#sri lanka attacks
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Trying to explain what the fuck just happened in Lankan politics today.
The leftist party has won 159 seats out of 218 in the Parliamentary elections. The single biggest landslide win since we broke from the British and achieved universal franchise in 1948.
Any party achieving a super majority in the executive and legislative is, objectively speaking, bad. It disables checks and balances, which is a catastrophic thing for any democracy, and the only two other times it's happened for us has irrevocably eroded the fabric of civic rights and democratic freedom. Also, the reason the NPP won the North and East is that the colonized, genocided and subjugated people there have no faith in electoralism anymore. The way this government has engaged minority issues has been utterly abysmal and now they've been rewarded for it.
On the other hand:
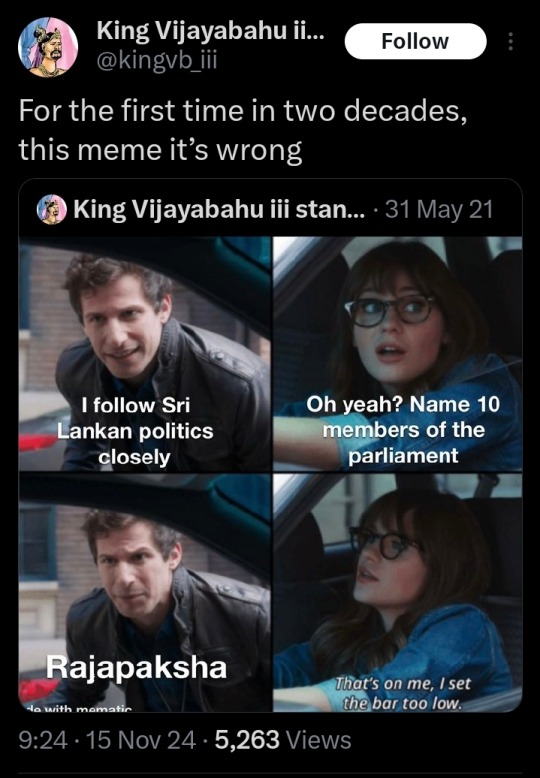
The winners. Are all. Grassroots. Candidates.¹
We have voted out every single career criminal that's been barnacled into the Lankan political arena since before I've been alive. The fascist party has only three seats.² The other fascists didn't win a single seat. The neoliberal legacy party won none. There are only forty people in Parliament that represent any sort of dynastic political legacy. After 76 solid years of nothing but political dynasties.
This is barely five years after the Rajapaksas swept in and absolutely glutted the Parliament with their family members and cronies end to end.
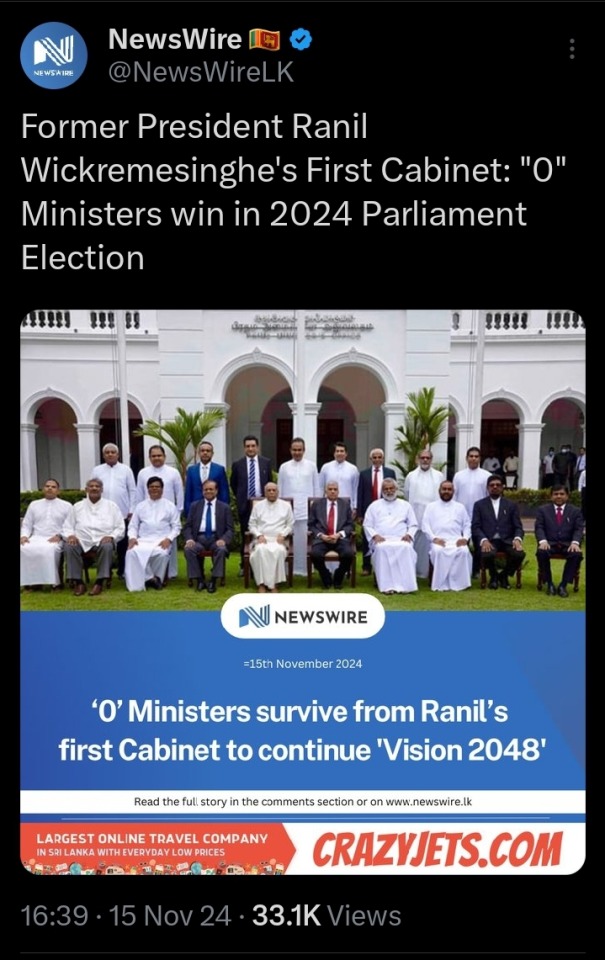
This is the illegitimate interim government we had for most of the last 18 months. We literally, physically, chased the Rajapaksas out of the country and this fucking demon set up a puppet government just so he could finally sit in that goddamn chair and be the despot he'd always dreamed of in exchange for letting them all come back. He's now gone. His entire circle is gone.
THEY ARE ALL FUCKING GONE.
In US terms, just imagine that, five years from now, when Trump's GOP has control of everything, the entire GOP and the worst of the Dems are all purged from Congress and Senate, the Green Party in control of all three branches of government under a pro-union left-wing President and an unmarried female LGBT rights activist Vice President, and the Dems reduced to barely 20% of the House.
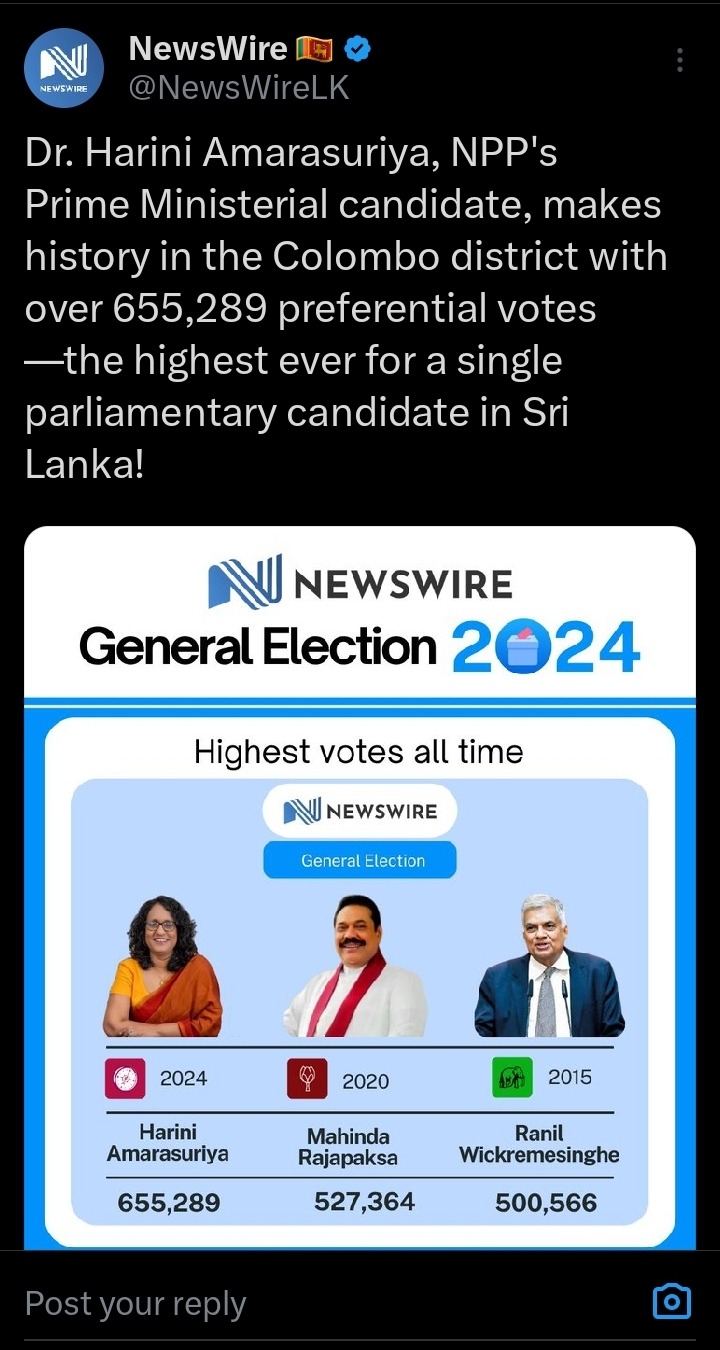
This is my anthropology professor. She joined politics from the small nascent leftist coalition to help keep the government accountable. She's now the Prime Minister and the most popular Parliamentary candidate in the nation's history. (Edit: She was knocked off first place by a dude in the final result. Boo.)
(On the other hand— the woman who helped make me a radical anarchist and literally helped write a book on political dissent and resistance...now is the state. Uh.)
But there are so many women in Parliament! We had the lowest female representation in a South Asian Parliament and some of them were from the list of seats reserved for parties rather than elected ones. Most were either anti-feminist conservative embarrassments, widows and daughters of elite politicians and neoliberal shills. It's still only an increase of a few percentage points (Edit: from the previous 5% to 10% in the final result!) but now we have elected academics, feminist advocates, activists! There Is a representative for Malaiyaha Tamils in the Central Province for the first time in history and it's a young woman! (Edit: now it's two female Malaiyaha MPS!!) This is the plantation community that still live in conditions closest to the slavery the British forced upon them two hundred years ago!
I'm like. Completely mindfucked. To be very very clear, the NPP coalition formed around the nucleus of the JVP that used to be communist but haven't been in 30 years, they're now just social democrats who are left of places like the US and UK, whose "left" is now center-right. They're only threatening to the Western mainstream media for some reason who can't stop bleating about how we have a "Marxist" government now. In reality, the actual chances for radical reform are still quite low, and the opportunity for further erosion is quite high with a super majority government regardless of affiliation.
On the other hand:
What the fuck.
Sometimes living through historical events is really damn amazing.
---
¹ Well, nearly. There are a few career politicians and a nepo baby but they aren't so bad either.
² Goddamn it, Baby Rajapaksa and Sri Lanka's answer to JD Vance have wormed their way in using the list of Constitutionally reserved party seats for non-elected members. FUCK the National List.
#five years ago i was working a news desk watching a band of violent ethnofascists known for genocide torture kidnappings and murder sweep in#and take control of the entire country#on the heels of the worst terrorist attack we've suffered that they orchestrated for this purpose#wondering how many of our colleagues would be safe#and watching the people that opposed them flee the country#i cannot tell you the enraging hopeless terror#and now#they're all gone#THEY'RE FUCKING GONE#sri lanka politics#sri lanka news#sri lanka protests#sri lankan parliamentary elections#sri lanka election 2024#anura kumara dissanayake#harini amarasuriya#feminism#leftism#world news#faith in humanity#power to the people#aragalaya#knee of huss#අරගලයට ජය!#අරගලයට ජය
4K notes
·
View notes
Text
Israel maintains robust arms trade with rogue regimes
**This is from 2017 but just shows what a sociopath Netanyahu is. Despite all of this, we still give Israel billions (yes billions with a B) every year for "defense". Clearly Bibi sees no irony in providing weapons to be used to perpetrate religious genocide. His ancestors must be turning in their mass graves**
"Many Western states sell arms, but what's unique about Israel is that, wherever war crimes & crimes against humanity are being committed, you find Israel is present," Mack told Al Jazeera. As well as fuelling the current violence in Myanmar & South Sudan, Israel has been accused of clandestinely providing arms used in notorious past episodes of genocide & ethnic cleansing in places such as Rwanda, the Balkans, Chile, Argentina, Sri Lanka, Haiti, El Salvador and Nicaragua. Israel also cultivated close ties to apartheid South Africa, Mack noted.
Yair Auron, a genocide researcher at Israel's Open University, said that Israel's supply of weapons to regimes such as Myanmar should be compared to the sending of arms to Nazi Germany during the Holocaust. "These sales turn me & all Israelis into criminals, because they are sent in our name," he told Al Jazeera. "We are abetting genocide."
Human rights activists are stepping up efforts to expose Israel's long & covert history of supplying weapons & military training to regimes while they actively commit massacres, ethnic cleansing & genocide. The issue of Israel's trade with rogue regimes has been thrust into the spotlight again after revelations that it is sending weapons to Myanmar, in defiance of a US & European arms embargo.
Formerly known as Burma, Myanmar was condemned last month by the United Nations for conducting what it called a "textbook ethnic cleansing" of the Rohingya, a Muslim minority. Hundreds of thousands of Rohingya are reported to have fled to neighbouring Bangladesh in recent weeks, after evidence of the torching of entire villages, massacres and systematic rapes.
Israel has not divulged details of its ties to Myanmar's military government, but public records show that it has sold the military there armed patrol boats, guns and surveillance equipment. Myanmar's special forces have also been trained by Israelis.
Israeli firms have also broken with the United States and Europe by supplying weapons and surveillance equipment to militias in South Sudan, where a civil war has raged since late 2013. Some 300,000 Sudanese are believed to have been killed in the fighting.
Eitay Mack, a human rights lawyer, has submitted a spate of petitions to the Israeli courts in an attempt to bring to light details of Israel's trade with such regimes. He said the cases were designed to hasten war crimes investigations of the officials and contractors involved.
Israel is the only major weapons exporter that has consistently bucked the global trend of a downturn in arms sales. In March, it was reported that Israel's weapons trade in 2016 was worth some $6.5bn, up from $5.7bn the year before. That included a 70 percent jump in sales to Africa.
If countries want the best arms, then they probably go to the US and Europe. But when no one else will sell to you, then you turn to Israel.
#israel is a terrorist state#israeli war crimes#arms trade#genocide#netanyahu#Netanyahu is a sociopath#warmonger#ethnic cleansing#stop islamophobia#israel is an apartheid state#gazaunderfire#gaza under attack#myanmar#rohingya#south sudan#rwanda#argentina#chile#sri lanka#balkans#haiti#el salvador#nicaragua#icc war crimes tribunal#united states is complicit in genocides#america has the blood of innocents on its hands
14 notes
·
View notes
Text
sri lanka navy attack indian fishermen: श्रीलंकाई नौसेना ने भारतीय मछुआरों पर चलाई गोली, 2 लोगों की हालत नाजुक MEA ने माँगा जबाब
sri lanka navy attack indian fishermen: श्रीलंकाई नौसेना द्वारा डेल्फ़्ट द्वीप के नजदीक गोलीबारी की घटना में पांच भारतीय मछुआरे घायल हो गए हैं, जिनमें से दो की हालत गंभीर बताई जा रही है। यह घटना मंगलवार, 28 जनवरी 2025 को हुई। इस घटना के बाद भारत ने श्रीलंका के खिलाफ कड़ी प्रतिक्रिया व्यक्त की है और द्वीप के हाई कमिश्नर को तलब करके इस मामले पर आपत्ति जताई है। भारत ने स्पष्ट किया है कि किसी भी…
#fishermen#indian fisherman#indian fishermen#indian fishermen hurt by sri lanka navy#indian fishermen injured by sri lankan navy#indian fishermen shot by sri lanka navy#sri lanka#sri lanka indian fishermen#sri lanka navy#sri lanka navy arrested indian fishermen#sri lanka navy attack indian fishermen#sri lankan fishermen#sri lankan navy#sri lankan navy arrests 15 indian fishermen#sri lankan navy fires on indian fishermen#sri lankan navy shoots indian fishermen
0 notes
Text
everyday i see clueless westerners (especially white people) peddle thinly veiled hindutva propaganda which they wouldn't know cause they know absolutely nothing about what goes on in india. so here are some signs that that the person you're talking to is a hindu nationalist:
they either do not acknowledge casteism or claim that caste is a western construct. my personal favourite however is dismissing anyone bringing up caste discrimination by saying that the indian constitution outlaws untouchability. they may also bring up the fact that the prime minister belongs to an other backwards class (obc) so clearly india has moved on from caste and hindutva isn't only for the upper castes. they possess a shallow understanding of caste
harping on about "islamic colonisation" : no, the mughals did not colonise india. when you point this out, they will immediately assume that you think muslim invaders were innocent beings who did nothing wrong, which is very much not what anyone is claiming here
while we're on the topic of "islamic colonisation" they will also refer to the demolishing of muslim sites of heritage and worship and then building hindu temples over them as "decolonisation" (cough cough ram mandir) the hindu right also goes around pretending that they're the indigenous people of india
along a similar vein, they will dismiss islamophobia by bringing up instances of hindu oppression in countries like pakistan and bangladesh. it is true that hindus are persecuted in these two countries, however they are used to fuel their oppression complex, that their upper caste hindu self is under attack in india of all places (think a white christian in the united states). you should be in solidarity with minorities everywhere. it is neither transactional or conditional (note: they will never bring up sri lanka. persecution of hindus exists only when the oppressors are muslim)
claiming that hindu nationalism and hindutva are not the same because hindutva means "hindu-ness". that is only the literal translation of the term. like it or not, they're the same thing
they support the indian military occupation of kashmir. they will call it an integral part of kashmir, one reason which will be "hinduism is indigenous to kashmir." they will also bring up the last maharaja of kashmir signing the instrument of accession as further proof, as if the consent of the people was taken
they're zionists. do i even need to explain this. hindutva is just zionism for hindus
they refer to buddhism and jainism (sikhism too sometimes) as branches of hinduism rather than separate, distinct religions
they condemn any resistance to the indian govt as a burden or terrorism (like calling the farmers who are currently protesting a hindrance or terrorists. funny how sikhs are the same as hindus when they support hindu causes but terrorists when they resist oppression...)
they call you a pseudo liberal or a fake leftist. i'm telling you, they don't know jackshit. they can't even tell the difference between a liberal and a leftist and call US unread lmao. bonus points if they call you a liberandu or a sickular 💀
they call india "bharat" when they talk in english. there are in fact multiple indian languages that call india bharat or bharatam, but if they say bharat while talking in english, that is absolutely a hindu nationalist no questions asked
please do your due diligence. read up on hindutva. hindu nationalists have already started making gains in the united states, thanks to rich upper caste nris. do not fall for propaganda
9K notes
·
View notes
Text
Woah
Beware the Pride
Being a model minority will not save you. It did not save the Sinhalese from the English; it did not save the Tamils from the Sinhalese; it will not save the Muslims. And once we are done eating them it will not save the Christians. And most of all It will not save us.
