#solar panel programs in california
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Off-Grid Solar Systems in California: A Complete Guide to Solar Independence
As California continues to lead the charge in sustainable energy, the popularity of off-grid solar systems has surged. Whether for remote areas, emergency backup, or achieving energy independence, off-grid solar systems offer a reliable solution. Coupled with a variety of solar panel programs in California, making the shift to solar energy has become more accessible and affordable for residents. This article explores the benefits of off-grid solar systems, the different programs available, and how you can get started with solar energy in California.
What Are Off-Grid Solar Systems?
Off-grid solar systems are standalone power systems that generate electricity from solar panels without relying on the traditional grid. These systems use solar panels to capture sunlight and convert it into electricity, which is then stored in batteries for use when the sun isn’t shining. Off-grid systems can be ideal for remote locations where connecting to the utility grid is challenging or for homeowners who want to achieve complete energy independence.
The components of an off-grid solar system typically include:
Solar Panels: Convert sunlight into direct current (DC) electricity.
Battery Storage: Stores the electricity generated for use when solar energy isn't available.
Charge Controller: Regulates the power going into the battery storage.
Inverter: Converts DC electricity from the batteries into alternating current (AC) for home use.
Backup Generator (Optional): Provides an additional power source during extended cloudy periods.
Benefits of Off-Grid Solar Systems in California
Energy Independence One of the main advantages of off-grid solar systems is the ability to generate your own power without relying on the utility grid. This independence ensures that your energy needs are met regardless of grid outages or utility rate hikes. For those living in remote areas, off-grid systems can provide a stable power source where traditional electricity is unavailable.
Cost Savings While the upfront cost of installing an off-grid solar system may be higher than grid-tied systems, the long-term savings can be significant. Off-grid systems eliminate monthly electricity bills, and with California’s high energy rates, this can translate to substantial savings over time. Additionally, advancements in technology have made solar components more affordable, allowing homeowners to recoup their investment faster.
Environmental Impact By using off-grid solar systems, you reduce reliance on fossil fuels and help decrease carbon emissions. Solar energy is a clean and renewable resource that contributes to a more sustainable future. California, being an environmentally conscious state, provides various incentives to promote the use of clean energy.
Resilience in Power Outages In recent years, California has experienced rolling blackouts and power shutoffs due to wildfires. Off-grid solar systems provide a reliable source of electricity during such events, allowing homeowners to maintain essential power even when the grid goes down.
Challenges of Off-Grid Solar Systems
Despite the benefits, there are some challenges associated with off-grid solar systems:
Higher Initial Costs: The upfront investment is typically higher than for grid-tied systems due to the need for battery storage and other components.
Energy Storage Limitations: Battery storage can be expensive and may not provide enough power for extended periods without sunlight. You may need a backup generator for extended cloudy days.
Maintenance Requirements: Off-grid systems require regular maintenance to ensure battery health and system performance.
Solar Panel Programs in California
California has various programs and incentives to encourage the adoption of solar energy. These programs aim to make solar installations more affordable, and they often include tax incentives, rebates, and financing options.
California Solar Initiative (CSI) The California Solar Initiative offers cash rebates for the installation of solar systems in homes and businesses. While the program's funds have been depleted in many areas, it remains one of the foundational programs that helped establish California as a leader in solar energy adoption.
Net Energy Metering (NEM) While primarily associated with grid-tied systems, Net Energy Metering allows solar customers to receive credits for excess electricity they generate and feed back into the grid. NEM can still benefit off-grid homeowners if they choose to remain connected to the grid as a backup or for selling excess power.
Self-Generation Incentive Program (SGIP) The SGIP offers incentives for energy storage systems, such as battery backup for solar power. This program is particularly beneficial for those with off-grid systems, as it helps reduce the cost of battery storage. The incentive amount is based on the size and type of battery system installed, making it easier for homeowners to add energy storage to their solar setup.
Property Assessed Clean Energy (PACE) PACE programs allow property owners to finance solar installations through their property taxes. The financing is repaid over time through an additional assessment on the property tax bill. This makes it easier for homeowners to cover the upfront costs of going solar without paying out-of-pocket.
Federal Solar Tax Credit (ITC) Although not specific to California, the Federal Solar Tax Credit allows homeowners to deduct a percentage of their solar installation costs from their federal taxes. This incentive applies to off-grid and grid-tied systems and significantly reduces the initial financial burden of installing solar panels.
Local Utility Programs Some local utilities in California offer additional rebates and incentives for solar installations. Checking with your local utility provider can uncover specific programs that apply to your region.
Steps to Install an Off-Grid Solar System in California
Evaluate Your Energy Needs Start by calculating your energy consumption. Understanding your power needs will help determine the size of your solar system and the required battery storage capacity.
Site Assessment A site assessment involves evaluating the location for solar panel installation, including the amount of sunlight, roof orientation, and space for panels and batteries. Solar professionals can conduct this assessment to ensure optimal performance.
Design the System The design phase involves selecting the appropriate components, including solar panels, battery storage, inverters, and charge controllers. Working with an experienced solar installer can ensure that your system is designed for maximum efficiency.
Obtain Permits and Incentives Before installation, you'll need to obtain the necessary permits and apply for any applicable incentives or rebates. California has streamlined processes for solar permitting, but local regulations may still apply.
Install the System Professional installation is recommended to ensure the system is correctly set up. Proper installation will ensure the system's safety, efficiency, and compliance with local regulations.
Regular Maintenance After installation, periodic maintenance is required, especially for the battery storage system. Ensuring the batteries are in good condition will extend the lifespan of the off-grid solar system.
Choosing the Right Installer for Off-Grid Solar Systems in California
Selecting a qualified installer is crucial for a successful off-grid solar installation. Look for companies that have:
Experience with off-grid systems.
Knowledge of local solar panel programs in California.
Good reviews and a strong reputation.
Proper licensing and insurance.
Conclusion
Off-grid solar systems in California provide an opportunity to achieve energy independence while contributing to environmental sustainability. With various solar panel programs and incentives available, the transition to solar power has never been more accessible. While the initial costs may be higher than grid-tied systems, the long-term benefits, such as cost savings, resilience during power outages, and reduced environmental impact, make off-grid solar an attractive option for many homeowners.
By understanding your energy needs and exploring the available programs, you can make informed decisions about installing an off-grid solar system. With the right planning and installation, you can enjoy the freedom and benefits that come with generating your own renewable energy.
0 notes
Text
Dandelion News - October 8-14
Like these weekly compilations? Tip me at $kaybarr1735 or check out my Dandelion Doodles on Patreon!
1. All 160 dogs at Florida shelter found homes ahead of Hurricane Milton

“[The shelter] offered crates, food and anything else the dogs would need in exchange for the animals to spend just five days with the foster parents if the human didn't want to keep them for longer. […A]fter about a day of receiving around 100 messages every 30 minutes, Bada said, all 160 were gone from the shelter and in safe and warm homes.”
2. Restoring Ecosystems and Rejuvenating Native Hawaiian Traditions in Maui

“[Volunteers] are restoring water flow to the refuge, removing invasive species, and restoring a loko iʻa kalo using ʻike kūpuna, ancestral knowledge. […] This human-made ecosystem will provide food for community members and habitat for wildlife while protecting coral reefs offshore.”
3. Solar-powered desalination system requires no extra batteries

“In contrast to other solar-driven desalination designs, the MIT system requires no extra batteries for energy storage, nor a supplemental power supply, such as from the grid. […] The system harnessed on average over 94 percent of the electrical energy generated from the system’s solar panels to produce up to 5,000 liters of water per day[….]”
4. Threatened pink sea fan coral breeds in UK aquarium for first time

“The spawning is part of University of Exeter Ph.D. student Kaila Wheatley Kornblum's research into the reproduction, larval dispersal and population connectivity of Eunicella verrucosa. […] Pink sea fans are believed to have been successfully bred by only one other institution, Lisbon Oceanarium, in 2023.”
5. Tiny 'backpacks' are being strapped to baby turtles[….]

