#surveillance in China
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
#lmao#lol#tiktok#national security#chinese spy#byteDance#espionage#data privacy#cybersecurity#congressional hearings#china-us relations#social media#misinformation#manipulation#intelligence agencies#hypothetical threat#chinese government#user data privacy#tiktok ownership#foreign influence#online surveillance#misinformation campaign
120 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Chinese government says that its policies in Xinjiang are intended to curb terrorism and separatism, and that the camps provide instruction in Chinese language and other skills to people who might be susceptible to extremist ideas.
But the Karakax spreadsheet shows how officials have monitored minute details of daily life to find targets for detention as Chen Quanguo, the Communist Party boss in Xinjiang, ordered officials to “round up everyone who should be rounded up.”
The authorities scrutinized three generations of each detainee’s family, as well as their neighbors and friends. Officials in charge of monitoring mosques reported on how actively the residents participated in ceremonies, including the naming of children, circumcision, weddings and funerals.
The list specified whether detainees learned about religion from parents and grandparents or elsewhere. Dozens were listed as having a “heavy religious environment” at home — a designation that was often followed by a recommendation that they not be released.
The authorities also studied how many times a day detainees prayed and whether they took part in — or were even interested in — religious pilgrimages.
Outward signs of piety were also recorded. “Wore a beard from March 2011 to July 2014,” reads a description of one detainee related to several people who had been sent to camps. Officials categorized as “trustworthy” another man, the father of two detainees, who had cut off his beard and started drinking alcohol after a year of abstaining.
— How China Tracked Detainees and Their Families
#austin ramzy#current events#racism#islamophobia#religion#islam#politics#chinese politics#surveillance#uyghur genocide#china#xinjiang#uyghurs
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
youtube
At its Friday hearings, the US Supreme Court sounded like it was likely to go ahead with approving the suspension of TikTok until it changes ownership.
Rep. Raja Krishnamoorthi (D-IL-08) spoke with MSNBC's Chris Jansing about the case. The congressman also commented on Trump's sentencing in the Stormy Daniels hush money trial.
The government of China is notorious for its hacking and digital espionage activities. Giving China a direct pipeline to half of all Americans' digital pockets is a security risk to those individuals and to the country as a whole.
China wants a back door to your data but hypocritically bans US digital companies like Google, Yahoo, Fandom, Zoom, Meta, Reddit, LinkedIn, and even DeviantArt – to name just a small percentage.
Prof. Shaomin Li of Old Dominion University has written extensively about international business and China in particular. In an article at The Conversation he has this to say about the relationship between ByteDance (parent company of TikTok) and the Communist Party of China.
I’m not convinced by TikTok’s argument that American users’ data is safe because it’s stored outside of China, in the U.S., Malaysia and Singapore. I also don’t think it’s relevant whether the party has members on the ByteDance board or gives explicit orders to TikTok. Regardless of whether ByteDance has formal ties with the party, there will be the tacit understanding that the management is working for two bosses: the investors of the company and – more importantly – their political overseers that represent the party. But most importantly, when the interests of the two bosses conflict, the party trumps.
In China, the ruling Communist Party has a say in everything.
US TikTok users should contact ByteDance and urge it to divest TikTok ASAP.
#tiktok#bytedance#china#communist party of china#hacking#digital surveillance#us supreme court#raja krishnamoorthi#il-08#chris jansing#shaomin li#social media#赤納粹
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
My observations of Northwest China illustrate the way that contemporary colonial projects tend toward the “operational enclosure,” which describes a digitally-mediated social hierarchy in which the movement and behaviour of certain racialized populations are made automatically detectable and thus controllable, while privileged settler populations are permitted to move around in a relatively frictionless way—for instance, doors are opened automatically for them by security workers who profile them, or by camera systems that identify them as non-Muslim. Coined by communications scholars Mark Andrejevic and Zala Volcic, this form of enclosure is being adapted by government agencies and corporations across the Global South to slot marginalized populations into the operative logics of actionable intelligence. For privileged settlers, a seamless digitally integrated society brings them pride in the advancement of their country’s capabilities along with consumer convenience. For Muslims, on the other hand, the operational enclosure provokes intense fear.
