicide5. High Court Temporarily Blocks eCitizen School Fee Payments6. DCI Seizes Massive Bhang Haul;…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Things the Biden-Harris Administration Did This Week #31
August 9-16 2024
President Biden and Vice-President Harris announced together the successful conclusion of the first negotiations between Medicare and pharmaceutical companies over drug prices. For years Medicare was not allow to directly negotiate princes with drug companies leaving seniors to pay high prices. It has been a Democratic goal for many years to change this. President Biden noted he first introduced a bill to allow these negotiations as a Senator back in 1973. Thanks to Inflation Reduction Act, passed with no Republican support using Vice-President Harris' tie breaking vote, this long time Democratic goal is now a reality. Savings on these first ten drugs are between 38% and 79% and will collectively save seniors $1.8 billion dollars in out of pocket costs. This comes on top of the Biden-Harris Administration already having capped the price of insulin for Medicare's 3.5 million diabetics at $35 a month, as well as the Administration's plan to cap Medicare out of pocket drug costs at $2,000 a year starting January 2025.
President Biden and Vice President Harris have launched a wide ranging all of government effort to crack down on companies wasting customers time with excessive paperwork, hold times, and robots rather than real people. Some of the actions from the "Time is Money" effort include: The FTC and FCC putting forward rules that require companies to make canceling a subscription or service as easy as signing up for it. The Department of Transportation has required automatic refunds for canceled flights. The CFPB is working on rules to require companies to have to allow customers to speak to a real person with just one button click ending endless "doom loops" of recored messages. The CFPB is also working on rules around chatbots, particularly their use from banks. The FTC is working on rules to ban companies from posting fake reviews, suppressing honest negative reviews, or paying for positive reviews. HHS and the Department of Labor are taking steps to require insurance companies to allow health claims to be submitted online. All these actions come on top of the Biden Administration's efforts to get rid of junk fees.
President Biden and First Lady Jill Biden announced further funding as part of the President's Cancer Moonshot. The Cancer Moonshot was launched by then Vice-President Biden in 2016 in the aftermath of his son Beau Biden's death from brain cancer in late 2015. It was scrapped by Trump as political retaliation against the Obama-Biden Administration. Revived by President Biden in 2022 it has the goal of cutting the number of cancer deaths in half over the next 25 years, saving 4 million lives. Part of the Moonshot is Advanced Research Projects Agency for Health (ARPA-H), grants to help develop cutting edge technology to prevent, detect, and treat cancer. The President and First Lady announced $150 million in ARPA-H grants this week focused on more successful cancer surgeries. With grants to Tulane, Rice, Johns Hopkins, and Dartmouth, among others, they'll help fund imaging and microscope technology that will allow surgeons to more successfully determine if all cancer has been remove, as well as medical imaging focused on preventing damage to healthy tissues during surgeries.
Vice-President Harris announced a 4-year plan to lower housing costs. The Vice-President plans on offering $25,000 to first time home buyers in down-payment support. It's believed this will help support 1 million first time buyers a year. She also called for the building of 3 million more housing units, and a $40 billion innovation fund to spur innovative housing construction. This adds to President Biden's call for a $10,000 tax credit for first time buyers and calls by the President to punish landlords who raise the rent by over 5%.
President Biden Designates the site of the 1908 Springfield Race Riot a National Monument. The two day riot in Illinois capital took place just blocks away from Abraham Lincoln's Springfield home. In August 1908, 17 people die, including a black infant, and 2,000 black refugees were forced to flee the city. As a direct result of the riot, black community leaders and white allies met a few months later in New York and founded the NAACP. The new National Monument will seek to preserve the history and educate the public both on the horrible race riot as well as the foundation of the NAACP. This is the second time President Biden has used his authority to set up a National Monument protecting black history, after setting up the Emmett Till and Mamie Till-Mobley National Monument on Emmett Till's 82nd birthday July 25th 2023.
The Department of The Interior announced $775 million to help cap and clean up orphaned oil and gas wells. The money will help cap wells in 21 states. The Biden-Harris Administration has allocated $4.7 billion to plug orphaned wells, a billion of which has already been distributed. More than 8,200 such wells have been capped since the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law passed in 2022. Orphaned wells leak toxins into communities and are leaking the super greenhouse gas methane. Plugging them will not only improve the health of nearby communities but help fight climate change on a global level.
Vice-President Harris announced plans to ban price-gouging in the food and grocery industries. This would be a first ever federal ban on price gouging and Harris called for clear "rules of the road" on price rises in food, and strong penalties from the FTC for those who break them. This is in line with President Biden's launching of a federal Strike Force on Unfair and Illegal Pricing in March, and Democratic Senator Bob Casey's bill to ban "shrinkflation". In response to this pressure from Democrats on price gouging and after aggressive questions by Senator Casey and Senator Elizabeth Warren, the supermarket giant Kroger proposed dropping prices by a billion dollars
#Thanks Biden#Joe Biden#kamala harris#Politics#us politics#american politics#Medicare#drug prices#health care#cancer#Cancer moonshot#customer service#Housing#housing crisis#racism#black history#race riot#climate crisis#cost of living#food prices#shrinkflation
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
I know we've all moved on from Mina's Brief Foray into Misogyny in favour of Jonathan Is Back, Hooray! but
I do think it's interesting to read real contemporary women's views on the early women's rights movement, and honestly Bram Stoker's depiction of how Mina sees things isn't all that far off (i.e. he's not just writing her that way because he's a clueless man).
