#$1.2 Billion
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Why is it that even today when you look up "three major religions" Judaism is in the top three on most of the search results?
Seriously y'all....why? Hinduism and Buddhism outnumber us by the hundreds of millions.
Hell even if you counted monotheistic faiths, we're still not top 3. Sikhism also outnumbers us.
We're 0.2% of the global population and 2.4% of the USA's population.
The only way this makes sense is if you're talking about the three major "Abrahamic" religions. But if that's the case maybe specifying that is important?
Btw there's also Bábism, Druzism, Samaritanism (Jewish kin), and the Baháʼí for "Abrahamic" religions.
537 notes
·
View notes
Text
it's so funny that Fall Out Boy is objectively more popular than My Chemical Romance but MCR gets more attention in bandom/as a fandom and festivals like When We Were Young bill accordingly, because, unlike MCR, it's possible to listen to Fall Out Boy and be normal
#there's also the comparative hype of MCR being martyred and then coming back from the dead#and fob's popularity peaking in the early 2010s for some reason. like 2018-2023 is a long gap but. covid happened#but Centuries has 2 BILLION streams on YOUTUBE. welcome to the black parade has HALF a billion#my theory definitely holds water#fall out boy#my chemical romance#fob#mcr#bandom#I said this#wait. how does. teenagers have 1 billions streams on spotify. and centuries is only 1.2 billion.#well their monthly listeners -- 25 mil vs 19 mil still support my point
37 notes
·
View notes
Text
Celebrate one billion by streaming!
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
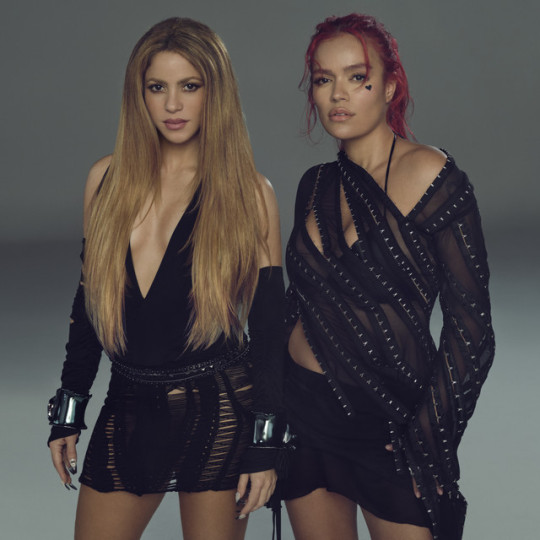


"TGQ" by Karol G and Shakira has surpassed 1.2 BILLION streams on Spotify.
— It is the most streamed Latin female collaboration on the platform.
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
Why is writing so hard
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
Things the Biden-Harris Administration Did This Week #39
October 18-25 2024.
President Biden issued the first presidential apology on behalf of the federal government to America's Native American population for the Indian boarding school policy. For 150 years the federal government operated a system of schools which aimed to destroy Native culture through the forced assimilation of native children. At these schools students faced physical, emotional, and sexual abuse, and close to 1,000 died. The Biden-Harris Administration has been historic for Native and Tribal rights. From the appointment of the first ever Native American cabinet member, Secretary of the Interior Deb Haaland, to the investment of $46 billion dollars on tribal land, to 200 new co-stewardship agreements. The last 4 years have seen a historic investment in and expansion of tribal rights.
The Biden-Harris Administration proposed a new rule which would make contraceptive medication (the pill) free over the counter with most Insurance. The new rule would ban cost sharing for contraception products, including the pill, condoms, and emergency contraception. On top of over the counter medications, the new rule will also strength protections for prescribed contraception without cost sharing as well.
The EPA announced its finalized rule strengthening standards for lead paint dust in pre-1978 housing and child care facilities. There is no safe level of exposure to lead particularly for children who can suffer long term developmental consequences from lead exposure. The new standards set the lowest level of lead particle that can be identified by a lab as the standard for lead abatement. It's estimated 31 million homes built before the ban on lead paint in 1978 have lead paint and 3.8 million of those have one or more children under the age of 6. The new rule will mean 1.2 million fewer people, including over 300,000 children will not be exposed to lead particles every year. This comes after the Biden-Harris Administration announced its goal to remove and replace all lead pipes in America by the end of the decade.
