#world wide web consortium
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Photo
Tim Berners-Lee was born on June 8, 1955. Also known as TimBL, he is an English computer scientist best known as the inventor of the World Wide Web. Berners-Lee proposed an information management system on March 12, 1989, then implemented the first successful communication between a Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) client and server via the Internet in mid-November. He is the director of the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C), which oversees the continued development of the Web.
#tim berners-lee#internet#world wide web#hypertext transfer protocol#http#world wide web consortium#w3c#TimBL#science#science birthdays#science history#on this day#on this day in science history
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Web “content”?
Web “content” generally refers to the information in a web page or web application, including:
natural information such as text, images, and sounds
code or markup that defines structure, presentation, etc.
I came across this surprisingly concise and thorough definition in the Introduction to the WCAG 2 Overview introducing “the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) international standard, including WCAG 2.0, WCAG 2.1, and WCAG 2.2.” That’s much better than I’ve found anywhere else.
Leave it to the Web Accessibility Initiative to understand that it’s about both “natural information” (e.g. written editorial content like an article or advertising content like an ad) and how it’s presented (like the elements of design within the article, where and how an ad is shown and its design).
And bonus points for putting “content” in quotes. As that term has been fraught—and seems to have it's origins in referring to web “content.” John Long arguing in The Drum in 2018 that “‘Content’ is a terrible term. Please stop using it.”:
“‘The principal substance offered by a website.’
And that’s the first thing everyone should remember about the word ‘content’ — it’s a website term that was probably initially used by programmers to generically describe the stuff that wasn’t code, i.e., the stuff that was mere ‘fluff’ to them. Like, say, The Iliad.
With that in mind, maybe the second part of the WCAG intro definition could be modified so it's not so much the “code or markup” itself but rather the “structure, presentation, etc.” definined by that code or markup.
(There’s a lot of great and useful information over on the Web Accessibility Initiative section of the Wolrd Wide Web Consortium (W3C) site, including the WAI Resources page describing “most technical and educational resources from the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) Web Accessibility Initiative (WAI).” Many things to keep in mind when making content—doing pretty much anything on the publishing side—on the web.)
#content#Web content#accessibility#WCAG#web content accessibility guidelines#WAI#Web Accessibility Initiative#W3C#World Wide Web Consortium#John Long#The Drum#terminology
0 notes
Text
accessibility online is super important and it's basically criminal that it's as bad as it is. we can, should, and must do better. that said the acronym a11y never fails to make me seethe with anger. terrible acronym it looks terrible, it's unclear what it is without context, it reads as leetspeek 'ally', etc. there were so many better choices and it just sucks massively.
or as i like to call it. a373y.
#kaia.mypost#if u have to write articles defending a11y as normal bc w3c uses it (no the fuck it doesn't#it's world wide web consortium it's like i2c not i18n)#then methinks ur acronym sucks shit#i18n makes sense it's a long ass word for a deeply specific field!! a11y is half the length and everybody needs to care abt it#also any post tagged a11y sucks shit and is half the time wrong and half the time meaningless. it feels like
35 notes
·
View notes
Text
did you know that you used to be able to specify the size of a scrollbar in pixels with CSS but you can't anymore and now the only 2 settings are 'auto' and 'thin' and buddy let me tell you something. 'auto' is whatever the hell it feels like being as long as what it feels like being isn't 'wide'
3 notes
·
View notes
Text

Inclusive Digital Experience
ADA Site Compliance creates an inclusive digital experience for schools, ensuring all students can engage with educational content regardless of their abilities!
#ada compliance for schools#digital accessibility in education#u.s. department of justice#ada title ii#world wide web consortium (w3c)#technical accessibility standards#accessibility features#accessible digital content#accessibility consultants#digital content creation#ada title ii 504 compliance#wcag 2.1 standards#ada compliance deadline 2027#universal design in education#school website#inclusive digital experience#assistive technologies#accessible digital content creation#website accessibility solutions#ADA site compliance#ADASiteCompliance#adasitecompliance.com
0 notes
Text
Post #83: Tumblr Opinion Poll by Python-Programming-Language, Question: Which programming resp. script language do you prefer?, 2023.