““We analysed the data and found that hatchlings show amazingly consistent head-up orientation – despite being in the complete dark, surrounded by sand [… and] they move as if they were swimming rather than digging[…. This new observation method is] answering questions about best conservation practices,” says Dor.”
6. New California Law Protects Wildlife Connectivity

“A new state law in California will instruct counties and municipalities to conserve wildlife corridors when planning new development. […] This could entail everything from creating wildlife crossings at roads or highways, employing wildlife-safe fencing, or not developing on certain land.”
7. ‘I think, boy, I’m a part of all this’: how local heroes reforested Rio’s green heart

“By 2019, [the program] had transformed the city’s landscape, having trained 15,000 local workers like Leleco, who have planted 10m seedlings across […] roughly 10 times the area of New York’s Central Park. Reforested sites include mangroves and vegetation-covered sandbars called restinga, as well as wooded mountainsides around favelas.”
8. Alabama Town Plans to Drop Criminal Charges Over Unpaid Garbage Bills

““Suspending garbage pickup, imposing harsh late penalties and prosecuting people who through no fault of their own are unable to pay their garbage and sewage bills does not make payment suddenly forthcoming,” West said. [… The city] has agreed to drop pending criminal charges against its residents over unpaid garbage bills.”
9. New Hampshire’s low-income community solar program finally moves forward

“The state energy department is reviewing seven proposals for community solar arrays that will allocate a portion of their bill credits to low-income households. […] New Hampshire’s strategy of working with utilities to automatically enroll households that have already been identified streamlines the process.”
10. The Future Looks Bright for Electric School Buses

“EPA has awarded about $3 billion in grants from the infrastructure law, which paid to replace about 8,700 buses. Of those, about 95 percent are electric. [… Electric buses are] cheaper to operate and require less maintenance than diesel buses and will soon be at cost parity when looking at the lifetime cost of ownership[….]”
October 1-7 news here | (all credit for images and written material can be found at the source linked; I don’t claim credit for anything but curating.)
#hopepunk#good news#dogs#hurricane milton#florida#animal shelters#foster dog#hawaii#hawaiʻi#maui#solar#water#solar energy#coral#endangered species#coral reef#turtles#sea turtle#technology#wildlife#habitat#nature#california#rio#south america#reforestation#poverty#anti capitalism#solar panels#electric vehicles
199 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Best News of Last Week
🦾 - High-Five for Bionic Hand
1. Houston-area school district announces free breakfast and lunch for students

Pasadena ISD students will be getting free breakfast and lunch for the 2023-24 school year, per an announcement on the district's social media pages.
The 2023-24 free lunch program is thanks to a Community Eligibility Provision grant the district applied for last year. The CEP, which is distributed by the Department of Agriculture, is specially geared toward providing free meals for low-income students.
2. Dolphin and her baby rescued after being trapped in pond for 2 years
youtube
A pair of dolphins that spent nearly two years stuck in a Louisiana pond system are back at sea thanks to the help of several agencies and volunteers.
According to the Audubon Nature Institute, wildlife observers believe the mother dolphin and her baby were pushed into the pond system near Grand Isle, Louisiana, during Hurricane Ida in late August 2021.
3. Studies show that putting solar panels over waterways could boost clean energy and conserve water. The first U.S. pilot project is getting underway in California.

Some 8,000 miles of federally owned canals snake across the United States, channeling water to replenish crops, fuel hydropower plants and supply drinking water to rural communities. In the future, these narrow waterways could serve an additional role: as hubs of solar energy generation.
4. Gene therapy eyedrops restored a boy's sight. Similar treatments could help millions

Antonio was born with dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa, a rare genetic condition that causes blisters all over his body and in his eyes. But his skin improved when he joined a clinical trial to test the world’s first topical gene therapy.
The same therapy was applied to his eyes. Antonio, who’s been legally blind for much of his 14 years, can see again.
5. Scientists develop game-changing vaccine against Lyme disease ticks!

A major step in battling Lyme disease and other dangerous tick-borne viruses may have been taken as researchers announced they have developed a vaccine against the ticks themselves.
Rather than combatting the effects of the bacteria or microbe that causes Lyme disease, the vaccine targets the microbiota of the tick, according to a paper published in the journal Microbiota on Monday.
6. HIV Transmission Virtually Eliminated in Inner Sydney, Australia

Sydney may be the first city in the world to end AIDS as a public health threat by 2030. Inner Sydney has reduced new HIV acquisitions by 88%, meaning it may be the first locality in the world to reach the UN target to end AIDS as a public health threat by 2030
7. New bionic hand allows amputees to control each finger with unprecedented accuracy

In a world first, surgeons and engineers have developed a new bionic hand that allows users with arm amputations to effortlessly control each finger as though it was their own body.
Successful testing of the bionic hand has already been conducted on a patient who lost his arm above the elbow.
----
That's it for this week :)
This newsletter will always be free. If you liked this post you can support me with a small kofi donation:
Support this newsletter ❤️
Also don’t forget to reblog.
897 notes
·
View notes
Text
california just these last couple years enacted drastic changes to their residential solar program due to a glut of power (it has to go somewhere, theres more being produced than being used) which predictably led to an enormous decline in new installations. the whatever-thousand panels going into this field could have been distributed across whatever-thousand houses if theyre needed so badly
78 notes
·
View notes
Text


