#12 February 1809
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text


Two world renowned men were born on this day, 12 February, 1809. One in the U.S. saved the Constitution and the Union. The other born in the U.K. established a new branch of biology, evolution.
0 notes
Text
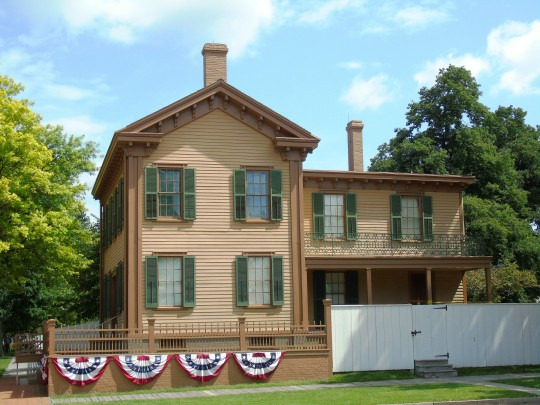
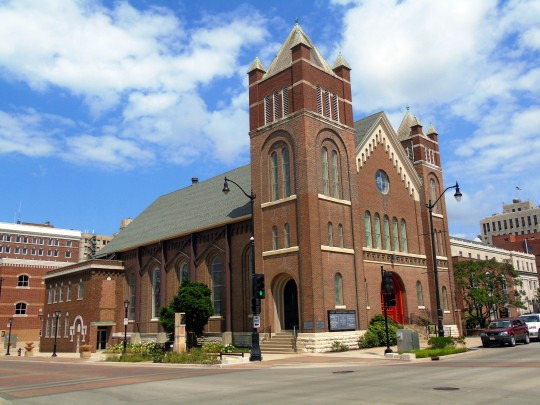
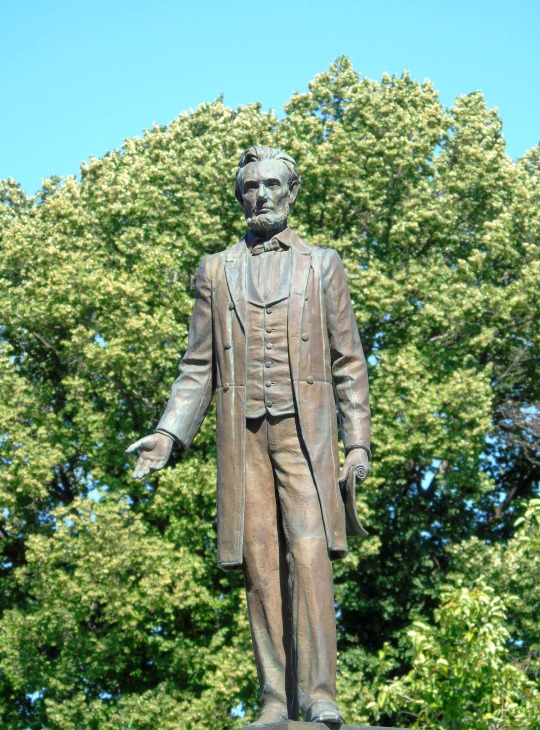
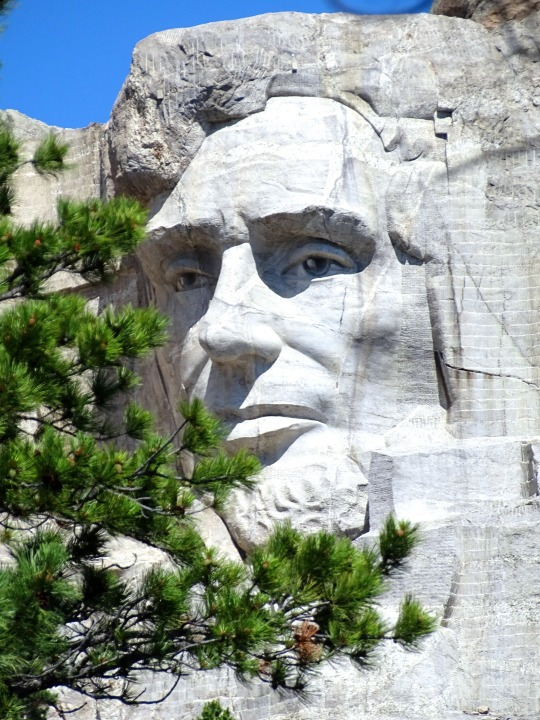


