#programming#coding#coding is fun#i love coding#learning#education#i love programming#programming language#python#c++#c sharp#visual basic#small visual basic#i love python#php#scratch#html#css#java#javascript#script language#opinion poll
201 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Human Microbiome: Your Body's Little Ecosystem
Within each of us exists a fantastic and complex microscopic universe known as the human microbiome. This ecosystem of microorganisms that inhabits our body plays a fundamental role in health and homeostasis. Today, we will fully explore this fascinating microbial world and its influence on our physiology.
What is the Human Microbiome?
The human microbiome is a profoundly intricate biological system integral to our health and well-being. This term, "the human microbiome," encompasses a diverse consortium of microorganisms that have firmly established themselves within and upon our bodies. This assemblage comprises a wide array of microorganisms, encompassing bacteria, viruses, fungi, and various other microbes, each with their specialized ecological niches within our anatomy.
Upon a deeper examination of the human microbiome, we uncover a meticulously organized distribution of these microorganisms. They do not merely coexist haphazardly within us; instead, they strategically colonize specific regions of our body. For instance, they form robust communities within the gastrointestinal tract, resulting in the gut harboring a densely populated microcosm. Similarly, they stake their claim on our skin, and even the respiratory tract serves as a habitat for these microbial entities.
The human microbiome's remarkable aspect lies in the intricate and dynamic interactions it maintains with our own organism. These microorganisms are not passive bystanders; they are active participants in the intricate orchestra of physiological processes. They exert influence over our digestion, bolster our immune system, and wield the potential to affect our mental and cognitive faculties. This complex web of symbiotic relationships between our human cells and these microorganisms constitutes an ever-evolving interplay that exerts a profound impact on our overall health.
The human microbiome is not a mere collection of microbes; it is an entire ecosystem nestled within us, a thriving and dynamic world with the potential to significantly modulate our health. Comprehending the intricacies and subtleties of this microscopic community represents an ongoing and critical pursuit in the realms of scientific and medical research, with profound implications for the fields of medicine and biology.
Solid Scientific Evidence
To support the importance of the human microbiome, here are three relevant scientific references:
Title: "The Human Microbiome: A Key Contributor to Health." Autores: Sender, R., Fuchs, S., & Milo, R. Revista: Journal of the American College of Nutrition, 2016. Abstract: This article reviews the role of the human microbiome in health and disease, highlighting its influence on digestion, immunity, and nutrient synthesis. It also emphasizes its contribution to metabolic and autoimmune diseases.
Títle: "The Human Microbiome: Gut Microbiota and Health." Autores: Marchesi, J. R., Adams, D. H., Fava, F., Hermes, G. D., Hirschfield, G. M., Hold, G., ... & Rook, G. A. Revista: The Journal of Infection, 2016. Abstract: This study focuses on the intestinal microbiota and its relationship with human health. Explore how alterations in the microbiome can contribute to gastrointestinal, inflammatory, and metabolic disorders.
Títle"The Skin Microbiome: Impact of Modern Environments on Skin Ecology, Barrier Integrity, and Systemic Immune Programming." Autores: Kong, H. H., Andersson, B., & Clavel, T. Revista: World Allergy Organization Journal, 2016. Summary: This article examines the skin microbiome's influence on skin health and immune response. It highlights how modern environmental factors can upset the microbial balance and affect the skin's health.
Future perspectives
Studying the human microbiome is a constantly evolving field that promises new therapeutic strategies and a deeper understanding of human health. As we continue to investigate this small ecosystem, doors are opening to personalized interventions to promote health and prevent disease.
Would you like to learn more about this fascinating subject? Share your thoughts and questions in the comments!

#science#biology#college#education#school#student#medicine#doctors#health#healthcare#nursing#nurses#higher education#microbiome#molecular biology
78 notes
·
View notes
Text
Want to help in the war against youtube's anti-adblock?
Well, you can!
Below is copy pasted directly from this comment by uBlock Origin dev u/eipi1_0:
"Actually I personally have never considered the anti-adblock "game" is a winning game for uBO. Websites are always the active ones because they are the ones who deliver the contents to users. uBO is just an extension, it cannot change websites' owners anti-user behaviors.
