#utgst
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Simplifying GST: How to Calculate Your Tax Payments Step-by-Step

The Goods and Services Tax (GST) has transformed the taxation system in India by consolidating a plethora of indirect taxes. Besides, achieving the aim of making compliance simple and easy, this transformation has also made the movement of goods and services all over the nation easier. While GST has brought a unified taxation structure for consumers, regarding calculations it can be a bit complex especially, for businesses sometimes they get confused regarding the calculations of GST. Calculating GST correctly is paramount one for the legal compliance and the other for sustaining the general health of the financial system within the business. To business owners, accountants or mere self-employed people, understanding how to calculate GST payments in a step by step process will be very crucial since this will enable you reduce on penalties and also enable you work smoothly.
Understanding the Basics of GST
GST is a complex system that every business owner needs to understand before adopting it. In this blog let us take a look at a basic rundown of GST. However, to embark on calculations, special attention should be paid to the structure and elements of GST. This knowledge will serve as the for foundational understanding of the tax regime and how to compute the correct rates and credits.
1. CGST and SGST/UTGST:
These taxes are applied when the supplying and receiving parties are in the same state or union territory respectively. In such cases:
Central GST (CGST): Gathered by the center administration of the country.
State GST (SGST) or Union Territory GST (UTGST): The sample is collected by the government of the respective state or union territory.
For example, if a business in Delhi sells goods worth ₹1,00,000 to a customer in Delhi with an 18% GST rate, the tax will be split equally:
CGST: ₹9,000
SGST: ₹9,000
2. IGST:
Integrated GST (IGST) is levied on inter-state transactions, where the supplier and recipient are in different states or when goods are imported into India.
IGST ensures seamless input tax credit across state borders, eliminating the cascading effect of taxes.
For example, if a business in Haryana sells goods worth ₹1,00,000 to a customer in Maharashtra at an 18% GST rate, the entire tax (₹18,000) is collected as IGST.
3. GST Rates:
In line with various economic policies and sectors needs, the GST council has divided goods and services into several tax rates. Here’s an overview of the common tax rates:
5%: These comprise of products like processed food, transport services, and even drugs.
12%: Ordinary products like processed food, cloth and apparel, household utensils and furnishings, etc.
18%: Most products and services category range, where the prices of electronics, restaurants, and IT solutions can be set.
28%: Car, tobacco and other luxury products and services and other financial services.
There are some products and services that anyone cannot do without, for example, perishable food articles, and some health services are out of the GST system so as to cost the common man heavily if subjected to the tax. Further, compensation cess may be levied on any item in the 28 % slab for instance luxury car and aerated drink.
• ₹ 20 lakh for services and ₹10 lakh for services in special category states.
• ₹40 lakh for goods, (₹20 lakh in special category states) and healthcare, are exempt from GST to ensure affordability. Additionally, compensation cess may apply to specific items in the 28% slab, like luxury cars and aerated drinks (while certain healthcare services are exempt, food articles are not universally exempt from GST. It would be beneficial to specify that GST exemptions may vary based on the classification of goods or services, and some perishable food items may fall under lower GST slabs rather than being entirely exempt)
.4. GST Registration Thresholds:
Businesses need to register for GST if their annual turnover exceeds:
₹10 lakh for services for the special category states
₹40 lakh for goods (₹20 lakh in special category states).
There is another tiny, Optional Composition Scheme for small taxpayers having a turnover below a threshold limit and they pay GST at a fixed rate
Key Components for GST Calculation
In order to arrive at your GST liability figures, it is important that you have a grasp of the key contouring factors which are deployed at the time of calculation. These elements would ensure that its structure conforms to the GST and enable you make the best of taxes.
1. Invoice Value
Invoicing value is the price of the goods or services apart from the GST tax which is to be charged. This is the amount on which the overall tax otherwise known as GST is charged. The invoice should include:
Product or service details.
Quantity and price of the goods or services.
Applicable discounts (if any).
For example: If a business sells a product with a base price of ₹50,000 and offers a 10% discount, the taxable value is: ₹50,000 - ₹5,000 = ₹45,000. GST is then calculated on ₹ 45,000/- together with other related charges.
2. GST Rate
The credit of GST is available to manufacturers of goods as well as it is also levied based on the type of goods. Another important factor I have discussed before is that the tax structure of GST in India is divided into several bands, which are 5%, 12%, 18%, and 28%.
Check the appropriate GST tax rate in a given product or service on the government published listing or go through the HSN code.
Penalties may be charged from wrongly classified rates hence the need for accuracy.
For example:
The commodities that include packed food items may be chargeable with 5% GST.
Electronic products like laptops are normally charged 18% GST.
3. Input Tax Credit (ITC)
Input Tax Credit (ITC) is another component of GST which is extremely popular with the registered dealer. It enables the business organization to offset the amount of GST charged on purchase materials used in the performance of business.
While implementing the ITC, the amount of tax paid on inputs which is purchase is deducted from the total amount tax collected on outputs which is sales.
Eligibility for ITC:
ITC is allowed when the goods or services for which credit availed are used solely and exclusively for business purposes.
The supplier has to have uploaded this invoice for the GST portal, and the buyer has to pay it on time.
Example of ITC Calculation:
A business buys a goods or service worth ₹1,00,000 having GST of 18%. The GST paid is: ₹1,00,000 × 18% = ₹18,000.
The same business sells the finished goods for ₹2,00,000 with 18% GST. The GST collected is: ₹2,00,000 × 18% = ₹36,000.
The net GST payable after ITC is: ₹36,000 - ₹18,000 = ₹18,000.
Key Points to Remember for ITC:
ITC cannot be claimed on personal expenses or goods and services listed under the negative list.
Maintain accurate records of all purchases and invoices to support ITC claims.
4. GST Liability (Output Tax)
The GST liability is the total tax amount which you have to pay to the government excluding ITC. It is calculated as: GST Liability = GST on Sales (Output Tax) - ITC (Input Tax Credit)
For example:
GST on Sales: ₹50,000
ITC: ₹30,000
Net GST Liability: ₹50,000 - ₹30,000 = ₹20,000.
5. Reverse Charge Mechanism (RCM)
At times, the protected receiver of goods or services charged by the supplier under the Reverse Charge Mechanism (RCM) has to pay GST instead of the supplier.
This in applies for example, services from companies that were not licenced prior to the law came into force and imported good/raw materials.
Under RCM, the recipient has to pay the GST upfront and can claim credit only if he is registered.is required to pay GST under the Reverse Charge Mechanism (RCM) instead of the supplier.
Step-by-Step Guide to GST Calculation
Step 1: Determine the Type of Transaction
Intra-State Transactions
GST is split into CGST (Central GST) and SGST (State GST), each receiving an equal share.
Inter-State Transactions
Only IGST (Integrated GST) is applied for transactions across state boundaries.
Step 2: Identify the GST Rate
GST rates depend on the type of goods or services. Common slabs are 5%, 12%, 18%, and 28%.
Examples:
Essential goods: 5% (e.g., food grains).
Standard goods: 12% or 18% (e.g., electronics).
Luxury goods: 28% (e.g., cars).
Step 3: Calculate GST Amount
1. For Intra-State Transactions
Divide the total GST equally into CGST and SGST.
Formula:
CGST = (Invoice Value × GST Rate) ÷ 2
SGST = (Invoice Value × GST Rate) ÷ 2
Example:
Invoice Value: ₹10,000
GST Rate: 18%
CGST = (₹10,000 × 18%) ÷ 2 = ₹900
SGST = ₹900
Total GST = ₹1,800
2. For Inter-State Transactions
IGST is calculated on the entire transaction value.
Formula:
IGST = Invoice Value × GST Rate
Example:
Invoice Value: ₹10,000
GST Rate: 18%
IGST = ₹10,000 × 18% = ₹1,800
Step 4: Factor in Input Tax Credit (ITC)
Input Tax Credit (ITC) reduces your tax liability by subtracting the GST paid on purchases from the GST collected on sales.
Formula:
Net GST Payable = Output Tax – Input Tax
Example:
Output Tax: ₹20,000
Input Tax: ₹10,000
Net GST Payable = ₹20,000 – ₹10,000 = ₹10,000
Step 5: Include Reverse Charge Mechanism (RCM)
For specific transactions, the recipient pays GST under the Reverse Charge Mechanism (RCM).
Example: If importing goods worth ₹1,00,000 at an 18% GST rate:
RCM GST Payable = ₹1,00,000 × 18% = ₹18,000
Step 6: Finalize GST Filing
Calculate the total GST payable after deducting ITC and any RCM liability. File GST returns through:
GSTR-1: Outward supplies.
GSTR-3B: Summary and payment.
Filing GST Returns
After calculating your GST liability, the next critical step is filing the appropriate GST returns to stay compliant. Here’s a brief overview of the common GST returns:
1. GSTR-1: Outward Supplies (Sales)
This return entails all details of outward supplies or sales made during a particular period.
Key Points:
Report invoice-wise details of B2B transactions.
Consolidated summary for B2C transactions.
Due Date: By the 11th of the following month for fiscal monthly filers.
2. GSTR-3B: Summary Return for Tax Payments
This is a simplified return for filing the summary of outward and inward supplies made during the period accompanied by payment of taxes.
Key Points:
Declare total sales, tax liability, and input tax credit.
Offset ITC against GST liability and pay the net amount.
Due Date: on the 20th of the following month if the return is filed monthly.
3. GSTR-2A/2B: Inward Supplies (Purchases)
These are auto-drafted returns that show details of inward supplies (purchases).
Key Points:
GSTR-2A form is auto populated and is updated every time.
GSTR-2B is static and fixed for a given period, aiding ITC reconciliation.
4. GSTR-9: Annual Return
This return is the summarized return of all the GST transactions in a particular financial year.
Key Points:
Required for any Tax Payer with a turnover or turnover limit of more than ₹2 crore.
Includes details from GSTR-1 and GSTR-3B.
Due Date: 31st December of the following financial year.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in GST Calculation
If not properly calculated, GST poses serious compliance problem or even financial loss to the businesses that compute it. Here's how to sidestep common pitfalls:
1. Incorrect Classification of Goods/Services
Failure to apply the right GST rate on goods or services is common among businesses. Such errors cause either under or over payment of tax thus attracting penalties.
Tip: Please check the official GST Rate Chart and keep yourself updated with any changes in it.
2. Overlooking ITC Eligibility
If you do not avail all the ITC as are possible then your tax burden goes up. ITC is admissible only in respect of the inputs that are incurred solely for the supply of business products accompanied by a valid invoice.
Tip: Regularly review and reconcile ITC claims against purchases in GSTR-2B.
3. Late GST Payments
Failing to pay GST leads to the accrual of an 18% of annual interest on the amount of tax as well as the fees for the returns.
Tip: Schedule the filing due dates and ensure that the payments are made automatically in order not to be left behind.
4. Errors in Invoice Details
Discrepancy in the invoice figures particularly GSTIN number, the taxable value, or the tax amount rates can lead to distortion of GST reconciliation as well as hinder ITC applications.
Tip: Ensure one verifies all invoices on cases of customer generation or uploading the same to GST portal.
Tips for Accurate GST Calculations
To ensure precision and compliance, follow these best practices:
1. Automate GST Calculations
This approach is very unproductive and full of many avenues of error. Accounting software with GST modules can be used to ease the process since the right templates for filing of the forms are already incorporated in the software.
Popular Options: Tally, Zoho Books, QuickBooks.
2. Keep Detailed Records
Preservation of records for sales, purchases and taxes is very important during auditing and balancing.
Tip: Scanned all documents and copies should be made often in order to avoid loss and for quick access.
3. Reconcile Regularly
This means that, when books are matched with GST returns, there are no compliance issues in terms of taxes.