Biden’s ironically named Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) was supposed to create millions of green jobs and launch the “sustainable power” industry.
Subsidies flowed to support electric vehicles, wind farms, and solar energy. We have been covering the slowdown in the EV market, and residents of the East Coast are questioning all the promises made by the wind energy companies after the Vineyard Wind blade failure.
Now, it’s time to turn our attention to solar power. SunPower, the company that provides solar panels to many Californian homes in the sunny Coachella Valley area, filed for bankruptcy this week.
It is the latest development in a saga that has seen the company facing numerous serious and seemingly escalating challenges over the past several months, including allegations about executives’ misconduct related to the company’s financial statements and a recent decision that SunPower would no longer offer new solar leases. Days after the latter announcement, Coachella Valley-based Renova Energy, which markets and installs SunPower systems, said it was ending its partnership with SunPower and temporarily pausing operations after not receiving required payments from SunPower. SunPower’s executive chairman wrote in a letter posted on the company’s website on Monday that the company had reached an agreement to sell certain divisions of its business and suggested it was looking for one or more buyers to take on the rest, including the company’s responsibilities to maintain solar systems it has previously sold or leased.
It is important to note that SunPower was the industry’s “darling” to understand the magnitude of this development.
Founded in 1985 by a Stanford professor, SunPower was, for the past two decades, a darling of the solar industry. The company helped build America’s biggest solar plant, called Solar Star and located near Rosamond, California, and has installed solar panels on more than 100,000 homes. The company’s stock price has fluctuated dramatically, peaking during the solar stock frenzy of late 2007. As recently as January 2021, SunPower’s valuation momentarily reached $10 billion, buoyed by the expansion of its residential solar panels program. But since then, the company’s value has cratered — and this year, its situation became particularly dire.
It is also important to note that earlier this month, the bankruptcy of a solar-powered company in South Florida created an array of problems on the South Coast of California. Subcontractors are scrambling to find ways to guarantee payment for work on homes with equipment from the firm.
Meanwhile, homeowners are regretting their misplaced trust in eco-activists and city officials.
The business — Electriq Power Inc. — was putting solar panels and batteries on Santa Barbara rooftops at no expense to homeowners and with the blessings of the cities of Santa Barbara, Goleta, and Carpinteria. But then Electriq filed Chapter 7 on May 3, freezing all its operations. This prompted one of its subcontractors, Axiom 360 of Grover Beach, to place mechanics liens on homes for which it had yet to be paid. This preserves Axiom’s options for full payment of its installation work and is not unusual among contractors. But for homeowners who didn’t expect any financial outlay, it came as a shock, especially as the recording notice lists foreclosure in 90 days among the penalties. “You’re helping the environment. You’re not paying high rates to Southern California Edison,” said homeowner Randy Freed, explaining why he signed on to Electriq’s PoweredUp Goleta program. He was pleased with the savings in the solar array and storage batteries, but then he received the mechanics lien in June. The possibility of foreclosure was unanticipated, Freed said, and he’d relied on the cities’ endorsements. “It’s a great program; we’ve checked them out,” he recalled the cities saying on a postcard he received.
Hot Air's Beege Welborne takes an in-depth look at the cascade of warnings that indicate SunPower and the residential solar market are in serious trouble. She also hits on a point that is true for all green energy schemes: Today’s technology cannot keep up with the promises being made about tomorrow.
The technology side still hasn’t ironed itself out and may never with as saturated as the market is. With interest rates as high as they are and home prices through the roof, no one wants to pay a fortune for something that’s not rock solid. …That “sustainable” growth is only possible once all the artificial supports are knocked away and the technology proves viable and worth the cost once and for all.
Of course, the solar industry isn’t helped by the fact that the cost savings for customers aren’t quite as lavish as originally promised.
12 notes
·
View notes
Text
Excerpt from this story from Grist:
California’s utilities regulator adopted new rules for community solar projects on Friday, despite warnings from clean energy advocates that the move will actually undercut efforts to expand solar power options for low-income customers.
The state’s biggest utility companies advocated for the new rules.
Community solar projects are generally small-scale, local solar arrays that can serve renters and homeowners who can’t afford to install their own rooftop solar panels. They are one part of the state’s overall strategy to eventually run the power grid entirely by renewable energy.
The California Public Utilities Commission’s 3-1 ruling preserves and expands programs that will allow any ratepayer to subscribe to a pool of projects and receive a 20 percent rate reduction, said Commission President Alice Reynolds. But it also reduces future compensation for solar providers and residents.
The commission calculates the benefits derived from distributed, small-scale solar power projects, which provide a “service” by sending clean energy to the power grid and reducing transmission costs by serving nearby communities. Solar developers are compensated for the value of the benefit their project provides.
The formula adopted this week essentially reduces the value of distributed small-scale renewable energy in the future, providing less of an incentive for new community solar projects to be built.
In the near term, the subsidies and incentives that help promote community solar installation will remain in place, paid for by a recent $250 million grant California received under the federal Solar For All program.
One of the concerns for solar advocates is what happens after that pot of funding runs out and the financial incentive to develop solar evaporates.
“The foundations of a sustainable program should not be built on one-time money,” said Derek Chernow, Western Regional Director for the Coalition for Community Solar Access.
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
McAuliffe is, by her own admission, lucky to have the option to live someplace else. All the renters have moved, she says, but for most of the homeowners in Last Chance, moving isn’t financially viable. The residents of Last Chance are not the only fire victims in the county stuck living in trailers and tents as they wait on building permits. Rural communities like Bonny Doon and Ben Lomand are also struggling to get cleared for permits: in Bonny Doon, the biggest hurdle is residents getting septic clearances, while in Ben Lomand people are struggling to receive geological clearances, according to Shaw and county officials. Following the fires in Oct. of 2020, the county made multiple promises that CZU fire victims would be able to benefit from streamlined permitting processes and relaxed building codes. But the people I spoke with say a number of roadblocks are preventing residents from rebuilding. The county even told Last Chance residents that they could be part of a pilot program that would streamline the building process, and allow them to use alternative means of construction, as long as the homes were found to be structurally sound and meet basic health and safety requirements. But because CalFire has not approved the road as fire safe, residents haven’t had a chance to put the pilot program into action. “The codes are killing us,” McAuliffe says.
[...] After the fires ravished Santa Cruz County, California’s Office of Emergency Services (Cal OES), hired San Francisco-based construction company Anvil Builders Inc. to help clear debris from the CZU fire, as part of a $225 million contract. But come last November, it became clear that in the debris removal process, Anvil had caused millions of dollars in damage to county and private roads, as well as to septic and storm drainage systems. To Last Chance Road alone, Anvil caused an estimated $2.7 million in damages down 7.8 miles of the road.
[...] The biggest sticking point for them as they work with the county to acquire their permits is getting their septic cleared. In the past two years, McKenzie and her husband have sunk around $10,000 on the permitting process, but you wouldn’t have guessed that from looking at their land; they haven’t been able to start the building process at all, as they apply and reapply to get their septic clearance. McKenzie doesn’t understand why this is the roadblock that is stopping them from rebuilding. For more than 34 years, she says, they have lived without issues with their septic tank; now, the county requires they move it further away from the creek that runs near her property. Already, she and her husband will have to adhere to new building codes, like indoor sprinkles, solar panels and a litany of other updates that their home that burned in the fire didn’t have. “It’s frustrating,” McKenzie says.
Paradise was an actual town, this is for weirdos who live in isolated houses in the middle of nowhere
3 notes
·
View notes
Text

NASA's new Deep Space Network antenna has its crowning moment
Deep Space Station 23's 133-ton reflector dish was recently installed, marking a key step in strengthening NASA's Deep Space Network.
NASA's Deep Space Network, an array of giant radio antennas, allows agency missions to track, send commands to, and receive scientific data from spacecraft venturing to the moon and beyond. NASA is adding a new antenna, bringing the total to 15, to support increased demand for the world's largest and most sensitive radio frequency telecommunication system.
Installation of the latest antenna took place on Dec. 18, when teams at NASA's Goldstone Deep Space Communications Complex near Barstow, California, installed the metal reflector framework for Deep Space Station 23, a multifrequency beam-waveguide antenna.
When operational in 2026, Deep Space Station 23 will receive transmissions from missions such as Perseverance, Psyche, Europa Clipper, Voyager 1, and a growing fleet of future human and robotic spacecraft in deep space.
"This addition to the Deep Space Network represents a crucial communication upgrade for the agency," said Kevin Coggins, deputy associate administrator of NASA's SCaN (Space Communications and Navigation) program.
"The communications infrastructure has been in continuous operation since its creation in 1963, and with this upgrade we are ensuring NASA is ready to support the growing number of missions exploring the moon, Mars, and beyond."
Construction of the new antenna has been under way for more than four years, and during the installation, teams used a crawler crane to lower the 133-ton metal skeleton of the 112-foot-wide (34-meter-wide) parabolic reflector before it was bolted to a 65-foot-high (20-meter-high) alidade, a platform above the antenna's pedestal that will steer the reflector during operations.
"One of the biggest challenges facing us during the lift was to ensure that 40 bolt-holes were perfectly aligned between the structure and alidade," said Germaine Aziz, systems engineer, Deep Space Network Aperture Enhancement Program of NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California.
"This required a meticulous emphasis on alignment prior to the lift to guarantee everything went smoothly on the day."
Following the main lift, engineers carried out a lighter lift to place a quadripod, a four-legged support structure weighing 16.5 tons, onto the center of the upward-facing reflector. The quadripod features a curved subreflector that will direct radio frequency signals from deep space that bounce off the main reflector into the antenna's pedestal, where the antenna's receivers are housed.
Engineers will now work to fit panels onto the steel skeleton to create a curved surface to reflect radio frequency signals. Once complete, Deep Space Station 23 will be the fifth of six new beam-waveguide antennas to join the network, following Deep Space Station 53, which was added at the Deep Space Network's Madrid complex in 2022.
"With the Deep Space Network, we are able to explore the Martian landscape with our rovers, see the James Webb Space Telescope's stunning cosmic observations, and so much more," said Laurie Leshin, director of JPL.
"The network enables over 40 deep space missions, including the farthest human-made objects in the universe, Voyager 1 and 2. With upgrades like these, the network will continue to support humanity's exploration of our solar system and beyond, enabling groundbreaking science and discovery far into the future."
NASA's Deep Space Network is managed by JPL, with the oversight of NASA's SCaN Program. More than 100 NASA and non-NASA missions rely on the Deep Space Network and Near Space Network, including supporting astronauts aboard the International Space Station and future Artemis missions, monitoring Earth's weather and the effects of climate change, supporting lunar exploration, and uncovering the solar system and beyond.
IMAGE: A crane lowers the steel reflector framework for Deep Space Station 23 into position Dec. 18 on a 65-foot-high (20-meter) platform above the antenna’s pedestal that will steer the reflector. Panels will be affixed to the structure to create a curved surface to collect radio frequency signals. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
youtube
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
1. The ACC will train and employ 20,000 people in climate and clean energy jobs
The ACC will mobilize a new, diverse generation by training them in skills crucial to combating climate change—everything from installing solar panels to improving communities' natural disaster resilience to restoring critical ecosystems. And with a shortage of skilled clean energy workers, the ACC couldn’t come at a better time. We need more tradespeople, installing things like electric vehicle chargers and heat pumps, to decarbonize our economy.
There’s an emphasis on building career pathways, not just jobs. To achieve this, the White House will partner with unions and is committed to providing members with the hard skills and transferable credentials that will allow them to find good-paying jobs or seek further training through apprenticeships and trade schools after their service. This includes potentially expanding access to scholarships and awards that would support post-secondary education and training or reduce student debt and streamlined pathways into civil service. The best part? No prior experience is required for most positions, and very few will require college degrees.
2. The ACC prioritizes equity and environmental justice
While the ACC draws upon the ambition of The New Deal and President Franklin Delano Roosevelt’s Civilian Conservation Corps, it also learns from its fundamental flaws.
FDR’s Corps lacked diversity, perpetuated white supremacy, and almost entirely excluded women, but Biden’s Corps puts equity and environmental justice at its core. It prioritizes communities traditionally left behind, including energy communities, whose lives have been dominated and shaped by the fossil fuel industry, and disadvantaged communities, who disproportionately suffer from a combination of environmental, economic, and health burdens.
The ACC follows the same targets of the administration’s Justice40 goal, where 40 percent of the benefits must be directed towards disadvantaged communities.
3. The ACC employs an all-of-government approach
The ACC is built on a hub-and-spoke model with AmeriCorps at the center. The White House is launching a dedicated ACC recruitment website, where participants can learn about and apply for opportunities in their communities, and across the country, that span all spheres of the clean energy economy.
The administration is partnering AmeriCorps with at least five other federal agencies (Department of Labor, Department of the Interior, U.S. Department of Agriculture, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, and Department of Energy) to pool resources, coordinate recruitment, and fund corps members to work on specific projects that address the climate crisis.
Additionally, the administration will partner with at least 10 states. California, Colorado, Maine, Michigan, and Washington have already launched similar programs, while five more (Arizona, Maryland, Minnesota, North Carolina, and Utah) are creating their own Corps.
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
President Joe Biden’s landmark Inflation Reduction Act is packed with billions of dollars’ worth of credits and rebates for purchasing electric cars and making home improvements that save energy.
If you earn enough each year to owe the federal government money in taxes, then the credits that kicked in on Jan. 1 for buying an electric vehicle or setting up charging stations at home will shave thousands of dollars off your bill to the Internal Revenue Service.
But if you’re a low- and middle-income homeowner looking for help covering the cost of swapping a fuel-burning furnace for an electric heat pump, you’ll have to wait until later next year for a rebate. If your existing appliance breaks in the meantime and you go green with the replacement, there’s no guarantee you’ll get any money back.
“It’s completely unacceptable,” Rep. Jared Huffman (D-Calif.) told HuffPost by phone Friday.
On Monday, Huffman and at least 65 other House Democrats signed a letter to Energy Secretary Jennifer Granholm demanding that her agency revise its rulebook to allow states to make all rebates retroactively available once states get programs started.
“If you’re one of the wealthy folks that can access tax credits, you’re doing just fine,” Huffman said. “But if you’re a middle-class or working family and you’re counting on those more generous rebates to make all of this feasible for you, the Department of Energy is telling you that you have to wait indefinitely: If you were dumb enough to go ahead and buy these things because we’ve all been telling you to do it, you’re out of luck.”