The only ones that can/should affect the websites are the users. Everyone can let the websites know that their actions are doing harm to the users by giving feedbacks/criticisms to them.
For example, in YouTube case, everyone can write feedbacks/criticisms directly to them that they are violating severely the ethics principle written by World Wide Web Consortium:
2.12 People should be able to render web content as they want People must be able to change web pages according to their needs. For example, people should be able to install style sheets, assistive browser extensions, and blockers of unwanted content or scripts or auto-played videos. We will build features and write specifications that respect peoples' agency, and will create user agents to represent those preferences on the web user's behalf.
in which they are a member of: https://www.w3.org/membership/list/?initial=g&ecosystem=
Google's mission is to organize the world’s information and make it universally accessible and useful.
Criticize them how the ads affect badly to the users. Ask them if they really respect Web Standards or not, and forcing users to not able to block malicious connections is totally unethical.
More people/users unite to oppose corporations, the better. Don't just rely on a tool and let companies control what should be run on your own device.
How to send feedbacks on youtube page: https://support.google.com/youtube/answer/4347644 (click on profile picture -> Send feedback)"
89 notes
·
View notes
Text
Okay so this is a background post about Text encoding, ASCII and Unicode
Text encoding is the process of turning characters to numbers. text encoding allows one to save text as computer data, and to move this data around.
It was understood very early on, that if every user will define their own encoding, no interface could use the data of another because one interface's "a" would be another interface's "p", and so the text would be read as gibberish.
and so, a long time ago (in the 1960s), in a continent far, far away, a standard for text encoding was invented: the American Standard for Character Interface Interchange: ASCII.
ASCII used the fact that in english, almost no characters exist, and so only needed to use 128 characters: each character took 7 bits (1s and 0s), and was sent over a wire. (notice, not everything is a character, there are also character like "delete" and "go down a line" here. this is not for displaying, this is for every interfaces)
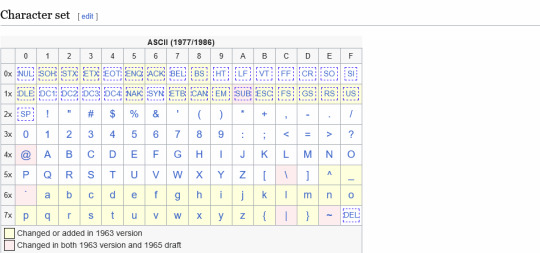
Something to remember for later: the number 0 is encoded as NULL, basically "nothing". This is useful because sometimes you want to enter text with an unspecified length, and so you stick a NULL in the end, and the interface reading it reads until it sees a NULL, and all is well. this will be important later
Standard explained, technical info for nerds, go to the next red section to pass
ASCII is a wonderful standard. remember: everything in electronics is easier with powers of 2 (1,2,4,8,16,32 etc.) because of the way we save data (if you want I can explain this further); the first 32 characters are the control characters. want to check if something isn't a control character? check if it's 128 or bigger than 32, and you're done (both powers of 2). the lowercase characters are 32 + their uppercase counterpart. all the numbers have a byte in common. truly, a marvel of engineering.
Standard explanation end
All was well until computers hit the scene not too long after, and used bytes. a byte is basically a whole number whose value can be only from 0-255. they are the standard building block of computer memory, and they have 8 bits.
some countries, like France, used encodings compatible with ASCII, and used the final bit to encode their language's characters. different countries used different versions of encodings, some countries (like Japan) had multiple encodings for the same characters. each encoding used a different number of bits, and different letters for each bit.
But that is fine since, well, how often do you need a computer in London to use an interface in Tokyo? all is well.
Then the World Wide Web happens, and suddenly computers speaking different languages read and write complete garbage everywhere.