Tip: Before availing credit on ITC, ensure that there is a match between GSTR-2A/2B with the purchase register.
4. Stay Updated
GST laws, laws and guidelines related to it and the methods of its functioning may alter from time to time. Trying to remain updated will save you from making much more mistakes not to mention the penalties that you are likely going to encounter.
Tip: Subscribe to government updates or consult tax professionals for the latest information.
Conclusion
Determining gross amount right to the last penny of GST is very important because of compliance issues as well as efficiency of the business. Understanding the structure of the GST tax, applying the right formulas and using technology most of the time makes the exercise a breeze. There are certain mistakes that people make while preparing and analyzing financial data, and by avoiding them, maintaining records accurately while using the best computer software to calculate the financial data, business people can save a lot of time while avoiding needless errors which could lead to the losing of marketing opportunities.
At The Legal Dost, we lay emphasis when it comes to handling complicated compliances which are as follows – GST Calculation and GST Filing. Small business or large business, the advice and services provided guarantee precision and no mistake. Join with us to enhance your tax solutions and bring your business towards success.
0 notes
Text
Master GST Filing with Our Comprehensive GST Course
GST Course: Fee, Duration, and Syllabus
Goods and Services Tax (GST) has become a cornerstone of India’s indirect taxation system, transforming the way businesses operate. With GST’s widespread implementation, the demand for professionals adept in GST laws and procedures has grown exponentially. A GST course equips individuals with the knowledge required to understand, implement, and comply with GST regulations. This guide delves into the fee structure, duration, and syllabus of GST courses, helping aspirants make informed decisions.
What is a GST Course?
A GST course is a specialized training program designed to provide comprehensive knowledge of the Goods and Services Tax system in India. These courses are suitable for:
Business Owners: To manage GST compliance effectively.
Accountants and Tax Professionals: To enhance their career prospects.
Students: To gain valuable skills for future job opportunities.
Entrepreneurs: To understand the tax implications for their businesses.
Why Enroll in a GST Course?
Understanding GST is crucial for businesses and professionals alike. Here are key reasons to enroll:
Enhanced Career Opportunities: Certified GST professionals are in high demand across industries.
Legal Compliance: Gain insights into GST rules to avoid penalties.
Business Efficiency: Learn how to optimize tax filings and input tax credits.
Entrepreneurial Growth: Entrepreneurs can better understand their tax obligations.
Types of GST Courses
GST courses are available in various formats to suit different learning needs:
Certification Courses: Short-term programs focused on fundamental GST knowledge.
Diploma Courses: Comprehensive programs covering advanced GST concepts and practical applications.
Online Courses: Flexible programs accessible from anywhere.
Classroom Courses: In-person training for hands-on learning.
GST Course Fee
The fee for a GST course varies based on factors like the course provider, duration, and mode of delivery. Below is a general overview:
Basic Certification Courses:
Fee Range: ₹5,000 to ₹20,000.
Ideal for beginners and professionals looking for an introduction to GST.
Advanced Diploma Courses:
Fee Range: ₹20,000 to ₹50,000.
Suitable for in-depth learning and practical training.
Online Courses:
Fee Range: ₹2,000 to ₹15,000.
Affordable and flexible options for working professionals.
Institutional Courses:
Fee Range: ₹10,000 to ₹30,000.
Offered by reputed institutes with expert faculty.
Additional costs may include GST software access, study materials, and examination fees.
Duration of GST Courses
The duration of GST courses varies depending on the course type and level of expertise offered. Here's a breakdown:
Short-Term Courses:
Duration: 1 week to 1 month.
Focus: Basics of GST, filing returns, and compliance.
Certification Courses:
Duration: 1 to 3 months.
Focus: Detailed understanding of GST laws, taxation procedures, and software training.
Diploma Courses:
Duration: 6 months to 1 year.
Focus: Advanced topics, practical applications, and case studies.
Crash Courses:
Duration: 2 to 5 days.
Focus: Quick overview for business owners and professionals.
Syllabus of GST Courses
The syllabus of a GST course is structured to provide theoretical knowledge and practical skills. While the syllabus varies across providers, the following topics are commonly included:
1. Introduction to GST
History and Evolution of GST in India.
Objectives and Benefits of GST.
GST Structure: CGST, SGST, IGST, and UTGST.
2. GST Registration
Eligibility Criteria for GST Registration.
Process of GST Registration.
Types of Taxpayers under GST.
Special Cases: Casual and Non-Resident Taxable Persons.
3. Taxable Events and Scope of Supply
Definition of Supply under GST.
Composite and Mixed Supplies.
Time, Place, and Value of Supply.
4. GST Returns
Types of GST Returns (GSTR-1, GSTR-2A, GSTR-3B, etc.).
Filing Procedures and Deadlines.
Rectification of Errors in Returns.
5. Input Tax Credit (ITC)
Eligibility and Conditions for Availing ITC.
ITC Reversals.
Matching Concept under GST.
6. GST Invoicing
Components of a GST Invoice.
E-Invoicing and its Benefits.
Debit and Credit Notes.
7. GST Payments
Modes of Payment: Online and Offline.
Challans and Payment Reconciliation.
Late Fees and Penalties.
8. GST Audit and Assessment
Types of Audits under GST.
Process of GST Assessment.
Appeals and Revisions.
9. Reverse Charge Mechanism (RCM)
Concept of RCM.
Applicability and Exceptions.
Compliance under RCM.
10. GST Compliance and Penalties
Compliance Requirements.
Common Errors and How to Avoid Them.
Overview of Penalties and Provisions.
11. GST in Special Cases
GST on E-Commerce.
GST for Exporters and Importers.
Composition Scheme under GST.
12. GST Software Training
Hands-on Training in GST Filing Software.
Usage of Tools like Tally and Zoho Books.
Troubleshooting Common Issues.
Top Institutes Offering GST Courses
Several reputed institutes offer GST courses. Here are a few notable ones:
Institute of Chartered Accountants of India (ICAI):
Offers specialized GST training for accounting professionals.
Fee: ₹10,000 to ₹15,000.
National Institute of Financial Management (NIFM):
Provides certification and diploma courses in GST.
Fee: ₹20,000 to ₹30,000.
TaxGuru Edu:
Known for online GST certification courses.
Fee: ₹2,000 to ₹5,000.
Simplilearn:
Offers online GST training with practical applications.
Fee: ₹7,000 to ₹12,000.
Coursera and Udemy:
Affordable and flexible GST courses.
Fee: ₹2,000 to ₹5,000.
Who Should Enroll in a GST Course?
GST courses are ideal for:
Accountants and Tax Consultants:
To expand their service offerings.
Business Owners and Entrepreneurs:
To ensure seamless GST compliance.
Commerce Students:
To gain practical knowledge and enhance employability.
Job Seekers in the Finance Domain:
To add value to their resumes.
Career Opportunities After Completing a GST Course
Completing a GST course opens doors to various career opportunities, including:
GST Practitioner:
Help businesses with GST registration, filing, and compliance.
Tax Consultant:
Advise clients on tax planning and compliance.
Accountant:
Manage company accounts with GST integration.
Finance Manager:
Oversee GST-related financial processes in organizations.
Self-Employment:
Start your own GST consultancy.
Conclusion
A GST course is an excellent investment for anyone looking to advance their career in taxation and finance. With flexible options available in terms of fees, duration, and modes of delivery, there’s a course for everyone’s needs. The structured syllabus ensures comprehensive learning, empowering individuals to navigate the complexities of GST with confidence. Whether you’re a student, professional, or business owner, mastering GST can pave the way for significant growth
IPA offers:-
Accounting Course , Diploma in Taxation, Courses after 12th Commerce , courses after b com
Diploma in Financial Accounting , SAP fico Course , Accounting and Taxation Course , GST Course , Basic Computer Course , Payroll Course, Tally Course , Advanced Excel Course , One year course , Computer adca course
0 notes
Text
GST Training Course for Beginners and Professionals
GST Course: Understanding the Gateway to Taxation Knowledge
जीएसटी कोर्स: कराधान ज्ञान का प्रवेशद्वार समझें
Introduction: What is GST? परिचय: जीएसटी क्या है?
Goods and Services Tax (GST) is a unified tax system implemented in India to simplify the tax structure. It eliminates the cascading effect of multiple taxes and promotes a transparent taxation mechanism. Understanding GST is crucial for businesses, accountants, and tax consultants, which is why enrolling in a GST course can be a valuable step. गुड्स एंड सर्विसेज़ टैक्स (जीएसटी) भारत में लागू एकीकृत कर प्रणाली है, जो कर ढांचे को सरल बनाती है। यह कई करों के दोहरे प्रभाव को स��ाप्त करती है और पारदर्शी कराधान प्रणाली को बढ़ावा देती है। जीएसटी को समझना व्यवसायों, लेखाकारों और कर सलाहकारों के लिए महत्वपूर्ण है। इसलिए, जीएसटी कोर्स में दाखिला लेना एक लाभदायक कदम हो सकता है।
Why Enroll in a GST Course?
जीएसटी कोर्स में दाखिला क्यों लें?
Practical Knowledge GST courses provide hands-on experience with tax calculations, filing GST returns, and understanding compliance regulations. जीएसटी कोर्स कर गणना, जीएसटी रिटर्न दाखिल करने और अनुपालन नियमों को समझने का व्यावहारिक अनुभव प्रदान करते हैं।
Career Advancement A GST certification boosts your resume and opens doors to opportunities in accounting, finance, and tax consultancy. जीएसटी सर्टिफिकेशन आपके रिज़्यूमे को मजबूत करता है और लेखांकन, वित्त और कर परामर्श में अवसर प्रदान करता है।
Business Benefits Entrepreneurs gain insights into managing taxes effectively, reducing penalties, and ensuring compliance. उद्यमी करों को प्रभावी ढंग से प्रबंधित करने, जुर्माने को कम करने और अनुपालन सुनिश्चित करने में विशेषज्ञता प्राप्त करते हैं।
Key Topics Covered in GST Courses
जीएसटी कोर्स में शामिल मुख्य विषय
Introduction to GST
History and need for GST.
Types of GST: CGST, SGST, IGST, and UTGST.
GST structure and framework. जीएसटी का इतिहास और आवश्यकता, सीजीएसटी, एसजीएसटी, आईजीएसटी और यूटीजीएसटी जैसे जीएसटी के प्रकार।
GST Registration Process
Eligibility for GST registration.
Step-by-step online registration.
Documents required for GST registration. जीएसटी पंजीकरण की पात्रता, ऑनलाइन पंजीकरण की चरणबद्ध प्रक्रिया, और आवश्यक दस्तावेज़।
GST Returns Filing
Types of GST returns (GSTR-1, GSTR-3B, etc.).
Due dates and penalties for late filing. जीएसटी रिटर्न के प्रकार, देरी से दाखिल करने के लिए समय सीमा और जुर्माना।
GST Compliance and Auditing
Importance of compliance in business.