The Department of Transportation announced a $50 million dollar fine against American Airlines for its treatment of disabled passengers and their wheelchairs. The fine stems from a number of incidences of humiliating and unfair treatment of passages between 2019 and 2023, as well as video documented evidence of mishandling wheelchairs and damaging them. Half the fine will go to replacing such damaged wheelchairs. The Biden administration has leveled a historic number of fines against the airlines ($225 million) for their failures. It also published a Airline Passengers with Disabilities Bill of Rights, passed a new rule accessible lavatories on aircraft, and is working on a rule to require airlines to replace lost or damaged wheelchairs with equal equipment at once.
The Department of Energy announced $430 million dollars to help boost domestic clean energy manufacturing in former coal communities. This invests in projects in 15 different communities, in places like Texas, West Virginia, Pennsylvania, Tennessee, Kentucky, and Michigan. The plan will bring about 1,900 new jobs in communities struggling with the loss of coal. Projects include making insulation out of recycled cardboard, low carbon cement production, and industrial fiber hemp processing.
The Department of Transportation announced $4.2 billion in new infrastructure investment. The money will go to 44 projects across the country. For example the MBTA will get $400 million to replace the 92 year old Draw 1 bridge and renovate North Station.
The Department of Transportation announced nearly $200 million to replace aging natural gas pipes. Leaking gas lines represent a serious public health risk and also cost costumers. Planned replacements in Georgia and North Carolina for example will save the average costumer there over $900 on their gas bill a year. Replacing leaking lines will also remove 1,000 metric tons of methane pollution, annually.
The Department of the Interior announced $244 million to address legacy pollution in Pennsylvania coal country. This comes on top of $400 million invested earlier this year. This investment will help close dangerous mine shafts, reclaim unstable slopes, improve water quality by treating acid mine drainage, and restore water supplies damaged by mining.
Data shows that President Biden's Inflation Reduction Act (passed with Vice-President Harris' tie breaking vote) has saved seniors $1 billion dollars on out-of-pocket drug costs. Seniors with certain high priced drugs saw their yearly out of pocket costs capped at $3,500 for 2024. In 2024 all seniors using Medicare Part D will see their out of pocket costs capped at $2,000 for the year. It's estimated if the $2,000 cap had been in effect this year 4.6 million seniors would have hit it by June and not have had to pay any more for medication for the rest of the year.
The Department of Education announced a new proposed rule to bring student debt relief for 8 million struggling borrowers. The Biden-Harris Administration has managed despite road blocks from Republicans in Congress, the courts and law suits from Republican states to bring student loan forgiveness to 5 million Americans so far through different programs. This latest rule would take into account many financial hardships faced by people to determine if they qualify to have their student loans forgiven. The final rule cannot be finalized before 2025 meaning its fate will be decided at the election.
The Department of Agriculture announced $1.5 billion in 92 partner-driven conservation projects. These projects aim at making farming more susceptible and environmental friendly, 16 projects are about water conservation in the West, 6 support use of innovative technologies to reduce enteric methane emissions in livestock. $100 million has been earmarked for Tribal-led projects.
#Thanks Biden#Joe Biden#Kamala Harris#politics#US politics#American politics#Native Americans#indigenous rights#lead paint#reproductive rights#reproductive health#lead poisoning#disability#infastructure#climate change#drug prices
6K notes
·
View notes
Text
welp time to unfollow strayc*tj
#if you use g3n A I for fun you're still. using it lmao. giving it validity as a service ppl want. while wasting water!!!!#micros*ft's water usage went up by like 30% one year (aka it went UP TO 1.2 BILLION GALLONS)#also these companies totally haven't figured out how to like. balance the water usage with yknow. residential needs or being green#the energy consumption isn't as bad as crypt0 in a way but it is also worse bc it's 'invisible'#idk what's worse the ppl goin dont criticize ppl ever or the ppl going dont infantilize someone but are thus infantilizing them
0 notes
Text
I have a bunch of very specific experimental timepoints today and in between im running a sample across campus to load into the sequencer help
#sample being transported ALSO has a deadline#we are sequencing at the core#1.2 billion reads#it better work
0 notes
Text
writing can be so ridiculous. I wanted to write a cute librarian AU, but since the non-librarian is going to the library for their mom's holds (they're not the bookish type), I had to figure out why they moved back in after having lived on their own for a while (since librarians need master's degrees it would mess with the dynamic have the older person suddenly two years younger & straight out of college).