A while ago, I read the memoirs of Maud Allan, an Edwardian dancer who lived a truly fascinating and often tragic life; it's worth reading her whole Wikipedia page. Her memoirs, published 1908, are not particularly worth reading (they were primarily publicity material), but there is one section where she talks about her views on women's suffrage.
Maud Allan was a highly educated, often controversial figure, who danced topless but for some intricate jewellery. She made her own living, and was most likely a lesbian - so all in all, much like Mina, not someone you would think of as likely to be ambivalent on gender equality. Nonetheless, she argued:
Women should "influence rather than dictate"
Women should be educated; she did not believe there was any difference between male and female intelligence, only in the opportunities they received
The rightful destiny of every woman was to be a wife and mother [even though she was neither]
Women were swayed by emotion more than men, so shouldn't become lawyers
Women would be swayed by the looks and personality of a political candidate, not by his views
As a result, in most areas men and women should be equal - but not in terms of the franchise, or at least not yet.
(The whole chapter is here).
I find this fascinating because from a modern-day perspective, it's so obviously inconsistent and muddled, in particular the sense of gender equality as a kind of grab-bag where women should be equal in some areas but not others. But these were the honest views of an educated, independent woman, and I could imagine a real-world Mina having a similar set of views.
891 notes
·
View notes
Note
i think you do a really impressive job balancing comprehensive/concise while referencing a lot of complex frameworks(contexts? schools of thought? lol idk what to call that. big brain ideas) but if you have any readings specifically on the institution of psychiatry topic that you would recommend/think are relevant, I'd be interested. it's absolutely not a conversation that's being had enough and I want to be able to articulate myself around it
yes i have readings >:)
first of all, the anti-psychiatry bibliography and resource guide is a great place to start getting oriented in this literature. it's split by sub-topic, and there are paragraphs interspersed throughout that give summaries of major thinkers' positions and short intros to key texts.
it's from 1979, though, so here are some recs from the last 4 decades:
overview critiques
mind fixers: psychiatry's troubled search for the biology of mental illness, by anne harrington
psychiatric hegemony: a marxist theory of mental illness, by bruce m z cohen
desperate remedies: psychiatry's turbulent quest to cure mental illness, by andrew scull
psychiatry and its discontents, by andrew scull
madness is civilization: when the diagnosis was social, 1948–1980, by michael e staub
contesting psychiatry: social movements in mental health, by nick crossley
the dsm & pharmacy
dsm: a history of psychiatry's bible, by allan v horwitz
the dsm-5 in perspective: philosophical reflections on the psychiatric babel, by steeves demazeux & patrick singy
pharmageddon, by david healy
pillaged: psychiatric medications and suicide risk, by ronald w maris
the making of dsm-iii: a diagnostic manual's conquest of american psychiatry, by hannah s decker
the myth of the chemical cure: a critique of psychiatric drug treatment, by joanna moncrieff
the book of woe: the dsm and the unmaking of psychiatry, by gary greenberg
prozac on the couch: prescribing gender in the era of wonder drugs, by jonathan metzl
the creation of psychopharmacology, by david healy
the bitterest pills: the troubling story of antipsychotic drugs, by joanna moncrieff
psychiatry & race
the protest psychosis: how schizophrenia became a black disease, by jonathan metzl
administrations of lunacy: racism and the haunting of american psychiatry at the milledgeville asylum, by mab segrest
the peculiar institution and the making of modern psychiatry, 1840–1880, by wendy gonaver
what's wrong with the poor? psychiatry, race, and the war on poverty, by mical raz
national and cross-national contexts
mad by the millions: mental disorders and the early years of the world health organization, by harry yi-jui wu
psychiatry and empire, by sloan mahone & megan vaughan
ʿaṣfūriyyeh: a history of madness, modernity, and war in the middle east, by joelle m abi-rached
surfacing up: psychiatry and social order in colonial zimbabwe, 1908–1968, by lynette jackson
the british anti-psychiatrists: from institutional psychiatry to the counter-culture, 1960–1971, by oisín wall
crime, madness, and politics in modern france: the medical concept of national decline, by robert a nye
reasoning against madness: psychiatry and the state in rio de janeiro, 1830–1944, by manuella meyer
colonial madness: psychiatry in french north africa, by richard keller
madhouse: psychiatry and politics in cuban history, by jennifer lynn lambe
depression in japan: psychiatric cures for a society in distress, by junko kitanaka
inheriting madness: professionalization and psychiatric knowledge in 19th century france, by ian r dowbiggin
mad in america: bad science, bad medicine, and the enduring mistreatment of the mentally ill, by robert whitaker
#sorry this is SO MANY things lmao#i wld recommend starting with harrington or scull as an intro and then maybe look at one of the more topic-specific texts#depending on what interests you specifically#book recs#psychiatry
649 notes
·
View notes
Text
Empire, Wyoming, was a pioneering African American settlement founded in 1908 near Torrington, Wyoming. The community was established by the Speese and Taylor families from Nebraska, who sought self-sufficiency and political autonomy during a time of widespread racial discrimination.
At its peak, Empire had a population of nearly 50 residents and notable institutions, including a post office, a Presbyterian church led by Reverend Russell Taylor, and a public school established in 1909. Sallie Thistle, a young teacher from Cheyenne, ensured the community’s children received an education. These achievements reflected the settlers’ determination to build a thriving and self-reliant town.