In Northwest China, advanced dataveillance technology is key in producing an efficient settler colonial state that can classify and segment its inhabitants. Two interrelated phenomena are at play here, one regarding the technology itself and the other about how it molds social reality. First, the technology is a black box—security workers do not really understand how it works beyond the reductive readouts they see on their screen: 99.11 percent match. Orange tag. Potentially “untrustworthy.”
Second, in practice these simplistic characterizations and predictions come to be seen as truth. The technology is viewed as an unquestioned authoritative good, since it is perceived as scientific and state-of-the-art intelligence. The predictions made become legally enforced truths.
Together, these two elements, the digital black box and the legal and social discourse of technological intelligence, are producing one of the first mass experiments in the colonial operational enclosure.
64 notes
·
View notes
Text
Why Socialist Democrats want the National or Digital ID.
As always, never buy anything made in china. Don't ever trust a democrat and NEVER leave your child alone with one.
#trump 2024#joe biden#Digital ID#National ID#surveillance#big brother#spying#Nazis#communism#socialism#china#russia#iran#NSA#cia#fbi#gestapo
9 notes
·
View notes
Text

JINZHOU, CHINA.
40 notes
·
View notes
Text
"why are you focused on america so much?"
first I live there, second


our government keeps doing this shit. there's so much, why is there hardly anyone talking about this THEY HAVE ACCESS TO BILLIONS OF SIM CARDS, NOT MLLIONS 'B' BILLIONS.

also we keep making stupid and mostly useless government agencies.


#there is so much mass surveillance in the us I feel like we should bring that up more#like we do with china#except we're doing more than them.#genuinely#people just don't talk about this.#mk ultra lead to the creation of discordanism#we don't even know what all they did#they burned that shit#like actually burned#the cia has been shown multiple times to just be doing whatever#and the fbi#the irs doesn't care if you commit crimes that aren't financial#this isn't even the worst shit#and there's probably more we just won't ever know about#also they are actively trying to force companies to back door their shit like constantly#and yet it can still barely stay together and is actively falling apart
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
China and Myanmar have the ‘worst environment’ for internet freedom
China and Myanmar have the ‘worst environment’ for internet freedom #censorship #China #Elections #FreedomHouse
#censorship#China#Elections#Freedom House#Human Rights#internet freedom#Myanmar#online expression#online surveillance#VPN bans
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
China's surveillance state is moving into the west. And its not all facial recognition.
#china#surveillance#spying#censorship#social credit#big tech#camera#cyber security#technology#wef#united nations
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
How Increased Surveillance by the China Government during the Global COVID-19 Pandemic Affects Online Communities?

In the wake of the global COVID-19 pandemic, governments worldwide, including China, intensified surveillance measures to curb the virus's spread. In this context, China's implementation of stringent surveillance, notably through Health Code Apps, has raised profound concerns about its impact on online communities. As facial recognition and data collection become intrinsic to daily life, the potential repercussions on digital spaces and the people within them demand careful examination. This discussion delves into the multifaceted consequences of increased surveillance by the Chinese government and its tangible effects on the dynamics of online communities.
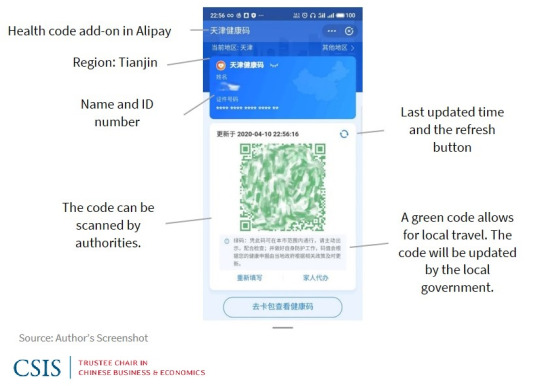

Privacy Erosion
In response to the global COVID-19 pandemic, various countries implemented measures to track and control the virus's spread, introducing tools such as contact tracing apps (Ojokoh et al., 2022), temperature checks (Qu & Lv, 2021) and travel restrictions (Burns et al., 2021). Simultaneously, In China, where stringent surveillance measures were already in place, the government leveraged technology to an even greater extent, using facial recognition and health QR codes to monitor citizens' movements. This involved the deployment of a series of applications known as "Health Code Apps," which have raised concerns about privacy erosion, particularly regarding the use of health code applications. Online communities are not immune to this erosion, as the data collected through these apps includes personal information, health status, and location details. This data is then utilized to assign one of three colours, indicating the user's health status (Ramos, 2020). However, Data is funnelled to entities like the provincial Big Data Bureau, Alibaba, and the telecommunications department, expanding the accessibility to user information, ranging from personal details to health status, location, and device specifics. This centralized model amplifies the risks of data aggregation and user re-identification, exemplified by the Beijing Health Bao system's data leak in December 2020. The incident exposed the photographs, ID numbers, and nucleic acid test information of celebrities, highlighting insufficient safeguards in place (Zhang, 2022). Online communities may find their members exposed to privacy breaches, leading to a chilling effect on open communication and expression within these digital spaces.