So now I'm writing a fic about the 2007-2009 financial recession.
#I don't know a damn thing about the Great Recession. I was 3 years old.#i COULD have him starting a job somehwere new and goign on his own but the tone of the fic is already 'turning your life around'#also that was part of the vision of the fic. flashback in the thrid paragraph of his mom telling him to go#I said this#writing#fanfiction#writing fanfic#writblr#my writing#fanfic#wait. how does. teenagers have 1 billions streams on spotify. and centuries is only 1.2 billion.#well their monthly listeners -- 25 mil vs 19 mil still support my point#<-- how are these tags on the wrong post????
5 notes
·
View notes
Note
Saw a tweet that said something around:
"cannot emphasize enough how horrid chatgpt is, y'all. it's depleting our global power & water supply, stopping us from thinking or writing critically, plagiarizing human artists. today's students are worried they won't have jobs because of AI tools. this isn't a world we deserve"
I've seen some of your AI posts and they seem nuanced, but how would you respond do this? Cause it seems fairly-on point and like the crux of most worries. Sorry if this is a troublesome ask, just trying to learn so any input would be appreciated.
i would simply respond that almost none of that is true.
'depleting the global power and water supply'
something i've seen making the roudns on tumblr is that chatgpt queries use 3 watt-hours per query. wow, that sounds like a lot, especially with all the articles emphasizing that this is ten times as much as google search. let's check some other very common power uses:
running a microwave for ten minutes is 133 watt-hours
gaming on your ps5 for an hour is 200 watt-hours
watching an hour of netflix is 800 watt-hours
and those are just domestic consumer electricty uses!
a single streetlight's typical operation 1.2 kilowatt-hours a day (or 1200 watt-hours)
a digital billboard being on for an hour is 4.7 kilowatt-hours (or 4700 watt-hours)
i think i've proved my point, so let's move on to the bigger picture: there are estimates that AI is going to cause datacenters to double or even triple in power consumption in the next year or two! damn that sounds scary. hey, how significant as a percentage of global power consumption are datecenters?
1-1.5%.
ah. well. nevertheless!
what about that water? yeah, datacenters use a lot of water for cooling. 1.7 billion gallons (microsoft's usage figure for 2021) is a lot of water! of course, when you look at those huge and scary numbers, there's some important context missing. it's not like that water is shipped to venus: some of it is evaporated and the rest is generally recycled in cooling towers. also, not all of the water used is potable--some datacenters cool themselves with filtered wastewater.
most importantly, this number is for all data centers. there's no good way to separate the 'AI' out for that, except to make educated guesses based on power consumption and percentage changes. that water figure isn't all attributable to AI, plenty of it is necessary to simply run regular web servers.
but sure, just taking that number in isolation, i think we can all broadly agree that it's bad that, for example, people are being asked to reduce their household water usage while google waltzes in and takes billions of gallons from those same public reservoirs.
but again, let's put this in perspective: in 2017, coca cola used 289 billion liters of water--that's 7 billion gallons! bayer (formerly monsanto) in 2018 used 124 million cubic meters--that's 32 billion gallons!
so, like. yeah, AI uses electricity, and water, to do a bunch of stuff that is basically silly and frivolous, and that is broadly speaking, as someone who likes living on a planet that is less than 30% on fire, bad. but if you look at the overall numbers involved it is a miniscule drop in the ocean! it is a functional irrelevance! it is not in any way 'depleting' anything!
'stopping us from thinking or writing critically'
this is the same old reactionary canard we hear over and over again in different forms. when was this mythic golden age when everyone was thinking and writing critically? surely we have all heard these same complaints about tiktok, about phones, about the internet itself? if we had been around a few hundred years earlier, we could have heard that "The free access which many young people have to romances, novels, and plays has poisoned the mind and corrupted the morals of many a promising youth."
it is a reactionary narrative of societal degeneration with no basis in anything. yes, it is very funny that laywers have lost the bar for trusting chatgpt to cite cases for them. but if you think that chatgpt somehow prevented them from thinking critically about its output, you're accusing the tail of wagging the dog.
nobody who says shit like "oh wow chatgpt can write every novel and movie now. yiou can just ask chatgpt to give you opinions and ideas and then use them its so great" was, like, sitting in the symposium debating the nature of the sublime before chatgpt released. there is no 'decay', there is no 'decline'. you should be suspicious of those narratives wherever you see them, especially if you are inclined to agree!
plagiarizing human artists
nah. i've been over this ad infinitum--nothing 'AI art' does could be considered plagiarism without a definition so preposterously expansive that it would curtail huge swathes of human creative expression.