However, Empire faced significant challenges. The settlers practiced dryland farming, which left them vulnerable to recurring droughts. Racial tensions with neighboring communities also posed threats. A tragic turning point occurred in 1913 when Baseman Taylor, one of the settlers, died after reportedly being beaten while in custody. This event demoralized the community and led to its decline.
By the 1920s, many residents had left due to hardships, with some moving south for better opportunities and others returning to Nebraska. By 1930, Empire had effectively disappeared. Today, its legacy is commemorated by historical markers in Wyoming, serving as a testament to the resilience and determination of African American homesteaders who pursued freedom and autonomy in the face of adversity.
#black history#black people#wyoming#american history#black excellence#black americans#black lives matter#blacklivesmatter#black economics
30 notes
·
View notes
Text
But Germany’s performances of repentance have their limits. They do not extend, for example, to the genocide the German colonial army committed in Namibia against Herero and Nama people between 1904 and 1908, killing tens of thousands. Germany did not officially apologize for those bloody acts until 2021 and has not agreed to pay meaningful reparations to descendants of the victims. If the new German identity relies on isolating the Holocaust as a shameful aberration in national history and nullifying it via solemn remembrance, there is little room for the memory of colonial violence in the nation’s self-mythology. Genocide scholar Dirk Moses named this approach the “German catechism” in a 2021 essay that sparked heated debate. “The catechism implies a redemptive story in which the sacrifice of Jews in the Holocaust by Nazis is the premise for the Federal Republic’s legitimacy,” wrote Moses. “That is why the Holocaust is more than an important historical event. It is a sacred trauma that cannot be contaminated by profane ones���meaning non-Jewish victims and other genocides—that would vitiate its sacrificial function.”
Accordingly, Germany now sees its post-Holocaust mandate as encompassing not a broader commitment against racism and violence but a specific fealty to a certain Jewish political formation: the State of Israel. Germany has relied on its close diplomatic relationship to Israel to emphasize its repudiation of Nazism, but its connection to the Jewish state goes even further. In 2008, then-chancellor Angela Merkel addressed the Israeli Knesset to declare that ensuring Israel’s security was part of Germany’s “Staatsraison,” the state’s very reason for existence. If asked why it is worth preserving a German nationalism that produced Auschwitz, Germany now has a pleasing, historically symmetrical answer—it exists to support the Jewish state.
To that end, in recent years, Germany’s laudable apparatus for public cultural funding has been used as a tool for enacting a 2019 Bundestag resolution declaring that the Boycott, Divestment, and Sanctions (BDS) movement targeting Israel is antisemitic. Although the resolution is technically nonbinding, its passage has led to an unending stream of firings and event cancellations, and to the effective blacklisting of distinguished academics, cultural workers, artists, and journalists for offenses like inviting a renowned scholar of postcolonialism to speak, tweeting criticism of the Bundestag resolution, or having attended a Palestinian solidarity rally in one’s youth. A network of antisemitism commissioners—a system explored in this issue in a feature by Peter Kuras—has been deputized to monitor such offenses. These commissioners are typically white, Christian Germans, who speak in the name of the Jews and often playact Jewishness on a public stage, posing for photo ops in yarmulkes, performing Jewish music, wearing the uniform of the Israeli police, and issuing decrees on who is next in the pillory. When they tangle with left-wing Jews in Germany, canceling their events and attacking them as antisemites in the pages of various newspapers, they suggest what Germany’s antisemitism commissioner Felix Klein has said directly: That the Jews are not being sensitive enough to what antisemitism means to the Germans—that, in fact, these Jews do not understand antisemitism at all. In a perverse twist, the fact that the Germans were the most successful antisemites in history has here become a credential. By becoming the Jews’ consummate protectors, Germans have so thoroughly absorbed the moral lessons bestowed by Jewish martyrdom that they have no more need for the Jew except as symbol; by the logic of this strange supersessionism, Germans have become the new Jews. This is not only a matter of rhetorical authority on Jewish matters but is also often literal, as this self-reflexive philosemitism has led to a wave of German converts to Judaism. According to Tzuberi, “The Jewish revival is desired precisely because it is a German revival.”
If Jews are negated by this formulation, Palestinians are villainized by it. Last year, when the German state banned Nakba Day demonstrations, only days after the murder of Palestinian journalist Shireen Abu Akleh, police justified this suppression by claiming, in a familiar racist trope, that protesters would not have been able to contain their violent rage. Indeed, in Germany Palestinian identity itself has become a marker of antisemitism, scarcely to be spoken aloud—even as the country is home to the largest Palestinian community in Europe, with a population of around 100,000. “Whenever I would mention that I was Palestinian, my teachers were outraged and said that I should refer to [Palestinians] as Jordanian,” one Palestinian German woman speaking of her secondary school education told the reporter Hebh Jamal. Palestinianness as such has thus been stricken from German public life. In The Moral Triangle, a 2020 anthropological study of Palestinian and Israeli communities in Germany by Sa’ed Atshan and Katharina Galor, many Palestinians interviewed said that to speak of pain or trauma they’ve experienced due to Israeli policy is to destroy their own futures in Germany. “The Palestinian collective body is inscribed as ontologically antisemitic until proven otherwise. Palestinians, in this sense, are collateral damage of the intensifying German wish for purification from antisemitism,” wrote Tzuberi.
