#zoos
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
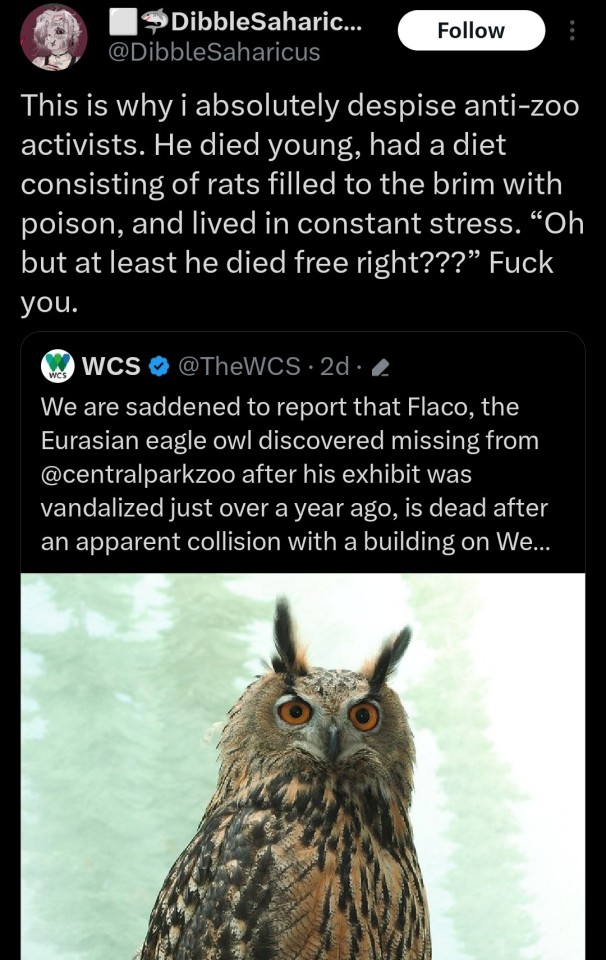
Woman at the zoo: Why do they look so sad? 😔
Sign literally 10 feet away:

66K notes
·
View notes
Text
youtube
I didn't know this, but I just found out that the Philadelphia Zoo has a network of animal walkways to allow their animals to roam around the zoo! They call it "Zoo360" and honestly it looks pretty cool.


They've also got goats and horses and great apes that all have the ability to Get Around places. I assume that they just loop back to the original enclosure eventually, but what a fun kind of enrichment for animals who travel great distances in the wild regularly! I can't believe other zoos haven't added anything like this to their setups! It looks like it's been up and running around 10 years now, and if so, it seems like it must be pretty safe for everyone involved, and the animals are still using it regularly enough there are lots of videos of them from zoo visits. What a neat concept!
7K notes
·
View notes
Text
I promised you some lions! Let's talk about manes, males, and management.
This is Tandie, the current male lion at the Woodland Park Zoo.

Notice anything odd about him? He's got one of those hilarious awkward teenager manes. Except... this cat is nine years old.