So an organization called the Unicode Consortium tries to solve the problem, and to create a unified symbol for all languages. They called the standard utf-8
This standard supports 1,114,112 different characters. at present, only around 10% of this data capability is actually used. this includes dead languages, and emojis (which is a wonderful story)
Standard explained, technical info for nerds, go to the next red section to pass
Issues to tackle in a universal text encoding standard:
The protocol must be backwards compatible with ASCII: if you are writing text in English, which is the language most users used, because ASCII is the standard for this language, your new standard must be readable as ASCII as well
The protocol must never send 8 zeros in a row, except for the NULL character, otherwise old computers will stop reading in the middle
You must be able to minimize space wasted: to create a universal standard one can just make every character 32 bytes long and call it a day, but you would waste a bunch of space that way, and space is expensive
You must be able to pass from letter to letter easily. no saving the index of each character in some sort of list.
english characters are just ASCII. no thinking there. the first bit is set to 0 and so it is very easy to spot
if not, here's what you do:
the first byte has its first bit set to 1, so it's not ASCII. from that point onwards, you count the number of remaining ones until a zero appears. in this case, 1. this is how many more bytes will come. from there on, the rest is data. the first 2 bits of every next byte would start with 10 until the character ends
let's say your character is 2 bytes long, here is how you would represent it:
110somec , 10haract
and when removing the headers, you'll have
somecharact
which will be some character.
let's say your character is 3 bytes long, here is how you would represent it:
1110some , 10charac , 10ter___
and when removing the headers, you'll have
somecharacter___
which will be another character.
if you wanna go back 1 character? just go back bytes until you find one that starts with something other than 10
no excess Nulls will appear because the only way to get 8 zeros
Standard explanation end
#ascii art#ascii entertainment#ascii#unicode#language#emoji#linguistics#hieroglyphs#programming#coding#encoding#standard
9 notes
·
View notes
Text

Por tiuj, kiuj verkas html-dosierojn kun enhavo en esperanto... La kodo por la lingvo esperanto estas eo, kvankam mi kredas, ke tio ankoraŭ ne estas "oficialigita" de la World Wide Web Consortium. Mi ne scias, kiel statas la afero.
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
word on the net is that the World Wide Web Consortium has voted to replace boy & girl with DOI & URL
17 notes
·
View notes
Text
HTML, RichText, and BB_Markup
Back in the day "RichText" or text that can be stylized like you would in Microsoft Word, or an E-Mail, wasn't often available in social media platforms.
And there's still some social media platforms who don't allow it at all.
This has multiple reasons, the processing is done in script at the browser level, and so there used to be performance reasons not to allow it. Or most of your users would experience a slow down just to view the text, why bother with it?
As browsers started getting more comfortable and fast enough to deliver HTML pages, with the markup allowed in HTML, HTML became the default. But as JavaScript grew in popularity, scope and use. HTML itself became a way for people to inject scripts directly into the page.
And instead of just, cleaning script tags and other injection vulnerabilities, websites took HTML away from users all together. This was a problem, in Part, directly influenced by the W3C {World-wide web consortium}, and big-browser (Microsoft, Netscape, and Mozilla, and later Google, Apple, and Opera) who all implemented HTML/CSS/JS differently.
Nobody knows why they did this, they just did. (Actually, there's a bunch of different reasons, but as you look deeper into the rabbit hole, the more absurd it gets.)
After that, forum and social media designers came up with *BB_Markup* I think BB means blackboard, but who knows for sure anymore.
BB was basically a shorthand HTML markup that used square-brackets instead of triangle-brackets, and at a server level, that markup got turned into *safe* HTML markup--to avoid user-level injection attacks.
We also get a bunch of other short hand that may or may not be used in certain platforms (like reddit) to this day. Wrapping text in asterisks to italicize a word, or tildes or the little wavey dash (~) which denote bolding under lining or strike through depending on what you're used to.
All sorts of things that some people who were netizens of the 90s and early-00s might still be in the habit of using.
Today, there's little reason for browsers to even allow <script> or script-referencing mark-up at that particular level anymore. Which would solve A LOT of early security issues. But they don't change it back because a lot of websites still use tricks like that, because that's what developers do.
Even though advertising still allows injection and browser-hijacking at a "user-level" just like in the olden days. Yep, if you host ads, there's a good chance you're allowing those ads to deliver malware to your users.
Looking at you YouTube and websites that say "Please stop using ad-block". They don't use them to prevent you from getting paid, they use them to stop you from injecting their device with malware.