July 5, 2023
248 notes
·
View notes
Text
Palestinian History Between Great Powers - Part 1
From Bronze Age to Ottoman Palestine
I started writing this article months ago but as it deserves proper research, it took me a long while, and at one point I started questioning is this helpful anymore. I thought it's obvious at this point to anyone not willfully ignorant that what we are seeing in real time is a genocide, and I'm not going to convince those who are willfully ignorant. I decided to finish it anyway since I do feel obligation to do something and maybe providing some accessible historical context is what I'm capable of doing. Even if I probably won't change any hearts and minds, I think the least we can do is not forget Palestinians and fall into apathy. And at the very least more understanding of the situation is always better even when we already oppose this genocide.
This is quite out of my area of focus, so I will be doing more of a general overview of the history and link in depth sources by more knowledgeable people than try to become an expert on this. My purpose is to offer an accessible starting point for the history of Palestine to help people put historical and current events into their proper context. I don't think the occupation and genocide in Palestine pose complex moral questions - it's pretty simple in my opinion that genocide, apartheid and colonialism are wrong and need to stop for peace to be possible - but the history is complex and it's understanding needs quite a lot of background. I will do my best to represent the complexity accurately and fairly while keeping this concise. Since there is a lot of history, even if this is very general overview, it's still very long, so I did need to cut this in two parts. First part will be covering everything to the beginning of WW1, second part the British Mandate period and Israel period.
Bibliography
I'm linking my sources and further reading here so it's easy to check some specific resources even if you don't want to/have time to read 5 000 years of history right now. Because there's so much misinformation and propaganda, I read as much as I could from academic sources, linked at the top here. They are really interesting and delve deeply into specific subjects so I do recommend checking out anything that peaks your interest (Sci-Hub is your friend against paywalled papers and in JSTOR you can make a free account to access most papers). Some of them I didn't really end up using, but I still linked them here since they provide some additional context that wouldn't fit in this overview. At the end there's some accessible resources (youtube videos, podcasts etc.) which are relevant and I think good.
Pre-Ottoman Era
On The Problem of Reconstructing Pre-Hellenistic Israelite (Palestinian) History - Critique of Biblical historical narratives
Canaanites and Philistines
Archaeological Sources for the History of Palestine: Between Large Forces: Palestine in the Hellenistic Period - Everyday life in Hellenistic Palestine
Ottoman Era
Rediscovering Ottoman Palestine: Writing Palestinians into History - Critique of politics of Ottoman Palestine historiography
The Peasantry of Late Ottoman Palestine
Consequences of the Ottoman Land Law: Agrarian and Privatization Processes in Palestine, 1858–1918
The route from informal peasant landownership to formal tenancy and eviction in Palestine, 1800s–1947
The Ottoman Empire, Zionism, and the Question of Palestine (1880–1908)
Origins of Zionism
Christian Zionism and Victorian Culture
Zionism and Imperialism: The Historical Origins
The Non-Jewish Origin of Zionism
Zionism and Its Jewish "Assimilationist" Critics (1897-1948)
The Jewish-Ottoman Land Company: Herzl's Blueprint for the Colonization of Palestine
Books
Boundaries and Baraka - Chapter II of Muslims and Others in Sacred Space - Local syncretic religious beliefs of Muslim and Christian Arabs in Palestine
Further "reading"
Israelis Are Not 'Indigenous' (and other ridiculous pro-Israel arguments) - Properly cited youtube video on settler colonialism of Zionism (Indigenous is defined here in postcolonialist way, in contrast with the colonialist, the video doesn't argue that diaspora Jews didn't originate from the Palestine area)
Gaza: A Clear Case of Genocide - Detailed Legal Analysis - Youtube video detailing current evidence on the ongoing genocide and assessing them through international law
What the Netanyahu Family Did To Palestine: Part 1 , Part 2 - Two part podcast episode of Behind the Bastards about Israel's history and Netanyahu Family's involvement in it with an expert quest
History of Israeli/Palestinian conflict since 1799 - Timeline of Palestinian history by Al Jazeera with documentaries produced by Al Jazeera for most of the entries in the timeline
Ancient Era (33th-4th century BCE)
Palestine's location in the fertile crescent, the connecting land between Africa and Asia and the strip of land between Mediterranean and Red Sea means since the earliest emergence of civilizations it has been in the middle of great powers. Thorough it's history it has been conquered many, many times for it's strategic value. Despite the changing rulers and migrating groups there has been a continuous history history of a people, which has changed, split and evolved, but not fully disappeared or replaced at any point, which is quite rare of a history spanning thousands of years.
Speakers of Semitic languages are the first recorded inhabitants of Palestine. At least from Bronze Age (c. 3300-1200 BCE) onward they inhabited Levant, Arabian peninsula and Ethiopian highlands. Semitic languages belong in the Afroasiatic language group, which includes three other branches; ancient Egypt, Amazigh languages and Cushitic languages of African Horn. Most prominent theories of the origins of proto-Afroasiatic is in Levant, African side of Red Sea or Ethiopia. In the Bronze Age the Levant's Semitic speakers were called Canaanites and there was already urban settlements in Early Bronze Age. Egypt had been extending it's control over Canaan for a while and in Late Bronze Age, 1457 BCE, it took over Canaan. Gaza, which had had habitation for thousand years already, became the Egypt's administrative capital in Canaan. Canaan stayed as Egypt's province until the Late Bronze Age collapse c. 1200-1150 BCE, when Egypt started losing it's hold on Levant. Egypt eventually retreated from Canaan around 1100 BCE. The causes of Late Bronze Age collapse are unknown, but theories suggest some kind of environmental changes that caused destruction of cities and wide-spread mass migration all around the East Mediterranean Bronze Age civilizations.
