#the musicians of the town of bremen
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Some scholarly notes about the Grimm fairytales (2)
A follow-up of this post.

The Frog King or Iron Henry (Der Froschkönig oder der eiserne Heinrich)
This story belongs to the AaTh 440, "The frog-king".
The story first appears in the 1810's manuscript, written by Wilhelm - it was probably told by Henriette Dorothea "Dortchen", Wilhelm's future wife. A second version, called "The frog prince", had been told to them by their friend Marie Hassenpflug and was published in the 1815 edition as the thirteenth tale, before being moved to the notes of the 1822 due to its too-great similarity with the KHM 1.
This fairytale was originally called "The king's daughter and the bewitched prince". The 1810 manuscript has, written by Jacob right next to the title, "The frog-king", while the paper on which he had placed all his notes about the fairytale bore the name "Iron Henry". The evolution of this fairytale is very interesting because it testifies the brothers' love and care for details, hich had the story double in sie throughout the editions. In the final text we have, for example, a long sentence describing how the princess sees the ball fall into a well so deep she can't see the end, and about her crying a lot and lamenting, etc, etc... In the 1810 manuscript it was just one short sentence "She stood near the well and she was sad."
The major editing of this tale was the removal of the erotic motif from the tale's ending. Originally, the frog asked the princess the authorizaton to sleep in her bed, and right after the frog became a human it was written "the princess joined the prince in bed". This, plus the addition by the Grimms of moral lessons delivered by the father (the king tells things such as "You must always keep your promise" and "You must not disdain the one who helps you"), completely changed the goal and purpose of the tale - it was originally about setting free an animal husband, but the Grimms turned it into a moral tale to learn a virtuous behavior.
The brothers Grimm considered this fairytale to be the oldest and most beautiful of their collection. Allusions to the frog-king tale can be found as early as the Middle-Ages and the 16th century. In the 1801 edtion of the 1548 Scottish book "Complaynt of Scotland", a note evokes how a tale is similar to "The Frog Prince" due to having a well, the presence of magic, and a frog complaining in rhymes. In this Scottish version, a girl is sent by her stepmother to fetch water at "the well of the world's end". There she meets the frog, who tells her it will offer her water only if she agrees to marry it - if not, the frog will rip the girl apart. The brothers Grimm themselves noted various literary sources for their tale, that they used in their compilation work. The name of Henry (Heinrich) comes from the novel "Der arme Heinrich" by Hartmann von Aue. They also listed the "Froschmeuseler", a didactic epic by Georg Rollenhagen depicting a war between frogs and mice: the association of sadness with "rings of iron" comes from this text, as well as the very name "frog-kng" which is found in the title of the second chapter "Tale of the encounter between Thief-of-Crumbs, son of the mice-king, with the frog-king".

The Wolf and the Seven young Goats (Der Wolf und die sieben jungen Geiblein)
It is the AaTh 123, "The wolf and the lambs".
Collected in the "region of Main" according to the Grimm, it is very likely that the brothers Grimm received this tale from someone of the Hassenpflug family, as they knew the French fables of La Fontaine which correspond to this fairytale. In the 5th edition of their book, the brothers Grimm modified their story due to the publication in 1842 of an Alsacian tale by Ströber, "Die sieben Gaislein", "The seven young goats" (collected in Volksbüchlein, "The Folks' Small Book) - Wilhelm Grimm borrowed several expressions from this text. The brothers Grimm listed this Alsacian tale in their notes.
In their notes the brothers Grimm listed a Pomeranian version about a child who, when his mother is out, is swallowed by a sort of bogeyman known as "The children's ghost". But since the ghost eats stone at the same time, he becomes slow and heavy - he falls and the child can escape his belly unharmed. The brothers Grimm also listed variations collected/written by Boner in his Edelstein, and by Buckhard Waldis - as well as the La Fontaine fables. They also knew of a French fairytale, from which they noted a passage where the wolf asks a miller to turn her paw white with flour, and since the miller refuses, the wolf threatens to eat him. The Grimms linked the episode of the wolf's belly filled with stones with the legend of a Nereid called Psamathe, who sent a wolf destroy the flocks of Peleas and Telamon, only for the wolf to be petrified.
This tale, like many others within the Grimm's collection (it is especially comparable "Cat and Mouse in Partnership) is aimed at educating young children, with the narrator highlighting how children should be wary and distrustful of the wickedness and cowardice of men. Unlike other versions and predecessors of the tale, the brothers Grimm insist on the mother's role as a teacher, and on the fact that she saves her kids.