Potential for Abuse of Power:
The potential for the abuse of power in the context of surveillance, inadequate transparency and compliance measures is a significant concern for online communities as well. This concern is exemplified by recent events in Henan Province, where health code apps were allegedly manipulated to suppress protests related to potential losses in rural banks on the brink of collapse (Zhang, 2022). The legitimacy of these health code apps faced a setback as city officials marked over a thousand individuals as red, restricting their entry into Zhengzhou City and highlighting the vulnerability of such systems to misuse (Zhang, 2022). This incident underscores the potential for health code apps, initially designed for public health purposes, to transform into tools of surveillance, allowing government agencies to exert control under the guise of maintaining public health. The lack of stringent transparency requirements heightens the risk of these technologies being misused for purposes beyond their intended scope, which negatively impacts the freedom of expression within online communities. As governments exploit surveillance tools to monitor and influence online discussions, online communities may face challenges related to censorship and control, further emphasising the interconnected nature of surveillance concerns and their impact on digital spaces.
Technological Dependence:
Embracing extensive surveillance often involves a reliance on advanced technologies. In the case of Health Code Apps, facial recognition technology is integrated into residential area access control systems, permitting entry only to those with a green code (Ramos, 2020), which has implications for online communities. This reliance on advanced technologies may neglect more human-centric approaches to online interaction, potentially excluding or disadvantaging certain members of digital communities. As surveillance technologies become integral to online platforms, the balance between security measures and preserving the inclusivity and diversity of online communities becomes a critical consideration.
Trust Deficit:
The colour-coded system assigned by health code applications has far-reaching consequences for millions of users in their interactions within both physical and online communities. Requiring individuals to display their health codes in public transportation, shopping malls, markets, and other public places may contribute to a trust deficit between citizens and the online platforms they engage with (Jao et al., 2020). Users within online communities may question the motives behind such surveillance measures, especially if their personal information is shared without their knowledge. Rebuilding trust within online communities, once eroded by mandatory health code reliance, poses a considerable challenge, impacting the dynamics of digital social spaces.
In conclusion, the surge in surveillance by the Chinese government amid the global COVID-19 pandemic undeniably leaves a lasting imprint on online communities. The colour-coded system mandated by health code applications not only infiltrates public spaces but also infiltrates the very essence of digital interactions. This imposition triggers a tangible trust deficit within online communities as individuals question the motives behind these surveillance measures. Rebuilding trust within these virtual spaces, essential for vibrant and open communication, becomes a formidable challenge in the aftermath of mandatory health code reliance. The delicate equilibrium between bolstering security measures and safeguarding the inclusivity of online communities emerges as the linchpin for preserving the dynamic and diverse nature of these digital spaces. In essence, the impact of increased surveillance by the Chinese government is intimately intertwined with the well-being and resilience of online communities.
"Considering the implications of increased surveillance by the Chinese government during the global COVID-19 pandemic on online communities, we'd like to hear your perspective. How do you perceive the effects on privacy erosion, potential abuse of power, technological dependence, and the trust deficit within these digital spaces? Share your insights and cast your vote below."