GST audit process and annual returns. व्यवसाय में अनुपालन का महत्व और जीएसटी ऑडिट प्रक्रिया।
Duration and Fees of GST Courses
जीएसटी कोर्स की अवधि और फीस
GST courses typically last between 1 to 3 months, depending on the mode of learning (online or offline). The fee ranges from ₹5,000 to ₹25,000, based on the institute and course content. जीएसटी कोर्स की अवधि आमतौर पर 1 से 3 महीने होती है, जो सीखने के माध्यम (ऑनलाइन या ऑफलाइन) पर निर्भर करती है। फीस संस्थान और पाठ्यक्रम सामग्री के आधार पर ₹5,000 से ₹25,000 तक हो सकती है।
Eligibility for GST Courses
जीएसटी कोर्स के लिए पात्रता
Basic Knowledge Candidates should have basic knowledge of accounting and taxation. उम्मीदवारों को लेखांकन और कराधान का बुनियादी ज्ञान होना चाहिए।
Educational Qualification A degree in commerce or related fields is preferred but not mandatory. वाणिज्य या संबंधित क्षेत्रों में डिग्री वांछनीय है, लेकिन अनिवार्य नहीं।
Job Opportunities After Completing GST Course
जीएसटी कोर्स पूरा करने के बाद रोजगार के अवसर
GST Consultant Assist businesses in GST compliance and filing returns. व्यवसायों को जीएसटी अनुपालन और रिटर्न दाखिल करने में सहायता करें।
Accountant Manage GST records and accounts for companies. कंपनियों के लिए जीएसटी रिकॉर्ड और खाते प्रबंधित करें।
Tax Advisor Provide advisory services related to GST planning and implementation. जीएसटी योजना और कार्यान्वयन से संबंधित परामर्श सेवाएं प्रदान करें।
Government Jobs Work in tax departments as a GST officer or auditor. कर विभागों में जीएसटी अधिकारी या लेखा परीक्षक के रूप में कार्य करें।
How to Choose the Best GST Course?
सर्वश्रेष्ठ जीएसटी ��ोर्स कैसे चुनें?
Accreditation Ensure the course is certified by a recognized institute. सुनिश्चित करें कि कोर्स किसी मान्यता प्राप्त संस्थान से प्रमाणित हो।
Faculty Expertise Check the qualifications and experience of instructors. प्रशिक्षकों की योग्यता और अनुभव की जांच करें।
Course Content Look for a comprehensive curriculum covering practical aspects. व्यावहारिक पहलुओं को शामिल करने वाले पाठ्यक्रम की तलाश करें।
Reviews and Testimonials Read reviews from previous students to gauge course effectiveness. पाठ्यक्रम की प्रभावशीलता का आकलन करने के लिए पूर्व छात्रों की समीक्षाएं पढ़ें।
Conclusion
निष्कर्ष
A GST course is a stepping stone for those looking to excel in taxation and finance. It not only enhances your skill set but also opens up diverse career opportunities. Whether you're an aspiring accountant, an entrepreneur, or a tax consultant, this course will equip you with the tools to succeed in the competitive world of taxation. जीएसटी कोर्स कराधान और वित्त में उत्कृष्टता प्राप्त करने के इच्छुक लोगों के लिए एक महत्वपूर्ण कदम है। यह न केवल आपके कौशल को बढ़ाता है बल्कि विविध करियर के अवसर भी प्रदान करता है। चाहे आप एक उभरते हुए लेखाकार हों, एक उद्यमी, या एक कर सलाहकार, यह कोर्स आपको प्रतिस्पर्धी कराधान की दुनिया में सफल होने के लिए आवश्यक उपकरण प्रदान करेगा।
IPA Offers
Diploma in Taxation, Courses after 12th Commerce , courses after bcom
Diploma in Financial Accounting , SAP fico Course , Accounting and Taxation Course , GST Course , Basic Computer Course , Payroll Course, Tally Course , Advanced Excel Course , One year course , Computer adca course , Income Tax Course
0 notes
Text
GST Registration Rules for Startups in Bangalore
Bangalore, known as the Silicon Valley of India, is a hub for startups, IT companies, and diverse business activities. With the rapid growth of businesses in the city, entrepreneurs and companies need to be aware of the Goods and Services Tax (GST) and the importance of GST registration. This article provides a detailed guide on GST Registration in Bangalore, including its benefits, eligibility, process, and required documents.
What is GST?
The Goods and Services Tax (GST) is a unified tax system that replaced various indirect taxes like VAT, excise duty, and service tax. It is levied on the supply of goods and services in India. GST is a destination-based tax, meaning it is collected at the point of consumption rather than the point of origin. The tax is divided into four categories:
CGST: Central Goods and Services Tax, collected by the Central Government.
SGST: State Goods and Services Tax, collected by the State Government.
IGST: Integrated Goods and Services Tax, levied on inter-state transactions.
UTGST: Union Territory Goods and Services Tax, applicable in Union Territories.
Why is GST Registration Important?
GST registration is mandatory for businesses with a turnover exceeding ₹40 lakhs (₹20 lakhs for service providers) or those involved in inter-state supply, e-commerce, or specific taxable services. GST registration allows businesses to:
Legally operate under the GST regime.
Claim input tax credit on purchases, reducing the overall tax burden.
Ensure compliance with tax regulations, avoiding penalties and legal consequences.
Enhance business credibility among customers and vendors.
Eligibility for GST Registration in Bangalore
GST registration is required for:
Businesses with annual turnover exceeding ₹40 lakhs (for goods) or ₹20 lakhs (for services).
Individuals and entities engaged in inter-state supply of goods or services.
E-commerce operators and those selling through online platforms.
Casual taxable persons are conducting occasional business.
Non-resident taxable persons providing goods or services in India.
Agents or distributors of taxable supplies.
Input service distributors.
Businesses are liable to pay reverse charges under GST.
Documents Required for GST Registration in Bangalore
To register for GST in Bangalore, companies need to provide the following documents:
PAN Card of the business or applicant.
Aadhaar Card of the authorised signatory.
Proof of business registration or incorporation certificate.
Identity proof and address proof of the authorised signatory (passport, driving license, or voter ID).
Bank account details, including a cancelled cheque or bank statement.
Address proof of the business premises (electricity bill, rent agreement, or property tax receipt).
Digital Signature Certificate (DSC) for companies and LLPs.
Photograph of the applicant (authorised signatory).
Steps for GST Registration in Bangalore
1. Visit the GST Portal
Go to the official GST portal at www.gst.gov.in and click on the “Services” tab. Under the "Registration" section, click on "New Registration."
2. Fill in the Details
Enter details like:
Business name and PAN.
Email address and mobile number.
Type of business (Proprietorship, LLP, Company, etc.).
3. Submit OTP Verification
An OTP (One-Time Password) will be sent to your registered mobile number and email. Enter this OTP to verify your details.
4. Fill in Business Information
Provide details like the business's legal name, trade name, principal place of business, and business constitution (LLP, partnership, etc.).
5. Upload Documents
Upload the required documents, including proof of business, identity, address, and bank details.
6. Digital Signature
If the business is a company or LLP, sign the application using a Digital Signature Certificate (DSC). Proprietorships and partnerships can use electronic verification codes (EVC).
7. Submit the Application
Once all details and documents are filled out, submit the application. After submission, you will receive an Application Reference Number (ARN) for tracking purposes.
8. GST Registration Certificate
The GST authorities will verify the application. If everything is in order, the GST registration certificate with a unique GST Identification Number (GSTIN) will be issued within seven working days.
GST Registration Fees in Bangalore
GST registration is free of cost. However, businesses may choose to hire professionals to assist with the process, which could involve a service fee depending on the complexity of the registration.
Penalties for Non-Registration
Failure to register for GST when required can result in penalties:
Late registration penalty: 10% of the tax amount due, subject to a minimum of ₹10,000.
Fraudulent evasion of tax: Penalty of 100% of the tax amount due.
Conclusion
GST Registration in Bangalore is essential for businesses to operate smoothly and in compliance with tax laws. It offers benefits like input tax credits and enhances a business's credibility. While the registration process can be completed online, ensuring all details are accurate and documents are in place is crucial to avoid delays. If needed, please be sure to consult a professional who can streamline the process.
0 notes
Text
Goods and Service Tax :What is GST in India? How Does GST Work?
Introduction to Goods and Service Tax (GST)
Goods and Service Tax (GST) is a unified tax system implemented in India to simplify and streamline the taxation process for goods and services. Launched on July 1, 2017, GST replaced multiple indirect taxes such as VAT, excise duty, and service tax, creating a single, nationwide tax. This system aimed to reduce tax burdens, encourage compliance, and promote a transparent economy.
What is Goods and Service Tax (GST)?
Goods and Service Tax, commonly referred to as GST, is a comprehensive, multi-stage, destination-based tax that is levied on every value addition across the supply chain. GST applies to goods and services alike, charging tax at each stage of production or distribution. Ultimately, the tax is borne by the end consumer, with businesses acting as intermediaries in the collection and remittance process.
How Does GST Work?
GST functions as a value-added tax, where tax is levied at each stage of production and supply but ultimately borne by the consumer. The tax collected from the buyer is partially credited to the seller, ensuring that only the value-added at each stage is taxed.
Types of Goods and Service Tax (GST)
To accommodate the federal structure of India, GST is divided into various types, each addressing different aspects of tax collection and allocation.
Central Goods and Service Tax (CGST)
CGST is the portion of GST collected by the Central Government for intra-state supplies of goods and services. Revenue collected from CGST is used for central welfare and development programs.
2. State Goods and Service Tax (SGST)
SGST is the counterpart to CGST, levied by individual state governments on intra-state transactions. The revenue from SGST goes directly to the state, supporting local infrastructure, health, and education programs.
3.Integrated Goods and Service Tax (IGST)
IGST applies to inter-state transactions and imports. This tax is collected by the Central Government but later distributed between the center and states to ensure equitable revenue sharing.
4.Union Territory Goods and Service Tax (UTGST)
For Union Territories that do not have their own legislature, UTGST is levied in place of SGST. It applies to intra-UT supplies, with revenue supporting the development of Union Territories.
Read also: How to track your GST Payment status? , GST return filing due dates
#goods and service tax portal#goods and service tax calculator#goods and service tax certificate download#goods and service tax rate#goods and service tax act#goods and service tax challan#goods and service tax online payment#objectives of goods and service tax#goods and service tax network#what is good and service tax#goods and service tax act 2017 pdf#goods and services tax book pdf#goods and service tax bare act#goods and services tax list#goods and service tax project
0 notes
Text

GST Online Course With Certificate
GST online course with certificate is the course which you can pursue that can help you add on a great skill in your life. You’ll have good knowledge of Goods And Services Tax, GSTR1, GSTR3B, GSTR2B, GSTR2A, How to do tax calculations and other stuff that accountants do.
GST online course with certificate syllabus/curriculum:
Introduction to GST (Goods And Services Tax)
Types of Gst (CGST, SGST, IGST, and UTGST)
Tax Slabs (5%, 12%, 18%, and 28%)
Input tax Credits
GST valuation
GST Returns
GST Penalties
GST Payments
GST Registration
By the end of the course, you’ll have the skill of Goods And services tax (GST Online Course With Certificate). And will receive the certification after the completion of the course that will help you build a strong portfolio that can help you in your higher education and in also landing an articleship, or in pursuing a job in the financial profession.
For More Information Visit Us: https://www.digischema.com/certified-accounting-course/
#Accounting Course#Online Tally Prime Course#Gst Online Course#Digital Accounting Course#Tally Prime Course Online#Articleship#job placement#Digi Schema
0 notes
Text
Highlights of the 53rd GST Council Meeting: Key Updates and Outcomes
Highlights of the 53rd GST Council Meeting: Key Updates and Outcomes. The 53rd GST Council meeting, held on June 22, 2024, in New Delhi, marked the first meeting after the 2024 Lok Sabha elections. Chaired by the newly appointed Union Finance Minister, Nirmala Sitharaman, the meeting addressed several critical issues to streamline GST compliance and enhance the tax structure. This blog provides a comprehensive overview of the meeting’s highlights, updates, outcomes, and the latest news. GST Registration.
Key Decisions and Updates from the 53rd GST Council Meeting
Ease of Compliance Burden for Taxpayers
1. Changes in GSTR-1 Filing:
Introduction of GSTR-1A: Taxpayers can now add or amend particulars in GSTR-1 of the current tax period/IFF for the 1st and 2nd month of the quarter before filing GSTR-3B.