I was, of course, immediately curious.
Manes serve a lot of purposes for male lions, including being an indicator of health and fitness - it's actually a sexually selected trait and a social signal. Mane texture / hair quality / length is dependent on nutrition and the body having energy to grow (and carry around!) that much hair! The color is also a signal: males with darker manes have been found to have higher testosterone levels.
In one research report, wild males were much more likely to avoid a lion decoy when it had a longer or darker mane - but the girls really loved a dark mane. It's thought this is because a long, dark mane is an indicator of mate quality. Males with longer, darker manes have higher testosterone and were pretty healthy: meaning they had more energy for fighting, had a better chance of recovering if they got injured, and generally had a higher rate of offspring survival. Manes matter!
So, back to Tandie. He was actually born at the Woodland Park Zoo in 2014 alongside two brothers, to dad Xerxes and mother Adia.
This was Xerxes (rip).
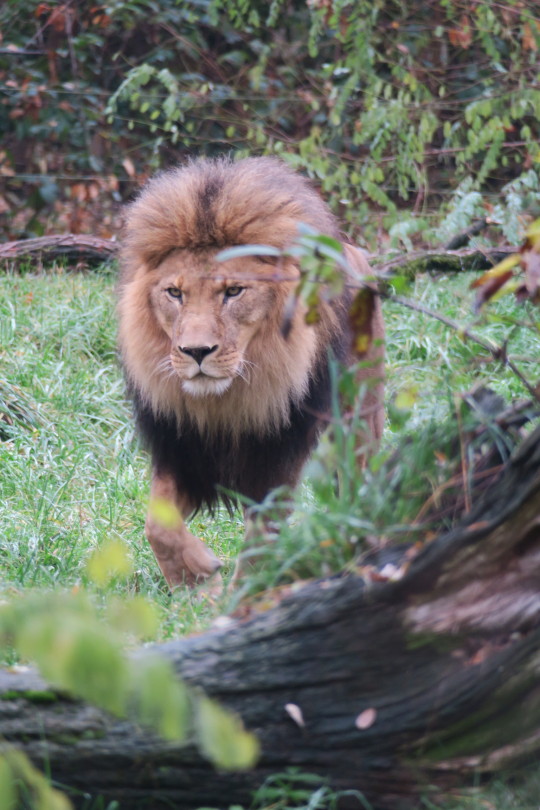

Obviously, a very large, dark, lush mane on Xerxes here. So where did these blond muttonchops come from on his son?
I asked the zoo docents and got an answer that didn't make a lot of sense. They told me that after the three cubs grew into adolescents, they were moved to the Oakland Zoo together. But living together suppressed his testosterone, and he never grew a mane.
Hmmmm.
Here's a photo from 2016, when the brothers debuted at Oakland. They're a year and a half old in this photo.

(Photo Credit: Oakland Zoo)
And here's from an announcement for their third birthday.

(Photo credit: Oakland Zoo)
Okay, so these dudes obviously all were growing manes as of 2017. I think Tandie is the one on the left in the first photo, and laying down in the middle on the second. What happened?
I was just in the Bay Area for a zoo road trip, of course I went to Oakland and tracked down a docent to ask some questions.
It turns out that shortly after the brothers turned three, they started acting like adult male lions: they started scuffling regularly. It's a normal social thing for male lions to live in groups, called coalitions, but according to my lion experts there's generally a baseline level of some social jostling within them. It wasn't quite clear from what the docent said if they couldn't manage the boys together, or if they just wanted to avoid the scratches and small wounds that result from normal lion behavior. Regardless, they put all three of the boys on testosterone blockers in order to be able to keep them together as a social group.
Now, I don't know a lot about the use of hormone alteration as a form of captive animal management, except in the case of birth control. I don't think it's something that's unethical - there was just a webinar on it that I saw go by - but I don't think it's commonly done with big cats. Lions have kind of complicated reproductive cycles, and for instance, we've been learning that female lions can take much longer to come into estrus again than expected after coming off hormonal birth control.
In males, testosterone blockers (or being neutered) means they lose their manes. This is why a lot of rescues will do a vasectomy on their males instead of a neuter - it allows them to keep their mane and the social signals that accompany it.
Tandie returned home to Woodland Park Zoo after Xerxes passed in early 2022, and the docent told me all of the lions had been off their blockers "for while." I'd guess those things happened around the same time, since bringing the trio down to a duo at Oakland would reduce some of the social tensions.
Hormones are such interesting things, though. One of Tandie's brothers has a full mane again, and the other is still totally mane-less.