You big dummys.
That's part of the reason why I'm an advocate of "ad-reform". Advertising companies are leveraging their ad-platforms for more than simply delivering ads.
There's a drive to put internet tools only in the hands of companies, taking net freedoms a lot of early-adopters take for granted, not like ad-block, more like not having to worry about malware being delivered to you while you're powerless to stop it.
I'm not even talking about internet surveillance, I'm talking about advertising companies delivering malware to office equipment. You know those hacks that seemingly target large databases everyday?
Paid Advertising.
Since a lot of, too many even, Internet users these days even know the basics of HTML/CSS/JS, they don't even get to see what it feels like to have the inspection tools be taken away from you so you can see how it is these websites are f* you.
I can't even [view source] on my phone anymore. *That's considered* a bigger security risk than ad-delivery hijacking *your* phone.
How much does ad delivery cost these days, and you can see, that's the price of delivering malware to the user. Not just advertising products.
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
How HTML Validation is Beneficial for SEO

Ensuring that your HTML is validated according to web standards is crucial for improving SEO. Valid HTML code helps search engines crawl and index your site more effectively, enhancing user experience and boosting overall site performance. Here’s how HTML validation benefits your SEO.
Introduction
HTML validation involves checking your HTML code against standards set by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C). This process helps identify and fix errors in your code, ensuring that your website functions properly across different browsers and devices.
1. Improved Search Engine Crawling
Search engines use bots to crawl websites. If your HTML is not valid, these bots might encounter issues that prevent them from indexing your site correctly. Valid HTML ensures that search engine crawlers can easily navigate and understand your website’s content, improving your chances of ranking higher in search results.
2. Enhanced User Experience
When HTML code is free from errors, it ensures that your website displays correctly across various browsers and devices. This consistency in user experience can lead to lower bounce rates and higher engagement, both of which are positive signals to search engines.
3. Faster Page Load Times
Valid HTML can lead to faster page load times, as browsers can interpret and render the code more efficiently. Faster-loading pages provide a better user experience and can positively impact your SEO, as page speed is a known ranking factor for search engines like Google.
For professional assistance in ensuring your website’s HTML is compliant and optimized for search engines, consider partnering with an experienced SEO services provider.
4. Better Accessibility
HTML validation helps ensure that your site is accessible to all users, including those using screen readers and other assistive technologies. Accessibility is not only important for user experience but also a consideration for SEO, as search engines aim to provide the best possible results for all users.
5. Reduced Technical Debt
Valid HTML reduces the likelihood of technical issues arising from poorly written code. This can save time and resources in the long run, allowing you to focus on creating quality content and improving other aspects of your SEO strategy.
Conclusion
HTML validation is a critical component of a robust SEO strategy. By ensuring your code complies with web standards, you can improve search engine crawling, enhance user experience, and boost your site’s overall performance. For comprehensive support and advanced digital marketing strategies, explore our Digital Marketing company services.
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
DEA 2024 NATIONAL DRUG THREAT ASSESSMENT MISSES THE BOAT
by James E. Gierach
The recently released National Drug Threat Assessment misses the boat. The report says:
“DEA’s top priority is reducing the supply of deadly drugs in our country and defeating the two cartels responsible for the vast majority of drug trafficking in the United States. The drug poisoning crisis remains a public safety, public health, and national security issue, which requires a new approach.
“The shift from plant-based drugs, like heroin and cocaine, to synthetic, chemical-based drugs, like fentanyl and methamphetamine, has resulted in the most dangerous and deadly drug crisis the United States has ever faced,” said DEA Administrator Anne Milgram. “At the heart of the synthetic drug crisis are the Sinaloa and Jalisco cartels and their associates, who DEA is tracking world-wide. The suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, and money launderers all play a role in the web of deliberate and calculated treachery orchestrated by these cartels. DEA will continue to use all available resources to target these networks and save American lives.”
DEA “TOP PRIORITY”: Reduce drug supply?