Not the poor Not the former war heroes with their limbs blown off their minds cracked open like eggshells seeping yellow drowning in the blood on their hands while their families starve and fathers take their lives because the crops have died.
But there are still enough with working limbs Expendables with no crops no jobs nothing but empty stomachs (acid rising between their teeth); to give them a gun point it at a human dartboard and let them all die as fodder for another Glorious Victory. Another slew of mothers to mourn at mass graves on roadsides.
For another ten years of the rich sucking the marrow bone of a steadily growing hoarde underfoot.
Being a model minority will not save us. Us the majority middle-class, with our struggling, smiling middle-class lives. Heads down, teeth closed, pontificating on these social media posts. They will take our voices one by one. Rupees dwindling to nothing one by one. Our children going bedraggled one by one. Until for them also awaits only a uniform and gun, and the promise of a glorious tomorrow.
They will rule this pile of skeletons. They will suck and suck the rivers dry, the fields arid, the villages buried under landslides, and swept away in avenging monsoons; while we burn alive under a steadily more blazing sun.
They will thrive as the poorest die; the middle class of today take their places. There will always be enough mouths to feed into the maw of greed. lions are gorgers you see.
As long as the saffron beasts roam unchecked; scavenging hyenas following our prides, feeding on the Buddha’s carcass; we are doomed. As long as we shake our heads and watch as the Devaduttas roar at mobs; tolling their gleeful war-bells, our death-knells - we are doomed. As long as democracy is just a screaming mob with a puppet or despot at the top - we are doomed. In a land of ten thousand temples there is no salvation of the Buddha. You see the lions ate Him first.
#written five years ago#when the Rajapaksas won the elections by a landslide in the wave of reactionary Islamophobia#from the Easter Sunday Attacks they were later found to have orchestrated themselves#there's no saving a country from the black rot of its own ethnosupremacy#my writing#sri lanka#sri lanka politics
33 notes
·
View notes
Text
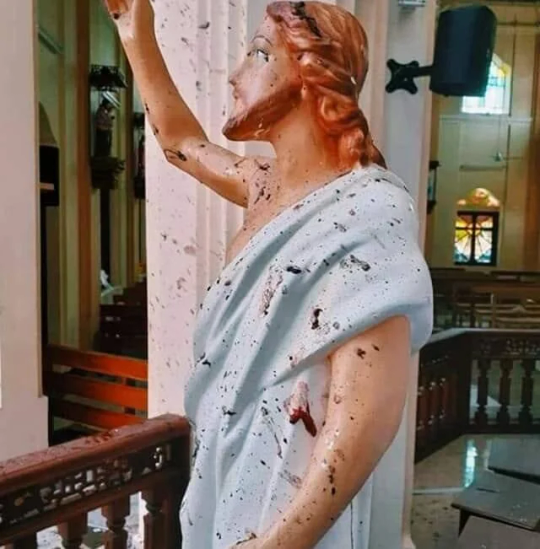

A statue of Jesus Christ spattered with blood following the 2019 Sri Lanka bombing.
On April 21, 2019, Sri Lanka was rocked by a series of devastating terrorist attacks targeting three churches and three luxury hotels. This tragic event, known as the 2019 Sri Lanka Easter bombings, marked one of the deadliest days in the country’s history, resulting in the loss of over 250 lives and leaving more than 500 injured.
The attacks were carried out by a local Islamist extremist group called National Thowheeth Jama'ath (NTJ), with alleged support from international terrorist networks. This marked a significant shift in the landscape of terrorism in Sri Lanka, a country that had endured decades of civil war primarily driven by ethnic tensions. The bombings were reportedly in retaliation for the Christchurch mosque shootings in New Zealand, which had occurred a month earlier.
59 notes
·
View notes
Text
IMPORTANT CRISES THAT ARE BEING IGNORED BY THE WORLD
[ we already are aware about palestine, NOT just gaza so i will refrain from mentioning anything here regarding it ]
these crises will not follow any specific order but i will be numbering them for the sake of proper structure.
i also did my best to find reliable and accurate information. please do not start hating me or questioning my efforts if i have mentioned something wrong or incorrect. instead you can correct me politely. additionally, if there are any crisis that i have missed out on, bring it to my awareness.
i am not going to be including all details but some major highlights so as to be able to keep ourselves updated of atleast the surface level knowledge (so i will try)
reblog and include (or highlight what needs to be excluded) any details that would serve in the best interest of this post.
1. TAMIL EELAM
sri lanka is an island historically inhabited by tamils, sinhalese, muslims, and other communities. the tamil nation is concentrated in the northeast. the muslim community generally speaks tamil. the majority of the country's sinhalese population lives in the southern part of the island and are buddhist.
following independence from britain, the sinhalese ruling class began to build an ethnocratic nation-state that entrenched sinhala-buddhist supremacy. tamil workers' rights were denied in the new nation-state, while tamil students were refused equal access to education. tamil people protested peacefully, but sri lanka responded with arrests and massacres.
in july 1983, the worst anti-tamil pogroms swept the island: tamil people were hunted in the streets, pulled out of their homes, and killed while sri lankan police watched on. In six days, 4000 tamils were killed. government ministers led mobs and targeted tamil homes in areas where tamils and sinhalese both lived, amounting to what the international commission of jurists labelled an act of genocide.
sri lanka booted the UN and international press from the country before relaunching its war against the tamil people in 2006. the state used banned chemical weapons like white phosphorous on civilians. a UN report estimates that 75,000 tamil civilians perished from september 2008-May 2009 alone. ground sources place the number much higher and estimate that over 120,000 people were killed in the final stages of the war.
nothing was spared. hospitals and religious buildings, full of the sick and wounded, were routinely bombed. the armed forces shelled food distribution lines and near International red cross ships picking up wounded civilians from beaches. even the government's own "no-fire zones," packed with thousands of civilians, were indiscriminately attacked from the ground and sky.
for the tamils, the last stages of the war fit into a broader pattern of sri lanka's post-colonial state-building project: a protracted genocide involving massacres, economic embargoes, indiscriminate bombings, discriminatory policies, and the dispossession of tamil lands. tamils fear their political identity, as a distinct group of peoples, a nation, will be dismantled and reduced to a scattered minority across the island.
12 years after the genocide, the sri lankan armed forces maintain complete control through a military occupation of the tamil homeland. five of the seven regional headquarters of the army are entrenched in the tamil homeland, with over 100,000 soldiers maintaining an environment of harassment and surveillance over the tamil people. like kashmir and palestine, the tamil homeland remains one of the most militarized places in the world.
HOW TO HELP
2. ROHINGYA
in august 2017, armed attacks, massive scale violence, and serious human rights violations forced thousands of rohingya to flee their homes in myanmar’s rakhine state. many walked for days through jungles and undertook dangerous sea journeys across the bay of bengal to reach safety in bangladesh. now, more than 960,000 people have found safety in bangladesh with a majority living in the cox bazar’s region - home to the world’s largest refugee camp. the united nations has described the rohingya as “the most persecuted minority in the world.”
the rohingya are a muslim ethnic minority group who have lived for centuries in predominantly buddhist myanmar - formerly known as burma. despite living in myanmar for many generations, the rohingya are not recognized as an official ethnic group and have been denied citizenship since 1982, making them the world’s largest stateless population.
as a stateless population, rohingya families are denied basic rights and protection and are extremely vulnerable to exploitation, sexual and gender-based violence (SGBV) and abuse.
the rohingya have suffered decades of violence, discrimination and persecution in myanmar. their largest exodus began in august 2017 after a massive wave of violence broke out in myanmar’s rakhine state, forcing more than 742,000 people - half of them children - to seek refuge in bangladesh. entire villages were burned to the ground, thousands of families were killed or separated and massive human rights violations were reported.
more than 1 million rohingya refugees have fled violence in myanmar in successive waves of displacement since the 1990s. now, more than 960,000 rohingya refugees are living in bangladesh with a majority settled in and around kutupalong and nayapara refugee camps in bangladesh’s cox’s bazar region — some of the largest and most densely populated camps in the world.
more than half of all rohingya refugees in bangladesh (52 percent) are children, while 51 percent are comprised of women and girls. the current refugee population accounts for one-third of the total population in the cox’s bazar region, making support to host communities essential for peaceful coexistence.
since 2021, to decongest the 33 camps in cox’s bazar, nearly 30,000 refugees have been relocated to bhasan char island by the government of bangladesh. while protection services and humanitarian assistance have been scaled up on the island, significant gaps remain in service delivery and the sustainability of critical assistance.
rohingya refugees have also sought refuge in other neighboring countries like thailand (92,000) and India (21,000), with smaller numbers settling in indonesia, nepal and other countries across the region.
armed clashes across myanmar have continued to trigger displacement, bringing the total number of internally displaced people (IDP) within the country to more than 1.8 million — including 1.5 million of whom have been internally displaced since february 2021.
as of december 2023, however, a new issue arose. the indonesian navy has pushed back a boat carrying rohingya refugees as it approached the coast of aceh amid resentment among some residents about a sudden increase in boat arrivals. the military said the coastguard first detected the wooden vessel entering indonesian waters on wednesday, before the navy ship KRI bontang-907 located the boat about 63 nautical miles (117km) off aceh on the northwestern tip of the archipelago and drove it out, “ensuring that the boat did not return to indonesian waters,” the navy said in a statement posted in its website.
military spokesperson nugraha gumilar said it was not known how many people were on board. they are suspected to be rohingya, a mostly muslim minority from myanmar who were forced into neighbouring bangladesh by a brutal military crackdown in 2017 that is now the subject of a genocide investigation.
more than 1,500 rohingya refugees have landed in indonesia on barely sea-worthy wooden boats since november, according to data from the united nations refugee agency (UNHCR), and the sudden jump in arrivals has aroused growing hostility among people in aceh.
indonesia has appealed to the international community for help and intensified patrols of its waters, promising to crack down on suspected human traffickers it says are involved in the latest wave of boat arrivals.
on wednesday, a mob of students stormed the basement of a local community hall in banda aceh, the acehnese capital, where about 137 rohingya were taking shelter and called for the group to be deported.
many of the refugees are in poor health after weeks at sea usually with insufficient supplies of food and water.
the UNHCR said it was “deeply disturbed to see a mob attack on a site sheltering vulnerable refugee families”.
indonesia, although not a signatory to the 1951 UN convention on refugees, was once known for providing a safe haven to the rohingya even as neighbouring malaysia and thailand pushed them away.
but the mood has soured this year, especially in aceh, where some residents claim the rohingya behave badly and create a burden on society.
muslims make up nearly 90 percent of indonesia’s 277 million people, and aceh is the only state in the archipelago to follow islamic law.
the growing hostility towards the rohingya has put pressure on president joko widodo’s government to take action.
“this is not an easy issue, this is an issue with enormous challenges,” foreign minister retno marsudi told reporters.
HOW TO HELP
3. MANIPUR
on may 3, members of the kuki and naga tribes, who inhabit manipur's hills and are regarded as scheduled tribes, or india's most disadvantaged groups, launched a protest against the possible extension of their benefits to the dominant meiteis.
meiteis account for half of manipur's population and extending limited affirmative action quotas to them would mean they would get a share in education and government jobs reserved for kukis and nagas.
meiteis have traditionally lived in manipur's more prosperous valley region that makes up 10% of the state's area. they have also had better access to employment and economic opportunities.
nagas and kukis live in the poorly developed hills.
the development imbalance favouring the valley over the hills has been a point of contention and rivalry between the ethnic groups.
the groups coexisted peacefully until unrelated events in recent months exposed old faultlines.
manipur shares a nearly 400-km (250-mile) border with myanmar and the coup there in 2021 pushed thousands of refugees into the indian state.
kukis share ethnic lineage with myanmar’s chin tribe and meiteis feared they would be outnumbered by the arrival of the refugees.
separately, the state government in february launched a drive to evict tribal communities from forests in the hills, saying they had encroached on government land, sparking anger among tribal people that they were being forced out of their homes.
"it has been building up for a long time, in some ways unseen and some ways quite openly, but the government was not paying attention," said pradip phanjoubam, editor of the imphal review of arts and politics.
although the first outburst of violence was put down by mid-may, sporadic reprisal attacks began within days.
both the meiteis and kukis are known to be flush with arms, including automatic weapons either stolen from the state police or sourced from across the border in myanmar.
new delhi has held talks with senior myanmar leaders to help control armed groups that operate from across the border but this is yet to produce results.
kuki and meitei groups also refused to join a peace panel formed by the federal government due to differences over names included in the panel.
the indian army and federal paramilitary forces in the state cannot act independently and are legally bound to work with state police and authorities, who analysts say are also divided along ethnic lines.
also, kukis accuse the bharatiya janata party-ruled state government's chief minister biren singh, a meitei, of complicity and inaction, and have sought his removal. singh denies the accusations.
HOW TO HELP
4. HAWA'II ( MAUI )
maui wildfires of 2023, a series of wildfires that burned parts of the island of maui in the U.S. state of hawaii in august 2023. the fires, which began on august 8, struck hardest the historic resort town of lahaina, on maui’s western peninsula, reducing most of the town to ash and ruins. 98 people were killed in lahaina by the smoke and flames or by drowning, making the wildfire one of the world’s deadliest on record. almost 3,000 structures were reported to have been either damaged or destroyed by the fire. in addition to the fires on maui, a series of less devastating wildfires burned parts of the island of hawaii starting on august 9.
while local and state government officials have hesitated to identify a specific cause of the wildfires (in general, uncontrolled fires in a forest, grassland, brushland, or cropland) as of august 17, some evidence suggests that sparks produced by a downed power line may have touched off at least one of the fires. meteorologists and climate researchers noted that the fires were likely to have been the product of several intersecting factors. the fires occurred at the height of hawaii’s dry season (which lasts from april to october). their severity was exacerbated by the presence of el nino—that is, the development of unusually warm ocean waters in the central and eastern tropical pacific ocean. el niño brings increased rainfall to south america’s west coast but brings drought conditions to the hawaiian islands. indeed, the interval of june to august 2023 was a period of worsening drought on maui and in other parts of hawaii. as the drought increased in severity, it dried vegetation, much of it made up of large tracts of fire-prone invasive shrubs and grasses.
in addition, the pool of warm water in the tropical pacific kept fueling hurricane dora, a powerful tropical cyclone that had formed off the western coast of mexico on august 2. dora passed some 1,100 km (about 700 miles) south of the hawaiian islands during the week of august 8, the day the fires began, which created a substantial difference in atmospheric pressure between the storm and a high-pressure system located north of the islands. that pressure difference drew high winds southward and funneled them into the centre of the tropical cyclone, which helped intensify and spread the wildfires. wind speeds reached as high as 107.8 km (67 miles) per hour on maui and up to 132 km (82 miles) per hour on the island of hawaii.
some researchers have noted that climate change may have played a part in worsening the wildfires’ severity. increases in global and regional surface temperatures due to ongoing global warming are thought to have caused grasses and other vegetation to dry out faster than usual. in addition, studies that considered trends in hawaii’s rainfall indicated that some 90 percent of the state had experienced at least some decline in overall rainfall between 1920 and 2012 and that rainfall amounts at higher elevations had fallen by more than 30 percent between 1990 and 2015 during the state’s wet season (november to march). in addition, the replacement of native vegetation with crops over the last century has affected local climate conditions, primarily in accessible areas in several parts of the state of hawaii, including near sections of coastline and in maui’s central valley—the sites of the island’s wildfires.