Lincoln's Birthday
Abraham Lincoln, the 16th President of the United States, was born on February 12, 1809. Over the years, he has become known as one of the greatest American presidents of all time. At the time of his death, in 1865, many saw him as a martyr, and it wasn't too long afterward that his birthday began being observed informally. In the mid-1870s, Julius Francis of Buffalo, New York, began honoring Lincoln on his birthday and petitioned Congress to make the day a legal holiday.
But, as of 2019, Lincoln's Birthday is not, nor has it ever been, its own federal holiday. On the state level, a handful of states celebrate Lincoln's birthday on its actual date. In recent years, it has been celebrated as a state holiday in Ohio, Missouri, New York, Illinois, and Connecticut. It is celebrated as such in California as well, but since 2009, it has no longer been a paid holiday there. Some states, Indiana being one example, have officially celebrated Lincoln's birthday, but not on the actual date of his birth. In prior years, more states officially celebrated his birthday; twenty-four states celebrated it in 1940, and ten celebrated it in 1990.
Although Lincoln's Birthday is not celebrated on its own on the federal level, it is often implicitly or explicitly celebrated as part of Washington's Birthday, which is usually called Presidents' Day, taking place on the third Monday in February. In some states, this holiday is known as Washington and Lincoln Day. However, there are other variations of the day; some states specifically celebrate only Washington, and some celebrate Washington and another president, such as Thomas Jefferson.
Besides state observances and informal federal observances, Lincoln's Birthday is celebrated at many places associated with him. Each year, there is a wreath-laying ceremony at the Abraham Lincoln Birthplace National Historical Park in Kentucky. Since its dedication in the early 1920s, there has also been a wreath-laying ceremony at the Lincoln Memorial, which is organized by the Lincoln Birthday National Commemorative Committee and the Military Order of the Loyal Legion of the United States. The reading of the Gettysburg Address is also a part of this event. For his bicentennial, on February 12, 2009, the Abraham Lincoln Bicentennial Commission organized a special event at the Lincoln Memorial. That same day, four new Lincoln pennies were released, with backs that depicted different stages of Lincoln's life. Each year on the day, events are also held at the Abraham Lincoln Presidential Library and Museum in Illinois. The Republican Party holds Lincoln Day dinners around the date because Lincoln was the first Republican president.
Abraham Lincoln was born in a one-room log cabin just south of present-day Hodgenville, Kentucky. When he was two, his family moved to Knob Creek Farm, which is northeast of Hodgenville. In 1816, he moved with his family to Indiana. He did not get much schooling while growing up and often had to work to help support his family, doing things such as farming and splitting rails for fences.
In 1830, his family moved to Macon County, Illinois. He got a job on a boat, hauling freight down the Mississippi River to New Orleans. He then settled in West Salem, Illinois, where he worked as a shopkeeper in a store as well as a postmaster. In 1832, he was a captain in the Black Hawk War and ran for a spot in the Illinois state legislature, which he lost. However, he ran again in 1834 and was successful. As a member of the Whig Party, he was influenced by other Whigs such as Henry Clay and Daniel Webster. Some policy positions he held at the time were in opposition to slavery's spread to the territories, and a goal of expanding the United States with a focus on commerce and cities.
Lincoln decided to teach himself law and passed the bar in 1836. Shortly thereafter, he moved to Springfield, a few years before it became the state's capital. He married Mary Todd in 1842; they had four sons together, although only one would live into adulthood. Lincoln was elected to the U.S. House of Representatives in 1846, but pledging to serve only one term, he returned to Springfield in 1849. His opposition to the Mexican-American War is the most remembered element of his term.
Politics were in Lincoln's blood, and he decided to return to them in 1854. That year, Democrat Stephen Douglas had helped get the Kansas-Nebraska Act passed, which said there should be popular sovereignty when it came to slavery in the territories, meaning that voters should be able to decide for themselves if slavery should be allowed in them. On October 16, 1854, in Peoria, Illinois, Lincoln debated Douglas about the act. During the debate, he spoke against slavery and said it was incongruous with the Declaration of Independence. That same year, he joined the recently formed Republican Party, a party that was created in large part on the belief that slavery should not expand into the territories.
In 1858, Lincoln ran against Stephen Douglas for a U.S. Senate seat in Illinois. In June, he gave his house divided speech, which said the country couldn't go on existing half slave and half free. Lincoln lost the race but gained national recognition, in part because of the debates he had with Douglas.
The Republicans nominated Lincoln as their candidate for president in the 1860 election. It was a four-way race: Stephen Douglas was the nominee of northern Democrats, John C. Breckenridge was the nominee of southern Democrats, and John Bell was the nominee of the Constitutional Union Party. Breckenridge and Bell split the southern votes, and Lincoln won most of the north. He won the electoral vote count, and thus the presidency. By the time he had taken the oath of office in March 1861, seven states had already seceded from the Union; the Civil War began the following month.
The Civil War engulfed Lincoln's presidency, but he proved to be an adept war leader. After George McClellan failed to pursue the Confederate Army after the Union victory at Antietam in September 1862, Lincoln removed him of his position of Commanding General. Lincoln also issued the Emancipation Proclamation after Antietam, which went into effect on January 1, 1863, freeing slaves in the southern states (slaves in the border states loyal to the Union were not freed). The emancipation laid the groundwork for slaves to be freed everywhere—the Thirteenth Amendment went into effect in 1865, after Lincoln's death.
In November 1863, Lincoln delivered the Gettysburg Address at a dedication of the national cemetery at Gettysburg. It became one of the most famous speeches in American history. Although Lincoln has been lauded for fulfilling the commander-in-chief role, he did so not completely without controversy, as he suspended habeas corpus.
In 1864, Lincoln faced the general he had relieved, George McClellan, in his bid for reelection. He prevailed, and at his second inaugural he spoke of the end of the war, and the need for a conciliatory reconstruction "with malice toward none; with charity for all." On April 9, 1865, Confederate commander Robert E. Lee surrendered to Union Commanding General Ulysses S. Grant at Appomattox Court House. Two days later, Lincoln gave a speech on the White House lawn.
On April 14, which happened to be Good Friday, President Lincoln was shot in the back of the head by John Wilkes Booth while at Ford's Theatre. He died early the next morning at a boarding house across from the theatre. Today we remember his remarkable life and his contributions to the United States at such a difficult time in its history.
How to Observe Lincoln's Birthday
The following are some ways to celebrate Lincoln's Birthday:
Visit the Abraham Lincoln Birthplace National Historical Park. This encompasses both his birthplace south of Hodgenville, as well as Knob Creek Farm, where he lived next. A wreath-laying ceremony takes place at the park.
Stop at the Lincoln Museum in downtown Hodgenville as well as the nearby Abraham Lincoln Statue.
Stop at other places along the Kentucky Lincoln Heritage Trail.
Attend the wreath-laying ceremony at the Lincoln Memorial.
Visit the Abraham Lincoln Presidential Library and Museum and The Lincoln Tomb in Springfield, Illinois.
Stop at the Lincoln Boyhood National Memorial in Indiana or at the Abraham Lincoln Library and Museum in Tennessee.
Go to Ford's Theatre.
Read a book about Lincoln.
Read some of Lincoln's own writings and speeches.
Source
#Lincoln's Birthday#Abraham Lincoln#born#12 February 1809#anniversary#Lincoln Memorial#Henry Hering#Lincoln Home#Lincoln Home National Historic Site#Seated Lincoln#Augustus Saint Gaudens#First Presbyterian Church of Springfield#Lincoln Family Church#statue#art#Washington DC.#Springfield#Indianapolis#Chicago#USA#photography#history#travel#original photography#vacation#tourist attraction#landmark#cityscape#architecture#US history
0 notes
Text

Happy birthday to Abraham Lincoln! (February 12, 1809)
13 notes
·
View notes
Text
“America will never be destroyed from the outside. If we falter and lose our freedoms, it will be because we destroyed ourselves.”
- Abraham Lincoln, born on February 12, 1809

243 notes
·
View notes
Text

Happy Birthday Charles Darwin Born today, 12 February 1809
194 notes
·
View notes
Text
and abe lincoln
happy birthday to the biologist of all time charles darwin it’s you and me in this together forever girl
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
Cabin Fever! How the log cabin shaped American history 🪓
Cabins have long been a symbol of the American frontier spirit, a testament to self-reliance and ingenuity. They played a vital role in the early settlement of the United States and have become an enduring symbol of the nation's pioneering past.

Early Colonial Period
Cabins were an essential form of shelter for European settlers in the 17th and 18th centuries. Built from logs with notched corners, cabins were relatively simple to construct, allowing settlers to establish shelter quickly. This design, known as the log cabin, became synonymous with frontier life.


Abraham Lincoln's Birthplace
One of the most famous cabins in American history is the one where Abraham Lincoln was born on February 12, 1809, in Hardin County, Kentucky. The symbolic importance of Lincoln's log cabin birthplace reflects the "log cabin to White House" narrative that emphasizes his rise from humble beginnings. Though the authenticity of the existing cabin at the Abraham Lincoln Birthplace National Historical Park is disputed, it still stands as a symbol of American perseverance and determination.

Western Expansion
As pioneers moved westward, log cabins continued to play a vital role in American expansion. The log cabin's simplicity made it an ideal choice for settlers needing to build shelter quickly. Many of these cabins became the nucleus of burgeoning communities.

Thoreau's Cabin at Walden Pond
In the 19th century, cabins also began to symbolize a return to nature and simple living. Henry David Thoreau's cabin at Walden Pond, where he lived from 1845 to 1847, became an emblem of deliberate, contemplative living. Thoreau's experiment was not only a personal retreat but also a critique of modern society, and his cabin remains an iconic representation of the American transcendentalist movement.

Presidential Retreats
Cabins have also served as retreats for American presidents. Camp David, officially known as the Naval Support Facility Thurmont, is the country's premier presidential retreat, featuring rustic cabins. It has been used by presidents for rest and diplomatic meetings since Franklin D. Roosevelt's administration.