As for Tandie, his mane is growing back in, and it looks like he might rival his dad for length and coloration.
He started here, in February:

Yesterday:


What a difference four months (and maybe proximity to a girl) makes!
#big cats#lion#african lion#big cat behavior#zoo animals#zoo animal welfare#captive animal management#zoos
13K notes
·
View notes
Text
"In one of Africa’s last great wildernesses, a remarkable thing has happened—the scimitar-horned oryx, once declared extinct in the wild, is now classified only as endangered.
It’s the first time the International Union for the Conservation of Nature (IUCN), the world’s largest conservation organization, has ever moved a species on its Red List from ‘Extinct in the Wild’ to ‘Endangered.’
The recovery was down to the conservation work of zoos around the world, but also from game breeders in the Texas hill country, who kept the oryx alive while the governments of Abu Dhabi and Chad worked together on a reintroduction program.
Chad... ranks second-lowest on the UN Development Index. Nevertheless, it is within this North African country that can be found the Ouadi Rimé-Ouadi Achim Faunal Reserve, a piece of protected desert and savannah the size of Scotland—around 30,000 square miles, or 10 times the size of Yellowstone.
At a workshop in Chad’s capital of N’Djamena, in 2012, Environment Abu Dhabi, the government of Chad, the Sahara Conservation Fund, and the Zoological Society of London, all secured the support of local landowners and nomadic herders for the reintroduction of the scimitar-horned oryx to the reserve.
Environment Abu Dhabi started the project, assembling captive animals from zoos and private collections the world over to ensure genetic diversity. In March 2016, the first 21 animals from this “world herd” were released over time into a fenced-off part of the reserve where they could acclimatize. Ranging over 30 miles, one female gave birth—the first oryx born into its once-native habitat in over three decades.
In late January 2017, 14 more animals were flown to the reserve in Chad from Abu Dhabi.
In 2022, the rewilded species was officially assessed by the IUCN’s Red List, and determined them to be just ‘Endangered,’ and not ‘Critically Endangered,’ with a population of between 140 and 160 individuals that was increasing, not decreasing.
It’s a tremendous achievement of international scientific and governmental collaboration and a sign that zoological efforts to breed endangered and even extinct animals in captivity can truly work if suitable habitat remains for them to return to."
-via Good News Network, December 13, 2023
#chad#abu dhabi#north africa#rewilding#endangered species#conservation#zoology#conservation biology#oryx#good news#hope#texas#big game#animals#endangered#environmentalism#environmental science#zoo#zoos#zoo animals
25K notes
·
View notes
Text


We were deprived of the ultimate psychotic Penguin vs Penguin fight.
838 notes
·
View notes
Text



Mmmmm, The Smell of Fresh Antler
Our animal care staff will place natural items, like antlers, that our wolves might encounter in the wild. Our carnivore staff will even bury items for the endangered Mexican wolves to uncover; this encourages the wolves to investigate for what they’re smelling.
via: Fossil Rim Wildlife Center
553 notes
·
View notes
Text

Arctic fox, Vulpes lagopus. 5/8/24.
#arctic fox#fox#foxes#canine#canines#canidae#canids#mine#nature#wildlife#nature photography#photography#mammals#ecology#naturalist#animals#animal#zoo animals#zoos#zoology#zoo#original photography#original photographers#wildlife biology#wildlife biologist
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
Learning anything about marine mammal training will make you re-evaluate so much of your relationship with your own pets. There is so much force involved in the way we handle domestic animals. Most of it isn’t even intentional, it just stems from impatience. I’m guilty of it myself!
But with the exception of certain veterinary settings where the animal’s health is the immediate priority, why is it so important to us that animals do exactly what we want exactly when we want it? Why do we have to invent all these tools and contraptions to force them to behave?
When a whale swam away from a session, that was that. The trainer just waited for them to decide to come back. If they flat out refused to participate in behaviors, they still got their allotment of fish. Nothing bad happened. Not even when 20-30 people were assembled for a procedure, and the whale chose not to enter the medical pool. No big deal. Their choice and comfort were prioritized over human convenience.
It’s almost shocking to return to domestic animal medicine afterwards and watch owners use shock collars and chokers and whips to control their animals. It’s no wonder that positive reinforcement was pioneered by marine mammal trainers. When you literally can’t force an animal to do what you want, it changes your entire perspective.
I want to see that mindset extended to our domestic animals.
#‘oh I can walk my dog off-leash down a crowded street’ why does that matter?????#the horse world is ESPECIALLY bad about this too#edit: the whips is referring to horses I have not seen anyone whip their dog#pets#horses#animal training#dog training#dolphin training#dolphins#belugas#orcas#killer whales#cetaceans#marine mammals#zoos#aquariums#cooperative care#vet med#vetblr
6K notes
·
View notes
Text