Rapunzel
It is the AaTh 310, "The maiden in the tower".
The literary sources of this fairytale are well-known. It was preceeded by the French literary tale "Persinette", by mademoiselle de La Force, itself inspired by Basile's story "Parsley Flower". In their notes the brothers Grimm explained they took inspiration from the almost-literal German translation of mademoiselle de La Force's story by Friedrich Schulz. However, in quite a misunderstanding, the brothers admired this tale as being an obvious "folktale" coming from the "oral tradition" - when we know it was a literary fairytale, though based on a folkloric motif.
The text was heavily edited after the many criticism the first edition of the book underwent - the scene depicting the prince's relationship with Rapunzel was regularly changed. In 1837 it is written that the prince asked Rapunzel to marry him almost right away, and she agreed since he was young and pretty, and they "held hands". In 1819, it was written that they lived together in "joy and pleasure" for a certain time, and "loved each other like woman and wife", and the "fairy" only realizes something is up when Rapunzel blurts out it is easier to make the prince climb than her "godmother". In the 1812 edition, it is said that Rapunzel and prince lived together in "joy and pleasure", but no mention of any marital couple whatsoever - and Rapunzel betrays her condition to the "sorceress" because she complains about her clothes getting too tight.
The Grimm noted that many versions of the "girl in the tower" fairytale existed, but with a different opening relying on the "forbidden room" motif: the witch punished the girl by locking her up in a tower because she had opened a door the witch explicitely forbade her to. The Grimm also listed several stories (outside of Basile's version) where a mother (sometimes a father) bargains their future child to satisfy a temporary craving - such as the Nordic "Alfkongs-Saga", where Odin offers Signy's wish for the better bear in the world in exchange of what is "between her and the barrel", aka the child she bears. In a book of Büsching we find a girl named "Petersilie" (Parsley in German) which loves eating prasley more than anything in the world and brushes her long hair by a window. The idea of using hair as a rope or ladder, long before Basile used it, seems first recorded by from the "Book of the Kings" of the poet of Persia Firdoussi, in the 10th century: the hero, Zal, joins the beautiful Roudebeh by climbing up her braids.
The name the sorceress wears in the German tale, "Frau Gothel", had been explained by the Grimm in such a way: "The godfather is not only called Vater (father) but also Pathe (godfather/"parrain" in French), or Goth or Dod ; the baptized child is also called "Pathe" or "Gothel", hence the confusion of the two within the legend". So, the dominating hypothesis (which seems confirmed by the variations of the fairytale) is that "Gothel" means "godmother".

Hansel and Gretel (Hänsel und Gretel)
It is of course the AaTh 327 A, "Hänsel and Gretel" (a subtype of "The children and the ogre"). It also covers the AaTh 1121, "Burning the witch in her own oven".
In the 1810 manuscript this fairytale was called "Little brother and Little sister", a name that would later be reused by another famous Grimm fairytale (KHM 11). It seems that one of the reasons for the Grimm's big edits on this tale was the publication in 1842 of the Alsacian version of this story by August Stöber, "The little house of pancakes" (Das Eierkuchenhäuslein) - which itself was inspired by the Grimm's original publication of "Hansel and Gretel" (full loop here). Wilhelm Grimm notably borrowed several turn of phrases from Stöber.
The motif of the children abandoned in the woods can be found back in Basile's Nennillo and Nennella, though the extension to the encounter of a child-eating monster is rather present within Perrault's Petit Poucet and madame d'Aulnoy's Finette Cendron (both also contain the motif of the treasures inside the ogre's house). While we know the Grimms were aware of Perrault's story, we also know that madame d'Aulnoy's fairytales, including "Cunning Cinders" had been brought to Germany by ther adaptation for the German branch of the "Bibliothèque Bleue" - Blaue Bibliothek. Ludwig Bechstein's own version of "Hansel and Gretel" was very famous - and he actually wrote it inspired by the German translation of Stöber's own tale.
The motif of ashes, crumbs or seeds left behind to tell the way is recurring within the brothers Grimm fairytales: it also appears on the KHM 40 (The Robber Bridegroom) and 169 (The Hut in the Forest), as well as in their first "Legend for children". This motif can be found back in German literature to 1559's Gartengesellschaft (The company within the garden) by Martin Montanus, where it appears in the tale "The small earth-cow", Das Erdkühlein.
It is recognized that this fairytale is the second most popular and famous Grimm fairytale right after Snow-White. It was heavily illustrated - first by none other than Ludwig Emil Grimm himself (another brother of the Grimms). As we said before, Bechstein's own fairytale was a strong "rival" to the Grimm's, and was illustrated by Ludwig Richter in 1853. The motif of the "bird leading to the Ohterworld" is found back in the KHM 123 (The Old Woman in the Wood), and in both cases the fact the bird is white indicates that it is an Otherworldy animal.