Reporting B2C Supplies: The threshold for reporting Business-to-Consumer (B2C) interstate supplies invoice-wise in Table 5 of GSTR-1 has been reduced from ₹2.5 lakh to ₹1 lakh.
2. GSTR-4 Due Date Revised:
The due date for filing GSTR-4 by composition taxable persons has been extended from April 30 to June 30, starting from the fiscal year 2024-25.
3. TCS Rate Reduction:
The Tax Collected at Source (TCS) rate for Electronic Commerce Operators (ECOs) has been reduced from 1% to 0.5% (0.25% each under CGST and SGST/UTGST or 0.5% under IGST).
4. Compulsory Filing of GSTR-7:
GSTR-7 must be filed mandatorily even if no Tax Deducted at Source (TDS) is deducted. No late fee will be charged for nil filing. GST Filing.
5. GSTR-9/9A Filing Exemption:
Taxpayers with an aggregate annual turnover up to ₹2 crore will be exempt from filing the annual return in GSTR-9/9A for the fiscal year 2023-24.
Modifications to Sections and Rules
1. Modification to Section 16(4):
The time limit to avail Input Tax Credit (ITC) for invoices or debit notes in any GSTR-3B filed up to November 30, 2021, is deemed to be November 30, 2021. This applies retrospectively from July 1, 2017. Section 16(4) shall be relaxed for returns filed within 30 days of the order of revocation.
2. Amendment to CGST Rule 88B:
No interest will be charged on the amount available in the electronic cash ledger on the due date of filing GSTR-3B, debited while filing the return in cases of delayed filing.
3. New Section 128A:
Waives interest and penalties for demand notices issued under Section 73 of CGST for fiscal years 2017-18, 2018-19, and 2019-20 in cases not involving fraud, suppression, and misstatement. This applies if the taxpayer pays the full amount in the notice by March 31, 2025.
4. Changes in Sections 73 and 74:
A common time limit will be set for issuing demand notices and orders. The time limit for taxpayers to claim the benefit of reduced penalty, by paying the tax demanded along with interest, is increased from 30 to 60 days.
https://www.finvertoassociates.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/07/Designer-5.jpeg
Monetary Limits and Appeals
1. Monetary Limits for GST Appeals:
Recommended monetary limits for filing appeals: ₹20 lakh for GST Appellate Tribunal, ₹1 crore for High Court, and ₹2 crore for Supreme Court.
2. Amending Sections 107 and 112:
The maximum amount for pre-deposit for filing an appeal before appellate authorities is reduced from ₹25 crore to ₹20 crore under both CGST and SGST. For appeals before the GST Appellate Tribunal, the pre-deposit is reduced from 20% with a maximum amount of ₹50 crores to 10% with a maximum of ₹20 crores under both CGST and SGST.
Additional Key Decisions
1. Sunset Clause for Anti-Profiteering Cases:
A sunset clause will be added for pending anti-profiteering cases. The hearing panel will shift from CCI to the principal bench of GSTAT. The sunset date for receiving new applications regarding anti-profiteering is set for April 1, 2025.
2. Time Limit for GSTAT Appeals:
Modifying Section 112 to provide a 3-month time frame for filing appeals before the GST Appellate Tribunal. The timeline will commence from a date yet to be notified, likely by August 5, 2024.
3. New Section 11A:
Allows regularization of non-levy or short levy of GST due to common trade practices.
4. IGST Refunds and Adjustments:
Mechanism introduced for claiming refunds of additional IGST paid due to upward price revisions after exports. No IGST refund will be allowed where export duty is payable.
5. Biometric-based Aadhaar Authentication:
Implementation of biometric-based Aadhaar authentication for GST registration will be rolled out nationwide in a phased manner.
6. DRC-03 Circular:
A circular will prescribe a mechanism for adjusting any demand amount paid through DRC-03 against the amount payable as a pre-deposit for filing a GST appeal.
7. Amendment to Section 122(1B):
Clarification that the penal provision is applicable only for those e-commerce operators required to collect TCS under Section 52 and not for other e-commerce operators.
The 53rd GST Council meeting has brought significant changes aimed at simplifying compliance, reducing the tax burden, and enhancing the efficiency of the GST system. These updates reflect the government’s ongoing efforts to create a more robust and taxpayer-friendly GST framework. Keep an eye on official announcements for further details and implementation guidelines.
Stay tuned for the latest updates and insights on GST and other financial regulations.
1 note
·
View note
Text
GST Basic Concepts: A Student's Simple Guide
GST was introduced in India from July 2017. This system integrated a set of taxes into one system and made the collection of taxes direct and transparent. For any finance, accounting, or business student, it is highly essential to study the details of GST since it is an integral part of the tax today. If you are studying GST Course in Kolkata, you would jump a step ahead of all others in your career.
What is GST?
GST stands for Goods and Services Tax. It is an indirect tax levied on the sale of both goods and services by the Central Government in India, effective for the entire country. GST constitutes a comprehensive package which abolished all the earlier cumbersome indirect taxes such as Value Added Tax, Central Excise Duty, and Service Tax. The main objective of GST is to collect tax on consumption instead of at the place of manufacture or place of provision of service.
This also eliminates the problem of "tax-on-tax" or cascading effect and simplifies India's tax landscape.
Why Learn GST?
The following are the reasons why GST knowledge is essential for a student of accounting or finance:
High Demand for GST Experts: Businesses have sound GST knowledge to enable proper tax filing and compliance.
Careers Opportunities: GST knowledge opens doors to tax, accountancy, auditing, and financial management careers that bring you one step closer.
Natively Appealing Salary Package: GST being a fresh subject, it inherently attracts experts so also the salary is a lucrative salary package. Types of GST For any Taxation Course in Kolkata, there are four basic categories of GST-
Central GST (CGST): Amount collected by the central government on intra-state sale.
State GST (SGST): Amount collected by the state governments for selling in their respective states.
Integrated GST: Amount charged by the central government on inter-state sales.
Union Territory GST (UTGST): Applied in the Union Territories instead of SGST .
This dual will aid the internal division of tax revenues between the central and state governments.
Gains of GST
Single Tax System: GST replaces a wide range of taxes, that is, VAT and service tax; rather, it has one uniform system, thereby making it easy to comply with.
Easy Compliance: Companies find it easier to follow the GST framework, as it is uniform.
Electronic Filing: Filing taxes through the GST portal is easy and time-saving.
Speed Logistics: Since there are no taxes at the state level, goods can be dispatched faster, which means more efficient business operations.
Push to 'Make in India': GST reduces the cost of manufacturing goods to such an extent that the Indian goods look cheaper in the global market.
Enhanced Revenue for the Government: Due to GST, the government has been able to save more through reduced tax evasions.
Transparence: The online filing and payment method brought transparence to the tax collection process.
Detriments of GST
Despite all these benefits, there are also some detriments that accompany GST:
Increased Operating Expenses: Businesses have to install new software compatible with GST and train staff accordingly to manage the system.
Costlier Software: After GST, corporations must employ the premium, sometimes costlier software also to avail compliance, thereby increasing the costs of operations.
How GST Functions
The key input tax credit system is one of the key innovations of GST that will enable corporations to offset the accruing amount of this tax by taking a credit for taxes paid on the purchase of inputs, thereby reducing the incidence of tax on consumers. It is perfectly feasible for Tally Course in Kolkata students to understand how they have to address the concerns of GST compliances through accounting software.
Tax Slabs Under GST
The rates of GST range from 0% to 28%. Various goods and services are taxable. The tax rates for indispensable items will be less, and the more costly items will charge a higher tax. As an accounting course in Kolkata or a GST course, you need to know this.
GST Registration
Businesses having a turnover above a certain threshold are required to be registered for GST. The entire process is entirely online, thus within the reach of the companies.
GST Return Filing
GST Return filing is yet another aspect of compliance. There are three types of returns in all:
GSTR-1: Sales return
GSTR-3B: Revenues of all the transactions in a month
GSTR-9: An annual return of all the transactions during the year.
Mastering these returns, more so through Tally software, is prime to accounting professionals.
Composition Scheme
Under GST, small businesses can opt for the Composition Scheme, whereby one pays a fixed percentage of tax, and some compliance requirements are exempted. There is no input tax credit available. Of course, this scheme is much helpful to the small retailers, traders, and restaurants.
GST Compliance
The registration of the company, record-keeping, issues of GST-compliant invoices, and return filing are some of the GST compliances. Businesses require GST and accounting tool in Tally thus can ascertain that they are on all the regulatory stipulations.
Reverse Charge Mechanism (RCM)
At some point, the recipient of goods or services pays GST instead of the supplier. This is a requirement that is termed as Reverse Charge Mechanism (RCM). One has to learn RCM so that they can specialize on GST compliance.
Conclusion
Students who desire to study in the field of financial, accounting, and business should take this course. GST streamlined the system of Indian taxes and made it clear. Even though one should monitor the changes the GST is facing in its doctrines and legal provisions, for attaining success in the long run, theoretical knowledge is indispensable along with practical experience.
#accounting course#gst course#taxation course#Accounting course in kolkata#gst course in kolkata#taxtaion course in kolkata#Tally course#Tally course in kolkata
0 notes
Text
GST in Gurgaon: A Comprehensive Guide to Compliance and Benefits
The Goods and Services Tax (GST) has revolutionized the tax machine in India, simplifying the complex internet of indirect taxes. For companies in Gurgaon, one of the maximum unexpectedly developing industrial hubs, information the nuances of GST is essential for seamless operation & increase. Adya Financial 'll provide a complete guide on GST in Gurgaon, along with its implications for businesses, registration approaches, and the way it is able to affect the hospitality industry, including luxury inn rooms in Dehradun and similar establishments.

Introduction to GST in India
The Goods and Services Tax (GST) become added in India on July 1, 2017, to unify a couple of oblique taxes right into unmarried, complete machine. It replaced taxes like Value Added Tax (VAT), Central Excise Duty, Service Tax, and different local levies. This simplification has made the tax machine greater obvious & less difficult to control, particularly for groups with multi-state operations like the ones in Gurgaon.
GST is levied at the supply of goods & offerings at every degree of the supply chain, from production to the final consumer. Its middle idea is to get rid of the "cascading effect" of taxes, because of this product is taxed most effective on the point of consumption.
Types of GST
Before diving into the specifics for Gurgaon, it’s essential to understand the 4 most important types of GST:
CGST (Central Goods and Services Tax): Levied by using the important government on intra-state transactions.
SGST (State Goods and Services Tax): Levied by using the kingdom authorities on intra-country transactions.
IGST (Integrated Goods and Services Tax): Levied on inter-country transactions.
UTGST (Union Territory Goods and Services Tax): Applicable for Union Territories like Chandigarh, Andaman and Nicobar Islands, & so forth.
Why GST is Important for Businesses in Gurgaon
Gurgaon, now formally known as Gurugram, has emerged as a chief enterprise hub, home to several multinational groups, startups, and industries spanning throughout IT, actual estate, finance, and hospitality. The advent of GST in Gurgaonplays essential position inside the ease of doing commercial enterprise on this metropolis by using:
Simplifying Taxation: GST has replaced a multitude of indirect taxes with one uniform tax, considerably lowering compliance burden for corporations in Gurgaon.
Increased Transparency: With GST, groups can now avail Input Tax Credit (ITC) for taxes paid on items & offerings used in their operations, reducing their usual tax legal responsibility.
Boost to the Hospitality Sector: Hotels & lodges, such as the ones imparting luxurious hotel rooms in Dehradun, enjoy the GST regime. GST simplifies the tax structure for hotels, ensuring that each agencies and customers understand their tax liabilities more truely.