Has the DEA and its leadership learned nothing over the 63 years of America’s War on Drugs? Has it not learned that whatever the drug (cannabis, heroin, crack cocaine, LSD, PCP, ecstasy, meth or fentanyl) DRUG PROHIBITION IS A BOON TO DRUG PRODUCTION, INVENTION, TRAFFICKING, ADDICTION, OVERDOSE, DEATH, ORGANIZED CRIME and VIOLENCE.
The supply-side tactics of interdiction, surveillance, crop-spraying, border-policing, undercover detective work and confidential-informant buying DO NOT REDUCE SUPPLY.
Drug prohibition is like Rumpelstiltskin Magic that guarantees more drugs, uncontrolled and unregulated, everywhere. See “The Silver Bullet Solution: Is it time to end the War on Drugs?” (Guadium, 2023) by James E. Gierach.
The DEA is right about one thing: more drugs (more drugs appearing based upon its insistence on the prohibition of drugs) increases the risk to “public safety, public health, and national security.”
Unfortunately, and equally obviously, the DEA does not know what to do about it. Drug poisoning from drug prohibition requires a “new approach.” How about legalized drugs, regulated markets, government inspection, dealer licensing, fixed places of business, regulated hours and health warnings. Recall how poisoning and crime from unregulated alcohol was stopped with legalized alcohol markets, not more unwanted, unworkable Prohibition.
Today, a century later: Same societal prohibition sickness; same societal fix. LEGALIZE DRUGS.
Second “DEA OVERSIGHT”: More of the same (continued prohibition) from the DEA will not help.
The DEA thrives on its drug-prohibition mandate. It plays Drug War, Monopoly Money and Cops and Robbers with the Sinaloa and Jalisco drug cartels. The result is more new synthetic drugs that DEA agents ever dreamed when plant-drugs were the prohibited enemy.
The 2018 Shadow Report (Marie Nougier, “A Taking Stock: a Decade of Drug Policy, a Civil Society Shadow Report,” International Drug Policy Consortium, 2018, p. 27, http://fileserver.idpc.net/library/Shadow_Report_FINAL_ENGLISH.pdf) is a study basically asking, “What has the World War on Drugs done for us lately?” The report was prepared by the well-respected International Drug Policy Consortium using United Nations drug use and drug-invention statistics.
The Shadow Report noted that during the preceding ten-year period analyzed, drug cartels had invented 803 new synthetic drugs. It’s fair to say, drug prohibition policy never before ever produced more new mind-altering, synthetic drugs in any previous ten-year historical period of human life. Again, “The Silver Bullet Solution:…”supra, explains how and why drug prohibition, New York Governor Nelson Rockefeller’s mandatory-minimum, drug-sentencing laws and constitutional ex post facto laws converged to create an unexpected and unintended deluge of new synthetic drugs.
It’s 2024. Time to end the lost War on Drugs. Half-measures (legalized beer, legalized marijuana, or Oregon-styled drug decriminalization) will only further delay what society needs: full-dose, LEGALIZED, REGULATED and CONTROLLED DRUGS.
Let the DEA pack up and go home. Let DEA agents, and other federal and state law enforcement agents and officers, keep their drug-war winnings and drug-policing pensions, a significant part of America’s trillion-dollar drug-war spending. But let society out from under the worst public in the history of mankind—DRUG PROHIBITION, common denominator to a dozen crises and problems: “Violence, Gangs, Guns, Drugs, Policing, Mass Incarceration, Racism, Immigration, Human Rights, Healthcare, AIDS, and Corruption.” (“The Silver Bullet Solution:…,” supra.)
Palos Park, Illinois
May 9, 2024
#drugprohibition#gierach#drug legalization#unodc#harm reduction#cnd#overdose#crime#violence#drug policy
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
the world wide web consortium is the coolest name for anything ever i imagine a bunch of computer wizards in a grand circle discussing their thoughts about the internet
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
U.S. Department Of Justice

Public Schools Need A Digital ADA Accessibility Makeover Within 2-3 Years
According to a new federal mandate from the U.S. Department of Justice, public schools must make all digital content accessible to students with disabilities.
The U.S. Department of Justice has issued under Title II of the ADA that stipulates compliance with the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) by 2027.
This means schools must ensure that websites, mobile apps, and other digital platforms used for education are usable by students with a wide range of impairments.