Cabins in Modern Culture
In modern times, cabins continue to symbolize simplicity and a connection to nature. They are often associated with vacation retreats and are emblematic of a desire to return to a less complicated way of life. Check out the hundreds of photographs of cabins in our Catalog!
283 notes
·
View notes
Text

Charles Darwin, b. 12 February 1809 / 2025


(images: Memorials of Charles Darwin. A collection of manuscripts, portraits, medals, books, and natural history specimens to commemorate the Centenary of his birth and the fiftieth anniversary of the publication of 'The origin of species', «British Museum (Natural History). Special Guide» 4, British Museum, London, 1909)
#graphic design#manuscript#biology#natural history#antropology#book#cover#book cover#charles darwin#birthday anniversary#british museum#1800s#1900s#2020s
12 notes
·
View notes
Text
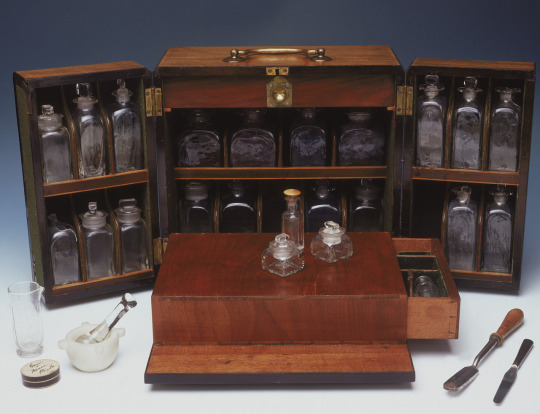