Something really neat I saw at Brookfield Zoo yesterday - not only are these signs not AI art but they actually credited the designers/illustrators AND the people who took the reference photos!
199 notes
·
View notes
Text


#moo deng#หมูเด้ง#cute#animals#wholesome#funny#meme#comedy#humor#memes#pygmy hippo#hippopotamus#baby animals#zoo#zoos#thailand#positivity
205 notes
·
View notes
Text
Today I learned a fact that kinda blew my mind, and I'm almost astonished I didn't know this before as someone whose chief interests include zoo animals, the U.S. Presidency, true crime, and D.C. history. What an opener, right? How could those topics possibly combine?
Well, buckle up and get ready to hear how negligent National Zoo leadership potentially could have killed a US President or started a local epidemic. Spoiler alert: They didn't. But only because luck was in their favor.
First, the part that I DID already know. In 2004, Lucy Spelman stepped down as the director of the National Zoo after a spate of controversial zoo incidents, including a string of unfortunate (and often preventable) animal deaths, misleading and missing zoo records, and other signs of negligence. The AZA even "tabled" renewing the National Zoo's accreditation for a year until they made some significant improvements. Spelman was also a vet and some of the cases she was accused of bungling happened at her own hands, not just under her supervision. It was a major disgrace for a zoo that was meant to represent the nation's capital.
I was in elementary school during these fraught years and I remember devouring articles about this in the newspaper, riveted with shock and dismay. Some of the deaths were just bad luck, but others were obviously negligent. The most infamous case was two red pandas killed by rat poison shallowly buried in their enclosures as a slapdash solution to the zoo's pest problem. A young zebra died of starvation and hypothermia after Spelman ordered the zebras' feed be cut in half, an orangutan was euthanized due to a recurrence of cancer that didn't exist (she actually had salmonella), a lion died after being administered over twice the usual amount of anesthetic, and more. I remember the names and details of these animals from when I first read these cases 20 years ago. But the one I'm talking about today is that of Nancy the elephant.
Nancy was a 46-year-old African elephant whose health had been steadily declining for several years. She suffered from a bone infection in her foot that seriously affected her mobility and quality of life. She had lost a lot of weight, she was fatigued, she even lay down at times. Nobody could be blamed for deciding to euthanize the obviously ill animal.
But they could be blamed for what was discovered in the necropsy after she was euthanized. While she did indeed have a diseased foot, the bone infection was only "moderate." Why, then, was she so obviously unwell? Her lungs had been destroyed by the effects of untreated tuberculosis. It was the tuberculosis, not the sore foot, that most contributed to her decline in health.
Here’s the scary part: nobody knows how long she'd had it because she hadn't been tested for tuberculosis, a known concern for zoo elephants, in TWO YEARS. All this despite the fact that it's MANDATORY for all zoo elephants to receive a tuberculosis test once per year-- and in fact, it was a National Zoo staff member who pushed for that reform in the first place. And the elephant was on Prednisone for her foot issues, which zoo staff noted in her records made her more vulnerable to illnesses like TB. In fact, none of the zoo's elephants had been tested recently, which meant any of them, including one who was pregnant, may have had tuberculosis, too.