the fire near lahaina, a municipality of 12,702 people, began as a small brush fire just beyond the town’s eastern outskirts in the early morning hours of august 8. although local officials considered it to have been contained by mid-morning, the fire flared up during mid-afternoon, forcing officials to close lahaina’s bypass road. driven by the high winds, the fire then moved downslope into the town, and it spread quickly between the parched grassy landscape and the town’s predominantly wooden buildings, generating an immense wall of black smoke. within 15 minutes, the fire had spread to the centre of the town, burning the area between the town’s two primary access roads, which prompted additional road closures that hindered evacuation. the process of alerting residents to the danger was severely hampered by the toppling of several telephone and electric power poles in the area by high winds earlier that day, which had cut power needed for wireless services and telephone lines used for 911 emergency communication. as the fire grew, it became so intense that it melted pipes delivering water to lahaina’s residences, which reduced the town’s overall water pressure and thus inhibited the fire department’s ability to contain the wildfire.
ny 5:30 PM large areas of lahaina, which included tracts of residences and the town’s central business district, were on fire as exploding gasoline tanks in vehicles and filling stations contributed to the conflagration. since emergency services had no way to alert people through their mobile devices, the fire caught many residents by surprise, forcing some to flee in haste while trapping others in their homes. many of those who fled became boxed in by fire, smoke, and road closures; some sheltered in place, whereas others sought refuge in the pacific ocean, clinging to docks, pilings, seawalls, and other infrastructure. by 7:00 PM the fire had reached the harbour, and boats caught fire from the mix of wind-whipped flames and flying embers, causing their fuel tanks to explode. although the fire continued to burn in lahaina throughout the night, U.S. coast guard boats arriving offshore were able to evacuate several people trapped along the coast.
during the morning of august 9 the winds abated enough to allow firefighting crews, helicopters, and other resources to begin to make their way into lahaina, where they found a grayed landscape of ruined buildings and burned-out vehicles. officials reported that the lahaina fire had been 80 percent contained by august 10 and that it had burned nearly 890 hectares (about 2,200 acres) by august 14. maui’s other wildfires, which included the pulehu/kihei fire in maui’s central valley and the upcountry/kula fire along the slopes of the island’s eastern peninsula, were less severe, resulting in far fewer damaged homes and other structures and no reports of serious injuries or deaths. similarly, on the island of hawaii, fires scorched some 600 hectares (about 1,500 acres) of ranchland in the north and south kohala sections of the island, but no injuries were reported.
even as the fires began to spread on maui, government officials started to issue disaster declarations to fund firefighting efforts, rescues, and recovery. hawaii’s lieutenant governor, sylvia luke, issued an emergency declaration during mid-afternoon of august 8, which was followed later that evening by the activation of hawaii’s national guard. the following day, as reports of the unfolding disaster in lahaina reached the outside world, the U.S. federal emergency management agency (FEMA) authorized payments to fire victims, and U.S. pres. joe biden promised that “all available federal assets on the Islands” would assist in relief efforts. such efforts had increased by august 16, aided by state and federal agencies (including the U.S. Army, which provided logistical support and assisted in road clearing) and private charter flights that delivered donations of food and other supplies. In the aftermath of the wildfires, thousands of displaced maui residents were taken to shelters and evacuation centres on the island, which included hotels abandoned by tourists who had been evacuated to other islands or to the U.S. mainland.
HOW TO HELP
5. KURDISTAN
kurds have never achieved nation-state status, making kurdistan a non-governmental region and one of the largest stateless nations in the world. portions of the region are recognized by two countries: iran, where the province of kordestan lies; and northern iraq, site of the autonomous region known as kurdistan regional government (KRG) or iraqi kurdistan.
the turkish government claims to be conducting operations against the kurdistan worker's party (PKK) - a kurdish rebel organization that is outlawed by the state. through the use of airstrikes, the turkish military is hitting targets across the region and pushing deeper into southern kurdistan, launching ground operations from the military bases that it controls in the area.
a consequence of this encroachment into southern kurdistan is that civilians are being hit by turkish drones. those who are being hit are not just fighters but also ordinary kurdish civilian. innocent lives are also being lost when those who are hit succumb to their injuries. turkey justifies such acts under the pretext of fighting the PKK a rationale that it has used repeatedly to justify other military incursions. is this conflict new? absolutely not. what is new is the response to these operations. In previous decades, the turkish state could get away with indiscriminate bombing and military incursions as long as its justification centered on fighting terrorism. this justification was, after all, what other state actors operating in the region would use to rationalize military incursions against those deemed state enemies. no longer are there just people from kurdish diasporas across the world calling out the turkish state for its disregard for international law, but also from non-kurds. even at the administrative level of the united states government, officials are no longer believing the rhetoric that the turkish state uses to justify its military incisions. there will be no peace in kurdistan until turkey withdraws. there will be no peace for victims until turkey is held accountable for its criminal actions now and in the past. and as long as these atrocities are left without a response by international state actors and multilateral organizations such as the united nations and NATO, turkey will continue to commit crimes against kurds, including kurdish civilians.
HOW TO HELP
6. YEMEN
yemen is in the middle of a complex humanitarian crisis driven by a brutal civil war. indiscriminate attacks and chronic shortages of medical staff and supplies have led to the closure of many of yemen's healthcare facilities. more than 4.5 million people have been displaced since the war started in 2014. qith an estimated 21 million currently in need of humanitarian assistance.
collapsed health system- warring factions have extensively damaged public infrastructure, notably health facilities. since the saudi-led coalition (SLC) imposed a blockade in 2015, import restrictions and soaring inflation have severely limited yemenis' access to healthcare and essential services. the blockade has led to the cessation of salaries for many of the 50,000 health workers within the country, compelling them to exit the public health system in search of alternative income sources.
disease- due to the ongoing war, obtaining clean water, waste disposal, and accessing medical care have become even more challenging for the people. coupled with limited access to vaccinations, this heightened vulnerability has left yemenis susceptible to preventable diseases and emerging epidemics. the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic was particularly severe, with yemen having one of the lowest vaccination rates globally in 2021. in 2017, a cholera outbreak led to 101,475 patients being admitted to hospital. the same year, cases of diphtheria emerged, a disease largely eradicated in most countries due to systematic childhood vaccinations.
trauma- continual fighting and indiscriminate attacks have affected the ability to provide trauma care, which remains a vital responsibility of hospitals in the area. teams in hospitals near the frontlines routinely react to mass-casualty incidents and continually strive to enhance their capacity year-round to address the frequent arrival of war-wounded and other trauma patients.
malnutrition- yemen is grappling with alarming rates of malnutrition. widespread food insecurity and limited access to essential healthcare services leave many children vulnerable to infectious diseases. Inflation exacerbates the situation, making it progressively challenging for yemeni families to provide nourishment for their children and cover the expenses of transporting them to hospitals.
it has been troubled by civil wars for decades, but the current conflict intensified in march 2015 when a saudi-led coalition intervened on behalf of the internationally recognised government against houthi rebels aligned with the former president ali abdullah saleh. the war is widely regarded as having turned a poor country into a humanitarian catastrophe. riyadh expected its air power, backed by regional coalition including the united arab emirates, could defeat the houthi insurgency in a matter of months. instead some reports suggest nearly 100,000 people have died. others put the death toll much lower, but fighting this year alone has displaced 250,000 people. there are more than 30 active front lines. a total of 80% of the population - more than 24 million people - need assistance and protection, including 10 million who rely on food aid to survive. its roots lie in the arab spring. pro-democracy protesters took to the streets in a bid to force the president, ali abdullah saleh, to end his 33-year rule. he responded with economic concessions but refused to resign. by march 2011, tensions on the streets of the capital city, sana'a, resulted in protesters dying at the hands of the military. following an internationally brokered deal, there was a transfer of power in november to the vice-president, abd rabbu mansour hadi, paving the way for elections in february 2012 - in which he was the only candidate to lead a transitional government. hadi's attempts at constitutional and budget reforms were rejected by houthi rebels from the north. the houthis belong to a small branch of shia muslims known as zaydis. they captured the capital, forcing hadi to flee eventually to riyadh. there is also a strong secessionist movement in the south. arguably too many sides benefit financially from the status quo. united nations officials warned that without more donations, nearly 400 hospitals and health care centers it finances would have to reduce services just as the coronavirus pandemic has surged in yemen. already, food rations have been halved for 8.5 million hungry yemenis, and 10,000 health care workers have lost the united nations payments that for many are their only salary, ms. grande said. since the war began five years ago, pitting the houthis against a government backed by saudi arabia and the united arab emirates, yemenis have endured doomsday after doomsday: relentless airstrikes against hospitals and schools by the saudi-led military coalition using american-made weapons, a severe cholera outbreak, the ever-present threat of famine, a health care system in collapse and now the coronavirus. "yemenis themselves say things are worse today than at any time in their recent history," mr. lowcock said in his appeal to donors, asking "whether the world is prepared to watch yemen fall off the cliff."
HOW TO HELP
7. SYRIA
over 80% of the population in syria is living below the poverty line. that means they make less than $1 a day. more than 11 million people require humanitarian assistance, 5 million of which are children. 93 million people across syria are now food insecure lacking reliable access to a sufficient quantity of affordable, nutritious food. 70% of the population is without regular access to safe drinking water. 6.1 million people have been internally displaced. up to 70% of healthcare professionals have left the country & 50% of hospitals are non-operational. 40% of school infrastructure has been destroyed or damaged.
government and allied forces continued to commit war crimes and other serious violations of international humanitarian law, including indiscriminate attacks and direct attacks on civilians and civilian objects. according to the UN, government forces did not approve around half of their requests to carry out humanitarian missions to:
monitor
assess and accompany aid deliveries,
provide security, logistics and
administrative support.
you may ask, how did the "war" start? even before the conflict began, many syrians were complaining about high unemployment, corruption and a lack of political freedom under president bashar al-assad, who succeeded his father, hafez, after he died in 2000. in march 2011, pro-democracy demonstrations erupted in the southern city of deraa, inspired by uprisings in neighbouring countries against repressive rulers. when the syrian government used deadly force to crush the dissent, protests demanding the president's resignation erupted nationwide.
the unrest spread and the crackdown intensified. opposition supporters took up arms, first to defend themselves and later to rid their areas of security forces. mr assad vowed to crush what he called "foreign-backed terrorism".
the violence rapidly escalated and the country descended into civil war. hundreds of rebel groups sprung up and it did not take long for the conflict to become more than a battle between syrians for or against mr assad. foreign powers began to take sides, sending money, weaponry and fighters, and as the chaos worsened extremist jihadist organisations with their own aims, such as the islamic state (IS) group and al-qaeda, became involved. that deepened concern among the international community who saw them as a major threat. syria's jurds, who want the right of self-government but have not fought mr assad's forces, have added another dimension to the conflict.
the united nations human rights office estimated last year that 306,887 civilians - 1.5% of the total pre-war population - were killed between march 2011 and march 2021 due to the conflict. it is said 143,350 civilian deaths were individually documented by various sources with detailed information, and that a further 163,537 deaths were estimated to have occurred using statistical techniques. at least 27,126 of those estimated to have been killed were children. the then-UN commissioner for human rights, michelle bachelet, stressed that the fatalities were the "direct result of war operations", adding: "this does not include the many, many more civilians who died due to the loss of access to healthcare, to food, to clean water and other essential human rights." the syrian observatory for human rights (SOHR), a UK-based monitoring group with a network of sources on the ground, had documented the deaths of 503,064 people by march 2023. it said at least 162,390 civilians had been killed, with the syrian government and its allies responsible for 139,609 of those deaths. the group estimated that the actual toll from the war was more than 613,400, with an additional 55,000 civilians believed to have died of torture in government-run prisons. another monitoring group, the violations documentation center, which relies on information from activists across the country, had documented 240,215 battle-related deaths, including 145,765 civilians, as of march 2023.
the government's key supporter has been russia while turkey, western powers and several gulf arab states have backed the opposition to varying degrees during the conflict.
russia - which had military bases in syria before the war - launched an air campaign in support of mr assad in 2015 that has been crucial in turning the tide of the war in the government's favour. the russian military says its strikes only target "terrorists" but activists say they regularly kill mainstream rebels and civilians.
the US, UK and France initially armed what they considered "moderate" rebel groups. but they have prioritised non-lethal assistance since jihadists became the dominant force in the armed opposition.
aUS-led global coalition has also carried out air strikes and deployed special forces in syria since 2014 to help an alliance of kurdish and arab militias called the syrian democratic forces (SDF) capture territory once held by IS militants in the north-east and stop the jihadist group rebuilding.
turkey is a major supporter of the opposition, but its focus has been on using rebel factions to contain the kurdish YPG militia that dominates the SDF, accusing it of being an extension of a banned kurdish rebel group in turkey.
turkish troops and allied rebels have seized stretches of territory along syria's northern border and intervened to stop an all-out assault by government forces on the last opposition stronghold of Idlib.
saudi arabia, which is keen to counter iranian influence, armed and financed the rebels at the start of the war. having refused to engage with president assad for more than a decade, it is now discussing how to facilitate syria's "return to the arab fold".
twelve years of war have inflicted immense suffering on the syrian people. in addition to the bloodshed, more than half of syria's pre-war population of 22 million have had to flee their homes. some 6.8 million are internally displaced, with more than two million living in tented camps with limited access to basic services. another 6 million are refugees or asylum-seekers abroad. neighbouring lebanon, jordan and turkey, which are hosting 5.3 million of them, have struggled to cope with one of the largest refugee exoduses in recent history. at the start of 2023, the UN said 15.3 million people inside syria were in need of some form of humanitarian assistance - an all-time high since the war began - and 12 million did not know where their next meal was coming from. the already dire humanitarian situation in north-western syria - the location of the last opposition stronghold - was made significantly worse by the huge earthquake that struck near the turkish city of gaziantep, about 80km (50 miles) from the syrian border, on 6 February 2023. more than 5,900 people were killed across Syria and another 8.8 million were affected, according to the UN. thousands of homes and critical infrastructure were destroyed, leaving many families without food, water and shelter. deliveries of life-saving aid to opposition-held areas were also delayed for days because of what a UN panel described as "shocking" failures by the warring parties as well as the international community. the disaster happened at a time when the prices of food and fuel in syria were already skyrocketing because of runaway inflation and the collapse of its currency, as well as the global crisis exacerbated by the war in ukraine. syria has also been one of the countries in the middle east worst affected by the covid-19 pandemic - although the true extent is not known because of limited testing - and is now also having to deal with a deadly cholera outbreak that was made worse by the earthquake. access to medical care is severely restricted for the sick and injured because only half of the country's hospitals are fully functional. despite their protected status, 601 attacks on at least 400 separate medical facilities had been documented by physicians for human rights as of february 2022, resulting in the deaths of 942 medical personnel. the vast majority of the attacks were blamed on government and russian forces. entire neighbourhoods and vital infrastructure across the country also remain in ruins. UN satellite analysis suggested that more than 35,000 structures were damaged or destroyed in aleppo city alone before it was recaptured by the government in late 2016. much of syria's rich cultural heritage has likewise been destroyed. all six of the country's unesco world heritage sites have been damaged significantly, with IS militants deliberately blowing up parts of the ancient city of palmyra. a UN commission of inquiry has concluded that the warring parties "have cumulatively committed almost every crime against humanity... and nearly every war crime applicable in a non-international armed conflict".
"syrians," a february 2021 report says, "have suffered vast aerial bombardments of densely populated areas; they have endured chemical weapons attacks and modern day sieges in which perpetrators deliberately starved the population along medieval scripts and indefensible and shameful restrictions on humanitarian aid".
HOW TO HELP
visit the websites [ save the children.org/ syria ] and [ islamic-relief.org /syria crises ]
8. LEBANON
lebanon is currently facing a deep economic crisis as a result of government corruption and financial debt. this is partly a repercussion of the lebanese civil war (1975-1990). during this time, the government piled up huge amounts of debt through corrupt and lavish spending. banks have now become unable to process transactions because the currency (lira) is crashing. this has left many unable to access funds, which are now worth only a fraction of their original value.
in recent years, the situation has only worsened with the pandemic completely shutting down tourism, previously an important source of income in lebanon's economy. this has left a large portion of the lebanese population impoverished and without access to basic necessities. for example, many people in lebanon now rely on private diesel generator operators to have sufficient electricity.
another event that worsened lebanon's current state is the explosion that happened in the port of Beirut in 2020, which killed over 200 people and left many without a home. over a year after the explosion, critics claim that the judicial investigation that should uncover what happened has been continuosly hindered by the country's political leaders. lebanon's current president, michael aoun, hasn't addressed these accusations, but he said no one will have political impunity if found guilty.