Improved energy efficiency with heat pump technology and new tax incentives have contributed to the popularity of heat pumps as many homeowners face increased heating costs.
The issue centers on a nearly $9 billion pot of funding in the IRA meant to help homeowners buy electric appliances and upgrade homes to cut back on energy usage. The federal government is set to give the money to states to distribute directly to homeowners. But it took until July 27 — nearly a year after the IRA’s passage — for the Department of Energy to finish writing its rulebook for determining who is eligible for rebates.
The guidance said appliances purchased between when the IRA passed and a state launches its rebate program would not be eligible for rebates — even though the law states that eligibility begins upon enactment of the statute.
In a historic law packed with incentives for corporations to buy electric vehicles and build solar-panel factories, the rebates were designed as one of the few consumer-facing programs and among the biggest to primarily benefit anyone who isn’t rich. That most homeowners won’t get a taste of those rebates until the fall of 2024 at the earliest will only make it harder for Democrats to sell voters on the legislation before they head to the polls next November.
The problem first came to light in Huffman’s home state of California, which arguably has the country’s most advanced existing rebate program for making energy-efficiency upgrades. In an Aug. 27 column, The San Francisco Chronicle’s Joe Garofoli detailed the woes of various homeowners who considered replacing fuel-burning furnaces with electric heat pumps until learning that the new federal rebates to cover as much as $8,000 of the $20,000 it could cost to buy and install the appliance were not guaranteed.
“This is California,” a Nevada City resident named Ken Bradford, who was waiting to replace his propane-fueled furnace, told the columnist. “You’d think that California would be ahead of the curve on this. But not so.”
The bottleneck, however, is on the federal level. California could not begin applying for its rebates program to distribute the IRA money until the federal Energy Department released its guidelines — which did not come out until July 27.
The state is now working on designing its program. But the California Energy Commission said it can’t guarantee that appliances purchased between now and the launch of its program sometime next year will be covered unless the Energy Department revises its guidance.
Despite months of back-and-forth with the Energy Department, Huffman said the agency has so far refused to change the rulebook.
An Energy Department spokesperson did not respond to a request for comment. ___________________
I always was told it was the GOP that was reducing taxes for the rich, so this is a shocker.
For an added layer of fun, go have a look at what's going on with medicare in California.
Huffman blamed understaffing for the delays in writing the rules in the first place and admitted that the highly technical nature of the rebate program made implementation difficult. He said he suspects the added complication of applying rebates retroactively is behind the holdup.
“It’s easier for bureaucrats to stand up a program that doesn’t apply retroactively; it’s easier to just make it point-of-sale, prospective only,” Huffman said. “It may take them another year and a half to do it, but it’s just easier for them.”
The IRA “clearly authorizes retroactive rebates, stating that Home Efficiency Rebates ‘shall’ be provided for ‘retrofits begun on or after the date of enactment’ and saying nothing to the contrary regarding the Home Electrification and Appliance Rebate,” the letter reads.
Until the administration begins distributing advanced administrative funds to help states hire for and develop their programs, the understaffing problems threaten to trickle down, further delaying payouts to homeowners, the letter said.
“Because of delays in finalizing program guidance and distributing administrative funds, we are informed that states may be unable to offer rebates until the Fall of 2024 or later, which would be more than two years after IRA enactment,” the letter reads. “We urge DOE to prioritize getting this critical program on a faster, more effective track by working with states, territories, and tribes to ensure there are no further delays or obstacles going forward.”
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
Incorporating Renewable Energy into Your EV Charging Routine
The shift towards electric vehicles (EVs) has been a significant stride in the collective effort to reduce carbon emissions and combat climate change. As the electric vehicle market continues to grow, with global sales hitting over 6.6 million in 2021, a 108% increase from the previous year, the focus now turns to how we power these vehicles. Transitioning from fossil fuels to renewable energy sources for EV charging is the next critical step in ensuring that the benefits of EVs are fully realized. This article explores the ways in which individuals and communities can incorporate renewable energy into their EV charging routines.
Firstly, the concept of 'green charging'—the process of using renewable energy to charge electric vehicles—is not only environmentally sound but also increasingly economically viable. The cost of solar photovoltaic (PV) systems has dropped by about 90% since 2010, making it an accessible option for many. Homeowners with EVs can install solar panels to capture energy during the day, which can then be used to charge their vehicles in the evening. For those without the option to install solar panels, choosing a green energy provider for their home charging setup that sources electricity from renewables is an effective alternative.
In addition to solar power, wind energy is another potent source for EV charging. Wind energy has experienced a dramatic increase in its adoption, with the global wind power capacity reaching 837 GW in 2021, an increase of 93% from the capacity in 2016. EV owners can tap into this resource by purchasing wind energy credits or by selecting energy plans that prioritize wind-sourced electricity. This ensures that the energy used for charging their EVs comes from clean sources, even if they are not directly connected to a wind farm.
The integration of smart chargers has made it easier for EV owners to charge their vehicles when renewable energy production is at its peak. Smart chargers can be programmed to operate when renewable energy generation is high, which usually coincides with low demand periods such as mid-day for solar or night-time for wind. By doing so, EV owners ensure their vehicles are charged using the cleanest energy possible while also taking advantage of lower energy prices during these off-peak times.
Another key element in aligning EV charging with renewable energy is the development of a robust public charging infrastructure that is powered by renewables. Governments and private companies are investing in the installation of public EV charging stations that are directly connected to renewable energy sources. For instance, in California, which leads the US with over 39% of the country's EV sales, there is a plan to install 250,000 charging stations by 2025, many of which will be powered by renewables.
On a larger scale, energy storage systems play a vital role in matching renewable energy supply with EV charging demand. Energy storage solutions, like lithium-ion batteries or pumped hydro storage, can store excess renewable energy generated during peak production times. This stored energy can then be used to provide a consistent and reliable source of green electricity for EV charging, regardless of the time of day or weather conditions.
There is also a growing trend towards vehicle-to-grid (V2G) systems, where EVs do not just consume power but also have the capability to return energy to the grid. This technology allows for a dynamic energy exchange where EVs can be charged during renewable energy peak production and then supply energy back to the grid when it's needed the most. This not only ensures optimal use of renewable energy but also provides stability to the energy grid and potentially offers financial benefits to EV owners.
Finally, to truly capitalize on renewable energy for EV charging, there needs to be increased collaboration between policymakers, renewable energy providers, and the automotive industry. Incentives for residential and commercial solar installations, tax benefits for purchasing green energy, and subsidies for smart chargers are just a few of the ways that can accelerate the adoption of renewable-powered EV charging.
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Empowering Sustainable Living: A Comprehensive Guide to California Solar Incentives and California Solar Panel Programs
As the push for renewable energy gains momentum, California stands out as a leader in solar energy adoption. With abundant sunshine and progressive environmental policies, the Golden State is an ideal place for solar energy investments. Homeowners and businesses alike can benefit from various California solar incentives and California solar panel programs designed to make solar energy more accessible and affordable. This blog will delve into the details of these incentives and programs, providing a thorough guide for anyone looking to harness the power of the sun in California.