GST Registration Process for Businesses in Gurgaon
Any enterprise operating in Gurgaon, with an annual turnover exceeding ₹40 lakh (₹20 lakh for service vendors), should check in for GST. The technique is entirely on line, making it less complicated for organizations to conform without travelling tax offices.
Steps to Register for GST:
Visit the GST Portal: Begin online gst registration in gurgaon by using journeying the reliable GST internet site (www.Gst.Gov.In).
Filing the Application: You will want to fill out Form GST REG-01. Ensure all info which includes the commercial enterprise name, sort of enterprise, & PAN are entered successfully.
Submission of Documents: Provide important documents like PAN card, Aadhaar card, enterprise registration proof, bank account information, and photos of the owner or enterprise companions.
Verification and Approval: Once submitted, the utility may be proven by means of tax authorities. Upon approval, you'll be issued unique GST Identification Number (GSTIN).
Completion: After acquiring your GSTIN, you are required to record GST returns often.
GST Compliances for Businesses in Gurgaon
Complying with GST guidelines is vital for groups to keep away from penalties and make certain clean operations. Here are some key compliances for GST in Gurgaon:
Monthly/Quarterly Filing of Returns: Depending on the enterprise length and turnover, groups need to report both monthly or quarterly GST returns. The paperwork consist of GSTR-1 (sales info), GSTR-3B (summary return), & GSTR-9 (annual return).
Payment of Taxes: GST is payable month-to-month or quarterly, relying at the form of enterprise. Delayed payments can result in interest & penalties.
Input Tax Credit (ITC): One of the foremost advantages of GST is the capacity to assert credit score for taxes paid on purchases. However, to claim ITC, businesses have to safeguard right document-preserving and matching of buy and income invoices.
Compliance with E-invoicing: For huge organizations, e-invoicing is mandatory. This ensures transparency & curbs tax evasion by means of digitizing the invoicing method.
GST Rates for Various Sectors in Gurgaon
GST quotes vary across industries, making it vital for businesses to live up to date. For groups in Gurgaon, mainly in hospitality, manufacturing, & IT, knowledge those costs is crucial for accurate tax compliance.
Hospitality Sector: Hotels with room price lists underneath ₹1,000 are exempt from GST. For room tariffs among ₹1,000 & ₹7,500, the GST charge is 12%, at the same time as tariffs above ₹7,500 are taxed at 18%. Resorts & comfort hotels, consisting of those providing luxury motel rooms in Dehradun, fall into this class.
Manufacturing Sector: The fashionable GST charge for production groups in Gurgaon is 18%. However, vital objects and meals merchandise may additionally attract a decrease price of 5%.
Information Technology (IT): The GST fee for IT services is 18%, making it vital for tech companies in Gurgaon to conform with this fee structure for software and IT-associated services.
The Role of GST in Boosting the Hospitality Industry
Gurgaon, being a major business & leisure destination, has seen its hospitality industry thrive under GST. The tax structure has brought transparency to hotel tariffs and increased accountability. Moreover, businesses in the hospitality sector, such as those managing luxury hotel rooms in Dehradun, can easily calculate & charge GST, ensuring that guests have a clear understanding of the tax component in their bills.
Additionally, the availability of Input Tax Credit (ITC) on goods and services used by hotels (like food, maintenance, & utilities) has led to cost reductions, allowing hotels to offer competitive pricing without compromising on quality.
Common Challenges for Businesses in Gurgaon Under GST
While GST has simplified the taxation system, agencies in Gurgaon face some demanding situations:
Frequent Updates to GST Laws: The Indian GST system undergoes common adjustments, which may be difficult for agencies to preserve track of. Staying up to date with the modern-day adjustments in tax slabs, ITC guidelines, and compliance requirements is vital.
Mismatch of Invoices: Many organizations face difficulties with invoice matching in the course of ITC claims. This can put off the refund manner & result in coins float troubles.
Penalties for Non-Compliance: Failing to comply with GST submitting or charge deadlines can cause consequences, which can also have an effect on small & medium-sized businesses the most.
Benefits of GST for Gurgaon’s Economy
Despite those demanding situations, GST has positively impacted Gurgaon’s economic system in numerous approaches:
Increased Efficiency: The streamlined tax process beneath GST has decreased paperwork and administrative hurdles for businesses.
Reduced Tax Evasion: GST’s digital infrastructure has curtailed tax evasion by making each transaction traceable.
Boost to Trade and Commerce: The ease of doing commercial enterprise in Gurgaon has stepped forward because of GST, attracting foreign investments & increasing the nearby financial system.
Enhanced Consumer Confidence: For purchasers, GST brings clarity to the tax shape, as they now recognize the precise amount of tax being paid on goods and services.

Conclusion
For corporations in Gurgaon, know-how & complying with gst registration in Gurgaon isn't always just a felony duty but vital issue of smooth operations and increase. Whether you’re walking a small startup or dealing with a series of luxury inn rooms in Dehradun, staying up to date with GST guidelines will make sure your commercial enterprise prospers on this competitive landscape.
By simplifying the tax shape, reducing redundancies, & bringing transparency, GST has paved the manner for corporations in Gurgaon to enlarge & flourish. With the right techniques in area, organizations can leverage GST for each compliance and profitability.
0 notes
Text
GST Registration in Bangalore: A Business Owner's Handbook
GST Registration in Bangalore: A Complete Guide
Bangalore, known as the Silicon Valley of India, is a hub for startups, IT companies, and diverse business activities. With the rapid growth of businesses in the city, entrepreneurs and companies need to be aware of the Goods and Services Tax (GST) and the importance of GST registration. This article provides a detailed guide on GST registration in Bangalore, including its benefits, eligibility, process, and required documents.
What is GST?
The Goods and Services Tax (GST) is a unified tax system that replaced various indirect taxes like VAT, excise duty, and service tax. It is levied on the supply of goods and services in India. GST is a destination-based tax, meaning it is collected at the point of consumption rather than the point of origin. The tax is divided into four categories:
CGST: Central Goods and Services Tax, collected by the Central Government.
SGST: State Goods and Services Tax, collected by the State Government.
IGST: Integrated Goods and Services Tax, levied on inter-state transactions.
UTGST: Union Territory Goods and Services Tax, applicable in Union Territories.
Why is GST Registration Important?
GST registration is mandatory for businesses with a turnover exceeding ₹40 lakhs (₹20 lakhs for service providers) or those involved in inter-state supply, e-commerce, or specific taxable services. GST registration allows businesses to:
Legally operate under the GST regime.
Claim input tax credit on purchases, reducing the overall tax burden.
Ensure compliance with tax regulations, avoiding penalties and legal consequences.
Enhance business credibility among customers and vendors.
Eligibility for GST Registration in Bangalore
GST registration is required for:
Businesses with annual turnover exceeding ₹40 lakhs (for goods) or ₹20 lakhs (for services).
Individuals and entities engaged in inter-state supply of goods or services.
E-commerce operators and those selling through online platforms.
Casual taxable persons are conducting occasional business.
Non-resident taxable persons providing goods or services in India.
Agents or distributors of taxable supplies.
Input service distributors.
Businesses are liable to pay reverse charges under GST.
Documents Required for GST Registration in Bangalore
To register for GST in Bangalore, companies need to provide the following documents:
PAN Card of the business or applicant.
Aadhaar Card of the authorised signatory.
Proof of business registration or incorporation certificate.
Identity proof and address proof of the authorised signatory (passport, driving license, or voter ID).
Bank account details, including a cancelled cheque or bank statement.
Address proof of the business premises (electricity bill, rent agreement, or property tax receipt).
Digital Signature Certificate (DSC) for companies and LLPs.
Photograph of the applicant (authorised signatory).
Steps for GST Registration in Bangalore
1. Visit the GST Portal
Go to the official GST portal at www.gst.gov.in and click on the “Services” tab. Under the "Registration" section, click on "New Registration."
2. Fill in the Details
Enter details like:
Business name and PAN.
Email address and mobile number.
Type of business (Proprietorship, LLP, Company, etc.).
3. Submit OTP Verification
An OTP (One-Time Password) will be sent to your registered mobile number and email. Enter this OTP to verify your details.
4. Fill in Business Information
Provide details like the business's legal name, trade name, principal place of business, and business constitution (LLP, partnership, etc.).
5. Upload Documents
Upload the required documents, including proof of business, identity, address, and bank details.
6. Digital Signature
If the business is a company or LLP, sign the application using a Digital Signature Certificate (DSC). Proprietorships and partnerships can use electronic verification codes (EVC).
7. Submit the Application
Once all details and documents are filled out, submit the application. After submission, you will receive an Application Reference Number (ARN) for tracking purposes.
8. GST Registration Certificate
The GST authorities will verify the application. If everything is in order, the GST registration certificate with a unique GST Identification Number (GSTIN) will be issued within seven working days.
GST Registration Fees in Bangalore
GST registration is free of cost. However, businesses may choose to hire professionals to assist with the process, which could involve a service fee depending on the complexity of the registration.
Penalties for Non-Registration
Failure to register for GST when required can result in penalties:
Late registration penalty: 10% of the tax amount due, subject to a minimum of ₹10,000.
Fraudulent evasion of tax: Penalty of 100% of the tax amount due.
Conclusion
GST registration in Bangalore is essential for businesses to operate smoothly and in compliance with tax laws. It offers benefits like input tax credits and enhances a business's credibility. While the registration process can be completed online, ensuring all details are accurate and documents are in place is crucial to avoid delays. If needed, consulting a professional can streamline the process.
0 notes
Text
What is GST? A Deep Dive into India’s Indirect Tax System
The Goods and Service Tax (GST) is one of the broadest tax reforms of polishing Indian markets which aims at consolidating the diverse and complicated indirect tax system of the country. Brought in from July 1, 2017, GST subsumed over a dozen central indirect taxes like central and state taxes like VAT, service tax, and excise duty. Now let us go through what GST is, how it operates and its effect on the Indian economy.
Understanding GST: The Basics
The Goods and Services Tax (GST) is an extensive value-added tax which is applied at the consumer’s end of the supply chain that centralizes a number of regnant indirect taxes in India. GST operates on the principle of “One Nation One Tax” in the sense that the rate and the principles governing the need should be similar throughout the country.
Key Components of GST
GST is categorized into four major components based on the nature of transactions:
Central GST (CGST):
collected by the central government.
Applicable on intra state sales (i.e. sale of goods within a state).
For instance, if goods are sold within Punjab, CGST will be charged along with SGST.
State GST (SGST):
They are collected by the state government itself.
SGST is applicable only in intra-state transactions.
Both CGST and SGST are charged at half rate (for instance, 9% for an 18% total GST). CGST.
Integrated GST (IGST):
Received by the central government.
Applicable to transactions of goods across states (for example Punjab to Delhi) and importation.
IGST generated is also divided between the central and the state government based on the consumption of the goods and services.
Union Territory GST (UTGST):
Applicable in the union territories lacking legislative assemblies like, Chandigarh, Lakshadweep, and Andaman & Nicobar Islands.
It works exactly like SGST but is collected in Union Territories and not in states.
How Does GST Work?
The GST system is designed to eliminate the cascading effect of taxes, where tax is levied on tax. Here’s how the mechanism works:
Input Tax Credit (ITC): Businesses have the option to take credit of tax paid on inputs used to supply final goods or services. This helps to lower their taxation.
Seamless Flow: Its base follows the value addition at each stage of the supply chain, so it is transparent.
Filing and Compliance: Business who deal with more than one state are required to register under GST; they are supposed to file returns either monthly, quarterly or annually depending on their turnover.