HOW TO HELP
visit [ savethechildren.org / lebanon ] and [ irusa.org /lebanon ]
9. AFGHANISTAN
even before the withdrawal of international forces and diplomatic missions and the takeover by the taliban in august 2021, afghanistan was one of the world's largest and most complex humanitarian emergencies (CHEs). more than two years after the withdrawal, and despite massive amounts of humanitarian assistance poured into the country, enormous humanitarian needs remain.
the 2023 afghanistan humanitarian needs Overview (HNO) says afghanistan is facing an unprecedented humanitarian crisis “with a very real risk of systemic collapse and human catastrophe.” while in past years humanitarian needs have been driven mainly by conflict, the key drivers of humanitarian need in 2023 include drought, climate change, protection threats (particularly for women and girls) and the economic crisis.
the UN 9ffice for the coordination of humanitarian affairs (UNOCHA) estimated at the beginning of 2023 that a record 28.3 million people will need humanitarian and protection assistance this year, up from 24.4 million in 2022 and 18.4 million in 2021. with 28.3 million people in need, afghanistan is the largest humanitarian crisis in the world. the 2023 afghanistan humanitarian response plan (HRP) requests $4.6 billion to reach 23.7 million people.
in addition to the political, social and economic shocks from conflict and the withdrawal of international forces, disaster risk is becoming an increasing driver of underlying need. a national drought was officially declared in june 2021 and is the worst in more than 30 years.
on oct. 7, 2023, two separate 6.3-magnitude earthquakes near herat in afghanistan’s northwest caused significant damage and killed thousands. another earthquake shook herat province on 9ct. 11, resulting in further damage. the herat earthquake response plan from UN and humanitarian partners asks for $93.6 million to support 114,000 earthquake-affected people in herat.
following the devastating June 2022 earthquake that hit eastern afghanistan, CDP hosted a webinar to provide funders with information about the intersection of a natural hazard disaster amid a humanitarian crisis. the insights and recommendations webinar panelists provided remain relevant.
in 2023, 28.3 million people will need life-saving assistance. humanitarian partners have prioritized 23.7 million people to receive multi-sectoral assistance in 2023.
according to WFP, nine out of 10 afghan families lacking adequate food and children and pregnant women are the hardest hit.
each year, the international rescue committee (IRC) releases a list of the 20 humanitarian crises expected to deteriorate the most over the next year. IRC’s 2023 watchlist puts afghanistan in the third spot due to widespread poverty, harsh winter conditions, disaster impacts and violence and exploitation against women and girls.
on average, 200,000 afghans are affected by disasters each year. from jan. 1, 2023 to oct. 5, 2023, 26,014 people were affected by disasters throughout afghanistan. this figure was before the deadly earthquakes on oct. 7 and oct. 11 in herat province, which affected more than 275,000 people. as of nov. 22, humanitarian actors had reached 242,400 affected people with assistance.
in 2022, humanitarian partners reached 25 million people with at least one form of assistance. yet, millions who received one form of assistance will continue to require multiple rounds of support in 2023 to survive.
humanitarian access constraints continue to impact the operational environment. in 2023, there has been a 21% spike in incidents reported by partners compared to the previous year, as of ict. 31.
the taliban’s ban on women working for NGOs and UN agencies in the country means assistance will not reach all targeted women and girls. as UN women survey of humanitarian partners released on feb. 8, 2023 showed that 93% of organizations saw an increased impact on their access to affected women.
decades of conflict and severe drought contributed to afghanistan’s humanitarian crisis, but economic shocks are a primary driver of the deteriorating situation.
according to the 2023 afghanistan HNO, “afghanistan’s economic crisis is widespread, with more than half of households experiencing an economic shock in the last six months.”
a study by the United Nations Development Programme in April 2023 found that “afghanistan’s economic output collapsed by 20.7 percent following the taliban takeover in 2021.” the study also says, “the edicts restricting the rights of women and girls, including a directive banning afghan women from working for the UN, directly affect economic productivity and may also impact the level of aid inflows.”
when the taliban assumed power in august 2021, the country faced daunting economic and development challenges, and recent political developments have pushed the country into an economic crisis.
according to the world bank, “rapiid reduction in international grant support, loss of access to offshore assets, and disruption to financial linkages are expected to lead to a major contraction of the economy, increasing poverty, and macroeconomic instability.”
before august 2021, afghanistan’s economy was 75% dependent on foreign assistance. after the taliban assumed power, most international assistance was cut off, which caused a drop in purchasing power. the U.S. renewed the blocking of afghanistan’s central bank’s foreign assets amounting to over $7 billion (Executive Order no. 14064). in april 2022, United Nations (UN) experts called on the U.S. government to unblock foreign assets to ease the humanitarian impact.
in august 2022, 32 afghan and international NGOs called for a clear roadmap to restore the afghan central bank’s essential functions and release afghanistan’s assets frozen abroad. however, western countries have not been ready to lift sanctions until the taliban sets up a more diverse government, permits girls to return to secondary school and allows independent control of the afghan central bank.
a significant development occurred in september 2022 when the U.S. said it will transfer $3.5 billion in afghan central bank assets into a new swiss-based trust fund to be used “for the benefit of the people of afghanistan.” the new trust fund was created after months of talks between the U.S., switzerland, other parties and the taliban. no funds will go to the afghan central bank. the unfreezing of afghan assets has been called for by humanitarians.
however, the mandate of the afghan fund does not include support for humanitarian assistance. in their january 2023 snapshot report of the afghan economy, ACAPS said the key functions of the fund include price and exchange rate stability, payment of world bank arrears, representing the Afghan Central Bank (DAB) in court, payment for some critical imports, assessment of the capacity of the DAB, and support to the third-party monitoring of DAB’s anti-money laundering and counterterrorism financing systems.
more than one million people were estimated to be without work in august 2022. an FAO household survey released in may 2022 found that 26% of respondents lost employment. severe cash shortages continue to limit economic activity within banks and local markets. another alarming statistic is that people's debts have increased both in terms of the number of people taking on debt (82% of all households) and the amount of debt (about 11% higher than the previous year).
in august 2022, dr. ramiz alakbarov, then the UN Deputy Special Representative in afghanistan, who is also the resident and humanitarian coordinator in the country, said, “without functional markets, without (an) operating banking sector, without investments in basic-level jobs, we will not be able to reverse the trends which we are observing now in afghanistan.”
HOW TO HELP
visit [ irusa.org ] and [ savethechildren.org /afghanistan ]
10. VENEZUELA
venezuela is engulfed in a political and economic crisis which has led to more than seven million people leaving the country since 2015.
since 1999, venezuela has been run by two men from the same party. hugo chávez was president from 1999 to his death in 2013 and was succeeded by his right-hand man, nicolás maduro.
their socialist PSUV party has over the past two decades gained control of key institutions, including much of the judiciary, the electoral council and the supreme court.
as a result, the role of the president has become much more powerful and the system of checks and balances has been severely weakened.
not long after mr maduro was elected, global oil prices plummeted and venezuela - which relies almost entirely on oil revenue for its income - went into a seven-year recession.
inflation skyrocketed and shortages of basic goods became widespread.
waves of anti-government protests in 2014 and 2017 fizzled out after a police crackdown.
millions of venezuelans left the country to escape economic hardship and political repression. But despite growing discontent, mr maduro was re-elected in 2018 in a presidential election widely dismissed as neither free nor fair.
with the executive and the judiciary under the control of the PSUV, venezuela's divided opposition in january 2019 united behind the only major institution where they were still influential: the National Assembly and its speaker, juan guaidó.
arguing that mr maduro's re-election was not valid and the presidency was therefore vacant, mr guaidó, with the backing of the National Assembly, declared himself "interim president".
he predicted he would be governing from the presidential palace "within months".
and while more than 50 countries, including the US and the UK, recognised mr guaidó as venezuela's legitimate leader, venezuela's military stayed loyal to mr maduro.
mr maduro, with the continued support of china and russia, remained firmly in charge of the country.
but tightened US sanctions made it harder for the maduro government to sell oil and restricted its access to foreign currency.
wiith the economy in freefall, mr maduro in 2019 relaxed some of the strict foreign currency regulations brought in by chávez.
shortages eased as a result and in 2021, the economy started growing. But extreme poverty remains shockingly high and many of those without access to foreign currency continue to struggle.
disillusioned with the failure of juan guaidó to seize control of anything more than some venezuelan embassies and assets abroad, the majority of opposition parties withdrew their support from him in december 2022 and dissolved his "interim government".
they said that their aim remained to defeat mraduro, but argued that mr guaidó's rival government was no longer the way to go about it.
negotiations between opposition and government representatives - which have stalled on several occasions in the past - resumed in november 2022.
the opposition hopes they will lead to free and fair presidential elections being held in 2024, for which they plan to field a unity candidate to take on mr maduro.
HOW TO HELP
visit [ globalgiving.org / venezuela ] and [ donate.worldvision.org / venezuela relief fund ]
11. HAITI
the country has been in a state of electoral and constitutional turmoil since the assassination of the president, jovenel moïse, in 2021 at the hands of colombian mercenaries with unknown paymasters, but the immediate crisis can be traced back further.
haiti has not held functional elections since 2019 – and the country has been in a fragile state since the 2010 earthquake that killed up to 300,000 people. but moïse’s death in July 2021 – and a new earthquake the following month – sent the situation spiralling out of control.
moïse was replaced by an acting president, ariel henry, who is unelected and widely viewed as illegitimate. in september, the G9 gang coalition blockaded the main port and fuel terminal after henry caused fuel prices to double when he announced a cut to fuel subsidies – a development that brought the crisis to new heights. haiti is now experiencing its worst-ever famine, with 4.7 million people facing acute hunger.
at the same time it is impossible to understand the current situation without acknowledging the dark history of international interventions, including US occupation from 1915-1934, that have blighted haiti. “those interventions have shaped haiti,” smith said. “there’s a chain-link connection.”
long before the litany of recent disasters, he said, “the duvalier dictatorship [the rule of father and son françois, or “papa doc”, and jean-claude, or “baby doc”, duvalier from 1957-1986] destroyed the hopes of a functioning state that serves the nation."
gangs have a longstanding role in political life, and have operated in tandem with political actors since the 1950s to intimidate rivals and deliver votes. there are suggestions of oligarchic figures with ties to the drugs trade pulling the strings – but “many of them are not affiliated to anybody”, smith said.
“the international drug trade is a very important part of it, but that was only the beginning. now gangs have secured their power locally, it is very hard to see that any more powerful actor can control them. the situation has dissolved into the incomprehensible.”
there are almost 100 gangs in port-au-prince, many of them in loose alliances at war with rival groups. gangs control major roads and draw income from customs, water and electricity distribution, and even bus services. membership has become so desirable for some young men that some gangs now have waiting lists for new recruits (pdf).
the country’s army – disbanded in 1995 after years of military interference in politics – has been reestablished but stands at just 500 soldiers, while police also appear impotent.
the ongoing violence has forced the closure of hospitals and has been blamed in part for the re-emergence of cholera, as well as fuel shortages that only worsen the crisis. last month, the UN estimated 155,000 people had fled their homes – almost one in six of the city’s population.
HOW TO HELP
visit [ savethechildren.org/ haiti ]
12. ETHIOPIA
between 2020 and 2022, ethiopia fought a war with militants from its northernmost region of tigray, then under the control of the tigrayan people’s liberation front (TPLF). the conflict was one of the deadliest in recent world history and drew international attention for a preponderance of alleged war crimes, human rights abuses, and ethnic cleansing in tigray. the war formally ended in november 2022; tigray was left in ruins, and its capital was turned over to the federal government.
for decades before the war, the TPLF was a dominant political force in ethiopia. between 1991 and his death in 2012, tigrayan soldier-politician meles zenawi governed ethiopia as an autocracy with the backing of a TPLF-dominated coalition. the zenawi regime oversaw rapid development and increased the international prominence of ethiopia, but his government marginalized ethnic groups, including the oromo and amhara, to solidify government power. additionally, ethiopia was at war with eritrea [PDF] from 1998 to 2000. the war was followed by a nearly twenty-year-long frozen conflict, effectively paralyzing both countries politically and economically.
the TPLF continued to govern ethiopia after zenawi’s passing until 2018, when protests, especially among the oromo population, prompted the government to appoint abiy ahmed ali as the next prime minister. abiy, born in oromia, was heralded by international actors and ethiopians alike as the country’s new hope for peace and ethnic harmony. abiy promised early in his premiership to heal broken trust between the country’s ethnic groups and began to roll back restrictions on certain political freedoms. in 2019, he received the nobel peace prize for negotiating an end to ethiopia’s two-decade standoff with eritrea.
by 2020, ethnic relations within ethiopia once again began to deteriorate. multiple delays of long-promised national elections and the declaration of an extension on abiy ahmed’s first term as prime minister in june 2020 drew indignation from the TPLF. the tigray state council’s choice to hold local elections in defiance of federal orders further inflamed tensions. the elections ultimately solidified the TPLF’s control of the region. on november 4, 2020, abiy accused tigrayan troops of attacking a federal military camp in the tigrayan capital of mekelle and ordered ethiopian national defense Force (ENDF) troops north. this began a military operation known as the mekelle offensive, which escalated quickly as the ENDF pushed further into tigray, and the tigray defense force, or TDF, ramped up their response.
abiy first framed the offensive as a targeted operation against TPLF leadership. a communications blackout implemented at the outset of the conflict shuttered coverage of ground conditions, but media and UN officials began sounding the alarm about improper treatment of civilians, especially ethnic tigrayans, by december 2020. ethiopia’s neighbor and former adversary, eritrea, intervened in the conflict militarily on the side of the ethiopian government. after months of denying their presence, in spring 2021, prime minister abiy ahmed admitted that eritrean troops were fighting in tigray.
in 2021, the United States characterized the war as an ethnic cleansing against tigrayans, and some NGOs raised concerns about the potential of genocide. in march 2021, the office of the UN high commissioner for human rights announced a joint probe with the ethiopian human rights commission (EHRC) to investigate alleged abuses and rights violations in tigray, although the impartiality and accuracy of the report [PDF] were called into question following its presentation at the United Nations.
tigrayan forces retook the regional capital of mekelle from the ENDF in june 2021. a month later, addis ababa announced the results of a national parliamentary election—which prime minister abiy ahmed won in a landslide. the TPLF boycotted the election, and opposition leadership in parliament accused the abiy government of banning poll observers in some states. later in the summer of 2021, abiy called on all capable citizens to join the war against tigrayan forces as the conflict began to spill over into the afar and amhara regions, growing closer to addis ababa. in november 2021, tigrayan troops and allied oromo militants marched within eighty-five miles of the capital but were forced back north by ENDF forces.
after a series of failed efforts to negotiate a settlement, the TPLF and the Ethiopian central government signed a cessation of hostilities agreement on november 2, 2022, in pretoria, south africa. followed by implementation negotiations in nairobi, the agreement promised to disarm tigrayan troops, hand control of tigray to the ethiopian government, end the mekelle offensive, and permit full humanitarian access to tigray.
notably, the pretoria agreement does not explicitly mention eritrea, nor were eritrean representatives present at the negotiations. this omission raised international concern that eritrean troops would continue operations within ethiopia in spite of the agreement between the ethiopian government and TPLF. as of january 2023, displaced tigrayans reported that amhara and eritrean soldiers continued to occupy western tigray. the amhara have contested ownership of the area; the displaced population was informed in late 2023 that they would be returned to their land, and the political fate of the territory would be decided in a referendum.
in 2021 alone, 5.1 million ethiopians became internally displaced, a record for the most people internally displaced in any country in any single year at the time. thousands also fled to sudan and other countries in the region. by the time the pretoria agreement took effect, the tigray war and its associated humanitarian disaster had killed approximately 600,000 people. in late 2022, humanitarian groups were permitted to meaningfully operate in tigray for the first time since november 2020.
HOW TO HELP
visit [ savethechildren.org/ethiopia ] and [ irusa.org/ethiopia ]
13. SUDAN
the dramatic evacuation of international residents from sudan has been a top media headline in recent days, as military conflict spreads across the country. violence in and around the capital of khartoum has forced Concern, along with other NGOs, to suspend activities and evacuate non-national staff.