The Brave Little Tailor (Das tapfere Schneiderlein)
This fairytale belongs to many different Aa-Th types: 1640 (The brave little tailor), 1051-1052 "Curb, cut and move a tree", 1060-1062 (Throwing-stone conquest), 1115 (Attempt to kill the hero in his bed).
The 1810 manuscript began with this tale as its opening, probably as an homage to Brentano, since Wilhelm Grimm found this tale within his library, in a book called "Wegkürtzer", by Martin Montanus.
Among the modifications of the 2nd edition, a very interesting one is the addition of a sentence closing the first paragraph "and his heart moved with joy like the tail of a small lamb". This sentence comes from a novel by Christian Weise calle "The three most mad madmen in the whole world/The three most foolish fools in the whole wide world" (1762). Wilhelm Grimm explained this, as well as several other similar "borrowings", in the preface of the sixth edition, as his desire to insert in his tales specific sentences and expressions he knew to be typically German.
The brothers Grimm notd that Montanus' Wegkürtzer was frequently alluded to within the Renaissance literature and the baroque one - for example, when Johann Fischart translated in German Rabelais' Gargantua he inserted the sentence "I will kill all these flies, nine at once, like this tailor once did." It was also evoked in the "Simplicissimus" of Grimmelshausen, but references to the Little Tailor story go back to the Middle-Ages. The episode of a giant crushing a stone until water comes out of it is found in "Brother Werner", from the Codex Manesse (which compiled German Minnesang, courtly poetry) ; and Heinrich von Freiberg's Tristan describes at one point the hero crushing a cheese until juice comes out of it. Montanus' text was also used by Ludwig Bechstein in his book of German fairytales. One can compare the story of the Grimms to Tabart's "Jack the giant-killer" and Afanassiev's "Foma Berennikov".
The measurements in this story make no sense at all. The tailor buys four half-ounces of marmelade. Given an ounce was roughly 32 gr, the tailor bought 60 gr roughly... Not a quarter of a pound, as he claims. The reason for this incoherence is because, before 1854, a "pound" varied depending on which area of Germany you were into (it was 467 gr in Berlin, 510 in Nuremberg). It was only in 1854 that the value of the pound was unified in Germany, at 500 gr. Finally we note the presence at the end of the tale of the common European belief n the "Wild Hunt".