Canaanites was not what most of the people called themselves, but rather what the surrounding empires, especially Egypt and Hittites in the north, called them. Philistines appear in Egyptian sources around the Late Bronze Age collapse as raiders against Egypt, who were likely populating southern parts of Canaan, the Palestine area. Several groups with mutually intelligble languages emerged after Egypt left the area: in Palestine area Philistines, Israelites, in Jordan are Ammonites, Moabites and Edomites, and in Lebanon area Canaanites, who were called by Phoenicians by Greeks. Israelites have been theorized to split from Philistines, possibly after Aegonean migrants during the Late Bronze Age collapse influenced the culture of the costal Philistine city states, and/or through Israelites development of monotheistic faith. During Iron Age these different groups descendant from Caananites had their own kingdoms. In the area of Palestine there was two Israelite kindgoms, Kingdom of Judah is the highlands of Judah, were Israelites likely originated, and Kindom of Israel or Samaria north to it, as well as Philistine city states in the coast around the area of current Gaza strip.
Earliest historical evidence of Israel is from mid 9th century BCE and of Judah from 7th century BCE, though Israelites as a group were mentioned earlier. It's entirely possible the kingdoms predate these mentions, but the archaeological evidence suggests likely not by much. Israel was conquered by the Neo-Assyrian empire in 722 BC, so it's entirely possible kingdom of Judah was created by retreating Israelites of the earlier kingdom. The remaining Israelites under Assyrian rule came to be known as Samaritans, marking also the split of Jewish faith into Judaism and Samaritanism. Neo-Assyrian lingua franca was Aramaic, a Semitic language from southwest Syria, which became the major spoken language in Samaria. Judah became a vassal state of Assyrians and later Babylonians. After a rebellion Babylonians fully conquered Judah in 586-587 BCE and exiled the rebels, though more recent historical study suggests it targeted the rebelling population and was not a mass exile. In 539 BCE Babylon and by extension Judah was conquered by Persian Achaemenid empire, which allowed the exiles to return and rule Judah as their vassals. Persia also conquered Samaria and Philistines. Aramaic was also the official language of the both Neo-Babylonian and Achaemenid empires and replaces Old Hebrew as spoken language in Judah too, though Old Hebrew continued to be written language of religious scripture and is known today as Biblical Hebrew. Otherwise in the Palestine area there were Edomites, who migrated to the southern parts of former Judah kingdom, and Qedarites, a nomadic Arabic tribal federation, in southern desert parts.
Biblical narratives tell this early history very differently, and for a long while, those were used as historical texts, but more recent historical study has cast a doubt on their usefulness in historical inquiry. Even more recent archaeological DNA studies (like this and this) have supported the historical narratives constructed from primary historical texts.
Antique Era (4th century BCE - 7th century CE)
Under Persian rule the people in the Palestine area had a relative amount of autonomy, which lasted about 200 years. In the 330s BCE Macedonians conquered Levant along with a lot of other places. The Macedonian empire broke down quickly after the death of Alexander the Great, and Levant was left under the control of the Seleucid empire, which included most of the Asian parts of the Macedonian empire. During this time the whole Palestine area was heavily Hellenized. In the 170s BCE the Seleucian emperor started a repression campaign against the Jewish religion, which led to a Maccabean Revolt in Judea, lasting from 167-160 BCE until the Seleucids were able to defeat the rebels. It started with guerilla violence in the countryside but evolved into a small civil war. Defeat of the rebelling Maccabees didn't curb the discontent and by 134 BCE Maccabees managed to take Judea and establish the Hasmonean dynasty. The dynasty ruled semi-autonomously under the Seleucian empire until it started disintegrating around 110 BCE, and Judea gained more independence and began to conquer the neighbouring areas. At most they controlled Samaria, Galilee, areas around Galilean Sea, Dead Sea and Jordan River between them, Idumea (formerly Kingdom of Edom) and Philistine city states. During the Hasmonean dynasty Judaism spread to some of the other Semitic peoples under their rule. It didn’t take long for the rising power of the Roman Republic to make Judea into their client state in 63 BCE. Next three decades the Roman Republic and Parthian Empire would fight over control of Judea, which ended by Rome gaining control and disposing of the Hasmonean dynasty from power. It was a client state until 6 CE Rome incorporated Judea proper, Samaria, Idumea and Philistine city states into the province of Judea.
The Jewish population was very much discontent under Roman rule and revolted frequently through the first century or so. It led to waves of Jewish migration around the Mediterranean area, which would eventually lead to the formation of European and North-African Jewish groups. The Roman emperor’s decision to build a Roman colony into Jerusalem, which they destroyed along with Second Temple while squashing the previous revolt, provoked a large-scale armed uprising from 132-136 among Judean Jews, which Rome suppressed brutally. Jerusalem was destroyed again, Jews and Christians were banned from there, and a lot of Judean Jews were killed, displaced and enslaved. Rome also suffered high losses. Jews and Christians hadn’t yet fully separated into different faiths yet, but this strained their relations as Christians hadn’t supported the uprising. Galilee and Judea was joined into one province, Syria Palaestina. Galilean Jews hadn’t participated in the revolt and had therefore survived it unscathed, so Galilee became the Jewish heartland. During the Constantine dynasty, in the first half of the 4th century, when Christianity was the Roman state religion, Jerusalem was rebuilt as very Christianized. After the Constantine dynasty the Jewish relations with Rome were briefly improved by a sympathetic emperor, until Justinian came into power in 527 and began authoritarian religious oppression of all non-Christians, casting the whole area into chaos. Samaritans rebelled repeatedly and were almost fully wiped out, while Jews joined forces with several foreign powers in an attempt to destabilize Byzantium rule. By 636 the first Muslim Caliphate emerged as victors over the control of Palestine.