The Importance of Solar Energy in California
Solar energy is crucial for California's ambitious climate goals. The state aims to achieve 100% clean electricity by 2045, and solar power is a key component of this plan. By transitioning to solar energy, Californians can reduce their reliance on fossil fuels, lower greenhouse gas emissions, and contribute to a sustainable future.
Overview of California Solar Incentives
California offers a variety of incentives to encourage the adoption of solar energy. These incentives are designed to reduce the upfront costs of solar installations and provide long-term financial benefits.
1. Federal Solar Investment Tax Credit (ITC)
While not specific to California, the federal Investment Tax Credit (ITC) is a significant incentive for solar adopters. The ITC allows homeowners and businesses to deduct a substantial percentage of their solar installation costs from their federal taxes. Currently, the ITC covers 26% of the installation costs for systems installed in 2021-2022, but this percentage is set to decrease unless extended by Congress.
2. California Solar Initiative (CSI)
The California Solar Initiative (CSI) is a comprehensive solar rebate program that has significantly contributed to the growth of solar energy in the state. While the program has largely concluded for residential customers, it still offers incentives for multifamily affordable housing and commercial properties. The CSI provides rebates based on the performance of the solar energy system, encouraging high-quality installations that maximize energy production.
3. Self-Generation Incentive Program (SGIP)
The Self-Generation Incentive Program (SGIP) provides incentives for energy storage systems, which are often paired with solar panels. By installing a battery storage system, homeowners and businesses can store excess solar energy for use during peak hours or power outages. SGIP offers substantial rebates that can cover a significant portion of the storage system's cost, making it an attractive option for those looking to enhance their energy resilience.
4. Net Energy Metering (NEM)
Net Energy Metering (NEM) is a crucial policy for solar adopters in California. NEM allows solar panel owners to send excess electricity back to the grid in exchange for credits on their utility bills. These credits can offset future energy costs, ensuring that homeowners and businesses get the most value from their solar installations. NEM 2.0, the current iteration of the program, maintains favorable terms for solar customers, but changes are expected with the upcoming NEM 3.0, so staying informed about policy updates is important.
5. Property Assessed Clean Energy (PACE) Financing
Property Assessed Clean Energy (PACE) financing is an innovative program that allows property owners to finance the cost of solar installations and other energy efficiency improvements through their property taxes. PACE financing offers low-interest rates and long repayment terms, making it easier for homeowners and businesses to invest in solar energy without a significant upfront cost.
6. Local Rebates and Incentives
In addition to state-wide programs, many local utilities and municipalities in California offer their own solar incentives. These can include additional rebates, grants, and low-interest loans. It's worth checking with your local utility company and government to see what specific incentives are available in your area.
California Solar Panel Programs
1. California Solar on Multifamily Affordable Housing (SOMAH) Program
The California Solar on Multifamily Affordable Housing (SOMAH) program aims to bring the benefits of solar energy to low-income communities. SOMAH provides financial incentives for installing solar energy systems on multifamily affordable housing properties. The program covers up to 100% of the installation costs, ensuring that low-income tenants can benefit from lower energy bills and increased energy independence.
2. Single-family Affordable Solar Homes (SASH) Program
The Single-family Affordable Solar Homes (SASH) program is designed to provide solar energy to low-income homeowners. The program offers substantial rebates to cover the cost of solar installations, making it possible for low-income families to access clean, renewable energy. SASH is part of California's broader effort to ensure that the benefits of solar energy are equitably distributed.
3. Disadvantaged Communities - Single-family Solar Homes (DAC-SASH) Program
Similar to the SASH program, the Disadvantaged Communities - Single-family Solar Homes (DAC-SASH) program targets low-income homeowners in disadvantaged communities. DAC-SASH offers upfront rebates to cover the cost of solar installations, helping to reduce energy bills and improve energy resilience for families in underserved areas.
4. GoSolarCalifornia Campaign
The GoSolarCalifornia campaign is an initiative that provides information and resources to help homeowners and businesses navigate the process of going solar. The campaign's website offers tools to estimate solar costs and savings, find qualified solar installers, and learn about available incentives. GoSolarCalifornia is a valuable resource for anyone considering solar energy in the state.
Financial Considerations and Benefits
1. Long-term Savings
While the initial cost of a solar installation can be significant, the long-term savings are substantial. Solar panels can drastically reduce or even eliminate electricity bills, providing a reliable return on investment. In many cases, the savings on utility bills can offset the installation costs within a few years, leading to significant financial benefits over the system's lifespan.
2. Increased Property Value
Installing solar panels can increase the value of your property. Prospective buyers are often willing to pay a premium for homes with solar energy systems due to the lower energy costs and environmental benefits. Studies have shown that homes with solar panels tend to sell faster and at higher prices compared to non-solar homes.
3. Environmental Impact
Switching to solar energy significantly reduces your carbon footprint. Solar power generates electricity without emitting greenhouse gases or other harmful pollutants. By using solar energy, homeowners and businesses can contribute to reducing air pollution and combating climate change, supporting California's ambitious environmental goals.
4. Energy Independence
Solar energy provides greater energy independence. By generating your own electricity, you become less reliant on the grid and less vulnerable to utility rate increases. Solar energy systems with battery storage can provide a reliable backup power source, enhancing your property's resilience during power outages.
The Installation Process
1. Site Assessment
The first step in installing a solar energy system is a site assessment. A solar installer will evaluate your property to determine its suitability for solar panels. Factors considered include the orientation and pitch of your roof, shading from trees or other structures, and the overall condition of the roof.
2. System Design
Based on the site assessment, the solar installer will design a custom system tailored to your energy needs and property characteristics. This includes determining the optimal number and placement of solar panels, selecting the appropriate inverters and other components, and planning the wiring and mounting systems.
3. Permitting and Approvals
Before installation can begin, you’ll need to obtain the necessary permits and approvals from local authorities and your utility company. Your solar installer will typically handle this process, ensuring that all requirements are met and that the installation complies with local building codes and regulations.
4. Installation
The actual installation of a California solar energy system usually takes a few days. The solar installer will mount the panels on your roof, connect them to the inverters, and complete the wiring to integrate the system with your property's electrical system. Once the installation is complete, the system will be inspected to ensure it meets safety and performance standards.
5. Activation and Monitoring
After passing inspection, your solar energy system can be activated. Your solar installer will guide you through the process of turning on the system and monitoring its performance. Most modern systems include online monitoring tools that provide real-time data on energy production and consumption.
Conclusion
California solar incentives and California solar panel programs offer substantial financial benefits and support for those looking to embrace solar energy. From federal and state tax credits to local rebates and innovative financing options, the opportunities to reduce the cost of solar installations are abundant. Additionally, programs like SOMAH, SASH, and DAC-SASH ensure that the benefits of solar energy are accessible to low-income and disadvantaged communities. By taking advantage of these incentives and programs, homeowners and businesses can reduce their energy costs, increase their property values, and contribute to a sustainable future. Now is the perfect time to explore solar energy in California and join the growing community of solar-powered properties.
0 notes
Text
Dandelion News - January 8-14
Like these weekly compilations? Tip me at $kaybarr1735 or check out my Dandelion Doodles!
1. In Chicago, all city buildings now use 100 percent clean power