Cinderella (Aschenputtel)
Of course, it is the Aa-Th 510A, "Cinderella".
As early as the first edition, this fairytale was a mix of several variations. In their notes, the brothers listed nine different versions of the tale. One of them is quite fascinating: the opening scene of the mother's death and her promises of help is missing, the story begins immediately on the heroine's misfortunes. The end of the version also greatly differs and enters the domain of the KHM 11 "Little-brother, Little-sister". Soon after his wedding with Cinderella, the prince forbids her to enter a specific room of the castle - but encouraged by her sister, she opens the room when the prince is absent. It contains a fountain of blood that Cinderella's sister uses for an evil use: after the queen gives birth to her first child, her sister throws her in the fountain and replaces her in the bed. But the guards of the castle hear the moans of Cinderella, rescue her and the wicked sister is punished. Another version, from Mecklembourg, has an ending which makes the tale close to the legend of saint Genevieve of Brabant: Cinderella's stepmother and stepsister steal away Cinderella's two first children and replace them with animals ; the third time she gives birth, they order the gardener to kill the queen and her child, but he rather hides them in a grotto in the woods, where the child is fed by a doe. One day the child, old enough, goes to the castle to speak to his father, revealing to him the fate of his mother.
Another version, this time from Paderborn, begins in a way very similar to "Snow-White": a queen wishes to have a child as red as a rose and as white as snow. She gets her wish, but then her servant pushes her outside of the window, to replace her as the king's wife. The usurper gives birth to two daughters, and from then on we return to the classical Cinderella tale - her dead mother helping her from beyond the grave by offering her a key, opening a hollow tree where Cnderella finds what she needs to wash herself and dress up pretty for the church (plus a prayer book). Büsching evoked the existence of another version in the Zittau area, where Cinderella is a miller's daughter that is forbidden to go to church, and where it is a dog that denounces the false fiancée. Outside of all these oral sources, the brothers Grimm took inspiration, of course, from Charles Perrault's Cinderella, as well as from the first German literary record of the Cinderella story, "Laskopal and Miliwka", published in an anonymous collection of legends in 1808 (Sagen der böhmischen Voreit aus einigen Gegenden alter Schlösser und Dörfer").
From the second edition onward, the brothers Grimm heavily edited the story. They removed all the words and passages that referenced too much Perrault's version, replacing them by elements taken specifically from the three versions they collected in Hesse (such as the demand for a branch of a nut-tree, and the motif of the tree growing on the grave). In the 1812 edition, it was Cinderella's own mother who advised her daughter to plant a tree on her grave, and who predicted that this tree will help her in the future. Throughout the rewrites, Wilhelm Grimm heavily insisted upon the heroine's virtues, accentuating them so that they would fit the feminine bourgeois ideal of the time.
The first European record of this tale is Basile's "The cat of the ashes", and other famous literary versions include Perrault's Cinderella, madame d'Aulnoy's Cunning Cinders, as well as Ludwig Bechstein's Aschenbrödel. These versions were massively spread throughout Europe, notably due to the "peddling literature", the cheap books sold by peddlers: they helped the "Cinderella" fairytale type becoming as popular as it is today, and it seems very likely they influenced all the versions of the tale that came after them.
In their notes, the brothers Grimm explicitely compared the motif of the shoe in Cinderella with the legend of Rhodopis, who had her shoe stolen by an eagle, and the pharaoh that found it had her owner searched throughout Egypt. However the motif of the animals helping a persecuted heroine (especially when it comes to splitting grains) is very common, and has been popularized by the Roman tale of "Cupid and Psyche".
This fairytale is closely tie to the KHM 130, "One-Eye, Two-Eyes and Three-Eyes", both sharing the idea of a young girl humiliated by her sisters, and who obtains a social ascension as a form of compensation. A. B. Rooth studied the evolution of the Cinderella fairytale-type, and its relation with other fairytale-types: they determined that it is very likely the "Cinderella" story was originally told as a sequel to the "One-Eye, Two-Eyes, Three-Eyes" story-type. Later, the second part of this story gained its own autonomy, and became the "Cinderella" we know today.
The sexual connotations within the motif of "trying on the shoe" has been repeatedly noted and analysed since the Grimms published their story. Jacob Grimm himself saw in this the remains of an archaic Germanic betrothing ritual. Heinz Rölleke highlighted another cultural ritual that involved the future husband of a bride removing her old shoes before marrying her. The idea of the slippers tied to a wedding is also found within the KHM 133 (The Shoes that were danced to Pieces).
The name of the heroine in Germa, "Aschenputtel" designates a type of kitchen girl who searches throughout the ashes, and thus "rolls" herself in them - but it also means figuratively an insignifiant and a dirty girl. It seems to derivate from the greek "achylia", cinders/ashes, and "puttos", female genital organs. A combination echoed by the French name "Culcendron", "Ashen-butt". By extension, the name "Aschenputtel" can also designate the younger brother when he is disdained by his brothers and considered to be an idiot by his family: there is a lot of male Cinderellas in folktales, especially in Northern and Central Europe, but also in all German-speaking countries.

Frau Holle
Belongs to the AaTh 480 "The kind and unkind girls".
This story was told to Wilhelm Grimm by his future wife, Henrietta Dorothea Wild, who was then 18 years old. A secondary source was a tale told to their by the Hanovre pastor, Georg August Friedrich Goldmann - this second version contained the episode of the rooster saluting the girls. The second edition of the brothers Grimm's book added several details to this story to "rationalize" it - notably the Grimm added of their own an explanation as to why the girl jumps into the well.
This fairytale comes from Hesse and Westphalia. The brothers Grimm listed in their notes four other versions of it - and the first is more noticeable, because it echoes "Hansel and Gretel", as the house where the girls arrive is made of pancakes (crêpes). Older literary versions of "Frau Holle" can be found in Basile's Pentamerone (The Months, The Three Fairies), as well as within a French fairytale written by Gabrielle-Suzanne de Villeneuve, "Les nymphes" (The Nymphs). Translated in German in 1765, Villeneuve's fairytale notably inspired the Grimms when they composed their 1810 manuscript - they adapted her tale as their own story called "The marmot". Before the brothers Grimm, "ancestors" of "Frau Holle" can be found in various German fairytales, present in the collections of W. Reynitzsch (1802) and Benedikte Naubert (1789). Ludwig Bechsten did his own version of the fairytale (Gold-Mary and Pitch-Mary, Die Goldamaria und die Pechmaria) which had a huge success in Germany.
This fairytale belongs to a wide series of tales in which young girls leave their house to enter a far-away country which might be the Otherworld, and where they become the servants of a spernatural being. There, by performing tasks in a disinterested manner, they are rewarded. As with other fairytales, "Frau Holle" shows how the Otherworld and our world are inter-dependant with each other. "Frau Holle" had a huge mediatic success: it was adapted several times as movies, it is heavily present in children's literature, and it was heavily illustrated. The character of Frau Holle ("Holle" derivading from the Middle-High-German "hulde", "benvolent") is an ambiguous character, and shares several characteristic with Germanic water-spirits. She is a giver of supernatural gifts and goods, but she also punishes the wicked. This supernatural character is very present in German legends, especially in the oral tradition which associates her with the works of weaving and spinning. She might have her roots in the figure of a spirit in charge of women's initiation rituals.