Naval Surgeon's medicine chest, belonging to surgeon Sir Benjamin F. Outram (1774-1856) and reputedly used at the battle of Copenhagen 1801
Outram was first employed in the naval medical service in 1794, and was promoted to the rank of surgeon in 1796. He served in HMS Harpy, HMS La Nymphe, and HMS Boadicea. He was surgeon in HMS Superb in the second battle of Algeciras, where Sir James Saumarez obtained a victory over the French and Spanish fleets on 12 July 1801. He received war medals and clasps for his services under Sir Richard Goodwin Keats. Then for a period he was surgeon to the royal yacht, HMS Royal Sovereign.
In 1806, with a view to private practice, Outram went to Edinburgh, and there graduated doctor of medicine on 24 June 1809. He was admitted a licentiate of the Royal College of Physicians of London on 16 April 1810, and then began as a physician at Hanover Square in London, where he lived more than 40 years. He acted as physician to the Welbeck Street Dispensary. On 3 May 1838 he was elected a fellow of the Royal Society; he also became an early member of the Royal Geographical Society.
In 1841 Outram became medical inspector of her Majesty's fleets and hospitals. He was appointed Knight Commander of the Order of the Bath (KCB) on 17 September 1850, and was admitted a fellow of the Royal College of Physicians on 9 July 1852. He died at Brighton on 16 February 1856, and was buried at Clifton, Bristol.
#naval history#naval artifacts#medicine chest#sir benjamin outram#battle of copenhagen#naval surgeon#early 19th century#age of sail#history
115 notes
·
View notes
Text
February 11, 2025
HEATHER COX RICHARDSON
FEB 12
On February 12, 1809, Nancy Hanks Lincoln gave birth to her second child, a son: Abraham.
Abraham Lincoln grew up to become the nation’s sixteenth president, leading the country from March 1861 until his assassination in April 1865, a little over a month into his second term. He piloted the country through the Civil War, preserving the concept of American democracy. It was a system that had never been fully realized but that he still saw as “the last, best hope of earth” to prove that people could govern themselves.
Lincoln grew up in rural poverty as wealthy enslavers took over prime land in his family's home state of Kentucky and pushed them across the Ohio River to Indiana, where Nancy Lincoln died. From there, they moved on to the frontier state of Illinois, where Abraham sowed seed, hoed fields, grubbed roots, cut trees, made fences, and harvested crops both at home and for farmers to whom his father hired him out for wages, for the elder Lincoln never managed to get his feet under him after leaving Kentucky.
In 1831, finally an adult, Abraham set out to make his mark in the world, as did thousands of other young men in his dynamic era. But making it on his own wasn’t much easier for the young Lincoln than it had been for his father. He settled in the town of New Salem, a village of about a hundred people on a bluff above the Sangamon River, where he failed as a storekeeper, then cobbled together various jobs, eking out a living splitting rails and making deliveries. Government appointments, first as a postmaster and then as a surveyor, kept him afloat and made him well enough known that in 1834, voters elected him to the state legislature, and he was on his way to prominence.
Lincoln’s time as a young man on the make had made him think hard about the relationship between Americans and their government. In his era, elite southern enslavers insisted that government had no role to play in the country except in protecting property, a concept of government that permitted them to amass fortunes thanks to the labor of their Black neighbors. But Lincoln had watched his town of New Salem die because its settlers—hard workers, eager to make the town succeed—could not dredge the Sangamon River to promote trade by themselves.
Lincoln later mused, “The legitimate object of government is ‘to do for the people what needs to be done, but which they can not, by individual effort, do at all, or do so well, for themselves,’… as public roads and highways, public schools, charities, pauperism, orphanage, estates of the deceased, and the machinery of government itself.”
Once elected to the presidency, Lincoln joined with members of his new Republican Party to make the government work for the American people. They created national money and the income tax. They took land from speculators and gave it to men willing to farm it. They established public colleges to enable poor men to get an education, the Department of Agriculture to make sure poor men had access to good seeds, and transcontinental railroads so poor men could both get to western lands and get their products back to eastern markets. And they used the power of the federal government to end human enslavement in the United States except as punishment for crime.