“As of January 1, every single one of [Chicago’s municipal buildings] — including 98 fire stations, two international airports, and two of the largest water treatment plants on the planet — is running on renewable energy, thanks largely to Illinois’ newest and largest solar farm.”
2. California Rice Fields Offer Threatened Migratory Waterbirds a Lifeline

“Cranes need nighttime roosting sites flooded to a depth of about 3 to 9 inches, so they can easily hear or feel predators moving through the water. [... Bird Returns pays] farmers to flood their fields during critical migration periods [... and] provide foraging sites by leaving harvested rice or corn fields untilled, so cranes can access the leftover grain.”
3. New York Climate Superfund Becomes Law

“[Funds recovered “from major oil and gas companies” will be used to pay for] the restoration of stormwater drainage and sewage treatment systems, upgrades to transit systems, roads and bridges, the installation of green spaces to mitigate city heat islands and even medical coverage and preventative health programs for illnesses and injuries induced by climate change.”
4. Austin says retooled process for opening overnight cold-weather shelters is paying off

“[... T]he city's moves to lower the temperature threshold to open shelters and announce their activation at least a day in advance were the result of community feedback. [Shelter operators also passed out hot food.]”
5. Helping Communities Find Funding for Nature-Based Solutions

““From coastal oyster reefs to urban stormwater greenways, nature-based solutions are becoming the new normal.” That’s because these types of projects are often less expensive to build and have additional community benefits, such as improving water quality or creating parkland.”
6. Saving the Iberian lynx: How humans rescued this rare feline from extinction

“Back in the early 2000s, fewer than 100 individuals roamed the wild, including only 25 reproductive females. [...] Conservation staff [...] shape these cats into resourceful hunters and get them ready for life outside the center. [...] They’re fine-tuning captive-breeding routines, improving veterinary procedures, and pushing for more wildlife corridors.”
7. Biden cancels student loans for 150,000 more borrowers

“The 150,000 new beneficiaries announced Monday include more than 80,000 borrowers who were cheated or defrauded by their schools, over 60,000 borrowers with total and permanent disabilities and more than 6,000 public service workers[...] bringing the number whose student debt has been canceled during [Biden’s] administration to over 5 million[....]”
8. PosiGen wins another $200M for lower-income rooftop solar

“PosiGen offers a “no credit check” [solar panel installation to] those with a higher percentage of their income going to power and fuel bills[....] “somewhere between 25 and 75 percent” of the consumer’s monthly energy savings could come from efficiency measures such as sealing heating and cooling leaks, replacing thermostats, and installing LED lights[....]”
9. Indigenous communities come together to protect the Colombian Amazon

“At this year’s COP, Indigenous peoples celebrated the [protection of] traditional knowledge, innovations and practices[... and] the Cali Fund, which ensures that communities, including Indigenous peoples, receive benefits from the commercial use of [...] genetic data derived from the biological resources that they have long stewarded.”
10. How the heartland of Poland’s coal industry is ditching fossil fuels - without sacrificing jobs

“[Katowice, a former coal city] committed to reducing CO2 emissions by 40 per cent compared to 1990, prioritising investments in green infrastructure, and promoting renewable energy and energy efficiency. [...”]The gradual departure from heavy industry did not bring high social costs in our city,” says Marcin Krupa, Mayor of Katowice City.”
January 1-7 news here | (all credit for images and written material can be found at the source linked; I don’t claim credit for anything but curating.)
#hopepunk#good news#chicago#clean energy#renewableenergy#california#birds#cranes#migratory birds#climate action#climate crisis#climate change#new york#texas#homelessness#unhoused#homeless shelter#nature#green infrastructure#lynx#iberian lynx#spain#endangered species#student debt#solar energy#indigenous#poland#solar panels#solar power#biodiversity
59 notes
·
View notes
Text
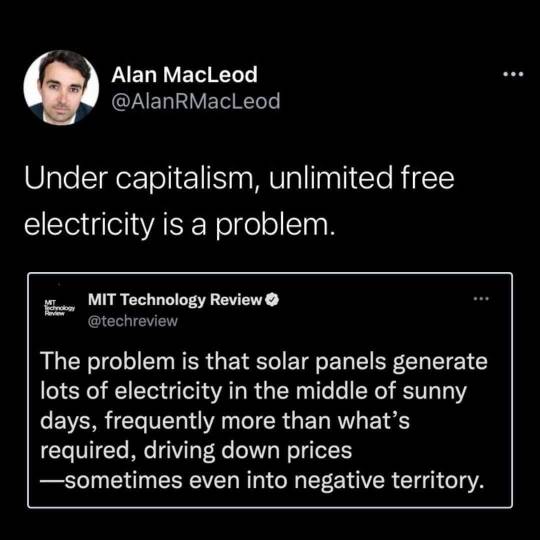
This article is actually about a very serious problem. If you overgenerate electricity it increases the phase frequency of the power grid, and if that goes out of sync with your generators (including solar panels) it can destroy them. In the kind of way where your power grid is fucked for months. It is very very very very bad.
California started a program to make solar panels more affordable by offering very low interest rates for solar panels, to allow people to benefit from their lifetime $/energy cost that's below fossil fuels, without having to worry about the high frontloaded cost. However they did not do this for batteries. And power grid quality batteries with massive energy storage and serious charge-discharge lifetimes, are expensive.
And they did this because while solar panels are cheaper than fossil fuels per kilowatt hour of electricity over their lifetime, solar panels plus batteries are not. And California wanted a supplemented free market solution and didn't really want to think about the part that direct government intervention in the form of taxation and paying for this change would be necessary.
So everyone in California just kept adding solar panels to the grid with no disconnect mechanisms, until eventually it hit a point where at noon, solar panels generated more power than the entire grid needed. With no batteries to store the excess. This is a motherfucking power grid killer. It is a scenario where people get left in the fucking dark for months because of how badly it destroys the powergrid.
So the power grid authorities did the only thing they could do. They called up every industrial plant with heavy duty equipment and ovens they could and paid them to turn it on full blast (because using that equipment costs money in wear and tear even without the electricity cost). And in doing so, avoided disaster.
That's what this article is talking about. They are solar panel researchers criticizing a capitalist adoption strategy and promoting direct government intervention to create renewable energy. However as with most newspapers they don't get to choose the title, the editor picks the most provocative title that will get clicks.
72K notes
·
View notes
Text
Save Big with Texas Solar Incentives – See If You Qualify Now!