“this conflict couldn’t have come at a worse time for the people of sudan, who were already suffering terribly,” explains dominic macsorley, humanitarian ambassador for concern US. “the country is just facing into the ‘lean’ season — that time when the remainder of last year’s harvest is gone and this year’s crops have not yet matured. the fact that most humanitarian supports have been suspended and conflict is restricting movement leaves many people in a truly horrific situation.”
violence in sudan has been a fact of life for years
many people last followed sudan in the headlines back in 2019, when months of civilian protest led to a transitional government. since then, however, slowed progress on this front has left room for uncertainty and violence. (similar circumstances have fuelled the crisis in neighboring south sudan for more than a decade.) according to UNOCHA, an estimated 300,000 people were displaced by conflict in 2022 — with nearly 33,000 displaced in november alone due to fighting in west kordofan and central darfur.
at the beginning of this year, concern listed sudan as one of the world’s “forgotten” humanitarian crises due to this fragile balance of security and instability. unfortunately, it is once again front-page news due to the crisis escalating out of the spotlight.
one out of every three sudanese requires humanitarian aid
the protracted nature of the situation in sudan has led to dramatic increases in humanitarian aid. as of december 2022, 15.8 million sudanese required humanitarian assistance, approximately one out of every three people in the country. this represents a 10% increase in humanitarian need compared to december 2021.
those numbers are expected to rise dramatically after the last two weeks. as of earlier this week, over 22,000 civilians have fled the country—many to neighboring chad, as well as nearly 3,000 to south sudan. as peter van der auweraert, the south sudan representative for the UN’s international organization for migration, told the new york times earlier this week: “The people that get out first are the people that have the means,” indicating that thousands more will likely be stuck in the country with increasing needs.
this new wave of violence will affect the global refugee crisis in more ways than one
sudan is both one of the largest host countries for refugees (1.11 million as of january 2023), and one of the largest countries of origin for refugees (844,000 as of january 2023). in the first two weeks of fighting, more than 20,000 sudanese have crossed the border into Clchad, with the UNHCR estimating an additional 100,000 could follow in the coming days.
the knock-on effects go beyond sudanese refugees. many of the foreign refugees (especially from ethiopia, syria, and eritrea) currently in sudan are also in areas affected by fighting. with fewer resources than locals, they will face additional challenges in moving around or outside of the country (much in the same way that refugees living in ukraine dealt with additional challenges in moving to safety). these large displacements will also create additional pressure on host communities in countries like chad and south sudan, where resources are already tight. psychological support will also be a key necessity for those who have been forced to flee.
“day and night the fighting went on — to save their lives people moved and left everything behind,” says concern sudan country director, AKM musha, who like many of concern’s in-country staff was advised to leave khartoum for his own safety. “the journey to escape was very difficult…a very frightening and horrible experience.”
for those remaining in sudan, there is a catastrophic combination of challenges beyond violence
as ranked in the 2022 global hunger index, sudan is the 15th hungriest country in the world. food insecurity and malnutrition have run high in the country for decades due to the combined impacts of conflict, drought, locusts, and disease. the conflict in ukraine and COVID-19-related impacts have contributed to inflation rates in excess of 400%. “hospitals are not working, people cannot buy food, water is in short supply — everything has been eroded,” says musha.
carol morgan, concern’s director of international programs, adds that healthcare will be a key issue for the people of sudan. “THere are only enough health personnel to cover about 17% of the population,” she explains. With the added pressures of conflict, this could seriously affect ongoing health concerns in the country, such as diarrhea — an issue responsible for one out of every ten child mortalities.
humanitarian assistance is not guaranteed
while humanitarian organizations both international and local are designed to help in times of crisis, the safety of staff is the number-one priority. the focus of violence in khartoum has led to concern evacuating its 10 non-sudanese staff members from the country. over 150 local staff members are either internally displaced or sheltering at home with challenges like rolling blackouts the rule versus the exception.
this means that not everyone who requires humanitarian assistance at this time will be able to get the help they need. concern had been working with the ministry of health in 73 health facilities and last year treated over 200,000 children for malnutrition. in total, the sudan team had planned to reach over 500,000 people through a variety of humanitarian programs in 2023, vital work which has now been put on hold.
concern has called for an immediate end to hostilities in sudan, as well as for protections to be put in place to allow aid workers to provide essential community support. “we need the fighting to stop and humanitarian access to be restored or else sudan is facing a really disastrous situation,” says musha.
HOW TO HELP
visit [ savethechildren.org/sudan ] and [ irusa.org/sudan ]
14. SOMALIA
during a year that marked the 30th anniversary of the collapse of the somali state, domestic and international attention was focused on plans for the delayed parliamentary and presidential electoral process. political tensions stalled reform efforts key to advancing human rights in the country, while conflict-related abuses, insecurity, and humanitarian and health crises took a heavy toll on civilians.
all parties to the conflict in somalia committed violations of international humanitarian law, some amounting to war crimes. the islamist armed group al-shabab conducted indiscriminate and targeted attacks on civilians and forcibly recruited children. Inter-clan and intra-security force violence killed, injured, and displaced civilians, as did sporadic military operations against al-shabab by somali government forces, troops from the african union mission in somalia (AMISOM), and other foreign forces.
Federal and regional authorities continued to intimidate, attack, arbitrarily arrest, and at times prosecute journalists, including by using the country’s outdated penal code. Somalia continued to rely on military court proceedings that violated international fair trial standards; it did not hand over Al-Shabab cases from military to civilian courts.
key legal and institutional reforms stagnated. the review of the country’s outdated penal code stopped; there was no movement on the passing of federal legislation on sexual offenses or on key child’s rights legislation. the government also failed to establish a national human rights commission; the appointment of commissioners has been pending since 2018.
allegations that somali soldiers were trained in eritrea and deployed in ethiopia’s tigray conflict added to the political tensions. the disappearance of the former intelligence official, ikran Tahlil farah, reportedly missing since late june, led to a standoff between president mohammed abdullahi “farmajo” and prime minister mohamed hussein roble, including over the control of the country’s powerful national intelligence and security agency (NISA).
attacks on civilians
the united nations assistance mission in somalia (UNSOM) recorded at least 899 civilian casualties, including 441 killings, between late november 2020 and late july; a marked increase compared to the same reporting period the previous year. most were killed during targeted and indiscriminate al-shabab attacks using improvised explosive devices (IEDs), suicide bombings, and shelling, as well as assassinations.
after the parliament extended the presidential term on april 25 by two years, armed confrontations between security forces linked to different political factions in various districts of mogadishu, the capital, resulted in the displacement of between 60,000 and 100,000 people, according to the United Nations.
federal and regional military courts continued to sentence people to death and carry out executions despite serious due process concerns. puntland executed 21 men convicted by military courts of al-shabab membership and killings on june 27, in three separate locations.
al-shabab fighters killed dozens of individuals it accused of working or spying for the government and foreign forces, often after unfair trials.
the UN attributed six civilian casualties to AMISOM forces between late 2020 and late july. AMISOM established a board of inquiry into an August 10 incident involving ugandan soldiers who were ambushed by al-shabab fighters around golweyn, lower shabelle and responded by killing seven civilians. a ugandan court martial found five soldiers responsible for the killings, sentencing two to death. reports of civilian harm as a result of airstrikes in the gedo region increased.
despite federal and regional investigations into the may 2020 massacre of seven health workers and a pharmacist in the village of gololey in balcad district, the outcome of these investigations remains unknown.
sexual violence
the UN reported an increase in incidents of sexual and gender-based violence, including of girls, which often resulted in the victims being killed.
key legal reforms stalled, notably the passing of progressive sexual violence legislation at the federal level. the somali criminal code classifies sexual violence as an “offense against modesty and sexual honor” rather than a violation of bodily integrity; it also punishes same-sex relations. article 4(1) of the provisional constitution (2012), places sharia law above the constitution and it continues to be applied by courts in criminal cases. consequently, the death penalty for consensual same-sex conduct could be enforced.
in puntland, the first region to pass a sexual offenses law, the UN reported on government interference and blocking of investigations into sexual violence incidents.
abuses against Children
children continue to bear a heavy burden of ongoing insecurity, conflict, and lack of key reforms in the country. all Somali parties to the conflict committed serious abuses against children, including killings, maiming, recruitment and use of child soldiers, and attacks on schools.
somali federal and regional security forces unlawfully detained children, notably for alleged ties with armed groups, undermining government commitments to treat children primarily as victims. the government failed to put in place child rights compliant justice measures.
the previous year, pending legal reforms sought to reduce the age of marriage, including a controversial draft law on sexual-intercourse related crimes—the status of which remained unknown—which would allow a child to marry at puberty regardless of their age.
when the covid-19 pandemic started in early 2020, schools were closed or partially closed for 134 days, including several weeks in march and april 2021, affecting at least 1.2 million children.
freedom of expression and association
federal and regional authorities throughout somalia repeatedly harassed, arbitrarily arrested, and attacked journalists. moments of heightened tensions around the electoral process correlated with an uptick in incidents of harassment toward journalists.
the UN and amnesty international reported an increase during the first quarter of the year in restrictions on journalist in puntland. in march, the military appeals court in puntland sentenced kilwe adan farah, a journalist, to three years in prison under the outdated penal code for his coverage of anti-government protests. earlier, a military court sentenced him to three months, despite the judge reportedly acknowledging a lack of evidence. the journalist received a presidential pardon.
several journalists covering protests in mogadishu were temporarily detained and harassed. on september 5, bashiir mohamud, producer at goobjoog media, was filmed being dragged through the streets by somali police while he covered protests demanding justice for the killing of a former intelligence officer, ikran tahlil farah. he was then held for a few hours at the hodan police station.
al-shabab claimed responsibility for the march 1 killing of journalist jamal farah adan in galkayo.
displacement and access to humanitarian assistance
over 2.6 million somalis are internally displaced, increasingly because of conflict. the UN said over 570,000 people were displaced between january and august 2021. droughts, flooding, and desert locust swarm—increasing in intensity and frequency due to climate change—exacerbated communities’ existing vulnerabilities and contributed to displacement. the UN and Norwegian Refugee Council (NRC) reported that between january and august, droughts and floods displaced over 90,000 and 49,000 people respectively. tens of thousands of internally displaced people were forcibly evicted, notably in mogadishu.
nearly 3.5 million people were expected to face acute food insecurity and need emergency food aid in the last quarter of the year.
humanitarian agencies continued to face serious access challenges due to conflict, targeted attacks on aid workers, generalized violence, restrictions imposed by parties to the conflict, including arbitrary “taxation” and bureaucratic hurdles, and physical constraints due to extreme weather. al-shabab continued to impose blockades on some government-controlled towns, notably the town of hudur, and occasionally attacked civilians who broke them.
an Amnesty International report documented somalia’s inadequate response to the Covid-19 pandemic, and highlighted the chronic underfunding of the country’s health system.
HOW TO HELP
visit [ rescue.org/ somalia ], [savethechildren.org/somalia ] and [ irusa.org/somalia ]
15. BURKINA FASO
the world’s fastest-growing humanitarian crisis is currently unfolding in burkina faso.
nearly 2 million people need shelter after being forced to flee their homes due to extremist violence.
burkina faso is under threat from extremist attack in the sahel, a belt of semi-arid land south of the sahara desert.
less than ten years ago, burkina faso seemed like a beacon of stability in west africa. in 2015 the country held its first democratic election ever, paving the way to what seemed like a bright future.
but since then burkina faso has seen an increase in violence from jihadist groups, spreading from mali. armed groups quickly started expanding, crossing borders and setting up local groups across the sahel region – including burkina faso, mali and niger.
since 2019, insecurity has reached devastating levels and the number of burkinabe people fleeing violence has skyrocketed.
right now, burkina faso is one of the fastest-growing displacement crises in the continent.
according to the UN, more than one in every 20 people are forced to flee the violence.
burkina faso is a landlocked country situated in west africa.
the country is surrounded by mali to the north and west, niger to the northeast, benin to the southeast, and côte d’Ivoire, ghana, and togo to the south.
its capital, ouagadougou, saw a horrific terrorist attack at the beginning of 2016 which left 28 people dead, and 56 people injured.
the central sahel region, which includes the countries of burkina faso, mali and niger, is facing one of the fastest-growing displacement crises in the world.
yet, it is one of the most forgotten.
it is estimated that over 3 million people have been forced to flee their homes and at least 29 million are in desperate need of humanitarian assistance.
the sahel region of africa is a 3,860-kilometre arc-like land mass lying to the immediate south of the sahara desert and stretching from east to west across the breadth of the african continent.
families started fleeing the central sahel region in 2011, after a violence outbreak in northern mali.
increased displacement was reinforced by poverty, food insecurity, unemployment and the presence of armed groups. climate change is also a challenge for families trying to flee.
HOW TO HELP
visit [ savethechildren.org/burkina faso ] or [ friendsofburkinafaso.org ]
16. JAMMU AND KASHMIR
as the sun rises over the picturesque landscape of kashmir, it’s easy to believe that all is well in the region. but beneath the scenic beauty is a harsh and unsettling reality — composed of a military occupation, oppression of the entire population and expression of fear, loathing and anger by the people of kashmir. the picture that the Indian government tries to paint — of normalcy and development in occupied jammu and kashmir — is a myth.
for the last seven decades, kashmir has been the epicenter of a bitter dispute between india and pakistan in which the people in jammu are an integral party. to resolve the conflict, the united nations security council adopted resolution 47 in 1948, and more than a dozen subsequent resolutions, stipulating that the final disposition of the state of jammu and kashmir would be decided by its people through a free and impartial plebiscite conducted under the auspices of the UN. this was accepted by india and pakistan and, in accordance with article 25 of the UN charter, both parties are obligated to implement these resolutions.
but this saturday, aug. 5, marks four years of india’s unilateral actions to consolidate its occupation of illegally indian occupied jammu and kashmir (IIOJK) and imposing what India’s leaders have ominously called a “final solution” for kashmir. to do so, india has resorted to a series of illegal actions, gross and consistent violations of human rights and other crimes that continue to this day.
india increased its military deployment in IIOJK to 900,000 troops right before aug. 5, 2019. this is the densest occupation in recent history — with one soldier for every eight kashmiri men, women and children. this massive force has perpetrated a vicious campaign of repressive actions, including extrajudicial killings of innocent kashmiris in fake encounters; custodial killings and “cordon-and-search” operations; use of pellet guns to kill, maim and blind peaceful protestors; abduction and enforced disappearances; and “collective punishments,” with the destruction and burning of entire villages and urban neighborhoods.
this brutal campaign is driven by the ideology of “hindutva,” which propagates the religious and ethnic supremacy of hindus and hate against muslims. noting this pattern, genocide watch has warned that “the indian government’s actions in kashmir have been an extreme case of persecution and could very well lead to genocide.”
to suppress the voice of the kashmiri people, indian authorities have used censorship and surveillance for decades in the occupied territory. since august 2019, information control has been fully institutionalized. journalists, lawyers, human rights defenders and the entire kashmiri political leadership are routinely incarcerated, beaten, humiliated, harassed and even accused of “terrorism” for reporting the human rights violations in IIOJK.
there is only one normality: the normalization of violence. generations have grown up witnessing violence, insecurity and trauma. numerous human rights organizations, international bodies and independent reports have documented use of rape, sexual assault and harassment perpetrated by Indian security forces against kashmiri civilians, particularly women as a weapon of war. emergency laws, such as the 1990-armed forces (special powers), have created an environment of complete impunity for indian security forces.
to extinguish the ethno-religious identity of kashmiris, historical sites have been destroyed and damaged. one of the most troubling aspects of the destruction of cultural heritage is the demolition of religious sites, particularly mosques, which inflicts deep emotional wounds on the muslim population.
in a classic settler-colonial project, india has initiated illegal demographic changes in the occupied territory, grossly violating international law, including the fourth geneva convention. this is central to its plan to convert IIOJK’s muslim majority into a hindu majority territory, to drown out the demand for freedom and self-determination. new “domicile rules” have been introduced, and more than four million fake domicile certificates have been issued to hindus from across india to settle in occupied jammu and kashmir. the land and properties of kashmiris are also being confiscated for military and other official use.
all the measures taken by India in the last four years are blatant violations of international law, including the relevant security council resolutions, specifically resolution 122 (1957). therefore, all the actions taken by India on and after aug. 5, 2019 are not only illegal but, ipso facto, null and void.
to justify its occupation and oppression, india has sought for decades, and particularly since 9/11, to portray the kashmiri freedom struggle as “terrorism.” likewise, to delegitimize the indigenous kashmiri struggle for self-determination, india falsely alleges that it is instigated by pakistan. to expose india’s falsehood, pakistan has proposed expanded patrolling by the UN military observer group in india and pakistan (UNMOGIP) along the line of control in jammu and kashmir. however, india refuses to allow the UN mission to patrol the line of control and to expand it. despite numerous attempts, india continues to deny access to jammu and kashmir to the office of high commissioner for human rights and other UN agencies as well as other human rights and humanitarian organizations and international media.
pakistan desires peaceful relations with all its neighbors, including india. pakistan has responded with responsibility and restraint to india’s repeated provocations. on the other hand, india continues to resort to aggressive rhetoric and repeated threats of the use of force against pakistan, even under the nuclear overhang. the onus is on india to create conditions that are conducive for a meaningful dialogue to resolve the jammu and kashmir dispute. to this end, india must:
• stop all human rights violations in jammu and kashmir
• halt and reverse its illegal demographic changes there
• reverse the illegal and unilateral measures imposed on and after aug. 5, 2019
• grant access to international observers, including human rights mechanisms of the UN and international media, to observe worsening human rights situation on the ground
the international community must play a proactive role obliging india to respect the human rights of the people of kashmir and to work toward a peaceful, inclusive resolution of the conflict. peace in south asia will be possible only when the jammu and kashmir dispute is resolved. the security council and the UN secretary-general must make concerted efforts, as empowered by the UN charter, to promote a peaceful settlement of the jammu and kashmir dispute, according to the relevant UN security council resolutions and wishes of the kashmiri people.
preventive measures to stop abuses in IIOJK and to promote global accountability is both a moral imperative and a collective human rights responsibility. millions of kashmiris have suffered for too long. to end their plight, they demand a peaceful resolution to the conflict. it is time to make peace a new normal.