Reference List
Burns, J., Movsisyan, A., Stratil, J. M., Biallas, R. L., Coenen, M., Emmert-Fees, K., Geffert, K., Hoffmann, S., Horstick, O., Laxy, M., Klinger, C., Kratzer, S., Litwin, T., Norris, S. L., Pfadenhauer, L. M., Von Philipsborn, P., Sell, K., Stadelmaier, J., Verboom, B., . . . Rehfuess, E. (2021). International travel-related control measures to contain the COVID-19 pandemic: a rapid review. The Cochrane Library, 2021(3). https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.cd013717.pub2
Jao, N., Cohen, D., & Udemans, C. (2020). How China is using QR code apps to contain Covid-19. TechNode. https://technode.com/2020/02/25/how-china-is-using-qr-code-apps-to-contain-covid-19/
Ojokoh, B. A., Aribisala, B. S., Sarumi, O. A., Gabriel, A. J., Omisore, O. M., Taiwo, A. E., Igbe, T., Chukwuocha, U. M., Yusuf, T. A., Afolayan, A., Babalola, O., Adebayo, T., & Afolabi, O. (2022). Contact Tracing Strategies for COVID-19 Prevention and Containment: A scoping review. Big Data and Cognitive Computing, 6(4), 111. https://doi.org/10.3390/bdcc6040111
Qu, J., & Lv, X. (2021). The response measures to the coronavirus disease 2019 outbreak in China. Open Forum Infectious Diseases, 8(2). https://doi.org/10.1093/ofid/ofab014
Ramos, L. F. (2020). Evaluating privacy during the COVID-19 public health emergency. The ACM Digital Library, 176–179. https://doi.org/10.1145/3428502.3428526
Zhang, X. (2022). Decoding China’s COVID-19 health code apps: the legal challenges. Healthcare, 10(8), 1479. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare10081479
4 notes
·
View notes
Text

Camouflage of a different tier in Hong Kong - a projector that displays a different face than yours to fool cameras and save social score.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
...contemporary colonial projects tend toward the “operational enclosure,” which describes a digitally-mediated social hierarchy in which the movement and behaviour of certain racialized populations are made automatically detectable and thus controllable, while privileged settler populations are permitted to move around in a relatively frictionless way. [...] this form of enclosure is being adapted by government agencies and corporations across the Global South to slot marginalized populations into the operative logics of actionable intelligence. For privileged settlers, a seamless digitally integrated society brings them pride in the advancement of their country’s capabilities along with consumer convenience. For Muslims, on the other hand, the operational enclosure provokes intense fear."
"...advanced dataveillance technology is key in producing an efficient settler colonial state that can classify and segment its inhabitants. Two interrelated phenomena are at play here, one regarding the technology itself and the other about how it molds social reality. First, the technology is a black box—security workers do not really understand how it works beyond the reductive readouts they see on their screen: 99.11 percent match. Orange tag. Potentially “untrustworthy.” Second, in practice these simplistic characterizations and predictions come to be seen as truth. The technology is viewed as an unquestioned authoritative good, since it is perceived as scientific and state-of-the-art intelligence. The predictions made become legally enforced truths. Together, these two elements, the digital black box and the legal and social discourse of technological intelligence, are producing one of the first mass experiments in the colonial operational enclosure.
A more nuanced view of contemporary colonialisms attempts to show how these different forms of imperialism are entangled with each other and how they need to be opposed simultaneously.
#uyghur#colonialism#datasurveillance#operational enclosure#settler colonialism#mass surveillance#technology#Meiya Pico#digital forensics#clean net guard#surveillance technology#human rights#civil rights#subimperialism#ethnonationalism#internal colonization#capitalism#population control#mass internment#state violence#china#israel#india#global north#profiling#islamophobia#police#r/#logic magazine#readings
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Mr. Xi is the son of an early Communist Party leader who in the 1980s supported more relaxed policies toward ethnic minority groups, and some analysts had expected he might follow his father’s milder ways when he assumed leadership of the party in November 2012.
But the speeches underscore how Mr. Xi sees risks to China through the prism of the collapse of the Soviet Union, which he blamed on ideological laxity and spineless leadership.
Across China, he set about eliminating challenges to party rule; dissidents and human rights lawyers disappeared in waves of arrests. In Xinjiang, he pointed to examples from the former Soviet bloc to argue that economic growth would not immunize a society against ethnic separatism.
The Baltic republics were among the most developed in the Soviet Union but also the first to leave when the country broke up, he told the leadership conference. Yugoslavia’s relative prosperity did not prevent its disintegration either, he added.