This Blog was Originally Published at :
Save Big with Texas Solar Incentives — See If You Qualify Now!
In recent years, Texas has emerged as a leader in solar energy adoption, surpassing California. This growth is backed by Federal tax credit, Texas solar incentives and other favourable policies. Plus, the benefits offered by local utility grids make it a more favorable option.
However, homeowners or businesses planning to go solar in Texas still have many questions like: Is Texas a good state for solar? How much is the solar tax exemption in Texas? Can I get solar panels for free in Texas? Are solar panels worth it in Texas? and so on?

Texas Solar Incentives: Local and Utility Rebates
There are no direct Texas solar incentives, but many municipalities and local utilities offer incentives to help homeowners and businesses. These incentives are provided in order to encourage them to adopt renewable energy. You can check the list of local rebates across Texas here.
Utility Company Incentives:
Oncor Electric Delivery: Oncor Electric Delivery offers many financial incentives to the solar contractors which they can pass on to the customers who purchase the qualifying solar power systems.
AEP Texas: AEP Texas a solar PV incentive program. This program offers financial incentives to help reduce the initial cost of installing a solar power system.
Garland Power & Light (GP&L): GP&L offers bill credits for solar panel installation. The solar rebate of $0.75 per watt, up to $5,000 per system, is renewed every October and is available until funds are exhausted.

Local Government Incentives:
SMTX Utilities (San Marcos): SMTX Utilities also has a rebate program offering a $2,500 rebate program for homeowners who install solar photovoltaic (PV) systems. It aims to promote solar power systems in Texas. For more details, you can visit the official SMTC Utilities website.
City of Sunset Valley: Residents of Sunset Valley who qualify for the Austin Energy solar rebate can receive extra Texas solar incentives from the city. The city offers an additional $1 per watt rebate of a maximum of $3,000 (if the solar power system cost doesn’t exceed $6,000). For more details on how specific eligibility criteria you can visit the official website of Sunset Valley.
NOTE: Texas solar incentives can reduce the upfront costs of solar power installations. However, the availability of these programs may vary based on your location and utility provider. For updated information, you can consult your local utility company or State Incentives for Renewables & Efficiency (DSIRE).
Learn the cheapest ways to get home power off the grid.
Property Tax Exemption for Solar Systems in Texas

Solar Buyback Programs
Solar buyback programs allow homeowners to sell excess electricity generated by solar panels back to the grid. In return, they can receive credits on their electricity bill. It helps to reduce the electricity bills.
TXU Energy: TXU Energy offers solar buyback plans allowing Texas homeowners to earn credits for the extra solar energy generated. These credits can offset up to 100% of your monthly energy charges.
Octopus Energy: Similarly, Octopus Energy provides a solar buyback program with unlimited credits that roll over without expiration. It allows you to take maximum benefits of the solar energy production.
Gexa Energy: Gexa Energy offers plans that let you sell back your unused solar energy and reduce electricity costs.
Learn how to compare solar panel quotes here.
Federal Solar Investment Tax Credit (ITC)
The Federal Solar Investment Tax Credit (ITC) deducts a certain percentage of your solar panel installation costs from your federal taxes. For systems installed between 2022 and 2032, you can claim 30% of the cost of installing solar panels. It includes both equipment and labor costs.