HOW TO HELP
visit [ pennyappeal.org/ kashmir ] and [ standwithkashmir.org ]
17. UYGHUR CRISIS
the chinese government has reportedly arbitrarily detained more than a million muslims in reeducation camps since 2017. most of the people who have been detained are uyghur, a predominantly turkic-speaking ethnic group primarily in china’s northwestern region of xinjiang. beyond the detentions, yyghurs in the region have been subjected to intense surveillance, forced labor, and involuntary sterilizations, among other rights abuses.
the united states and several other foreign governments have described china’s actions in xinjiang as genocide, while the UN human rights office said that the violations could constitute crimes against humanity. chinese officials have said that they have not infringed on uyghurs’ rights and claimed that they closed the reeducation camps in 2019. however, international journalists and researchers have documented an ongoing system of mass detention throughout the region using satellite images, individual testimonies, and leaked chinese government documents.
when did mass detentions of muslims start?
an estimated eight hundred thousand to two million uyghurs and other muslims, including ethnic kazakhs and uzbeks, have been detained since 2017, according to international researchers and U.S. government officials [PDF]. the chinese government calls the facilities “vocational education and training centers;” the most common terms used by international media organizations and researchers are reeducation camps, internment camps, and detention camps. some activists describe them as concentration camps.
outside of the camps, the eleven million uyghurs living in xinjiang—officially called the xinjiang uyghur autonomous region—have continued to suffer from a decades-long crackdown by chinese authorities.
experts estimate that reeducation efforts started in xinjiang in 2014 and were drastically expanded in 2017. beginning that year, they documented the construction of new reeducation camps and expansion of existing facilities for mass detention. reuters journalists, observing satellite imagery, found that thirty-nine of the camps almost tripled in size between april 2017 and august 2018; they covered a total area roughly the size of 140 soccer fields. similarly, analyzing local and national budgets over the past few years, germany-based xinjiang expert adrian zenz found that construction spending on security-related facilities in xinjiang increased by 20 billion yuan (around $2.96 billion) in 2017.
in late 2019, xinjiang’s governor said that people detained in the reeducation camps had “graduated.” journalists found that several camps were indeed closed. but the following year, researchers at the australian strategic policy institute (ASPI) identified [PDF] more than 380 suspected detention facilities using satellite images. they found that china refashioned some lower-security reeducation camps into formal detention centers or prisons; expanded existing detention centers; and constructed new, high-security detention centers throughout xinjiang. (chinese officials have said that ASPI is an anti-china tool funded by australia and the united states.) instead of detaining people in reeducation camps, authorities have increasingly used the formal justice system to imprison people for years. In 2022, human rights watch reported that half a million people had been prosecuted since 2017, according to xinjiang government figures. the associated press found that in one county, an estimated one in twenty-five people had been sentenced to prison on terrorism-related charges, all of them uyghurs.
what has happened in the reeducation camps?
most people detained in the reeducation camps were never charged with crimes and had no legal avenues to challenge their detentions. the detainees seem to have been targeted for a variety of reasons, according to media reports, including traveling to or contacting people from any of the twenty-six countries china considers sensitive, such as turkey and afghanistan; attending services at mosques; having more than three children; and sending texts containing Quranic verses. often, their only crime is being muslim, human rights groups say, adding that many uyghurs have been labeled as extremists simply for practicing their religion.
information on what happened in the camps remains limited, but many detainees who have since fled china described harsh conditions. the UN human rights office released a report [PDF] in 2022 based on interviews with dozens of people, including twenty-six individuals who were detained, that found “patterns of torture or other forms of cruel, inhuman, or degrading treatment” in the camps between 2017 and 2019.
the UN report affirmed previous findings by international journalists, researchers, and rights organizations. various exposés showed that detainees were forced to pledge loyalty to the CCP and renounce Islam, as well as sing praises for communism and learn mandarin. some people reported prison-like conditions, with cameras and microphones monitoring their every move and utterance. others said they were tortured and subjected to sleep deprivation during interrogations. Women have shared stories of sexual abuse, including rape.
some released detainees contemplated suicide or witnessed others kill themselves.
detention also disrupted families. children whose parents were sent to the camps were often forced to stay in state-run orphanages. many uyghur parents living outside of china faced a difficult choice: return home to be with their children and risk detention, or stay abroad, separated from their children and unable to contact them.
what do chinese officials say about the camps?
government officials first denied the camps’ existence. by late 2018, they started acknowledging that there were “vocational education and training centers” in xinjiang. they publicly stated that the camps had two purposes: to teach mandarin, chinese laws, and vocational skills, and to prevent citizens from becoming influenced by extremist ideas, to “nip terrorist activities in the bud,” according to a government report. pointing out that xinjiang has not experienced a terrorist attack since december 2016, officials claimed the camps have prevented violence.
as global condemnation of the abuses has grown, chinese officials and state media have worked to discredit reports on xinjiang using a range of tactics, including disseminating disinformation and harassing activists. they have repeated a narrative that “anti-china forces” in the united states and other western countries are spreading “vicious lies.” beijing tried to prevent the UN human rights office from releasing its report. after its release, chinese officials described it as false information and published a rebuttal describing how foreign governments and organizations “spread numerous rumors and lies” about xinjiang.
why is china targeting uyghurs in xinjiang?
chinese officials are concerned that uyghurs hold extremist and separatist ideas, and they viewed the camps as a way of eliminating threats to china’s territorial integrity, government, and population.
xinjiang has been claimed by china since the chinese communist party (CCP) took power in 1949. some uyghurs living there refer to the region as east turkestan and argue that it ought to be independent from china. xinjiang takes up one-sixth of china’s landmass and borders eight countries, including afghanistan, pakistan, and kazakhstan.
HOW TO HELP
visit [ uhrp.org ] and [ saveuighur.org ]
18. THE REPUBLIC OF CONGO
the democratic republic of congo (DRC) is a country rich in resources, yet fraught with conflict and violence. the country is currently experiencing the largest displacement crisis in africa.
many of its people have not seen peace in more than 20 years.
the democratic republic of congo (DRC) is host to one of the world’s most complex and long-standing humanitarian crises, centered particularly in the east of the country. More than 2.1 million people were forced to flee their homes in 2017 alone — equivalent to an average of 50 families fleeing every hour, every day.
there are currently more than 100 different armed groups vying for territory and control in eastern DRC. this conflict is causing massive displacement and urgent humanitarian needs as families flee their homes for safety.
the armed conflict and insecurity has displaced 4.5 million people within the country. 13.1 million people need humanitarian assistance — 5.6 million more than in 2017. over the last year with intensified fighting, the humanitarian situation has dramatically worsened.
the rise of ebola has made the situation even more dire.
yes, ebola is endemic to DRC. the country is currently battling its tenth ebola outbreak, which has already killed more than 1,500 people. it is now the worst ebola outbreak in DRC’s history. over 50 percent of the total cases have occurred in the past three months.
on july 17, the world health organization declared the ebola outbreak in DRC a "public health emergency of international concern" (PHEIC). previous PHEICs include swine flu in 2009, polio in 2014, ebola in 2014 and the zika virus in 2016.
“We hope that [this] declaration by the WHO will translate into urgent and practical action, including more funding from international donors,” said laura miller, mercy corps’ acting country director in DR Congo. “every day, women, men and children are dying of the ebola virus and it is becoming too easy to forget that the ever-climbing case numbers are people.”
this particular outbreak is happening in the densely populated and conflict-affected provinces of north kivu and ituri, making it more difficult and dangerous to access affected people and areas.
a previous ebola outbreak in 2018 affected 54 people and resulted in 33 deaths.
what is the kivu conflict?
the conflict in north and south kivu began in 1996 in eastern congo in the aftermath of the rwandan genocide. the conflict involves numerous armed actors, including the DRC military, foreign rebel groups such as the democratic forces for the liberation of rwanda and allied defence forces of uganda and more than 100 local armed groups. due to this ongoing fighting, DRC is currently home to the largest UN peacekeeping force in the world, consisting of 21,000 people.
is there still war in DRC?
not technically. but there is still ongoing conflict, insecurity and a lack of effective governance. there are now more than 100 armed groups vying for territory and control in eastern DRC. the current president, joseph kabila, has been in position since 2001 following the assassination of his father, laurent kabila. the presidential election in december 2018 has thrown the country into further turmoil. in its 58 years of independence from belgium, the DRC has never had a peaceful political transition.
how densely populated is the democratic republic of congo?
DRC is the size of western durope and the second-largest country in africa. its population of 80 million people is spread throughout the country, with 40 percent of people living in urban areas. cities in eastern congo, like goma and bukavu, have been experiencing an influx of people fleeing violence from the more rural areas. people are seeking safety and security, and new opportunities to earn an income, as the conflict has forced many of them off their land.
this escalating displacement, coupled with resource mismanagement, is putting increasing pressure on the cities’ services. to respond to these needs, we’ve developed an integrated water initiative to improve access to water for the most vulnerable citizens of goma and bukavu. it also aims to provide equitable access to water for all.
how wealthy is the democratic republic of congo?
the DRC has vast human and natural resources, which could, arguably, make it one of the richest countries in the world. this central african country is home to the world’s largest reserves of coltan, used in mobile phones and electric cars, as well as significant quantities of the world’s cobalt and copper, as well and diamonds, gold and many other minerals.
yet, because of the ongoing conflict, poor governance and a lack of infrastructure, the congolese people are not benefiting from this immense wealth. in fact, in 2019, DRC will become the country with the second highest number of people living below the poverty line.
who is affected by the conflict in DRC?
in the conflict-ridden eastern part of the country, women and children are often most affected by the conflict, as is the case with many crises. more than 2 million children suffer from severe acute malnutrition. one in 10 women and girls experienced sexual violence in 2016. in some cases, women and their children have no choice but to flee the violence and hunger. women often leave their homes with very little but their children and the clothes they were wearing. men too are frightened of being killed or forced to join armed groups.
HOW TO HELP
visit [ savethechildren.org/ democratic republic of congo ] and [ ngocongo.org ]
19. WEST PAPUA
ever since the invasion of west papua over fifty years ago, the Indonesian security forces have committed a never ending catalogue of extreme human rights violations.
over 500,000 civilians have been killed in a genocide against the indigenous population. thousands more have been raped, tortured, imprisoned or ‘disappeared’ after being detained. basic human rights such as freedom of speech are denied and papuans live in a constant state of fear and intimidation.
genocide
almost all papuans will be able to tell you stories of friends or family who have been murdered. a paper prepared by the yale law school for the indonesian human rights campaign in 2004 found “in the available evidence a strong indication that the indonesian government has committed genocide against the west papuans”.
the use of torture by the Indonesian security forces against the indigenous papuan population is widespread.
there is much documented evidence of this endemic behaviour and in recent years video footage (captured as ‘trophy footage’ by indonesian soldiers) has been leaked and broadcast on international news channels such as al jazeera and channel 4 news.
rape
sexual assault and rape has been repeatedly used as a weapon by the indonesian military and police.
in a public report to the U.N. commission on human rights in 1999, the special rapporteur on violence against women concluded that the indonesian security forces used rape “as an instrument of torture and intimidation” in west papua, and “torture of women detained by the indonesian security forces was widespread”.
the robert f. Kennedy memorial centre for human rights prepared a full report on “rape and other human rights abuses by the indonesian military in iran jaya (west papua), indonesia”.
freedom of expression
the basic rights to freedom of expression are almost completely denied in west papua. anyone expressing any criticism of indonesian rule and in particular aspirations for west papuan independence can expect to be persecuted by the police and imprisoned.
recently, leading human rights organizations kontraS papua and the commission for the disappeared and the victims of violence, published a report on the increasing tendency of the indonesian state to charge people peacefully expressing their desire for political independence with treason. they state:
'in 2010, cases with a political dimension have characteristically become ensnared by the charge of makar, the indonesian word for treason or rebellion… altogether in 2010, 32 people were charged or investigated in connection with article 106 on makar.’
political prisoners
yusak pakage, sentenced to 10 years in prison for attending a west papua flag raising ceremony.
there are currently hundreds of west papuan political prisoners being held in west papua and across indonesia. many are serving long prison terms for peacefully protesting against indonesian rule or for being members of organisations calling for west papuan independence.
filep karma is a particular case in point, serving a 15 year jail sentence simply for raising the west papuan national flag. he is an amnesty international prisoner of conscience. conditions in the prisons are often very poor and maltreatment of prisoners is common with many being beaten and tortured while detained. prisoners have often developed severe health problems and been denied access to medical care.
lives lived in fear
papuans return to find their homes in burnt to the ground by the Indonesian army following a ‘sweeping operation’
papuans return to find their homes in burnt to the ground by the indonesian army
many papuans live in a constant state of fear and intimidation. people living in villages across west papua can at any time be subject to military sweeping operations.
under the pretence of looking for insurgents, the military have repeatedly swept through entire rural areas killing arbitrarily and burning whole villages to the ground, destroying subsistence food crops and livestock and forcing people to flee into the forests where they are prone to starvation and disease.
impunity
imdonesian special army force (KOPASSUS) have committed widespread human rights abuses in west papua
despite public statements that the Indonesian government is improving its human rights record, the situation on the ground seems very different. there are often limited or no investigations into human rights abuses and if any discipline is handed out it is normally of little significance to the perpetrators of the abuses. amnesty international states:
“impunity for human rights violations is commonplace. accountability mechanisms to deal with police abuse remain weak, and reports of torture by members of the security forces often go unchecked and unpunished. many victims of past human rights violations in papua are still awaiting justice.”
access to journalists and NGOs
west papua is currently off limits to international journalists. if discovered without permission they are arrested and deported by the Indonesian authorities. some have even been attacked and imprisoned.
it is clear that Indonesian authorities will stop at nothing to keep the ongoing genocide they are directing in west papua out of the international media agenda. west papua has also become impossible to operate in for many NGOs. in 2010 the international red cross were expelled, and in 2012 peace brigades international were forced to leave. International human rights organisations such as amnesty and human rights watch are also denied access to west papua.
HOW TO HELP
visit [ freewestpapua.org ] and [ freepapuamovement.org ]
20. ARMENIA
azerbaijan launched "anti-terrorist activities" in the nagorno-karabakh region on tuesday, saying it wanted to restore constitutional order and drive out what it said were armenian troops, a move that could foreshadow a new war.
armenia and azerbaijan have already fought two wars over karabakh in the three decades since the soviet union they were both members of collapsed.
here is a look at the history of the conflict and the latest developments.
WHAT IS NAGORNO-KARABAKH?
nagorno-karabakh, known as artsakh by armenians, is a mountainous region at the southern end of the karabakh mountain range, within azerbaijan. it is internationally recognised as part of azerbaijan, but its 120,000 inhabitants are predominantly ethnic armenians. they have their own government which is close to armenia but not officially recognised by armenia or any other country.
armenians, who are christian, claim a long presence in the area, dating back to several centuries before christ. azerbaijan, whose inhabitants are mostly turkic muslims, also claims deep historical ties to the region, which over the centuries has come under the sway of persians, turks and russians. bloody conflict between the two peoples goes back more than a century.
under the soviet union, nagorno-karabakh became an autonomous region within the republic of azerbaijan.
FIRST KARABAKH WAR
as the soviet union crumbled, the first karabakh war (1988-1994) erupted between armenians and their azeri neighbours. about 30,000 people were killed and more than a million displaced. most of those were azeris driven from their homes when the armenian side ended up in control of nagorno-karabakh itself and swathes of seven surrounding districts.
44-DAY WAR IN 2020
in 2020, after decades of intermittent skirmishes, azerbaijan began a military operation that became the second karabakh war, swiftly breaking through armenian defences. it won a resounding victory in 44 days, taking back the seven districts and about a third of nagorno-karabakh itself.
the use of drones bought from turkey and israel was cited by military analysts as one of the main reasons for azerbaijan's victory. at least 6,500 people were killed.
russia, which has a defence treaty with armenia but also has good relations with azerbaijan, negotiated a ceasefire.
the deal provided for 1,960 russian peacekeepers to guard the territory's lifeline to armenia: the road through the "lachin corridor", which armenian forces no longer controlled.
PEACE TALKS
analysts say successive rounds of talks, mediated variously by the european union, the united states and russia, have brought the two sides closer to a permanent peace treaty than they have been for years, but a final settlement remains elusive. the most sensitive issue is the status of the 120,000 ethnic armenians in karabakh, whose rights and security armenia says must be guaranteed. prime minister nikol pashinyan has said armenia recognises the sovereignty and territorial integrity of azerbaijan, but baku says it is not certain the assertion was made in good faith and accuses armenia of fuelling separatism.