The United States Department of Justice has endorsed the WCAG 2.1 to provide clear guidance for ADA compliance for web content and mobile apps.
These guidelines, established by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C), are recognized globally and offer a comprehensive framework for creating accessible digital experiences. Although W3C released an updated version of these guidelines in 2023, public schools must adhere to the WCAG 2.1 standards from 2018.
Public schools nationwide face a formidable challenge: ensuring all students can access digital resources by 2027. However, navigating the complexities of digital accessibility can be overwhelming for schools.
Meeting the 2027 deadline for compliance while creating an inclusive online environment requires expertise and precision. At ADA Site Compliance, we simplify the process.
Our team ensures your school’s digital platforms adhere to accessibility standards, preventing legal issues and fostering a welcoming environment for all students. Let us help you create a truly inclusive digital experience.
Schools Face Steep Climb to ADA Compliance
Public educational institutions across the U.S. have two or three years, depending on their size, to ensure their web content and mobile apps meet technical accessibility standards adopted in April under Title II of the Americans with Disabilities Act.
Smaller school districts have until April 26, 2027, to achieve compliance, while larger districts exceeding populations of 50,000 have till April 24, 2026, to meet compliance.
Attaining ADA compliance is an uphill battle for many educational institutions.
This requirement has placed significant pressure on school districts, many grappling with limited resources and poor technological expertise.
The standards cover a wide range of accessibility features, including providing alternative text for images, ensuring keyboard navigation, and maintaining adequate color contrast.
That’s why some experts say they should start preparing now. The transition to a fully accessible digital infrastructure is a technical upgrade and comprehensive overhaul of existing systems and practices.
Revamping their digital infrastructure to create inclusive online learning environments necessitates strategic planning, substantial investments, and continuous professional development for staff.
Schools must adopt a phased approach to ensure compliance within the given timeframe. This involves thorough audits of current digital assets, identifying accessibility gaps, and implementing necessary modifications.
These principles are not just technical requirements; they are essential for enhancing the educational experience of students with disabilities and fostering a more equitable learning environment for all.
Accessibility: More Than Just Website Compliance
The shift towards accessibility isn’t solely a technological endeavor for schools. It also demands a cultural change within educational institutions, fostering an environment where inclusivity is a core value.
Professional development opportunities will play a crucial role in this transformation.
Staff must have the knowledge and skills to create and maintain accessible digital content. This includes understanding universal design, becoming proficient with assistive technologies, and staying updated with the latest accessibility standards.
Additionally, schools must allocate budgetary resources to support this initiative. This might include hiring accessibility consultants, investing in accessible technology, and ensuring ongoing maintenance and updates to digital content.
Collaboration with stakeholders, including parents, students, and disability advocacy groups, is essential to address diverse needs and gather feedback on accessibility improvements.
Consequences of non-compliance
The consequence of non-compliance with WCAG is the risk of facing potential legal ramifications with time. The legal fees associated with non-compliance can get expensive, much more than the cost of attaining web compliance.
While the Department of Justice has outlined specific exemptions—such as archival information, legacy papers, content from third parties, social media postings, and password-protected files—it’s important to note that these exceptions are limited and may not apply universally.
Educators must thus thoroughly analyze their digital assets to determine which information falls under these exemptions.
Benefits of accessibility to educational institutions
According to CAST, a leading accessibility organization, this regulatory reform is a significant milestone in the quest for accessibility. By integrating accessibility standards into digital content, educational institutions can offer a more equitable learning environment for students with disabilities.
Furthermore, universal design principles benefit all users by making content easier to understand and navigate. Lindsay Jones, CEO of CAST, underscores that accessibility is not just about compliance; it’s about providing a better user experience for the entire school community.
This emphasis on enhancing user experience is the true driving force behind accessibility.
The Ripple Effect of ADA-Compliance on Student Success
Compliance with ADA Title II 504 is more than just a legal obligation; it’s a commitment to fostering an inclusive and supportive learning environment. Schools that prioritize accessibility adhere to legal standards and are dedicated to educational equity.