A generation later, under Republican president Theodore Roosevelt, progressives at the turn of the twentieth century expanded on Lincoln's understanding of the role of government in supporting the American people. In that era, corrupt industrialists increased their profits by abusing their workers, adulterating milk with formaldehyde and painting candies with lead paint, dumping toxic waste into neighborhoods, and paying legislators to let them do whatever they wished.
Those concerned about the survival of democracy worried that individuals were not actually free when their lives were controlled by the corporations that poisoned their food and water while making it impossible for individuals to get an education or make enough money ever to become independent.
To restore the rights of individuals, progressives of both parties argued that individuals needed a strong, active government to protect them from the excesses and powerful industrialists of the modern world. Under the new governmental system that Theodore Roosevelt pioneered, the government cleaned up the sewage systems and tenements in cities, protected public lands, invested in public health and education, raised taxes, and called for universal health insurance, all to protect the ability of individuals to live freely without being crushed by outside influences.
Reformers sought, as Roosevelt said, to return to “an economic system under which each man shall be guaranteed the opportunity to show the best that there is in him.”
In the 1920s, the idea that the government should be run as a business eclipsed Roosevelt’s progressive government, but after the Great Crash of 1929 and the ensuing Great Depression, Democrats under President Franklin Delano Roosevelt in the 1930s offered a “new deal for the American people.” That New Deal meant that the government would no longer work simply to promote business, but would also regulate business, provide a basic social safety net, and promote infrastructure. World War II accelerated the construction of that active government, and by the time it was over, Americans quite liked the new system.
After the war, Republican Dwight Eisenhower embraced the active government. He explained that in the modern world, the government must protect people from disasters created by forces outside their control, and it must provide social services that would protect people from unemployment, old age, illness, accidents, unsafe food and drugs, homelessness, and disease.
He called his version of the New Deal “a middle way between untrammeled freedom of the individual and the demands of the welfare of the whole Nation.” One of his supporters echoed Lincoln when he explained, “If a job has to be done to meet the needs of the people, and no one else can do it, then it is the proper function of the federal government.” Both Republicans and Democrats embraced this idea, which became known as the “liberal consensus.” In the second half of the twentieth century, they expanded the role of government to protect civil rights, the environment, access to healthcare and education, equal opportunity in employment, and so on.
But those who objected to the liberal consensus rejected the idea that the government had any role to play in the economy or in social welfare and made no distinction between the liberal consensus and international communism. They insisted that the country was made up of “liberals,” who were pushing the nation toward socialism, and “conservatives” like themselves, who were standing alone against the Democrats and Republicans who made up a majority of the country and liked the new business regulations, safety net, infrastructure, and protection of civil rights.
That reactionary mindset came to dominate the Republican Party after Ronald Reagan’s election in 1980. Republicans began to insist that anyone who embraced the liberal consensus of the past several decades was un-American and had no right to govern, no matter how many Americans supported that ideology. And now, forty-five years later, we are watching as a group of reactionaries dismantle the government that serves the needs of ordinary Americans and work, once again, to concentrate wealth and power in the hands of an elite.
The idea of a small government that serves the needs of a few wealthy people, Lincoln warned in his era, is “the same old serpent that says you work and I eat, you toil and I will enjoy the fruits of it. Turn in whatever way you will—whether it come from the mouth of a King, an excuse for enslaving the people of his country, or from the mouth of men of one race as a reason for enslaving the men of another race, it is all the same old serpent.”
—-
9 notes
·
View notes