Key Features of GST
· Comprehensive Coverage:
Wide Applicability: GST is in force across India irrespective of the state for almost all the products and services replacing many indirect taxes like Value Added Tax, Service Tax and Central Excise Tax, etc.
Exceptions: Some items are still beyond the ambit of GST like, ‘all goods, except for alcoholic liquor for human consumption, and all services, except services of petroleum, crude or natural gas’. Both the central and state tax authorities impose tax on these items individually.
Unified Framework: This broad coverage makes the whole concept of taxes to be brought under one umbrella and hence unifying the tax systems across the country.
· Multiple Tax Slabs:
Tax Rates: Under the GST regime, the GST rates are in number of slabs depending on the type of goods or services rendered with an aim of meeting the needs of the different income categories of the society.
0% (Exempted Items): Basic need goods and service which include raw food grains and health care sector services.
5% (Lower Rate): That means products of tertiary consumption like canned goods, and other essential commodities.
12% and 18% (Standard Rates): similar types of consumption items such as furniture, electronic goods, and eating out services.
28% (Luxury and Sin Goods): Luxury and sin goods, such as cars and cigarettes and consumer durables are the examples of convenience goods.
Dynamic Adjustments: The GST Council regularly reviews and adjusts rates to balance revenue generation and consumer affordability.
· Digital Framework:
GST Network (GSTN): Goods and Services Tax is coordinated through an integrated web based system hence making tasks like registration, filing, payment, and application for refund easier.
User-Friendly Interface: It is intended to be user friendly as one who is a taxpayer.
Real-Time Updates: Makes work more transparent and decreases time in which one has to wait for compliance.
E-Invoicing and Automation: Launched for starting creation of invoices that are connected to the GST system, decrease the possibility of mistakes made by hand and improve the accuracy.
Benefits:
Reducing paperwork and therefore, saves time.
Reduces the client’s possibility of evading tax payments through enhanced surveillance and tracking.
Enhances the use of automated reminders and the error alert system. Ugh, better monitoring and tracking.
Improves compliance with automated reminders and error detection features.
Benefits of GST
Simplified Tax Structure:
Unified Tax System: If we talk about GST, it subsuming many indirect taxes such as VAT, excise duty, and service tax etc.
Eliminates Cascading Effect: Since GST taxes only the value addition, it cuts down the tax on tax issue.
Example: A simple GST structure helps in determining prices and these variables affecting it.
Ease of Doing Business:
Uniform Tax Rates: Various types of business in different states experience unified taxes.
Centralized Registration: One-stop solution for compliance is available in the case of GST.
Encourages Investments: There is one that speaks of a stable tax environment that in fact fosters the startups.
Boost to Economy:
Supply Chain Efficiency: Increased speed at which goods are moved and general decrease in cost of logistics.
Competitive Pricing: Reduced cost of production results in cheaper priced products and hence services.
Promotes Exports: Exporting under zero rating degree make the products to be competent with those of other nations.
Increased Transparency:
Digitized Processes: Records accessible through online means reduce on errors and interference with manual manipulations.
Reduced Corruption: There are few vectors to engage in malpractice in case of automation.
Better Compliance: Real-time tracking also helps to avoid violations of the existing legislation.
Additional Benefits:
Consumer Advantage: Purveyors are also in a position to lower costs and provide more choices owing to higher efficiency.
Revenue Growth: As a VAT, GST expands the tax net, increases government’s tax revenue as well as efficiency by minimizing bureaucratic expenses.
Challenges in GST Implementation
Despite its benefits, GST faced initial hurdles such as:
· Compliance Issues:
Adaptation to Digital Filing: Traditional small businesses and those who lack adequate accounting infrastructure found it capable of managing GST in its digital environment, return filing and record management, etc.
Solution: The government implemented training to undertake and the regulation made easier for small business to deal with, but the early stages were quite difficult for many business people.
· Multiple Tax Slabs:
Complexity: There were variations in the tax rates which include 0%, 5%, 12%, 18% and 28%; these made the system large and complicated.
Result: This made the management more complex as businesses were to deal with different rates for different products and services.
Solution: Despite periodic adjustments by the GST Council, some of these rates continue to be complicated for selected industries.
· Impact on Inflation:
Short-Term Price Increases: They also said in the very first phase of GST implementation, some goods and services became costlier due to changes in their tax base to reflect from the earlier exempt or lower tax rates slab.
Impact: This put inflation pressure on the consumers particularly on the necessary goods to be consumed.
Solution: In the long run, concluding from the advantages of GST, more stable prices have been established, as earlier the production costs have been lowered.
Impact of GST on Various Sectors
· Manufacturing:
Reduction in Logistics Costs: Interstate check posts are no longer required thereby cutting down on time and cost of transportation within the different States due to GST.
Elimination of Tax Cascading: The application of tax-on-tax effect has been done away with hence cutting out on cost increases in manufacturing.
Efficiency Gains: The single tax system is advantageous since there are no difficult conforming requirements for use of state taxes with the unified structure.
· E-commerce:
Uniform Tax Laws: Since GST has been implemented, e-commerce businesses can be sure that they will not be harassed by a plethora of different state taxes.
Simplified Operations: Hence, there have been relatively easy ways of following the compliance and regulations needed for vendors operating across several states in the country through the e commerce platforms.
Growth Opportunities: Another constraint which GST has helped in overcoming is the regional taxes which e-commerce firms used to encounter in their fast expansion.
· Services Sector:
Uniform Tax Rate: One standard nominal taxation rate has been imposed on services making it convenient for service providers to deal with states.
Simplified Compliance: More gone when there is only single registration and filing of service business to administer their tax liabilities.
Improved Business Environment: Uniformity of GST allows service providers tender better pricing structures as well as gain more market share.
Conclusion
It can be summed up that GST has revolutionalised the Indian taxation structure and boosted economic liberalisation and official rationalization. That is why, despite the certain problems, which arise during the consolidation, including the compliance and the changes in prices, the further perspectives of functioning with the united framework of taxation are more advantageous.
Reducing the cascading effect of taxes; implementing a more straightforward taxation system; and encouraging easier business operations, GST has promoted a more efficient business model. India is already a developing country that is on the right phase of growth.
The Legal Dost is here to assist you to make your head around the GST especially for the new businessmen and woman, your go-to gentleman! Please contact us for professional advice and compliance with minimal problems for your business.
0 notes
Text
A Comprehensive Guide to GST Verification

The Goods and Services Tax (GST) is a landmark reform in the Indian taxation system, introduced to streamline the indirect tax structure and bring about greater transparency in business transactions. Since its implementation, GST has revolutionised how businesses operate, ensuring a more uniform tax regime nationwide. As GST becomes an integral part of the business landscape, the need for accurate GST verification has emerged as a critical aspect of compliance and financial integrity. This guide aims to provide an in-depth understanding of GST verification, its processes, challenges, and benefits.
Understanding GST (Goods and Services Tax)
The Goods and Services Tax (GST) is a comprehensive, multi-stage, destination-based tax levied on every value addition. GST has subsumed various indirect taxes previously imposed by the central and state governments, including excise duty, VAT, and service tax. This unified tax structure simplifies the tax system, reduces the cascading effect of taxes, and promotes ease of doing business.
The journey of GST in India began in 2000 when a committee was set up to draft the law. After several years of deliberation and amendments, the GST Bill was finally passed in the Parliament in 2017, and GST was implemented on July 1, 2017. Since its inception, GST has undergone numerous amendments to address industry concerns and streamline processes.
History of Goods and Services Tax (GST) in India - Timeline
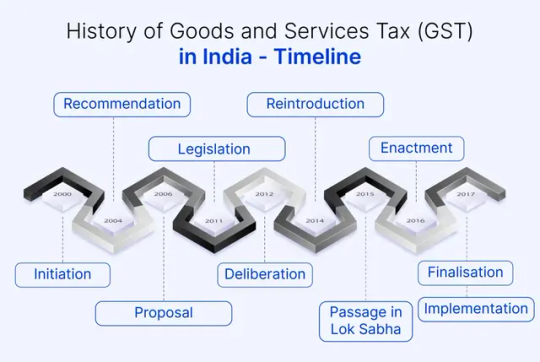
Key Components of GST
GST is divided into several components to ensure a fair distribution of tax revenue between the central and state governments:
Central Goods and Services Tax (CGST): Levied by the central government on intra-state supplies of goods and services.
State Goods and Services Tax (SGST): Levied by the state government on intra-state supplies of goods and services.
Integrated Goods and Services Tax (IGST): Levied on inter-state supplies of goods and services and is collected by the central government.
Union Territory Goods and Services Tax (UTGST): Levied on the supply of goods and services in Union Territories.
Old Tax Regime and New Tax Regime
Old Tax Regime Overview
The old tax regime in India is characterized by its complexity and numerous exemptions and deductions that taxpayers can claim to reduce their taxable income. It has been in place for many years and has evolved with changes and additions to tax laws.
Features
Income Tax Slabs: The old regime has different tax slabs based on age categories, including those below 60 years, senior citizens (60-80 years), and super senior citizens (above 80 years).
Exemptions and Deductions:
Section 80C: Deductions up to INR 1.5 lakh for investments in PPF, EPF, life insurance premiums, and other specified instruments.
Section 80D: Deductions for medical insurance premiums.
Section 24(b): Deductions on home loan interest.
House Rent Allowance (HRA): Exemption on HRA based on rent paid and salary structure.
Standard Deduction: For salaried individuals.
Other Deductions: Various other deductions for education loans, donations to charitable institutions, and more.
Complexity: The old regime requires taxpayers to maintain records and proofs for all exemptions and deductions claimed, making it relatively complicated.
Advantages
Tax Savings: Numerous exemptions and deductions allow taxpayers to significantly reduce their taxable income.
Encouragement for Savings and Investments: Various deductions encourage taxpayers to invest in specific financial instruments and savings schemes.
Disadvantages
Complexity: Managing and documenting the various exemptions and deductions can be cumbersome.
High Compliance Requirement: Taxpayers must be well-versed with tax laws and maintain proper documentation.
Old Tax Slab
Income up to INR 2.5 lakh: NIL
Income from INR 2.5 lakh to INR 5 lakh: 5%
Income from INR 5 lakh to INR 10 lakh: 20%
Income from INR 10 lakh and above: 30%
New Tax Regime Overview
Introduced in the Union Budget 2020, the new tax regime offers simplified tax slabs with lower rates but without most of the exemptions and deductions available under the old regime. It aims to simplify the tax filing process and reduce the compliance burden.
Features
Income Tax Slabs: The new regime provides different tax slabs with lower rates but does not differentiate based on age.
No Exemptions and Deductions: Most exemptions and deductions available in the old regime are not applicable in the new regime.
Optional: Taxpayers can choose between the old and new regimes based on what is more beneficial for them.
New Tax Slabs (FY 2020-21 onwards)
Income up to INR 2.5 lakh: NIL
Income from INR 2.5 lakh to INR 5 lakh: 5%
Income from INR 5 lakh to INR 7.5 lakh: 10%
Income from INR 7.5 lakh to INR 10 lakh: 15%
Income from INR 10 lakh to INR 12.5 lakh: 20%
Income from INR 12.5 lakh to INR 15 lakh: 25%
Income above INR 15 lakh: 30%
Advantages
Simplicity: The absence of numerous exemptions and deductions simplifies the tax filing process.
Lower Tax Rates: For many taxpayers, the lower tax rates can result in tax savings even without claiming deductions.
Disadvantages
No Incentives for Savings and Investments: The lack of deductions may discourage taxpayers from investing in specific financial instruments or savings schemes.
Comparison Required: Taxpayers must calculate their tax liability under both regimes to determine which is more beneficial.