This proactive stance can lead to numerous benefits:
Enhanced Student Engagement: Accessible digital content ensures all students can fully participate in educational activities. This inclusivity can lead to higher levels of engagement and academic success.
Improved Academic Outcomes: Studies have shown that when students have access to resources that cater to their individual needs, their academic performance improves. By removing barriers, schools can help all students reach their full potential.
Positive Institutional Reputation: Schools known for their inclusive practices attract a diverse student body and staff. This positive reputation can enhance the institution’s standing in the community and attract more resources and partnerships.
Legal and Financial Safeguards: Proactively addressing accessibility reduces the risk of legal challenges and the associated financial costs. Schools can avoid costly lawsuits and fines by complying with ADA Title II 504.
Equal access for everyone: ADA compliance ensures that students with disabilities have the same access to educational resources as their peers, which is fundamental for their academic success and overall well-being.
Universal design approach: Accessible digital environments benefit all students, as they promote a universal design approach that can accommodate diverse learning needs and preferences.
Digital accessibility extends beyond the classroom: Accessible online learning platforms and resources prepare students for the future, equipping them with the skills to navigate an increasingly digital world.
A Roadmap to ADA Compliance: Nine Essential Steps for Schools
As schools work towards meeting these compliance deadlines, they must also consider the ongoing training and support for educators and staff to use and create accessible digital content.
To effectively comply with ADA Title II 504 within the given timeframe, schools can adopt these nine practical steps:
Conduct Regular Accessibility Audits: Regularly conduct audits of school websites and mobile apps to identify and address accessibility issues. Use both automated tools and manual testing to ensure a thorough evaluation.
Invest in Training: Educate staff about the importance of digital accessibility and provide training on creating and maintaining accessible content. This includes understanding how to use accessibility features in various software and platforms.
Utilize Accessible Technology: Integrate and support using assistive technologies that can aid students with disabilities. Ensure website compatibility with screen readers, voice recognition software, and other assistive tools.
Engage with the Community: Involve students, parents, and community members in the accessibility planning process. Their feedback can provide valuable insights and ensure that the solutions implemented meet the needs of all users.
Incorporate Accessibility in Procurement: When acquiring new digital tools or platforms, ensure they meet WCAG 2.1 standards. Include accessibility requirements in procurement processes to avoid future compliance issues.
Develop an Accessibility Plan: Create a detailed plan outlining the steps to achieve compliance. This plan should include timelines, responsible parties, and measurable goals.
Policy Development: Develop and enforce policies prioritizing accessibility in all digital content creation and management processes. Make accessibility a core component of the school’s digital strategy.
Fostering collaborations: Collaborating with students, parents, and advocacy groups can provide valuable insights and help identify areas that need attention.
Continuous Monitoring and Updates: Accessibility is not a one-time effort. Continuously monitor digital content for compliance and stay updated with the latest accessibility standards and best practices. Implement regular updates to address new accessibility challenges as they arise.
By following these nine steps, public schools can meet the requirements of ADA Title II 504 and also create a more inclusive and supportive learning environment for all students.
As technology evolves, so should our commitment to accessibility, ensuring no student is left behind.
Conclusion
The journey toward compliance with ADA Title II 504 is challenging but an opportunity for schools to enhance their digital offerings and ensure that all students, regardless of their abilities, have equitable access to educational resources.
By embracing this mandate, schools can foster a more inclusive learning environment that supports the diverse needs of their student population. However, meeting the 2027 deadline for compliance while creating an inclusive online environment requires expertise and precision.
At ADA Site Compliance, we simplify the process. Our team ensures your school’s digital platforms adhere to accessibility standards, preventing legal issues and fostering a welcoming environment for all students. Let us help you create a truly inclusive digital experience!
#ada compliance for schools#digital accessibility in education#u.s. department of justice#ada title ii#world wide web consortium (w3c)#technical accessibility standards#accessibility features#accessible digital content#accessibility consultants#digital content creation#ada title ii 504 compliance#wcag 2.1 standards#ada compliance deadline 2027#universal design in education#school website#inclusive digital experience#assistive technologies#accessible digital content creation#website accessibility solutions#ADA site compliance#ADASiteCompliance#adasitecompliance.com
0 notes