Little Red Riding Hood (Rotkäppchen)
It is of course the AaTh 333: "Little Red Riding Hood".
The two versions the brothers Grimm used to create this story were told to them by Johanna Isabella and Marie Hassenpflug. Isabella's version was most notable for being an obvious transposition of Charles Perrault's fairytales - with two elements changed. The tragic ending was modifed so that the girl and her grandmother would be saved ; and the erotic connotations of Perrault's fairytale (where the wolf was presented as a dangerous seducer) were removed.
Charles Perrault's fairytale was also present in German literature through Ludwig Tieck's verse tragedy "The life and death of little Red Riding Hood" (Leben und Tod des kleinen Rotkäppchens), published in 1800. As for Ludwig Bechstein, he inspired himself from the brothers Grimm tale to create his own "Little Red Riding Hood". M-L-Tenèze has worked on collecting all the oral and popular versions of Little Red Riding Hood in France, its birth-country, and has identified its original format as it must have been told before Perrault: usually they end like his tale in a tragic way for the girl, but rarely she notices she is in bed with a monster and manages to trick it to escape. However a detail Perrault erased and that is present in these versions is how the wolf keeps a bit of the grandmother's flesh and blood, that he offers to the little girl as food.
The first version of this story, in the original edition of the brothers Grimm book, was much more didactic than the one we have today, heavily insisting on how the little girl should have obeyed to her mother, and how there are specific ways to interact with strangers on the road - and in fact, it seems that the reason this fairytale was so popular and widespread was precisely because of its didactic nature. Because everybody knows the "original" version of the Grimm better than the final one, their second and revised text that shows a heroine able to learn from her mistakes, and ending up defeating the wolf of her own without any outside help. It should be noted that the first version of the Grimm tale had an echoing motif with the KHM 5 "The Wolf and the Seven Young Kids".
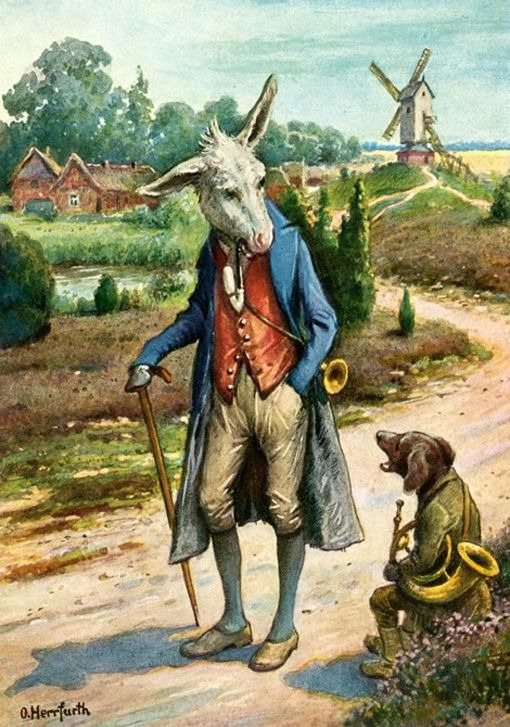