Old Tax Regime VS New Tax Regime
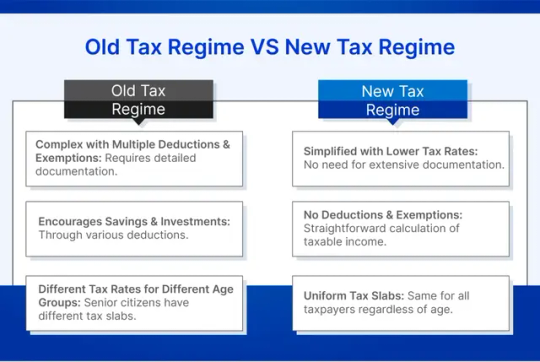
Choosing Between the Two
Taxpayers must assess their income, available exemptions, and deductions to decide which regime is more beneficial. Generally:
Old Regime: Beneficial for those with significant exemptions and deductions.
New Regime: Suitable for those who prefer simplicity and have fewer deductions to claim.
GST Registration
Eligibility Criteria for GST Registration: GST registration is mandatory for businesses whose turnover exceeds a specified threshold limit, which varies for goods and services. Additionally, companies such as e-commerce operators, casual taxable persons, and input service distributors must register for GST regardless of turnover.
Step-by-Step Guide to GST Registration
Visit the GST Portal: Access the GST registration page on the official GST portal.
Fill Part-A of the Form: Provide basic details such as PAN, mobile number, and email ID.
Verification: An OTP will be sent to your mobile number and email for verification.
Fill Part-B of the Form: Enter detailed business information, including business address, bank account details, and the principal place of business.
Upload Documents: Submit required documents such as proof of business address, bank account statement, and identity proof.
Submit Application: Complete the application and submit it for processing.
Receive GSTIN: Upon approval, you will receive a unique Goods and Services Tax Identification Number (GSTIN).
Documents Required for GST Registration
PAN card of the business or applicant
Proof of business registration or incorporation certificate
Identity and address proof of promoters/directors with photographs
Business address proof
Bank account statement/canceled cheque
Digital signature
Benefits of GST Registration
Legal recognition as a supplier of goods or services
Ability to collect tax from customers and pass on the credit
Seamless flow of input tax credit
Competitive advantage by enhancing business credibility
GST verification is the process of validating the GSTIN (Goods and Services Tax Identification Number) of a business entity. It ensures that the GSTIN provided by suppliers or vendors is authentic and registered under the GST regime. Verification helps prevent tax evasion and ensures compliance with tax laws.
What is GST Verification?
GST verification is the process of validating the GSTIN (Goods and Services Tax Identification Number) of a business entity. It ensures that the GSTIN provided by suppliers or vendors is authentic and registered under the GST regime. Verification helps prevent tax evasion and ensures compliance with tax laws.
When and Why GST Verification is Needed?
GST verification is essential during various business transactions, including:
Onboarding new suppliers or vendors
Filing GST returns
Conducting audits
Ensuring compliance with anti-profiteering laws
Verification helps businesses avoid fraudulent transactions, incorrect GST credits, and legal complications arising from non-compliance.
Learn More:
How Verification APIs are helping businesses transform and scale-up
Everything You Need To Know About Aadhaar Verification
Identity Verification - How to Check PAN Aadhaar Linking Status with API
Types of GST Verification
Manual Verification Manual verification involves checking the GSTIN details on the official GST portal. This method is time-consuming and prone to human errors but is useful for verifying a small number of GSTINs.
Online Verification Online verification is done using the GST portal, where businesses can enter the GSTIN and verify its authenticity. This method is quicker than manual verification but still requires individual input for each GSTIN.
Automated Verification Tools Automated verification tools streamline the verification process by allowing bulk verification of GSTINs. These tools integrate with the GST portal and provide real-time verification, reducing the time and effort required for manual checks.
Challenges in GST Verification
Common Issues Faced During Verification
Incorrect GSTIN entries leading to invalid results
Network or portal downtime affecting verification
Discrepancies in registered details
Errors and Discrepancies in GST Numbers: Errors in GST numbers can arise due to manual entry mistakes or misinformation. Common discrepancies include incorrect PAN linkage, invalid business details, or outdated information.
Dealing with Fraudulent GST Numbers: Fraudulent GST numbers pose a significant risk to businesses. To combat this, businesses should regularly verify GSTINs, maintain accurate records, and report suspicious activities to tax authorities.
Benefits of GST Verification
Ensuring Compliance with Tax Regulations Regular GST verification ensures that businesses comply with tax regulations, avoiding penalties and legal issues. It helps maintain accurate records and timely filing of GST returns.
Reducing the Risk of Fraud Verification helps identify and eliminate fraudulent GSTINs, protecting businesses from financial losses and reputational damage.
Enhancing Business Credibility and Trust Businesses that regularly verify GSTINs demonstrate their commitment to compliance and transparency, enhancing credibility and trust among stakeholders.
Technological Advancements in GST Verification: Emerging technologies like blockchain, artificial intelligence (AI), and machine learning are poised to transform GST verification, delivering superior security, precision, and efficiency.
How to Verify GST Numbers?
Step-by-Step Process for Manual GST Verification
Visit the GST Portal: Go to the official GST portal (www.gst.gov.in).
Navigate to Search Taxpayer: Under the "Services" tab, select "Search Taxpayer" and then "Search by GSTIN/UIN."
Enter GSTIN: Input the GSTIN you wish to verify and complete the captcha.
View Details: The portal will display the registration status, trade name, and other relevant details of the GSTIN.
Using the GST Portal for Verification The GST portal offers a dedicated search facility to verify GSTINs. This feature provides instant access to the registration status and other details of the GSTIN holder, ensuring authenticity.
Third-Party Tools and Software for GST Verification Several third-party tools and software are available for GST verification. These tools offer features such as bulk verification, real-time updates, and integration with ERP systems, making the verification process efficient and error-free.
Streamlined PAN to GSTIN Verification for Businesses
Instantpay's PAN to GSTIN Verification API offers businesses a seamless solution to confirm the linkage between a customer's PAN (Permanent Account Number) and GSTIN. By integrating this API, companies can enhance the accuracy of their customer data and ensure compliance with GST regulations. This efficient verification process minimises errors and mitigates risks, contributing to a more secure and trustworthy business environment. Leverage Instantpay's advanced verification technology to streamline operations and maintain regulatory compliance with ease.

Conclusion
In conclusion, GST verification is an essential aspect of compliance and financial integrity for businesses operating under the GST regime in India. By ensuring the authenticity of GSTINs, businesses can prevent tax evasion, maintain accurate records, and enhance credibility with stakeholders. The evolution of technology, including AI and machine learning, promises to streamline GST verification processes, making them more efficient and effective.
As businesses continue to navigate the complexities of GST compliance, investing in reliable verification tools and staying abreast of regulatory changes will be key to ensuring smooth operations and mitigating risks. By understanding the nuances of GST verification and implementing best practices, businesses can position themselves for sustainable growth in India's dynamic business environment.
This comprehensive guide has provided insights into the fundamentals of GST, the intricacies of GST verification, common challenges faced, and the future outlook for verification processes. Embracing the principles outlined in this guide will empower businesses to navigate the complexities of GST compliance with confidence and clarity.
0 notes
Text
Demystifying Taxes: Your Guide to Using a GST Calculator Effectively

Demystifying Taxes: Your Guide to Using a GST Calculator Effectively
Navigating taxes can be a daunting task for many individuals and businesses alike. Among the various taxes levied worldwide, the Goods and Services Tax (GST) stands out as a significant indirect tax that impacts consumers, businesses, and the economy at large. Understanding how GST is calculated and its implications is crucial for compliance and financial planning. In this guide, we delve into the essentials of GST and explore how a GST calculator can simplify these complexities, empowering users to manage their tax obligations effectively.
What is GST?
GST is a consumption tax imposed on the supply of goods and services in most countries around the world. It is designed to be a more transparent and efficient way of collecting taxes compared to traditional sales taxes. The GST system aims to reduce cascading taxes (taxes on taxes) and streamline tax administration by applying a single tax rate across the supply chain.
Components of GST
GST typically consists of two main components:
Central GST (CGST): Collected by the central government on intra-state supplies of goods and services.
State GST (SGST): Collected by the state government on intra-state supplies of goods and services.
In addition to CGST and SGST, there is also an Integrated GST (IGST) applicable on inter-state supplies of goods and services, which is collected by the central government.
Understanding GST Calculations
Calculating GST involves applying the applicable GST rate (which varies depending on the type of goods or services) to the transaction value. For example, if the GST rate is 18% and the transaction value of a product is $100, the GST amount would be $18 ($100 * 18%).
GST calculators simplify this process by automating the calculation based on the entered transaction value and GST rate. They ensure accuracy and efficiency, especially when dealing with multiple transactions or complex tax scenarios.
Benefits of Using a GST Calculator
Accuracy: GST calculators minimize the risk of manual errors in tax calculations, ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements.
Time Efficiency: They save time by instantly computing GST amounts, allowing businesses to focus on core operations rather than repetitive calculations.
Financial Planning: GST calculators facilitate financial planning by providing clear insights into tax liabilities, helping businesses budget effectively.
Types of GST Calculators
There are various types of GST calculators available to cater to different needs:
Basic GST Calculator: Computes GST amounts based on transaction values and GST rates.
Reverse Charge Mechanism (RCM) Calculator: Calculates GST under RCM, where the liability to pay tax is on the recipient of goods or services rather than the supplier.
Input Tax Credit (ITC) Calculator: Determines eligible ITC, allowing businesses to claim credits for GST paid on inputs used in the course of business.
Using a GST Calculator Effectively
To use a GST calculator effectively, follow these steps:
Enter Transaction Details: Input the transaction value and applicable GST rate.
Compute GST: The calculator will automatically calculate GST amounts (CGST, SGST/UTGST, or IGST) based on the information provided.
Review Results: Verify the calculated GST amounts to ensure accuracy.
Generate Reports: Some advanced calculators allow users to generate reports for record-keeping and tax filing purposes.
Compliance and Regulatory Considerations
While GST calculators simplify tax calculations, it is essential to adhere to regulatory guidelines and maintain accurate records. Businesses must ensure that GST calculations are in line with applicable laws and regulations to avoid penalties or legal repercussions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding and effectively managing GST calculations are crucial for businesses and individuals alike. A GST calculator serves as a valuable tool in navigating the complexities of tax compliance, offering accuracy, efficiency, and insights into financial planning. By leveraging the capabilities of a GST calculator, users can streamline their tax-related processes, minimize errors, and focus on strategic business initiatives.
0 notes
Text
GST Calculator: Simplifying Your Tax Calculations

Goods and Services Tax (GST) is a comprehensive, multi-stage, destination-based tax that is levied on every value addition. It was introduced in India on July 1, 2017, replacing multiple indirect taxes previously levied by the central and state governments. GST aims to create a single, unified market and reduce the cascading effect of taxes on the cost of goods and services.
Types of GST in India
GST in India is divided into four types to facilitate better tax collection and distribution:
CGST: Central Goods and Services Tax
Levied by the central government on intra-state supplies of goods and services, CGST is collected by the central authority and goes into the central treasury.
SGST: State Goods and Services Tax
SGST is levied by the state government on the same intra-state transactions as CGST, with the revenue going to the respective state government.
IGST: Integrated Goods and Services Tax
IGST is applied on inter-state transactions of goods and services, collected by the central government, and then apportioned between the central and state governments.
UTGST: Union Territory Goods and Services Tax
Similar to SGST, UTGST is applicable to union territories where SGST is not applicable.
How GST Works
GST operates on an input tax credit mechanism, allowing businesses to claim credit for the tax paid on purchases. This credit can be used to offset the GST liability on sales. GST has multiple tax slabs – 0%, 5%, 12%, 18%, and 28%, varying based on the type of goods and services.