AI art models do not contain or reproduce any images. the result of them being trained on images is a very very complex statistical model that contains a lot of large-scale statistical data about all those images put together (and no data about any of those individual images).
to draw a very tortured comparison, imagine you had a great idea for how to make the next Great American Painting. you loaded up a big file of every norman rockwell painting, and you made a gigantic excel spreadsheet. in this spreadsheet you noticed how regularly elements recurred: in each cell you would have something like "naturalistic lighting" or "sexually unawakened farmers" and the % of times it appears in his paintings. from this, you then drew links between these cells--what % of paintings containing sexually unawakened farmers also contained naturalistic lighting? what % also contained a white guy?
then, if you told someone else with moderately competent skill at painting to use your excel spreadsheet to generate a Great American Painting, you would likely end up with something that is recognizably similar to a Norman Rockwell painting: but any charge of 'plagiarism' would be absolutely fucking absurd!
this is a gross oversimplification, of course, but it is much closer to how AI art works than the 'collage machine' description most people who are all het up about plagiarism talk about--and if it were a collage machine, it would still not be plagiarising because collages aren't plagiarism.
(for a better and smarter explanation of the process from soneone who actually understands it check out this great twitter thread by @reachartwork)
today's students are worried they won't have jobs because of AI tools
i mean, this is true! AI tools are definitely going to destroy livelihoods. they will increase productivty for skilled writers and artists who learn to use them, which will immiserate those jobs--they will outright replace a lot of artists and writers for whom quality is not actually important to the work they do (this has already essentially happened to the SEO slop website industry and is in the process of happening to stock images).
jobs in, for example, product support are being cut for chatgpt. and that sucks for everyone involved. but this isn't some unique evil of chatgpt or machine learning, this is just the effect that technological innovation has on industries under capitalism!
there are plenty of innovations that wiped out other job sectors overnight. the camera was disastrous for portrait artists. the spinning jenny was famously disastrous for the hand-textile workers from which the luddites drew their ranks. retail work was hit hard by self-checkout machines. this is the shape of every single innovation that can increase productivity, as marx explains in wage labour and capital:
“The greater division of labour enables one labourer to accomplish the work of five, 10, or 20 labourers; it therefore increases competition among the labourers fivefold, tenfold, or twentyfold. The labourers compete not only by selling themselves one cheaper than the other, but also by one doing the work of five, 10, or 20; and they are forced to compete in this manner by the division of labour, which is introduced and steadily improved by capital. Furthermore, to the same degree in which the division of labour increases, is the labour simplified. The special skill of the labourer becomes worthless. He becomes transformed into a simple monotonous force of production, with neither physical nor mental elasticity. His work becomes accessible to all; therefore competitors press upon him from all sides. Moreover, it must be remembered that the more simple, the more easily learned the work is, so much the less is its cost to production, the expense of its acquisition, and so much the lower must the wages sink – for, like the price of any other commodity, they are determined by the cost of production. Therefore, in the same manner in which labour becomes more unsatisfactory, more repulsive, do competition increase and wages decrease”
this is the process by which every technological advancement is used to increase the domination of the owning class over the working class. not due to some inherent flaw or malice of the technology itself, but due to the material realtions of production.
so again the overarching point is that none of this is uniquely symptomatic of AI art or whatever ever most recent technological innovation. it is symptomatic of capitalism. we remember the luddites primarily for failing and not accomplishing anything of meaning.
if you think it's bad that this new technology is being used with no consideration for the planet, for social good, for the flourishing of human beings, then i agree with you! but then your problem shouldn't be with the technology--it should be with the economic system under which its use is controlled and dictated by the bourgeoisie.