The Musicians of the Town of Bremen (De Bremer Stadtmusikanten)
They eblong to the AT type 130 "The animals find a house for the night", more specifically the AT 130 B, "The animals flee after a death threat".
This fairytale, like many of those present in the brothers Grimm collection, was actually the fusion of two distinct stories they collected. The brothers Grimm described in their notes a literary source for this story: a long extract from "Froschmeuseler", a didactic epic by Georg Rollenhagen published in 1595 and which had animals as protagonists. In this text however, it is a dog that leads the six other animals (an ox, a donkey, a cat, a rooster and a goose). For this poem (of 20 000 verses) Rollenhagen himself had another literary inspiration: a first-century epic describing a war between frogs and mice.
The nicknames of the various animals were only added in the third edition of the book. The notes of the brothers contain a third version of the tale they did not use, and which mostly differs when they arrive at the robbers' house. Instead of chasing them away, the animals enter peacefully in the robbers' den, play music and are fed as a reward. Then the robbers leave, and when they return they send one of theirs to check if everything is alright in the house - and he suffers the fate described in the Grimm's final tale. There are other versions of the story where there are only two animals involved (a dog and a rooster), who get involved with a fox that the dog ultimately kills. In fact, the oldest versions of this tale all deal with domestic animals confronting, not human criminals, but rather savage animals of the forest. Outside of Rollenhagen's text, another literary precedent was a poem of Hans Sachs from 1551, where the house is inhabited by wolves.
The title of this story seems to refer to traditional mockeries of the music of the town of Bremen, which was a very famous city at the time. Anti-Aarne wrote an entire monography about this tale-type, "The travelling animals" (Die Tiere auf der Wanderschaft) where he highlighted how this story was the Western "sibling" of a more Oriental fairytale-type, the AaTh 210 "The rooster, the chicken, the duck, the pin and the needle are travelling". This tale is mostly present in the Far-East (Middle-East?), and very rare in Western Europe - but it is still present within the brothers Grimm's collection as the KHM 10 (The Pack of Ragamuffins), 41 (Herr Korbes), and 80 (The Death of the Little Hen). The oldest Western form of this other fairytale type is within the Latin poem by Nivard of Gand, 1150's "Ysengrimus", where animals considered too old are banished by their masters or about to be killed, and flee into the forest. The "Roman de Renart" (the Roman of Reynard) also contains ths motif in its eighth branch - and the ingratitude of mankind towards the creatures that served them all their life is also a theme of the KHM 48 (Old Sultan).
#german fairytales#grimm fairytales#brothers grimm#the frog king#rapunzel#hansel and gretel#cinderella#history of fairytales#evolution of fairytales#the musicians of the town of bremen#little red riding hood#frau holle#the brave little tailor
19 notes
·
View notes
Text






Я нарисовала коллекцию Царевен Союзмультфильма по аналогии с Принцессами Диснея. Часть первая. В этом посте у меня Царевны из мультфильмов: I drew a collection of Soyuzmultfilm Princesses similar to the Disney Princesses. In this post (Part 1) I have Princesses from cartoons: «Бременские музыканты» 1969 и 1973 (The Bremen Town Musicians) «Летучий корабль» 1979 (The Flying Ship) «Василиса Микулишна» 1975 (Vasilisa Mikulishna) «Золушка» 1979 (Cinderella) «Русалочка» 1968 (The Little Mermaid) «Дюймовочка» 1964 (Thumbelina)
#soviet animation#Soyuzmultfilm#The Bremen Town Musicians#disney princess#царевны#tsarevny#princess#ussr#my fanart#rabemar art#soviet union
201 notes
·
View notes
Text
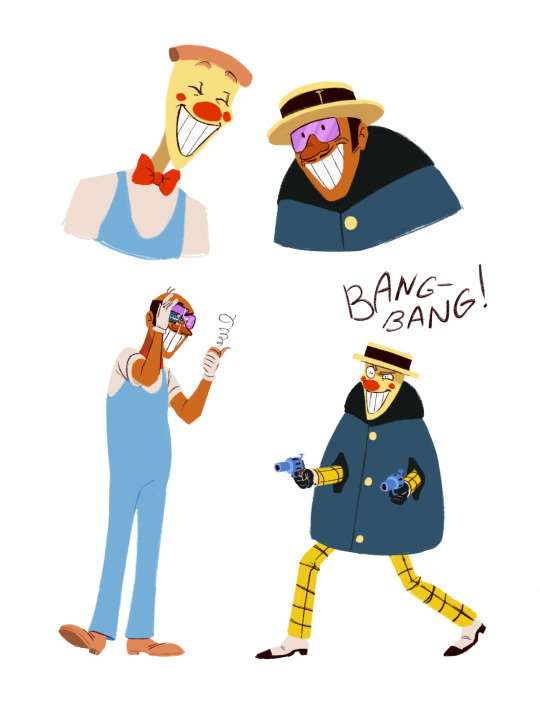