“We say that development is the top priority and the basis for achieving lasting security, and that’s right,” Mr. Xi said. “But it would be wrong to believe that with development every problem solves itself.”
In the speeches, Mr. Xi showed a deep familiarity with the history of Uighur resistance to Chinese rule, or at least Beijing’s official version of it, and discussed episodes rarely if ever mentioned by Chinese leaders in public, including brief periods of Uighur self-rule in the first half of the 20th century.
Violence by Uighur militants has never threatened Communist control of the region. Though attacks grew deadlier after 2009, when nearly 200 people died in ethnic riots in Urumqi, they remained relatively small, scattered and unsophisticated.
Even so, Mr. Xi warned that the violence was spilling from Xinjiang into other parts of China and could taint the party’s image of strength. Unless the threat was extinguished, Mr. Xi told the leadership conference, “social stability will suffer shocks, the general unity of people of every ethnicity will be damaged, and the broad outlook for reform, development and stability will be affected.”
Setting aside diplomatic niceties, he traced the origins of Islamic extremism in Xinjiang to the Middle East, and warned that turmoil in Syria and Afghanistan would magnify the risks for China. Uighurs had traveled to both countries, he said, and could return to China as seasoned fighters seeking an independent homeland, which they called East Turkestan.
“After the United States pulls troops out of Afghanistan, terrorist organizations positioned on the frontiers of Afghanistan and Pakistan may quickly infiltrate into Central Asia,” Mr. Xi said. “East Turkestan’s terrorists who have received real-war training in Syria and Afghanistan could at any time launch terrorist attacks in Xinjiang.”
Mr. Xi’s predecessor, Hu Jintao, responded to the 2009 riots in Urumqi with a clampdown but he also stressed economic development as a cure for ethnic discontent — longstanding party policy. But Mr. Xi signaled a break with Mr. Hu’s approach in the speeches.
“In recent years, Xinjiang has grown very quickly and the standard of living has consistently risen, but even so ethnic separatism and terrorist violence have still been on the rise,” he said. “This goes to show that economic development does not automatically bring lasting order and security.”
Ensuring stability in Xinjiang would require a sweeping campaign of surveillance and intelligence gathering to root out resistance in Uighur society, Mr. Xi argued.
He said new technology must be part of the solution, foreshadowing the party’s deployment of facial recognition, genetic testing and big data in Xinjiang. But he also emphasized old-fashioned methods, such as neighborhood informants, and urged officials to study how Americans responded to the Sept. 11 attacks.
Like the United States, he said, China “must make the public an important resource in protecting national security.”
“We Communists should be naturals at fighting a people’s war,” he said. “We’re the best at organizing for a task.”
The only suggestion in these speeches that Mr. Xi envisioned the internment camps now at the heart of the crackdown was an endorsement of more intense indoctrination programs in Xinjiang’s prisons.
“There must be effective educational remolding and transformation of criminals,” he told officials in southern Xinjiang on the second day of his trip. “And even after these people are released, their education and transformation must continue.”
Within months, indoctrination sites began opening across Xinjiang — mostly small facilities at first, which held dozens or hundreds of Uighurs at a time for sessions intended to pressure them into disavowing devotion to Islam and professing gratitude for the party.
Then in August 2016, a hard-liner named Chen Quanguo was transferred from Tibet to govern Xinjiang. Within weeks, he called on local officials to “remobilize” around Mr. Xi’s goals and declared that Mr. Xi’s speeches “set the direction for making a success of Xinjiang.”
New security controls and a drastic expansion of the indoctrination camps followed.
The crackdown appears to have smothered violent unrest in Xinjiang, but many experts have warned that the extreme security measures and mass detentions are likely to breed resentment that could eventually inspire worse ethnic clashes.
— ‘Absolutely No Mercy’: Leaked Files Expose How China Organized Mass Detentions of Muslims
#austin ramzy#chris buckley#‘absolutely no mercy’: leaked files expose how china organized mass detentions of muslims#current events#racism#islamophobia#politics#chinese politics#terrorism#history#communism#surveillance#uyghur genocide#xinjiang conflict#war in afghanistan#war on terror#china#xinjiang#east turkestan#uyghurs#xi jinping#hu jintao#chen quanguo
4 notes
·
View notes