You Own the New Solar Panel System: If you have fully installed a new solar panel system outright or through financing, you are eligible for it. Leasing or signing a power purchase agreement (PPA) does not qualify for the same. It doesn’t apply to refurbished ones.
The Panels are Installed at a Qualifying Property: The solar panels must be installed at your home which includes: primary/secondary residence or rental properties that allow installation in the United States. Leased properties don’t qualify for it.
You Must Owe Federal Taxes: As ITC is a tax credit you must ower federal taxes to take advantage of it. In case your credit exceeds what you owe, you can roll the remainder next year.
Battery Storage May Count: As of the new updates in 2023, you can also be eligible for credit if your solar panel system includes a battery with a storage capacity of 3 kilowatt-hours or more.
NOTE: It’s important to note that this tax credit is non-refundable, meaning it can reduce your tax liability to zero, but you won’t receive a refund for any remaining credit. However, any unused credit can be carried forward to the next tax year.
How to Claim Texas Solar Incentives
Install Your Solar Energy System: Choose a solar provider and install your solar power systems. The installation must be completed during the tax year for which you’re claiming the credit. If it is not done, you can claim it in the next year.
Gather Necessary Documentation: Keep a proper record of all the expenses related to the installation in the form of invoices or receipts. It will support your claim for the federal tax credit.
Complete IRS Form 5695 and Submit: When filing your federal income tax return, fill out Form 5695, titled “Residential Energy Credits.” This form helps you calculate the credit amount based on your solar installation costs. Include the completed Form 5695 with your annual tax return to claim the credit.
Final Words: Is Solar Worth it in Texas with Solar Incentives?
Switching to solar energy in Texas is undoubtedly a smart move for both your wallet and the environment. Backed by federal tax credits, property tax exemptions, local rebates, and supportive policies, going solar has never been more affordable.
By investing in solar, you not only save on energy bills but also increase the value of your home while contributing to a cleaner, greener future.
Here are three quick tips to get started:
Research local utility and city-specific rebates to maximize savings.
Choose a reliable solar installer with experience in Texas incentives.
Keep all your installation receipts and documents handy for claiming tax credits.
Read More:
Flexible Solar Panels
Is Solar Worth It in California
Cost of Solar Panels in California
FAQs on Texas Solar Incentives
Does Texas offer incentives for solar panels? Yes, Texas offers several incentives for solar panel installation, including federal tax credits, property tax exemptions, and utility or local rebates. However, there is no statewide net metering policy.
How much is the solar tax exemption in Texas? In Texas, the property tax exemption eliminates any increase in property taxes due to the added value of a solar energy system. This means you won’t pay extra property taxes even if your home’s value rises because of the solar installation.
Is Texas a good state for solar? Absolutely. With abundant sunshine, falling solar installation costs, and various incentives, Texas is one of the best states for solar energy adoption.
Is Texas more solar than California? Yes, Texas has surpassed California in utility-scale solar capacity, making it a leader in solar energy growth.
Do homes in Texas sell faster with solar? Homes with solar panels often sell faster and at a higher price in Texas because buyers value the long-term energy savings and environmental benefits.
0 notes
Text
Tuesday, January 21, 2025
Triumphant Trump returns to White House, launching new era of upheaval (Reuters/AP) Donald Trump was sworn in as U.S. president on Monday, ushering in another turbulent four-year term with promises to push the limits of executive power, deport millions of immigrants, secure retribution against his political enemies and transform the role of the U.S. on the world stage. Trump’s inauguration completes a triumphant comeback for a political disruptor who survived two impeachment trials, a felony conviction, two assassination attempts and an indictment for attempting to overturn his 2020 election loss. Trump is the first U.S. president since the 19th century to win a second term after losing the White House, and he planned to act swiftly after the ceremony. Dozens of executive orders were prepared for his signature to clamp down on border crossings, increase fossil fuel development and end diversity and inclusion programs across the federal government. Trump said he would lead a government that “expands our territory,” a reference to his goals of acquiring Greenland from Denmark and restoring U.S. control of the Panama Canal. He also said he would “pursue our manifest destiny into the stars” by launching American astronauts to Mars. Democrats who once formed a “resistance” are now divided over whether to work with Trump or defy him. Billionaires have lined up to meet with Trump as they acknowledge his unrivaled power in Washington and his ability to wield the levers of government to help or hurt their interests.
Why are lone homes left standing after the fires? It’s not entirely luck (AP) Emails and videos of burned buildings in Los Angeles next to those left standing have been flying back and forth among architects, builders and fire safety specialists around the world. For many homeowners, the sometimes scattershot nature of the carnage can seem like random chance. Many experts say luck does play a part. After all, wind can shift 180 degrees in a split second, pushing fire away from your house and towards a neighbor’s. But they also say there are many ways that homes can be made less vulnerable to fire. “Because there are, say, 50 ways a fire can burn your house,” said Greg Faulkner of Faulkner Architects in California, who has focused on less combustible home exteriors for more than a decade. “If you eliminate half of those, or three-quarters of them, that’s not luck, that’s increasing your odds.”
Solar farms are booming in the US and putting thousands of hungry sheep to work (AP) On rural Texas farmland, beneath hundreds of rows of solar panels, a troop of stocky sheep rummage through pasture, casually bumping into one another as they remain committed to a single task: chewing grass. The booming solar industry has found an unlikely mascot in sheep as large-scale solar farms crop up across the U.S. and in the plain fields of Texas. In Milam County, outside Austin, SB Energy operates the fifth-largest solar project in the country, capable of generating 900 megawatts of power across 4,000 acres. How do they manage all that grass? With the help of about 3,000 sheep, which are better suited than lawnmowers to fit between small crevices and chew away rain or shine. The proliferation of sheep on solar farms is part of a broader trend—solar grazing—that has exploded alongside the solar industry.
China on the border? (Washington Post) Over the years, a “mini-Detroit” blossomed in these desert highlands 200 miles south of the Texas border. General Motors, Stellantis and Daimler Trucks set up sprawling plants to churn out vehicles for export. Around them, a constellation of factories sprung up, with names like Detroit Diesel and Liberty Steel. But a peek into the massive Alianza industrial park here shows a novel development. Trucks are smoothing the pale dirt for a Chinese tire factory. Workers are building a Chinese car-part plant the size of four football fields. These companies are a sign of China’s increasing presence in Mexico—a trend that’s worrying the incoming Trump administration. President-elect Donald Trump fears that Chinese companies could start pumping out cheap electric vehicles in Mexico and sending them over the border. That could “destroy every automobile manufacturer” in America, he said recently on the PBD Podcast. Yet there’s only one tiny Chinese auto manufacturer in Mexico—and it opened during Trump’s first term. Those increasing Chinese imports? Many are items ordered by American and other foreign companies in Mexico. “It fits into a very good narrative, about these things that come in through the southern border—immigrants, fentanyl and now Chinese goods,” said Jorge Guajardo, Mexico’s former ambassador to China. “It’s a narrative that lacks substance.”
At least 80 people killed in northeast Colombia as peace talks fail, official says (AP) More than 80 people were killed in the country’s northeast over the weekend following the government’s failed attempts to hold peace talks with the National Liberation Army, a Colombian official said. Twenty others were injured in the violence that has forced thousands to flee as Colombia’s army scrambled to evacuate people on Sunday, according to William Villamizar, governor of North Santander, where many of the killings took place. Officials said the attacks happened in several towns located in the Catatumbo region near the border with Venezuela, with at least three people who were part of the peace talks being kidnapped. Thousands of people are fleeing the area, with some hiding in the nearby lush mountains or seeking help at government shelters.
Oxfam report finds billionaires' wealth soared in 2024 as global elite prepare for Davos (AFP) Billionaires saw their wealth grow by $5.7 billion per day in 2024—three times faster than 2023—according to an Oxfam report ahead of the World Economic Forum in Davos, Switzerland. The group predicts that unchecked wealth accumulation could produce five trillionaires within a decade, five times the number they predicted just a year ago. Meanwhile, global poverty rates have remained largely stagnant since 1990, with billions living on less than $6.85 a day.
Economic grievances fuel support for hostile actions, Edelman global survey shows (Reuters) Economic fears have escalated into grievances among 60% of people, with many believing hostile actions such as violence can be necessary to bring about change, according to a global poll by communications firm Edelman. The survey of the 33,000 respondents across 28 countries showed severe levels of distrust in government and business, with many respondents viewing them as serving the narrow interests of the wealthy while regular people struggle. Four in 10 respondents approved of hostile acts to bring about change, including violence or threats, online attacks, intentionally spreading disinformation and damaging property, the survey showed. Among respondents aged 18 to 34, support for hostile actions was even higher at 53%. The results are "profound," said the firm's CEO Richard Edelman. "We've now seen a slide over a 10-year period from fears, to polarization to grievance," as the public becomes more anxious about the cost of living and job security tied to artificial intelligence, he said.
Accidents, not Russian sabotage, behind undersea cable damage, officials say (Washington Post) Ruptures of undersea cables that have rattled European security officials in recent months were likely the result of maritime accidents rather than Russian sabotage, according to several U.S. and European intelligence officials. The determination reflects an emerging consensus among U.S. and European security services, according to senior officials from three countries involved in ongoing investigations of a string of incidents in which critical seabed energy and communications lines have been severed. So far, officials said, investigations involving the United States and a half-dozen European security services have turned up no indication that commercial ships suspected of dragging anchors across seabed systems did so intentionally or at the direction of Moscow. Instead, U.S. and European officials said that the evidence gathered points to accidents caused by inexperienced crews serving aboard poorly maintained vessels.
Ukraine Braces for Trump’s Return, Eager for Peace, but Wary of the Terms (NYT) Could this be the year, as President-elect Donald J. Trump has promised, when Russia’s war against Ukraine is brought to an end? The possibility of peace brings “tears to my eyes,” said Valeria, 30, an English teacher from eastern Ukraine. As Mr. Trump prepares to return to the White House on Monday, he is promising peace in Ukraine, but publicly offering no strategy for how to achieve it—aside from his stated desire to meet with President Vladimir V. Putin of Russia. So Ukrainians can only guess at what the coming months will bring. No one, Valeria said, wants peace more than Ukrainians. But having suffered so much loss, with hundreds of thousands killed and injured, Ukrainians will not accept peace at any price, she said. “Europe and America must remember that any cease-fire or negotiations will only be legitimate if they respect the sacrifices made by Ukrainians and ensure a just, secure and independent future for Ukraine,” she said.
China's frugal young adults accelerate saving (Reuters) The frugal trend that began in China during the economic disruption of the pandemic and deepened amid the crisis in the property market is intensifying as Gen Z shuns government calls to spend, spend, spend and doubles down on saving. On China's Instagram-like Xiaohongshu, or RedNote as it is known in the West, many under-30s are swapping notes on how to spend less on office lunches and shop on the cheap. Influencers are also sharing tips on turning financial discipline into a lifestyle. Posts on how to save money total more than 1.5 million with more than 130 million views. "I feel that the economy is quite bad, and it seems like it's hard for everyone to make money, so I think it's important to protect my own wallet," said Ava Su, who joined Alibaba after graduating just over six months ago and earns a relatively comfortable salary. The situation is a stark contrast to the free-spending attitudes of the so-called "moonlight" generation, a term used to describe those born in the 1980s and 1990s.
Gaza rebuild will take 'a lot of time', says UN official (BBC) The rebuilding process in the devastated Palestinian territory will "take an awful lot of time" despite the promised surge in humanitarian deliveries, a UN official in Gaza has warned. After a ceasefire and hostage release deal between Israel and Hamas took effect on Sunday, more than 630 aid lorries have crossed into Gaza, with at least 300 going to the north. The lorries brought in desperately needed food, tents, blankets, mattresses and clothes for the winter which had been stuck outside Gaza for months. The ceasefire deal reportedly requires 600 aid lorries, including 50 carrying fuel, to be allowed into Gaza every day during the first phase lasting six weeks, during which Hamas should release 33 Israeli hostages in return for hundreds of Palestinian prisoners in Israeli jails. On Sunday night, UN humanitarian chief Tom Fletcher warned that the humanitarian needs of Palestinians in Gaza were "staggering".
Stores clear shelves in January. Dumpster divers have never been happier. (Washington Post) Melanie Diaz was excited to stock up on January clearance items at her favorite stores in Tampa this month, so she put her usual battle plan into action. First, she slipped into a pair of old sweatpants and her dirtiest sneakers. Then around 10 a.m., she headed to T.J. Maxx—the first store on her list—and drove around to the back to case the area and make sure nobody was watching. Satisfied that she could make a clean getaway, Diaz put on a pair of rubber gloves and climbed into the store’s dumpster to begin her free shopping spree. Everything from hand soap to puzzles and Christmas ornaments had been tossed out, most of it in original packaging. Diaz figures the store wanted to clear shelves of old merchandise and didn’t or couldn’t send it back from where it came. “January is my favorite time to go dumpster diving,” she said. “It’s the time when the stores are throwing out all the Christmas stuff and gearing up for spring. But I usually find all kinds of treasures, seven days a week.” She estimated that she’s found more than $20,000 in after-Christmas merchandise since she started dumpster diving two years ago.
1 note
·
View note