Finally I realized who Pizzahead reminded me of with his big smile (The Genius Detective from the Soviet cartoon "On the Trail of the Bremen Musicians")
bonus timelapse
#pizza tower#the bremen town musicians#бременские музыканты#soviet cartoons#genius detective#pizzahead#my art#crossover
209 notes
·
View notes
Text
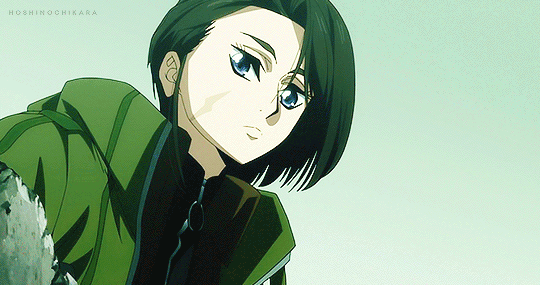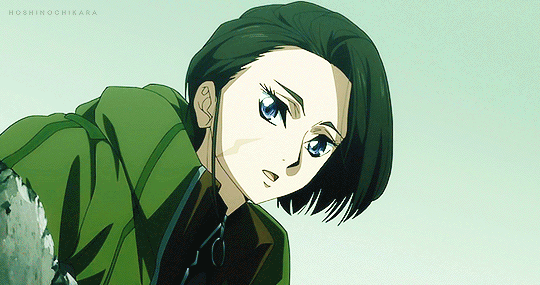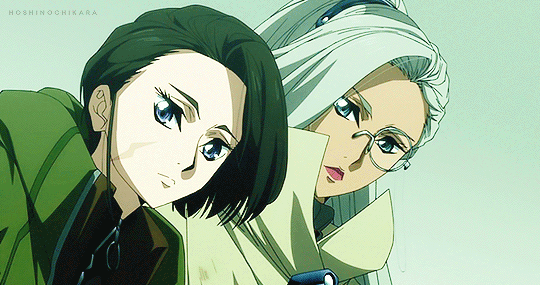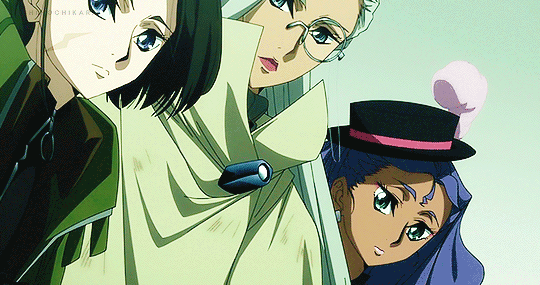
#the grimm variations#the town musicians of bremen#clamplove#clampgif#i was sat#the second i saw roba
83 notes
·
View notes
Text
Just watched "The Grimm Variations" on Netflix and I can't tell if my favorite episode is the Little Red Riding Hood episode where the wolf is a cyberpunk bishounen serial killer or the Bremen Town Musician episode where the main characters are a lesbian sci-fi cowboy throuple who adopt a lonely gremlin child before committing vigilante justice.
#the grimm variations#netflix#little red riding hood#bremen town musicians#sci-fi#adaptation#cyberpunk#lesbian#lesbians#found family#bishounen#mr grey#scarlet#dog#donkey#cat#anime
91 notes
·
View notes
Text

Die Bremer Stadtmusikanten (Town Musicians of Bremen) Statue
149 notes
·
View notes
Photo
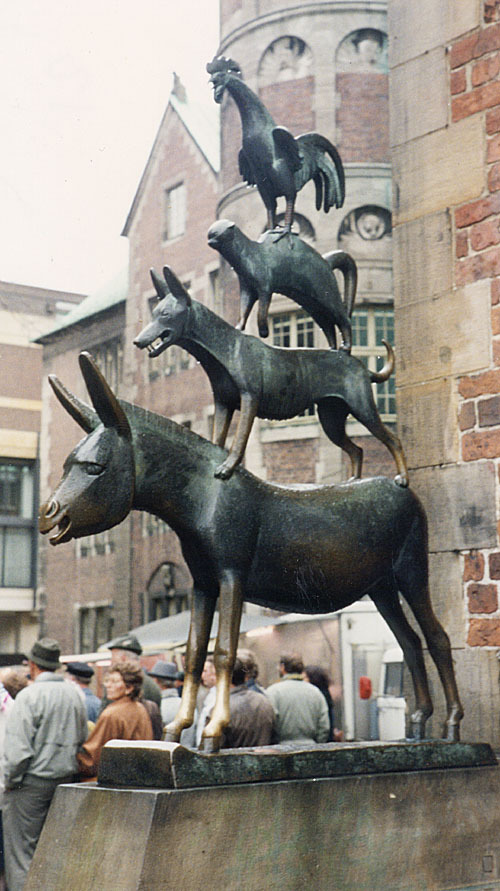


What the hell is happening here!
Source
Town Musicians of Bremen Wikipedia
#photos#omg#animals#roads#wtfmemes#incredible#haters will say it's photoshop#fairy tails#town musicians of bremen
479 notes
·
View notes
Text