The Need for a GST Calculator
Calculating GST can be complex due to the multiple tax slabs and the input tax credit system. A gst calculator simplifies these calculations, reducing the chances of errors and saving time. It ensures accurate computation, which is crucial for compliance and financial planning.
Features of a Good GST Calculator
A reliable GST calculator should have the following features:
User-friendly Interface
An intuitive interface makes it easy for users to input data and obtain results without confusion.
Accurate Tax Computation
The primary purpose of a GST calculator is to provide precise tax calculations based on the input provided.
Multiple Tax Slab Support
A good calculator supports all the GST slabs, ensuring it can be used for any type of product or service.
Invoice Generation
Some advanced GST calculators also offer invoice generation, which is beneficial for businesses.
How to Use a GST Calculator
Using a GST calculator is straightforward. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
Enter the Original Amount Input the original price of the goods or services.
Select the GST Rate Choose the applicable GST rate from the available options.
Calculate Click on the calculate button to get the GST amount and the total price including GST.
Example Scenario
Imagine you bought a gadget for ₹10,000 with an 18% GST rate. By entering these details into the calculator, you’d get a GST amount of ₹1,800 and a total cost of ₹11,800.
Benefits of Using a GST Calculator
Time-saving
Manual calculations can be time-consuming and prone to errors. A GST calculator speeds up the process.
Accuracy
Automated calculations reduce the risk of human errors, ensuring accurate results.
Ease of Compliance
Helps in maintaining accurate records, making GST return filing easier and error-free.
GST Calculator for Businesses
For businesses, accurate GST calculation is crucial for pricing, accounting, and compliance. Whether you run a small business or a large enterprise, using a GST calculator ensures that you charge the correct tax amount and stay compliant with regulations.
GST Calculator in Accounting Software
Many accounting software solutions now include built-in GST calculators, streamlining the entire process from invoicing to tax filing.
GST Calculator for Consumers
Consumers can also benefit from GST calculators. It helps them understand the tax component in their purchases, ensuring transparency and better financial planning.
Examples in Everyday Purchases
From buying groceries to electronics, using a GST calculator can help consumers see how much tax they are paying and the final cost of their purchases.
Online vs Offline GST Calculators
Advantages of Online Tools
Online GST calculators are readily accessible and always up-to-date with the latest tax rates and rules. They are easy to use from any device with internet access.
Offline Alternatives and Their Uses
Offline GST calculators can be useful in areas with limited internet connectivity. These tools, often available as downloadable software or mobile apps, provide similar functionality without requiring an internet connection.
Popular GST Calculator Tools
List of Reliable Online GST Calculators
ClearTax GST Calculator
Tally GST Calculator
IndiaFilings GST Calculator
Zoho GST Calculator
Features Comparison
Each of these tools offers unique features like multi-device support, detailed reports, and integration with accounting software.
GST Calculator Apps
Benefits of Mobile Apps
Mobile GST calculator apps offer the convenience of on-the-go calculations, ensuring you can compute taxes anytime, anywhere.
Top GST Calculator Apps Available
ClearTax GST
H&R Block GST
Zoho Books
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Using a GST Calculator
Incorrect Data Entry
Ensure you enter the correct figures to get accurate results.
Misunderstanding Tax Slabs
Be clear about the applicable GST rates for different goods and services.
Ignoring Updated Tax Rates
GST rates can change, so always use a calculator that updates regularly to reflect the latest rates.
Incorporating a GST calculator into your financial toolkit can make a significant difference in how you manage taxes. It simplifies the process, saves time, and ensures accuracy, making it an indispensable tool for both businesses and consumers. Embrace this technology to stay compliant and efficient in your tax computations.
Contact Us: Email: [email protected]
Visit Here: https://finnovent.org/gst-calculator-india/
1 note
·
View note
Text
TDS under GST: Everything You Need to Know

In terms of indirect taxation, the advent of Goods and Services Tax (GST) in India has substantially modified the earlier tax machine Tax deduction at supply (TDS) gadget which has provisions of Under GST plays an essential position in tax compliance and greater transparency Understanding the filing of TDS returns and the method is important to live compliant and keep away from penalties. This article delves into the complexities of TDS below GST, together with who has to claim TDS, truthful price, and most importantly, the way to report a TDS return
What is TDS under GST? Under GST, tax deduction at supply (TDS) is a method of deducting a positive percent of tax from payments made to providers of taxable items or offerings The principal goal of this scheme in and to make sure timely collection of profits taxes and increase the tax base by means of tracking big groups and authorities entities Who should deduct TDS under GST? The following companies are mandatory to deduct TDS under GST: government departments or offices. Local Government. Creation of public offices. Institutions notified by the Government. These companies are required to deduct TDS when the total value of the goods supplied exceeds Rs. 2.5 lakh (inclusive of GST). Valid prices for TDS under GST The rate of TDS under GST is 2%, which is broken down as follows. 1% CGST (Central Goods and Services Tax) . In case of intra-State transactions, 1% SGST (State Goods and Services Tax) or 1% UTGST (Under Territory Goods and Services Tax). 2% IGST (Integrated Goods and Services Tax) on inter-State transactions. Steps for TDS Return Filing Under GST, filing of TDS return is a mandatory action to be taken through the deductor. Here is the step by step guide on a way to record TDS go back:
Registration: Ensure that the withdrawer is registered below GST and has a legitimate GSTIN. Form GSTR-7: Those who've deducted TDS need to document their returns thru Form GSTR-7. Deduction Details: Provide information of providers (deductees) from whom TDS has been deducted. TDS Certificate: Submit Form GSTR-7A for TDS certificates for deductions. Due date: Submit your TDS go back by the 10th of the subsequent month. Comprehensive process for filing TDS return Step 1: Go to GST Portal Apply your credentials to the GST portal (www.Gst.Gov.In). Go to the ‘Services’ tab, then visit ‘Returns’ and pick ‘Returns Dashboard’. Step 2: Select the ideal monetary 12 months and time Select the proper financial 12 months and go back length (month) from the drop-down menus. Step 3: Fill GSTR-7 form Click on ‘Prepare Online’ under the GSTR-7 tile. Enter the required details like GSTIN deduction, deduction payment, amount of TDS deduction. Be sure to be consistent to avoid contradictions. Step 4: Check before you can submit Fill in all of the info and test the shape before making sure all the information are correct. Click the ‘Submit’ button to post the shape. Step five: Payment of TDS Use the to be had fee strategies (Net Banking, NEFT, RTGS) to pay the TDS quantity. Once the charge is made, the GSTR-7 fame may be updated. Step 6: To publish TDS certificates Generate TDS certificates (Form GSTR-7A) from GST portal. For deductees, these certificates ought to be submitted as evidence of TDS deduction. Consequences of noncompliance Failure to conform with the TDS regime beneath GST may additionally bring about consequences and interest. Here are the principle results:
Late Fee: Late fee is Rs. 200 per day (Rs. A hundred for CGST and SGST) may be charged for overdue submitting, as much as a most of Rs. 5,000 rectangular feet. Benefits: Interest is charged on late TDS at 18% consistent with annum. Credit disallowance: If the drawee fails to deposit TDS on time, the deductees might also face disallowance of Investment Tax Credit (ITC). Key points to consider TDS applies to supplies of goods or services for which the contract price exceeds Rs. 2.Five lakhs is available. The TDS ought to be submitted to the authorities through the tenth of the following month. The deductors have to difficulty TDS certificates to the deductees inside five days of depositing the TDS. Deductibles should document GSTR-7 every month, and deductibles can declare TDS income in their electronic earnings library. Benefits of TDS beneath GST Ensures compliance: Helps manage high-price transactions and ensures compliance with tax laws. Reduces Tax Evasion: Reduces tax evasion by using keeping records of transactions. Improves transparency: Improves transparency in transactions and decreases the chances of disputes. The demanding situations they confronted Despite the advantages, corporations generally tend to stand numerous demanding situations associated with TDS under GST:
Complexity: Understanding the provisions and efficiently implementing TDS may be hard for corporations. Compliance burden: The burden of clearing TDS, issuing returns and certificate will increase the compliance burden. Technical Issues: Navigating the GST portal and troubleshooting technical challenges may be tough. Conclusion Under GST, TDS is one of the most crucial measures geared toward increasing tax compliance and transparency. Understanding the provisions, prices and manner for submitting TDS returns is vital for agencies to avoid penalties and make certain easy operations. By following the noted steps and staying abreast of the cutting-edge information, corporations can manage their TDS legal responsibility below GST efficaciously. Remember, timely and accurate filing of TDS returns no longer best guarantees compliance however also creates a subculture of transparency and responsibility in the business environment also.
0 notes
Text
A Complete Guide to GST Registration
GST registration has become an important aspect for any business. The full form of GST is Goods and Services Tax, which is a comprehensive indirect tax charged on the supply of goods and services within Indian territory, and GST registration is compulsory for businesses with a certified annual turnover that differs from business to business.
The Goods and Service Tax Act was introduced by the Indian government on July 1, 2017. The introduction of GST aimed to simplify the indirect tax system in India by merging multiple taxes into one and improving the tax collection process.

Types of GST
In order to know the GST tax liability of a business, it is essential to know the type of GST:
State Goods and Services Tax (SGST): It is the tax charged on the sale of services and products within a state. It eradicated earlier taxation that included entry tax, state sales tax, entertainment tax, surcharges, and others.
Central Goods and Services Tax (CGST): It is charged by the central government on the supply of intra-state products. It replaced many taxes like service tax, central excise duty, and customs duty.
Union Territory Goods and Services Tax (UTGST): It is applicable to the sale of products and services in Union Territories like Andaman, Nicobar, and Chandigarh, among other union territories.
Integrated Goods and Services Tax (IGST): This tax is charged on the sale of interstate products and services.
Applicability of GST Registration
According to the GST Act, any business that fulfills any of the below-mentioned criteria is bound for GST registration.
Businesses that cross the annual turnover threshold of Rs. 40 lakh are liable for online GST registration.
Any individual selling goods through an e-commerce platform is also liable for GST registration.
Non-residents and casual taxable persons should also file GST.
To ensure the smooth functioning of GST registration, it is important for the above-mentioned people or firms to file for GST and comply with the related eligibility and documentation to avoid any penalties and future hurdles.
List of the Top Benefits of GST Registration
There are various benefits of GST registration that you, as an individual or business, can avail of. Below are some of the top benefits of GST registration:
Eradication of the cascading effects: The introduction of GST removes the cascading effects of earlier indirect taxation, causing dual taxation at every step. GST registration has reduced the tax liability of business entities.
Easy registration procedure: The process of GST registration can be easily done through the GSTN portal, making it time-efficient and easy.
Lesser compliance: Earlier businesses had to file several returns accorded with different indirect taxes like VAT, excise, and service tax. But GST is a single tax regime, so it lowers the number of filings, making it less problematic for businesses to file a return.
Transparency: Registration under GST consists of various provisions such as compliance, payment of taxes, and perks of input credit, ensuring clarity in the tax collection system.
Regulation of the unorganized sector: GST registration also helps to regulate the unorganized sector, like construction sites.
Final Words Whether you are a small business owner or a large business owner, or freelancer the GST registration services can help you gain certain benefits. You can easily track your registration process through GSTIN on the GST portal. If you are looking for reliable GST billing software that assists you with GST registration and compliance requirements, then consider Eazybills, as it is a one-stop solution for all the billing requirements, as it is easy to use software that doesn’t require any additional training.
#billing software#invoicing software#free billing software#gst billing software#GST#GSTIN#IGST#SGST#full form of gst#gst registration#free invoicing software#free gst billing software
0 notes