HUMANITARIAN CRISIS
in december 2022 azerbaijani civilians identifying themselves as environmental activists began blocking the lachin corridor, and in april 2023 azerbaijan set up an official checkpoint, saying it was preventing weapons smuggling. the flow of people and goods between armenia and nagorno-karabakh was largely cut off. the united states bemoaned the "rapidly deteriorating humanitarian situation".
this week, the international committee of the red cross (ICRC) was able to make simultaneous aid deliveries via the lachin corridor and a separate road linking karabakh to the azerbaijani city of aghdam.
despite that, tensions have risen sharply this month, with armenia and azerbaijan accusing each other of building up troops.
HOW TO HELP
visit [ armeniafund.org ]
#palestine#gaza#somalia#sudan#armenia#congo#west papua#lebanon#yemen#syria#tamil eelam#manipur#uyghurs#jammu and kashmir#burkina faso#ethiopia#haiti#venezuela#afghanistan#kurdistan#hawaii#rohingya
186 notes
·
View notes
Text
“Gender wars in 2024 is insane 😭🙏”
Ok here is list of other things that happened in 2024:
Asia
1. January 15 - Bangladesh: A woman was killed by her husband after requesting a divorce.
2. February 5 - India: A brutal attack in Uttar Pradesh left a woman mutilated.
3. March 23 - Pakistan: A woman was murdered by her husband in Punjab in a femicide case.
4. April 14 - Nepal: A woman was assaulted by her partner; her family reported prolonged abuse.
5. May 3 - Malaysia: A woman was beaten to death by her partner.
6. June 21 - China: A woman was severely injured in an attack at a restaurant in Tangshan.
7. August 9 - Philippines: Several women were sexually assaulted during a party.
8. September 28 - Kazakhstan: A woman was murdered by her ex-partner in a femicide case.
9. October 15 - Sri Lanka: A woman was murdered by her husband in Colombo.
Africa
1. January - South Africa: A woman was murdered by her partner, sparking protests in Pretoria.
2. January - Kenya: At least 10 women were murdered in femicide cases; protests erupted in Nairobi.
3. February - Malawi: A woman was killed by her partner after trying to leave him.
4. February - Tanzania: A women’s rights activist was attacked by her ex-partner.
5. March - Nigeria: A woman was found dead in Oyo, in a suspected femicide case.
6. March - South Africa: A young woman was murdered in a rural area, leading to protests.
7. April - Kenya: Over 500 femicides reported since 2016, sparking outrage.
8. May - South Sudan: A woman was raped and killed during an armed conflict.
9. June - Uganda: A woman was attacked and murdered by her partner in Kampala.
10. July - Ethiopia: A series of women were killed in rural areas, raising concerns of femicide.
Europe
1. February 12 - Spain: A 45-year-old woman was murdered by her partner in Barcelona.
2. March 4 - France: A femicide in Lyon where a woman was stabbed by her husband.
3. April 20 - Italy: A woman was killed in Rome by her ex-partner after reporting him.
4. June 7 - Germany: A femicide in Berlin where a woman was murdered by her husband.
5. July 29 - United Kingdom: A woman was murdered by her boyfriend in a prolonged abuse case.
6. August 15 - Poland: A woman was murdered in Warsaw by her partner in a femicide case.
7. September 10 - Spain: A young woman was found dead in Madrid after reporting domestic violence.
8. October 18 - France: A femicide in Marseille; the woman had previously reported abuse.
North America
1. January - United States: A woman was murdered in Texas by her partner, despite having a restraining order.
2. February - Canada: A femicide in Toronto, where a woman was murdered by her ex-boyfriend after trying to leave the relationship.
3. March - United States: A woman was killed by her husband in a Chicago suburb in a domestic violence case.
4. April - Canada: A femicide in Montreal, where a woman was attacked by her partner after reporting abuse.
5. May - United States: A femicide in California; a woman was murdered by her partner in front of her children.
6. June - Canada: A woman was murdered by her husband in Vancouver after years of abuse.
7. July - United States: A woman was murdered in New York by her partner in an attack caught on video.
8. August - Canada: A femicide in Alberta; a woman was found murdered in her home by her husband.
9. September - United States: A woman was killed by her partner in Florida, highlighting the ineffectiveness of protective laws.
10. October - Canada: A femicide in Ottawa; a woman was murdered after months of harassment by her ex-partner.
South America
1. January 14 - Argentina: A 24-year-old woman was killed by her ex-partner in Buenos Aires after months of harassment. The case sparked protests demanding stronger measures to protect women.
2. February 9 - Colombia: In Bogotá, a woman was murdered by her husband, who had a history of domestic abuse. The victim had filed multiple complaints but received little protection.
3. March 3 - Brazil: A femicide occurred in Rio de Janeiro, where a young woman was found dead after being attacked by her partner. The country’s high rates of violence against women remain a significant concern.
4. April 20 - Chile: A woman was killed by her ex-boyfriend in Santiago. The incident highlighted the growing issue of intimate partner violence, with activists calling for increased enforcement of protective measures.
5. May 15 - Peru: A 30-year-old woman was murdered by her spouse in Lima after years of documented domestic abuse. The case ignited a public outcry for better legal responses to gender-based violence.
6. June 4 - Bolivia: A woman was killed in La Paz by her partner, who had previously been reported for abusive behavior. Her death added to the growing number of femicides in Bolivia.
7. July 10 - Ecuador: In Quito, a woman was murdered by her husband in a case of domestic violence. The incident underscored the country’s challenges in addressing violence against women, despite existing laws.
8. August 8 - Uruguay: A woman was brutally attacked and killed by her ex-partner in Montevideo. The case raised concerns about the effectiveness of restraining orders and protective laws in the country.
9. September 25 - Paraguay: A young woman was found dead after being assaulted by her partner in Asunción. The case prompted discussions on the inadequacies of the justice system in dealing with gender-based violence.
10. October 13 - Venezuela: A woman was murdered by her husband in Caracas. The case shed light on the country’s increasing rates of domestic violence, which have been exacerbated by economic instability.
Global
1. February - India: A woman was murdered by her obsessive ex-boyfriend in New Delhi.
2. March - Brazil: A femicide in São Paulo, where a woman was murdered by her partner.
3. April - Turkey: A woman was killed in an honor killing in Istanbul.
4. May - South Africa: A femicide in Cape Town where a young woman’s body was discovered.
5. June - Nigeria: A woman was raped and murdered in a rural area, sparking protests.
6. July - Mexico: A student was abducted and murdered, raising alarm over violence in the country.
7. August - Philippines: A woman was murdered by her husband in a domestic violence case.
8. September - Afghanistan: Increased violence against women in rural areas, including forced marriages.
9. October - Pakistan: A woman was murdered in a suspected honor killing.
#radical feminism#radical feminist community#radblr#radical feminst#radical feminist safe#radical feminists please interact#radical misandrist#radfeminism#trans exclusionary radical feminist#radical feminist#female rage#real feminism#riot grrrl#radfemsafe#radical feminists do interact#radical feminists do touch#radical feminists please touch#punk feminist#feminicide#fight the patriarchy#angry feminist#feminism#terfblr#terfsafe#terf
41 notes
·
View notes
Text
Everything You Need to Know About Crystals: Amethyst
Amethyst (“The World’s Most Popular Purple Gem”)




Color: Dark Vivid Purple to Pale Lilac
Hardness: 7
Rarity: Easy to Acquire
Type: Quartz
Chakra Association: Third Eye, Crown
Deities: Buddha, Dionysus, Diana, Artemis
Birthstone: February
Astrological Signs: Pisces, Aries and Aquarius
Element: Air
Planet: Jupiter
Origin: USA, Britain, Canada, Brazil, Mexico, Russia, Sri Lanka, Uruguay, East Africa, Siberia, India
Powers: Pride, Sobriety, Peace, Spirit World, Protection, Celibacy, Luck, and Homesickness
Crystals It Works Well With: Ametrine, Citrine, and Moonstone
How It Is Created: Amethyst receives its color beginning at the crystal’s growth. At the first stage, trace amounts of iron are incorporated into the crystal as it starts to grow. After the crystallization starts, gamma rays are emitted by radioactive materials within the host rock and the irradiated iron gives the amethyst its beautiful purple color.
History: One of the earliest references to amethyst is in the Old Testament book of Exodus as it is mentioned that one of the stones in the breastplate of Aaron the High Priest was an amethyst. There is not a clear indication to where the name comes from but it is said that it is derived from the Greek word “amethyst” which means “not drunk”. Despite this, it is associated with the god, Dionysus, because the purple hue of the crystal looks like delicious grape wine. Wine goblets were carved of this stone to prevent drunkenness. There is also a Greek lore involving Dionysus with a young girl named Amethyst. The lore reads:
“Dionysus was angry one day and swore that he would exact his revenge on the next mortal that came by. He created several tigers, informed him of their mission and went his way. As it would happen, a lovely young girl named Amethyst was the next to come by, on her way to pay homage to Artemis and was attacked. Artemis quickly changed the girl into a statue of solid quartz. When Dionysus returned to see what he had wrought, he was overcome with remorse and wept tears of purple wine which flowed over the statue, staining it permanently.”
The color was also in demand throughout history since the color purple is associated with royalty and was worn by royals in Egypt and Europe. In some traditions, Catholic Bishops wear amethyst rings to symbolize their piety and celibacy, and rosaries are still fashioned with this stone.
What It Can Do:
Excellent focal point for meditation and scrying
Used to unlock mysteries and figure out spiritual matters, such as death and rebirth
Helps cleanses, purify and heal the body, spirit, and mind
Balances emotions and prevents nightmares
Useful for spells to help let go of addictions
Uses on the tip of wands for healing and can produce high spiritual energy
Brings a sense of calm and clarity
Helps with decision making
Can open your third eye and connect to the crown chakra
Protects the mind from dark magic
A gateway stone to connecting with the spirit world
Helps with transmitting energies to a specific point
How to Get the Best Out of Amethyst: Wearing it on your person with a bracelet or necklace. Putting amethyst on bare skin invites the stone to release its vibrations directly into the body, amplifying its power.
How to Cleanse and Charge Amethyst:
To cleanse: Leave your Amethyst stone placed under the light of the full Moon for a whole night, that is, about 8 hours
To charge: It can also be recharge via the moon so just leaving it in the moonlight can do double duty.
Crystal Grid:
Protection and Cleansing (Hexagram)
Amethyst
Selenite
Snow Quartz
Hold your crystals in your hands and state your intention for the grid.
Lay the first triangle, placing clearing crystals on each point.
Join up the points and spray the grid with clearing essence.
Lay the light-bringing crystals in an overlocking triangle over the top of the first. Join up the points, starting with the first crystal you laid.
Place your keystone in the center, stating your intention once more.
Sources
#amethyst#witchblr#witch community#witchcraft#astrology#occulltism#paganblr#nature#rocks#minerals#quartz#crystal grid#crystals#crystal witch#witchcraft 101#baby witch#dionysus#witches of tumblr#witchcraft resources#witch blog#beginner witch#geology#gemstones
221 notes
·
View notes
Text
Sanjana Karanth at HuffPost:
Israel’s actions since it laid siege to war-torn Gaza last year are “consistent with the characteristics of genocide,” according to a new report by the United Nations committee investigating how the state’s policies and practices impact the Palestinian people’s human rights. Since launching its military offensive more than 400 days ago, Israel has “publicly supported policies that strip Palestinians of the very necessities required to sustain life — food, water and fuel,” the committee said in a Thursday statement about its report, which will be presented to the General Assembly on Nov. 18.
“These statements along with the systematic and unlawful interference of humanitarian aid make clear Israel’s intent to instrumentalize life-saving supplies for political and military gains,” it continued. The Israeli government has not yet publicly responded to the report, though officials have repeatedly denied any violations of international law and framed such accusations as antisemitic. Israeli officials have also consistently criticized the U.N. as being biased against their country. The U.N. established the Special Committee to Investigate Israeli Practices in 1968 to monitor the state of human rights in the occupied Syrian Golan, the West Bank, East Jerusalem and the Gaza Strip. The committee is made up of representatives from Sri Lanka, Malaysia and Senegal, who said they were unable to visit the areas in question because Israel never responded to their requests.
The new report covers the first nine months of Israel’s ongoing military campaign, which began in October 2023 after Hamas militants launched an attack in Israel that killed around 1,200 people and took about 250 hostage. Some 100 Israelis remain in captivity. Israel has since displaced 1.9 million Palestinians in Gaza and killed more than 43,000, most of whom are believed to be women and children. Outside experts and medical workers estimate the true death toll is much higher, but that deaths have been undercounted because the Ministry of Health’s infrastructure has been destroyed; because bodies remain stuck under rubble, where rescuers can’t reach; and because some victims’ bodies were damaged so severely that they can’t be identified. The casualty count from the war likewise does not account for deaths from starvation, from diseases that the collapsed health care system in Gaza couldn’t treat or from what the committee called “an environmental catastrophe.”
[...] The findings are consistent with those from other U.N. agencies, human rights groups, humanitarians and media investigations. On the same day the U.N. committee released its conclusions, Human Rights Watch published its own thorough report describing Israel’s actions as the mass “forced displacement” and “ethnic cleansing” of Palestinians — actions that amount to war crimes and crimes against humanity.
The latest UN report reveals that Israel Apartheid State’s actions towards Palestinians in occupied territories since October 2023 qualify as genocidal.
#Gaza Genocide#Israel#United Nations#Palestine#Gaza#Israel/Hamas War#Israel Apartheid State#UN General Assembly#Occupation of Palestine
23 notes
·
View notes
Text
🇮🇱SRI LANKA TRAVEL WARNING, POLICE DRAMA - Real time from Israel
ISRAEL REALTIME - Connecting to Israel in Realtime
( VIDEO - The remains of Kfar Kila, a southern Lebanese near-border Hezbollah village that also acted as a major launch site. )
✡️Tonight is SIMCHAT TORAH starts tonight, where we celebrate with the Torah! Chag Samayach, a joyful holiday!
.. Several rabbis have noted: How can we celebrate when this war started on this holiday last year? When so many fell, so many remain hostages, so many are fighting and so many have given their lives in our defense?
They answer: very much in the name of the fallen, in the name of the hostages, in the name of the Jewish people and those who have sacrificed, WE WILL NOT ALLOW THE ENEMY to destroy our holiday, to destroy our joy and celebration.
AM YISROEL CHAI, the Jewish people live! We will celebrate, we will win, we will honor their sacrifice.
✡️As a Jewish holy-day, we DO NOT POST news from sundown for 26 hours unless there is a LIFE THREATENING EMERGENCY.
⚠️ISRAEL NATIONAL SECURITY TRAVEL WARNING.. calls on the Israelis to immediately leave the Arugam Bay area and the coastal area in the south and west of Sri Lanka due to terror threat to Israeli tourists, following a warning about a terrorist squad of the Revolutionary Guards mission in the area.
⚠️ HOME FRONT COMMAND - - if you find rocket or drone debris during holiday outdoor activity, DO NOT TOUCH IT - contact Home Front (dial 104) or the Police (dial 100). The parts may be dangerous or toxic, or be important for security.
♦️LEBANON - TZUR-TYRE.. Civil Defense in Tyre walks the streets of the city and asks citizens through loudspeakers to evacuate immediately. The Civil Defense closed the entrances to the city of Tyre to prevent entry. Heavy IDF attacks.
♦️LEBANON - (enemy reports) Dozens of IDF air force attacks on more than 20 villages and towns in Lebanon.
🔹IRANIAN TERROR PROPAGANDA.. a new mural in the center of Tehran: No (Israeli) hostage will be released.
🔹HOUTHIS CLEAR THEIR PORT? Houthi leader Abdel Malik al Houthi issued an urgent order to the owners of the containers in the port to clear out the Hodediah port, immediately. ???
🔹GERMANY SAYS.. German Foreign Minister: Israel succeeded in weakening Hezbollah to a great extent, and the task now is to reach an effective diplomatic solution.
🔹US INTEL AIRCRAFT.. The US is operating reconnaissance aircraft in the Persian Gulf to monitor the movements of Iranian surface-to-surface missiles.
🔹US SEC STATE GOES TO SAUDI ARABIA.. from Israel. Riyadh: The American Secretary of State in Lincoln met with Saudi Crown Prince Mohammed bin Salman and Saudi Foreign Minister Faisal bin Farhan, and talked with them about "the developments in Gaza and Lebanon"
▪️ON ISRAEL APPROVING THE NEW COVID VACCINE.. I received significant STRONG negative feedback about the Israel Min. Of Health approving and bringing into the fall vaxx schedule the new COVID vaccine. It has become ridiculously difficult to determine the facts around COVID vaccines, and I can only advise to consult with a trusted medical professional before taking this vaccine, and there are categories of people who should clearly avoid it such as men under 30.