The Bremen Town Muscians
31 notes
·
View notes
Text

RetrOCtober Day 23: Mänkki
Mänkki the Donkey is the epitome of the dumb bassist jokes, while repeatedly managing to astonish listeners with their surprisingly complex and bad-ass (pun intended) basslines in the Bremen Town Musicians. Mänkki often ends up carrying the whole band, both musically and physically. 🫏⭐
#mänkki#bremen town musicians#bremen#tiernapojat#original character#cartoon#donkey#anthropomorphic#bassist
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
Now that I have finished watching "Grimm Variations" on netflix, allow me to express my opinion of each chapter with these brief words:
1) Cinderella: Oh! So good! This is looking awesome! 😀
2) Little Red Riding Hood: OH MY GOD! NOO! STOP! OH MY GOD! 😨😱
3) Hansel & Gretel: Please don't smoke funny weed during working hours. Thank you. 😑
4) The Elves and the Shoemaker: Not bad, I like this adaptation. 🤔
5) The Town Musicians of Bremen: GO! GO! LESBIANS! 😁
6) Pied Piper of Hamelin: Please don't smoke funny weed or consume substances of questionable origin during working hours. Thank you very much x2. 😑🤦🏻♀️
#the grimm variations#clamp#netflix#anime#grimm brothers#fairytale#cinderella#little red riding hood#hansel and gretel#the elves and the shoemaker#the town musicians of Bremen#Pied Piper of Hamelin
53 notes
·
View notes
Text
Oh my stars I just thought of the best crochet project for next time I have nothing going on
#so the town musicians of bremen exist in my series#and making a crochet version of them? would be so fun#land of the tales#hazel rambles about her original writing#crafting with hazel
11 notes
·
View notes
Text

the beatles if they slayed...
#the characters are from a 1969 short movie called bremenskie muzykante (bremen town musicians)#but idk where this specific gif is from...#its a good movie though! if you like old cartoons#the beatles
16 notes
·
View notes
Text
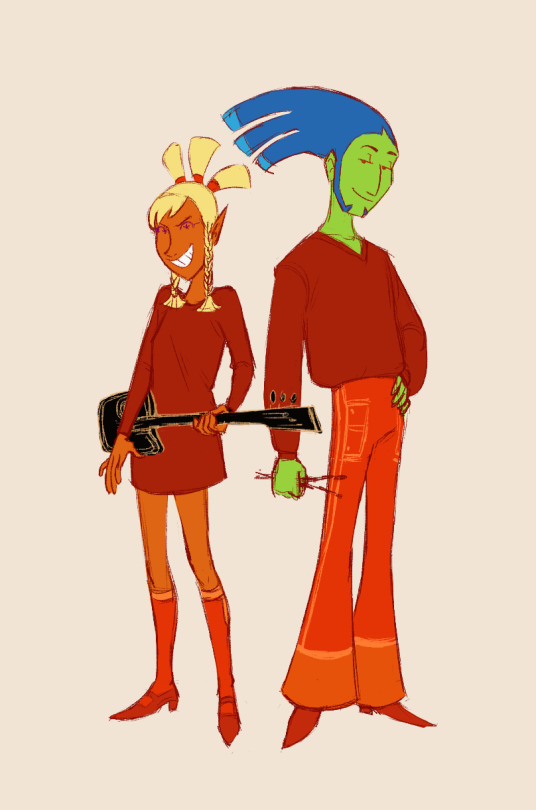

Mayday and Zuke dressed up as the Princess and the Troubadour from Soviet cartoon "The Bremen Town Musicians"
#no straight roads#nsr#the bremen town musicians#бременские музыканты#soviet cartoons#mayday#nsr mayday#nsr zuke#zuke#my art#crossover
146 notes
·
View notes
Text

THE BREMEN TOWN MUSICIANS
#the bremen town musicians#fairy tale#cuento de hadas#musicos#pueblo de bremen#brothers grimm#hermanos grimm#die bremer sta dtmusikanten#donkey#burro#esel#dog#perro#hund#cat#gato#katze#rooster#gallo#hahn#deutschland#germany#alemania#europe#europa
101 notes
·
View notes
Text
THE GRIMM VARIATIONS
Classic childhood fairytales with a twist.






#the grimm variations#animated gif#anime recommendation#anime gif#anime#fantasy#horror#space#thriller#suspense#magic#grimm#grimm fairy tales#wit studio#cinderella#little red riding hood#hansel and gretel#the elves and the shoemaker#the town musicians of bremen#pied piper of hamelin
12 notes
·
View notes
Text

Snippet from Jacob Grimm, Wilhelm Grimm, Max Stebich (Austria1896-1972. Mein Liebstes Märchen Buch. Vienna: J. Breitschopf Jun, 1966. I appreciate the feline and canine representation in this version of the Bremen Town Musicians. Thanks to @lagunavintage for the tip.
#gato#perro#dog#illustration#hund#hond#chat#katze#chien#cat#Bremen town musicians#grimm tales#max stebich
8 notes
·
View notes