Note
How many presidents have had both of their parents alive when they were president?
Three Presidents have had both parents alive when they became President:
•Ulysses S. Grant Grant was the first President with both of his parents alive at the time of his inauguration. His father, Jesse Root Grant, died on June 29, 1873 during Grant’s second term. His mother, Hannah Simpson Grant, survived both of his terms and died two years before he did, on May 11, 1883. •John F. Kennedy Not only were both of JFK’s Presidents alive when he became President, but they are the only parents of a President who both outlived him. JFK was assassinated in 1963. His father, Joseph P. Kennedy Sr., died in 1969, and his mother, Rose Fitzgerald Kennedy died in 1995 at the age of 104. •George W. Bush Both of Bush’s parents were alive when he took office and survived his entire two-term Presidency. His father, former President George H.W. Bush, died on November 30, 2018, just six months after the death of his mother, Barbara Bush, in April 2018.
Several Presidents have had either their father or mother still alive when they became President:
FATHER •John Quincy Adams: The first son of a President to be elected President himself was also the first President whose father was still alive at the time of his inauguration. John Adams died July 4, 1826, a little over a year into JQA’s Presidency. •Millard Fillmore: Nathaniel Fillmore lived through his son’s entire Presidency (1850-1853) and died in his 90s during the Civil War, on March 28, 1863. •Warren G. Harding: Harding’s father, George Tryon Harding, lived through his son’s entire Administration and died on November 19, 1928. Harding, who died in office on August 2, 1923, was the first President who was outlived by his father. •Calvin Coolidge: Not only did Coolidge’s father, John Calvin Coolidge, live to see his son become President, but he actually administered the oath of office. Coolidge, the Vice President at the time, was visiting his father when President Harding died in office and the elder Coolidge, a notary public, administered the Presidential oath at the family home in Vermont. Coolidge’s father died on March 18, 1926 during President Coolidge’s second term.
MOTHER •George Washington: Mary Ball Washington died August 25, 1789, a little less than four months after his first inauguration. •John Adams: Susanna Boylston Adams died April 21, 1797, just under two months after Adams became President. •James Madison: Eleanor Conway Madison lived through both of her son’s terms as President (1809-1817) and died February 11, 1829 at the age of 98. •James K. Polk: Polk was the first President who didn’t outlive his mother. She died on January 11, 1852, almost three years after Polk left office and died. •James Garfield: Garfield’s mother, Eliza Ballou Garfield, lived to see him become President and die in office. She died on January 21, 1888, almost seven years after he was assassinated. •William McKinley: McKinley’s mother, Nancy Allison McKinley, lived to attend her son’s first inauguration, but died several months later, December 12, 1897. •Franklin D. Roosevelt: FDR’s mother, Sara Delano Roosevelt, lived to see her son inaugurated three times. She died during her son’s third term, on September 7, 1941. •Harry S. Truman: Truman’s mother, Martha Young Truman, lived to see her son succeed to the Presidency in April 1945. She died during his first term, on July 26, 1947, at the age of 94. •Jimmy Carter: Lillian Carter lived through her son’s entire Presidency and was even sent to represent him at events overseas several times, which made her a celebrity in her own right during his Presidency. She died on April 30, 1983, two years after Carter left the White House. •George H.W. Bush: Bush’s mother, Dorothy Walker Bush, lived to see her son become President. She died on November 19, 1992, two weeks after her son lost his bid for re-election. •Bill Clinton: Virginia Cassidy Kelley, Clinton’s mother, lived to see him become President but died less than a year later, on January 6, 1994.
#Presidents#History#Presidency#Presidential History#Presidential Stats#Presidential Data#POTUS Stats#POTUS Data#First Families#Presidential Parents#Parents of the Presidents#Fathers of the Presidents#Mothers of the Presidents#Presidential Families
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
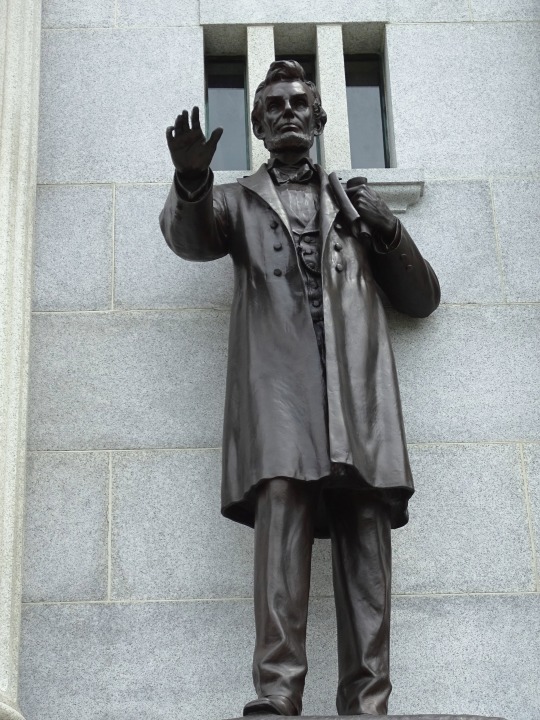
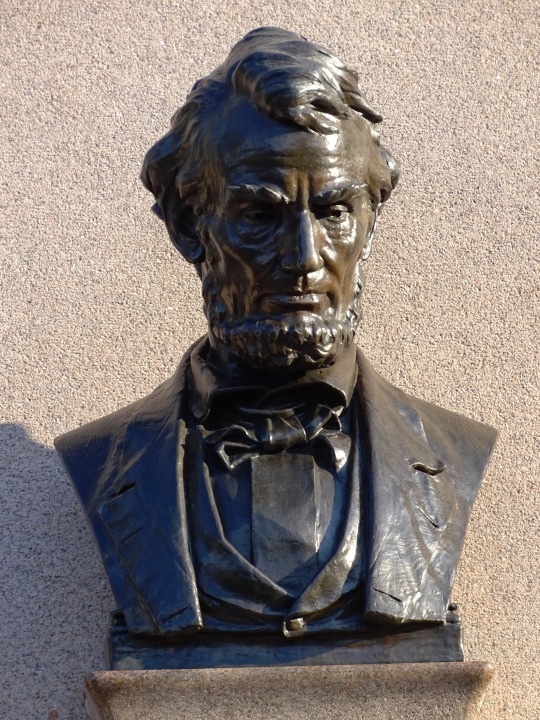
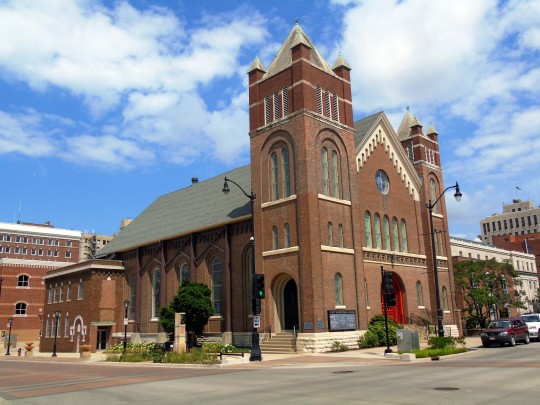
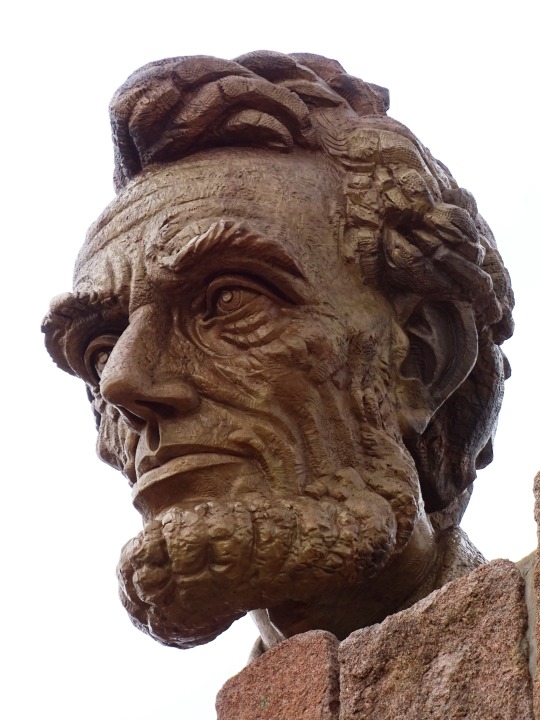
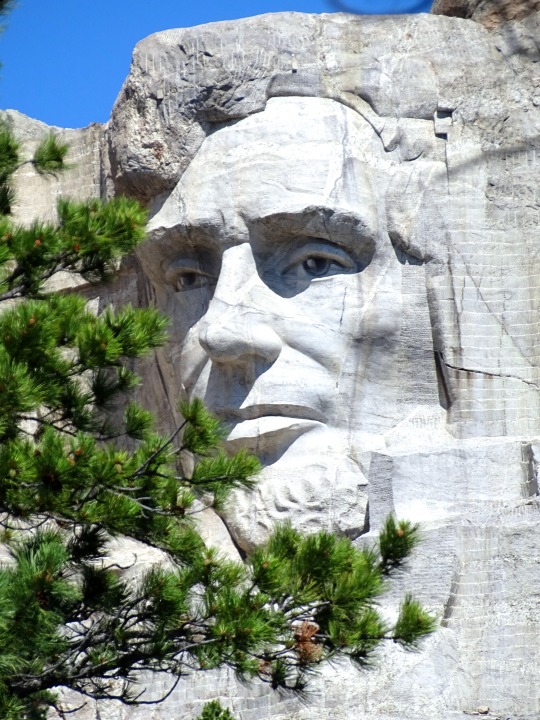
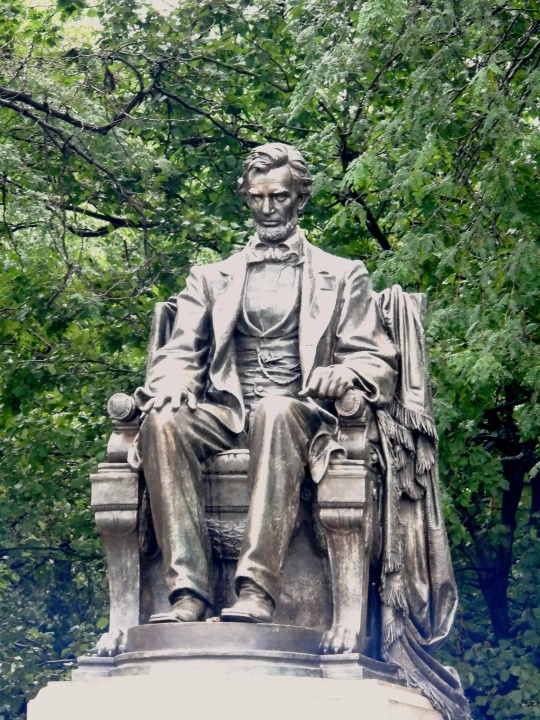
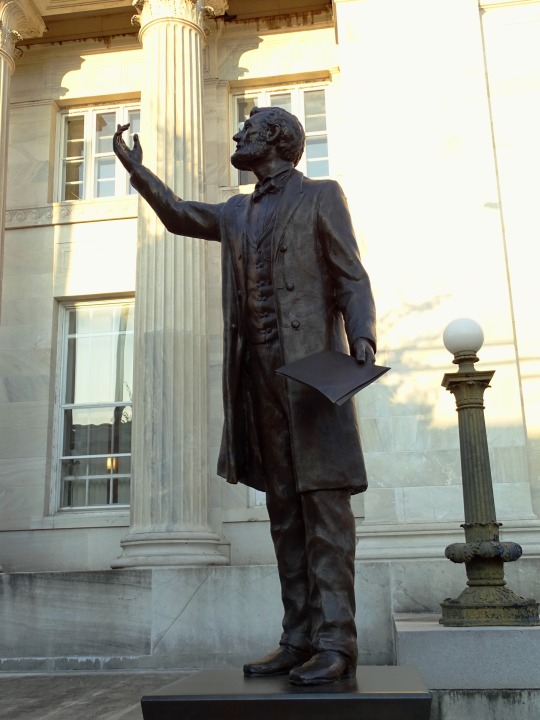
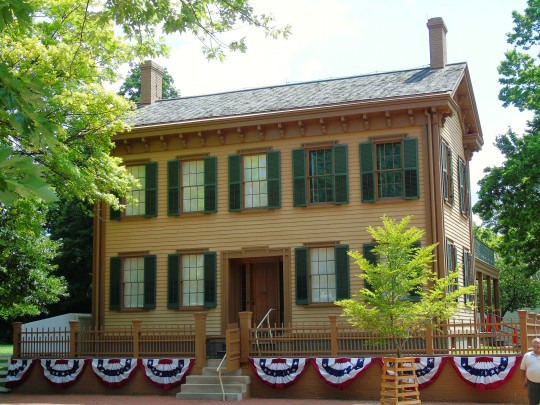
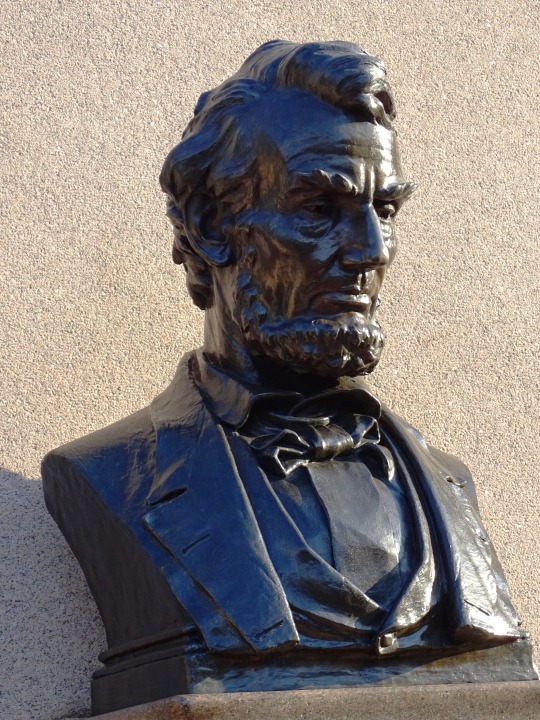
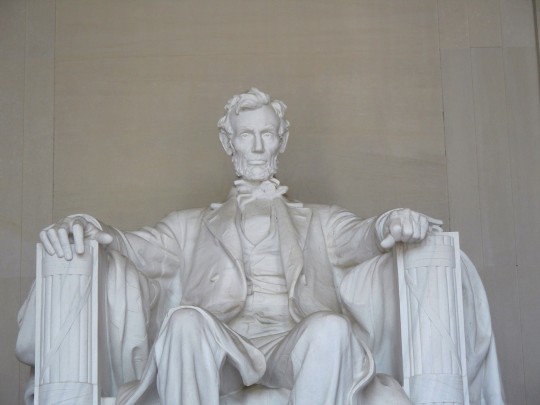




