.. Israel no longer has public COVID testing, COVID (and flu, and both together, and strep - quick test kits are available at pharmacies), so there is no case rate data.
.. The last info I can find on COVID in Israel is 14 cases hospitalized in June, all seniors with other health problems. This is the “from COVID or with COVID” argument, and the article seems to state “with”.
#Israel#October 7#HamasMassacre#Israel/HamasWar#IDF#Gaza#Palestinians#Realtime Israel#Hezbollah#Lebanon
22 notes
·
View notes
Note
hey so you're the only like popular ish sri lankan on tumblr that i know
and the easter attack anniversary is coming up
so i want to know whether you think there will be a controversy again since eid may fall on the day of or the next day
I am so checked out these days that I had forgotten about both and I'm certainly not following the news anymore (see: mental breakdown, hospitalization etc.). But I really hope there won't be. More people have by now glommed to the fact that the Rajapaksas were behind the attacks, or at least had a hand in them, and that the persecution of the Muslim community was fruitless and unfair. And the Muslim community will themselves be hyperaware of the confluence of circumstances sadly, and try to mitigate any resentment with subdued celebrations and interfaith events.
I also want to say that with everything else going on, and the fact that our people are fundamentally selfish assholes, the Easter attacks are now a blip in the consciousness of non-Catholics. However, the opportunity to be a racist, rabble-rousing shithead might be too good to pass up for some.
TL;DR: I have no idea. But I hope not.
#sri lanka news#sri lanka politics#easter sunday attacks#sri lanka#racism#islamphobia#anon#asks#knee of huss
8 notes
·
View notes
Note
Thoughts on the FMA IA 58 Pucará?



A neat looking ground attack light aircraft which on paper packed quite the punch, with 2 20mm cannons, 4 .30 machine guns, and about 1.5 tons of ordinance, either bombs, rockets or s combination of both.
In practice though, it was a bit of a paper tiger, as while both tough and fast, it had a massive design flaw in which the faster you were flying, the stiffer the controls got, to the point that if you were ever to reach the maximum speed, the plane was effectively uncontrollable, made worse the lower you flew, meaning that it couldn’t really aim during combat runs unless it slowed down, so either you actually hit what you were aiming at, and ensured you yourself were an easy target, or you prayed to god whatever you wanted death actually died the moment you pulled the trigger, which the Falklands War proved barely of ever happened.
So yeah, good in theory, shit in practice, made worse by the fact that it was designed around an engine that became obsolete the moment the plane entered service, effectively killing its export potential, hence why it only had three export customers, Colombia, Uruguay and Sri Lanka, with only two of them actually buying the damn thing (Colombia’s were a donation), and only seeing real combat outside the Falklands in Sri Lanka, with a combat record so poor most planes were lost to accidents/combat, and the survivors were retired early due to lack of spare parts, courtesy of the aforementioned shitty engines.
In Colombia, a country desperate for combat aircraft to deal with the massive surge of attacks from communist guerrillas, the damn thing was never used in combat, it was that bad.
What a shitshow of a plane.
23 notes
·
View notes
Text
I've seen arguing over how many people were slaughtered on Oct 7 itself. IDK the exact answer, because from what I've gathered, no one does so far. The last time I saw an article addressing the forensic work on this (which was about a week ago), it said 1,248 people had been identified, but I know there have been victims of the massacre identified since, I know there's still the unidentified victims to take into account, and the missing people (those that we can't know yet whether they'd been murdered on that day, kidnapped, or murdered and their body was kidnapped). There have been some bodies that were brought in together with all the rest, but were then identified as Hamas terrorists (my guess is their bodies weren't among those the forensic experts struggled to identify, unlike the bodies of their victims, often mutilated and burnt beyond recognition). Based on the number identified already, and the number of bodies still unidentified, over two months after the massacre, I find it hard to believe that the final number of Oct 7 victims will be less than 1,300 people. But like I said, nobody knows, there's still no official number, not until either the work of identification will be done, or until it's confirmed that there are no more ways to identify the remaining victims of Hamas' slaughter.
Even before the final number, it is the biggest massacre of Jews since the Holocaust, it is the second deadliest terrorist attack ever (if we take the lowest possible number of fatalities. The worst one is Sep 11, when 2,996 Americans were murdered by al-Qaeda), and the deadliest one ever if we adjust the number of victims to the attacked country's population size (if we take the not final figure of 1,248 people massacred on Oct 7, once adjusted for population size, this would be roughly equivalent to over 42,500 Americans murdered, meaning that for the Israeli population, this is over 14 times the scale of the Sep 11 attacks). Think about the number of Israelis (and Jews) impacted by this attack, before we start talking about the over 5,000 people injured on Oct 7, or those kidnapped. Hamas' massacre is also the single bloodiest day in the history of the Israeli-Arab conflict for one side. So anyone telling you that the Palestinians have been "suffering Oct 7 every single day for years," is either incredibly ignorant, or straight up lying. Anyone who knows the history of the conflict, or of terrorism, knows that there is no underestimating the unique brutality of Hamas' massacre.
Out of the people massacred on Oct 7, who were not Israeli citizens, there were at least: 39 victims from Thailand, 10 from Nepal, 4 from the Philippines, 3 from China, 2 from The United Kingdom, 2 from Sri Lanka, 1 from Canada, 1 from Cambodia, 1 from Germany, 1 from Moldova, 1 from The United States, 1 from Tanzania, and 1 from Eritrea. Altogether, at least 67 foreign nationals.
At least 26 people have been killed by direct rocket hits, of which at least 15 were killed on Oct 7. At least 20 were killed by Hamas and PIJ (Palestinian Islamic Jihad) rockets from Gaza, and at least 6 by Hezbollah rockets from Lebanon. Of the 26 known victims of rocket fire, 2 were citizens of Thailand, 14 were Israeli Jews, and 10 were Israeli Arabs. This doesn't reflect the full effect of the rockets on Oct 7, since the fate of many people was sealed when they started fleeing the barrage of around 4,000 rockets fired into Israel, only to run straight into ambushes set up by Hamas terrorists, like many of the Nova music festival victims, where over 360 people were murdered.
This is 5 years old Yazan Abu Jama'a, who was killed by a direct rocket hit on Oct 7:

I think the worst part about this post is writing "at least" so many times, knowing that every single one of these figures may be updated with a greater number.
(for all of my updates and ask replies regarding Israel, click here)
#israel#antisemitism#israeli#israel news#israel under attack#israel under fire#israelunderattack#terrorism#anti terrorism#hamas#antisemitic#antisemites#jews#jew#judaism#jumblr#frumblr#jewish
123 notes
·
View notes
Text
Many thousands of civilians have reportedly been killed. The number of people displaced from their homes is well into seven figures. Densely populated urban areas have been reduced to rubble. Supplies of electricity, food, and water have been cut off. Hospitals have come under attack. Many of those fleeing, injured, or dead are children.
I could be describing Russia’s full-scale invasion of Ukraine, which has raged on for almost two years now, or the terrible human costs of Israel’s military offensive in the Gaza Strip following the horrific Hamas attacks on Oct. 7. But I am referring to a conflict that has received much less international attention: the civil war in Sudan that broke out last April. Even as one lethal war captures the world’s attention, others roil on in the background.
Unsurprisingly, given its geopolitical significance, Ukraine has received considerable attention in the West, where leaders have been quick to condemn Russia’s war crimes. The new conflict in the Middle East has dominated headlines over the past couple of months. But Sudan’s crisis has gone woefully underdiscussed, like many others that for various circumstantial, political, or geographic reasons seem to matter less to the international community.
The West likes to think it has abandoned the racist habit of ascribing different value to human life in different places. We profess our respect for international law, which codifies the principle of equality. But in practice, our behavior does not always reflect this. Accusations of double standards from non-Western counterparts sting precisely because they have a point.
This is not to advocate for a zero-sum redistribution of attention and diplomatic energy from one conflict to another. Nor is it to say that we should care any less about innocent people killed, for example, in Kharkiv than those killed in Khan Yunis or Khartoum. Instead, more than 75 years after the United Nations adopted the Universal Declaration of Human Rights, the international community needs to rediscover the tradition of humanitarian universalism. We must avow in word and deed that all human lives possess the same value and that the killing of civilians is unacceptable wherever it occurs.
Never before in recent memory has this been more urgent. The world has entered what David Miliband, the president and CEO of the International Rescue Committee, has called an “age of impunity.” War crimes often go unpunished. Nations increasingly disregard the laws of war: Torture, sexual violence, acts of collective punishment, and indiscriminate destruction of civilian homes and services are tragically common.
In a fragmenting international order, old mechanisms such as naming and shaming no longer work. Multilateral peacekeeping operations are in decline. These days, when wars do end, it is more often the result of one side vanquishing the other than a negotiated settlement. This new disorder arrived gradually—as the optimism of the immediate post-Cold War era gave way to new wars, power shifts, and then global economic crisis in the 2000s—and then accelerated in the early 2020s.
Wars are now more frequent, they are lasting longer, and they are killing more people. In 2022, more than 200,000 people died in state-based conflicts globally—the highest death toll since 1986 (excluding unilateral acts of violence such as the Rwandan genocide). Mass civilian casualties in recent years include the massacres of Tamils in Sri Lanka; the killing of tens of thousands of civilians in Yemen; and the deaths of hundreds of thousands of people in Ethiopia’s Tigray region. Such conflicts are forcing more civilians to flee, which is one of several factors that has driven the number of displaced people worldwide to a record 114 million.
Open Society Foundations, the philanthropy I run, provides funding to several of the largest humanitarian organizations to support their work on these overlooked conflicts. We also fund a range of advocacy and policy groups working to bring attention to the roots of these crises and mobilize the political will to address them. But this work can feel like a drop in the ocean. It needs more funding and scaled-up operations, particularly at a time when there is less news coverage of international conflicts, as media outlets have fewer resources to send foreign correspondents to distant war zones. When these conflicts are out of public sight, they too easily become out of mind for officials and politicians.
The time has come, then, for a new universalist global campaign for solidarity with victims of conflict everywhere that reestablishes the norm of equally valuable human life. This may seem like an obvious principle, woven as it is through the constitutions of multilateral institutions such as the U.N. But it is evidently getting lost in today’s world.
Civil society activists capable of crossing national and partisan divides should lead this campaign. They should cooperate with existing multinational institutions, such as the U.N.; nongovernmental organizations, such as ONE Campaign and Amnesty International; and far-sighted cultural and media figures with the reach needed to build momentum.
This global campaign should demand deeper pools of core funding for emergency aid, especially from groups of national governments, ensuring that aid responses do not depend merely on media attention or the largesse of individual governments. It should challenge both media and government to widen their attention spans and scope for empathy. And it should also demand swifter multilateral responses to crises, including by pressuring the U.N. Security Council to speak out immediately for basic humanitarian principles rather than deliberating for weeks.
Perhaps most fundamentally, the campaign should draw in a network of civil society groups, cultural leaders, and new generations of human rights champions to proclaim: no more hierarchies of civilian suffering, no more double standards, no more selective blind spots.
In an age of multiplying and interlocking crises, the international community must find room for solidarity for more than one or two benighted groups at a time. Global civil society should convene, whether in person or online, to launch this new campaign and reassert fundamental but increasingly sidelined principles of equality, solidarity, and shared humanity. As the English poet John Donne put it: “Any man’s death diminishes me, because I am involved in mankind.”
77 notes
·
View notes
Text

Christmas trees 🌲 🎄 history 🍎🍐🥒❤️💚🎄🌹🕷️🕸️
(I’ll be using Xmas and Christmas interchangeably)
It’s a tradition from Central Europe, especially 🇩🇪 Germany. It’s specifically a Protestant tradition. Though St Boniface used a fir tree as a symbol for Christianity after vandalizing Thor’s oak, it wasn’t a Xmas tree.
That said, pre Christians world wide did value evergreens and that didn’t end with Christianity or other religious conversations. Use of conifers synchronized by Christians and continued to be used as protection. As far as we know Actual XMas trees weren’t mentioned until 16th century in 🇱🇻 Latvia. In the Lutheran regions of Central Europe and the Baltics were they were set up in public areas like Cathedrals. The first recorded private use was in Alsace, 🇫🇷 france, then part of Germany. . 🌲
In the 18th century Xmas trees were popular in the cities/towns in the upper Rhineland then spread to the countryside. It stayed there for awhile because Protestant, and Lower Rhine was Catholic. Then Prussian officers thought the tradition was cool and spread it. By the early 19th century nobility in mainland Europe decided Xmas trees were cool and adopted them. German born Queen Charolette of Britain 🇬🇧 introduced it to the country but it didn’t become popular to the non German general public until Queen Victoria. A year after she married princess Albert, zBritsh aristocracy adopted it and it spread from there.
In the North America the trees were introduced by Hessian soldiers, mercenaries from what is now Germany who worked for the English.
Some people have a traditional time they get, set up, like Xmas tree like Advent Sunday, Christmas Eve. They may be taken down Epiphany Eve or Candlemas. My job keeps it up year around and decorates it for whatever holiday is coming up. (I’m not sure how pagans or Wiccans choose when to put up and take down their trees if they use them)
Old school decor for Xmas trees were 🍎 apples, candy canes, pastries that were shaped like ⭐️ stars, ♥️ hearts, and 🌹 flowers. Later glass baubles 🔴🟢🔵(possibly 1st made in Lauscha, Germany) and 🕯️ candles, tinsel, were added. The star on top was supposed to be the star of Bethlehem or the angel, which was supposed to be Gabriel. Now they appear to be used mostly out of habit. (At least in my family)
People in the 1800s would make trees by wrapping cotton batting around a branch.
Most Xmas trees in the US and Georgia(the country) are from tree farms.
Artificial Xmas trees were around since the 1700s, they actually predated natural Xmas trees in the US. The German Morovian Church created in Bethlehem, Pennsylvania. In Germany in the 19th century they were making artificial trees of feathers, this was a response to deforestation. Aluminum trees were first produced in Chicago in 1958 but most of them were originally made in Manitowac, Wisconsin. They became less popular around the time A Charlie Brown Christmas came out. Most artificial trees now are made of PVC. PVC trees use tin or barium, as a stabilizer but they used to use lead. (My family has a pvc tree we reuse every year, no idea if it’s one of the lead ones) the National Christmas Tree Association has a video game called Attack of the Mutant Artificial Christmas Trees, it’s to promote using natural trees. The world’s largest artificial Xmas tree as of 2017 was in Sri Lanka 🇱🇰 at 72.1 m (236ft 6.58 in) if received a lot of criticism for not being Xmas trees-ish and a waste of money. Which is stupid, most of the criticisms are. It’s since been dismantled.
Christmas trees are not without out controversy, much like everything else. The Soviet Union tried to force Atheism throughout their empire and part of that was banning religious holidays. This included banning Xmas trees. They converted them into new-years trees eventually. Catholics didn’t really approve at first, it’s originally a Protestant tradition and the two Christian sects don’t really get along historically. So when the John Paul II had one set up in the 80s not everyone was on board.
Boston called their spruce tree a holiday tree but changed it back because a bunch people threatened to sue for som reason. I would have kept calling it that out of spite.
🕷️🥒
Chrismon tree is put in knave of churches. It’s a conifer decorated in gold and white ornaments called Christmons. The tradition was started by Lutherans but has been adopted by other Christian sects.
Hanukkah Bush is used by some North American Jewish families and may be considered kind of a joke by some. Most Rabbis discourage its use, pointing out that Xmas trees were Christian symbols and Christians had a habit of murderously persecuting Jews for some reason. Rabbis that don’t mind point out that the trees have been secularized for the most part.
Wiccans and pagans often use Yule trees when celebrating Yule/winter solstice or 12 days of Yule respectively. (I consider my tree a Yule tree)
Poland 🇵🇱 particularly Lesser Poland and Upper Silesia has the Podłaźniczka(different localities may have different names). A decorated branch or ring, usually the top of a conifer. It was hung upside down above the wigilia table. Wigilia, a traditional Christmas eve vigil dinner. 🇸🇮 Slovenia has a similar tradition.
🇬🇪 Georgia (the country) has a version of a Xmas tree called Chichilaki. They trees made of dried hazelnut and walnut branches that are shaved and put together in a conifer tree shape. They are most popular in the Guria and Samegrelo regions. They are burned on Georgian Epiphany on Jan 19. The Soviets tried to ban them.
Sources…
Various articles on Wikipedia (I’ve got to start using better sources)
Christmas tree
(Used other sources but I’m having trouble linking them)
Next will either be the Christmas spider or pickle.
#holiday#christmas#Yule#Xmas#Christmas tree#Yule tree#history#trees#evergreen#conifer#pagan#winter solstice
9 notes
·
View notes