Muslim Period and Crusades (636-1516)
For more than 300 years under the rule of Muslim Caliphate, Palestine saw a much more peaceful period, with relative freedom and economic prosperity. Christianity continued to be the majority religion and Christians, Jews and usually Samaritans were considered People of the Book, who were guaranteed religious freedom. Non-muslims though had to pay taxes and depending on the caliph had more or less restrictions posed upon them. The position of Samaritans as People of the Book was unstable and at points they were persecuted. For the position of Jews it was a marked improvement, and after the expulsion of Jews from Jerusalem by Rome in the 2nd century, they were finally allowed to return. Jerusalem became a religious center for the Muslims too, as it was considered the third most holy place of Islam. Cities, especially Jerusalem, saw Arab immigration. The rural agricultural population was mostly Aramaic speaking, though even while Palestinian Arabs had mostly been bedouins in the southern deserts, there were few Arabic villages from the Roman era. People of the Book were protected from forced conversions, but over time conversions among the Christian population slowly increased, until Islam became the majority religion. Cities became Arabicized and slowly Arabic (also Semitic language) replaced Aramaic as the majority language. Towards the end of the first millennium persecution of Christianity increased with the threat of Byzantium.
In 970 a competing dynasty, Fatimids, conquered Palestine beginning a new era of continuous warfare and conquest by foreign powers. In the beginning of the new millennium Palestine was conquered by the Turco-Persian Seljuk empire for a couple of decades, recaptured by Fatimids for only a year, until the Crusaders took Palestine in 1099. During the next two centuries Palestine exchanged hands several times between the Crusaders and the Egyptian Ayyubid Sultanate. After internal struggle the Ayyubid dynasty was overthrown by the mamluk military caste and them in lead, the Sultanate secured Palestine. First they repelled the invading Mongol empire in 1260 and by 1291 they had defeated the remnants of the Cusaders and their Kingdom of Jerusalem. The period was devastating to the Palestinian populations, cities and economic life. The Crusaders especially committed numerous massacres against non-Christians and under Muslim rule Christians were persecuted and forcibly converted. The next two centuries under the Mamluk Sultanate were peaceful and Christian and Jewish communities were afforded some self-governance and relatively high religious freedom for being recognised as People of the Book again. The state had a more contentious relationship with Christians as the wars with the Crusaders were still looming between Christians and Muslims, and at some points Christians faced persecution and forced conversions.
Ottoman Period (1516-1917)
The Ottoman Empire gained dominance in western Asia over the Mamluk Sultanate during the late 15th century and conquered Palestine in 1516. It became a great imperial power in Asia and Europe for two centuries and in the 18th century started a slow decline, eventually becoming the "Sick man of Europe". The Ottoman Empire was very decentralized and under it Palestine was at first ruled by three Palestinian families semi-autonomously. The Ottoman state didn’t pay much attention to economic development, as they considered it contrary to their chivalric culture, so they instead attracted foreign businesses with the capitulation system. Capitulations were treaties between Ottomans and a foreign power by which the citizens of that foreign power were under their jurisdiction inside Ottoman borders. This guaranteed safety and religious freedom for non-Muslim merchants and exempted them from any additional taxes applying to foreigners and non-Muslims, which encouraged them to build businesses in the Ottoman Empire. Ottomans also intentionally attracted European Jews, who faced persecution and pogroms, and had built effective international trade networks through the tight knit diaspora communities. Jews and Christians had quite well secured position in the empire as People of the Book, but Samaritans were persecuted after they had sided with the Mamluk Sultanate against Ottomans and later for being considered "pagans". City elites adopted Turkish culture, while in rural areas peasant villages and Bedouin clans remained Arabic. The rural areas were very much self-governing as both villages and Bedouin clans were fairly self-reliant with their own political structures. Villages consisted of clan-like family groups, hamulas, and the village lands were distributed between their collective ownership.
In the 19th century the Ottoman Empire was leaving behind European imperial powers in economic and military development. With the rise of the international capitalist markets, capitulation approach, which had worked well for the empire in previous centuries, was extended to markets as a very laissez faire economic policy. This did not lead to hoped economic growth however, but rather deindustrialization. The Ottoman Empire opened itself to markets it couldn’t compete in and its resources were then easy to exploit by stronger economies. The other powers, such as the European powers, avoided this by first cultivating strong national industries with protectionist policies, and then opened to international markets. The capitulation system also became a political liability the way it interacted with the protégé system. The Ottoman Empire had agreed to allow some European powers to give their protection over certain minority religious groups (mostly Christian groups) in the Empire, allowing members of those groups to claim citizenship of their protectorate nation. This had allowed those Ottoman citizens to claim the benefits of the capitulation system and cultivated trade and business for the Empire. In the 19th century the European powers, notably France, British Empire, Germany and Russia, turned their interests towards Levant which was important for their access to their colonial interests in Asia and Africa. They had a vested interest in the continuing power of the weakening Ottoman Empire, which they believed they could control through economic dominance and the protégé system. It became a competition on who could gain the most influence in the Ottoman Empire. In Palestine this led to a change in class dynamics. Christian protégés of European imperial powers were given tax exemptions from the increasing taxes, which were implemented to balance the national deposit, and better opportunities to gain wealth from international trade, turning the urban Christian Arabs into elite.