Lincoln's Birthday
Abraham Lincoln, the 16th President of the United States, was born on February 12, 1809. Over the years, he has become known as one of the greatest American presidents of all time. At the time of his death, in 1865, many saw him as a martyr, and it wasn't too long afterward that his birthday began being observed informally. In the mid-1870s, Julius Francis of Buffalo, New York, began honoring Lincoln on his birthday and petitioned Congress to make the day a legal holiday.
But, as of 2019, Lincoln's Birthday is not, nor has it ever been, its own federal holiday. On the state level, a handful of states celebrate Lincoln's birthday on its actual date. In recent years, it has been celebrated as a state holiday in Ohio, Missouri, New York, Illinois, and Connecticut. It is celebrated as such in California as well, but since 2009, it has no longer been a paid holiday there. Some states, Indiana being one example, have officially celebrated Lincoln's birthday, but not on the actual date of his birth. In prior years, more states officially celebrated his birthday; twenty-four states celebrated it in 1940, and ten celebrated it in 1990.
Although Lincoln's Birthday is not celebrated on its own on the federal level, it is often implicitly or explicitly celebrated as part of Washington's Birthday, which is usually called Presidents' Day, taking place on the third Monday in February. In some states, this holiday is known as Washington and Lincoln Day. However, there are other variations of the day; some states specifically celebrate only Washington, and some celebrate Washington and another president, such as Thomas Jefferson.
Besides state observances and informal federal observances, Lincoln's Birthday is celebrated at many places associated with him. Each year, there is a wreath-laying ceremony at the Abraham Lincoln Birthplace National Historical Park in Kentucky. Since its dedication in the early 1920s, there has also been a wreath-laying ceremony at the Lincoln Memorial, which is organized by the Lincoln Birthday National Commemorative Committee and the Military Order of the Loyal Legion of the United States. The reading of the Gettysburg Address is also a part of this event. For his bicentennial, on February 12, 2009, the Abraham Lincoln Bicentennial Commission organized a special event at the Lincoln Memorial. That same day, four new Lincoln pennies were released, with backs that depicted different stages of Lincoln's life. Each year on the day, events are also held at the Abraham Lincoln Presidential Library and Museum in Illinois. The Republican Party holds Lincoln Day dinners around the date because Lincoln was the first Republican president.
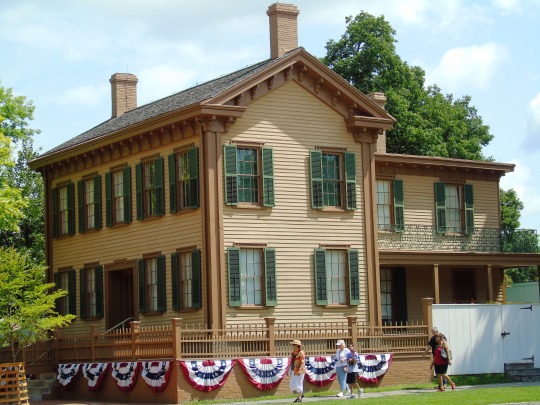
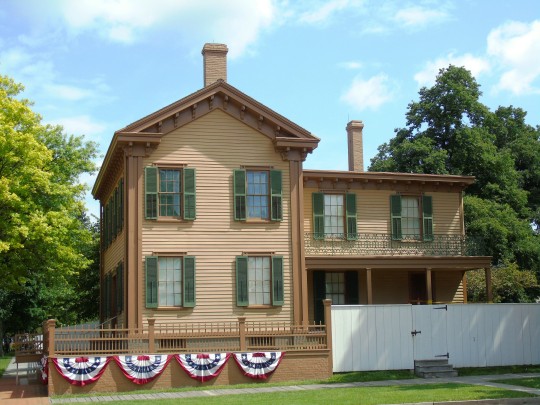
Abraham Lincoln was born in a one-room log cabin just south of present-day Hodgenville, Kentucky. When he was two, his family moved to Knob Creek Farm, which is northeast of Hodgenville. In 1816, he moved with his family to Indiana. He did not get much schooling while growing up and often had to work to help support his family, doing things such as farming and splitting rails for fences.
In 1830, his family moved to Macon County, Illinois. He got a job on a boat, hauling freight down the Mississippi River to New Orleans. He then settled in West Salem, Illinois, where he worked as a shopkeeper in a store as well as a postmaster. In 1832, he was a captain in the Black Hawk War and ran for a spot in the Illinois state legislature, which he lost. However, he ran again in 1834 and was successful. As a member of the Whig Party, he was influenced by other Whigs such as Henry Clay and Daniel Webster. Some policy positions he held at the time were in opposition to slavery's spread to the territories, and a goal of expanding the United States with a focus on commerce and cities.
Lincoln decided to teach himself law and passed the bar in 1836. Shortly thereafter, he moved to Springfield, a few years before it became the state's capital. He married Mary Todd in 1842; they had four sons together, although only one would live into adulthood. Lincoln was elected to the U.S. House of Representatives in 1846, but pledging to serve only one term, he returned to Springfield in 1849. His opposition to the Mexican-American War is the most remembered element of his term.
Politics were in Lincoln's blood, and he decided to return to them in 1854. That year, Democrat Stephen Douglas had helped get the Kansas-Nebraska Act passed, which said there should be popular sovereignty when it came to slavery in the territories, meaning that voters should be able to decide for themselves if slavery should be allowed in them. On October 16, 1854, in Peoria, Illinois, Lincoln debated Douglas about the act. During the debate, he spoke against slavery and said it was incongruous with the Declaration of Independence. That same year, he joined the recently formed Republican Party, a party that was created in large part on the belief that slavery should not expand into the territories.
In 1858, Lincoln ran against Stephen Douglas for a U.S. Senate seat in Illinois. In June, he gave his house divided speech, which said the country couldn't go on existing half slave and half free. Lincoln lost the race but gained national recognition, in part because of the debates he had with Douglas.
The Republicans nominated Lincoln as their candidate for president in the 1860 election. It was a four-way race: Stephen Douglas was the nominee of northern Democrats, John C. Breckenridge was the nominee of southern Democrats, and John Bell was the nominee of the Constitutional Union Party. Breckenridge and Bell split the southern votes, and Lincoln won most of the north. He won the electoral vote count, and thus the presidency. By the time he had taken the oath of office in March 1861, seven states had already seceded from the Union; the Civil War began the following month.
The Civil War engulfed Lincoln's presidency, but he proved to be an adept war leader. After George McClellan failed to pursue the Confederate Army after the Union victory at Antietam in September 1862, Lincoln removed him of his position of Commanding General. Lincoln also issued the Emancipation Proclamation after Antietam, which went into effect on January 1, 1863, freeing slaves in the southern states (slaves in the border states loyal to the Union were not freed). The emancipation laid the groundwork for slaves to be freed everywhere—the Thirteenth Amendment went into effect in 1865, after Lincoln's death.
In November 1863, Lincoln delivered the Gettysburg Address at a dedication of the national cemetery at Gettysburg. It became one of the most famous speeches in American history. Although Lincoln has been lauded for fulfilling the commander-in-chief role, he did so not completely without controversy, as he suspended habeas corpus.
In 1864, Lincoln faced the general he had relieved, George McClellan, in his bid for reelection. He prevailed, and at his second inaugural he spoke of the end of the war, and the need for a conciliatory reconstruction "with malice toward none; with charity for all." On April 9, 1865, Confederate commander Robert E. Lee surrendered to Union Commanding General Ulysses S. Grant at Appomattox Court House. Two days later, Lincoln gave a speech on the White House lawn.
On April 14, which happened to be Good Friday, President Lincoln was shot in the back of the head by John Wilkes Booth while at Ford's Theatre. He died early the next morning at a boarding house across from the theatre. Today we remember his remarkable life and his contributions to the United States at such a difficult time in its history.
How to Observe Lincoln's Birthday
The following are some ways to celebrate Lincoln's Birthday:
Visit the Abraham Lincoln Birthplace National Historical Park. This encompasses both his birthplace south of Hodgenville, as well as Knob Creek Farm, where he lived next. A wreath-laying ceremony takes place at the park.
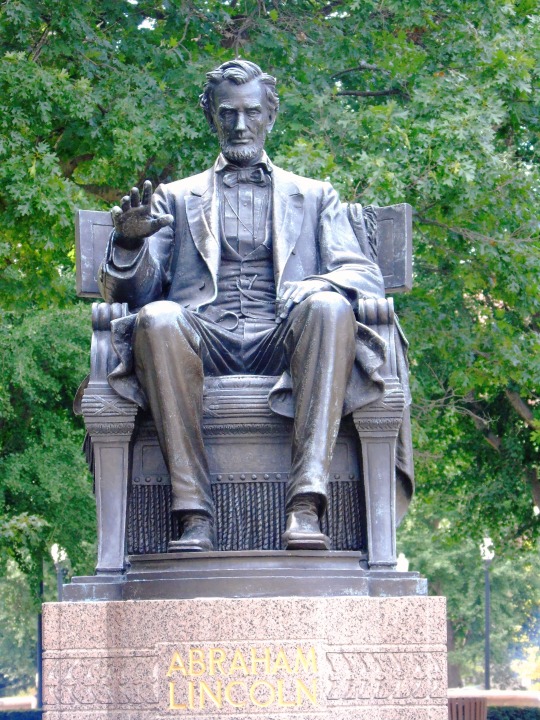
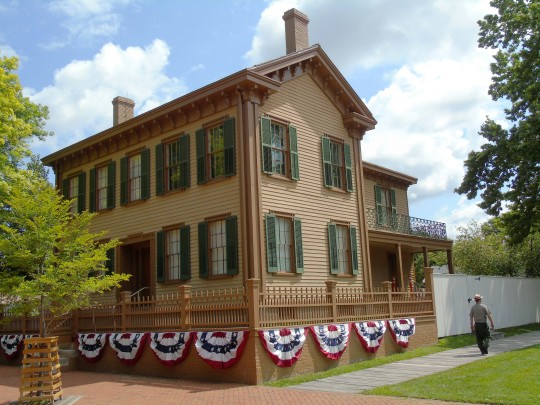
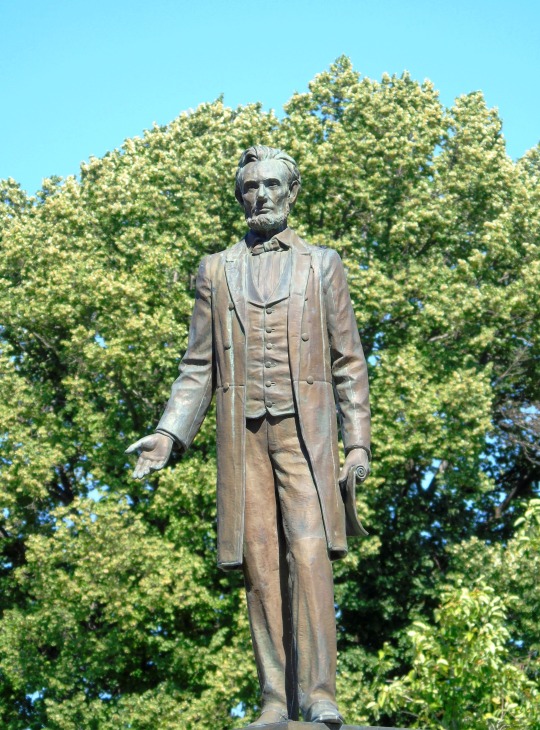
Stop at the Lincoln Museum in downtown Hodgenville as well as the nearby Abraham Lincoln Statue.
Stop at other places along the Kentucky Lincoln Heritage Trail.
Attend the wreath-laying ceremony at the Lincoln Memorial.
Visit the Abraham Lincoln Presidential Library and Museum and The Lincoln Tomb in Springfield, Illinois.
Stop at the Lincoln Boyhood National Memorial in Indiana or at the Abraham Lincoln Library and Museum in Tennessee.
Go to Ford's Theatre.
Read a book about Lincoln.
Read some of Lincoln's own writings and speeches.
Source
#Lincoln's Birthday#Abraham Lincoln#born#12 February 1809#215th anniversary#Lincoln Memorial#Henry Hering#Lincoln Home#Lincoln Home National Historic Site#Seated Lincoln#Augustus Saint Gaudens#First Presbyterian Church of Springfield#Lincoln Family Church#statue#art#Washington DC.#Springfield#Indianapolis#Chicago#USA#photography#history#travel#original photography#vacation#tourist attraction#landmark#cityscape#architecture#US history
1 note
·
View note
Text
"The idea of a small government that serves the needs of a few wealthy people, Lincoln warned in his era, is 'the same old serpent that says you work and I eat, you toil and I will enjoy the fruits of it. Turn in whatever way you will—whether it come from the mouth of a King, an excuse for enslaving the people of his country, or from the mouth of men of one race as a reason for enslaving the men of another race, it is all the same old serpent.'"
#us politics#american politics#USpol#politics#political#heather cox richardson#government#united states#coup#autogolpe#self coup#abraham lincoln#lincoln#small government#wealth gap#wealth inequality
4 notes
·
View notes
Link
To restore the rights of individuals, progressives of both parties argued that individuals needed a strong, active government to protect them from the excesses and powerful industrialists of the modern world. Under the new governmental system that Theodore Roosevelt pioneered, the government cleaned up the sewage systems and tenements in cities, protected public lands, invested in public health and education, raised taxes, and called for universal health insurance, all to protect the ability of individuals to live freely without being crushed by outside influences.
Reformers sought, as Roosevelt said, to return to “an economic system under which each man shall be guaranteed the opportunity to show the best that there is in him.”
In the 1920s, the idea that the government should be run as a business eclipsed Roosevelt’s progressive government, but after the Great Crash of 1929 and the ensuing Great Depression, Democrats under President Franklin Delano Roosevelt in the 1930s offered a “new deal for the American people.” That New Deal meant that the government would no longer work simply to promote business, but would also regulate business, provide a basic social safety net, and promote infrastructure. World War II accelerated the construction of that active government, and by the time it was over, Americans quite liked the new system.
After the war, Republican Dwight Eisenhower embraced the active government. He explained that in the modern world, the government must protect people from disasters created by forces outside their control, and it must provide social services that would protect people from unemployment, old age, illness, accidents, unsafe food and drugs, homelessness, and disease.
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
On February 12, 1809
Abraham Lincoln and Charles Darwin were born on the exact same day. I'm not into astrology but should there be some connections?
Many babies were born on February 12 in 1809. I suppose that if you believe in astrology, they were born under the same sign and star map. So shoukd they be similar? Abraham Lincoln and Charles Darwin are two of the babies born that day. I’m searching for connections across an ocean and finding none – other than greatness and changing their world and changing yours and mine too – which is no…