There are documented cases of humans catching tuberculosis from elephants. Now, Nancy the elephant had bovine tuberculosis, which seems to be less contagious to humans and which elephants haven't so far spread to humans... BUT it has spread to humans from black rhinos, a fairly close relative, so it seems likely that elephants COULD spread it. It can also take a while for TB for incubate (and can also be latent without symptoms), especially for elephants, so the elephants OR keepers who were around Nancy were at serious risk for TB.
NOW HERE IS THE PART THAT I DIDN'T KNOW ABOUT UNTIL TODAY:
Spelman actively tried to COVER UP the situation, potentially putting many more people at risk. The elephant house was closed to zoo guests, but they were only told it was for "renovations." (The actual renovations, incidentally, were to improve ventilation so that illness would be less likely to spread.)
A BBC news crew that came to film the elephants was asked to keep a healthy distance from the elephants for their emotional health and the crew's safety-- the explanation given was that the elephants' group dynamics had been thrown off by Nancy's death. Spelman instructed zoo staff not to mention the TB situation to the BBC crew and, if asked why Nancy died, they were to respond that it was for multiple reasons and that the official test results weren't all back yet.
And here's the most shocking part of all, the part that made me GASP out loud. Spelman still personally gave some special VIP behind-the-scenes tours of the elephant house during the months that the elephant house was closed, a time when the remaining elephant inhabitants could potentially still develop active TB.
One VIP who received an elephant house tour was PRESIDENT BILL CLINTON and five family members!!!!
BILL. CLINTON. THE GOSHDARN PRESIDENT.
While zoo staff says that the tour was deliberately distanced and nobody got close to an elephant, there are photos of Bill Clinton's nephew about a foot away from an elephant's trunk. You know, their nose. The part they can spread disease with. So, uh, definitely in the danger zone there.
Hillary Clinton's brother, Tony Rodham, was on the tour and he said that nobody in the party was warned about TB risk or asked if they had any medical conditions that might (a. make them susceptible to communicable disease, or (b. be contagious to the elephants. This is especially egregious because according to zoo guidelines, all behind-the-scenes tour participants MUST be asked these questions-- not just when there's a very real possibility of a TB outbreak at the zoo.
Fortunately, none of the zoo's other elephants OR keepers ever tested positive for tuberculosis. But it was certainly a close call! And imagine what would have happened if a US President caught TB from a close encounter with an elephant thanks to poorly managed zoo staff.
Presidents meet a lot of people. In fact, this zoo visit happened only 2 weeks before the inauguration of President George W. Bush, which Clinton attended. He very well could have started a TB outbreak there. Heck, TWO US Presidents could have been infected!
Now THAT is something I will be thinking about for a long time!
173 notes
·
View notes
Text
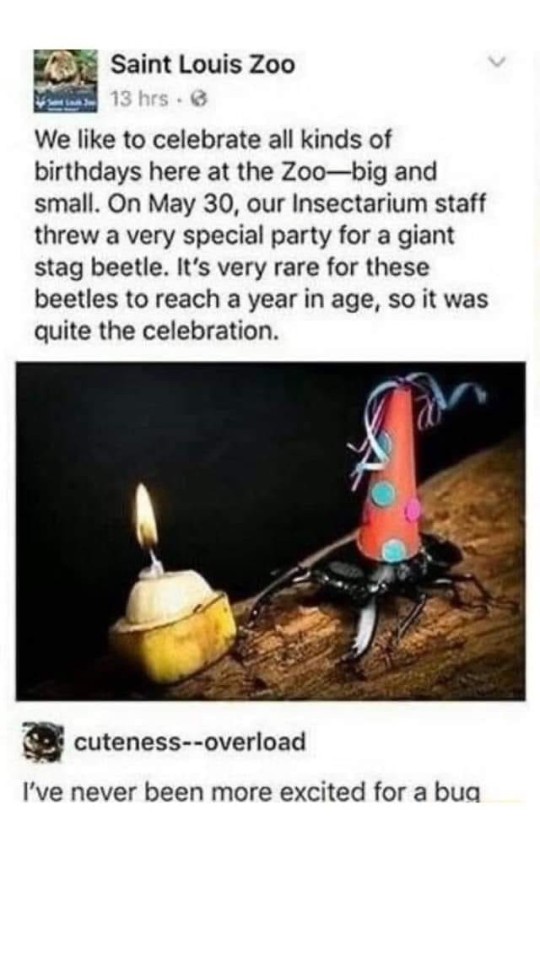
6K notes
·
View notes