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
World development is so hard. Like I gotta figure out why the core of the earth would change from lava to pure electricity when there's no way to scientifically explain that. Like i don't NEED to explain it but it's gonna bug me if i don't have a reason at all even if it's a ridiculous one
#world development stuff#best reason i got right now is 'there's so many robots on the planet that the core decided 'Wow i wanna do electricity too''#I have a timeframe to work with. i have 1.2 billion years of humans being dead and robots dominating the planet to work with here
1 note
·
View note
Text
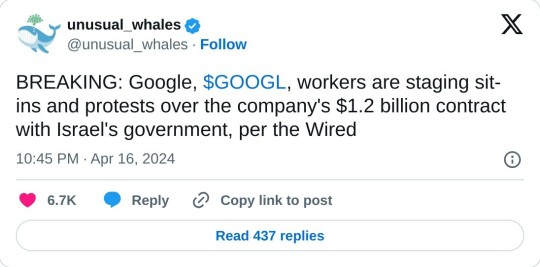
Dozens of Google employees began occupying company offices in New York City and Sunnyvale, California, on Tuesday in protest of the company’s $1.2 billion contract providing cloud computing services to the Israeli government. The sit-in, organized by the activist group No Tech for Apartheid, is happening at Google Cloud CEO Thomas Kurian’s office in Sunnyvale and the 10th floor commons of Google’s New York office. The sit-in will be accompanied by outdoor protests at Google offices in New York, Sunnyvale, San Francisco, and Seattle beginning at 2 pm ET and 11 am PT. Tuesday’s actions mark an escalation in a series of recent protests organized by tech workers who oppose their employer’s relationship with the Israeli government, especially in light of Israel’s ongoing assault on Gaza. Just over a dozen people gathered outside Google’s offices in New York and Sunnyvale on Tuesday. Among those in New York was Google cloud software engineer Eddie Hatfield, who was fired days after disrupting Google Israel’s managing director at March’s Mind The Tech, a company-sponsored conference focused on the Israeli tech industry, in early March. Several hours into the sit-ins on Tuesday, Google security began to accuse the workers of “trespassing” and disrupting work, prompting several people to leave while others vowed to remain until they were forced out. The 2021 contract, known as Project Nimbus, involves Google and Amazon jointly providing cloud computing infrastructure and services across branches of the Israeli government. Last week, Time reported that Google’s work on Project Nimbus involves providing direct services to the Israel Defense Forces. No Tech for Apartheid is a coalition of tech workers and organizers with MPower Change and Jewish Voice for Peace, which are respectively Muslim- and Jewish-led peace-focused activist organizations. The coalition came together shortly after Project Nimbus was signed and its details became public in 2021.
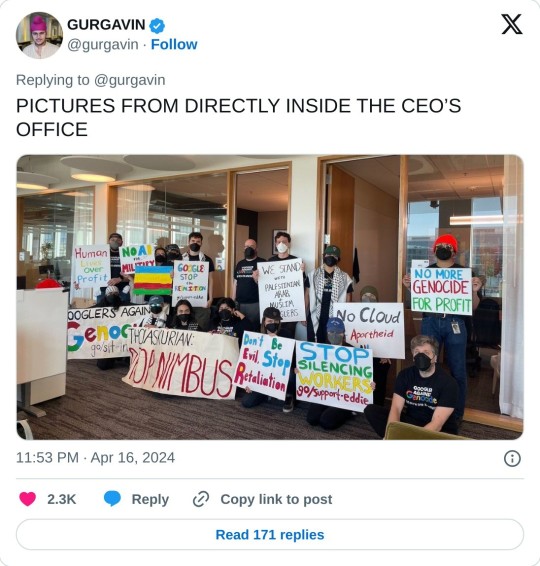
You can read No Tech for Apartheid's open letter here.
#yemen#jerusalem#tel aviv#current events#palestine#free palestine#gaza#free gaza#news on gaza#palestine news#news update#war news#war on gaza#apartheid#gaza genocide#genocide#boycott divest sanction#boycott google#bds movement#Edited
5K notes
·
View notes
Text
Peter: I'm sorry... *dies*
Tony: Yeah you better be sorry, you just turned a brand new 1.2 billion dollar nanotech suit into DUST
Nebula: (0_0;)
#irondad and spiderson#irondad#peter parker#tony stark#incorrect marvel quotes#incorrect mcu quotes#avengers infinity war#marvel#mcu#marvel incorrect quotes#incorrect tony stark#nebula#spider man#iron man
541 notes
·
View notes
Text

Hoping to have all his holiday decorations up by the weekend, His Holiness Pope Francis has spent the past two hours rummaging through the basement of the papal apartments in search of the Vatican’s plastic nativity scene figures, sources confirmed Friday.