View On WordPress
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Bessières's correspondence
This is for @flowwochair: the index of the documents in the "Fonds Maréchal Bessières" in the French National Archives. Not much about the content, unfortunately. I summarised some points that I imagined were not all that interesting to you. Please let me know if there is something you'd want to have more details on and I will look if there is more.
1) Letters and orders by Napoleon to Bessières, dating from 1796 to 1813. It’s organized by the different armies and contains mostly »official« stuff of some importance, like documents related to the double abdication of the two Spanish Bourbon kings in 1808. Murat’s name is mentioned once, in connection with one document:
copies of Napoleon's instructions to Murat on how to deal with the Spanish, 17 and 28 April 1808
Maybe also of interest: some of the documents concern the reorganisation of the troops after the Russian campaign and date as late as mid and end-April 1813, so only days before his death
2) Letters from princes of the imperial family to Bessières
Mostly interesting because a large chunk seems to be labeled »a.s.«, which I believe to mean »autographe signée«, i.e., handwritten and signed. Most correspondence of important people would have been in the hands of secretaries, with the sender merely signing them. Bessières being worthy of receiving letters that these imperial princes had written themselves hints at a special position of trust.
41 letters from Joseph Bonaparte, related to events in Spain (1808 – 1811)
2 letters (not written by Jerome himself) about uprisings in Kassel in 1813
And here you go: 29 letters by Murat, in his own handwriting, relating to the daily report on the Guard, the policy to be followed, and to military events in Spain (dated 5 August 1805 to 5 June 1808)
Followed by some stuff for me: 22 letters from Eugène de Beauharnais, in his own handwriting and »d’un caractère surtout personnel« (of primarily private nature), dated 27 January 1805 - 5 June 1808
Other than that, there are letters from Josephine, Lebrun, Hortense, Stéphanie de Beauharnais, Méneval and the secretary of Madame Mère.
The rest of this section are documents related to Bessières’s military career, decorations etc.
3) Some personal letters. The connection between them escapes me
from Bessières to his sister-in-law (?), 22 February 1808.
from Bessières to a marshal on the reorganisation of the Guard, 27 January 1813.
from Madame la Maréchale concerning her financial distress, 12 December 1813 and 12 December 1814.
Facsimile of a letter from the Marshal to his wife, after his departure for the 1813 campaign
4) Certificates, letters of service and appointment, decorations
Some documents as early as 1792 among them, but mostly bits and bobs that seem unrelated
5) Letters adressed to Bessières – Army of Italy and Army of Egypt. 55 pieces
6) Ministers' reports to the Emperor and various letters. Plenty of documents and letters among them that are neither written by or adressed at Bessières
7) Imperial Guard I (Organisation, financial reports etc.)
8) Imperial Guard II (contains one more letter by Eugène!)
9) Imperial Guard III (Holland in 1810)
10) Legion of Honour and pay. 73 pieces, 1804 to 1813
11) Russia. Letters adressed to Bessières, situation reports, mostly from before the campaign started
12) Letters from Napoleon, the imperial family, the royal family and several famous personalities. A lot of them obviously from after Bessières’s death, among them (condolation) letters to Madame la Maréchale from
Napoleon - 6 May 1813
Madame Mère – 7 May 1813
Marie Louise – 5 May 1813
Caroline Murat – 25 May 1813
Eugène Beauharnais – 2 June 1813
Joachim Murat – 8 June 1813
Also contains 18 letters from Hortense de Beauharnais to Madame la Maréchale, dated 1809 to 1813, letters from Madame la Maréchale Oudinot, from Laure Junot, from Wellington (handwritten!) and plenty more
And on a happier note: a letter by Joachim Murat dated 1 Germinal year VIII (22 March 1800)
13) Related to Bessières’s city house
14) Correspondence between Marshal Bessières and Madame la Maréchale I
3 letters from Bessières to his wife, 2 prairial-15 vendémiaire an XIV (22 January-7 October 1805)
75 letters of Madame la Maréchale to Bessières, found in the cassette of the marshal after his death, 5 January 1806-1 May 1807
29 letters of Bessières to his wife, 26 March-13 December 1808
15) Correspondence between Marshal Bessières and Madame la Maréchale II. Continuation from above
72 (? I’m not sure about the numbering here) letters from Bessières to his wife, 5 January 1809, 28 September and ... 1811
48 (?) letters from Madame la Maréchale to the Marshal, January-9 December 1811
16) Correspondence between Marshal Bessières and Madame la Maréchale III. Continuation from above
9 letters from the Maréchale Bessières to her husband, 19 March - 16 December 1812
40 letters from Bessières to his wife, 13 January 1812 - 24 April 1813
17) Related to the electoral college of département Haute-Garonne
18) Personal papers, financial documents, real estate etc.
19) Letters to Madame la Maréchale during Restauration and July Monarchy
20) Collection of autographed letters unrelated to Bessières
39 notes
·
View notes