In 1832 Egypt invaded Palestine, marking a point of more rapid decline of Ottoman rule. Egypt attempted to “modernize” Palestine, which was considered backward, but Egypt's policies, especially conscription, were considered intrusive. The local self-ruling clans and families were resistant to outside powers and with their sway over the population, they rose to a popular uprising after two years of Egyptian rule. The suppression of the uprising devastated many villages and Egypt still failed to enforce order and halt violence. In 1840 Britain intervened, returning its control back to the Ottomans. They didn’t yet have capitulations with the Ottomans and were concerned over the other European powers gaining influence over the aging empire, so in return for their military assistance, they gained capitulations and named Jews and Protestants as their protégés in Levant. Palestine rapidly opened to the international markets with the increase in capitulations combined with the laissez faire fiscal policies of the empire, allowing European powers to turn Palestinian cities, especially in the coast, to centers of trade. In 1858 the Ottoman Empire also attempted to privatize land ownership to increase agricultural production and profitability in order to help with their financial troubles. Most Palestinian land was public land, but in practice owned informally by the villagers cultivating it. As long as they paid taxes, they couldn’t be evicted, which rarely happened in those cases either, and their rights to the land were hereditary. The land reform codified and formalized land ownership and removed barriers to non-villagers gaining ownership of peasant land, laying groundwork for commodifying land. The Ottoman Empire also allowed foreigners to purchase private land. This didn’t immediately lead to large-scale transfer of land ownership, but increasing taxes impoverishing the peasantry and indebting them transferred land from its cultivators to urban absentee landlords. Peasants started to turn into landless tenants and a new type of large estates were established.
Birth of Zionism
The British pushed for more control over Levant, since they wanted to secure their access to India and their colonial ventures in Africa. They didn’t have much interest in colonizing Levant themselves, which is why they were interested in backing the Ottoman Empire and gaining stronger control over it via European Jewish immigrants. European Jews had been immigrating to Palestine in small numbers for a while for religious reasons, to escape persecution and to take advantage of the economic opportunities offered by the Ottoman Empire. The British though also had religious interests in supporting Jewish migration to Palestine. Since the early 19th century, there had been a growing religious movement of Christian Zionism, who sought to restore Jews into Palestine and then convert them to Christianity to cause the second coming of Jesus and the end times. As you do. They were considered fanatics, even lunatics, for their literal interpretations of prophecy, but they were enthusiastic imperialists and when they expressed the idea of restoration of Jewish Palestine in imperial terms, it gained popular acceptance in Britain. Some of the common talking points originating from Christian Zionism were Jews had the right to Palestinian land for Biblical reasons, the only way to not let the “underdeveloped” agrarian land go to waste was colonialism, and Jews would be a civilizing force in Palestine. While the end goal of Christian Zionists was conversion of Jews, they had Orientalist reverence for Jews, but among the wider imperialist support for these ideas there was in addition an explicitly antisemitic aspect. The imperialists' idea was that Britain, and Europe more broadly, could this way also get rid of the Jews.
The trouble was that at the time there was no wide interest at all among Jews to colonize Palestine. The Jews who were migrating there during the first half of the 19th century did so with all intentions of integrating to the Palestinian society. European Jews had since Enlightenment and the French Revolution gained unprecedented levels of social acceptance and equality (which still wasn’t very much), and liberal assimilationism had become the dominant ideology especially among Jewish elites. Assimilationist Jews considered Judaism a religious identity, not an ethnic one, and they rather identified with their nationality. In the latter half of 19th century Jewish socialism was contesting the liberal Jewish idea that antisemitism could be overcome with individualist approach and instead demanded structural change. During the century it became increasingly clear that the assimilationist approach couldn’t fix antisemitism as racial ideology and exclusionist ethnonationalism were gaining traction and fueling antisemitism, which culminated in the 1880s pogroms in Russia and 1894 Dreyfus Affair in France. These events certainly promoted socialist approach among many Jews, but the Jewish elite were certainly not interested in socialist solutions, where they would lose their elite status, even if for white Christians they were all second class citizens. So instead, like many elites facing the threat of socialism, they turned to nationalism. To the question of how to build a nation from a diverse diaspora, they found the answer from Christian Zionism. Jewish Zionism was distinctly secular, so while they did adopt many religious and biblical narratives and goals of Christian Zionism, they put them in nationalist terms. Their end goal was of course different from that of the millennialist Christians so Jewish Zionism was presented as a practical and rational alternative to utopian fanaticism, but they were still natural allies. Zionism was opposed in the European Jewish communities by both assimilationists and socialists, who both viewed it as countering the efforts of opposing antisemitism, which Zionists saw as an inherently impossible endeavor, and also by Orthodox Jews from a religious standpoint. Orthodox Jews denounced the secularization of the Promised Land, which according to them could only be bestowed by God and couldn’t be a state with secular power.
Before Zionism was fully formalized as a movement, there were proto-Zionist movements in Eastern-Europe as a direct response to the pogroms, with the goal of settling Eastern Jewish refugees to Palestine from 1881 forward. This is considered to be the start of the First Aliyah, the explicitly Zionist mass migrations to Palestine. The funding was secured from the European Jews, and with it the Zionists bought land from the absentee urban landlords with large estates and evicted the tenants in order to form Zionist colonies. This raised concern among Ottoman officials, who had become vary of the European exploitation of their capitulation system, which increased European influence with the immigration of European Jews. They were also concerned about the rising Arab nationalism in Palestine provoked by the European economic exploitation and even more pressingly the peasant displacement. The Ottoman Empire was already facing massive difficulties with nationalist movements in different parts of the empire, like in Armenia. They attempted to restrict Zionist land purchases with legal restrictions and failed.