After climbing over dusty cases of sacramental wine and bins filled with mothballed vestments, the pope reportedly found the set’s plywood manger in a corner of the room near the sump pump, though sources noted he has yet to locate all the blow-molded polyethylene representations of the Holy Family and their Christmas visitors.
“Oh, come on, where’s the third wise man?” the spiritual leader of 1.2 billion Roman Catholics said as he pushed aside several priceless Raphael and Fra Angelico paintings to peer into a cardboard box, aided by the dim light of a bare bulb hanging overhead. “I could’ve sworn I put him away with everybody else. There’s a ton of donkeys and sheep in here, but a lot of good that does me with only two wise men. Jeez.”
“I don’t have time for this,” he added. “I’ve still got an epistle that needs to be finished.” Full Story
405 notes
·
View notes
Text
In 2024, wealth concentration rose to an all-time high. According to Forbes’ Billionaires List, not only are there more billionaires than ever—2,781—but those billionaires are also richer than ever, with an aggregate worth of $14.2 trillion. This is a trend that looks set to continue unabated. A recent report from the financial data company Altrata estimated that about 1.2 million individuals who are worth more than $5 million will pass on a collective wealth of almost $31 trillion over the next decade.
Discontentment and concern over the consequences of extreme wealth in our society is growing. Senator Bernie Sanders, for instance, stated that the “obscene level of income and wealth inequality in America is a profoundly moral issue.” In a joint op-ed for CNN in 2023, Democratic congresswoman Barbara Lee and Disney heiress Abigail Disney wrote that “extreme wealth inequality is a threat to our economy and democracy.” In 2024, when the board of Tesla put to vote a $56 billion pay package for Elon Musk, some major shareholders voted against it, declaring that such a compensation level was “absurd” and “ridiculous.”
In 2025, the fight against rising wealth inequality will be high on the political agenda. In July 2024, the G20—the world’s 20 biggest economies—agreed to work on a proposal by Brazil to introduce a new global “billionaire tax” that would levy a 2 percent tax on assets worth more than $1 billion. This would raise an estimated $250 billion a year. While this specific proposal was not endorsed in the Rio declaration, the G20 countries agreed that the super rich should be taxed more.
Progressive politicians won’t be the only ones trying to address this problem. In 2025, millionaires themselves will increasingly mobilize and put pressure on political leaders. One such movement is Patriotic Millionaires, a nonpartisan group of multimillionaires who are already publicly campaigning and privately lobbying the American Congress for a guaranteed living wage for all, a fair tax system, and the protection of equal representation. “Millionaires and large corporations—who have benefited most from our country’s assets—should pay a larger percentage of the tab for running the country,” reads their value statement. Members include Abigail Disney, former BlackRock executive Morris Pearl, legal scholar Lawrence Lessig, screenwriter Norman Lear, and investor Lawrence Benenson.
Another example is TaxMeNow, a lobby group founded in 2021 by young multimillionaires in Germany, Austria, and Switzerland which also advocates for higher wealth taxation. Its most famous member is the 32-year old Marlene Engelhorn, descendant of Friedrich Engelhorn, founder of German pharma giant BASF. She recently set up a council made up of 50 randomly selected Austrian citizens to decide what should happen to her €25 million inheritance. “I have inherited a fortune, and therefore power, without having done anything for it,” she said in a statement. “If politicians don’t do their job and redistribute, then I have to redistribute my wealth myself.”
Earlier this year, Patriotic Millionaires, TaxMeNow, Oxfam, and another activist group called Millionaires For Humanity formed a coalition called Proud to Pay More, and addressed a letter to global leaders during the annual gathering of the World Economic Forum in Davos. Signed by hundreds of high-net-worth individuals—including heiress Valerie Rockefeller, actor Simon Pegg, and filmmaker Richard Curtis—the letter stated: “We all know that ‘trickle down economics’ has not translated into reality. Instead it has given us stagnating wages, crumbling infrastructure, failing public services, and destabilized the very institution of democracy.” It concluded: “We ask you to take this necessary and inevitable step before it’s too late. Make your countries proud. Tax extreme wealth.” In 2025, thanks to the nascent movement of activist millionaires, these calls will grow even louder.
#it's nice to think about but it's not going to happen anytime soon#not with this congress and president
605 notes
·
View notes