The 1880s settling to Palestine was still unorganized and leaderless until Theodor Herzl, who is considered to be the founder of Zionism, joined Zionist ranks in mid-1890s and began formulating a colonialist venture in earnest. The British were supportive of the Zionist project, but as long as the Ottoman Empire was in charge of Palestine and the British could extend control over it, they weren’t interested in establishing such a state themselves. So the Zionist movement with Herzl in the lead turned to the Ottoman Empire in 1901. He envisioned the Zionist colonial project as a land company, modeled after the British and Dutch East Indian Companies, which would under imperial blessing operate fairly independently and govern over colonized land. The end goal was to build an ethnonationalist Jewish state and expel the native population. There were even dreams of Jewish empire that would colonize neighbouring countries, “civilize” them and bring them “prosperity”. To persuade the Sultan, Herz proposed to pay for the Ottoman Empire’s depts with European Jewish investments in exchange for allowing the Zionists to settle and govern Palestine. The Ottoman government was well aware of Zionist movement’s end goals and their alliances with European Imperialism, rejecting their proposals.
The Zionists evaded Ottoman restrictions anyway and continued to settle Palestine with British backing. European powers then pressured Ottomans to abolish those restrictions allowing a new wave of Zionist colonialism. The violence and pogroms in Russia had convinced some of the Eastern European Jewish socialists that fighting antisemitism was impossible, so they created Labor Zionism and used the “untouched land” to experiment with utopian socialist communes. In the process they displaced indigenous peasant hamulas, which had often for centuries farmed the land in communal ownership. Mass migration and eviction quickly provoked a predictable opposition in the Palestinian population and spread of Arab nationalist thought. This second wave of Aliyah ended at the First World War, which was also the end of the Ottoman Empire.
#history#palestine#palestinian genocide#palestinian history#colonization#colonial history#zionism#islamophobia#ottoman empire
164 notes
·
View notes
Note
I think Bryan was actually a Democratic nominee, not Republican.
Yes, thanks for catching that so I could fix it! William Jennings Bryan was indeed the Democratic Presidential nominee in 1896, 1900, and 1908 and lost all three races (twice to William McKinley and the third time to William Howard Taft). Bryan's brother, Charles W. Bryan -- who was Governor of Nebraska at the time -- was also nominated by the Democrats as their 1924 Vice Presidential nominee on the ticket with John W. Davis. (He also lost.)
#Presidential Campaigns#History#Politics#Presidential Politics#Presidential Elections#Presidential nominees#William Jennings Bryan#1896 Election#1900 Election#1908 Election#Charles W. Bryan#1924 Election#Democratic Party#Democratic Presidential nominees
6 notes
·
View notes
Text

Waking Up!
September 24, 1908
The voter wakes up to Taft as the sun, while the alarm clock that woke him up for the primaries lies on the floor.
As President Roosevelt's hand-picked nominee, Taft stood a very good chance of winning the election, and was set to make an appearance in the Twin Cities on the September 26th, according to the September 24th edition of the Minneapolis Tribune.
See Also: William Howard Taft
From Hennepin County Library
Original available at: https://digitalcollections.hclib.org/digital/collection/Bart/id/5722/rec/2081
#charles bartholomew#political cartoon#1908 presidential election#william howard taft#american history
4 notes
·
View notes
Text

Hello there, looks like my last post was actually just a WIP.
Guess who took that picture ;)
Some nerd details I want to elaborate on here, this picture was taken in 1907 because the Ishbal civil war started on 1908, In my head Roy and Riza got deployed to Resembool (that is right beside Ishbal) in some kind of stationary job in the military as a preventive measure for the conflicts before they got to evolve into war.
Given that Roy and Riza met in 1905 as teenagers, they got roped into this political conflict and war at a very young age so I like to think they got to have some peace and enjoy their last teenage years.
The “Colonel Roy Mustang” comment can be taken as both the literal meaning of him being a colonel or as a satiric remark made by Riza in a teasing manner (if we want to do a deep dive into canon and think that he wasn’t a colonel at the time, he was most likely 19 or 20 when the war begun.)
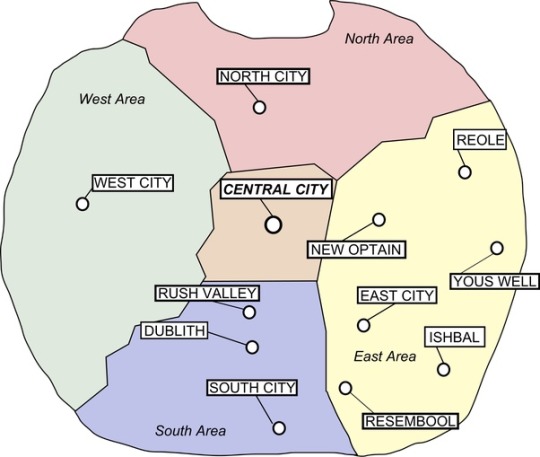
#someone is going to have to take this out of my cold dead hands#young royai#fullmetal alchemist brotherhood#fma fanart#fullmetal alchemist#fullmetal Alchemist fanart#fmab#fmab fanart#fma brotherhood#roy mustang/riza hawkeye#roy mustang#riza hawkeye#royai#royai fanart#fma royai#fmab roy#fmab riza#my art
271 notes
·
View notes